Lymphatic System. Great things are done by a series of small things brought together.
|
|
|
- Jacob Maxwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lymphatic System Great things are done by a series of small things brought together... ~Van Gogh
2 Many of the truths we cling to depend greatly on our point of view.
3 Lymphatic System: Overview Figure 20.1a
4 Lymphatic Structures Tonsils Spleen Thymus MALT Appendix Liver Lymph Nodes
5 Lymphatic Functions Maintain fluid balance by: Returning fluid that has escaped from the bloodstream in the capillaries Returning proteins to the bloodstream that have leaked out from the capillaries Immunity the lymph organs house phagocytic cells & lymphocytes, which play essential roles in the body s defense mechanism Absorption & Transport of Lipids from the G.I. tract when fatty food are ingested & digested, they are absorbed into lymphatic vessels in the small intestines One of the body's many natural defenses against infection
6 Lymph fluid derived from blood plasma that has leaked from the capillaries into the interstitial fluid Most lymph is made in the liver & intestines Contain varying concentrations of WBCs, proteins & fats Fatty Lymph fluid absorbed from the intestine Consists of Emulsified (Free) fatty acids & lymph
7 Composition & Characteristics of Lymph Similar to blood plasma, but with fewer proteins Alkaline, clear & colorless Mostly water Albumins & globulins Salts Urea Lymphocytes & Monocytes (lymph in lacteals in the small intestine can appear milky white due to the presence of absorbed fats)
8 Lymph & Interstitial Fluid Although we think of fluids in the body as occupying completely separate compartments (blood, intracellular fluid, interstitial fluid, etc), they actually move from one compartment to another & they ultimately have the same source What we call Plasma in the blood stream we call Cytosol in the cells, Interstitial Fluid in tissues & Lymph in the lymphatic vessels All of these fluid compartments are interconnected & loss of fluid volume from one will affect the others
9 Lymph & Interstitial Fluid Recall when blood enters the capillaries some of the plasma is forced out under hydrostatic pressure & becomes interstitial fluid Most of that fluid (90%) reenters the blood capillaries The remaining 10% is drained by lymph capillaries & at that point is referred to as lymph As much as 3 Liters of fluid each day is collected by the lymphatic system & returned to the bloodstream
10 Lymphoid Cells Lymphocytes arise from red bone marrow & mature into immune cells that protect the body against foreign cells & substances: T-Lymphocytes (T cells) foreign cells such as bacteria or viruses mature in the (behind the breast bone) B-Lymphocytes (B cells) produce plasma cells which secrete against foreign cells mature in the
11 Other Leukocytes Macrophages Protect the body by phagocytizing foreign substances & by activating T lymphocytes Dendritic cells found in lymphoid tissue play a role in T lymphocyte activation Reticular cells produce the stroma (Matrix), which is the network that supports the other cell types in the lymphoid tissue
12 Cell Mediated Immune Response By Macrophages, Lymphocytes Protection Against Microbes & Antigens (anything foreign to the body) What is the Lifespan of various Lymphocytes? see Text
13 Lymphocyte All lymphocytes originate in the bone marrow as immature cells called? Answer: Both Reside in the Lymphatic Nodes Sore Throat notice enlargement of lymph nodes in your neck, a sign that your body is fighting the infection
14 Principal Lymphatic Functions & interstitial fluid, including plasma protein to the blood Helps maintain fluid balance/homeostasis lipids from the intestine & transport them to the blood, triglycerides combine with cholesterol, lipoprotein & phospholipids to form globules called Defend the body against disease by lymphocyte production & action
15 Lymphatic System Soaks up leaked interstitial fluid & plasma proteins that leak from capillary beds into interstitium like a sponge Receives liters/daily & return it to the circulatory system, transports ADEK, dietary lipids & carry out immune responses Increases capillary pressure, interstitial fluid protein, capillary permeability Decreases Plasma Colloid Osmotic Pressure (Albumin, Globulin)
16 Lymphatic Vessels Lymphatic vessels are widespread in the body, woven between tissue cells Contain that prevent backflow Pump fluid in only 1 directional flow towards the
17 Lacteals Networks of in the lining of the small intestine absorb digested fats from the small intestine (similar to those of the circulatory system) Parts of the body without lacteals: teeth, bones, bone marrow & the CNS
18 Lymphatic Capillaries & their characteristics Unlike capillaries of the circulatory system that are within a closed system, lymph capillaries are, meaning that they have an end that is not connected to another vessel Endothelial cells forming the walls of the lymphatic vessels are not tightly joined The edges of adjacent cells overlap each other loosely, forming Mini-valves
19 Lymphatic Capillaries & their characteristics When fluid pressure in the interstitial space is high, the mini-valves are forced open & fluid enters the lymph capillaries Then, as fluid pressure builds up inside the lymph capillaries, the mini-valves are forced closed from the inside, preventing leaking of the lymph back into the interstitial space Endothelial cells of lymphatics are attached to surrounding tissue cells by collagen fibers
20 Lymphatic Capillaries Figure 20.1b
21 Lymph transport through Lymphatic vessels -pressure vessels that use the same mechanisms as veins to return the lymph to the circulatory system: Contractions & Movement Contractions Smooth muscles in the walls of lymphatic trunks & thoracic duct
22 Lymphatic Vessels Larger Lymphatic Vessels have the same 3 layers (tunics) as circulatory vessels, but there some important structural differences Closely resemble The major differences between veins & lymph vessels: The walls of the lymphatic vessels are Lymphatic vessels have internal valves than veins The lymphatic vessels anastomose!
