G-Protein Coupled Receptors: Structure and Function
|
|
|
- Lester Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PCTH 400 G-Protein Coupled Receptors: Structure and Function Dr. Rishi Somvanshi 2405 Wesbrook Mall
2 Learning Objectives 1. GPCR? Structure and Synthesis 2. Function? Receptor coupling to second messenger and Trafficking 3. Regulation? Pharmacology and Signaling Dimerization 4. Role in Pathological og Conditions o?
3 GPCRs (Structure and Synthesis)
4 G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) Largest and most diverse membrane protein families Encoded by more than 800 genes (or 4% of the entire protein- coding genome) Detects Dt t a wide spectrum of extracellular l signals, including photons, ions, small organic molecules and entire proteins. Enormous potential for the development of new drugs to target neurological disorders, cancer, cardiac malfunction, asthma, tumours and migraines.
5 Time-line of GPCR Structures Nature 477: (2011) Nature 494, (2013)
6 Characteristics of GPCRs N-terminal segment Seven Transmembrane Domains which constitute i. TM Core ii. Three exoloops iii. Three Cytoloops C-terminal segment Pharmacol Ther Jul;103(1):21-80
7 Characteristics of all GPCRs N-terminal segments has aa C-terminal segments contains aa Each of the 7 TMs is generally composed of aa Loops p are normally y5-230 aa long h d f h d Variation in size is the indication of their diverse structure and functions!
8 G-Protein Coupled Receptors - Classification Class A (or 1) )(Rhodopsin-like) (85% of the GPCR genes) Class B (or 2) (Secretin receptor family) Class C (or 3) (Metabotropic glutamate/pheromone) Class D (or 4) (Fungal mating pheromone receptors) Class E (or 5) (Cyclic AMP receptors) Class F (or 6) (Frizzled/Smoothened) GRAFS (Glutamate Rhodopsin Adhesion Frizzled/Taste2 GRAFS (Glutamate, Rhodopsin, Adhesion, Frizzled/Taste2, Secretin)
9 GPCRs Synthesis and Trafficking COPII, coat protein II, transport of proteins from the rough ER to the Golgi apparatus; ERGIC, ER Golgi intermediate compartment; COPI: coat protein I, (retrograde transport to the ER); ERAD, ER-associated degradation pathway. Trends in pharmacological Sciences, Volume 29, Issue 10, Pages
10 GPCRs Synthesis and Trafficking Large dense-core vesicles (LDCVs) Trends in pharmacological Sciences, Volume 28, Issue 1, 2007, Pages 23 31
11 Sorting of Endocytosed GPCRs Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol :
12 How GPCRs Function?
13 Typical cycle of G-Protein Coupled Receptor Nature Volume: 477, Pages: , 2011
14 GPCRs and Signaling Networks Trends in pharmacological Sciences, Volume 22, Issue 7, 1 July 2001, Pages
15 camp Signaling Pathway O'Connor, C. M. & Adams, J. U. Essentials of Cell Biology. Cambridge, MA: NPG Education, 2010.
16 Mechanism for the Modulation of Receptor Function DIMERIZATION
17 Molecular determinants of G-protein- coupled-receptor dimerization Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2,
18 Biophysical Techniques to Study GPCR Colocalization Dimerization Co-immunoprecipitation /Western blot analysis Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) ½ YFP ½ YFP Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET) Renilla luciferase GFP DeepBlue Photobleaching FRET (PbFRET)
19 Pb-FRET Microscopy Intensity Inten nsity Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) GFP-tagged receptors Fluorescently Fl l labeled l b l d antibodies ib di Fluorescently labeled ligands Time Time
20 GPCR Functions are Altered upon Dimerization GABA receptors - Receptor functionality and sorting (GABA B R1 and GABA B R2) Dissociation of receptor homodimers is essential for proper receptor trafficking - SSTR2 and d-or Inhibition of internalization of the β 2 AR - when heterodimerize with β 1 AR Heterodimerization has synergistic (hsstr4/hsstr5) or y g ( 4/ 5) result in a non-synergistic effect (hsstr1/hsstr5) on camp signaling
21 Role of Dimerization in the Transport of GPCRs Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2,
22 Taste Qualities and the Taste Receptors J Cell Biol 2010;190:
23 Role in Pathological Conditions
