Comprehensive molecular screening: from the RT-PCR to the RNA-seq
|
|
|
- Elaine Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Article Comprehensive molecular screening: from the RT-PCR to the RNA-seq Carlota Costa 1, Ana Giménez-Capitán 1, Niki Karachaliou 1, Rafael Rosell 1,2 1 Breakthrough Cancer Research Unit, Pangaea Biotech S.L, USP Dexeus University Institute, Barcelona, Spain; 2 Catalan Institute of Oncology, Hospital Germans Trias i Pujol, Ctra. de Can Ruti s/n Badalona, Spain Corresponding to: Carlota Costa, PhD. PangaeaBiotech/USP Instituto Universitario Dexeus, Laboratorio de Oncología, c/sabino de Arana 5-19, Spain. ccosta@pangaeabiotech.com. Abstract: Up to now, the analysis of the mrna expression in tumoral and non-tumoral has been conducted via RT-PCR. It is considered to be the gold standard for measuring the number of copies of specific cdna targets. The application of RT-PCR has demonstrated that levels of RNA transcripts stratify patients and predict outcomes in a variety of diseases, providing the basis for several important clinical tests. However, the inherent variability in the quality of any quantitative PCR data makes it difficult to replicate and the analysis is time consuming in the laboratory for the analysis of one gene. Moreover, comparing expression levels across different experiments is often difficult and can require complicated normalization methods. Many techniques have been developed over the years but without good clinical applications. A new, simple and effective way to measure transcriptome composition and to discover new exons or genes is by the RNA-seq. Some advantages of this technique are high reproducibility, the large dynamic range, requirement of less sample RNA, and the ability to detect novel transcripts, alternative splicing, even in the absence of a sequenced genome. However, this RNA-Seq technique will not likely replace current RT-PCR methods, but will be complementary depending on the needs and the resources of the clinic and the laboratory as the results of the RNA-Seq will identify those genes that need to then be examined using RT-PCR methods. The application of the two complementary technologies in the routine analysis of cancer laboratories would be useful in characterizing patients and would assist oncologists in making clinical decisions, as it allows us to identify all molecular characteristics of the tumor. Key Words: Molecular screening; RT-PCR; RNA-seq; mrna expression Submitted Jan 18, Accepted for publication Feb 19, doi: /j.issn Scan to your mobile device or view this article at: The analysis of the mrna expression in tumoral and nontumoral samples is becoming increasingly important in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer patients. Until the end of the 1990s, Northern blot had been used extensively for RNA quantification (1,2). However, the discovery of the reverse transcriptase enzyme led to the development of reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technique which has since displaced Northern blot as the method of choice for RNA detection and quantification (3). This enzyme allows the transformation of the mrna in cdna which allows it to be quantified. In 2000, Bustin et al. (3) describes a new technology based on this concept. RT- PCR is used to qualitatively detect gene expression through the creation of complementary DNA (cdna) transcripts from mrna, and quantitatively measure the amplification of cdna using fluorescent probes (3). The process of RT-PCR consists of three steps: reverse transcriptase-based conversion of RNA to cdna, the amplification of cdna by PCR, and the
2 88 Costa et al. Comprehensive molecular screening detection and quantification of amplified products-referred as amplicons (4). RT-PCR can be utilized to quantify mrna in both relative (5) and absolute terms (6). It has become one of the most widely used methods of gene quantification as it has a large dynamic range, with high sensitivity and can be highly sequence-specific. The scope of the RT-PCR technique makes it applicable across a wide range of experimental conditions, and allows experimental comparisons between normal and abnormal tissues (4). Until now, quantitative RT-PCR assay is considered to be the gold standard for measuring the number of copies of specific cdna targets. The extensive use of this technique has resulted in the development of various protocols that enable the generation of quantitative data using fresh, frozen, or archived FFPE samples, whole-tissue biopsies, microdissected samples, single cells, tissue cultured cells, total or mrna, different cdna, assays of distinct efficiencies, sensitivities, and robustness, diverse detection chemistry, reaction conditions, thermal cyclers, individual analysis and reporting methods (7). As a result, while there are numerous publications describing the technique, the inherent variability in the quality of any quantitative PCR data makes it difficult to replicate (8). For this reason, the international consortium of academic scientists has published the Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments (MIQE) guidelines to standardize a protocol. The MIQE guidelines describe the minimum information required to evaluate RT-PCR experiments (9). The application of RT-PCR has demonstrated that levels of RNA transcripts stratify patients and predict outcomes in a variety of diseases, providing the basis for several important clinical tests (10-12). An example is a 21-gene RT- PCR-based test, which interrogates tumor RNA to predict recurrence risk and magnitude of chemotherapy benefit in early estrogen receptor positive (ER+) breast cancer. This test is now used to guide treatment decisions for about half of ER+ breast cancer patients in the USA (13-16). The problems with this technique are the time consumed in the laboratory for the analysis of one gene and the variability of the results. Moreover, comparing expression levels across different experiments is often difficult and can require complicated normalization methods. To address the first problem, the scientific community developed new systems to analyze many genes at the same time. Several technologies are available in the market, such as Serial Analysis of Gene (SAGE), high-density oligo microarrays gene expression (SAGE), cap analysis of gene expression (CAGE) and massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS) (17-19). With these techniques it is possible to obtain the mrna expression data for hundreds of genes in one experiment. However, these new techniques have their own limitations. In the case of the methods based on hybridization, the main problems are: the limit in the detection of RNA splice patterns and previously unmapped genes (it is mandatory to know the genome sequence); the high background levels due to cross-hybridization; and the limited dynamic range of detection (20). In the techniques based on Sanger sequencing technology, which use cdna sequencing, only a portion of the transcript is analyzed and isoforms are generally indistinguishable. These disadvantages limit the use of these methods in the translational investigation and clinical daily practice (21). One simple and effective way to measure transcriptome composition and to discover new exons or genes is by the direct ultra-high-throughput sequencing of cdna. This method, termed RNASeq, also