23 Large Lymphatic Ducts Anterior to L1/L2 (lumbar spine) Drains digestive organs 2 large lymphatic ducts are located in the thoracic region of the body Duct Drains lymph from right arm & right side of head, neck & thorax (the RUQ) Empties into the Right Subclavian Vein Duct the larger of the 2 ducts It collects lymph from the rest of the body & empties into the Left Subclavian Vein
24 Lymphatic System: Overview Figure 20.2a
25 Lymphatic Trunks Figure 20.2b
26 Inflammation Inflammatory Response Micro-organisms/MO s that penetrate endothelial barriers are fought by the inflammatory process
27 Lymph Nodes Over 600 Solid, spherical bodies of Reticular Tissue, shaped like kidney beans 1-2 cm Convex side (IN) vessels, Concave side is the HILUS (OUT) vessels Afferent vessels, Efferent vessels Found embedded in connective tissues: inguinal, axillary, cervical & others sites
28 Lymph Nodes Capsule, Cortex & Medulla, Lobules & Trabecula Filtering cells, debris & MO & Monitoring stations for antigens B & T Lymphocytes B Lymphocytes & Macrophages When overwhelmed with MO s swollen glands 2 nd CA sites swollen, but not tender
29 Lymph Nodes The principle lymphoid organs in the body, which act as filters to remove & destroy microorganisms & other debris from the lymph before it is transported back to the bloodstream Each lymph node is surrounded by a fibrous capsule (septum), which extends inward, dividing the node into several sections called nodules
30 Lymph Nodes Around each nodule are open spaces called Cortical Sinuses, filled with the Lymph & also lined with Phagocytic Reticuloendothelial Cells (Macrophages) Lymph enters the cortical sinuses from several Afferent lymph vessels, circulates through the sinuses & gets filtered by the B-cells & macrophages Lymph flows out few Efferent lymph vessels Lymph nodes range in size, but most < 1 inch in length
31 Lymph Nodes See Text Benefit of more Afferent vessels than Efferent vessels? Hotel California You can check out, but you can never leave
32 Lymph nodes Widely distributed throughout the body lymph nodes located under skin just anterior to external ear flap (known as the auricle) lymph nodes located in neck alongside the sternocleidomastoid muscles lymph nodes located in the axillary (armpit) region lymph nodes located in the inguinal (groin) region
33 Structure of a Lymph Node Figure 20.4a, b
34 Clinical Note What do swollen lymph nodes indicate? Swollen lymph nodes can be symptomatic of any of a number of causes Palpation can indicate the cause, as can the presence or absence of pain Painful, Swollen nodes usually indicate infection Painless swollen nodes may indicate a tumor or cancer
35 Lymphoid Tissue & Organs Mostly Loose Reticular Connective Tissue Large number of Reticular Protein Fibers in the tissue matrix Most of the lymph organs, with the exception of the thymus (glandular), are composed largely of this reticular tissue Tissue is arranged differently to form the various lymphatic organs, which serve specific purposes
36 Lymphatic Flow (collect excess interstitial fluid) (receive lymph from the lymph capillaries) (formed from the merging of collecting vessels) Right Lymphatic & Thoracic Ducts) Right & Left Veins (lymph reenters bloodstream)
37 Spleen Lymphoid Organ Shaped like a loose fist ~½ lb. Located in the directly below the diaphragm Has Hilus, Splenic artery & vein
38 Spleen Surrounded by a fibrous capsule & contains 2 internal areas of tissue: White pulp Red pulp
39 White pulp tissue areas within the spleen that are composed primarily of lymphocytes suspended on reticular fibers form small clusters within the splenic tissue Because of the presence of the lymphocytes, the white pulp areas are involved with the immune functions of the spleen site of lymphocyte proliferation
40 Red pulp most of the spleen tissue is made up of red pulp areas, which are rich in blood vessels & macrophages The red pulp areas are mainly involved in removing old erythrocytes & any blood-borne pathogens Stores & Recycles breakdown products of erythrocytes for later use, such as Heme (Fe) to needed to make more new hemoglobin
41 Spleen Site of erythrocyte production in the fetus (this stops after birth) Storage of blood platelets Malaria or Mono can also cause splenomegaly Enlargement of the spleen seen with: Rheumatoid Arthritis, Systemic Lupus, Sickle Cell Anemia, Leukemia & Lymphomas
42 Structure of the Spleen Figure 20.6a-d
43 Clinical Note Spleen lies in the LUQ & is easily ruptured by blows to the left side If ruptured, it can release large amounts of blood into the abdominal cavity including any bacteria that it had filtered out This can lead to severe internal hemorrhaging & bacterial infections of internal organs Splenectomy Removal of a traumatized spleen Liver takes over function (> risk of Bacterial infection, if younger than age 12 regeneration is possible) If injured and not removed mortality rate is about 90%
44 Thymus Encapsulated, Bi-lobed glandular organ Trabeculae divide lobes into lobules Located atop the Heart within the in size & function with age 70 g infant 3 g in elderly Fibrous Fatty in Elderly T-cells w/in Cortex Macrophages w/in Medulla T-cells proliferate throughout our lifetime
