n Educational support from GE and Volpara n Reduce mortality n Healthy women will not be harmed
|
|
|
- Amberly Lester
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dense Breasts: What to Know and What to Do Wendie A. Berg, MD, PhD, FACR Professor of Radiology Magee-Womens Hospital of UPMC University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosures n I am a radiologist specializing in breast imaging n Hologic, General Electric Healthcare, Gamma Medica, Inc. provide equipment and research support to the institution n Unpaid Chief Scientific Advisor to DenseBreast-info.org n Educational support from GE and Volpara Basic Principles SCREENING n Early detection will alter the natural history n Reduce mortality n Earlier detection will allow more breast conservation, less harmful treatments n Healthy women will not be harmed n Test widely available, cost effective, well tolerated Survival by Invasive Tumor size at Detection Survival probability Time in years since diagnosis Mammo CBE 1-9 mm mm mm mm mm 50+ mm Tabar Rad Clin NA 2000;38: , via R. Edward Hendrick, PhD, U. Colorado 1
2 RCT Results in Women n Mammography is the only screening test for which randomized trials have been conducted n Mammography has been shown to reduce deaths due to breast cancer Randomized Trial Relative Risk 95% Confidence Interval HIP of NY Malmo Sw. 2 County Gothenburg Stockholm Edinburgh CNBSS Combined Combined results demonstrate a statistically significant 22% mortality reduction from invitation to screening RCT Results in Women Randomized Trial Relative Risk 95% Confidence Interval HIP of NY Malmo Sw. 2 County Gothenburg Stockholm Edinburgh CNBSS Age Trial (GB) Combined Nelson et al. meta-analysis released with the USPSTF guidelines demonstrated a statistically significant 15% mortality reduction Delay in Benefit of Screening Tabar L et al Lancet 2003;361: Life Expectancy 10-Year Horizon n Stop screening when life expectancy < 10 years n Healthiest quartile at age 85 n Comorbidities: Lowest quartile at age 70 n Applies to supplemental screening as well Walter LC and Covinsky KE. JAMA 2001;285:2570 2
3 Why isn t screening more effective at reducing mortality? n Nonparticipation n Diagnosed at young age before screening would have commenced n Cancer not detected n Cancer has already spread at time of detection Webb ML et al Cancer 2013 n Invasive breast cancers Partners Health dx , followed through 2007, median 12.5 yrs, 609 breast cancer deaths n Median age at dx of fatal cancer = 49 yrs n 118 (19.4%) deaths screen-detected ca n 60 (9.8%) from interval cancers (lumps) n 395 (64.9%) in women never screened n 36 (5.9%) in women screened > 2 yr prior n 71% of deaths in women without regular screening n Median age at diagnosis of fatal breast cancer is 49 Webb ML et al: Cancer 2013 epub n Women should participate in screening by age 40 n Improve efforts to identify high-risk women who may be diagnosed even earlier Supplemental Screening n At best, can reduce n 10% of breast cancer deaths due to interval cancers, palpable in the interval between screens n Another ~20% of deaths by earlier detection of screen-detected cancers Deaths n 34% of all deaths in women screened are due to interval cancers n 60% of deaths if dx < age 40 n 47% of deaths n 28% of deaths n 26% of deaths n 24% of deaths 70 or older Webb ML et al: Cancer 2013 epub
4 Reasons for Mammographic Nondetection n #1: Dense breasts n Benign appearing: seen and dismissed n Asymmetries n Benign-appearing mass n Stable calcifications n Overlooked n Calcifications, distortion n Rapidly growing cancer, not present on prior mammogram Reasons for Mammographic Nondetection n #1: Dense breasts Supplemental screen n Benign appearing: seen and dismissed n Asymmetries n Benign-appearing mass - Feedback n Stable calcifications n Overlooked CAD n Calcifications, distortion n Rapidly growing cancer, not present on prior mammogram Screen more often What is Breast Density? DENSE BREASTS n Dense tissue in a mammogram is comprised of ducts, glands and fibrous tissue from Courtesy Hologic Inc. Breast Density n Is determined on imaging: mammography or MRI, but also CT and ultrasound n Not related to the way the breast feels 4
5 Tabar Classification Low Risk Gram IT et al Eur J Radiol 1997;24: High Risk BI-RADS Density n Visual n A. Almost entirely fatty n B. Scattered fibroglandular density n C. Heterogeneously dense which could obscure detection of small masses n D. Extremely dense, which lowers the sensitivity of mammography A B C D Volumetric Density vs. 2D Visual Relative Risk n Risk of developing breast cancer for women with that risk factor compared to risk for women without that risk factor n Usually stated as risk with extremely dense vs. fatty breasts 100 BIRADS 1, 2, 3 and 4 from University of Virginia, courtesy Volpara, Inc. 5
6 Boyd, 1995 via J. Harvey, UVA Interval Cancer n Cancer diagnosed because of clinical symptoms in the interval between recommended screenings n Worse prognosis and worse outcome Relative Risk! None <10 % % 25 50% % >75% n ~Half of deaths in screened women who are diagnosed in their 40 s are due to interval cancers Interval Cancers and Breast Density Increased Deaths Density Odds Ratio 95% CI* < 10% % 2.1 (0.9, 5.2) 25-49% 3.6 (1.5, 8.7) 50-74% 5.6 (2.1, 15.3) 75% 17.8 (4.8, 65.9) Adjusted for age, BMI, parity, menarche, #childbirths, menopausal status, HRT use *p<0.001 Boyd NF, et al. NEJM 2007;356: Chiu SY et al. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2010;19: n 25 yr f/u Sweden 15,658 women n 12.7% had dense breasts n Increased breast cancer mortality in women with dense breasts n RR 1.91 (95%CI ) n Attributed to higher incidence n Shorter sojourn time Dense Breasts, 25 Yr F/U Density Decreases with Age RR 95% CI Incidence Tumors > 2 cm Node Grade 2-3 tumor Death Chiu SY et al. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2010;19: Age 52 Age 54 Courtesy Wendie Berg, MD, PhD 6
7 Breast Density as Function of Age Dense Breasts n Heterogeneously or extremely dense n > 1/2 of women < age 50 n > 1/3 of women age 50 n Dense tissue itself a risk factor: 3-6 X compared to fatty breasts n Mammographic sensitivity reduced: Masking n 30 to 48% in densest breasts n Digital mammography slightly better than film Kerlikowske et al. JNCI 2007; 99: Harvey and Bovbjerg Radiology 2004;230:29-41 Boyd NF et al NEJM 2007;356: Hormones Increase Density Additive Risk of HT and Density n Combination estrogen (E) and progesterone (P) therapy increases breast density n Increases risk for breast cancer Kerlikowske K et al J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: Fatty Minimal Hetero Ext Dense Premenopausal Post, no HT Post, E use Post, E+P RR stage III or IV disease in post-menopausal nonusers 1.75 RR stage III or IV disease in post-menopausal HT users What is the referent standard? n Average woman has scattered fibroglandular density n Relative to average, extreme breast density only 1.5-2X risk Biennial vs. Annual Mammography, Extremely Dense Kerlikowske K et al JAMA Int Med 2013:173: Stage IIB, III, IV Tumor Size > 2 cm Node positive yrs no HT 1.89 ( ) 2.39 ( ) 1.34 ( ) 1.21 ( ) 1.10 ( ) 1.14 ( ) E+P 1.56 ( ) 1.59 ( ) 1.05 ( ) 7
