Original Article Diagnostic and prognostic value of retraction phenomenon observed in 3D ultrasonography of breast masses
|
|
|
- Arthur Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9): /ISSN: /IJCEM Original Article Diagnostic and prognostic value of retraction phenomenon observed in 3D ultrasonography of breast masses Wei Wang 1, Biekezhati Zaizitihan 1, Bing Zhang 2, Xiao-Yan Wang 2, Mei-Fen Nong 2, Yan He 2, Hai-Ming Wei 3, Xiang-Hong Huang 2, Bing Ling 2 1 Normal Surgical Department No. 2, Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China; Departments of 2 Ultrasonography, 3 Pathology, Guangxi People s Hospital, Nanning, China Received December 7, 2015; Accepted July 3, 2016; Epub September 15, 2016; Published September 30, 2016 Abstract: This study aimed to investigate the clinical value of the retraction phenomenon observed in 3D ultrasonography (RP-3DU) in diagnosing breast masses and evaluating their prognosis. Preoperative 3D ultrasonography was performed on 165 patients with breast masses. The observed RP of the masses was then compared with the tumor size, histological grade, lymph node status, and clinical biomarkers such as the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor 2 (CerbB-2), and Ki-67 to analyze the correlation between RP-3DU and the above indexes. The sensitivity and specificity of RP-3DU in diagnosing malignant breast masses were 67.7% and 93.1%, respectively. The observed rate of RP in 3DU was significantly different (P < 0.001) between the invasive and non-invasive cancers. Compared to the non-rp-3du group, the tumor size in the RP-3DU group was 20 mm (P < 0.05), and the histological grade was mostly grade II (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the RP-3DU group showed significantly higher numbers of ER and PR positive masses (P < 0.05), while there was no significant difference between the two groups with respect to lymph node status, CerbB-2, and Ki-67 expression (P > 0.05). The occurrence of RP in 3DU could therefore contribute to the prognostic evaluation of breast cancer. Keywords: 3D ultrasonography, breast mass, retraction phenomenon, prognosis Introduction Breast cancer (BC) is a common and frequently occurring disease in women with a continued decrease in the onset age. In 2012, 229,060 cases of BC were reported in the USA, of which 39,220 cases were fatal [1]. In some cities of China, the incidence of BC exceeded that of cervical cancer and showed the highest incidence among female malignant cancers [2]. Mammography is an effective diagnostic modality recognized internationally for the diagnosis of BC, but its diagnostic accuracy might be influenced by the densities of the mammary glands. Therefore, the mammography images of dense breast glandular lesions are not very satisfactory [3]. As one of the preferred methods in the screening of breast diseases, the sonographic features and color blood flow distributions of 2D ultrasonography provide preliminary information that can identify benign and malignant breast masses. 3D ultrasonography inherits the merits of 2D ultrasonography, such as simplicity, low cost of use, no pain for the patient, no-radioactivity, and excellent repeatability. Furthermore, it has exhibited significant advantages in the imaging of dense breast masses and small breast cancers [4, 5]. The unique retraction phenomenon (RP) observed in the coronal plane is considered an important indicator in the diagnosis of BC [6]. The biological factors of BC determine its biological behavior and histopathological changes, thus determining the imaging features. The mass size, histological grade, and lymph node status are the three most important indicators for the clinical prognostic evaluation of BC. Estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor 2 (CerbB- 2), and Ki-67 are the biological factors that could effectively assess the prognosis of BC. Certain studies have shown that the lesions with a mass diameter of 20 mm, low histological grade, and non-lymph node metastasis have relatively good prognosis [7]. ER and PR
2 positivity usually indicates high survival rate and low invasion, while the CerbB-2 and Ki-67 positivity indicates the opposite [8]. Currently, 3D ultrasonography is widely used to identify benign and malignant breast masses, while investigations focusing on the relationship between RP in 3D ultrasonography (RP-3DU) and the above prognostic factors are rare [9, 10]. As it is an imaging manifestation of histopathological factors, RP is not uniquely expressed in all malignant breast masses. Some benign lesions may also exhibit certain types of RP. Therefore, our focus is to gain a better understanding of the pathological basis of RP-3DU, as well as to effectively connect them with the prognostic evaluation of BC. The present study investigated the diagnostic value of RP-3DU in benign and malignant breast masses and their relationship with the expression patterns and prognostic indicators in different