called Whole Transcriptome Shotgun Sequencing ( WTSS ), has clear advantages over existing approaches and allows the mapping and quantification of transcriptomes. It is expected to revolutionize the field of transcriptom analysis (21). RNA-seq refers to the use of high-throughput sequencing technologies to sequence cdna in order to obtain information about RNA content (22). A single experiment can provide information about gene expression, novel transcripts, novel isoforms, alternative splice sites, allele-specific expression, csnps, and rare transcripts. Ideally, it should be able to directly identify and quantify all RNAs, small or large (23-26). The sample analysis can be done with a variety of platforms, for example, the Illumina Genome Analyzer platform (27), the ABI Solid Sequencing (28), or the Life Science s 454 Sequencing (29) (Figure 1). RNA-Seq is not a mature technology. It is undergoing rapid evolution in the biochemistry of sample preparation; in sequencing platforms; in computational pipelines; and in the subsequent analysis methods that include statistical treatments and transcript model building. The ENCODE Consortium develops guidelines which include the most important aspects to bear in mind in study design (30). The main steps of the technique are: isolate the RNAs from a sample, convert them to cdna fragments using RT, then a high-throughput sequencer is used to generate millions of reads from the cdna fragments, reads are
3 Translational lung cancer research, Vol 2, No 2 April Figure 1 Different platforms for RNAseq analysis mapped to a reference genome or transcript set with an alignment tool, and counts of reads mapped to each gene. For transcriptome sequencing, expression levels of different genes are determined by counting the number of reads mapped to the gene and then normalizing this read count by the length of the gene model and the total number of mapped reads in the sample (31). In the case of RNA-Seq, the mapping of reads is only the first step in a complex data processing schema. However, it is essential that the results are analyzed by a specialized bioinformatician. This role requires an extensive background to be able to analyze the results of complex experiments with a large number of data sets. To address this need, software systems and guidelines have recently been developed for analyzing the data (32,33). The primary advantages of this technique are high reproducibility, the large dynamic range, low background noise, requirement of less sample RNA, and the ability to detect novel transcripts, even in the absence of a sequenced genome (20). Several recent examples of identification of novel mutations in tumor cell populations reveal the utility of RNA-Seq in disease classification. David Huntsman s group has applied RNA-Seq methodologies to identify mutations in gynecological tumors, novel mutations in FOXL2 in the previously ill-defined and treatmentresistant granulosa cell tumor of the ovary, and in ARID1A in endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinomas (34,35). Diagnosis of granulosa cell tumors is difficult given the lack of knowledge of their pathogenesis and their relatively ambiguous histology, making a genetic variant associated with these tumors particularly valuable. Paired-end RNA- Seq analysis of several primary tumor samples identified mutations in the transcription factor FOXL2, specifically in tumor cell populations (34). Another study used RNA-seq of cell lines derived from tumors to discover somatic mutations associated with human activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, identifying MYD88 as a candidate oncogenic mutation (36). That result was used to focus on studies of primary patient samples to rapidly identify mutations specific to this lymphoma subtype. These examples indicate the utility of RNA-Seq-based analysis of tumors to identify novel mutations. For cancer expression profiling, RNA-seq has been applied to the expression profiling of melanoma. They identified 11 novel melanoma gene fusions and 12 novel read-through transcripts, providing an example of novel avenues for target discovery in cancers (37). Another application of the RNA-Seq was the ability to detect transcripts from single cells [circulating tumor cells (CTCs)]. The characterization of these cells would
4 90 Costa et al. Comprehensive molecular screening Table 1 Advantages and disadvantages of RT-PCR and RNAseq Technique Advantages Disadvantages High sensitivity Time consumed High sequence-specific Analyze one gene each time RT-PCR Variability of the results depending the laboratory Necessary to know the gene sequence Require many amount of RNA A single experiment can provide information Needs a bioinformatician for the analysis of the results about all the genes (translocation, ) High cost for one analysis RNA-seq High reproducibility Require low amount of RNA provide a highly sensitive and effective method for potential diagnosis and monitoring of disease status (38). As the cost of next-generation sequencing drops rapidly, RNA-Seq may replace current methods in transcriptome surveys of gene expression. Compared to the rest, RNA- Seq has several advantages, including the ability to simultaneously detect mutations, discovering alternative transcript and alternative splicing. However, this RNA-Seq technique will not likely replace current RT-PCR methods, but will be complementary (Table 1). The results of the RNA-Seq will identify those genes that need to then be examined using RT-PCR methods, more so in those laboratories with resource constraints. The application of the two complementary technologies in the routine analysis of cancer laboratories would be useful in characterizing patients and would assist oncologists in making clinical decisions, as it allows us to identify all molecular characteristics of the tumor. Acknowledgements Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest. References 1. Alwine JC, Kemp DJ, Stark GR. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1977;74: Streit S, Michalski CW, Erkan M, et al. Northern blot analysis for detection and quantification of RNA in pancreatic cancer cells and tissues. Nat Protoc 2009;4: Bustin SA. Absolute quantification of mrna using realtime reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J Mol Endocrinol 2000;25: Jozefczuk J, Adjaye J. Quantitative real-time PCRbased analysis of gene expression. Methods Enzymol 2011;500: Kang XP, Jiang T, Li YQ, et al. A duplex real-time RT- PCR assay for detecting H5N1 avian influenza virus and pandemic H1N1 influenza virus. Virol J 2010;7: Bustin SA, Benes V, Nolan T, et al. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR--a perspective. J Mol Endocrinol 2005;34: Nolan T, Hands RE, Bustin SA. Quantification of mrna using real-time RT-PCR. Nat Protoc 2006;1: Bustin SA. Why the need for qpcr publication guidelines?--the case for MIQE. Methods 2010;50: Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, et al. The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 2009;55: Rosell R, Molina MA, Costa C, et al. Pretreatment EGFR T790M mutation and BRCA1 mrna expression in erlotinib-treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations. Clin Cancer Res 2011;17: Soda M, Takada S, Takeuchi K, et al. A mouse model for EML4-ALK-positive lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008;105: Akiyama T, Dass CR, Choong PF. Bim-targeted cancer therapy: a link between drug action and underlying molecular changes. Mol Cancer Ther 2009;8: Paik S, Shak S, Tang G, et al. A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2004;351: Paik S, Tang G, Shak S, et al. Gene expression and benefit of chemotherapy in women with node-negative, estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2006;24:
5 Translational lung cancer research, Vol 2, No 2 April Habel LA, Shak S, Jacobs MK, et al. A population-based study of tumor gene expression and risk of breast cancer death among lymph node-negative patients. Breast Cancer Res 2006;8:R Gianni L, Zambetti M, Clark K, et al. Gene expression profiles in paraffin-embedded core biopsy tissue predict response to chemotherapy in women with locally advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2005;23: Velculescu VE, Zhang L, Vogelstein B, et al. Serial analysis of gene expression. Science 1995;270: Kodzius R, Kojima M, Nishiyori H, et al. CAGE: cap analysis of gene expression. Nat Methods 2006;3: Brenner S, Johnson M, Bridgham J, et al. Gene expression analysis by massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS) on microbead arrays. Nat Biotechnol 2000;18: Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 2009;10: Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, et al. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 2008;5: Morin R, Bainbridge M, Fejes A, et al. Profiling the HeLa S3 transcriptome using randomly primed cdna and massively parallel short-read sequencing. Biotechniques 2008;45: Shah SP, Köbel M, Senz J, et al. Mutation of FOXL2 in granulosa-cell tumors of the ovary. N Engl J Med 2009;360: Wiegand KC, Shah SP, Al-Agha OM, et al. ARID1A mutations in endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinomas. N Engl J Med 2010;363: Ngo VN, Young RM, Schmitz R, et al. Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma. Nature 2011;470: Pepke S, Wold B, Mortazavi A. Computation for ChIPseq and RNA-seq studies. Nat Methods 2009;6:S Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, et al. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 2008;5: Cloonan N, Forrest AR, Kolle G, et al. Stem cell transcriptome profiling via massive-scale mrna sequencing. Nat Methods 2008;5: Barbazuk WB, Emrich SJ, Chen HD, et al. SNP discovery via 454 transcriptome sequencing. Plant J 2007;51: Standards, Guidelines and Best Practices for RNA-Seq. V The ENCODE Consortium. 31. Li B, Ruotti V, Stewart RM, et al. RNA-Seq gene expression estimation with read mapping uncertainty. Bioinformatics 2010;26: Goncalves A, Tikhonov A, Brazma A, et al. A pipeline for RNA-seq data processing and quality assessment. Bioinformatics 2011;27: Shah SP, Köbel M, Senz J, et al. Mutation of FOXL2 in granulosa-cell tumors of the ovary. N Engl J Med 2009;360: Knowles DG, Röder M, Merkel A, et al. Grape RNA- Seq analysis pipeline environment. Bioinformatics 2013;29: Wiegand KC, Shah SP, Al-Agha OM, et al. ARID1A mutations in endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinomas. N Engl J Med 2010;363: Ngo VN, Young RM, Schmitz R, et al. Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma. Nature 2011;470: Berger MF, Levin JZ, Vijayendran K, et al. Integrative analysis of the melanoma transcriptome. Genome Res 2010;20: Helzer KT, Barnes HE, Day L, et al. Circulating tumor cells are transcriptionally similar to the primary tumor in a murine prostate model. Cancer Res 2009;69: Cite this article as: Costa C, Giménez-Capitán A, Karachaliou N, Rosell R. Comprehensive molecular screening: from the RT- PCR to the RNA-seq.. doi: /j.issn
genomics for systems biology / ISB2020 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq)
 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers
 Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays
 Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical Informatics (CoSBBI) Outline. Molecular Biology of Cancer AND. Goals/Expectations. David Boone 7/1/2015
 Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Simple, rapid, and reliable RNA sequencing
 Simple, rapid, and reliable RNA sequencing RNA sequencing applications RNA sequencing provides fundamental insights into how genomes are organized and regulated, giving us valuable information about the
Simple, rapid, and reliable RNA sequencing RNA sequencing applications RNA sequencing provides fundamental insights into how genomes are organized and regulated, giving us valuable information about the
RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS
 RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS Length of mrna transcripts in the human genome 5,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 4,000 1,000 0 0 200 400 600 800 3,000 2,000 1,000 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 Length
RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS Length of mrna transcripts in the human genome 5,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 4,000 1,000 0 0 200 400 600 800 3,000 2,000 1,000 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 Length
Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis
 5/17/13 Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis Johannes Kratz, MD Post-doctoral Fellow, Thoracic Oncology Laboratory
5/17/13 Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis Johannes Kratz, MD Post-doctoral Fellow, Thoracic Oncology Laboratory
Roadmap for Developing and Validating Therapeutically Relevant Genomic Classifiers. Richard Simon, J Clin Oncol 23:
 Roadmap for Developing and Validating Therapeutically Relevant Genomic Classifiers. Richard Simon, J Clin Oncol 23:7332-7341 Presented by Deming Mi 7/25/2006 Major reasons for few prognostic factors to
Roadmap for Developing and Validating Therapeutically Relevant Genomic Classifiers. Richard Simon, J Clin Oncol 23:7332-7341 Presented by Deming Mi 7/25/2006 Major reasons for few prognostic factors to
Ambient temperature regulated flowering time
 Ambient temperature regulated flowering time Applications of RNAseq RNA- seq course: The power of RNA-seq June 7 th, 2013; Richard Immink Overview Introduction: Biological research question/hypothesis
Ambient temperature regulated flowering time Applications of RNAseq RNA- seq course: The power of RNA-seq June 7 th, 2013; Richard Immink Overview Introduction: Biological research question/hypothesis
NGS in tissue and liquid biopsy
 NGS in tissue and liquid biopsy Ana Vivancos, PhD Referencias So, why NGS in the clinics? 2000 Sanger Sequencing (1977-) 2016 NGS (2006-) ABIPrism (Applied Biosystems) Up to 2304 per day (96 sequences
NGS in tissue and liquid biopsy Ana Vivancos, PhD Referencias So, why NGS in the clinics? 2000 Sanger Sequencing (1977-) 2016 NGS (2006-) ABIPrism (Applied Biosystems) Up to 2304 per day (96 sequences
OverView Circulating Nucleic Acids (CFNA) in Cancer Patients. Dave S.B. Hoon John Wayne Cancer Institute Santa Monica, CA, USA
 OverView Circulating Nucleic Acids (CFNA) in Cancer Patients Dave S.B. Hoon John Wayne Cancer Institute Santa Monica, CA, USA cfna Blood Assays Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients.
OverView Circulating Nucleic Acids (CFNA) in Cancer Patients Dave S.B. Hoon John Wayne Cancer Institute Santa Monica, CA, USA cfna Blood Assays Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients.