8 Outcomes from Dense Breasts 48F screening n Cancer more often found as a lump n Clinically detected in interval between screens n Increased risk of recurrence (if no XRT) n More often stage IIb, III n More often multifocal, multicentric, mastectomy more often needed n May increase risk of death from breast cancer (requires very long term follow-up) Courtesy Dr. Wei Yang, MD Anderson n Stereotactic biopsy: High nuclear grade DCIS solid type with comedo necrosis, with microinvasion, ER, PR-, HER2 + n Skin-sparing mastectomy, 0/4 SLN RT CC MAG RT ML MAG Courtesy Dr. Wei Yang, MD Anderson BREAST DENSITY INFORM LAWS 24 states require notification: 67% of USA population 8
9 PA Act 86 PA 86 n Effective 1/30/14, each mammography report shall include written notification of breast density based on BI-RADS This notice contains the results of your recent mammogram, including information about breast density. If your mammogram shows that your breast tissue is dense, you should know that dense breast tissue is a common finding and is not abnormal. Statistics show many women could have dense or highly dense breasts. Dense breast tissue can make it harder to find cancer on a mammogram and may be associated with an increased risk of cancer. This information about the result of your mammogram is given to you to raise your awareness and to inform your conversations with your physician. Together, you can decide which screening options are right for you, based on your mammogram results, individual risk factors or physical examination. A report of your results was sent to your physician. Possible tests to add to mammography SUPPLEMENTAL SCREENING Modality vs. Mammography alone Absolute Cancer Detection per 1000 screens Clinical breast exam 0.3 Double Read 1 CAD 1 Tomosynthesis 1-2 Ultrasound 2-4 Molecular Breast 8 Imaging, CE-Mammo MRI 10 Summary Screening Results by Modality/Combination Berg WA, AJR 2009;192:390 n 36% cancers seen on mammography n 40% cancers seen on US n 64% cancers seen if both mammo+us n 81% cancers seen on MRI n 93% cancers seen if both mammo+mri How Do We Measure Impact of Supplemental Screening? n Reduction in interval cancer rate n Ideally fewer than 10% of all cancers n Reduction in # node-positive cancers n Reduction in stage II-IV disease 9
10 Standard Mammography Tube TOMOSYNTHESIS Compression paddle Detector Courtesy Rita Zuley, MD Digital close up Tomosynthesis close up Compression paddle Detector Invasive Ductal CA Courtesy Rita Zuley, MD Rafferty EA et al. Radiology 2013, 266: Tomo n 120 µm resolution vs. 70 µm 2D n 4 to 7 sec acquisition vs. 1-3 sec: greater potential for motion n Radiation dose to pt similar to single 2D digital mammogram: 2X dose if have both n FDA requires standard 2D mammogram in addition to tomo ( combo mode): can be created synthetically from projection images if facility has the software 40F with lump noted after fall on bicycle 10
11 Single slices from tomosynthesis Sagittal post-contrast MRI Multifocal grade 3 IDC (ER, PR, HER2 positive) Oslo Screening Trial: Interim Analysis Addition of 3D (Tomo) Added Cancers Detected Tomo Cancer Detection Rate False positive rate Time to interpret 2D alone 2D+3D Diff. P-value 6.1/ / / % 5.3% -0.8% < sec 91 sec +46 sec <.001 Skaane P et al Radiology, e-pub 1/7/2013 n 1.9 per 1000 n Nearly all invasive n 83% (19/23) with node staging N0 n 60% grade 1 n 68% spiculated masses or distortions n Same detection benefit for each category of breast density n Requires soft tissue contrast: Likely less effective if extremely dense Skaane P et al Radiology, e-pub 1/7/
12 Tomosynthesis Performance Study Design ICDR per 1000 Absolute Change in Recall Rate Skaane 2013 Prospective % Ciatto 2013 Prospective % Rose 2013 Historical control % Friedewald 2014 Historical control % Greenberg 2014 Historical control % Overall % Unanswered Questions Tomo Close up of 2D Synthetic 2D from 3D acquisition: C view n Yield from annual (incidence) screening n Interval cancer rate, esp. in dense breasts n Yield from US after tomo (do patients benefit from both) n Preliminary data suggest CDR of HHUS after tomo of ~2/1000 n Hooley RJ et al 12/5/13 RSNA SS Arie Crown MRI Screening High-Risk Women: MRI Women w/cancer Mammo (%) US (%) MRI (%) Hartman NP 1 (100) Warner (36) 7 (32) 17 (77) Kuhl (33) 17(40) 39 (91) Leach (40) NP 27 (77) Lehman (25) NP 4 (100) Kriege (31) NP 34 (76) Sardanelli (60) 9 (60) 13 (87) Lehman (33) 1 (17) 4 (67) Hagen (38) NP 16 (76) TOTAL (36) 34/86 (40) 155 (81) From Berg WA, AJR 2009;192:390 12
13 MRI Recommended for High-Risk Women n Of 192 women with cancer, 158 (82%) were invasive, 24 of those (15%) node positive n Across series: 2 cancers only on US in 1037 women vs. 31 only on MRI n No need for screening US if patient is having MRI From Berg WA, AJR 2009;192:390 Annual MRI in addition to mammography n BRCA mutation carrier n First degree relative of BRCA carrier but untested n Lifetime risk of 20-25% or greater as estimated by risk model (e.g. Claus, BRCAPRO, Tyrer- Cuzick, BOADICEA) n Prior chest radiation age Saslow et al. Ca Cancer J Clin 2007;57:75 When to Start Screening Women at Increased Risk n When risk is equivalent to a woman at age yr Probability (%) of Breast Cancer Age Relatives with Breast Cancer BRCA 1 None One 1º Two 1º carrier BRCA 2 carrier Unknown Unknown Berg WA; AJR 2009;192: When to Start Screening n BRCA-1 carriers: begin at age 25 n BRCA-2 carriers: start by age 30 n Radiation risk of mammography highest at young age, prevalence of dz lowest n Avoid mammography before age 30 n Annual MRI only for BRCA carriers under 30 Efficacy MRI Ellen Warner et al. JCO 2011;29: n Women with pathogenic BRCA mutations n Not all women can have MRI n 445 in MRI group n 830 controls matched for age and mutation n Mean 3.2 yr follow-up NCCN Genetic/Familial High Risk Assessment: Breast and Ovarian Updated 2/28/