pathological types of BC. The study aimed to improve the diagnostic efficiency and prognostic evaluation capability of 3D ultrasonography of breast masses and to avoid unnecessary biopsy. Materials and methods General information A total of 165 female patients with breast masses, who had no prior history of radiotherapy or chemotherapy, and underwent 3D ultrasonography in our hospital from Apr 2013 to Mar 2014, were included in this study. All the lesions were confirmed by surgical pathologies, among which 72 cases (aged years; 39.0 ± 11.6 years) were benign lesions with maximum diameters ranging from 5 to 40 mm (20.4 ± 8.5 mm); 93 cases (aged years; 51.8 ± 11.2 years) involved malignant lesions with maximum diameters ranging from 8 to 44 mm (22.5 ± 9.25 mm). The malignant masses included 72 cases of non-specific invasive carcinoma, two cases of invasive lobular carcinoma, one case of invasive cribriform carcinoma, one case of mucinous carcinoma, two cases of lobular carcinoma in situ, eight cases of ductal carcinoma in situ, and seven cases of intraductal papillary carcinoma. The benign masses included 32 cases of fibroadenoma, 17 cases of adenosis-like hyperplasia, 10 cases of breast hyperplasia, five cases of benign phyllodes tumor, three cases of inflammatory lesion, four cases of catheter dilatation, and one case of papilloma. Due to the limited scanning range of the probes, masses with long diameters 50 mm were excluded. This study was conducted in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki. This study was conducted with approval from the Ethics Committee of Guangxi People s Hospital. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Instruments and methods GE Voluson E8 Expert 3D ultrasonography imaging system (GE Healthcare, GmbH & Co OG Austria) together with 6-16D RSP 3D volume high-frequency probe (linear array broadband probe, frequency 6-12 MHz) was used for the inspection. The patient was placed in the supine position, maintaining calm breathing and fully exposing the breasts and armpits. First, 2D ultrasonography was performed on both breasts to record the mass location, number, size, shape, border, and internal echo, etc. Secondly, both armpits were scanned to verify the existence of lymphadenectasis. The same settings were then applied for all the patients (pulse repetition frequency of 0.9 khz, wall filtering set at low 1, image quality at high 2, scanning angle of 25 ), and the regions of interest were selected. The sampling frame was then adjusted for real-time 3D imaging and the 3D tissue tomographic technology was used for the offline analysis. The coronal section of mass was selected, using a layer distance of 0.5 mm, to observe RP on each layer. The image analysis was independently performed by two experienced ultrasonographers (without knowledge of the pathological results), and the disagreements over the results were resolved after consultations. RP was defined by the presence of funicular starlight-shaped signs, with medium or high echo, radially extending around the lesions. Pathological inspection All the specimens were sampled within 24 h after the surgery: Ki-67, ER, PR, and CerbB-2 expression was determined by immunohistochemical analysis, using the two-step MaxVision assay following the manufacturers instructions (Fuzhou Maxim Bioengineering Co. Ltd.). The expression levels of Ki-67, ER, PR, and CerbB-2 were analyzed by pathologists without prior knowledge of the sample conditions. A positive Ki-67 sample was defined as a sample with 20% positive cells. ER and PR positivity was defined as the presence of 10% positive cells Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):
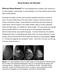
3 Figure 1. 3D ultrasonographic and pathological findings of granulomatous mastitis. A: The coronal image showed irregular tumor border and no envelope, appearing the manifestations of RP; B: Fibrous tissues proliferated around, mutually intertwined and dragged, appearing the radial shape (HE 10). Table 1. Comparison of RP-3DU and pathologic findings [n (%)] RP-3DU Pathologic findings Malignant Benign Sum Malignant 63 (67.7%) 5 (6.9%) 68 Benign 30 (32.3%) 67 (93.1%) 97 Sum Table 2. Relationships between the BC histologic types and manifestations of RP Group Cases Pathological type Non-invasive cancer invasive cancer RP group 63 2 (3.2%) 61 (96.8%) Non-RP group (50%) 15 (50%) x P A positive result for CerbB-2 was defined based on the presence of brown particles inside the tumor cells and graded as follows: 0 point, no stained cell or stained cells < 10%; 1+, stained cells 10% together with the appearance of an incomplete weak brown membrane; 2+, stained cells 10% and complete positive membrane; 3+, stained cells > 30% and a complete strong positive membrane. 