24 GPCRs and Diseases Cancer Breast cancer Receptor PAR1; EP2; EP4; CXCR4; GPR30 Colon cancer EP2, EP4; LPA 1; ET receptors; PAR1; Frizzled Head and neck cancer CXCR2; CXCR4; EP receptors; GRPR; PAR1 Small-cell lung cancer GRPR; NMB-R; CXCR4; CCK 1 1; CCK 2 Non-small-cell lung cancer Ovarian cancer EP receptors; CXCR2; CXCR4; 1AR; 2AR LPA 1 LPA 3 ; CXCR2 Pancreatic cancer GRPR; CCK 1 ; CCK 2 Parathyroid gland cancer CASR Pituitary ta cancer ce TSH receptor; ACTHR Prostate cancer Melanoma Basal-cell carcinoma Testicular cancer Thyroid cancer PAR1; ET A ; AT1; EP2, EP4; LPA 1 ; B1, B2; GRPR MC1R; CXCR2; ET B Smoothened LH receptor TSH receptor Nature Reviews Cancer 7, 79 94, 2007
25 GPCRs and Diseases Nephrogenic diabetes insipides V2 vasopressin receptor Precocious puberty LH receptor Congenital night blindness Rhodopsin Receptor Virus entry: HIV - CCR JCV - 5HT2 R (Serotonin receptor) Familial gestational hyperthyroidism Thyrotropin receptor
26 Some Drugs Acting Through GPCRs Biotecnol Apl v.26 n.1 La Habana ene.-mar. 2009
27 Heterodimers in Pathophysiological Conditions Acromegaly: Somatostatin Receptor 5 and Dopamine receptor 2 agonist (Dopastatins) in regulation of Tumors. AIDS: Chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) / CCR5 or C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) via modulating CXCR4 expression. Cardiac Failure: Angiotensin Receptor 1/ β-adrenergic Receptor via blocking AT 1 R mediated signaling. Parkinson s Disease: Adenosine Receptor 2a and Dopamine Receptor 2 via modulating cell surface expression.
28 QUESTIONS?
INTERACTION DRUG BODY
 INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET)-based studies of receptor dynamics in living cells with Berthold s Mithras
 Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET)-based studies of receptor dynamics in living cells with Berthold s Mithras Tarik Issad, Ralf Jockers and Stefano Marullo 1 Because they play a pivotal role
Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET)-based studies of receptor dynamics in living cells with Berthold s Mithras Tarik Issad, Ralf Jockers and Stefano Marullo 1 Because they play a pivotal role
Lecture 15. Signal Transduction Pathways - Introduction
 Lecture 15 Signal Transduction Pathways - Introduction So far.. Regulation of mrna synthesis Regulation of rrna synthesis Regulation of trna & 5S rrna synthesis Regulation of gene expression by signals
Lecture 15 Signal Transduction Pathways - Introduction So far.. Regulation of mrna synthesis Regulation of rrna synthesis Regulation of trna & 5S rrna synthesis Regulation of gene expression by signals
G-Protein Coupled Receptors GPCRs. GPCRs
 2 type of ligands 1 G-Protein Coupled Receptors GPCRs One of the largest protein families: > 1000 type of GPCRs in mammals >3% of the human genes Major drug targets: ~ 60 % of approved drugs interact with
2 type of ligands 1 G-Protein Coupled Receptors GPCRs One of the largest protein families: > 1000 type of GPCRs in mammals >3% of the human genes Major drug targets: ~ 60 % of approved drugs interact with
Signal Transduction Pathways in Human Diseases
 Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct 29, 2015 Signal Transduction Pathways in Human Diseases Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Introduction
Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct 29, 2015 Signal Transduction Pathways in Human Diseases Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Introduction
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system
 Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
PHSI3009 Frontiers in Cellular Physiology 2017
 Overview of PHSI3009 L2 Cell membrane and Principles of cell communication L3 Signalling via G protein-coupled receptor L4 Calcium Signalling L5 Signalling via Growth Factors L6 Signalling via small G-protein
Overview of PHSI3009 L2 Cell membrane and Principles of cell communication L3 Signalling via G protein-coupled receptor L4 Calcium Signalling L5 Signalling via Growth Factors L6 Signalling via small G-protein
G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Drug Targets
 G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Drug Targets Analysis of Activation and Constitutive Activity Edited by Roland Seifert and Thomas Wieland WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Table of Contents Preface
