Prof. V. Grégoire Dr. P. Smeesters Mr M. Despiegeleer
|
|
|
- Gervais Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 1. Grandeurs et Unités - Mécanismes biologiques de l action des rayonnements ionisants 2. Effets aigus d une irradiation accidentelle 3. Cancers radio-induits 4. Effets héréditaires radio-induits 5. Effets de l irradiation in utero 6. Législation: les normes de bases; principes de radioprotection opérationnelle 7. Travaux pratiques: emploi de détecteurs en situation de routine; dosimétrie des travailleurs; visites des installations du contrôle physique Prof. V. Grégoire Dr. P. Smeesters Mr M. Despiegeleer
3 Radiobiology for the Radiologist, Eric J. Hall. J.B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection, Annals of the ICRP, publication 60, Exposure to ionizing radiations: radiobiological effects and pathogenesis, A. Wambersie et al., Revue Médicale de Bruxelles, 17: et 75-84, 1996 ou Louvain Med., 114: S97-S132,
4 Electromagnetic radiation (low LET): photons, γ-rays, X-rays Particulate Radiation(high LET) - charged particles: electrons, protons, α particles - neutrons - heavy charged ions: carbon, neons, argon, 4
5 E = hν ν = c/λ 5
6 Indirectly ionizing radiation: X-rays, γ-rays, neutrons - photoelectric process: Z 3 - Compton process: higher photon energy - pair production Directly ionizing radiation: charged particles 6
7 7
8 8
9 9
10 10
11 11
12 12
13 Low LET High LET 13
14 Electrons Photons 14
15 15
16 X- and γ-rays are indirectly ionizing; the first step in their absorption is the production of fast recoil electrons. Neutrons are also indirectly ionizing; the first step in their absorption is the production of fast recoil protons, α-particles, and heavier nuclear fragments. Electrons and other charged particles are directly ionizing; they lost their energy by progressive collision. The shape of the depth-dose curves (and thus the absorption) depends on the type of ionizing radiation and their energy. 16
17 Biological effects of X-rays may be due to the direct or indirect action About two thirds of the biological damage by X-rays is due to indirect action High-LET radiations produce most biological damage by the direct action, which cannot be modified by chemical sensitizers and protectors The physics of the absorption process is over second; the chemistry takes longer; the biology takes days to months for cell killings, years for carcinogenesis, and generations for heritable damage 17
18 Absorbed dose: 1 Gray (Gy) = 1 joule/kg = increase of C per gr water 18
19 Equivalent dose = absorbed dose * radiation weighting factor (W R ) Type and energy range in Sievert (Sv) W R Photons, all energies 1 Electrons, all energies 1 Neutrons, < 10 kev 5 > 10 kev < 100 kev 10 > 100 kev < 2 MeV 20 > 2 MeV < 20 MeV 10 > 20 MeV 5 Protons, > 2 MeV 5 α-particles, fission fragments, heavy nuclei 20 From ICRP 60 19
20 Effective dose = Σ absorbed dose * W R * tissue weighting factor (W T ) in Sievert (Sv) Tissue or organ W T Gonads 0.20 Bone Marrow 0.12 Colon 0.12 Lung 0.12 Stomach 0.12 Bladder 0.05 Breast 0.05 Liver 0.05 Esophagus 0.05 Thyroid 0.05 Skin 0.01 Bone surface 0.01 Remainder 0.05 From ICRP 60 20
21 Committed equivalent dose = equivalent dose over 50 years (70 years for children) Committed effective dose = effective dose over 50 years (70 years for children) 21
22 Collective equivalent dose = equivalent dose * number of persons exposed (in person-sievert) Collective effective dose = effective dose * number of persons exposed (in person-sievert) Collective effective dose commitment = committed effective dose * number of persons exposed (in person-sievert) 22
23 For individuals - absorbed dose - equivalent dose - effective dose - committed equivalent dose - committed effective dose For populations - collective equivalent dose - collective effective dose - collective effective dose commitment 23
24 Cellular processes involved in # cell death after ionizing radiations. Ionizing radiations Ionizations / Excitations Free-radical production Direct effect Cell surface receptor Repair processes Initial genomic damage (DNA / chromosome) Division delay Signal transduction pathways Residual genomic damage (DNA / chromosome) Programmed cell death Clonogenic cell death Tumor shrinkage Loss of normal tissue functional Integrity including carcinogenesis 24
25 Clonogenic cell survival. 25
26 Time-lapse microcinematography 26
27 Clonogenic cell survival. 27
28 Clonogenic cell survival. 28
29 Clonogenic cell survival Surviving fraction SCC 61 SCC 12 B Absorbed dose (Gy) 29 From Schwartz et al.
30 The key function of DNA 30
31 Structure of DNA 31
32 Structure of DNA 32
33 DNA damages 33
34 DNA damages Type of lesion Number per Gray Double strand breaks (dsb) 40 Single strand breaks (ssb) Base damage Sugar damage DNA-DNA crosslinks 30 DNA-protein crosslinks (dpc) 150 Alkali-labile sites
35 0.5 Quantification of DNA damages Fraction of activity released Absorbed dose (Gy) 35
36 DNA Repair 36
37 DNA Repair 37
38 HR and NHEJ Non-homologous end-joining Homologous recombination 3 3 Joint molecule formation Re-ligation Fill-in or deletion, ligation Repair DNA synthesis Resolution of intermediates, ligation 38
39 HR versus NHEJ NHEJ Repairs most DSB - 80% Important for radiosensitivity Error prone All parts of the cell cycle ½ time ~2-4 hours Defects rare in cancer Non-proliferating tissues Early versus late responding tissue HR Repairs fewer DSB 20% Important for radiosensitivity Error free S and G2 phase responsible for change in sensitivity in the cell cycle ½ time long 24hours? Varies more between cell lines (high in stem cells) Defects common in cancer Proliferating tissues 39
40 Quantification of DNA Repair Percent of initial damage BR HF Repair time (min.) 40 From Badie et al.
41 Structure of chromosome 41
42 Chromosome and chromatid aberrations 42
43 Chromosome aberrations 43
44 Quantification of chromosome breaks Chromosome breaks per cell SCC12 B2 SCC Absorbed dose (Gy) 44 From Hittelman et al.