45 Thymus During adolescence its growth stops & it starts to atrophy While it is active, its cells (thymocytes) secrete hormones (thymosin & thymopoietin) that cause T lymphocytes to become immunocompetent (enables them to recognize foreign cells & substances) While it is functional, the thymus gland does not directly fight infections, making it different from other lymph organs
46 MALT Lymphatic Tissue Collective Name for all small lymphoid tissues in the body: Appendix, Peyer s patches, Tonsils & lymphoid follicles in the walls of the respiratory passageways MALT protects the digestive & respiratory tracts from foreign matter that constantly enter Distal Ileum & Appendix
47 Tonsils/Adenoids Ring of Fire the simplest lymphoid organs & form a ring of lymphoid tissue around the openings to the pharynx, they appear as swellings of the mucosa that gather & remove many of the pathogens entering the pharynx in food or inhaled air
48 Tonsils/Adenoids Ring of Fire (paired, lie at the base of the tongue) Pharyngeal (, located in the posterior wall of the nasopharynx) (paired lateral to pharyngeal) on either side of the pharynx directly behind the nasal cavity Largest & most frequently infected
49 Clinical Note when the pharyngeal tonsils become infected & inflamed they are referred to as Adenoids as they swell forwards into the nasal cavity, they can interfere with normal breathing & are often removed Tonsil removal Tonsilectomy
50 Peyer s Patches Nodes of lymphatic tissue located w/in Small Intestine clusters of lymphoid follicles that are found in the wall of the distal portion of the small intestine & the appendix (located in the RLQ of the abdominal cavity), also contains small masses of lymphoid follicles The lymph tissue in these areas serve 2 strategic purposes: Destruction of bacteria, which occur in large numbers in the intestine Generation of memory lymphocytes for long-term immunity
51 Buboes Swollen lymph nodes Bubonic Plague Also known as Black Death Disease caused by bacteria (Yersinia pestis) Transferred from rats to humans by bites from the rat flea The bacteria localize in the lymph nodes, causing them to enlarge Without treatment, the bacteria can spread throughout the body, rapidly causing death in 70 90% of those infected! In the 14th century, the plague killed 200 million victims & constituted the largest death toll from any known epidemic Today, only about 15 cases are reported annually in the US & current antibiotic treatments are usually effective
52 Lymphatic Vessel Disorders Lymphedema Lymphangitis Elephantiasis Lymphoma
53 Lymphangitis Inflammation of the superficial lymphatic vessels, most often due to a streptococcus infection Red streaks are present along the inflamed vessels & are accompanied by rubor, dolor, calor, tumor & functio laesa Lymph nodes in the area are often enlarged & tender Treatment consists of antibiotics & elevating the affected part of the body so that local lymphatics can drain
54 Lymphedema abnormal accumulation of fluid in the interstitial space because of a blockage of uptake by the lymphatic vessels In other words, the interstitial fluid can t enter the lymphatic capillaries and become lymph, or the larger collecting vessels are blocked & the lymph backs up through the lymph capillaries & out into the interstitial space Causes include blockage by tumors, infection & interference with lymph flow following surgery
55 Elephantiasis (lymphatic filariasis) Severe Swelling of Lymphatic Vessels due to blockage by roundworms (filaria) Swelling can become so severe that the overlying tissues can become deformed & the lower limbs can resemble an elephant s leg Lymphatic blockage of Lymph flow can be due to parasitic worms, recurrent attacks of a bacterial infection that causes inflammation of the lymphatic vessels (streptococcal lymphangitis) When the lymphatic obstruction is large enough, back pressure in the lymphatic channels produces dilation of the superficial vessels resulting in Extreme Swelling Without medical intervention, the cycle continues until the affected area is Grotesquely Enlarged Death of surrounding tissues may also occur from an obstructed blood supply (Gangrene) Skin usually develops a thickened, pebbly, ulcerated & darkened appearance Fever, chills & Malaise
56 Lymphoma Any tumor of the lymphatic tissue (Benign or Malignant) Symptoms: Night sweats or unexplained fever, Loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss and fatigue Children may develop a cough or breathlessness may also complain of abdominal pain or you may notice a lump in your child's abdomen or persistent itching of the skin all over the body Divided into 2 groups: Hodgkin s lymphoma Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
57 Hodgkin s Lymphoma/Disease Malignancy of the lymph nodes The Diagnostic Sign is the presence of large, deformed B lymphocytes known as Reed-Sternberg cells in the lymph nodes The lymphoma usually begins in a single lymph node in the neck, axillary region, or groin & spreads to nearby lymph nodes Signs/Symptoms: include swollen, non-painful lymph nodes, fatigue, persistent fever & night sweats It is categorized into stages based on the degree of metastasis (spreading) Stages 1 or 2 mean that the cancer is in one or a few lymph nodes Stage 5 means it has spread throughout the body The lower the stage, the better the prognosis for survival Patients with stage 1 Hodgkin s lymphoma have a 90% survival rate 5 years after diagnosis