G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Drug Targets Analysis of Activation and Constitutive Activity Edited by Roland Seifert and Thomas Wieland WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Table of Contents Preface
11/8/16. Cell Signaling Mechanisms. Dr. Abercrombie 11/8/2016. Principal Parts of Neurons A Signal Processing Computer
 Cell Signaling Mechanisms Dr. Abercrombie 11/8/2016 Principal Parts of Neurons A Signal Processing Computer A Multitude of Synapses and Synaptic Actions Summation/Synaptic Integration 1 The Synapse Signal
Cell Signaling Mechanisms Dr. Abercrombie 11/8/2016 Principal Parts of Neurons A Signal Processing Computer A Multitude of Synapses and Synaptic Actions Summation/Synaptic Integration 1 The Synapse Signal
Vets 111/Biov 111 Cell Signalling-2. Secondary messengers the cyclic AMP intracellular signalling system
 Vets 111/Biov 111 Cell Signalling-2 Secondary messengers the cyclic AMP intracellular signalling system The classical secondary messenger model of intracellular signalling A cell surface receptor binds
Vets 111/Biov 111 Cell Signalling-2 Secondary messengers the cyclic AMP intracellular signalling system The classical secondary messenger model of intracellular signalling A cell surface receptor binds
Identification of GLP1R agonists using a novel high throughput screening assay Wan Namkung, Ph.D.
 Identification of GLP1R agonists using a novel high throughput screening assay Wan Namkung, Ph.D. College of Pharmacy, Yonsei University Contents High-throughput screening (HTS) HTS assays for identification
Identification of GLP1R agonists using a novel high throughput screening assay Wan Namkung, Ph.D. College of Pharmacy, Yonsei University Contents High-throughput screening (HTS) HTS assays for identification
SERPENTINE RECEPTOR ADENYL CYCLASE. camp TWO PRINCIPAL SIGNALLING PATHWAYS. cgmp
 SERPENTINE RECEPTOR Receptor contains 7 transmembrane alpha-helical segments & intracellular and extracelullardomains ADENYL CYCLASE camp Enzyme contains about1100 aminoacids, two clusters of six transmembrane
SERPENTINE RECEPTOR Receptor contains 7 transmembrane alpha-helical segments & intracellular and extracelullardomains ADENYL CYCLASE camp Enzyme contains about1100 aminoacids, two clusters of six transmembrane
Receptors Families. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
MBG301. Class IV. Classification of GPCRs according to their effector function (according to Lodish)
 MBG301 Class IV Classification of GPCRs according to their effector function (according to Lodish) 1. Adenylcyclase activation by GPCRs 2. Ion channel regulation by GPCRs 3. Phospholipase C (PLC) activation
MBG301 Class IV Classification of GPCRs according to their effector function (according to Lodish) 1. Adenylcyclase activation by GPCRs 2. Ion channel regulation by GPCRs 3. Phospholipase C (PLC) activation
Growth Hormone, Somatostatin, and Prolactin 1 & 2 Mohammed Y. Kalimi, Ph.D.
 Growth Hormone, Somatostatin, and Prolactin 1 & 2 Mohammed Y. Kalimi, Ph.D. I. Growth Hormone (somatotropin): Growth hormone (GH) is a 191 amino acid single chain polypeptide (MW 22,000 daltons). Growth
Growth Hormone, Somatostatin, and Prolactin 1 & 2 Mohammed Y. Kalimi, Ph.D. I. Growth Hormone (somatotropin): Growth hormone (GH) is a 191 amino acid single chain polypeptide (MW 22,000 daltons). Growth
Vesicle Transport. Vesicle pathway: many compartments, interconnected by trafficking routes 3/17/14
 Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Structure and Activation of the Visual Pigment Rhodopsin
 Seminar 02.12.2011 Structure and Activation of the Visual Pigment Rhodopsin by Steven O.Smith, 2010 Constantin Schneider FB Physik, FU Berlin GPCR: Overview Rhodopsin is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)
Seminar 02.12.2011 Structure and Activation of the Visual Pigment Rhodopsin by Steven O.Smith, 2010 Constantin Schneider FB Physik, FU Berlin GPCR: Overview Rhodopsin is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)
Goals and Challenges of Communication. Communication and Signal Transduction. How Do Cells Communicate?