45 Quantification of chromosome dicentrics and rings 45
46 HR and Human Disease Many diseases associated with the sensors and transducers Ataxia Telangiectasia mutations in ATM Patients are radiosensitive Elevated risk of cancer Have several developmental and neural abnormalities AT like disorder mutations in MRE11 Nijmegen breakage syndrome mutations in NBS Familial (inherited) breast cancer - BRCA1, BRCA2 Inherited breast and ovarian cancer Fanconi s Anemia FANCA,B,C,D1,D2,E FANCB,D1=BRCA2 Sensitive to crosslinking agents Increased risk of cancer 46
47 Overview of the cell cycle 47
48 Cell cycle control: G1-S transition 48
49 Tumor suppressor gene: the retinoblastoma example 49
50 Programmed cell death - apoptosis >< necrosis APOPTOSE NECROSE gonflement cellulaire, lésion des organites, altération de la chromatine. lyse cellulaire, destruction des organites, destruction de la chromatine. condensation de la chromatine, diminution du volume cellulaire, changements membranaires. formation des corps apoptotiques chromatine fragmentée, organites intacts. phagocytose inflammation 50
51 Programmed cell death - apoptosis 51
52 Programmed cell death - apoptosis: an active process privation en facteurs stress oxidatif FasL, de croissance perforine radiations ionisantes TNFα granzyme B lésions à l ADN (p53) autres 1 signal 3 exécution Bcl-2, Bcl-xL mitochondrie CrmA p35 ZVAD YVAD DEVD caspases mitochondrie ψm, cytochrome c AIF, radicaux libres Apoptose boucle d autoamplification 2 contrôle point de non retour 52
53 Programmed cell death - apoptosis: DNA fragmentation 53
54 The p53-dependant signaling pathways 54
55 The p53-dependant signaling pathways 55
56 Hypersensitivity syndromes.99 Nl Cumulative frequency AT + + AT + - FA Mean inactivating dose (Gy) 56 Deschavanne & Malaise, 1986
57 Relative Biological Effectiveness (RBE) D high LET D low LET Dose (Gy) Surviving fraction Low LET RBE = D low LET / D high LET High LET 57
58 RBE and LET 58
59 Many single-strand damages are produced in DNA by radiation but are readily and faithfully repaired using the opposite DNA strand as a template. Damages in both strands that are opposite, separated by only a few base pairs, or locally multiple may lead to a double-strand break (dsb). In mammalian cells, double-strand breaks are mainly repaired by nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ). Damages that are not repaired or that are mis-repaired in pre-replication phase (G0-G1 cells) may lead to chromosome aberrations. Damages that are not repaired or that are mis-repaired in post-replication phase (late-s or G2 cells) may lead to chromatid aberrations. 59
60 #Asymetrical exchange aberrations (dicentrics and rings) are mainly lethal. Symetrical exchange aberrations (translocations and deletions) resulting from mis-repaired DNA damages may lead to carcinogenesis. Techniques available to study DNA dsbs are not sensitive enough to be used as biological dosimetry in case of accidental irradiation. Scoring aberrations in lymphocytes from peripheral blood may be used to estimate total-body doses in humans with a sensitivity of 0,25 Gy. Ionizing radiation induce a cell cycle arrest at the G1-S border to prevent damaged DNA to be replicated in S-phase. 60
61 #After exposure to ionizing radiation, cells mainly die from necrosis (clonogenic cell death). Apoptosis is an active form of cell death which is involved in tissue homeostasis after ionizing radiation (e.g. preventing carcinogenesis). Genetic predisposition (e.g. mutations in p53, Rb, or AT gene) may render cells more sensitive to ionizing radiations. Hight LET radiations (e.g. neutrons, α-particles) are much more effective than X-rays or γ-rays (RBE > 1). 61
Nature of Radiation and DNA damage
 Nature of Radiation and DNA damage Index 1. What is radiation? 2. Ionizing Radiation 3. Interaction of Gamma-radiation with Matter 4. Radiobiology 5. Direct and Indirect action of radiation 6. Steps of
Nature of Radiation and DNA damage Index 1. What is radiation? 2. Ionizing Radiation 3. Interaction of Gamma-radiation with Matter 4. Radiobiology 5. Direct and Indirect action of radiation 6. Steps of
Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 2 & 3 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM How does radiation injure people? - High energy radiation
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 2 & 3 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM How does radiation injure people? - High energy radiation
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA
 LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 3, 4 & 5 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM How does radiation injure people? - High energy
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 3, 4 & 5 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM How does radiation injure people? - High energy
Biological Effects of Radiation
 Radiation and Radioisotope Applications EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031 Biological Effects of Radiation Lecture 09 Rafael Macian 23.11.06 EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031: Radioisotope and Radiation Applications
Radiation and Radioisotope Applications EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031 Biological Effects of Radiation Lecture 09 Rafael Macian 23.11.06 EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031: Radioisotope and Radiation Applications
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
Radiation Oncology. Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology
 Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK
 Norges teknisk-naturvitenskaplige universitet Institutt for fysikk EKSAMENSOPPGÅVER med løysingsforslag Examination papers with solution proposals TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK Biophysics of Ionizing Radiation
Norges teknisk-naturvitenskaplige universitet Institutt for fysikk EKSAMENSOPPGÅVER med løysingsforslag Examination papers with solution proposals TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK Biophysics of Ionizing Radiation
Radiation Carcinogenesis
 Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
Chapter 7. What is Radiation Biology? Ionizing Radiation. Energy Transfer Determinants 09/21/2014
 Chapter 7 Molecular & Cellular Radiation Biology What is Radiation Biology? A branch of biology concerned with how ionizing radiation effects living systems. Biological damage that occurs from different
Chapter 7 Molecular & Cellular Radiation Biology What is Radiation Biology? A branch of biology concerned with how ionizing radiation effects living systems. Biological damage that occurs from different
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350.
 Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT
 RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT EXPOSURE and TOXITY ASSESSMENT Osipova Nina, associated professor, PhD in chemistry, Matveenko Irina, Associate professor, PhD in philology TOMSK -2013 The contents 1.What is
RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT EXPOSURE and TOXITY ASSESSMENT Osipova Nina, associated professor, PhD in chemistry, Matveenko Irina, Associate professor, PhD in philology TOMSK -2013 The contents 1.What is
ICRP = International Commission on. recommendations and guidance on. Functioning since 1928.
 ICRP = International Commission on Radiological Protection; An advisory body providing recommendations and guidance on radiation protection; Functioning since 1928. While the use of ionising radiation
ICRP = International Commission on Radiological Protection; An advisory body providing recommendations and guidance on radiation protection; Functioning since 1928. While the use of ionising radiation
Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden
 Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden September 2006 The aim of this text is to explain some of the basic quantities and units
Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden September 2006 The aim of this text is to explain some of the basic quantities and units
GUIDELINES ON IONISING RADIATION DOSE LIMITS AND ANNUAL LIMITS ON INTAKE OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL
 RADIATION PROTECTION AUTHORITY OF ZIMBABWE (RPAZ) RADIATION PROTECTION ACT [CHAPTER 15:15] GUIDELINES ON IONISING RADIATION DOSE LIMITS AND ANNUAL LIMITS ON INTAKE OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL Compiled by Radiation
RADIATION PROTECTION AUTHORITY OF ZIMBABWE (RPAZ) RADIATION PROTECTION ACT [CHAPTER 15:15] GUIDELINES ON IONISING RADIATION DOSE LIMITS AND ANNUAL LIMITS ON INTAKE OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL Compiled by Radiation
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF
 BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
María José Mesa López
 María José Mesa López q Radiobiology. q Ionizing Radiations. q Mutations. q Stochastic Effects Vs Deterministic Effects. q Cellular Radiosensitivity. q Bibliography. Science which combines the basic principles
María José Mesa López q Radiobiology. q Ionizing Radiations. q Mutations. q Stochastic Effects Vs Deterministic Effects. q Cellular Radiosensitivity. q Bibliography. Science which combines the basic principles
Dosimetric Consideration in Diagnostic Radiology
 Dosimetric Consideration in Diagnostic Radiology Prof. Ng Kwan-Hoong Department of Biomedical Imaging University of Malaya ngkh@um.edu.my Radiation Dosimetry Workshop, 28-29 March 2014 2 Why do we measure
Dosimetric Consideration in Diagnostic Radiology Prof. Ng Kwan-Hoong Department of Biomedical Imaging University of Malaya ngkh@um.edu.my Radiation Dosimetry Workshop, 28-29 March 2014 2 Why do we measure
Neutrons. ρ σ. where. Neutrons act like photons in the sense that they are attenuated as. Unlike photons, neutrons interact via the strong interaction
 Neutrons Neutrons act like photons in the sense that they are attenuated as I = I 0 e μx where Unlike photons, neutrons interact via the strong interaction μ = The cross sections are much smaller than
Neutrons Neutrons act like photons in the sense that they are attenuated as I = I 0 e μx where Unlike photons, neutrons interact via the strong interaction μ = The cross sections are much smaller than
What is radiation quality?
 What is radiation quality? Dudley T Goodhead Medical Research Council, UK DoReMi Radiation Quality workshop Brussels. 9-10 July 2013 What is radiation quality? Let s start at the very beginning. A very
What is radiation quality? Dudley T Goodhead Medical Research Council, UK DoReMi Radiation Quality workshop Brussels. 9-10 July 2013 What is radiation quality? Let s start at the very beginning. A very
COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE
 COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE I. Petrovi a, A. Risti -Fira a, L. Kori anac a, J. Požega a, F. Di Rosa b, P. Cirrone b and G. Cuttone
COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE I. Petrovi a, A. Risti -Fira a, L. Kori anac a, J. Požega a, F. Di Rosa b, P. Cirrone b and G. Cuttone
Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model
 Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model Understanding Radiation and Its Effects John Baunach Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN What is health physics? Outline What organizational bodies govern
Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model Understanding Radiation and Its Effects John Baunach Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN What is health physics? Outline What organizational bodies govern
Radiation physics and radiation protection. University of Szeged Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Radiation physics and radiation protection University of Szeged Department of Nuclear Medicine Radiation doses to the population 1 Radiation doses to the population 2 Sources of radiation 1 Radiation we
Radiation physics and radiation protection University of Szeged Department of Nuclear Medicine Radiation doses to the population 1 Radiation doses to the population 2 Sources of radiation 1 Radiation we
Radiation Protection Program Update: The Details. July 2010
 Radiation Protection Program Update: The Details July 2010 Update Topics 2 Changes mandated by Title 10, Code of Federal Regulations, Part 835, Occupational Radiation Protection (10 CFR 835) How changes
Radiation Protection Program Update: The Details July 2010 Update Topics 2 Changes mandated by Title 10, Code of Federal Regulations, Part 835, Occupational Radiation Protection (10 CFR 835) How changes
Ernest Rutherford:
 November 1895: Roentgen discovers x rays February 1896: Becquerel discovers radioactivity Ernest Rutherford 1898-99 Ernest Rutherford: 1898-99 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Interaction of Charged Particles
November 1895: Roentgen discovers x rays February 1896: Becquerel discovers radioactivity Ernest Rutherford 1898-99 Ernest Rutherford: 1898-99 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Interaction of Charged Particles