58 Non Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma All cancers of lymphatic tissue Except Hodgkin s disease Involves uncontrolled growth & metastasis (spread) of immature lymphocytes, with nonpainful swelling of lymph nodes, spleen & Peyer s patches Eventually it may spread to other tissues Signs/Symptoms: fever, night sweats & rapid weight loss 1 st sign NHL is a painless swelling of a lymph node in the neck, armpit or groin There are low-grade & high-grade varieties The high-grade type is more common in younger people, grows more quickly, but responds better to chemotherapy The low-grade type is more common in the elderly & though it doesn t spread as rapidly it is more resistant to treatment, so it is often fatal
59 Sentinel Node the very 1 st lymph node that filters fluid draining away from the area of concern (Infections & Cancer) Sentinel = guard, watchdog or protector
60 Edema excess accumulation of interstitial fluid in tissue spaces due to obstruction (infected node or blocked vessel) filtration faster than reabsorption Metastasis spreading via lymphatic or blood vessels All malignant tumors eventually exhibit metastasis 1 2 tumors- seeding Infected enlarge not firm, movable, very tender Cancerous enlarged, firm, non-tender
61 Lymphatic Learning Objectives Describe the general characteristics & functions of the LS Describe the location of the major lymphatic pathways Describe the formation of tissue fluid & lymph Describe major functions of the lymph nodes, thymus & spleen Define immunity Relate the role of the LS to immunity
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
2/19/2018. Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues. What is Lymph?
 Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic Systems Overview General Functions Organization Components Lymphatic System General Functions Transportation Excess fluid from capillary exchange Fats & fat soluble vitamins
The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic Systems Overview General Functions Organization Components Lymphatic System General Functions Transportation Excess fluid from capillary exchange Fats & fat soluble vitamins
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System
 Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Lymphatic System. The most important functions of the lymphatic system are: Maintenance of fluid balance in the internal environment
 Lymphatic System Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is a complex network of connective tissue that is composed of: Lymphoid organs Lymph nodes Lymph ducts Lymph vessels Lymph capillaries Lymphatic System
Lymphatic System Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is a complex network of connective tissue that is composed of: Lymphoid organs Lymph nodes Lymph ducts Lymph vessels Lymph capillaries Lymphatic System
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
The Lymphatic System. General Functions of Lymphatic System:
 The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues
 The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic Pathways. Lymphatic Capillaries. network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids
 Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
3/17/2014. The Lymphatic System. Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs
 The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
Chapt 21: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Chapt 21: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Goals 1. Discuss the organization of the lymphatic system, including the vessels, principal lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen 2. Explain the relationship between
Chapt 21: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Goals 1. Discuss the organization of the lymphatic system, including the vessels, principal lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen 2. Explain the relationship between
CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Lymphatic System: Lymphatic System which consists of vessels and organs plays two vital roles in our lives: 1) The vessels
CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Lymphatic System: Lymphatic System which consists of vessels and organs plays two vital roles in our lives: 1) The vessels
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
2/28/18. Lymphatic System and Immunity. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 27. Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
- Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body. - Has disease-fighting functions - Helps maintain homeostasis
 Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Cardiovascular & lymphatic system both are supply fluid flow in to the body. but bothe are deferent type of fluid..
 Hap unit 6th Introduction:- All body tissues are bathed in tissue fluid, consisting of the diffusible constituent of blood & waste material from cell. Some tissue fluid returnes to capillaries at their
Hap unit 6th Introduction:- All body tissues are bathed in tissue fluid, consisting of the diffusible constituent of blood & waste material from cell. Some tissue fluid returnes to capillaries at their
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
The Lymphoid System Pearson Education, Inc.
