Ultrastructural Observations in an Alcoholic Patient with Post-Surgical Pseudomonas Infection
|
|
|
- Benedict Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANNALS O F CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIEN CE, Vol. 11, No. 2 Copyright 1981, Institute for Clinical Science, Inc. Ultrastructural Observations in an Alcoholic Patient with Post-Surgical Pseudomonas Infection A. COPPOLA, M.D., P. L. CHORDIA, M.D., and J. DE ROSA, M.D. Department o f Pathology and Medicine Kings County Hospital-Downstate Medical Center,. State University o f New York, ' / Brooklyn, NY ABSTRACT Gram negative bacteria were seen in the peripheral blood and within the neutrophils of a patient with bacteremic shock secondary to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. By electron microscopy, bacteria were present either in vacuoles or in the cytoplasm of neutrophils. When seen in the cytoplasm, they were surrounded by amorphous material which most probably represented fused lysosomal granules. In both cases, the microorganisms appeared morphologically normal. The presumption is that there was a pre-existing defect of neutrophilic lysosomal formation or function. These findings indicate the importance of studying neutrophil morphology and function in patients with persistent infections. Introduction In a study o f3500 routine blood smears, Zieve et al found the leukocytes of only 122 patients had vacuolization. Of these, 119 had bacterial infections. 14 Neutrophilic vacuolization is therefore a cardinal feature of septicemia and one which is immediately available to the clinician, whereas results of blood culture may require 24 hours or more. Neutrophils may phagocytize bacteria, which are then digested by cytoplasmic Request for reprints: A. Coppola, M.D., Box #25, D epartm ent of Pathology, D.M.C., 450 Clarkson Avenue, Brooklyn, NY granules. The hydrolytic enzymes and peroxidase of neutrophils are known to destroy the bacteria. 7, 9,1 5 If digestion is impaired either by defective processes within the cell or by overwhelming infection, bactericidal activity may be defective. 12 The bacteria can, then, be seen microscopically in the cytoplasm. Patients with gram negative septicemia classically show leukocytosis, toxic granulation, and vacuolization of the neutrophils in the peripheral blood. In a three year period at Kings County Hospital, where approximately 400 complete blood counts (CBC) are done daily, intraleukocytic gram negative organisms have /81/ $00.90 Institute for Clinical Science, Inc.
2 ULTRASTRUCTURAL OBSERVATIONS IN PSEUDOM ONAS IN FEC T IO N 153 not previously been found in a peripheral blood smear. This report describes a postoperative patient who developed overwhelming Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and was treated with appropriate antibiotic therapy as judged by sensitivity test. N evertheless, the patient developed shock, and at that time the neutrophils of the perip h eral blood sm ear showed marked vacuolization and intracytoplasmic bacteria. Case Report A 34-year-old black man was adm itted to Kings County Hospital with epigastric pain, nausea, and vomiting of one day s duration. He gave a history of chronic alcoholism. L aboratory data in clu d ed hemoglobin, 14.6 gms; hematocrit 44 percent; white blood cell count 9.5 per cu mm with normal differential; blood urea nitrogen, 8 mg p er dl; serum creatinine, 1 mg per dl; serum glucose, 178 mg per dl; and serum calcium, 7.8 mg per dl. Physical examination revealed marked epigastric tenderness, and a diagnosis of acute pancreatitis was made. Peritoneal and pleural taps showed bloody fluid. On the sixth hospital day, the hematocrit fell to 26 percent and an exploratory laparotomy was performed. D uring this procedure, acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis was found and a distal pancreatectomy, splenectom y, cholecystectom y, and gastrostomy w ere performed. Following surgery, the patient s tem perature rose to 105 F. The sputum culture revealed Psuedomonas aeruginosa sensitive to gentamycin and cephalothin. Although the patient was promptly treated w ith the antibiotics, the following days w ere storm y. T he fever p