Ionizing Radiation. Nuclear Medicine
 Ionizing Radiation Nuclear Medicine Somatic Deterministic Effect Erythema Somatic Stochastic Effect Leukemia Genetic Effects DNA BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION ON TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS
Ionizing Radiation Nuclear Medicine Somatic Deterministic Effect Erythema Somatic Stochastic Effect Leukemia Genetic Effects DNA BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION ON TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS
2005 RECOMMENDATIONS OF ICRP
 IRPA 11 11 th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association 23 28 May 2004, Madrid, Spain 2005 RECOMMENDATIONS OF ICRP ROGER H CLARKE CHAIRMAN FEATURES OF RECOMMENDATIONS
IRPA 11 11 th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association 23 28 May 2004, Madrid, Spain 2005 RECOMMENDATIONS OF ICRP ROGER H CLARKE CHAIRMAN FEATURES OF RECOMMENDATIONS
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation
 Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Basics of Radiation Biology
 Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Basics of Radiation Biology
 Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Radiobiology of radionuclide therapy
 Radiobiology of radionuclide therapy Prof Sarah Baatout Sarah.Baatout@sckcen.be Head of the Radiobiology Unit, SCK CEN Faculty of Biosciences Engineering, Universiteit Gent, Belgium Faculté des Sciences,
Radiobiology of radionuclide therapy Prof Sarah Baatout Sarah.Baatout@sckcen.be Head of the Radiobiology Unit, SCK CEN Faculty of Biosciences Engineering, Universiteit Gent, Belgium Faculté des Sciences,
Modelling of Biological Processes
 Modelling of Biological Processes WHAT HAPPENS AFTER EARLY MOLECULAR DAMAGE? Stephen McMahon Queen s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland 3 rd August 2016 1 Do we need biology? The Linear-quadratic relationship
Modelling of Biological Processes WHAT HAPPENS AFTER EARLY MOLECULAR DAMAGE? Stephen McMahon Queen s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland 3 rd August 2016 1 Do we need biology? The Linear-quadratic relationship
Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons
 Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons M.P. Carante 1,2 and F. Ballarini 1,2, * 1 University of Pavia, Physics Department, Pavia, Italy 2 INFN, Sezione di Pavia,
Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons M.P. Carante 1,2 and F. Ballarini 1,2, * 1 University of Pavia, Physics Department, Pavia, Italy 2 INFN, Sezione di Pavia,
Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs. Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica
 Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica Radiobiology It is fundamental in radiation oncology Radiobiology
Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica Radiobiology It is fundamental in radiation oncology Radiobiology
Radiation Effects in Life Sciences
 Radiation Effects in Life Sciences oocyte eggs in uterus spermatheca gonad Quality of Radiation Biological Effects Applications of SSD in Life sciences Nanodosimetry Particle Microscope (pct) vulva Radiation
Radiation Effects in Life Sciences oocyte eggs in uterus spermatheca gonad Quality of Radiation Biological Effects Applications of SSD in Life sciences Nanodosimetry Particle Microscope (pct) vulva Radiation
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3
 Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Dosimetry - Measurement of Ionising Radiation
 Dosimetry - Measurement of Ionising Radiation Assoc. Prof. Katarína Kozlíková, RN., PhD. IMPhBPhITM FM CU in Bratislava katarina.kozlikova@fmed.uniba.sk Contents Dosimetry Dose Radiation dose Absorbed
Dosimetry - Measurement of Ionising Radiation Assoc. Prof. Katarína Kozlíková, RN., PhD. IMPhBPhITM FM CU in Bratislava katarina.kozlikova@fmed.uniba.sk Contents Dosimetry Dose Radiation dose Absorbed
Review of the Radiobiological Principles of Radiation Protection
 1 Review of the Radiobiological Principles of Radiation Protection Cari Borrás, D.Sc., FACR, FAAPM Radiological Physics and Health Services Consultant Adjunct Assistant Professor (Radiology) GWU School
1 Review of the Radiobiological Principles of Radiation Protection Cari Borrás, D.Sc., FACR, FAAPM Radiological Physics and Health Services Consultant Adjunct Assistant Professor (Radiology) GWU School
Chapter 14 Basic Radiobiology
 Chapter 14 Basic Radiobiology This set of 88 slides is based on Chapter 14 authored by N. Suntharalingam, E.B. Podgorsak, J.H. Hendry of the IAEA publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6): Radiation Oncology Physics:
Chapter 14 Basic Radiobiology This set of 88 slides is based on Chapter 14 authored by N. Suntharalingam, E.B. Podgorsak, J.H. Hendry of the IAEA publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6): Radiation Oncology Physics:
Peak temperature ratio of TLD glow curves to investigate the spatial variation of LET in a clinical proton beam
 Peak temperature ratio of TLD glow curves to investigate the spatial variation of LET in a clinical proton beam University of Chicago CDH Proton Center LET study C. Reft 1, H. Ramirez 2 and M. Pankuch
Peak temperature ratio of TLD glow curves to investigate the spatial variation of LET in a clinical proton beam University of Chicago CDH Proton Center LET study C. Reft 1, H. Ramirez 2 and M. Pankuch
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
PHYS 383: Applications of physics in medicine (offered at the University of Waterloo from Jan 2015)
 PHYS 383: Applications of physics in medicine (offered at the University of Waterloo from Jan 2015) Course Description: This course is an introduction to physics in medicine and is intended to introduce
PHYS 383: Applications of physics in medicine (offered at the University of Waterloo from Jan 2015) Course Description: This course is an introduction to physics in medicine and is intended to introduce
A general mechanistic model enables predictions of the biological effectiveness of different qualities of radiation
 A general mechanistic model enables predictions of the biological effectiveness of different qualities of radiation McMahon, S. J., McNamara, A. L., Schuemann, J., Paganetti, H., & Prise, K. M. (2017).