0~1+ was defined as negative expression, and 2+ to 3+ were defined as positive. The pathological and histological grading of the masses was performed according to the BC histological classification and diagnostic criteria of WHO [11]. Statistical methods All the data in our study were presented as counting data. Comparison of the features between RP group and non-rp group were performed using the x 2 test. The sensitivity and specificity of the RP-3DU in diagnosing malignant breast masses were obtained using the method with the best diagnostic performance. Then the receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve was used to analyze the diagnostic performance of RP-3DU in diagnosing malignant breast masses. A p value of < 0.05 was regarded as statistically significant. These analyses were performed with SPSS1 software for windows (Version 16.0, SPSS Inc). Results Diagnostic value of RP-3DU in the evaluation of benign and malignant breast masses Sixty-three cases of malignant masses (67.7%), and five cases of benign masses (6.9%) displayed RP. The RP-3DU and pathological findings of granulomatous mastitis are shown in Figure 1. The sensitivity and specificity of RP-3DU in diagnosing malignant breast masses were 67.7% and 93.1%, respectively. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis showed that AUC of the RP-3DU diag Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):
4 Figure 2. 3D ultrasonographic and pathological results of mucinous carcinoma. A: The coronal image showed clear and smooth tumor border while no RP; B: The cancer cells floated in the mucus, exhibiting low inductive effects towards the surrounding interstitial tissues (HE 10). Table 3. Relationships between the manifestations of RP and clinical prognostic indicators of BC [n (%)] Group Cases Mass size Histologic grade Axillary lymph node metastasis 0 < d 20 mm 20 < d 50 mm Grade I Grade II Grade III Yes No RP group (57.1%) 27( 42.9%) 7 (11.9%) 48 (81.3%) 4 (6.8%) 28 (44.4%) 35 (55.6%) Non-RP group 30 8 (26.7%) 22 (73.3%) 4 (15.4%) 8 (30.8%) 14 (53.8%) 18 (60%) 12 (40%) x P nostic curve was (95% CI = , k = 0.585), indicating that the diagnostic efficacy of RP-3DU for BC was low (Table 1). Expressions of RP in different pathological types of BC Among the 93 cases of breast masses, the RP was observed in 80.3% (61 out of 76) of the invasive cancers and 11.8% of non-invasive cancers (2 out of 17); the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.001, Table 2). The 3D image and pathological findings of mucinous carcinoma are shown in Figure 2. Relationship between the manifestation of RP and clinical prognostic indicators of BC The manifestation of the RP in malignant breast masses showed statistically significant differences with the tumor size and histologic grading (P < 0.05). The RP was prevalent in the invasive masses with diameters 20 mm (81.8% to 18.2%, P < 0.05) and histological grade II (81.3% to 14.3%, P < 0.05). However, the lymph node status showed no significant difference between the RP and non-rp groups (P > 0.05, Table 3). The 3D images with and without typical RP, as well as the corresponding pathological findings of the invasive breast cancer, are shown in Figures 3 and 4. Relationships between the RP and immunohistochemical prognostic indicators of BC Among the 93 cases, the positive expression rates of ER and PR in the RP group were higher than the non-rp group (P < 0.05) while no statistically significant differences were observed in CerbB-2 and Ki-67 expression between the two groups (P > 0.05, Table 4). Discussion Observing the tissue around the breast masses is one of the methods used to identify benign Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):
5 Figure 3. 3D ultrasonographic and pathological findings of non-specific invasive carcinoma (mass size mm). A: The coronal image exhibited the typical RP; B: Histological grade II, the fibrous tissues proliferated around, mutually intertwined and dragged, appearing the radial shape (HE 10); C: ER-positive ( 10); D: PR-positive ( 20). and malignant breast masses. 3D ultrasonographic reconstruction technique can identify the infiltration between the masses and surrounding tissues [12]. Previous studies have shown that the RP has significant value in differentiating and diagnosing benign and malignant breast masses [13]. Other investigators have also pointed out that the sensitivity and specificity of RP towards the diagnosis of BC was in the range of 55%-89% and 93%-100%, respectively [6, 13-15]. Therefore, investigating the pathological basis of the observed high specificity and low sensitivity of RP towards the diagnosis of BC as well as the relationship between their expression and prognostic factors in BC were the main objectives of this study. The results of this study showed that the observed rates of RP between the invasive and non-invasive cancers are significantly different (80.3% vs. 11.8%, P > 0.05). RP typically manifested in most non-specific invasive cancers (mass diameter 20 mm, histological grade II), while it was less prevalent in partial non-invasive cancers and some specific invasive cancers. This is in agreement