FISH mcgh Karyotyping ISH RT-PCR. Expression arrays RNA. Tissue microarrays Protein arrays MS. Protein IHC
 Classification of Breast Cancer in the Molecular Era Susan J. Done University Health Network, Toronto Why classify? Prognosis Prediction of response to therapy Pathogenesis Invasive breast cancer can have
Classification of Breast Cancer in the Molecular Era Susan J. Done University Health Network, Toronto Why classify? Prognosis Prediction of response to therapy Pathogenesis Invasive breast cancer can have
Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor
 Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Elizabeth H. Moore, MD Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Genomic testing has resulted in a paradigm shift in the
Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Elizabeth H. Moore, MD Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Genomic testing has resulted in a paradigm shift in the
Introduction to Systems Biology of Cancer Lecture 2
 Introduction to Systems Biology of Cancer Lecture 2 Gustavo Stolovitzky IBM Research Icahn School of Medicine at Mt Sinai DREAM Challenges High throughput measurements: The age of omics Systems Biology
Introduction to Systems Biology of Cancer Lecture 2 Gustavo Stolovitzky IBM Research Icahn School of Medicine at Mt Sinai DREAM Challenges High throughput measurements: The age of omics Systems Biology
PD-L1 Analyte Control DR
 Quality in Control PD-L1 Analyte Control DR PD-L1_PI_v2 Product Codes: HCL019, HCL020 and HCL021 Contents PD-L1 Analyte Control DR 2 What is PD-L1? 3 The Role of PD-L1 in Cancer 3 PD-L1 Assessment 4 PD-L1
Quality in Control PD-L1 Analyte Control DR PD-L1_PI_v2 Product Codes: HCL019, HCL020 and HCL021 Contents PD-L1 Analyte Control DR 2 What is PD-L1? 3 The Role of PD-L1 in Cancer 3 PD-L1 Assessment 4 PD-L1
Cell-free tumor DNA for cancer monitoring
 Learning objectives Cell-free tumor DNA for cancer monitoring Christina Lockwood, PhD, DABCC, DABMGG Department of Laboratory Medicine 1. Define circulating, cell-free tumor DNA (ctdna) 2. Understand the
Learning objectives Cell-free tumor DNA for cancer monitoring Christina Lockwood, PhD, DABCC, DABMGG Department of Laboratory Medicine 1. Define circulating, cell-free tumor DNA (ctdna) 2. Understand the
Deploying the full transcriptome using RNA sequencing. Jo Vandesompele, CSO and co-founder The Non-Coding Genome May 12, 2016, Leuven
 Deploying the full transcriptome using RNA sequencing Jo Vandesompele, CSO and co-founder The Non-Coding Genome May 12, 2016, Leuven Roadmap Biogazelle the power of RNA reasons to study non-coding RNA
Deploying the full transcriptome using RNA sequencing Jo Vandesompele, CSO and co-founder The Non-Coding Genome May 12, 2016, Leuven Roadmap Biogazelle the power of RNA reasons to study non-coding RNA
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Molecular Markers. Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC
 Molecular Markers Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC Overview Testing methods Rationale for molecular testing
Molecular Markers Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC Overview Testing methods Rationale for molecular testing
Genomic Medicine: What every pathologist needs to know
 Genomic Medicine: What every pathologist needs to know Stephen P. Ethier, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, MUSC Director, MUSC Center for Genomic Medicine Genomics and
Genomic Medicine: What every pathologist needs to know Stephen P. Ethier, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, MUSC Director, MUSC Center for Genomic Medicine Genomics and
Non-Profit Startup Paradigm Launches Cancer Panel Based on DNA, RNA Sequencing
 Non-Profit Startup Paradigm Launches Cancer Panel Based on DNA, RNA Sequencing April 11, 2014 By Tony Fong Non-profit diagnostics outfit Paradigm last month joined a growing list of entrants in the clinical
Non-Profit Startup Paradigm Launches Cancer Panel Based on DNA, RNA Sequencing April 11, 2014 By Tony Fong Non-profit diagnostics outfit Paradigm last month joined a growing list of entrants in the clinical
Breast cancer. Risk factors you cannot change include: Treatment Plan Selection. Inferring Transcriptional Module from Breast Cancer Profile Data
 Breast cancer Inferring Transcriptional Module from Breast Cancer Profile Data Breast Cancer and Targeted Therapy Microarray Profile Data Inferring Transcriptional Module Methods CSC 177 Data Warehousing
Breast cancer Inferring Transcriptional Module from Breast Cancer Profile Data Breast Cancer and Targeted Therapy Microarray Profile Data Inferring Transcriptional Module Methods CSC 177 Data Warehousing
of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed.
 Supplementary Note The potential association and implications of HBV integration at known and putative cancer genes of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed. Human telomerase
Supplementary Note The potential association and implications of HBV integration at known and putative cancer genes of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed. Human telomerase
NGS ONCOPANELS: FDA S PERSPECTIVE
 NGS ONCOPANELS: FDA S PERSPECTIVE CBA Workshop: Biomarker and Application in Drug Development August 11, 2018 Rockville, MD You Li, Ph.D. Division of Molecular Genetics and Pathology Food and Drug Administration
NGS ONCOPANELS: FDA S PERSPECTIVE CBA Workshop: Biomarker and Application in Drug Development August 11, 2018 Rockville, MD You Li, Ph.D. Division of Molecular Genetics and Pathology Food and Drug Administration
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes ~ 4.6 -
 Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
Identification of Novel Variant of EML4-ALK Fusion Gene in NSCLC: Potential Benefits of the RT-PCR Method
 International journal of Biomedical science ORIGINAL ARTICLE Identification of Novel Variant of EML4-ALK Fusion Gene in NSCLC: Potential Benefits of the RT-PCR Method Martin K. H. Maus 1, 2, Craig Stephens
International journal of Biomedical science ORIGINAL ARTICLE Identification of Novel Variant of EML4-ALK Fusion Gene in NSCLC: Potential Benefits of the RT-PCR Method Martin K. H. Maus 1, 2, Craig Stephens
Raymond Auerbach PhD Candidate, Yale University Gerstein and Snyder Labs August 30, 2012
 Elucidating Transcriptional Regulation at Multiple Scales Using High-Throughput Sequencing, Data Integration, and Computational Methods Raymond Auerbach PhD Candidate, Yale University Gerstein and Snyder
Elucidating Transcriptional Regulation at Multiple Scales Using High-Throughput Sequencing, Data Integration, and Computational Methods Raymond Auerbach PhD Candidate, Yale University Gerstein and Snyder
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
Molecular Testing in Lung Cancer
 Molecular Testing in Lung Cancer Pimpin Incharoen, M.D. Assistant Professor, Thoracic Pathology Department of Pathology, Ramathibodi Hospital Genetic alterations in lung cancer Source: Khono et al, Trans
Molecular Testing in Lung Cancer Pimpin Incharoen, M.D. Assistant Professor, Thoracic Pathology Department of Pathology, Ramathibodi Hospital Genetic alterations in lung cancer Source: Khono et al, Trans
Characterisation of structural variation in breast. cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on. the Illumina Genome Analyser
 Characterisation of structural variation in breast cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on the Illumina Genome Analyser Phil Stephens Cancer Genome Project Why is it important to study cancer? Why
Characterisation of structural variation in breast cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on the Illumina Genome Analyser Phil Stephens Cancer Genome Project Why is it important to study cancer? Why