A general mechanistic model enables predictions of the biological effectiveness of different qualities of radiation McMahon, S. J., McNamara, A. L., Schuemann, J., Paganetti, H., & Prise, K. M. (2017).
The range of radiosensitivity in the human population: hyper- and hypo-sensitivity
 International Conference on Modern Radiotherapy The range of radiosensitivity in the human population: hyper- and hypo-sensitivity Simon Bouffler December 2009 Indicators of radiosenitivity In Patients
International Conference on Modern Radiotherapy The range of radiosensitivity in the human population: hyper- and hypo-sensitivity Simon Bouffler December 2009 Indicators of radiosenitivity In Patients
ICRP Recommendations Evolution or Revolution? John R Cooper Main Commission
 ICRP Recommendations Evolution or Revolution? John R Cooper Main Commission 3 September 2009 ICRP Recommendations 1. Reasons for new Recommendations 2. Summary of health risks 3. Summary of changes to
ICRP Recommendations Evolution or Revolution? John R Cooper Main Commission 3 September 2009 ICRP Recommendations 1. Reasons for new Recommendations 2. Summary of health risks 3. Summary of changes to
Accelerated heavy ions as a tool for solving problems in fundamental and space radiobiology
 Accelerated heavy ions as a tool for solving problems in fundamental and space radiobiology E. Krasavin Round Table 2 Italy-Russia@Dubna on SPACE PHISICS and BIOLOGY On Earth - accelerators of heavy charged
Accelerated heavy ions as a tool for solving problems in fundamental and space radiobiology E. Krasavin Round Table 2 Italy-Russia@Dubna on SPACE PHISICS and BIOLOGY On Earth - accelerators of heavy charged
Skyscan 1076 in vivo scanning: X-ray dosimetry
 Skyscan 1076 in vivo scanning: X-ray dosimetry DOSIMETRY OF HIGH RESOLUTION IN VIVO RODENT MICRO-CT IMAGING WITH THE SKYSCAN 1076 An important distinction is drawn between local tissue absorbed dose in
Skyscan 1076 in vivo scanning: X-ray dosimetry DOSIMETRY OF HIGH RESOLUTION IN VIVO RODENT MICRO-CT IMAGING WITH THE SKYSCAN 1076 An important distinction is drawn between local tissue absorbed dose in
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
Radiation Biology: A Handbook for Teachers and Students
 Radiation Biology: A Handbook for Teachers and Students Slide Series prepared in 2011 by J.H. Hendry. The IAEA officer responsible for this publication is J. Wondergem of the Division of Human Health,
Radiation Biology: A Handbook for Teachers and Students Slide Series prepared in 2011 by J.H. Hendry. The IAEA officer responsible for this publication is J. Wondergem of the Division of Human Health,
PHY138Y Nuclear and Radiation
 PHY38Y Nuclear and Radiation Professor Tony Key MP40 key@physics.utoronto.ca Announcements MP problems set #4 due Sunday at midnight PS#5 WRITTEN now posted! - do in teams, no Lone Wolves!! NB correction
PHY38Y Nuclear and Radiation Professor Tony Key MP40 key@physics.utoronto.ca Announcements MP problems set #4 due Sunday at midnight PS#5 WRITTEN now posted! - do in teams, no Lone Wolves!! NB correction
The In-flux of Nuclear Science to Radiobiology
 The In-flux of Nuclear Science to Radiobiology G. Taucher-Scholz, G. Kraft (GSI) 1 B. Michael (Gray Lab) 2 M. Belli (INFN) 3 1 GSI, Biophysik, Planckstr. 1, 64291 Darmstadt, Germany 2 Gray Lab.,Cancer
The In-flux of Nuclear Science to Radiobiology G. Taucher-Scholz, G. Kraft (GSI) 1 B. Michael (Gray Lab) 2 M. Belli (INFN) 3 1 GSI, Biophysik, Planckstr. 1, 64291 Darmstadt, Germany 2 Gray Lab.,Cancer
Physical Bases : Which Isotopes?
 Physical Bases : Which Isotopes? S. Gnesin Institute of Radiation Physics, Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland 1/53 Theranostic Bruxelles, 2 Octobrer 2017 Theranostic : use of diagnostic
Physical Bases : Which Isotopes? S. Gnesin Institute of Radiation Physics, Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland 1/53 Theranostic Bruxelles, 2 Octobrer 2017 Theranostic : use of diagnostic
Radiation Protection
 2007 CERN Accelerator School (The bases of) Radiation Protection Marco Silari CERN, Geneva, Switzerland M. Silari Radiation Protection 21.09.2007 1 Introduction To tell you in one hour all about radiation
2007 CERN Accelerator School (The bases of) Radiation Protection Marco Silari CERN, Geneva, Switzerland M. Silari Radiation Protection 21.09.2007 1 Introduction To tell you in one hour all about radiation
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY
 LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
Learning Objectives. Review of the Radiobiological Principles of Radiation Protection. Radiation Effects
 1 Review of the Radiobiological Principles of Radiation Protection Cari Borrás, D.Sc., FAAPM, FACR Radiological Physics and Health Services Consultant Washington DC, USA Learning Objectives 1. To understand
1 Review of the Radiobiological Principles of Radiation Protection Cari Borrás, D.Sc., FAAPM, FACR Radiological Physics and Health Services Consultant Washington DC, USA Learning Objectives 1. To understand
Brian T Burgess, DO, PhD, GYN Oncology Fellow Rachel W. Miller, MD, GYN Oncology
 Brian T Burgess, DO, PhD, GYN Oncology Fellow Rachel W. Miller, MD, GYN Oncology Epithelial Ovarian Cancer - Standard Current Treatment: Surgery with De-bulking + Platinum-Taxane based Chemotherapy - No
Brian T Burgess, DO, PhD, GYN Oncology Fellow Rachel W. Miller, MD, GYN Oncology Epithelial Ovarian Cancer - Standard Current Treatment: Surgery with De-bulking + Platinum-Taxane based Chemotherapy - No
Use of radiation to kill diseased cells. Cancer is the disease that is almost always treated when using radiation.