 23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Overview of the Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Protects us against disease Lymphatic system cells respond to: Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells,
Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Overview of the Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Protects us against disease Lymphatic system cells respond to: Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells,
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System
 37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System 1 Blood Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs,
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System 1 Blood Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs,
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Cardiovascular System. Chapters 11, 12
 Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50%
 BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
The Lymphatic System
 الكلية االسالمية الجامعة قسم تقنيات التحليالت المرضية االسم التدريسي: ا.د.عبد الهادي صالل المرحلة الثانية المادة : التشريح / النظري 2018-2017 م. م. عباس حسين عبيد The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system
الكلية االسالمية الجامعة قسم تقنيات التحليالت المرضية االسم التدريسي: ا.د.عبد الهادي صالل المرحلة الثانية المادة : التشريح / النظري 2018-2017 م. م. عباس حسين عبيد The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system
Lymphatic Vessels & Lymph lymphatic vessels. 20 The Lymphatic System. They can't all be superstars! The Lymphatic System. Keeps us healthy!
 They can't all be superstars! The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System: 1. lymphatic vessels 2. lymph 3. irculation, P, Supports immune & clotting, etc... cardiovascular system! Lymphoid Organs & Tissues:
They can't all be superstars! The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System: 1. lymphatic vessels 2. lymph 3. irculation, P, Supports immune & clotting, etc... cardiovascular system! Lymphoid Organs & Tissues:
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES. Transport dietary fat. Transport excess tissue fluid back to blood stream
 CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES 1. Name the organs that compose the lymphatic system and give three general functions performed by this system. Bone Marrow Control Disease Thymus Lymph
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES 1. Name the organs that compose the lymphatic system and give three general functions performed by this system. Bone Marrow Control Disease Thymus Lymph
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS. Chapter 33
 LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB. BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM ORGANS PRIMARY BONE MARROW THYMUS SECONDARY LYMPH NODES SPLEEN FUNCTIONS CONTROL DISEASE TRANSPORT
LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM ORGANS PRIMARY BONE MARROW THYMUS SECONDARY LYMPH NODES SPLEEN FUNCTIONS CONTROL DISEASE TRANSPORT
A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa!
 A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa! tonsils (two oval masses in the back of the throat) Lymphoid organs include: adenoids (two glands located at the back of the nasal passage) appendix
A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa! tonsils (two oval masses in the back of the throat) Lymphoid organs include: adenoids (two glands located at the back of the nasal passage) appendix
Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Lymphatic and Immune www.vastaccess.com 2 Specialized component of circulatory system Lymphatic system functions: Maintenance of internal fluid balance Immunity Lymph derived from blood and tissue fluid
Lymphatic and Immune www.vastaccess.com 2 Specialized component of circulatory system Lymphatic system functions: Maintenance of internal fluid balance Immunity Lymph derived from blood and tissue fluid
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Lymphatic System Lymphatic capillaries reabsorb excessive tissue fluid and transport the fluid through the lymphatic pathway, and ultimately dispose
The Lymphatic System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Lymphatic System Lymphatic capillaries reabsorb excessive tissue fluid and transport the fluid through the lymphatic pathway, and ultimately dispose
The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 21 Part 1 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Lymphatic system Main function
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 21 Part 1 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Lymphatic system Main function
Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts
 Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System
 Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Lymphatic System. Chapter 14. Introduction. Main Channels of Lymphatics. Lymphatics. Lymph Tissue. Major Lymphatic Vessels of the Trunk
 Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
Chapter 14. Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue. nur
 8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue nur Lymphatic vascular system Functions return to the blood extracellular fluid (Lymph) from connective tissue spaces. ensures the return of water, electrolytes
8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue nur Lymphatic vascular system Functions return to the blood extracellular fluid (Lymph) from connective tissue spaces. ensures the return of water, electrolytes
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 28 The Immune System Lesson 1: The Immune System Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson,
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 28 The Immune System Lesson 1: The Immune System Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson,
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
When an ordinary man attains knowledge, he becomes a sage. When a sage attains knowledge, he becomes an ordinary man. -Zen saying.
 When an ordinary man attains knowledge, he becomes a sage. When a sage attains knowledge, he becomes an ordinary man. -Zen saying Lymphatic System Lesson Plan: Lymphatic System 5 minutes: Breath of Arrival
When an ordinary man attains knowledge, he becomes a sage. When a sage attains knowledge, he becomes an ordinary man. -Zen saying Lymphatic System Lesson Plan: Lymphatic System 5 minutes: Breath of Arrival
Overview of the Lymphoid System
 Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Anatomy & Physiology Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Anatomy & Physiology Lymphatic System and Immunity BELL WORK: DEFINE THE TERMS USING YOUR NEW BOOKS (PAGES 335-336): LYMPHOCYTE PHAGOCYTE PATHOGEN A NTIGEN A NTIBODIES A&P State Standards 33) Describe
Anatomy & Physiology Lymphatic System and Immunity BELL WORK: DEFINE THE TERMS USING YOUR NEW BOOKS (PAGES 335-336): LYMPHOCYTE PHAGOCYTE PATHOGEN A NTIGEN A NTIBODIES A&P State Standards 33) Describe
Lymphatic System and Immune System. Blood capillaries. Lymphatic vessels/ lymph nodes. Then, identify by labeling these specific structures in part B.