14 Stage Distribution of Cancers MRI Cohort N=41 Controls N=77 Mean Age DCIS 24% 12% Invasive, mean 0.9 cm 1.8 cm 1 cm 74% 35% > 2 cm 3% 29% Node + 13% 40% Warner, E. et al. JCO 2011;29: Cumulative Incidence MRI Group (%) Control Group (%) P- value DCIS or 13.8 (9.1 to 18.5) 7.2 (4.5 to 9.9).01 Stage I Stage II to IV 1.9 (0.2 to 3.7) 6.6 (3.8 to 9.3).02 Hazard ratio for development of stage II-IV breast cancer associated with MRI screening was 0.30 (0.12 to 0.72, p=.008) Approximately 2% more women dx with cancer in the MRI group Warner E et al JCO 2011;29: Interval Cancers: MR Screening Benchmarks Screening MRI BRCA1 BRCA2 Women Women-Yrs Cancers Interval 8 2 Cancers Interval Ca 3.6/ /1000 Rate % Interval Ca 10.9% 3.9% Heijnsdijk EAM et al Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev2012;21: UK, Dutch, Canadian trials combined n Cancer detection rate 10/1000 n Percent node-negative >80% n Minimal cancer ( 1 cm or DCIS) >50% n Recall rate 10-15% n PPV3 (of biopsy) 20-50% n Sensitivity >80% n Specificity 85-90% Morris EA et al BI-RADS: MRI (ACR, Reston), 2013 Insufficient Evidence for or Against MRI n Lifetime risk of 15-20% by risk model n LCIS/ALH (LIN) or ADH n Personal history of breast cancer n Dense breasts Saslow et al. Ca Cancer J Clin 2007;57:75 Worse Outcomes with PHBC? Houssami NH et al JAMA 2011;305: Interval Ca Rate per 1000 Node Positive interval ca Interval Ca Stage IIB* PHBC No PHBC P-value 3.6 ( ) 1.4 ( ) < % 29.0% 21.4% 17.9% *% advanced stage after excluding cases with missing stage 14
15 PHBC Mammography Outcomes Berg W et al JAMA 2012;307: n More interval cancers and lower sensitivity of mammography in women with PHBC n But, no difference in rates of node positive or advanced stage disease n ACRIN 6666: 612 women had MRI after 3 rounds of screening mammo+us n Overall yield 15/1000 of MR n 7.3 per 1000 in women with PHBC n 26.7 per 1000 in women without PHBC n Supplemental MRI less likely to prompt unnecessary recall or biopsy for PHBC n Sensitivity and specificity > for PHBC vs. those with other risk factors 607 women with PHBC, negative mammogram, screening MR n 18.1 cancers per 1000 n Sensitivity of MR 91.7% n Specificity of MR 82.2% n Modeling suggests all women treated with BCT and dx age 50 meet the 20% LTR threshold for screening MR (assuming at least 10-yr life expectancy) Gweon et al. Radiology 2014;272: MRI Screening Average Risk Women Schrading S et al SABCS Dec n 1705 MRI exams (mix of prevalent and incident screens), no personal or family hx of breast or ovarian cancer or dx of atypia, normal mammograms; 89% had US (-) n 54/1705 (3.2%) suspicious findings biopsied n 18/54 (33%) malignant n ICDR 10.6 per 1000 n 11/18 (61%) invasive, median size 10 mm, N0 51F with no known risk factors MRI Screen-Detected Courtesy Dr. Simone Schrading Courtesy Dr. Simone Schrading 15
16 n Why isn t screening MRI offered to everyone? n Cost n Availability of equipment/personnel n Injection of contrast n Renal function n Pacemaker, some other metal implants Courtesy Dr. Simone Schrading FAST MR FAST MR Performance FAST MR Full Diagnostic Protocol MIP MIP Single post-contrast sequence One pre- and three postcontrast sequences STIR/T2W 3 min table time 17 min table time 30 sec reading time 90 sec reading time FAST MR FULL PROTOCOL Sensitivity 11/11 (100) 11/11 (100) Specificity 561/595 (94.3) 559/595 (93.9) Recall rate 45/606 (7.4) 47/606 (7.8) PPV of recall 11/45 (24.4) 11/47 (23.4) BI-RADS 3 rate 53/606 (8.7) 33/606 (5.4) Kuhl CK et al JCO 2014;32: Kuhl CK et al JCO 2014;32: n 7/11 (64%) cancers invasive; all invasive cancers T1N0 n 10/11 not seen prospectively on US n 1/11 not seen on targeted US after MR n None were grade 1 n No interval cancers n Abbreviated MR protocol requires further validation n Prospective trial in development (ACRIN/ ECOG) Kuhl CK et al JCO 2014;32:
17 Unable to Tolerate MRI Supplemental US n 18.5% (1 in 5.4) (95% CI 16.4 to 20.8%) of high-risk women who had completed 3 years of annual screening with US and mammography were unable to undergo an MRI n Physician Performed n Technologist Performed n Automated Berg WA et al. Radiology 2010;254:79-87 Handheld US n High-frequency transducer, MHz linear array n Survey scanning transverse and sagittal n Document 1 image per quadrant, 1 behind nipple for negative exam n Lesions (all studies to date): Orthogonal views ± calipers; optional color or power Doppler image n Positive test: BI-RADS 3 or higher assessment, or recommendation for further imaging (BI- RADS 0) Physician Performed US: Multicenter Results Author N screens ICDR per 1000 Recall Rate (%) Bx Rate (% women) PPV3 Bx Performed Corsetti NS 449 (4.9) 50/623 (8.0) Berg yr (15.1) 207 (7.8) 14/264 (5.3) Berg (7.4) 242 (5.0) 21/276 (7.6) yr2-3 TOTAL 16, % 898 (5.4) 85/1163 (7.3) 4.9% of women had biopsies for benign findings Tech-Performed US (USA): Prevalent Screens Is the ICDR Lower for Technologist- Performed US? Author N ICDR per 1000 Recall Rate (%) Bx Rate (%) PPV3 Bx Performed Kaplan, , (9.5) 97 (5.2) 6/96 (6.3) Hooley, * (23.8) 46 (7.1) 3/58 (5.2) Weigert, , ,196 (13.8) 429 (5.0) 25/418 (6.7) Parris, , (12.3) 185 (3.3) 10/181 (5.5) Overall 16, ,206 (13.2) 757 (4.5) 47/753 (6.2) n Direct prospective comparison of technologistand physician-performed HHUS has not been performed n 2.5 vs. 4.3 per 1000 on prevalent screens (p<. 0067) n Likely due to differences in disease prevalence with broader populations screened *analysis presented for women with negative screening mammograms Berg WA and Mendelson EB. Radiology 2014;272:
18 Disease Prevalence Affects Yield Node-Negative Invasive Cancers Kolb 2002 Crystal 2003 Moderate Risk* No Known Risks P-value 14/2914 (4.8 per 1000) 14/7901 (1.8 per 1000).011 4/318 (12.5 per 1000) 3/1199 (2.5 per 1000) <.04 n Across 10 series, 475 cancers seen only on US, 415 (87.4%) invasive n 273/303 (90.1%) with staging were node negative n 22/91 (24%) ILC Overall 18/3232 (5.6 per 1000) 17/9100 (1.9 per 1000) *Personal hx of breast cancer or first-degree relative with breast cancer vs. no risks Types of Cancers Found with Screening US Bae MS et al Cancer Sci 2011;102: (Korea) US Mammo P-value N Age (mean, yrs) <.0001 BCT 84.4% 68.4% <.0001 Invasive 81.2% 73.5% <.0001 Mean invasive size 1.3 cm 1.7 cm <.0001 N <.0001 More likely US detected: < 1 cm (RR 2.2); luminal A vs. Her-2+; 3.7x more likely to have dense breasts; 89% of US-detected cancers were in dense breasts (vs. 65% of mammo-detected) By Participant, Yield/1000, ACRIN 6666 Year M+US M Supp. Yield, 95% CI P-value (2.1, 8.4) (0.9, 6.4) (0.9, 6.8).004 Supplemental yield of US is significant each year and similar for incidence and prevalence screens Berg WA et al JAMA 2012;307: Radial Antiradial 60F, 5-yr risk 2.5%, 24-mo US: 12 mm grade 1 IDC-DCIS, N0 70F personal hx rt mastectomy, BRCA-1 mutation carrier 24 mo screen US+ 19 mm grade 3 IDC-DCIS, N0 Courtesy WP Evans, III, MD Courtesy Dr. Mary Mahoney, U Cincinnati 18