 Radiation Therapy Use of radiation to kill diseased cells. Cancer is the disease that is almost always treated when using radiation. One person in three will develop some form of cancer in their lifetime.
Radiation Therapy Use of radiation to kill diseased cells. Cancer is the disease that is almost always treated when using radiation. One person in three will develop some form of cancer in their lifetime.
CELL CYCLE,CHECK POINTS. Prof S.N.Senapati, A.H.REGIONAL CANCER CENTRE, MANGALABAG, CUTTACK
 CELL CYCLE,CHECK POINTS Prof S.N.Senapati, A.H.REGIONAL CANCER CENTRE, MANGALABAG, CUTTACK E-Mail:-snsenapati2007@gmail.com IN RADIATION ONCOLOGY TUMOR CELL DEATH CELL DEATH AFTER IRRADIATION OCCURS MOSTLY
CELL CYCLE,CHECK POINTS Prof S.N.Senapati, A.H.REGIONAL CANCER CENTRE, MANGALABAG, CUTTACK E-Mail:-snsenapati2007@gmail.com IN RADIATION ONCOLOGY TUMOR CELL DEATH CELL DEATH AFTER IRRADIATION OCCURS MOSTLY
Introduction to Radiation Biology
 Introduction to Radiation Biology Survey of Clinical Radiation Oncology Outline Ionizing radiation Development of radiobiological damage Cell cycle Cell survival curves Tissue response and fractionation
Introduction to Radiation Biology Survey of Clinical Radiation Oncology Outline Ionizing radiation Development of radiobiological damage Cell cycle Cell survival curves Tissue response and fractionation
Radiation Biology & Radiation Therapy
 Radiation Biology & Radiation Therapy for Medical Students 2nd Semester 1393-1394 1 st & 2 nd Sessions Professor of Medical Physics mmortazavi@sums.ac.ir LET & RBE LET Linear energy transfer (LET) represents
Radiation Biology & Radiation Therapy for Medical Students 2nd Semester 1393-1394 1 st & 2 nd Sessions Professor of Medical Physics mmortazavi@sums.ac.ir LET & RBE LET Linear energy transfer (LET) represents
The impact of different radiation qualities on cancer cells
 The impact of different radiation qualities on cancer cells Marjan Moreels, PhD Radiobiology Unit,, Belgium XXth Colloque GANIL Session 10, Amboise, France Oct 19, 2017 1 The Belgian Nuclear Research Center
The impact of different radiation qualities on cancer cells Marjan Moreels, PhD Radiobiology Unit,, Belgium XXth Colloque GANIL Session 10, Amboise, France Oct 19, 2017 1 The Belgian Nuclear Research Center
Radioactivity. Lecture 8 Biological Effects of Radiation
 Radioactivity Lecture 8 Biological Effects of Radiation Studies of impact of ionizing radiation on the human body - Hiroshima - US-Japanese teams medical tests, autopsies, human organ analysis, on-site
Radioactivity Lecture 8 Biological Effects of Radiation Studies of impact of ionizing radiation on the human body - Hiroshima - US-Japanese teams medical tests, autopsies, human organ analysis, on-site
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay
 The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D. Chief Scientific Officer Trevigen, Inc. Gaithersburg, MD Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases are promising therapeutic targets. In response
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D. Chief Scientific Officer Trevigen, Inc. Gaithersburg, MD Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases are promising therapeutic targets. In response
CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS
 10-2 densely ionizing radiation CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS 2.0 INTRODUCTION Cell survival curves describe the relationship between the fractional survival, S, of a population of radiated
10-2 densely ionizing radiation CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS 2.0 INTRODUCTION Cell survival curves describe the relationship between the fractional survival, S, of a population of radiated
Radiation Physiology and Effects
 Sources and types of space radiation Effects of radiation Shielding approaches 1 2011 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu The Electromagnetic Spectrum Ref: Alan C. Tribble,
Sources and types of space radiation Effects of radiation Shielding approaches 1 2011 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu The Electromagnetic Spectrum Ref: Alan C. Tribble,
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis. Dr H Awad 2017/18
 Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Evidence for variation in human radiosensitivity: potential impact on radiological protection
 Evidence for variation in human radiosensitivity: potential impact on radiological protection Simon Bouffler 22 October 2015 ICRP Symposium 2015, Seoul, South Korea Current system of protection Avoid tissue
Evidence for variation in human radiosensitivity: potential impact on radiological protection Simon Bouffler 22 October 2015 ICRP Symposium 2015, Seoul, South Korea Current system of protection Avoid tissue
Radiopharmaceuticals. Radionuclides in NM. Radionuclides NUCLEAR MEDICINE. Modes of radioactive decays DIAGNOSTIC THERAPY CHEMICAL COMPOUND
 Univerzita Karlova v Praze - 1. Lékařská fakulta Radiation protection NUCLEAR MEDICINE Involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear medicine study