NGS in Cancer Pathology After the Microscope: From Nucleic Acid to Interpretation
 NGS in Cancer Pathology After the Microscope: From Nucleic Acid to Interpretation Michael R. Rossi, PhD, FACMG Assistant Professor Division of Cancer Biology, Department of Radiation Oncology Department
NGS in Cancer Pathology After the Microscope: From Nucleic Acid to Interpretation Michael R. Rossi, PhD, FACMG Assistant Professor Division of Cancer Biology, Department of Radiation Oncology Department
Transform genomic data into real-life results
 CLINICAL SUMMARY Transform genomic data into real-life results Biomarker testing and targeted therapies can drive improved outcomes in clinical practice New FDA-Approved Broad Companion Diagnostic for
CLINICAL SUMMARY Transform genomic data into real-life results Biomarker testing and targeted therapies can drive improved outcomes in clinical practice New FDA-Approved Broad Companion Diagnostic for
Quality in Control. ROS1 Analyte Control. Product Codes: HCL022, HCL023 and HCL024
 Quality in Control ROS1 Analyte Control Product Codes: HCL022, HCL023 and HCL024 Contents What is ROS1? 2 The Role of ROS1 in Cancer 3 ROS1 Assessment 3 ROS1 Analyte Control Product Details 4 ROS1 Analyte
Quality in Control ROS1 Analyte Control Product Codes: HCL022, HCL023 and HCL024 Contents What is ROS1? 2 The Role of ROS1 in Cancer 3 ROS1 Assessment 3 ROS1 Analyte Control Product Details 4 ROS1 Analyte
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance.! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014
 Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Evolution of Pathology
 1 Traditional pathology Molecular pathology 2 Evolution of Pathology Gross Pathology Cellular Pathology Morphologic Pathology Molecular/Predictive Pathology Antonio Benivieni (1443-1502): First autopsy
1 Traditional pathology Molecular pathology 2 Evolution of Pathology Gross Pathology Cellular Pathology Morphologic Pathology Molecular/Predictive Pathology Antonio Benivieni (1443-1502): First autopsy
Osimertinib: a breakthrough for the treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung adenocarcinoma
 Editorial : a breakthrough for the treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung adenocarcinoma Niki Karachaliou 1, Feliciano Barron Barron 2, Santiago Viteri 3, Miguel Angel Molina 4, Rafael
Editorial : a breakthrough for the treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung adenocarcinoma Niki Karachaliou 1, Feliciano Barron Barron 2, Santiago Viteri 3, Miguel Angel Molina 4, Rafael
AVENIO family of NGS oncology assays ctdna and Tumor Tissue Analysis Kits
 AVENIO family of NGS oncology assays ctdna and Tumor Tissue Analysis Kits Accelerating clinical research Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has the ability to interrogate many different genes and detect
AVENIO family of NGS oncology assays ctdna and Tumor Tissue Analysis Kits Accelerating clinical research Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has the ability to interrogate many different genes and detect
NGS IN ONCOLOGY: FDA S PERSPECTIVE
 NGS IN ONCOLOGY: FDA S PERSPECTIVE ASQ Biomed/Biotech SIG Event April 26, 2018 Gaithersburg, MD You Li, Ph.D. Division of Molecular Genetics and Pathology Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Center for
NGS IN ONCOLOGY: FDA S PERSPECTIVE ASQ Biomed/Biotech SIG Event April 26, 2018 Gaithersburg, MD You Li, Ph.D. Division of Molecular Genetics and Pathology Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Center for
ACE ImmunoID. ACE ImmunoID. Precision immunogenomics. Precision Genomics for Immuno-Oncology
 ACE ImmunoID ACE ImmunoID Precision immunogenomics Precision Genomics for Immuno-Oncology Personalis, Inc. A universal biomarker platform for immuno-oncology Patient response to cancer immunotherapies
ACE ImmunoID ACE ImmunoID Precision immunogenomics Precision Genomics for Immuno-Oncology Personalis, Inc. A universal biomarker platform for immuno-oncology Patient response to cancer immunotherapies
SH Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of an ALK-Negative, Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with DUSP22 rearrangement
 SH2017-0277 Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of an ALK-Negative, Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with DUSP22 rearrangement Caleb Ho, M.D.; Alexander Chan, M.D., Yanming Zhang, M.D.; Lu Wang, M.D., Ph.D;
SH2017-0277 Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of an ALK-Negative, Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with DUSP22 rearrangement Caleb Ho, M.D.; Alexander Chan, M.D., Yanming Zhang, M.D.; Lu Wang, M.D., Ph.D;
Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma. Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
 Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Outline Anaplastic meningioma compared to other cancers Whole genomes
Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Outline Anaplastic meningioma compared to other cancers Whole genomes
FONS Nové sekvenační technologie vklinickédiagnostice?
 FONS 2010 Nové sekvenační technologie vklinickédiagnostice? Sekvenování amplikonů Sequence capture Celogenomové sekvenování FONS 2010 Sekvenování amplikonů Amplicon sequencing - amplicon sequencing enables
FONS 2010 Nové sekvenační technologie vklinickédiagnostice? Sekvenování amplikonů Sequence capture Celogenomové sekvenování FONS 2010 Sekvenování amplikonů Amplicon sequencing - amplicon sequencing enables
Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy
 Outline Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy Radiation Biology Introduction Early predictive assays Recent trends in predictive assays Examples for specific tumors Summary Lecture 4-23-2014 Introduction
Outline Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy Radiation Biology Introduction Early predictive assays Recent trends in predictive assays Examples for specific tumors Summary Lecture 4-23-2014 Introduction
ncounter Assay Automated Process Immobilize and align reporter for image collecting and barcode counting ncounter Prep Station
 ncounter Assay ncounter Prep Station Automated Process Hybridize Reporter to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes Immobilize and
ncounter Assay ncounter Prep Station Automated Process Hybridize Reporter to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes Immobilize and
Claudia Adams Barr Program in Innovative Cancer Research Dana-Farber Cancer Institute BARR PROGRAM IMPACT STATEMENTS
 Claudia Adams Barr Program in Innovative Cancer Research Dana-Farber Cancer Institute BARR PROGRAM IMPACT STATEMENTS Brain Cancer New Treatment Opportunities - Discovery of new pathways in brain cancers
Claudia Adams Barr Program in Innovative Cancer Research Dana-Farber Cancer Institute BARR PROGRAM IMPACT STATEMENTS Brain Cancer New Treatment Opportunities - Discovery of new pathways in brain cancers
Accel-Amplicon Panels
 Accel-Amplicon Panels Amplicon sequencing has emerged as a reliable, cost-effective method for ultra-deep targeted sequencing. This highly adaptable approach is especially applicable for in-depth interrogation
Accel-Amplicon Panels Amplicon sequencing has emerged as a reliable, cost-effective method for ultra-deep targeted sequencing. This highly adaptable approach is especially applicable for in-depth interrogation
Analyse de données de séquençage haut débit
 Analyse de données de séquençage haut débit Vincent Lacroix Laboratoire de Biométrie et Biologie Évolutive INRIA ERABLE 9ème journée ITS 21 & 22 novembre 2017 Lyon https://its.aviesan.fr Sequencing is