ersisted, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa grew in the drainage from the abdominal wound. The patient was again explored by laparotomy because of bleeding into the peritoneal cavity and upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Pseudomonas aeruginosa was cultured on several different occasions from endotracheal aspirate and from the purulent discharge of the abdominal surgical wound, but never from the blood. On the 34th hospital day, a subphrenic abscess was discovered from which Pseudomonas aeruginosa was cultured. The blood revealed leukocytosis betw een 20,000 and 30,000 per cmm. Although antibiotic treatm ent of gentamycin and cephalothin contin u e d, th e fev er p ersisted. P seudom onas aeruginosa was again cultured from the purulent discharge and again it was sensitive to gentamycin and cephalothin. On the 52nd hospital day, there was a leukocytosis of 16,000 per cmm, but a differential was not done. D espite all treatm ent the patient continued to deteriorate. On the 53rd hospital day, th e blood pressure suddenly fell to 80/40, the patient developed oliguria, and the tem perature fell to 95 F. Blood was drawn for a complete blood count. Soon after this, the patient w ent into deep coma and expired. Permission for autopsy was not obtained. Material and Methods Blood obtained from the patient on the 53rd hospital day was im m ediately brought to the hematology laboratory for a complete blood count. Hemoglobin was 3.8 g per dl, hematocrit was 11.9, and the white cell count was 16,700 per cmm. Smears were stained with Wright s and Gram stain. The differential count revealed 92 percent polymorphs, 5 percent lymphocytes, 2 percent monocytes, and 1 percent band. Approximately 400 /xl of blood was left for ultrastructural studies. The buffy coat was collected and prepared for electron microscopy according to the methods previously described.3,4 Results L i g h t M i c r o s c o p y The exam ination of the peripheral blood revealed that 42 percent of the neutrophils contained Gram negative organisms (figure 1). In some neutrophils, the bacteria were seen in division. This phenemenon was also seen extracellularly. The neutrophils contained toxic granulations and/or vacuoles. In the majority of neutrophils the toxic granulations were few, large and unevenly distributed. The number of vacuoles varied from cell to cell; often there was only a single large vacuole, empty or containing bacteria (figure 2). Occasionally, many small vacuoles w ere seen w ithin polym orphonuclear leukocytes which often lacked granules. The lymphocytes, monocytes, red cells, and the few platelets were normal. E l e c t r o n M i c r o s c o p y The nuclei of the neutrophils had a normal arrangement of the chromatin and heterochrom atin. T he cytoplasm had
3 154 C O P P O L A, C H O R D IA, AND D E ROSA F ig u r e 1. N eutrophils of the peripheral blood with bacteria in the cytoplasm (arrow) and toxic granula tions. W right s stain; x F ig u r e 2. A n eu tro p h il co n ta in in g b acteria in th e cy to p la sm and in a v a c u o le (arrow). W right s stain; x F i g u r e 3. N eutrophil in phagocytic activity: the bacterium about to be ingested, with fragments of flagella. N = nucleus; GL = glycogen; Ly = lysosomes. Uranyl acetate; x 55,965. scanty ribosom es and occasional vesicles o f the rough end o p lasm ic reticulum. T he am ount of glycogen was also norm al. T he n u m b er of g ran u les varied. In som e n e u trophils, th e y w ere abundant; in some, esp ecially in those having m any vacuoles, th ey w ere sparse or absent. T h e vacuoles w ere o f various size and often contained b acteria. M any neutrophils p re s e n te d one bacteriu m in th e cytoplasm b u t occasion-
4 U L TR A ST R U C TU R A L OBSERVATIONS IN PSEU D O M O N A S IN F E C T IO N 155 F ig u r e 4. N eutrophil with phagocytized bacterium. Vacuole is not apparent, bu t a dense, amorphous material (arrow) is seen. N = nucleus; B = bacterium ; Ly = lysosomes. Uranyl acetate; x 26,368. F ig u r e 5. Bacterium pinched in the center and surrounded by dense, amorphous material w hich is partially bounded by a discontinuous m em brane (arrow). B = bacterium. Uranyl acetate; x 55,965.