Univerzita Karlova v Praze - 1. Lékařská fakulta Radiation protection NUCLEAR MEDICINE Involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear medicine study
Lecture 14 Exposure to Ionizing Radiation
 Lecture 14 Exposure to Ionizing Radiation Course Director, Conrad Daniel Volz, DrPH, MPH Assistant Professor, Environmental & Occupational Health, University of Pittsburgh, Graduate School of Public Health
Lecture 14 Exposure to Ionizing Radiation Course Director, Conrad Daniel Volz, DrPH, MPH Assistant Professor, Environmental & Occupational Health, University of Pittsburgh, Graduate School of Public Health
RADIATION BIOLOGY. 1. Radiation Units. 1.1 Absorbed Dose. 1.2 Equivalent Dose
 Ing. Daniela Skibová, Ph.D., 1. Radiation Units The biological effect of radiation can be understood in terms of the transfer of energy from the radiation (photons and particles) to the tissue. When the
Ing. Daniela Skibová, Ph.D., 1. Radiation Units The biological effect of radiation can be understood in terms of the transfer of energy from the radiation (photons and particles) to the tissue. When the
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
RADIOLOGY AN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING
 Day 2 p. 1 RADIOLOGY AN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Dr hab. Zbigniew Serafin, MD, PhD serafin@cm.umk.pl and Radiation Protection mainly based on: C. Scott Pease, MD, Allen R. Goode, MS, J. Kevin McGraw, MD, Don
Day 2 p. 1 RADIOLOGY AN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Dr hab. Zbigniew Serafin, MD, PhD serafin@cm.umk.pl and Radiation Protection mainly based on: C. Scott Pease, MD, Allen R. Goode, MS, J. Kevin McGraw, MD, Don
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over Why? Double crossovers
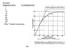 Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration between LNS INFN and Vinca Institute of Nuclear Sciences
 ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
ADVANCES IN RADIATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF CANCER
 ADVANCES IN RADIATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF CANCER Bro. Dr. Collie Miller IARC/WHO Based on trends in the incidence of cancer, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and WHO
ADVANCES IN RADIATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF CANCER Bro. Dr. Collie Miller IARC/WHO Based on trends in the incidence of cancer, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and WHO
Therapeutic Medical Physics. Stephen J. Amadon Jr., Ph.D., DABR
 Therapeutic Medical Physics Stephen J. Amadon Jr., Ph.D., DABR Outline 1. Why physicists are needed in medicine 2. Branches of medical physics 3. Physics in Radiation Oncology 4. Treatment types and Treatment
Therapeutic Medical Physics Stephen J. Amadon Jr., Ph.D., DABR Outline 1. Why physicists are needed in medicine 2. Branches of medical physics 3. Physics in Radiation Oncology 4. Treatment types and Treatment
Multistep Carcinogenesis
 Multistep Carcinogenesis M.Rosemann, Institute for Radiation Biology Helmholtz Center Munich, Research Centre for Health and Environment The Hallmarks of Cancer D.Hanahan, Cell 2011 The Hallmarks of Cancer
Multistep Carcinogenesis M.Rosemann, Institute for Radiation Biology Helmholtz Center Munich, Research Centre for Health and Environment The Hallmarks of Cancer D.Hanahan, Cell 2011 The Hallmarks of Cancer
C-Beam Induces More Chromosomal Damage In Chemo-Radio-Resistant Cells Than. O-Beam
 1 C-Beam Induces More Chromosomal Damage In Chemo-Radio-Resistant Cells Than 16 O-Beam Utpal Ghosh 1, Regina Lichti Binz, Ratan Sadhukhan, Asitikantha Sarma 3, Subrata Kumar Dey 4,Martin Hauer-Jensen,
1 C-Beam Induces More Chromosomal Damage In Chemo-Radio-Resistant Cells Than 16 O-Beam Utpal Ghosh 1, Regina Lichti Binz, Ratan Sadhukhan, Asitikantha Sarma 3, Subrata Kumar Dey 4,Martin Hauer-Jensen,
CONTENTS NOTE TO THE READER...1 LIST OF PARTICIPANTS...3
 CONTENTS NOTE TO THE READER...1 LIST OF PARTICIPANTS...3 PREAMBLE...9 Background...9 Objective and Scope...9 Selection of Topics for Monographs...10 Data for Monographs...11 The Working Group...11 Working
CONTENTS NOTE TO THE READER...1 LIST OF PARTICIPANTS...3 PREAMBLE...9 Background...9 Objective and Scope...9 Selection of Topics for Monographs...10 Data for Monographs...11 The Working Group...11 Working
Cancer. Questions about cancer. What is cancer? What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage?
 Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Basic radiation protection & radiobiology
 Basic radiation protection & radiobiology By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Patient care & management 202 Wednesday, October 13, 2010 Ionizing radiation. Discussion issues Protecting the patient. Protecting the radiographer.
Basic radiation protection & radiobiology By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Patient care & management 202 Wednesday, October 13, 2010 Ionizing radiation. Discussion issues Protecting the patient. Protecting the radiographer.