 Name: Date: Period: Lymphatic System and Immune System 1. Figure 21.1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular
Name: Date: Period: Lymphatic System and Immune System 1. Figure 21.1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular
Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream (fluid balance) Immunity. Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
 Lymphatic System L Y M P H A T I C C O M P O N E N T S What is a Lymphatic System? The lymphatic system is a complex system of fluid drainage and transport, immune response, and disease resistance. Fluid
Lymphatic System L Y M P H A T I C C O M P O N E N T S What is a Lymphatic System? The lymphatic system is a complex system of fluid drainage and transport, immune response, and disease resistance. Fluid
Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students
 University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy
 Haematology Lectures Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy 1 Objectives 1. Define the term Reticuloendothelial system (RES). 2. Describe the cellular components of RES. 3. Describe
Haematology Lectures Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy 1 Objectives 1. Define the term Reticuloendothelial system (RES). 2. Describe the cellular components of RES. 3. Describe
Chapter10 Immune system
 Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System Combining Forms Aden/o Angi/o Hem/o Hist/o Immun/o Lymph/o Splen/o Thym/o Tox/o gland vessel (blood or lymph) blood tissue immune lymph spleen thymus gland poison Prefixes / Suffixes
The Lymphatic System Combining Forms Aden/o Angi/o Hem/o Hist/o Immun/o Lymph/o Splen/o Thym/o Tox/o gland vessel (blood or lymph) blood tissue immune lymph spleen thymus gland poison Prefixes / Suffixes
Portal System & Lymphatic System. When the vein of any organ of the body does not open in the caval vein or heart.
 1. Introduction of portal system 2. Renal portal system 3. Hepatic portal system 4. Hypophysial portal system 5. Introduction of lymphatic system 6. The lymph 7. Lymph vessels 8. Lymph nodes 9. Lymphoid
1. Introduction of portal system 2. Renal portal system 3. Hepatic portal system 4. Hypophysial portal system 5. Introduction of lymphatic system 6. The lymph 7. Lymph vessels 8. Lymph nodes 9. Lymphoid
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
Anatomy. Lymph: Tissue fluid that enters a lymphatic capillary (clear fluid that surrounds new piercings!)
 Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
OBJECTIVES. The Amazing Immune System
 The Amazing Immune System Graphic source: (l) Jeanne Kelly, NIAID; (r) Wikimedia Commons OBJECTIVES Describe at least three components of the immune system Describe the role in our immune response of at
The Amazing Immune System Graphic source: (l) Jeanne Kelly, NIAID; (r) Wikimedia Commons OBJECTIVES Describe at least three components of the immune system Describe the role in our immune response of at
Equine biological systems
 Equine biological systems Pack 20 The lymphatic system Pack Code: EBS20 This pack will help you to: List the functions of the lymphatic system. Describe the components of the lymphatic system.. www.lbcnc.org.uk
Equine biological systems Pack 20 The lymphatic system Pack Code: EBS20 This pack will help you to: List the functions of the lymphatic system. Describe the components of the lymphatic system.. www.lbcnc.org.uk
What are bacteria? Microbes are microscopic(bacteria, viruses, prions, & some fungi etc.) How do the sizes of our cells, bacteria and viruses compare?
 7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
Chapter 14. Part 2. An Introduction to Host Defenses Innate Immunities
 Chapter 14 Part 2 An Introduction to Host Defenses Innate Immunities Host defense mechanisms To protect the body against pathogens, the immune system relies on a multilevel network of physical barriers,
Chapter 14 Part 2 An Introduction to Host Defenses Innate Immunities Host defense mechanisms To protect the body against pathogens, the immune system relies on a multilevel network of physical barriers,
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM LAB WORKSHEET
 NAME: Pd 4 DATE: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM LAB WORKSHEET ACTIVITY 1: Answer the following questions 1. What is lymph? What is the normal composition of lymph? How does the composition of lymph differs from that
NAME: Pd 4 DATE: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM LAB WORKSHEET ACTIVITY 1: Answer the following questions 1. What is lymph? What is the normal composition of lymph? How does the composition of lymph differs from that
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
Blood and the Lymphatic System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Blood and the Lymphatic System
 Lesson Overview 33.2 Blood and the Lymphatic System THINK ABOUT IT When you think about body tissues, you probably picture something with a definite shape, like muscle or skin. But blood is a tissue too
Lesson Overview 33.2 Blood and the Lymphatic System THINK ABOUT IT When you think about body tissues, you probably picture something with a definite shape, like muscle or skin. But blood is a tissue too
CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS. Has a pump (heart)
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS Cardiovascular Derived from mesoderm Transport System Has a pump (heart) Arteries Veins for return Veins have valves Carries RC, WBC, plasma Lymphatic Derived from mesoderm Transport
CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS Cardiovascular Derived from mesoderm Transport System Has a pump (heart) Arteries Veins for return Veins have valves Carries RC, WBC, plasma Lymphatic Derived from mesoderm Transport
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 7 Lymphatic System & Immune System Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions and Structure of the lymphatic
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 7 Lymphatic System & Immune System Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions and Structure of the lymphatic
Clinical Lymphatic System
 Quiz Description Clinical Lymphatic System Q.1) Q.2) The right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct empty into the jugular vein inferior vena cava portal vein subclavian veins Lymph from the right arm
Quiz Description Clinical Lymphatic System Q.1) Q.2) The right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct empty into the jugular vein inferior vena cava portal vein subclavian veins Lymph from the right arm
Lymphoid tissue. 1. Central Lymphoid tissue. - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus.