5 156 CO PPO LA, CHORD IA, AND D E ROSA ally two or three organisms were also seen. Rarely neutrophils were seen in phagocytic activity actively engulfing a bacterium (figure 3). The great majority of bacteria seen in the cytoplasmic vacuoles appeared unaltered. The microorganisms were also seen in the cytoplasm where the vacuoles were not apparent (figure 4). In these cases, the bacteria were surrounded by amorphous material which most probably represents fused lysosomal granules as revealed by the presence of residual lysosomal membrane or residual membranes of the vacuole. Even in these instances, the bacterial body appeared intact. Of particular interest was the presence of dividing bacteria within the cytoplasm of few neutrophils (figure 5). Bacteria were also seen extracellularly, and no difference was noticed between phagocytized and nonphagocytized microorganisms. Discussion The post-surgical course in this patient was characterized by a severe intractable Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection, and the final clinical events were typical of septicem ia. In general, infection of wounds by Pseudomonas aeruginosa is not unusual, but involvement of the respiratory tract is uncommon; in debilitated persons, fatal sepsis may occur.5,1 3 In the present case, bacterial growth not only occurred at the site of the surgical wound but also in the respiratory and urinary tract. Term inally, Pseudomonas aeruginosa invaded the blood stream to such an extent that bacteria were seen both in plasma and within leukocytes. The poor response of this patient to antibiotic treatment might have been the result of many factors. For example, in chronic alcoholics decreased marrow granulocyte reserve has been suggested. 10 In our case, the sustained leukocytosis made it unlikely that there was any decrease in marrow granulocyte reserve. Although there is no good correlation between alcohol ingestion and infections, it is well known that alcohol ingestion may lead to abnorm al granulocyte mobilization. 1 There are few microscopic descriptions of microorganisms w ithin circulating leukocytes, 2,8 and the intraleukocytic demonstration of bacteria in division is an unusual finding. The present authors are not aware of electron microscopy being performed in similar conditions. The mechanism of cell division of gram negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa has been a matter of debate. Steed and Murray11 mentioned that division occurs by constriction. In our case, the cells appear pinched in the middle, and septa are not seen. Later, however, Gilleland and Murray6 emphasized that although technically it is difficult to demonstrate, septation is the mode of cell division in gram negative bacteria, and constriction is a fixation artifact. In the case just described, evidence is presented by microscopy that while the neutrophils retained their phagocytic activity, their function was altered because they had lost their bactericidal activity. In fact, by electron microscopy, all bacteria including those in division appeared unaltered within the cytoplasmic vacuoles and resembled those seen extracellularly. Similarly, in the cytoplasm itself, being surrounded by amorphous material of probable lysosomal origin, the bacteria were morphologically well preserved. This, perhaps, was due to the fact that the lysosomal enzymes had not yet initiated the process of bactericidal digestion or most probably were defective. The presumption is that there was a pre-existing defect of neutrophilic lysosomal formation or function. In view of findings in cases like this one, it may be possible to elucidate the antibiotic unresponsiveness much earlier by electron microscopic studies of the peripheral blood as well as with studies to determine the function of the neutrophils.
6 ULTRASTRUCTURAL OBSERVATIONS IN PSEUDOM ONAS IN FEC T IO N 157 Acknowledgm ents The authors are grateful to Doctors J. D. Broome, J. Sher, and S. Kaufmann for their interest in this report and help in the preparation of the manuscript. T hanks are e x ten d e d to N ilda Stahl, Ramon Camacho, Alan Lieberman, and T. S. Deutsch for technical assistance. References 1. Br a y t o n, R. G., St o k e s, P. E., Sc h w a r t z, M. S., and L o n r ie, D. B.: Effect of alcohol and various diseases on and intracellular bacterial killing. New Eng. J. Med. 282: , Br o o k s, G. F., P r ib b l e, A. H., and Be a t y, H. N.: Early diagnosis of bacterem ia by buffy-coat examinations. Arch. Intern. Med. 132: , C o p p o l a, A., M u n o z, A., and Sh e r, J.: Morp h o lo g ic o b serv atio n of lym phocytes of Pom pe s disease. J. Pediat. 93:824, COPPOLA, A.: A rapid method for electron microscopy examination of blood cells. J. Clin. Path. 32:162, D a v id s o h n, J. and H e n r y, J. B.: Todd-Sanford, C linical D iagnosis by Laboratory M ethods, 15th ed. Philadelphia, W. B. Saunders Co., 1974, p G il l e l a n d, H. E., Jr. and Murray, R. G. E.: D em onstration of cell division by septation in a variety of gram negative rods. J. Bact. 121: , H ir s c h, J. D. and Co h n, Z. A.: Degranulation of polym orphonuclear leukocytes follow ing phagocytosis of microorganisms. J. Exp. Med. ii2: , KUBERSKI, T. T.: Intraleukocytic spore formation and leukocytic vacuolization during Clostridium perfringens septicemia. Amer. J. Clin. Path. 68: , M c Ca l l, C. E., Katayam a, I., Co t r a n, R. S., and F in l a n d, M.: Lysosomal and ultrastructural changes in human toxin neutrophils during bacterial infection. J. Exp. Med. 129: , Mc F a r l a n d, W. and Lib r e, E. P.: Abnormal leukocytes response in alcoholism. Ann. Intern. Med. 59: , St e e d, P. and M u rray, R. G. E.: The cell wall and cell division of gram negative bacteria. Canad. J. Microb. 12: , St OSSELL, T. P.: Phagocytosis. Granulocyte: Function and Clinical Utilization. Greenwald, T. J. and Jamieson, G. A., eds. New York, Alan R. Liss Inc., 1977, p Yo u n g, L. S. and Ar m st r o n g, D.: H um an imm unity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In vitro interaction of bacteria, polym orphonuclear leukocytes and serum factors. J. Infect. Dis. 126: , Zie v e, P. D., H a g h s h e n a s s, M., Bl a n k s, M., and Kr e v e n S, J. R.: Vacuolization of the neutrophil. An aid in the diagnosis of septicemia. Arch. Intern. Med. 118: , Z u c k e r-f r a n k lin D. and H ir s c h, J. D.: E lectron microscope study on the degranulation of rab b it perito n eal leukocyte during phagocytosis. J. Exp. Med. 120:569, 1966.