 Goals and Challenges of Communication Reaching (only) the correct recipient(s) Imparting correct information Timeliness Causing the desired effect Effective termination Communication and Signal Transduction
Goals and Challenges of Communication Reaching (only) the correct recipient(s) Imparting correct information Timeliness Causing the desired effect Effective termination Communication and Signal Transduction
Receptors and Drug Action. Dr. Subasini Pharmacology Department Ishik University, Erbil
 Receptors and Drug Action Dr. Subasini Pharmacology Department Ishik University, Erbil Receptors and Drug Action Receptor Receptor is defined as a macromolecule or binding site located on the surface or
Receptors and Drug Action Dr. Subasini Pharmacology Department Ishik University, Erbil Receptors and Drug Action Receptor Receptor is defined as a macromolecule or binding site located on the surface or
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2
 Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 Introduction to Physiology (0501110) Summer 2012 Subject Lecture No. Lecturer Pages in the 11 th edition.
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 Introduction to Physiology (0501110) Summer 2012 Subject Lecture No. Lecturer Pages in the 11 th edition.
Hormones and Signal Transduction. Dr. Kevin Ahern
 Dr. Kevin Ahern Signaling Outline Signaling Outline Background Signaling Outline Background Membranes Signaling Outline Background Membranes Hormones & Receptors Signaling Outline Background Membranes
Dr. Kevin Ahern Signaling Outline Signaling Outline Background Signaling Outline Background Membranes Signaling Outline Background Membranes Hormones & Receptors Signaling Outline Background Membranes
Membrane associated receptor transfers the information. Second messengers relay information
 Membrane associated receptor transfers the information Most signals are polar and large Few of the signals are nonpolar Receptors are intrinsic membrane proteins Extracellular and intracellular domains
Membrane associated receptor transfers the information Most signals are polar and large Few of the signals are nonpolar Receptors are intrinsic membrane proteins Extracellular and intracellular domains
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Model Answer. M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology)
 Model Answer M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination-2013 Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology) Section A 1. (i) d (ii) b (iii) b (iv) c (v) c (vi) a (vii) c (viii) a (ix) d (x) b Section B Q.2 Answer Hormonal
Model Answer M.Sc. Zoology (First Semester) Examination-2013 Paper LZT 103 (Endocrinology) Section A 1. (i) d (ii) b (iii) b (iv) c (v) c (vi) a (vii) c (viii) a (ix) d (x) b Section B Q.2 Answer Hormonal
1 Higher National Unit credit at SCQF level 8: (8 SCQF credit points at SCQF level 8)
 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H928 35 Superclass: PB Publication date: May 2015 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H928 35 Superclass: PB Publication date: May 2015 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 11 Cell Communication
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 11 Cell Communication BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 210, and for Concept 11.1, read from the first full paragraph on p. 212. Read all of Concept 11.2. Pay
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 11 Cell Communication BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 210, and for Concept 11.1, read from the first full paragraph on p. 212. Read all of Concept 11.2. Pay
Leen Osama, Lujain Hamdan, Osama Mohd, Razi Kittaneh... Faisal Mohammad
 23 Leen Osama, Lujain Hamdan, Osama Mohd, Razi Kittaneh... Faisal Mohammad Revision of previous lectures G-proteins coupled receptors mechanism: When a hormone binds to G-protein coupled receptor, GTP
23 Leen Osama, Lujain Hamdan, Osama Mohd, Razi Kittaneh... Faisal Mohammad Revision of previous lectures G-proteins coupled receptors mechanism: When a hormone binds to G-protein coupled receptor, GTP
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human
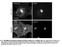 Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins
 Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Session ID: 1001 June 14, 2012
 It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness
 It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II)
 Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Pathophysiology of GPCR Homo- and Heterodimerization: Special Emphasis on Somatostatin Receptors
 Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 417-446; doi:10.3390/ph5050417 Review OPEN ACCESS Pharmaceuticals ISSN 1424-8247 www.mdpi.com/journal/pharmaceuticals Pathophysiology of GPCR Homo- and Heterodimerization: Special
Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 417-446; doi:10.3390/ph5050417 Review OPEN ACCESS Pharmaceuticals ISSN 1424-8247 www.mdpi.com/journal/pharmaceuticals Pathophysiology of GPCR Homo- and Heterodimerization: Special
Receptors. Dr. Sanaa Bardaweel
 Receptors Types and Theories Dr. Sanaa Bardaweel Some terms in receptor-drug interactions Agonists: drugs that mimic the natural messengers and activate receptors. Antagonist: drugs that block receptors.