Analyse de données de séquençage haut débit Vincent Lacroix Laboratoire de Biométrie et Biologie Évolutive INRIA ERABLE 9ème journée ITS 21 & 22 novembre 2017 Lyon https://its.aviesan.fr Sequencing is
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers
 micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
The Cancer Genome Atlas & International Cancer Genome Consortium
 The Cancer Genome Atlas & International Cancer Genome Consortium Session 3 Dr Jason Wong Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 31 st July 2014 1
The Cancer Genome Atlas & International Cancer Genome Consortium Session 3 Dr Jason Wong Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 31 st July 2014 1
Molecular Methods in the Diagnosis and Prognostication of Melanoma: Pros & Cons
 Molecular Methods in the Diagnosis and Prognostication of Melanoma: Pros & Cons Ben J. Friedman, MD Senior Staff Physician Department of Dermatology Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Henry
Molecular Methods in the Diagnosis and Prognostication of Melanoma: Pros & Cons Ben J. Friedman, MD Senior Staff Physician Department of Dermatology Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Henry
Breast and ovarian cancer in Serbia: the importance of mutation detection in hereditary predisposition genes using NGS
 Breast and ovarian cancer in Serbia: the importance of mutation detection in hereditary predisposition genes using NGS dr sc. Ana Krivokuća Laboratory for molecular genetics Institute for Oncology and
Breast and ovarian cancer in Serbia: the importance of mutation detection in hereditary predisposition genes using NGS dr sc. Ana Krivokuća Laboratory for molecular genetics Institute for Oncology and
La biopsia liquida. Aldo Scarpa. Anatomia Patologica e ARC-NET Centro di Ricerca Applicata sul Cancro
 La biopsia liquida Aldo Scarpa Anatomia Patologica e ARC-NET Centro di Ricerca Applicata sul Cancro Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata di Verona Obstacles to precision oncology Genomic heterogeneity
La biopsia liquida Aldo Scarpa Anatomia Patologica e ARC-NET Centro di Ricerca Applicata sul Cancro Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata di Verona Obstacles to precision oncology Genomic heterogeneity
New Drug development and Personalized Therapy in The Era of Molecular Medicine
 New Drug development and Personalized Therapy in The Era of Molecular Medicine Ramesh K. Ramanathan MD Virginia G. Piper Cancer Center Translational Genomics Research Institute Scottsdale, AZ Clinical
New Drug development and Personalized Therapy in The Era of Molecular Medicine Ramesh K. Ramanathan MD Virginia G. Piper Cancer Center Translational Genomics Research Institute Scottsdale, AZ Clinical
Additional Disclosure
 Additional Disclosure The Genetics of Prostate Cancer: Clinical Implications William J. Catalona, MD Collaborator with decode genetics, Inc. Non-paid consultant with no financial interest or support Northwestern
Additional Disclosure The Genetics of Prostate Cancer: Clinical Implications William J. Catalona, MD Collaborator with decode genetics, Inc. Non-paid consultant with no financial interest or support Northwestern
Accessing and Using ENCODE Data Dr. Peggy J. Farnham
 1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
Cytogenetics Technologies, Companies & Markets
 Cytogenetics Technologies, Companies & Markets By Prof. K. K. Jain MD, FRACS, FFPM Jain PharmaBiotech Basel, Switzerland November 2018 A Jain PharmaBiotech Report A U T H O R ' S B I O G R A P H Y Professor
Cytogenetics Technologies, Companies & Markets By Prof. K. K. Jain MD, FRACS, FFPM Jain PharmaBiotech Basel, Switzerland November 2018 A Jain PharmaBiotech Report A U T H O R ' S B I O G R A P H Y Professor
Disclosure. Summary. Circulating DNA and NGS technology 3/27/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. JS Reis-Filho, MD, PhD, FRCPath
 Circulating DNA and NGS technology JS Reis-Filho, MD, PhD, FRCPath Director of Experimental Pathology, Department of Pathology Affiliate Member, Human Oncology and Pathogenesis Program Disclosure of Relevant
Circulating DNA and NGS technology JS Reis-Filho, MD, PhD, FRCPath Director of Experimental Pathology, Department of Pathology Affiliate Member, Human Oncology and Pathogenesis Program Disclosure of Relevant
QIAGEN Complete Solutions for Liquid Biopsy Molecular Testing
 QIAGEN Complete Solutions for Liquid Biopsy Molecular Testing Christopher Swagell, PhD Market Development Manager, Advanced Molecular Pathology QIAGEN 1 Agenda QIAGEN Solid Tumor Testing and Liquid Biopsy
QIAGEN Complete Solutions for Liquid Biopsy Molecular Testing Christopher Swagell, PhD Market Development Manager, Advanced Molecular Pathology QIAGEN 1 Agenda QIAGEN Solid Tumor Testing and Liquid Biopsy
ncounter TM Analysis System
 ncounter TM Analysis System Molecules That Count TM www.nanostring.com Agenda NanoString Technologies History Introduction to the ncounter Analysis System CodeSet Design and Assay Principals System Performance
ncounter TM Analysis System Molecules That Count TM www.nanostring.com Agenda NanoString Technologies History Introduction to the ncounter Analysis System CodeSet Design and Assay Principals System Performance
RNA-seq Introduction
 RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
patients in the era of
 Communicating with cancer patients in the era of personalized medicine September 9 th, 2017 Gerald Prager, M.D. Comprehensive Cancer Center Vienna Medical University of Vienna, Austria Gerald Prager, M.D.
Communicating with cancer patients in the era of personalized medicine September 9 th, 2017 Gerald Prager, M.D. Comprehensive Cancer Center Vienna Medical University of Vienna, Austria Gerald Prager, M.D.
WHO Prequalification of In Vitro Diagnostics PUBLIC REPORT. Product: Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect WHO reference number: PQDx
 WHO Prequalification of In Vitro Diagnostics PUBLIC REPORT Product: Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect WHO reference number: PQDx 0226-032-00 Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect with product codes 270110050, 270110010 and 270300001,
WHO Prequalification of In Vitro Diagnostics PUBLIC REPORT Product: Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect WHO reference number: PQDx 0226-032-00 Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect with product codes 270110050, 270110010 and 270300001,
Profili di espressione genica
 Profili di espressione genica Giampaolo Bianchini MD Ospedale San Raffaele, Milan - Italy Gene expression profiles Transcriptomics Gene DNA mrna mirnas Protein metilation Metabolite Genomics Transcriptomics
Profili di espressione genica Giampaolo Bianchini MD Ospedale San Raffaele, Milan - Italy Gene expression profiles Transcriptomics Gene DNA mrna mirnas Protein metilation Metabolite Genomics Transcriptomics
ABS04. ~ Inaugural Applied Bayesian Statistics School EXPRESSION
 ABS04-2004 Applied Bayesian Statistics School STATISTICS & GENE EXPRESSION GENOMICS: METHODS AND COMPUTATIONS Mike West Duke University Centro Congressi Panorama, Trento,, Italy 15th-19th 19th June 2004
ABS04-2004 Applied Bayesian Statistics School STATISTICS & GENE EXPRESSION GENOMICS: METHODS AND COMPUTATIONS Mike West Duke University Centro Congressi Panorama, Trento,, Italy 15th-19th 19th June 2004
Personalised cancer care Information for Medical Specialists. A new way to unlock treatment options for your patients
 Personalised cancer care Information for Medical Specialists A new way to unlock treatment options for your patients Contents Optimised for clinical benefit 4 Development history 4 Full FIND IT panel vs