 1. Central Lymphoid tissue Lymphoid tissue - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus. Bone Morrow - The major site of hematopoiesis in humans. - Hematopoiesis
1. Central Lymphoid tissue Lymphoid tissue - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus. Bone Morrow - The major site of hematopoiesis in humans. - Hematopoiesis
5 Lymphatic System. Chapter
 67 Chapter 5 Lymphatic System Overview -The lymphatic system consists of the following components (Figure 5.1, Derrickson): (i) lymphatic vessels, which contain a fluid called lymph, (ii) lymphatic organs,
67 Chapter 5 Lymphatic System Overview -The lymphatic system consists of the following components (Figure 5.1, Derrickson): (i) lymphatic vessels, which contain a fluid called lymph, (ii) lymphatic organs,
You see it every rainy day water, water everywhere, rushing along gutters and down
 Chapter 11 Keeping Up Your Defenses: The Lymphatic System In This Chapter Delving into lymphatic ducts Noodling around with nodes Exploring the lymphatic organs You see it every rainy day water, water
Chapter 11 Keeping Up Your Defenses: The Lymphatic System In This Chapter Delving into lymphatic ducts Noodling around with nodes Exploring the lymphatic organs You see it every rainy day water, water
Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Immunity- ability to resist infection and disease through the activation of specific defenses These defenses can be found in the lymphatic system Lymphatic
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Immunity- ability to resist infection and disease through the activation of specific defenses These defenses can be found in the lymphatic system Lymphatic
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Lymphatic System. Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph. Organs and structures involved. similar to interstitial fluid
 Lymphatic System Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph similar to interstitial fluid Organs and structures involved red bone marrow thymus spleen lymph nodes diffuse lymphatic tissue tonsils, adenoids
Lymphatic System Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph similar to interstitial fluid Organs and structures involved red bone marrow thymus spleen lymph nodes diffuse lymphatic tissue tonsils, adenoids
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment
 BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved
 Bio 100 Guide 21 Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved inorganic ions, proteins, nutrients,
Bio 100 Guide 21 Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved inorganic ions, proteins, nutrients,
Immune System.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Immune system 1st, 2nd and 3rd line of defense Immune disorders
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Immune system 1st, 2nd and 3rd line of defense Immune disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM p.382 386 Immune system A complex system involving several organs and tissues (e.g.
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Immune system 1st, 2nd and 3rd line of defense Immune disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM p.382 386 Immune system A complex system involving several organs and tissues (e.g.
Chapter 22. The Lymphatic System. AP2 Chapter 22 1
 Chapter 22 The Lymphatic System AP2 Chapter 22 1 Chapter 22 Outline I. Lymphatic System II. Immunity III. Innate Immunity IV. Adaptive Immunity V. Immune Interactions VI. Immunotherapy VII. Acquired Immunity
Chapter 22 The Lymphatic System AP2 Chapter 22 1 Chapter 22 Outline I. Lymphatic System II. Immunity III. Innate Immunity IV. Adaptive Immunity V. Immune Interactions VI. Immunotherapy VII. Acquired Immunity
Circulatory System. The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system
 Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy
 Systematic Anatomy Department of Anatomy,Histology & Embryology Shanghai Medical College,Fudan University Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: Zhanghq58@126.com Office: Building 9,Room308, 54237151-9308 Mobile:13761809799
Systematic Anatomy Department of Anatomy,Histology & Embryology Shanghai Medical College,Fudan University Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: Zhanghq58@126.com Office: Building 9,Room308, 54237151-9308 Mobile:13761809799
Chapter Lymphatic Cells, Lymphatic Tissues, and Lymphatic Organs
 Chapter 22.2 Lymphatic Cells, Lymphatic Tissues, and Lymphatic Organs Lymphatic Cells These are the cells that play a key roll in the structure and function of the immune system. We have already introduced
Chapter 22.2 Lymphatic Cells, Lymphatic Tissues, and Lymphatic Organs Lymphatic Cells These are the cells that play a key roll in the structure and function of the immune system. We have already introduced
Lymphatic System Disorders
 Lymphatic System Disorders Lymphomas Malignant neoplasms involving lymphocyte proliferation in lymph nodes Specific causes not identified // Higher risk in adults who received radiation during childhood
Lymphatic System Disorders Lymphomas Malignant neoplasms involving lymphocyte proliferation in lymph nodes Specific causes not identified // Higher risk in adults who received radiation during childhood
General Biology. A summary of innate and acquired immunity. 11. The Immune System. Repetition. The Lymphatic System. Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.