Receptors Types and Theories Dr. Sanaa Bardaweel Some terms in receptor-drug interactions Agonists: drugs that mimic the natural messengers and activate receptors. Antagonist: drugs that block receptors.
Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al.
 Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al. The endocytic and biosynthetic-secretory pathways The intracellular compartments of the eucaryotic ell involved in the biosynthetic-secretory
Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al. The endocytic and biosynthetic-secretory pathways The intracellular compartments of the eucaryotic ell involved in the biosynthetic-secretory
The recruitment of leukocytes and plasma proteins from the blood to sites of infection and tissue injury is called inflammation
 The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
HORMONES (Biomedical Importance)
 hormones HORMONES (Biomedical Importance) Hormones are the chemical messengers of the body. They are defined as organic substances secreted into blood stream to control the metabolic and biological activities.
hormones HORMONES (Biomedical Importance) Hormones are the chemical messengers of the body. They are defined as organic substances secreted into blood stream to control the metabolic and biological activities.
Pharmacodynamics. Prof. Dr. Öner Süzer Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology
 Pharmacodynamics Prof. Dr. Öner Süzer Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology www.onersuzer.com Last updated: 13.05.2010 English Pharmacology Textbooks 2 2 1 3 3
Pharmacodynamics Prof. Dr. Öner Süzer Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology www.onersuzer.com Last updated: 13.05.2010 English Pharmacology Textbooks 2 2 1 3 3
Angiotensin Type 1 Receptor and β-arrestin. Ki-Seok Kim, M.D. Jeju National University Hospital
 Angiotensin Type 1 Receptor and β-arrestin Ki-Seok Kim, M.D. Jeju National University Hospital GPCR in Heart RAS system Angiotensin II and AT1R β-arrestin Biased Agonism of AT1R AT1R β-arrestin biased
Angiotensin Type 1 Receptor and β-arrestin Ki-Seok Kim, M.D. Jeju National University Hospital GPCR in Heart RAS system Angiotensin II and AT1R β-arrestin Biased Agonism of AT1R AT1R β-arrestin biased
Neuron types and Neurotransmitters
 Neuron types and Neurotransmitters Faisal I. Mohammed. PhD, MD University of Jordan 1 Transmission of Receptor Information to the Brain the larger the nerve fiber diameter the faster the rate of transmission
Neuron types and Neurotransmitters Faisal I. Mohammed. PhD, MD University of Jordan 1 Transmission of Receptor Information to the Brain the larger the nerve fiber diameter the faster the rate of transmission
Synaptic transmission
 Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Omran Saeed. Mamoon Mohammad alqtamin. Ebaa ALzayadneh
 52 Omran Saeed Mamoon Mohammad alqtamin Ebaa ALzayadneh Revision: *classification the signals according to the location of their receptors: (signals have receptors either) 1 transmembrane receptors ( integral
52 Omran Saeed Mamoon Mohammad alqtamin Ebaa ALzayadneh Revision: *classification the signals according to the location of their receptors: (signals have receptors either) 1 transmembrane receptors ( integral
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 16, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
A Primer on G Protein Signaling. Elliott Ross UT-Southwestern Medical Center
 A Primer on G Protein Signaling Elliott Ross UT-Southwestern Medical Center Receptor G Effector The MODULE Rhodopsins Adrenergics Muscarinics Serotonin, Dopamine Histamine, GABA b, Glutamate Eiscosanoids
A Primer on G Protein Signaling Elliott Ross UT-Southwestern Medical Center Receptor G Effector The MODULE Rhodopsins Adrenergics Muscarinics Serotonin, Dopamine Histamine, GABA b, Glutamate Eiscosanoids
Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization. Lorene M. Lanier Department of Neuroscience
 Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization Lorene M. Lanier Department of Neuroscience Diversity in dendritic arbors Pyramidal Purkinje Medium Spiny http://youtu.be/_tqpca6wx84
Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization Lorene M. Lanier Department of Neuroscience Diversity in dendritic arbors Pyramidal Purkinje Medium Spiny http://youtu.be/_tqpca6wx84
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Endocrine system. General principle of endocrinology. Mode of hormone delivery to target. Mode of hormone delivery to target
 Endocrine system General principle of endocrinology Co-ordinating system to regulate and integrate function of different cells - Nervous system -Endocrine system Neuro-endocrine system Hormone Molecules
Endocrine system General principle of endocrinology Co-ordinating system to regulate and integrate function of different cells - Nervous system -Endocrine system Neuro-endocrine system Hormone Molecules
Synaptic Communication. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Tuesday, Sept. 14, Is an enzyme a rigid system?