Personalised cancer care Information for Medical Specialists A new way to unlock treatment options for your patients Contents Optimised for clinical benefit 4 Development history 4 Full FIND IT panel vs
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11. Dr H Awad FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11 Dr H Awad FRCPath Clinical aspects of neoplasia Tumors affect patients by: 1. their location 2. hormonal secretions 3. paraneoplastic syndromes 4. cachexia Tumor location Even
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11 Dr H Awad FRCPath Clinical aspects of neoplasia Tumors affect patients by: 1. their location 2. hormonal secretions 3. paraneoplastic syndromes 4. cachexia Tumor location Even
FAQs for UK Pathology Departments
 FAQs for UK Pathology Departments This is an educational piece written for Healthcare Professionals FAQs for UK Pathology Departments If you would like to discuss any of the listed FAQs further, or have
FAQs for UK Pathology Departments This is an educational piece written for Healthcare Professionals FAQs for UK Pathology Departments If you would like to discuss any of the listed FAQs further, or have
Selective depletion of abundant RNAs to enable transcriptome analysis of lowinput and highly-degraded RNA from FFPE breast cancer samples
 DNA CLONING DNA AMPLIFICATION & PCR EPIGENETICS RNA ANALYSIS Selective depletion of abundant RNAs to enable transcriptome analysis of lowinput and highly-degraded RNA from FFPE breast cancer samples LIBRARY
DNA CLONING DNA AMPLIFICATION & PCR EPIGENETICS RNA ANALYSIS Selective depletion of abundant RNAs to enable transcriptome analysis of lowinput and highly-degraded RNA from FFPE breast cancer samples LIBRARY
ROR1 as a novel therapeutic target for EGFR-mutant non-smallcell lung cancer patients with the EGFR T790M mutation
 Original Article ROR1 as a novel therapeutic target for EGFR-mutant non-smallcell lung cancer patients with the EGFR T790M mutation Niki Karachaliou 1, Ana Gimenez-Capitan 2, Ana Drozdowskyj 3, Santiago
Original Article ROR1 as a novel therapeutic target for EGFR-mutant non-smallcell lung cancer patients with the EGFR T790M mutation Niki Karachaliou 1, Ana Gimenez-Capitan 2, Ana Drozdowskyj 3, Santiago
Multigene Panel Testing for Hereditary Cancer Risk
 Multigene Panel Testing for Hereditary Cancer Risk Dana Zakalik, M.D. Director, Nancy and James Grosfeld Cancer Genetics Center Professor, OUWB Medical School MCC Annual Meeting November 4, 2015 Outline
Multigene Panel Testing for Hereditary Cancer Risk Dana Zakalik, M.D. Director, Nancy and James Grosfeld Cancer Genetics Center Professor, OUWB Medical School MCC Annual Meeting November 4, 2015 Outline
Session 4 Rebecca Poulos
 The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) & International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) Session 4 Rebecca Poulos Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 20
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) & International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) Session 4 Rebecca Poulos Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 20
PRECISION INSIGHTS. Liquid GPS. Blood-based tumor profiling and quantitative monitoring. Reveal more with cfdna + cfrna.
 PRECISION INSIGHTS Liquid GPS Blood-based tumor profiling and quantitative monitoring Reveal more with cfdna + cfrna www.nanthealth.com Why Blood-Based Tumor Profiling? Although tissue-based molecular
PRECISION INSIGHTS Liquid GPS Blood-based tumor profiling and quantitative monitoring Reveal more with cfdna + cfrna www.nanthealth.com Why Blood-Based Tumor Profiling? Although tissue-based molecular
Implementation of nation-wide molecular testing in oncology in the French Health care system : quality assurance issues & challenges
 Implementation of nation-wide molecular testing in oncology in the French Health care system : quality assurance issues & challenges Frédérique Nowak - 21 october 2015 "Putting Science into Standards event:
Implementation of nation-wide molecular testing in oncology in the French Health care system : quality assurance issues & challenges Frédérique Nowak - 21 october 2015 "Putting Science into Standards event:
ncounter Assay Automated Process Capture & Reporter Probes Bind reporter to surface Remove excess reporters Hybridize CodeSet to RNA
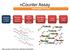 ncounter Assay Automated Process Hybridize CodeSet to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes mrna Capture & Reporter Probes slides
ncounter Assay Automated Process Hybridize CodeSet to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes mrna Capture & Reporter Probes slides
Generating Spontaneous Copy Number Variants (CNVs) Jennifer Freeman Assistant Professor of Toxicology School of Health Sciences Purdue University
 Role of Chemical lexposure in Generating Spontaneous Copy Number Variants (CNVs) Jennifer Freeman Assistant Professor of Toxicology School of Health Sciences Purdue University CNV Discovery Reference Genetic
Role of Chemical lexposure in Generating Spontaneous Copy Number Variants (CNVs) Jennifer Freeman Assistant Professor of Toxicology School of Health Sciences Purdue University CNV Discovery Reference Genetic
The lymphoma-associated NPM-ALK oncogene elicits a p16ink4a/prb-dependent tumor-suppressive pathway. Blood Jun 16;117(24):
 DNA Sequencing Publications Standard Sequencing 1 Carro MS et al. DEK Expression is controlled by E2F and deregulated in diverse tumor types. Cell Cycle. 2006 Jun;5(11) 2 Lassandro L et al. The DNA sequence
DNA Sequencing Publications Standard Sequencing 1 Carro MS et al. DEK Expression is controlled by E2F and deregulated in diverse tumor types. Cell Cycle. 2006 Jun;5(11) 2 Lassandro L et al. The DNA sequence
Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data
 Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data Gary M. Clark, Ph.D. Vice President Biostatistics & Data Management Array BioPharma Inc. Boulder, CO NCIC Clinical Trials Group New Investigator Clinical Trials Course
Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data Gary M. Clark, Ph.D. Vice President Biostatistics & Data Management Array BioPharma Inc. Boulder, CO NCIC Clinical Trials Group New Investigator Clinical Trials Course
Next generation diagnostics Bringing high-throughput sequencing into clinical application
 Next generation diagnostics Bringing high-throughput sequencing into clinical application Leonardo A. Meza-Zepeda, PhD Translational Genomics Group Institute for Cancer Research Leonardo.Meza-Zepeda@rr-research.no
Next generation diagnostics Bringing high-throughput sequencing into clinical application Leonardo A. Meza-Zepeda, PhD Translational Genomics Group Institute for Cancer Research Leonardo.Meza-Zepeda@rr-research.no
TITLE: High throughput sequencing of germline and tumor from men with early-onset, metastatic prostate cancer
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0371 TITLE: High throughput sequencing of germline and tumor from men with early-onset, metastatic prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: A. Cooney, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0371 TITLE: High throughput sequencing of germline and tumor from men with early-onset, metastatic prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: A. Cooney, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Next Generation Cancer Diagnostics For First Time Right Therapy Choice. Anja van de Stolpe
 Next Generation Cancer Diagnostics For First Time Right Therapy Choice Anja van de Stolpe Paradigm shift in cancer treatment towards personalized treatment Chemotherapy for all therapy targeting cancer