19 ACRIN 6666: Breast Density Density n Yield per % P-value 26-40% % % >80% Berg WA, et al., RSNA 2009 Berg W et al JAMA 2012;307: Mammo Combined Mammo+ US Difference CDR per 1000 PHBC No PHBC Sensitivity PHBC 55.9% 84.7% 28.8% No PHBC 50% 78.8% 28.8% Specificity PHBC 91.4% 83.1% -8.3% No PHBC 89.4% 77.8% -11.6% Recall rate PHBC 9.3% 17.9% 8.6% No PHBC 11.1% 23.0% 11.9% Bx Rate PHBC No PHBC PPV3 PHBC No PHBC Berg W et al JAMA 2012;307: Interval Cancer Rate: ACRIN 6666 n Supplemental yield and sensitivity of US same in women with PHBC as without n Supplemental US less likely to cause unnecessary recall or biopsy in women with PHBC than those without n Study supports the use of annual supplemental screening with ultrasound in addition to mammography Yr N Interval N Cancers (%) All Interval Ca Rate: 9/7473 screens = 1.2 per % of all cancers Berg WA et al JAMA 2012;307: Interval Cancer Rate Italy Benchmarks HH Screening US Corsetti V et al Cancer 2011;47: n Interval cancer rate in fatty breasts n 1.0 per 1000 n Interval cancer rate in dense breasts after adding screening US n 1.1 per 1000 n Cancer detection rate 3-4/1000 n Percent node negative 85% n Minimal cancer ( 1 cm or DCIS) 50% n Recall rate 8-15% n PPV3 10% n Sensitivity? n Specificity 85-90% 19
20 Semi-Automated US Automated Arm Results A Tower B Y-axis Gantry & Transducer Carrier C X-axis Gantry D Ultrasound Machine Monitor E Touch Screen / Monitor F Transducer Holster G Patient Bed Kelly KM et al Eur Radiol 2010; 20: n 4419 women, 6425 exams, 8 facilities n 40% women at intermediate risk n 23 cancers mammography n 46 cancers M+US n Supplemental yield 3.6 per 1000 (95% CI 2.3 to 5.4) n 10% recall rate n 23/75 (31%) biopsies prompted only by ABUS showed cancer Automated Breast US n 12 MHz n 15 cm footprint n 3 acquisitions in ~15 minutes n 3D dataset n Transverse n Created coronal and sagittal displays ABUS Results Three-Step Implementation Brem RF et al RSNA 2012; Tabar L et al Radiology 2015 n 15,000 women BI-RADS 1 or 2 mammo, dense breasts, automated whole breast US n 30 (2/1000) cancers only by ABUS n 25 detailed: 23 (92%) invasive, mean size 13 mm, 18 (78%) of those N0 n 20/23 (87%) ER+ n 3/22 (14%) stage IIB or higher n 13% absolute increase in recall rate n 1) Does the woman have at least 10-yr life expectancy? n No, then CBE only, with mammography only if warranted by symptoms 20
21 n 2) Is the patient at high risk for breast cancer and under age 60-70? n Yes, then MRI annually beginning: n When ascertained to be high risk n Age 25 if BRCA1/2 or other pathogenic mutation n 8yr prior to chest XRT n If unable to tolerate MRI, then US n 3) Dense? n Yes: Option to supplement annual mammography with US beginning at age 40 n No: Tomosynthesis beginning at age 40 Get Smart About Being Dense Iceland-Bargmundsson 21
Screening with New Modalities: Breast Ultrasound
 Screening with New Modalities: Breast Ultrasound Wendie A. Berg, MD, PhD Professor of Radiology Magee-Womens Hospital of UPMC University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosures No personal financial
Screening with New Modalities: Breast Ultrasound Wendie A. Berg, MD, PhD Professor of Radiology Magee-Womens Hospital of UPMC University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosures No personal financial
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound
 Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
What s New in Breast Imaging. Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia
 What s New in Breast Imaging Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia Disclosure Hologic, Inc. Shareholder and research agreement. Volpara Solutions, Ltd. Shareholder
What s New in Breast Imaging Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia Disclosure Hologic, Inc. Shareholder and research agreement. Volpara Solutions, Ltd. Shareholder
Dense Breasts, Get Educated
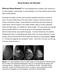 Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
Breast density: imaging, risks and recommendations
 Breast density: imaging, risks and recommendations Maureen Baxter, MD Radiologist Director of Ruth J. Spear Breast Center Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Alison Conlin, MD/MPH Medical Oncologist
Breast density: imaging, risks and recommendations Maureen Baxter, MD Radiologist Director of Ruth J. Spear Breast Center Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Alison Conlin, MD/MPH Medical Oncologist
Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts. Reagan Leverett, MD, MS
 Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts Reagan Leverett, MD, MS Outline Anatomy and Density Risk of dense breasts Theory of Supplemental Screening Options for supplemental screening Tomosynthesis Ultrasound
Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts Reagan Leverett, MD, MS Outline Anatomy and Density Risk of dense breasts Theory of Supplemental Screening Options for supplemental screening Tomosynthesis Ultrasound
Current Strategies in the Detection of Breast Cancer. Karla Kerlikowske, M.D. Professor of Medicine & Epidemiology and Biostatistics, UCSF
 Current Strategies in the Detection of Breast Cancer Karla Kerlikowske, M.D. Professor of Medicine & Epidemiology and Biostatistics, UCSF Outline ν Screening Film Mammography ν Film ν Digital ν Screening
Current Strategies in the Detection of Breast Cancer Karla Kerlikowske, M.D. Professor of Medicine & Epidemiology and Biostatistics, UCSF Outline ν Screening Film Mammography ν Film ν Digital ν Screening
BREAST DENSITY WHAT IS IT? WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? & What IOWA SF250 Means to Patients and Providers
 BREAST DENSITY WHAT IS IT? WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? & What IOWA SF250 Means to Patients and Providers Arnold Honick, MD Radiology Consultants of Iowa, PLC ahonick@rciowa.com BREAST DENSITY LEGISLATION Nancy
BREAST DENSITY WHAT IS IT? WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? & What IOWA SF250 Means to Patients and Providers Arnold Honick, MD Radiology Consultants of Iowa, PLC ahonick@rciowa.com BREAST DENSITY LEGISLATION Nancy
Update in Breast Cancer Screening
 Disclosure information: Update in Breast Cancer Screening Karla Kerlikowske, MDDis Update in Breast Cancer Screening Grant/Research support from: National Cancer Institute and Grail - and - Karla Kerlikowske,
Disclosure information: Update in Breast Cancer Screening Karla Kerlikowske, MDDis Update in Breast Cancer Screening Grant/Research support from: National Cancer Institute and Grail - and - Karla Kerlikowske,
Dense Breasts. A Breast Cancer Risk Factor and Imaging Challenge
 Dense Breasts A Breast Cancer Risk Factor and Imaging Challenge Renee Pinsky, MD University of Michigan Department of Radiology Division of Breast Imaging No Disclosures QUIZ: ARE YOU DENSE? a. Breast
Dense Breasts A Breast Cancer Risk Factor and Imaging Challenge Renee Pinsky, MD University of Michigan Department of Radiology Division of Breast Imaging No Disclosures QUIZ: ARE YOU DENSE? a. Breast
Breast Imaging! Ravi Adhikary, MD!
 Breast Imaging! Ravi Adhikary, MD! ACS Estimated Cancers Statistics 2014! Breast! New Cases in Women! 232,670 (+67,570 in situ)! Deaths in Women! 40,000! Colon! 48,380! 24,040! Cervical! 12,360! 4,020!
Breast Imaging! Ravi Adhikary, MD! ACS Estimated Cancers Statistics 2014! Breast! New Cases in Women! 232,670 (+67,570 in situ)! Deaths in Women! 40,000! Colon! 48,380! 24,040! Cervical! 12,360! 4,020!