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
ICRP RECOMMENDATIONS AND IAEA SAFETY STANDARDS: THEN AND NOW
 ICRP RECOMMENDATIONS AND IAEA SAFETY STANDARDS: THEN AND NOW Abdalla N. Al-Haj, PhD, FIPEM, CRadP, CSci, MSRP Chief Health Physicist King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
ICRP RECOMMENDATIONS AND IAEA SAFETY STANDARDS: THEN AND NOW Abdalla N. Al-Haj, PhD, FIPEM, CRadP, CSci, MSRP Chief Health Physicist King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
STUDY OF MUTATION PROCESSES IN BONE MARROW AND BLOOD CELLS AFTER SEPARATE AND COMBINED EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL γ-irradiation OF ORGANISM
 STUDY OF MUTATION PROCESSES IN BONE MARROW AND BLOOD CELLS AFTER SEPARATE AND COMBINED EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL γ-irradiation OF ORGANISM L.N. Nikolaevich Institute of Radiobiology of National Academy of
STUDY OF MUTATION PROCESSES IN BONE MARROW AND BLOOD CELLS AFTER SEPARATE AND COMBINED EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL γ-irradiation OF ORGANISM L.N. Nikolaevich Institute of Radiobiology of National Academy of
Radiation Safety. Bethany Gillett 14th Feb After this lecture, you should be able to:
 Radiation Safety Bethany Gillett bethany.gillett@addenbrookes.nhs.uk 14th Feb 2018 Learning Outcomes After this lecture, you should be able to: Understand different radiation protection quantities Explain
Radiation Safety Bethany Gillett bethany.gillett@addenbrookes.nhs.uk 14th Feb 2018 Learning Outcomes After this lecture, you should be able to: Understand different radiation protection quantities Explain
Genome Instability is Breathtaking
 Genome Instability is Breathtaking Effects of Alpha Radiation exposure on DNA at a molecular level and consequences to cell health Dr. Aaron Goodarzi A.Goodarzi@ucalgary.ca Radiation what do you think
Genome Instability is Breathtaking Effects of Alpha Radiation exposure on DNA at a molecular level and consequences to cell health Dr. Aaron Goodarzi A.Goodarzi@ucalgary.ca Radiation what do you think
Introductory Radiation Biology Exam I 2013 WHEREVER POSSIBLE, SHOW ALL WORK!!! NO WORK, NO CREDIT!!!
 Name: Introductory Radiation Biology Exam I 2013 WHEREVER POSSIBLE, SHOW ALL WORK!!! NO WORK, NO CREDIT!!! 1. The energy of a microwave photon is 6.15 10-5 ev. What is the wavelength of this photon? 2.
Name: Introductory Radiation Biology Exam I 2013 WHEREVER POSSIBLE, SHOW ALL WORK!!! NO WORK, NO CREDIT!!! 1. The energy of a microwave photon is 6.15 10-5 ev. What is the wavelength of this photon? 2.
1/31/2014. Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public
 Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public Dr. David C. Medich University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell MA 01854 Introduction Definition: Radiation Biology is the field of science that studies the biological
Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public Dr. David C. Medich University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell MA 01854 Introduction Definition: Radiation Biology is the field of science that studies the biological
Cancer genetics
 Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
Murat Beyzadeoglu, Gokhan Ozyigit, and Cuneyt Ebruli
 Radiobiology 2 Murat Beyzadeoglu, Gokhan Ozyigit, and Cuneyt Ebruli 2.1 Cell Biology and Carcinogenesis Radiobiology, in general terms, is the science that evaluates the effects of radiation in living
Radiobiology 2 Murat Beyzadeoglu, Gokhan Ozyigit, and Cuneyt Ebruli 2.1 Cell Biology and Carcinogenesis Radiobiology, in general terms, is the science that evaluates the effects of radiation in living
The ANDANTE project: a multidisciplinary approach to neutron RBE
 The ANDANTE project: a multidisciplinary approach to neutron RBE Andrea Ottolenghi, Klaus Trott, Giorgio Baiocco, Vere Smyth Università degli Studi di Pavia, Italy On behalf of the ANDANTE project MELODI
The ANDANTE project: a multidisciplinary approach to neutron RBE Andrea Ottolenghi, Klaus Trott, Giorgio Baiocco, Vere Smyth Università degli Studi di Pavia, Italy On behalf of the ANDANTE project MELODI
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
Ploidy and Human Cell Types. Cell Cycle and Mitosis. DNA and Chromosomes. Where It All Began 11/19/2014. Chapter 12 Pg
 Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
AN INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MEDICINE
 AN INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MEDICINE WITH RESPECT TO THYROID DISORDERS By: B.Shafiei MD Nuclear Physician Taleghani Medical Center Radioactive: An element with Unstable Nucleus (Excess Energy), can achieve
AN INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MEDICINE WITH RESPECT TO THYROID DISORDERS By: B.Shafiei MD Nuclear Physician Taleghani Medical Center Radioactive: An element with Unstable Nucleus (Excess Energy), can achieve
Impact of variable proton relative biological effectiveness on estimates of secondary cancer risk in paediatric cancer patients Vilde Grandemo
 Impact of variable proton relative biological effectiveness on estimates of secondary cancer risk in paediatric cancer patients Vilde Grandemo Supervisors: Kristian Smeland Ytre-Hauge and Camilla Hanquist
Impact of variable proton relative biological effectiveness on estimates of secondary cancer risk in paediatric cancer patients Vilde Grandemo Supervisors: Kristian Smeland Ytre-Hauge and Camilla Hanquist
Radiobiological Characterization of Clinical Proton and Carbon-Ion Beams
 Proceedings of the CAS-CERN Accelerator School: Accelerators for Medical Applications, Vösendorf, Austria, 26 May 5 June 2015, edited by R. Bailey, CERN Yellow Reports: School Proceedings, Vol. 1/2017,
Proceedings of the CAS-CERN Accelerator School: Accelerators for Medical Applications, Vösendorf, Austria, 26 May 5 June 2015, edited by R. Bailey, CERN Yellow Reports: School Proceedings, Vol. 1/2017,
Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage
 1 Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage Jann Sarkaria Department of Oncology Mayo Clinic 2 EDUCATIONAL GOALS How proteins can transmit signals to each other. The definition of a tumor suppressor
1 Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage Jann Sarkaria Department of Oncology Mayo Clinic 2 EDUCATIONAL GOALS How proteins can transmit signals to each other. The definition of a tumor suppressor