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Analysis of Two Types of Granulocyte Transfusions in Patients with Acute Leukemia and Septicemia
 ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE, Vol. 12, No. 2 Copyright 1982, Institute for Clinical Science, Inc. Analysis of Two Types of Granulocyte Transfusions in Patients with Acute Leukemia and Septicemia
ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE, Vol. 12, No. 2 Copyright 1982, Institute for Clinical Science, Inc. Analysis of Two Types of Granulocyte Transfusions in Patients with Acute Leukemia and Septicemia
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY BLOOD AND BODY FLUID PHYSIOLOGY LECTURER: MR A.O. AKINOLA OBJECTIVES Leukopoiesis Thrombopoiesis Leukopoiesis and Lymphopoiesis White blood
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY BLOOD AND BODY FLUID PHYSIOLOGY LECTURER: MR A.O. AKINOLA OBJECTIVES Leukopoiesis Thrombopoiesis Leukopoiesis and Lymphopoiesis White blood
Chapter 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
 Module 10 Chapter 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host The concept of immunity Immunity: ability to protect against from microbes and their o Aka, Susceptibility: vulnerability or lack
Module 10 Chapter 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host The concept of immunity Immunity: ability to protect against from microbes and their o Aka, Susceptibility: vulnerability or lack
BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS
 BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS A pathogen is a microorganism that is able to cause disease. Pathogenicity is the ability to produce disease in a host organism. Virulence a term which refers to the degree of pathogenicity
BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS A pathogen is a microorganism that is able to cause disease. Pathogenicity is the ability to produce disease in a host organism. Virulence a term which refers to the degree of pathogenicity
lysosomes Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types:
 lysosomes Digests Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types: Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Lipids Single membrane bound vesicle, contains up to 50 digestive
lysosomes Digests Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types: Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Lipids Single membrane bound vesicle, contains up to 50 digestive
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Blood: Functions. Liquid connective tissue 3 general functions 1. Transportation. 2. Regulation. 3. Protection
 Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
human cell Mader s Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapters 1, 3 and 4
 1 The human cell INTRODUCTION All living things are composed of cells, which are the smallest units of life and are so small they can only be viewed through a microscope. Cells are made from pre-existing
1 The human cell INTRODUCTION All living things are composed of cells, which are the smallest units of life and are so small they can only be viewed through a microscope. Cells are made from pre-existing
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DIFFERENTIATING IMMATURE PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity
 Part 1 Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity Bacteria Most common pathogens Anthrax Cholera Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria Bacterial diseases Tuberculosis Cholera Bubonic Plague Tetanus Effects
Part 1 Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity Bacteria Most common pathogens Anthrax Cholera Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria Bacterial diseases Tuberculosis Cholera Bubonic Plague Tetanus Effects
Improved Immunodiagnosis of Neutrophil Dysfunction in the Newborn and Infant
 ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE, Vol. 12, No. 2 Copyright 1982, Institute for Clinical Science, Inc. Improved Immunodiagnosis of Neutrophil Dysfunction in the Newborn and Infant ALAN B. LOREN,
ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE, Vol. 12, No. 2 Copyright 1982, Institute for Clinical Science, Inc. Improved Immunodiagnosis of Neutrophil Dysfunction in the Newborn and Infant ALAN B. LOREN,
Offending agents like: 1. Infectious agents: 2. toxic agents(toxins) Micro-organisms Bacteria Viruses Parasites Fungi
 Immunity Dr.Talar Immunity: is the ability of the human body to resist almost all types of offending agents that tend to damage the tissues and organs or it s a special system for combating different infectious