 Tuesday, Sept. 14, Is an enzyme a rigid system? Early researchers thought of enzymes as rigid entities, recognizing their substrates the way a lock would recognize a key. Today's researchers, however,
Tuesday, Sept. 14, Is an enzyme a rigid system? Early researchers thought of enzymes as rigid entities, recognizing their substrates the way a lock would recognize a key. Today's researchers, however,
2) Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain. 2)
 AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
Living Control Mechanisms
 Living Control Mechanisms Dr Kate Earp MBChB MRCP Specialty Registrar Chemical Pathology & Metabolic Medicine kate.earp@sth.nhs.uk 15/10/2015 Contents Aims & objectives Homeostasis Cell communication Introduction
Living Control Mechanisms Dr Kate Earp MBChB MRCP Specialty Registrar Chemical Pathology & Metabolic Medicine kate.earp@sth.nhs.uk 15/10/2015 Contents Aims & objectives Homeostasis Cell communication Introduction
Week 5 Section. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Week 5 Section Junaid Malek, M.D. HIV: Anatomy Membrane (partiallystolen from host cell) 2 Glycoproteins (proteins modified by added sugar) 2 copies of RNA Capsid HIV Genome Encodes: Structural Proteins
Week 5 Section Junaid Malek, M.D. HIV: Anatomy Membrane (partiallystolen from host cell) 2 Glycoproteins (proteins modified by added sugar) 2 copies of RNA Capsid HIV Genome Encodes: Structural Proteins
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Hormones. Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6
 Hormones Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6 Tel. 030-8385-6920 (Sekret.) 030-8385-6922 (direkt) e-mail: vhaucke@chemie.fu-berlin.de http://userpage.chemie.fu-berlin.de/biochemie/aghaucke/teaching.html
Hormones Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6 Tel. 030-8385-6920 (Sekret.) 030-8385-6922 (direkt) e-mail: vhaucke@chemie.fu-berlin.de http://userpage.chemie.fu-berlin.de/biochemie/aghaucke/teaching.html
2013 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. PROTEIN SORTING. Lecture 10 BIOL 266/ Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S.
 PROTEIN SORTING Lecture 10 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Introduction Membranes divide the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells into distinct compartments. The endomembrane
PROTEIN SORTING Lecture 10 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Introduction Membranes divide the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells into distinct compartments. The endomembrane
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
MCB130 Midterm. GSI s Name:
 1. Peroxisomes are small, membrane-enclosed organelles that function in the degradation of fatty acids and in the degradation of H 2 O 2. Peroxisomes are not part of the secretory pathway and peroxisomal
1. Peroxisomes are small, membrane-enclosed organelles that function in the degradation of fatty acids and in the degradation of H 2 O 2. Peroxisomes are not part of the secretory pathway and peroxisomal
Cellular Signaling Pathways. Signaling Overview
 Cellular Signaling Pathways Signaling Overview Signaling steps Synthesis and release of signaling molecules (ligands) by the signaling cell. Transport of the signal to the target cell Detection of the
Cellular Signaling Pathways Signaling Overview Signaling steps Synthesis and release of signaling molecules (ligands) by the signaling cell. Transport of the signal to the target cell Detection of the
Endocrine System. Chapter 7
 Endocrine System Chapter 7 15 Endocrine Endocrine System: System Cont. collection of structures (glands,cells) which secrete hormones directly into the Chapter 7 circulation to affect metabolism, reproduction,
Endocrine System Chapter 7 15 Endocrine Endocrine System: System Cont. collection of structures (glands,cells) which secrete hormones directly into the Chapter 7 circulation to affect metabolism, reproduction,
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work!
 PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2
 Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 Introduction to Physiology (0501110) Spring 2013 Subject Receptors: types and adaptation - Membrane
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 Introduction to Physiology (0501110) Spring 2013 Subject Receptors: types and adaptation - Membrane
Cell Signaling part 2
 15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
Intracellular vesicular traffic. B. Balen
 Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Communication Between
 Communication Between Neurons Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The electrical changes taking place within a neuron, as described in the previous section, are similar to a light switch being turned on. A stimulus starts
Communication Between Neurons Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The electrical changes taking place within a neuron, as described in the previous section, are similar to a light switch being turned on. A stimulus starts
Thanks to: Signal Transduction. BCB 570 "Signal Transduction" 4/8/08. Drena Dobbs, ISU 1. An Aging Biologist s. One Biologist s Perspective
 BCB 570 "" Thanks to: One Biologist s Perspective Drena Dobbs BCB & GDCB Iowa State University Howard Booth Biology Eastern Michigan University for Slides modified from his lecture Cell-Cell Communication
BCB 570 "" Thanks to: One Biologist s Perspective Drena Dobbs BCB & GDCB Iowa State University Howard Booth Biology Eastern Michigan University for Slides modified from his lecture Cell-Cell Communication
Antigen presenting cells
 Antigen recognition by T and B cells - T and B cells exhibit fundamental differences in antigen recognition - B cells recognize antigen free in solution (native antigen). - T cells recognize antigen after
Antigen recognition by T and B cells - T and B cells exhibit fundamental differences in antigen recognition - B cells recognize antigen free in solution (native antigen). - T cells recognize antigen after
Close to site of release (at synapse); binds to receptors in
 Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Chemical Messengers 1. Neural 2. Endocrine 3. Neuroendocrine 4. Paracrine 5. Autocrine Endocrine System --Endocrine and nervous systems work together --Endocrine vs. Nervous
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Chemical Messengers 1. Neural 2. Endocrine 3. Neuroendocrine 4. Paracrine 5. Autocrine Endocrine System --Endocrine and nervous systems work together --Endocrine vs. Nervous
Thyroid hormones derived from two iodinated tyrosine molecules
 Thyroid Hormones OBJECTIVES Chemical nature of the thyroid hormones How different enzymes play a role in thyroid hormone formation? And what drugs affect them? Describe Function & Metabolism of thyroid
Thyroid Hormones OBJECTIVES Chemical nature of the thyroid hormones How different enzymes play a role in thyroid hormone formation? And what drugs affect them? Describe Function & Metabolism of thyroid
Diuretic Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting
 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Cell Communication CHAPTER 11
 Cell Communication CHAPTER 11 What you should know: The 3 stages of cell communication: reception, transduction, and response. How a receptor protein recognizes signal molecules and starts transduction.
Cell Communication CHAPTER 11 What you should know: The 3 stages of cell communication: reception, transduction, and response. How a receptor protein recognizes signal molecules and starts transduction.
Chapter 9. Cellular Signaling
 Chapter 9 Cellular Signaling Cellular Messaging Page 215 Cells can signal to each other and interpret the signals they receive from other cells and the environment Signals are most often chemicals The
Chapter 9 Cellular Signaling Cellular Messaging Page 215 Cells can signal to each other and interpret the signals they receive from other cells and the environment Signals are most often chemicals The
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2
 Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 Objectives Define first messenger (Hormones) List hormone types Describe receptor types Outline the
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 Objectives Define first messenger (Hormones) List hormone types Describe receptor types Outline the
INTERACTION DRUG BODY
 INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
Cell Biology (BIOL 4374 and BCHS 4313) Third Exam 4/24/01
 Cell Biology (BIOL 4374 and BCHS 4313) Third Exam 4/24/01 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. For multiple choice questions,
Cell Biology (BIOL 4374 and BCHS 4313) Third Exam 4/24/01 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. For multiple choice questions,
REVIEW ARTICLES. G Protein coupled Receptors
 REVIEW ARTICLES David C. Warltier, M.D., Ph.D., Editor Anesthesiology 2005; 103:1066 78 2005 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Receptors, G Proteins, and Their
REVIEW ARTICLES David C. Warltier, M.D., Ph.D., Editor Anesthesiology 2005; 103:1066 78 2005 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Receptors, G Proteins, and Their
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (Follitropin) As many people know, the vast complexities and intricacies involved in the
 Wayne Heath Professor Champlin BIO 421 19 February 2014 Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (Follitropin) As many people know, the vast complexities and intricacies involved in the functioning of the human body
Wayne Heath Professor Champlin BIO 421 19 February 2014 Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (Follitropin) As many people know, the vast complexities and intricacies involved in the functioning of the human body
Mohammad Tarek. Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat. Faisal Mohammad
 15 Mohammad Tarek Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Things to remember Types of synapse: Neuron types and neurotransmitters When it happens between an axon and dendrites it is called axodendritic
15 Mohammad Tarek Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Things to remember Types of synapse: Neuron types and neurotransmitters When it happens between an axon and dendrites it is called axodendritic
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
endomembrane system internal membranes origins transport of proteins chapter 15 endomembrane system
 endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
Basics of Pharmacology
 Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Propagation of the Signal
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
1st Year MB/BDS Plenary Lecture What is a Hormone?