5/24/16. Current Issues in Breast Cancer Screening. Breast cancer screening guidelines. Outline
 Disclosure information: An Evidence based Approach to Breast Cancer Karla Kerlikowske, MDDis Current Issues in Breast Cancer Screening Grant/Research support from: National Cancer Institute - and - Karla
Disclosure information: An Evidence based Approach to Breast Cancer Karla Kerlikowske, MDDis Current Issues in Breast Cancer Screening Grant/Research support from: National Cancer Institute - and - Karla
Update in Breast Cancer Screening
 Disclosure information: Update in Breast Cancer Screening Karla Kerlikowske, MDDis Update in Breast Cancer Screening Grant/Research support from: National Cancer Institute - and - Karla Kerlikowske, MD
Disclosure information: Update in Breast Cancer Screening Karla Kerlikowske, MDDis Update in Breast Cancer Screening Grant/Research support from: National Cancer Institute - and - Karla Kerlikowske, MD
Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis
 Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis Priya Thomas, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Cancer Prevention and Breast Medical Oncology University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Disclosures Dr. Thomas has
Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis Priya Thomas, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Cancer Prevention and Breast Medical Oncology University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Disclosures Dr. Thomas has
Disclosures. Breast Cancer. Breast Imaging Modalities. Breast Cancer Screening. Breast Cancer 6/4/2014
 : Information for the Primary Care Physician Disclosures No financial relationships with commercial entities producing health care products/services. Roxsann Roberts, MD Section Chief, MRI Erlanger/EmCare
: Information for the Primary Care Physician Disclosures No financial relationships with commercial entities producing health care products/services. Roxsann Roberts, MD Section Chief, MRI Erlanger/EmCare
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Outline. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation. Tomosynthesis Dataset: 2D/3D (Hologic Combo Acquisition)
 Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
Breast Density and Breast Tomosynthesis. How have they changed our lives?
 Breast Density and Breast Tomosynthesis How have they changed our lives? Renee W. Pinsky, MD Associate Professor of Radiology University of Michigan The only thing that is constant is change Heraclitus
Breast Density and Breast Tomosynthesis How have they changed our lives? Renee W. Pinsky, MD Associate Professor of Radiology University of Michigan The only thing that is constant is change Heraclitus
Breast Cancer Screening and High Risk
 Breast Cancer Screening and High Risk Mary Freyvogel, DO Breast Surgeon Clinical Assistant Professor of Surgery University Hospitals Case Medical Center St. John Medical Center / Elyria Medical Center
Breast Cancer Screening and High Risk Mary Freyvogel, DO Breast Surgeon Clinical Assistant Professor of Surgery University Hospitals Case Medical Center St. John Medical Center / Elyria Medical Center
Challenges to Delivery of High Quality Mammography
 Challenges to Delivery of High Quality Mammography Overview of Current Challenges Barbara Monsees, Washington University Geographic Access, Equity and Impact on Quality Tracy Onega, Dartmouth Medical School
Challenges to Delivery of High Quality Mammography Overview of Current Challenges Barbara Monsees, Washington University Geographic Access, Equity and Impact on Quality Tracy Onega, Dartmouth Medical School
Why it matters and what to do
 Breast density: Why it matters and what to do Breast density is a frequent topic on social media, in the news and within medical literature - and your patients may be asking you about it. Dense breast
Breast density: Why it matters and what to do Breast density is a frequent topic on social media, in the news and within medical literature - and your patients may be asking you about it. Dense breast
Detection to Prediction: Imaging Markers of Breast Cancer Risk
 Detection to Prediction: Imaging Markers of Breast Cancer Risk Carrie B. Hruska, PhD, DABR Associate Professor of Medical Physics Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 2017 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure Per agreement
Detection to Prediction: Imaging Markers of Breast Cancer Risk Carrie B. Hruska, PhD, DABR Associate Professor of Medical Physics Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 2017 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure Per agreement
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. Susan Orel Roth, MD
 Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
Melissa Hartman, DO Women s Health Orlando VA Medical Center
 Melissa Hartman, DO Women s Health Orlando VA Medical Center Most common non-skin cancer and Second deadliest cancer in women Majority are diagnosed by abnormal screening study An approach to breast cancer
Melissa Hartman, DO Women s Health Orlando VA Medical Center Most common non-skin cancer and Second deadliest cancer in women Majority are diagnosed by abnormal screening study An approach to breast cancer
BREAST MRI. Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
High Risk Screening: A Multimodality Approach
 High Risk Screening: A Multimodality Approach John Lewin, M.D., FACR, FSBI The Women s Imaging Center Denver, Colorado Disclosures Consultant to Hologic Previously received research funds from Hologic
High Risk Screening: A Multimodality Approach John Lewin, M.D., FACR, FSBI The Women s Imaging Center Denver, Colorado Disclosures Consultant to Hologic Previously received research funds from Hologic
Frequently Asked Questions about Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk, and the Breast Density Notification Law in California: A Consensus Document
 RSNA, 2013 Appendix E1 Frequently Asked Questions about Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk, and the Breast Density Notification Law in California: A Consensus Document 1. I have been getting more questions
RSNA, 2013 Appendix E1 Frequently Asked Questions about Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk, and the Breast Density Notification Law in California: A Consensus Document 1. I have been getting more questions
BREAST MRI. Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
Screening Options in Dense Breasts. Donna Plecha, M.D. Co-Director UHCMC Breast Centers Associate Professor of Radiology Director of Breast Imaging
 Screening Options in Dense Breasts Donna Plecha, M.D. Co-Director UHCMC Breast Centers Associate Professor of Radiology Director of Breast Imaging Dense Breasted Women Decreased sensitivity of mammography
Screening Options in Dense Breasts Donna Plecha, M.D. Co-Director UHCMC Breast Centers Associate Professor of Radiology Director of Breast Imaging Dense Breasted Women Decreased sensitivity of mammography
SCREENING FOR BREAST CANCER BREAST IMAGING
 SCREENING FOR BREAST CANCER BREAST IMAGING Liane Philpotts, MD, FSBI, FACR Professor, Radiology and Biomedical Imaging Division Chief, Breast Imaging Dec. 5, 2017 Warner, E. NEJM 2011 Screening for
SCREENING FOR BREAST CANCER BREAST IMAGING Liane Philpotts, MD, FSBI, FACR Professor, Radiology and Biomedical Imaging Division Chief, Breast Imaging Dec. 5, 2017 Warner, E. NEJM 2011 Screening for
Breast Cancer Screening
 Breast Cancer Screening Eileen Rakovitch MD MSc FRCPC Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre Medical Director, Louise Temerty Breast Cancer Centre LC Campbell Chair in Breast Cancer Research Associate Professor,
Breast Cancer Screening Eileen Rakovitch MD MSc FRCPC Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre Medical Director, Louise Temerty Breast Cancer Centre LC Campbell Chair in Breast Cancer Research Associate Professor,
Financial Disclosures
 Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
The Dilemma of Breast Density in Screening
 The Dilemma of Breast Density in Screening Priscilla J. Slanetz MD, MPH, FACR, FSBI Associate Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA No financial
The Dilemma of Breast Density in Screening Priscilla J. Slanetz MD, MPH, FACR, FSBI Associate Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA No financial
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Early Detection and Diagnosis Early Detection and Diagnosis Version 2005: Junkermann Version 2006 2009: Schreer / Albert Version
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Early Detection and Diagnosis Early Detection and Diagnosis Version 2005: Junkermann Version 2006 2009: Schreer / Albert Version
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities. Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine
 Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI
 Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update. Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
 Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
Screening Mammography: Who, what, where, when, why and how?