Immunity Dr.Talar Immunity: is the ability of the human body to resist almost all types of offending agents that tend to damage the tissues and organs or it s a special system for combating different infectious
HEMOTOLOGY. B. Helps stabilize body temperature -heats up and cools down slowly which moderates body temp
 I. Body H 2 O = HEMOTOLOGY A. Variable quantities 1. sweating and urination ( ) decreases H 2 O 2. drinking H 2 O increases B. Water is found in two compartments 1. contains 2/3 of all water in your body
I. Body H 2 O = HEMOTOLOGY A. Variable quantities 1. sweating and urination ( ) decreases H 2 O 2. drinking H 2 O increases B. Water is found in two compartments 1. contains 2/3 of all water in your body
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
Blood Cells. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Lifeblood Lab Activity
 History of Blood: It is the universal symbol of horror, of death, yet it is the one thing that keeps you living. It is the blood that is coursing through your veins. But, what do you really know about
History of Blood: It is the universal symbol of horror, of death, yet it is the one thing that keeps you living. It is the blood that is coursing through your veins. But, what do you really know about
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Blood and Defense. Chapter 11
 Blood and Defense Chapter 11 Functions of Blood 1. Carry nutrients from the small intestine and oxygen from the lung to tissues in the body 2. Transport wastes from tissues to the kidneys and carbon dioxide
Blood and Defense Chapter 11 Functions of Blood 1. Carry nutrients from the small intestine and oxygen from the lung to tissues in the body 2. Transport wastes from tissues to the kidneys and carbon dioxide
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
Composition of Blood
 Blood is a connective tissue, specialized to transport the respiratory gasses as well as hormones, nutrients, and wastes, and the distribution of heat. The various cells of the blood perform specific functions.
Blood is a connective tissue, specialized to transport the respiratory gasses as well as hormones, nutrients, and wastes, and the distribution of heat. The various cells of the blood perform specific functions.
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Heyam Awad
 number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
The Innate Immune Response
 The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
Innate Immunity. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 2: Composition and Function of Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 2: Composition and Function of Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Cells & Cell Transport. Cells
 Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
five lineages of stem cells producing all of the various formed elements.
 Chapter 6 Blood Tissue 6.1. Basic Composition of Blood Blood is a connective tissue composed of free cells in a fluid matrix. Unlike other types of connective tissues, blood lacks fibers except during
Chapter 6 Blood Tissue 6.1. Basic Composition of Blood Blood is a connective tissue composed of free cells in a fluid matrix. Unlike other types of connective tissues, blood lacks fibers except during
11/25/2017. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS BARRIER DEFENSES INNATE IMMUNITY OF VERTEBRATES
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
MACROPHAGE "MONOCYTES" SURFACE RECEPTORS
 LECTURE: 13 Title: MACROPHAGE "MONOCYTES" SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Describe the blood monocytes (size, and shape of nucleus). Enumerate some of the monocytes
LECTURE: 13 Title: MACROPHAGE "MONOCYTES" SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Describe the blood monocytes (size, and shape of nucleus). Enumerate some of the monocytes
Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements
 Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements Plasma 55% of whole blood 90% water 8% proteins from liver 2% misc. Nutrients: AA, glucose, lipids vitamins, minerals Wastes: urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium
Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements Plasma 55% of whole blood 90% water 8% proteins from liver 2% misc. Nutrients: AA, glucose, lipids vitamins, minerals Wastes: urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium
The % of blood consisting of packed RBCs is known as the hematocrit. Blood s color ranges from scarlet (oxygen-rich) to dark red (oxygen poor).