with the observations of Chen et al. [16]. The reason for this observation might be that the pathological basis of the RP is based on the various degrees of inductive effects between the cancer cells and interstitial substances. When the cancer cells infiltrate the surrounding tissues, they stimulate the proliferation of the fibrous connective tissues around the lesions, thus generating the radial high echo caused by the mutual traction among the above proliferating tissues [17]. However, due to the different growth patterns of invasive and non-invasive cancers, the extent of these kinds of inductive effects towards the surrounding interstitial substances is also different. Since the cells of the non-invasive cancers are only limited to the inside of their ducts or lobe, and cannot break through the peripheral breast duct or acinar basement, they will have low inductive effects on the surrounding tissues and therefore demonstrate insignificant signs of infiltration. However, in partial specific invasive cancers, such as mucinous carcinoma, the cancer cells float around Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):
6 Figure 4. 3D ultrasonographic and pathological findings of non-specific invasive carcinoma (mass size mm). A: The coronal image showed that the mass shape was irregular, the envelope was not obvious, and no obvious RP; B: Histological grade III, the fibrous tissues proliferated around, with irregular arrangement while no obvious radial shape (HE 10); C: ER-negative ( 20); D: PR-negative ( 20). Table 4. Relationships between the RP and immunohistochemical prognostic indicators of BC [n (%)] Group Cased Ki-67 ER PR CerbB-2 Positive Negative Positive Negative Positive Negative Positive Negative RP group (69.8%) 19 (30.2%) 50 (79.4%) 13 (20.6%) 49 (77.8%) 14 (22.2%) 48 (76.2%) 15 (23.8%) Non-RP group (86.7%) 4 (13.3%) 17 (56.7%) 13 (43.3%) 16 (53.3%) 14 (46.7%) 20 (66.7%) 10 (33.3%) x P in a lot of mucus, whose border is separated by fibrous tissues, thus preventing significant diffusion and infiltration of the cancer cells towards the surrounding tissues. Therefore, ultrasonography might display the mass with a relatively clear and smooth border. The reason that such benign lesions, such as granulomatous mastitis, exhibited the RP was because the inflammatory cells could also chronically infiltrate the surrounding fibrous connective tissues, thus inducing their proliferation. However, because the degree and nature of this kind of induction was different from the cancer cells, the RP was mostly atypical. The mass size, armpit lymph node status, and histological grade are important prognostic factors in the clinical diagnosis of BS [18]. In this study, the RP exhibited typical manifestations in lesions with a diameter 20 mm, but less in lesions with a diameter of > 30 mm and higher histological grades. Evans et al. [19] and Irshad et al. [20] observed that the cases with apparent glitches around the lesions by mammography and ultrasonography, respectively, had lower histological grade and invasiveness, consistent with our findings. Lamb et al. [21] pointed out that there was no significant correlation between the peri-lesion glitch signs and mass Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):
7 size in mammography. In contrast, Jiang et al. [10] opined that the RP was more sensitive in the masses with a maximum diameter of < 20 mm, and the diagnostic sensitivity would decrease with increasing mass size, similar to the results of this study. The possible reason might be that those small masses had a low histological grade, slow growth, and low invasive ability. Therefore, the surrounding fibrous connective tissues would have enough proliferation time, resulting in a significant RP. It might also be due to the fact that highly invasive cancer cells grow rapidly, and break through the original proliferated tissues and continued to spread peripherally, thus resulting in the interweaving of the proliferated fibrous tissues and attracted mutually, and structures were deficient accordingly [20]. It is also possibly caused by the limits of the probe s scanning range, which prevents masses with large diameters from completely displaying their surrounding tissue. This affects the observation of the RP to some extent, thus making it difficult to make accurate judgments. In addition, this study shows that there was no significant difference in auxiliary lymph node status between the two groups (P > 0.05). Contrary to our study, Xu et al. [22] reported that the RP had high prevalence rate in a patient group with lymph node metastasis, and they inferred that the masses with obvious RP usually grew faster and had stronger invasion strength. The reason for this difference between the two studies might be due to the fact that the auxiliary lymph node metastasis might be related not only to the tumor invasion strength but also to the location, pathologic type, size, and blood supply branch of the primary