Next Generation Cancer Diagnostics For First Time Right Therapy Choice Anja van de Stolpe Paradigm shift in cancer treatment towards personalized treatment Chemotherapy for all therapy targeting cancer
Personalized oncology: the potential for tissue and cell-free DNA
 Open Citation: J Med Discov (2016); 1(1):jmd16005; doi:10.24262/jmd.1.1.16005 Commentary Personalized oncology: the potential for tissue and cell-free DNA biopsies to capture tumor heterogeneity Young
Open Citation: J Med Discov (2016); 1(1):jmd16005; doi:10.24262/jmd.1.1.16005 Commentary Personalized oncology: the potential for tissue and cell-free DNA biopsies to capture tumor heterogeneity Young
Applications of IHC. Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin
 Applications of IHC Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin Classification of tumors that appear 'undifferentiated' by standard light microscopy Precise classification
Applications of IHC Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin Classification of tumors that appear 'undifferentiated' by standard light microscopy Precise classification
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Incorporating pharmacodynamic, response and patient selection biomarkers. Paul Elvin PhD Chief Translational Science Officer Aptus Clinical
 Incorporating pharmacodynamic, response and patient selection biomarkers Paul Elvin PhD Chief Translational Science Officer Aptus Clinical 22 Oncology drug development Biomarkers key for: Strong hypothesis
Incorporating pharmacodynamic, response and patient selection biomarkers Paul Elvin PhD Chief Translational Science Officer Aptus Clinical 22 Oncology drug development Biomarkers key for: Strong hypothesis
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Molecular Genetics of Paediatric Tumours. Gino Somers MBBS, BMedSci, PhD, FRCPA Pathologist-in-Chief Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON, CANADA
 Molecular Genetics of Paediatric Tumours Gino Somers MBBS, BMedSci, PhD, FRCPA Pathologist-in-Chief Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON, CANADA Financial Disclosure NanoString - conference costs for
Molecular Genetics of Paediatric Tumours Gino Somers MBBS, BMedSci, PhD, FRCPA Pathologist-in-Chief Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON, CANADA Financial Disclosure NanoString - conference costs for
Multigene Testing in NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines, v1.2011
 Multigene Testing in NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines, v1.2011 Robert W. Carlson, M.D. Professor of Medicine Stanford University Chair, NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines Panel Selection of
Multigene Testing in NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines, v1.2011 Robert W. Carlson, M.D. Professor of Medicine Stanford University Chair, NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines Panel Selection of
Breast Cancer: Who Gets It? Who Survives? The Latest Information
 Breast Cancer: Who Gets It? Who Survives? The Latest Information James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Director of Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine
Breast Cancer: Who Gets It? Who Survives? The Latest Information James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Director of Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine
P. Tang ( 鄧致剛 ); PJ Huang ( 黄栢榕 ) g( ); g ( ) Bioinformatics Center, Chang Gung University.
 Databases and Tools for High Throughput Sequencing Analysis P. Tang ( 鄧致剛 ); PJ Huang ( 黄栢榕 ) g( ); g ( ) Bioinformatics Center, Chang Gung University. HTseq Platforms Applications on Biomedical Sciences
Databases and Tools for High Throughput Sequencing Analysis P. Tang ( 鄧致剛 ); PJ Huang ( 黄栢榕 ) g( ); g ( ) Bioinformatics Center, Chang Gung University. HTseq Platforms Applications on Biomedical Sciences
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Jacobsen E, Shanmugam V, Jagannathan J. Rosai Dorfman disease
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Jacobsen E, Shanmugam V, Jagannathan J. Rosai Dorfman disease
Gene expression in cancer diagnostics
 Gene expression in cancer diagnostics Aron Eklund eklund@cbs.dtu.dk Cancer Systems Biology group Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Technical University of Denmark Introduction to Systems Biology
Gene expression in cancer diagnostics Aron Eklund eklund@cbs.dtu.dk Cancer Systems Biology group Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Technical University of Denmark Introduction to Systems Biology
MET skipping mutation, EGFR
 New NSCLC biomarkers in clinical research: detection of MET skipping mutation, EGFR T790M, and other important biomarkers Fernando López-Ríos Laboratorio de Dianas Terapéuticas Hospital Universitario HM
New NSCLC biomarkers in clinical research: detection of MET skipping mutation, EGFR T790M, and other important biomarkers Fernando López-Ríos Laboratorio de Dianas Terapéuticas Hospital Universitario HM
AVENIO ctdna Analysis Kits The complete NGS liquid biopsy solution EMPOWER YOUR LAB
 Analysis Kits The complete NGS liquid biopsy solution EMPOWER YOUR LAB Analysis Kits Next-generation performance in liquid biopsies 2 Accelerating clinical research From liquid biopsy to next-generation
Analysis Kits The complete NGS liquid biopsy solution EMPOWER YOUR LAB Analysis Kits Next-generation performance in liquid biopsies 2 Accelerating clinical research From liquid biopsy to next-generation
ACE ImmunoID Biomarker Discovery Solutions ACE ImmunoID Platform for Tumor Immunogenomics
 ACE ImmunoID Biomarker Discovery Solutions ACE ImmunoID Platform for Tumor Immunogenomics Precision Genomics for Immuno-Oncology Personalis, Inc. ACE ImmunoID When one biomarker doesn t tell the whole
ACE ImmunoID Biomarker Discovery Solutions ACE ImmunoID Platform for Tumor Immunogenomics Precision Genomics for Immuno-Oncology Personalis, Inc. ACE ImmunoID When one biomarker doesn t tell the whole
Consensus statement between CM-Path, CRUK and the PHG Foundation following on from the Liquid Biopsy workshop on the 8th March 2018
 Consensus statement between CM-Path, CRUK and the PHG Foundation following on from the Liquid Biopsy workshop on the 8th March 2018 Summary: This document follows on from the findings of the CM-Path The
Consensus statement between CM-Path, CRUK and the PHG Foundation following on from the Liquid Biopsy workshop on the 8th March 2018 Summary: This document follows on from the findings of the CM-Path The
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq
 Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Oncology Drug Development Using Molecular Pathology
 Oncology Drug Development Using Molecular Pathology Introduction PRESENTERS Lee Schacter, PhD, MD, FACP Executive Medical Director, Oncology Clinipace Worldwide Martha Bonino Director, Strategic Accounts
Oncology Drug Development Using Molecular Pathology Introduction PRESENTERS Lee Schacter, PhD, MD, FACP Executive Medical Director, Oncology Clinipace Worldwide Martha Bonino Director, Strategic Accounts
Introduction to Cancer Bioinformatics and cancer biology. Anthony Gitter Cancer Bioinformatics (BMI 826/CS 838) January 20, 2015
 Introduction to Cancer Bioinformatics and cancer biology Anthony Gitter Cancer Bioinformatics (BMI 826/CS 838) January 20, 2015 Why cancer bioinformatics? Devastating disease, no cure on the horizon Major
Introduction to Cancer Bioinformatics and cancer biology Anthony Gitter Cancer Bioinformatics (BMI 826/CS 838) January 20, 2015 Why cancer bioinformatics? Devastating disease, no cure on the horizon Major