 1st Year MB/BDS Plenary Lecture What is a Hormone? The term hormone (from the Greek for I arouse to activity or I excite) was first used by Starling in 1905. Hormones are just one type of first (or primary)
1st Year MB/BDS Plenary Lecture What is a Hormone? The term hormone (from the Greek for I arouse to activity or I excite) was first used by Starling in 1905. Hormones are just one type of first (or primary)
Review II: Cell Biology
 Review II: Cell Biology Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2006 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2006 Outline Cell Cycle Signal Transduction 1 Cell Cycle Four
Review II: Cell Biology Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2006 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2006 Outline Cell Cycle Signal Transduction 1 Cell Cycle Four
Significance of the MHC
 CHAPTER 8 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
CHAPTER 8 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
Examples of smallmolecule. peptide neurotransmitters
 Examples of smallmolecule and peptide neurotransmitters Small- molecule transmitters are transported from the cytosol into vesicles or from the synaptic cleft to the cytosol by TRANSPORTERS Neuromodulatory
Examples of smallmolecule and peptide neurotransmitters Small- molecule transmitters are transported from the cytosol into vesicles or from the synaptic cleft to the cytosol by TRANSPORTERS Neuromodulatory
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 12 Signal Transduction
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 12 Signal Transduction CHAPTER 12 Signal Transduction Key topics: General features of signal transduction Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors Structure
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 12 Signal Transduction CHAPTER 12 Signal Transduction Key topics: General features of signal transduction Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors Structure
Signal Transduction Pathways
 Signal Transduction Pathways If it helps, think of signal transduction pathways like what happens when you get a text message: Reception = Your phone vibrates or dings. Transduction = You unlock the phone
Signal Transduction Pathways If it helps, think of signal transduction pathways like what happens when you get a text message: Reception = Your phone vibrates or dings. Transduction = You unlock the phone
Supplementary Figure 1. Rab27a-KD inhibits speed and persistence of HEp3 cells migrating in the chick CAM. (a) Western blot analysis of Rab27a
 Supplementary Figure 1. Rab27a-KD inhibits speed and persistence of HEp3 cells migrating in the chick CAM. (a) Western blot analysis of Rab27a expression in GFP-expressing HEp3 cells. (b) Representative
Supplementary Figure 1. Rab27a-KD inhibits speed and persistence of HEp3 cells migrating in the chick CAM. (a) Western blot analysis of Rab27a expression in GFP-expressing HEp3 cells. (b) Representative
Lecture: CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways
 Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
* * 11. GnRH. Molecular Biology of the Cell 5th Ed. Alberts et al., Garland Science, 2008
 I e-mail: okay@bs.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp http://www.bs.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~naibunpi/lab.html Molecular Biology of the Cell 5th Ed. Alberts et al., Garland Science, 2008 Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes 3rd Ed.
I e-mail: okay@bs.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp http://www.bs.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~naibunpi/lab.html Molecular Biology of the Cell 5th Ed. Alberts et al., Garland Science, 2008 Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes 3rd Ed.
Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs. ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani
 Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani 2017-2018 Adrenergic agonists The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that
Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani 2017-2018 Adrenergic agonists The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that
04_polarity. The formation of synaptic vesicles
 Brefeldin prevents assembly of the coats required for budding Nocodazole disrupts microtubules Constitutive: coatomer-coated Selected: clathrin-coated The formation of synaptic vesicles Nerve cells (and
Brefeldin prevents assembly of the coats required for budding Nocodazole disrupts microtubules Constitutive: coatomer-coated Selected: clathrin-coated The formation of synaptic vesicles Nerve cells (and