 Screening Mammography: Who, what, where, when, why and how? Jillian Lloyd, MD, MPH Breast Surgical Oncologist University Surgical Oncology Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Medical Center Disclosures
Screening Mammography: Who, what, where, when, why and how? Jillian Lloyd, MD, MPH Breast Surgical Oncologist University Surgical Oncology Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Medical Center Disclosures
Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR)
 Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR) Christopher Comstock, MD, FACR, FSBI Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of our approach to screening
Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR) Christopher Comstock, MD, FACR, FSBI Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of our approach to screening
MANAGEMENT OF DENSE BREASTS. Nichole K Ingalls, MD, MPH NW Surgical Specialists September 25, 2015
 MANAGEMENT OF DENSE BREASTS Nichole K Ingalls, MD, MPH NW Surgical Specialists September 25, 2015 No financial disclosures National Cancer Institute National Cancer Institute Increased Cancer Risk... DENSITY
MANAGEMENT OF DENSE BREASTS Nichole K Ingalls, MD, MPH NW Surgical Specialists September 25, 2015 No financial disclosures National Cancer Institute National Cancer Institute Increased Cancer Risk... DENSITY
Breast Density: Significance and Notification. Carol H. Lee Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY
 Breast Density: Significance and Notification Carol H. Lee Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Significance of Breast Density Association with increased risk for breast cancer Decreased
Breast Density: Significance and Notification Carol H. Lee Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Significance of Breast Density Association with increased risk for breast cancer Decreased
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue. Public Meeting December 13, 2013
 Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue Public Meeting December 13, 2013 Agenda Meeting Convened 10am-10:15am Presentation of the Evidence and Voting Questions, Q&A 10:15am 11:15am Discussion
Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue Public Meeting December 13, 2013 Agenda Meeting Convened 10am-10:15am Presentation of the Evidence and Voting Questions, Q&A 10:15am 11:15am Discussion
Screening Mammography: The Controversy, Risk Assessment and Individualized Screening recommendations. Jonathan T. Sims MD, MBA
 Screening Mammography: The Controversy, Risk Assessment and Individualized Screening recommendations. Jonathan T. Sims MD, MBA I have no relevant Financial Disclosures Agenda Discuss the recent studies
Screening Mammography: The Controversy, Risk Assessment and Individualized Screening recommendations. Jonathan T. Sims MD, MBA I have no relevant Financial Disclosures Agenda Discuss the recent studies
Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese
 Dansk Radiologisk Selskab 9.årsmøde Odense 3.januar, 214 Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese Professor dr. med. Per Skaane Oslo University Hospital Ullevaal Breast Imaging Center Oslo / Norway PERSKA@ous-hf.no
Dansk Radiologisk Selskab 9.årsmøde Odense 3.januar, 214 Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese Professor dr. med. Per Skaane Oslo University Hospital Ullevaal Breast Imaging Center Oslo / Norway PERSKA@ous-hf.no
Dr Robin Wilson, The Royal Marsden
 Screening: State of the Art High risk and dense breasts Robin Wilson Smart Breast Screening? 1 in 8 women in the will get breast cancer 8 in 9 will not 55% of breast cancers are not screen detected One
Screening: State of the Art High risk and dense breasts Robin Wilson Smart Breast Screening? 1 in 8 women in the will get breast cancer 8 in 9 will not 55% of breast cancers are not screen detected One
#46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? TERMS (AKA) WHAT IS TOMOSYNTHESIS? 3/3/2014. Digital breast tomosynthesis =
 #46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? January K. Lopez, MD Hoag Breast Care Center Newport Beach, CA Disclosures: None TERMS (AKA) Digital breast tomosynthesis = DBT Tomo 3D Full
#46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? January K. Lopez, MD Hoag Breast Care Center Newport Beach, CA Disclosures: None TERMS (AKA) Digital breast tomosynthesis = DBT Tomo 3D Full
Breast MRI: Friend or Foe?
 Breast MRI: Friend or Foe? UCSF Postgraduate Course May 18, 2013 Cheryl Ewing, MD Clinical Professor of Surgery UCSF Department of Surgery APPLEGATE HAS DOUBLE MASTECTOMY IN CANCER SCARE DIAGNOSED WITH
Breast MRI: Friend or Foe? UCSF Postgraduate Course May 18, 2013 Cheryl Ewing, MD Clinical Professor of Surgery UCSF Department of Surgery APPLEGATE HAS DOUBLE MASTECTOMY IN CANCER SCARE DIAGNOSED WITH
Imaging Guidelines for Breast Cancer Screening
 Imaging Guidelines for Breast Cancer Screening Sarah Colwick, MD Dr. Sarah Colwick was born and raised in Sikeston, MO. She attended college and medical school at the University of Missouri-Kansas City
Imaging Guidelines for Breast Cancer Screening Sarah Colwick, MD Dr. Sarah Colwick was born and raised in Sikeston, MO. She attended college and medical school at the University of Missouri-Kansas City
Ruud Pijnappel Professor of Radiology, UMC Utrecht. Chair Dutch Expert Centre for Screening Board EUSOBI
 Ruud Pijnappel Professor of Radiology, UMC Utrecht Best practice in Breast Imaging: what s new and what women need to know and Update on the Second Implementation Report of the 2003 Council Recommendation
Ruud Pijnappel Professor of Radiology, UMC Utrecht Best practice in Breast Imaging: what s new and what women need to know and Update on the Second Implementation Report of the 2003 Council Recommendation
Angela Gilliam, MD University of Colorado Surgical Grand Rounds November 3, 2008
 Angela Gilliam, MD University of Colorado Surgical Grand Rounds November 3, 2008 Breast Cancer Most common cancer in American women 180,000 new cases per year Second most common cause of cancer death 44,000
Angela Gilliam, MD University of Colorado Surgical Grand Rounds November 3, 2008 Breast Cancer Most common cancer in American women 180,000 new cases per year Second most common cause of cancer death 44,000
Tissue Breast Density
 Tissue Breast Density Reporting breast density within the letter to the patient is now mandated by VA law. Therefore, this website has been established by Peninsula Radiological Associates (PRA), the radiologists
Tissue Breast Density Reporting breast density within the letter to the patient is now mandated by VA law. Therefore, this website has been established by Peninsula Radiological Associates (PRA), the radiologists
BREAST CANCER SCREENING:
 BREAST CANCER SCREENING: controversies D David Dershaw Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Areas of general agreement about mammographic screening Screening mammography has been demonstrated
BREAST CANCER SCREENING: controversies D David Dershaw Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Areas of general agreement about mammographic screening Screening mammography has been demonstrated
Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become
 Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
The Future of Breast MRI Improving Outcomes
 The Future of Breast MRI Improving Outcomes Connie Lehman MD PhD Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director of Breast Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Opportunities New technology provides
The Future of Breast MRI Improving Outcomes Connie Lehman MD PhD Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director of Breast Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Opportunities New technology provides
Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography
 2015 ARRS Breast Symposium Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography John Lewin, M.D. Diversified Radiology of Colorado CEDM - Outline History Technique Literature Review / Cases Clinical Status Inexpensive,
2015 ARRS Breast Symposium Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography John Lewin, M.D. Diversified Radiology of Colorado CEDM - Outline History Technique Literature Review / Cases Clinical Status Inexpensive,
Breast Imaging & You
 Breast Imaging & You What s Inside: Breast Imaging... 2 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) mammograms... 4 Breast cancer screening... 6 Dense breast tissue... 8 Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS)... 9
Breast Imaging & You What s Inside: Breast Imaging... 2 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) mammograms... 4 Breast cancer screening... 6 Dense breast tissue... 8 Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS)... 9
Breast Cancer Screening
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Screening What is breast cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to find disease before symptoms begin. The goal of screening is to detect disease
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Screening What is breast cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to find disease before symptoms begin. The goal of screening is to detect disease
Mammography. What is Mammography? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Mammography What is Mammography? Mammography is a specific type of imaging that uses a low-dose x-ray system to examine breasts. A mammography exam, called a mammogram, is used to aid in the early detection
Mammography What is Mammography? Mammography is a specific type of imaging that uses a low-dose x-ray system to examine breasts. A mammography exam, called a mammogram, is used to aid in the early detection
Breast Imaging & You
 Breast Imaging & You What s Inside: Breast Imaging... 2 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) mammograms... 4 Breast cancer screening... 6 Dense breast tissue... 8 Automated breast ultrasound (ABUS)... 9
Breast Imaging & You What s Inside: Breast Imaging... 2 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) mammograms... 4 Breast cancer screening... 6 Dense breast tissue... 8 Automated breast ultrasound (ABUS)... 9
Imaging Surveillance in Women with a History of Treated Breast Cancer. Wei Tse Yang, M.D.