 A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
Lympha'c System. Unit 6.9 (6 th Edi-on) Chapter 7.9 (7 th Edi-on)
 Lympha'c System Unit 6.9 (6 th Edi-on) Chapter 7.9 (7 th Edi-on) 1 Learning Objec'ves Iden-fy main components and organs of the lympha-c system and their func-ons. Explain the func-ons (physiology) of
Lympha'c System Unit 6.9 (6 th Edi-on) Chapter 7.9 (7 th Edi-on) 1 Learning Objec'ves Iden-fy main components and organs of the lympha-c system and their func-ons. Explain the func-ons (physiology) of
Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System And Body Defenses Key
 Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System And Body Defenses Key CHAPTER 12 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND BODY DEFENSES KEY PDF - Are you looking for chapter 12 the lymphatic system and body defenses key Books? Now, you
Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System And Body Defenses Key CHAPTER 12 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND BODY DEFENSES KEY PDF - Are you looking for chapter 12 the lymphatic system and body defenses key Books? Now, you
1. Lymph, the fluid of the lymphatic system, is collected from nearly every tissue and organ and transported to.
 (2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
(2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System A. Consists of two semi-independent parts 1. Lymphatic vessels 2. Lymphoid tissues and organs B. Lymphatic system functions 1. Transports
Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System A. Consists of two semi-independent parts 1. Lymphatic vessels 2. Lymphoid tissues and organs B. Lymphatic system functions 1. Transports
Lifeblood Lab Activity
 History of Blood: It is the universal symbol of horror, of death, yet it is the one thing that keeps you living. It is the blood that is coursing through your veins. But, what do you really know about
History of Blood: It is the universal symbol of horror, of death, yet it is the one thing that keeps you living. It is the blood that is coursing through your veins. But, what do you really know about
The Lymphatic System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
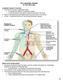 The Lymphatic System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Lymphatic System: Overview Consists of two semi-independent parts o A meandering network of lymphatic vessels o Lymphoid tissues and organs scattered throughout the
The Lymphatic System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Lymphatic System: Overview Consists of two semi-independent parts o A meandering network of lymphatic vessels o Lymphoid tissues and organs scattered throughout the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
Blood and Defense. Chapter 11
 Blood and Defense Chapter 11 Functions of Blood 1. Carry nutrients from the small intestine and oxygen from the lung to tissues in the body 2. Transport wastes from tissues to the kidneys and carbon dioxide
Blood and Defense Chapter 11 Functions of Blood 1. Carry nutrients from the small intestine and oxygen from the lung to tissues in the body 2. Transport wastes from tissues to the kidneys and carbon dioxide
Lymphatic vessels purpose arterial side of the capillaries lose more fluid then venous end reabsorbs
 Chapter 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity composed of 1. lymphatic vessels 2. specialized cells called lymphocytes 2. numerous lymphoid tissues and organs function of the lymphatic system 1. production,
Chapter 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity composed of 1. lymphatic vessels 2. specialized cells called lymphocytes 2. numerous lymphoid tissues and organs function of the lymphatic system 1. production,
Unit 12 - The Lymphatic System and 1
 Unit 12 - The Lymphatic System and 1 I. Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses A. The Lymphatic System 1. Consists of two semi-independent parts a) Lymphatic vessels b) Lymphoid tissues and organs
Unit 12 - The Lymphatic System and 1 I. Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses A. The Lymphatic System 1. Consists of two semi-independent parts a) Lymphatic vessels b) Lymphoid tissues and organs
(b) fluid returns to venous end of capillary due to hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Lymphatic System and Immunity (Body Defenses) I. (Slide 2) Introduction A) General 1) Lymphatic System performs 2 basic functions: 2) Organs of the Lymphatic System (a) lymphatic
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Lymphatic System and Immunity (Body Defenses) I. (Slide 2) Introduction A) General 1) Lymphatic System performs 2 basic functions: 2) Organs of the Lymphatic System (a) lymphatic
Immune - lymphatic system
 Immune system - organisation: Immune - lymphatic system - histology & embryology organised lymphoid structures cell components lymphocytes event. lymphatic follicles accessory cells monocytes-macrophages
Immune system - organisation: Immune - lymphatic system - histology & embryology organised lymphoid structures cell components lymphocytes event. lymphatic follicles accessory cells monocytes-macrophages
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System
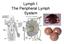 Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Carries essential nutrients to the cells Collects cellular waste Plays an important role in the immune system of the body Lymph A fluid that
The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Carries essential nutrients to the cells Collects cellular waste Plays an important role in the immune system of the body Lymph A fluid that
The Lymphatic System
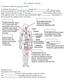 The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three main functions: It maintains the balance of between the and, known as fluid homeostasis. It forms part of the body's system and helps defend against
The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three main functions: It maintains the balance of between the and, known as fluid homeostasis. It forms part of the body's system and helps defend against