 Biology Blood Blood is a fluid connective tissue consisting of cells suspended in a liquid fibrous matrix. The cells are called formed elements and the liquid matrix is known as plasma. The formed elements
Biology Blood Blood is a fluid connective tissue consisting of cells suspended in a liquid fibrous matrix. The cells are called formed elements and the liquid matrix is known as plasma. The formed elements
NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, AND PLATELETS SURFACE RECEPTORS
 LECTURE: 15 Title NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, AND PLATELETS SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Determine the relative percentages in blood for the various types
LECTURE: 15 Title NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, AND PLATELETS SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Determine the relative percentages in blood for the various types
Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy
 Haematology Lectures Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy 1 Objectives 1. Define the term Reticuloendothelial system (RES). 2. Describe the cellular components of RES. 3. Describe
Haematology Lectures Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy 1 Objectives 1. Define the term Reticuloendothelial system (RES). 2. Describe the cellular components of RES. 3. Describe
SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells
 SACE Biology Year 2016 Mark 20.00 Pages 26 Published Jan 4, 2017 SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells By Elizabeth (99.75 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Elizabeth. Elizabeth achieved
SACE Biology Year 2016 Mark 20.00 Pages 26 Published Jan 4, 2017 SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells By Elizabeth (99.75 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Elizabeth. Elizabeth achieved
1. Overview of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 15: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity Chapter Reading pp. 449-456 The Body s Defenses The
Chapter 15: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity Chapter Reading pp. 449-456 The Body s Defenses The
Chapter 43. Immune System. phagocytosis. lymphocytes. AP Biology
 Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
Chapter Lymphatic Cells, Lymphatic Tissues, and Lymphatic Organs
 Chapter 22.2 Lymphatic Cells, Lymphatic Tissues, and Lymphatic Organs Lymphatic Cells These are the cells that play a key roll in the structure and function of the immune system. We have already introduced
Chapter 22.2 Lymphatic Cells, Lymphatic Tissues, and Lymphatic Organs Lymphatic Cells These are the cells that play a key roll in the structure and function of the immune system. We have already introduced
Chapter 06 Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 06 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. 2012 Pearson Permission Education,
Chapter 06 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. 2012 Pearson Permission Education,
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz
 Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz Question Prompt: 1 Mononuclear white blood cells (agranulocyte) formed in lymph tissue, also a phagocyte and a precursor of macrophages are leukocytes. True False Question Prompt:
Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz Question Prompt: 1 Mononuclear white blood cells (agranulocyte) formed in lymph tissue, also a phagocyte and a precursor of macrophages are leukocytes. True False Question Prompt:
G. Types of White Blood Cells
 1. White blood cells are also called leukocytes. G. Types of White Blood Cells 2. White blood cells function to protect against diseases. 3. Two hormones that stimulate white blood cell production are
1. White blood cells are also called leukocytes. G. Types of White Blood Cells 2. White blood cells function to protect against diseases. 3. Two hormones that stimulate white blood cell production are
Chapter 14. Blood. Blood Volume. Blood Composition. Blood
 Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
1 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II PLATELETS. Mature Stage: No nucleus. Only 2-3 µm in diameter: significantly smaller than RBCs
 1 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II LAB BLOOD PLATES EOSINOPHIL Contains large red-staining granules Usually 2 lobes 12-17 µm: about the size of neutrophils (2X erythrocytes) regulation/reduction of Histamine.
1 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II LAB BLOOD PLATES EOSINOPHIL Contains large red-staining granules Usually 2 lobes 12-17 µm: about the size of neutrophils (2X erythrocytes) regulation/reduction of Histamine.
By Lucy Simpson and Taylor Meyers
 By Lucy Simpson and Taylor Meyers Two Types of Immunity Innate immunity- Innate immunity consists of external barriers formed by the skin and mucous membranes, plus a set of internal cellular and chemical
By Lucy Simpson and Taylor Meyers Two Types of Immunity Innate immunity- Innate immunity consists of external barriers formed by the skin and mucous membranes, plus a set of internal cellular and chemical
CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Blood Clotting Functions of Blood Transportation
 1 CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Functions of Blood Transportation Protection Regulation ph Temperature Composition of Blood Plasma: liquid
1 CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Functions of Blood Transportation Protection Regulation ph Temperature Composition of Blood Plasma: liquid
Lysosomes. Gr: lysis solution, soma body. Membrane bounded vesicles. Usually round ovoid or irregular electron dense bodies m.
 Lysosomes Gr: lysis solution, soma body Membrane bounded vesicles Usually round ovoid or irregular electron dense bodies 0.05 0.5 m. Lysosomes No. varies from a few to several hundred per cell, in different
Lysosomes Gr: lysis solution, soma body Membrane bounded vesicles Usually round ovoid or irregular electron dense bodies 0.05 0.5 m. Lysosomes No. varies from a few to several hundred per cell, in different
Nonspecific Defenses of the Host. Chapter 16
 Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Chapter 16 I. Introduction: Overview of host defenses A. Resistance Ability to ward off disease through body defenses 1. Nonspecific All body defenses that protect one
Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Chapter 16 I. Introduction: Overview of host defenses A. Resistance Ability to ward off disease through body defenses 1. Nonspecific All body defenses that protect one
Blood and Haemopoiesis
 Blood and Haemopoiesis Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Connective Tissue Connective tissue proper Connective tissue with special properties Loose connective tissue Dense
Blood and Haemopoiesis Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Connective Tissue Connective tissue proper Connective tissue with special properties Loose connective tissue Dense
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood
 Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood vessels hematology = the
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood vessels hematology = the