 Imaging Surveillance in Women with a History of Treated Breast Cancer Wei Tse Yang, M.D. Breast Cancer 1. Extent 2. Response 3. Recurrence Surveillance Breast Cancer 1. Extent 2. Response Surveillance
Imaging Surveillance in Women with a History of Treated Breast Cancer Wei Tse Yang, M.D. Breast Cancer 1. Extent 2. Response 3. Recurrence Surveillance Breast Cancer 1. Extent 2. Response Surveillance
Outline. Abbreviated MRI and the Dense Breast. 2D Analog Screen Mammography. RCTs of Mammographic Screening
 Abbreviated MRI and the Dense Breast Christopher Comstock, MD FACR Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of mammographic screening
Abbreviated MRI and the Dense Breast Christopher Comstock, MD FACR Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of mammographic screening
New Imaging Modalities for better Screening and Diagnosis
 New Imaging Modalities for better Screening and Diagnosis Miri Sklair-Levy, MD Department of Diagnostic Imaging Sheba Medical Center, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Department of Diagnostic
New Imaging Modalities for better Screening and Diagnosis Miri Sklair-Levy, MD Department of Diagnostic Imaging Sheba Medical Center, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Department of Diagnostic
When do you need PET/CT or MRI in early breast cancer?
 When do you need PET/CT or MRI in early breast cancer? Elizabeth A. Morris MD FACR Chief, Breast Imaging Service Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center NY, NY Objectives What is the role of MRI in initial
When do you need PET/CT or MRI in early breast cancer? Elizabeth A. Morris MD FACR Chief, Breast Imaging Service Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center NY, NY Objectives What is the role of MRI in initial
Breast MRI: Friend or Foe?
 Breast : Friend or Foe? APPLEGATE HAS DOUBLE MASTECTOMY IN CANCER SCARE DIAGNOSED WITH CANCER IN ONE BREAST Comments: 0 ASSOCIATED PRESS 8/19/2008 UCSF Postgraduate Course March 19, 2009 E. Shelley Hwang
Breast : Friend or Foe? APPLEGATE HAS DOUBLE MASTECTOMY IN CANCER SCARE DIAGNOSED WITH CANCER IN ONE BREAST Comments: 0 ASSOCIATED PRESS 8/19/2008 UCSF Postgraduate Course March 19, 2009 E. Shelley Hwang
Breast Tomosynthesis. What is breast tomosynthesis?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
Breast Cancer: Selected Topics for the Primary Care Clinician
 Breast Cancer: Selected Topics for the Primary Care Clinician Leah Karliner, MD MAS October 2009 Primary Care Medicine: Principles and Practice OUTLINE Incidence and Mortality Risk Factors and Risk Reduction/Prevention
Breast Cancer: Selected Topics for the Primary Care Clinician Leah Karliner, MD MAS October 2009 Primary Care Medicine: Principles and Practice OUTLINE Incidence and Mortality Risk Factors and Risk Reduction/Prevention
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening?
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening? Sophia Zackrisson MD, PhD, Assoc Prof of Radiology Skåne University Healthcare, Lund University, Sweden 1 Mammography screening 20% reduced breast
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening? Sophia Zackrisson MD, PhD, Assoc Prof of Radiology Skåne University Healthcare, Lund University, Sweden 1 Mammography screening 20% reduced breast
Breast MRI Update. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR Yale University School of Medicine
 Breast MRI Update Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine I disclose the following financial relationships with relevant commercial interests: Bracco Bayer
Breast MRI Update Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine I disclose the following financial relationships with relevant commercial interests: Bracco Bayer
MR sin plass i brystkreftdiagnostikk, dagens anbefalinger og fremtidsperspektiver
 MR sin plass i brystkreftdiagnostikk, dagens anbefalinger og fremtidsperspektiver Kathinka Kurz, MD, PhD, seksjonsoverlege SUS, kathinka.dehli.kurz@sus.no Technique - Subtraction Without contrast agent
MR sin plass i brystkreftdiagnostikk, dagens anbefalinger og fremtidsperspektiver Kathinka Kurz, MD, PhD, seksjonsoverlege SUS, kathinka.dehli.kurz@sus.no Technique - Subtraction Without contrast agent
TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE?
 X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
Breast Cancer Imaging
 Breast Cancer Imaging I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will cover breast imaging when such services meet the medical criteria guidelines (subject to limitations and exclusions) indicated below.
Breast Cancer Imaging I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will cover breast imaging when such services meet the medical criteria guidelines (subject to limitations and exclusions) indicated below.
Case 1. BREAST CANCER From Diagnosis to Treatment: The Role of Primary Care
 BREAST CANCER From Diagnosis to Treatment: The Role of Primary Care Leah Karliner, MD MAS University of California San Francisco Primary Care Medicine Update 2009 April 2009 Case 1 AR, a 60 year old African
BREAST CANCER From Diagnosis to Treatment: The Role of Primary Care Leah Karliner, MD MAS University of California San Francisco Primary Care Medicine Update 2009 April 2009 Case 1 AR, a 60 year old African
Final Evidence Report
 20, 2012 Health Technology Assessment Appropriate Imaging for Breast Cancer Screening in Special Populations Final Evidence Report December 10, 2014 Health Technology Assessment Program (HTA) Washington
20, 2012 Health Technology Assessment Appropriate Imaging for Breast Cancer Screening in Special Populations Final Evidence Report December 10, 2014 Health Technology Assessment Program (HTA) Washington
Breast cancer screening: Does tomosynthesis augment mammography?
 REVIEW TRACI A. TAKAHASHI, MD, MPH Director, Seattle VA Women Veterans Clinic at VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA; Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle CHRISTOPH
REVIEW TRACI A. TAKAHASHI, MD, MPH Director, Seattle VA Women Veterans Clinic at VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA; Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle CHRISTOPH
Examine breast cancer trends, statistics, and death rates, and impact of screenings. Discuss benefits and risks of screening
 Define Breast Cancer Screening Examine breast cancer trends, statistics, and death rates, and impact of screenings Discuss benefits and risks of screening Compare and contrast Screening Guidelines Optimal
Define Breast Cancer Screening Examine breast cancer trends, statistics, and death rates, and impact of screenings Discuss benefits and risks of screening Compare and contrast Screening Guidelines Optimal
Evaluations & CE Credits
 Evaluations & CE Credits Nursing Contact Hours, CME and CHES credits are available. Please visit www.phlive.org to fill out your evaluation and complete the post-test. 1 Breast Density and Breast Cancer
Evaluations & CE Credits Nursing Contact Hours, CME and CHES credits are available. Please visit www.phlive.org to fill out your evaluation and complete the post-test. 1 Breast Density and Breast Cancer
TOMOSYNTHESIS. Daniela Bernardi. U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy
 TOMOSYNTHESIS Daniela Bernardi U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy BACKGROUND early detection through screening MAMMOGRAPHY is associated with reduced breast cancer morbidity
TOMOSYNTHESIS Daniela Bernardi U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy BACKGROUND early detection through screening MAMMOGRAPHY is associated with reduced breast cancer morbidity
Scenarios for Clinicians
 Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk and Wisconsin Breast Density Notification Law (2017 Wisconsin Act 201) Scenarios for Clinicians Content adapted from the California Breast Density Information Group,
Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk and Wisconsin Breast Density Notification Law (2017 Wisconsin Act 201) Scenarios for Clinicians Content adapted from the California Breast Density Information Group,
The Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Value of Supplemental Screening Tests Following Negative Mammography in Women with Dense Breast Tissue
 The New England Comparative Effectiveness Public Advisory Council Public Meeting December 13, 2013 The Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Value of Supplemental Screening Tests Following Negative Mammography
The New England Comparative Effectiveness Public Advisory Council Public Meeting December 13, 2013 The Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Value of Supplemental Screening Tests Following Negative Mammography
Dense breasts: Cancer risk and supplemental imaging modalities
 Continuing Education Dense breasts: Cancer risk and supplemental imaging modalities By Mary Ellen Egger, APN, WHNP, CBPN and Diana L. Lam, MD To participate in this CE program, click here A. Faculty: Mary
Continuing Education Dense breasts: Cancer risk and supplemental imaging modalities By Mary Ellen Egger, APN, WHNP, CBPN and Diana L. Lam, MD To participate in this CE program, click here A. Faculty: Mary
Throughout this policy, bracketed numbers link topics across multiple sections according to the indication numbers in the following list.
 Subject: Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast Page: 1 of 33 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast Description Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the breast
Subject: Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast Page: 1 of 33 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast Description Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the breast
Updates in Mammography. Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University Malaya Medical Centre
 Updates in Mammography Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University Malaya Medical Centre Updates in Mammography Breast Imaging Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical
Updates in Mammography Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University Malaya Medical Centre Updates in Mammography Breast Imaging Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical
The Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Value of Supplemental Screening Tests Following Negative Mammography in Women with Dense Breast Tissue
 TITLE: AUTHORS: The Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Value of Supplemental Screening Tests Following Negative Mammography in Women with Dense Breast Tissue Jeffrey A. Tice, MD Associate Professor
TITLE: AUTHORS: The Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Value of Supplemental Screening Tests Following Negative Mammography in Women with Dense Breast Tissue Jeffrey A. Tice, MD Associate Professor
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 SAM - Breast MRI 1
 National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach. Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina
 Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Breast Density. Update 2018: Implications for Clinical Practice
 Breast Density Update 2018: Implications for Clinical Practice Matthew A. Stein, MD Assistant professor Breast Imaging Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Disclosures
Breast Density Update 2018: Implications for Clinical Practice Matthew A. Stein, MD Assistant professor Breast Imaging Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Disclosures
Screening Mammography Policy and Politics. Kevin L. Piggott, MD, MPH August 29, 2015
 Screening Mammography Policy and Politics Kevin L. Piggott, MD, MPH August 29, 2015 Objectives 1. To review the current recommendations for screening mammography by various national groups 2. To provide
Screening Mammography Policy and Politics Kevin L. Piggott, MD, MPH August 29, 2015 Objectives 1. To review the current recommendations for screening mammography by various national groups 2. To provide
Understanding the Breast Density Law. 10th Annual Breast Cancer Connections Conference
 Understanding the Breast Density Law 10th Annual Breast Cancer Connections Conference Redwood Shores, California November 2, 2013 Debra M. Ikeda, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director of Breast Imaging
Understanding the Breast Density Law 10th Annual Breast Cancer Connections Conference Redwood Shores, California November 2, 2013 Debra M. Ikeda, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director of Breast Imaging
BREAST IMAGING and NEW IMAGING MODALITIES- A Surgeons view
 BREAST IMAGING and NEW IMAGING MODALITIES- A Surgeons view DR CHANTEL THORNTON SPECIALIST BREAST CANCER SURGEON BMSc (hons) MBBS (hons) FRACS Epworth Hospital, Richmond- Agora Centre for Women s Health
BREAST IMAGING and NEW IMAGING MODALITIES- A Surgeons view DR CHANTEL THORNTON SPECIALIST BREAST CANCER SURGEON BMSc (hons) MBBS (hons) FRACS Epworth Hospital, Richmond- Agora Centre for Women s Health
The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning. Dr. med. M. Golatta
 The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning Dr. med. M. Golatta Automated Breast Volume US: Why? o Mammography is limited in dense breasts: high false negative rate o Many of these tumors
The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning Dr. med. M. Golatta Automated Breast Volume US: Why? o Mammography is limited in dense breasts: high false negative rate o Many of these tumors
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Professional Institutional Original Effective
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Professional Institutional Original Effective
BR 1 Palpable breast lump
 BR 1 Palpable breast lump Palpable breast lump in patient 40 years of age or above MMG +/- spot compression or digital breast tomosynthesis over palpable findings Suspicious or malignant findings (BIRADS
BR 1 Palpable breast lump Palpable breast lump in patient 40 years of age or above MMG +/- spot compression or digital breast tomosynthesis over palpable findings Suspicious or malignant findings (BIRADS
7/12/2018. Disclosures. The Questions. conventional film mammograms? Controversies in Breast Imaging REBECCA JACKSON, MD
 Disclosures Controversies in Breast Imaging REBECCA JACKSON, MD oi am not a radiologist o I have no financial conflicts of interest Laze =Lava + Haze The Questions 1. Is digital mammography better than
Disclosures Controversies in Breast Imaging REBECCA JACKSON, MD oi am not a radiologist o I have no financial conflicts of interest Laze =Lava + Haze The Questions 1. Is digital mammography better than
Low Dose Molecular Breast Imaging
 Low Dose Molecular Breast Imaging Dr. M.K. O Connor Conflict of Interest Royalties - Gamma Medica Research funding GE Healthcare Research support MTTI Michael O Connor, Ph.D Dept. of Radiology Mayo Clinic
Low Dose Molecular Breast Imaging Dr. M.K. O Connor Conflict of Interest Royalties - Gamma Medica Research funding GE Healthcare Research support MTTI Michael O Connor, Ph.D Dept. of Radiology Mayo Clinic
Combined Screening With Ultrasound and Mammography vs Mammography Alone in Women at Elevated Risk of Breast Cancer JAMA. 2008;299(18):
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Combined Screening With Ultrasound and vs Alone in Women at Elevated Risk of Breast Cancer Wendie A. Berg, MD, PhD Jeffrey D. Blume, PhD Jean B. Cormack, PhD Ellen B. Mendelson, MD
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Combined Screening With Ultrasound and vs Alone in Women at Elevated Risk of Breast Cancer Wendie A. Berg, MD, PhD Jeffrey D. Blume, PhD Jean B. Cormack, PhD Ellen B. Mendelson, MD
Breast Cancer. What is breast cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