3. Which cell has the greater ratio of surface area to volume?
 Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Host Response to Disease Resistance- ability
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Host Response to Disease Resistance- ability
immunity defenses invertebrates vertebrates chapter 48 Animal defenses --
 defenses Animal defenses -- immunity chapter 48 invertebrates coelomocytes, amoebocytes, hemocytes sponges, cnidarians, etc. annelids basophilic amoebocytes, acidophilic granulocytes arthropod immune systems
defenses Animal defenses -- immunity chapter 48 invertebrates coelomocytes, amoebocytes, hemocytes sponges, cnidarians, etc. annelids basophilic amoebocytes, acidophilic granulocytes arthropod immune systems
Hematology 101. Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD
 Hematology 101 Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD Hematocrits Plasma White cells Red cells Normal, Hemorrhage, IDA, Leukemia,
Hematology 101 Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD Hematocrits Plasma White cells Red cells Normal, Hemorrhage, IDA, Leukemia,
Basophilic. Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue
 Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 5 Eukaryotic Cell Structure 1 5.1 A typical eukaryotic cell 1. Compare and contrast eukaryotic, bacterial, and archaeal cells in terms of their use of membranes, size, morphological diversity, and organelles.
5 Eukaryotic Cell Structure 1 5.1 A typical eukaryotic cell 1. Compare and contrast eukaryotic, bacterial, and archaeal cells in terms of their use of membranes, size, morphological diversity, and organelles.
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Medical PCCN. AACN Progressive Critical Care Nursing.
 Medical PCCN AACN Progressive Critical Care Nursing http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pccn Question: 83 What would be identified on the arterial blood gas results as a reflection of acute respiratory
Medical PCCN AACN Progressive Critical Care Nursing http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pccn Question: 83 What would be identified on the arterial blood gas results as a reflection of acute respiratory
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood
 Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System VS Cardiovascular System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System VS Cardiovascular System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood
Bacteriemia and sepsis
 Bacteriemia and sepsis Case 1 An 80-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his son, who noted that his father had become lethargic and has decreased urination over the past 4 days. The patient
Bacteriemia and sepsis Case 1 An 80-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his son, who noted that his father had become lethargic and has decreased urination over the past 4 days. The patient
A CYTOCHEMICAL ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF RABBIT HETEROPHILIC LEUKOCYTES DORING PHAGOCYTOSIS
 Nagoya J. med. Sci. 33: 287-294, 1971 A CYTOCHEMICAL ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF RABBIT HETEROPHILIC LEUKOCYTES DORING PHAGOCYTOSIS ACID AND ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE REACTIONS MoRIHIKO NnMr 1st Department
Nagoya J. med. Sci. 33: 287-294, 1971 A CYTOCHEMICAL ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF RABBIT HETEROPHILIC LEUKOCYTES DORING PHAGOCYTOSIS ACID AND ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE REACTIONS MoRIHIKO NnMr 1st Department
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism
 Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
1. Specificity: specific activity for each type of pathogens. Immunity is directed against a particular pathogen or foreign substance.
 L13: Acquired or adaptive (specific) immunity The resistance, which absent at the time of first exposure to a pathogen, but develops after being exposed to the pathogen is called acquired immunity. It
L13: Acquired or adaptive (specific) immunity The resistance, which absent at the time of first exposure to a pathogen, but develops after being exposed to the pathogen is called acquired immunity. It
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Active Lecture Questions for use with Classroom Response Systems Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Active Lecture Questions for use with Classroom Response Systems Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Edited by William Wischusen, Louisiana State University
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Active Lecture Questions for use with Classroom Response Systems Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Edited by William Wischusen, Louisiana State University
All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood. Functions:
 Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Functions: Transports nutrients, oxygen, cellular waste products, and hormones Aids in distribution of heat Regulates acid-base balance Helps protect against infection
Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Functions: Transports nutrients, oxygen, cellular waste products, and hormones Aids in distribution of heat Regulates acid-base balance Helps protect against infection
OpenStax-CNX module: m Innate Immunity. OpenStax College. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45542 1 Innate Immunity OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m45542 1 Innate Immunity OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Hemopoiesis and Blood
 Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*)
 Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
4/28/2016. Host Defenses. Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System. Types of Innate Defenses. Defensive Cells Leukocytes
 Host Defenses Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System CH 16-18 Host defenses that produce resistance can be either innate or adaptive: Innate: those that protect against any type of invading agent Adaptive:
Host Defenses Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System CH 16-18 Host defenses that produce resistance can be either innate or adaptive: Innate: those that protect against any type of invading agent Adaptive:
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 8 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
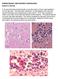 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 8 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 12 year-old male presented with a one-day history of fever and headache on the right side. Two days after admission, he developed a stiff neck
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 8 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 12 year-old male presented with a one-day history of fever and headache on the right side. Two days after admission, he developed a stiff neck
Name: Per/row: Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology
 Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology Name: Per/row: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the box next to its description/function. Cell membrane Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatin
Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology Name: Per/row: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the box next to its description/function. Cell membrane Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatin
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTERS 16, 17, 18 AND 19
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTERS 16, 17, 18 AND 19 CHAPTER 16: NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES OF THE HOST I. THE FIRST LINE OF DEFENSE A. Mechanical Barriers (Physical
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTERS 16, 17, 18 AND 19 CHAPTER 16: NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES OF THE HOST I. THE FIRST LINE OF DEFENSE A. Mechanical Barriers (Physical
Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Same bacteria on pinhead Fig. 4-1c, p.50 Review: Ionic Bonds Na has 11p and 10e making it (+) Cl has 18e and 17 p making it (-) The attraction
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Same bacteria on pinhead Fig. 4-1c, p.50 Review: Ionic Bonds Na has 11p and 10e making it (+) Cl has 18e and 17 p making it (-) The attraction
Questions in Cell Biology
 Name: Questions in Cell Biology Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on the subject of cell biology. Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the
Name: Questions in Cell Biology Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on the subject of cell biology. Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology
 Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY
 CONTRIBUTOR NAME Daniel Heinrich, DVM CONTRIBUTOR EMAIL dheinric@umn.edu COAUTHORS Jed Overmann, DVM, DACVP; Davis Seelig DVM, PhD, DACVP & Matthew Sturos, DVM COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY University of Minnesota
CONTRIBUTOR NAME Daniel Heinrich, DVM CONTRIBUTOR EMAIL dheinric@umn.edu COAUTHORS Jed Overmann, DVM, DACVP; Davis Seelig DVM, PhD, DACVP & Matthew Sturos, DVM COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY University of Minnesota
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD. MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. BLOOD A connective tissue Average volume of 5 liters (70 kg male) 45% solid cells or formed elements (hematocrit [HCT] quantitation)
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. BLOOD A connective tissue Average volume of 5 liters (70 kg male) 45% solid cells or formed elements (hematocrit [HCT] quantitation)
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY
 BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
Hematocrit. Hematocrit = using a centrifuge to separate out the parts of blood. Plasma Formed elements:
 Blood Notes Hematocrit Hematocrit = using a centrifuge to separate out the parts of blood Plasma Formed elements: Buffy Coat = Leukocytes and Platelets Erythrocytes General Facts Blood ph = 7.4 Volume
Blood Notes Hematocrit Hematocrit = using a centrifuge to separate out the parts of blood Plasma Formed elements: Buffy Coat = Leukocytes and Platelets Erythrocytes General Facts Blood ph = 7.4 Volume
A. Incorrect! The resistance that an individual acquires during life is known as specific immunity.
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 13: Innate Immunity No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of immunity is attributed to the Anatomic, Physiologic, Phagocytic and inflammatory barriers? A. Specific Immunity B. Adaptive
Microbiology - Problem Drill 13: Innate Immunity No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of immunity is attributed to the Anatomic, Physiologic, Phagocytic and inflammatory barriers? A. Specific Immunity B. Adaptive
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences
 Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Section VII. Pathogenesis and Host Defense Mechanisms Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 14. Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases 1 Chapter
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Section VII. Pathogenesis and Host Defense Mechanisms Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 14. Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases 1 Chapter
Yersinia pestis. Yersinia and plague. Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Determination of Acid Phosphatase Activity in Normal Human Lymphocytes
 ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE, Vol. 12, No. 1 Copyright 1982, Institute for Clinical Science, Inc. Determination of Acid Phosphatase Activity in Normal Human Lymphocytes PAUL I. LIU, M.D.,
ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE, Vol. 12, No. 1 Copyright 1982, Institute for Clinical Science, Inc. Determination of Acid Phosphatase Activity in Normal Human Lymphocytes PAUL I. LIU, M.D.,
Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved
 Bio 100 Guide 21 Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved inorganic ions, proteins, nutrients,
Bio 100 Guide 21 Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved inorganic ions, proteins, nutrients,