lesion. Therefore, it should be considered as the result of the combined influence of multiple factors. ER, PR, and CerbB-2 are important factors for the prognostic evaluation of BC and in the selection of a clinical treatment protocol [23]. Previous studies have shown that the positive results of ER and PR in the mammary glandular epithelial cell carcinoma indicate that the growth and reproduction of the masses were still under the endocrine regulation. Therefore, the endocrine treatment would be effective and results in high survival rate [24]. The results of this study showed the positive rates of ER and PR in the positive RP group were higher than those in the non-positive RP group (P < 0.05). This might imply that the RP were the manifestation of low invasiveness, namely the proliferated fibrous connective tissues around the tumor, limiting the spread of the cancer cells to some extent and play a kind of self-protection role. In addition, during this study, we observed a lower incidence rate of the RP in BC with high histological grade, which also verified the conjecture that the RP were the manifestation of low invasiveness. CerbB-2 participates in regulating the growth, proliferation and differentiation of cells, and its over-expression suggested early recurrence, a tendency for distant metastasis, as well as poor prognosis of BC [25]. The Ki-67 antigen is currently accepted as the confirmatory nuclear proliferation marker, and better reflects the proliferation activity of tumor cells. Its positive expression exhibits a great significance for the development, metastasis, and prognosis of BC [26]. Previous studies have shown that the expression of CerbB-2 was associated with ultrasonographic characteristic as glitches [22], and of course, there were other studies proposing the opposite view [27]. In this study, the expression levels of CerbB-2 and Ki-67 were not significantly different between the two groups (P > 0.05). The possible reason might be that the expression of the RP was not only related to the invasiveness and proliferation of BC, but also affected by tumor size, or histological grade. In addition, as important prognostic factors of BC, CerbB-2 and Ki-67 have not yet been thoroughly studied, and requires an expanded sample size for further studies. Our study was limited by the small sample size. Since it was a retrospective study, its diagnostic value towards non-invasive cancers, such as intraductal carcinoma and mucinous carcinoma, as well as other special types of invasive cancers could only be ascertained after further studies involving a larger cohort of cases. Our study was also limited by the probe size and adjustable angles, which limited the observation in the coronal plane of some large masses (> 30 mm). This prevented an effective judgment of the RP due to the truncated collection of signal from the surrounding normal tissue. Further studies using a larger sample size, with minimum human errors, and long-term prospective experiments designed to evaluate effectively the relationship between the 3D ultrasonographic performance and the progno Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):
8 sis of BC, are needed. This can further enrich and validate our presumptions and the results obtained in this study. In summary, the RP observed in the coronal plane of 3D ultrasonography was the result of low invasiveness of BC to some extent. BC with obvious RP was usually less than 20 mm, with lower histological grade, and was ER- and PR-positive. Therefore, RP had some predictive ability for the biological behavior of breast masses, thus exhibiting significant factors for the prognostic evaluation and in the development of a treatment plan for BC. Acknowledgements This work was funded by Key scientific projects of Guangxi medicine and public health (No ); Guangxi Science research & Technology Development Projects (No C); Guangxi Scientific Research and Technology Development Projects (No. Guikegong ). Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Dr. Xiao-Yan Wang, Department of Ultrasonography, Guangxi People s Hospital, Nanning , China. Tel: ; Fax: ; xiaoyanwangdoc@163.com References [1] Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A. Cancer statistics, CA Cancer J Clin 2012; 62: [2] Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S and He J. Annual report on status of cancer in China, Chin J Cancer Res 2015; 27: [3] Huang Y, Pang Y, Wang Q and Li JY. Evaluation on the accuracy of high frequency ultrasound being used in the breast cancer screening program in women from Asian countries: a systematic review. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2010; 31: [4] Brem RF, Tabár L, Duffy SW, Inciardi MF, Guingrich JA, Hashimoto BE, Lander MR, Lapidus RL, Peterson MK, Rapelyea JA, Roux S, Schilling KJ, Shah BA, Torrente J, Wynn RT and Miller DP. Assessing improvement in detection of breast cancer with three-dimensional automated breast US in women with dense breast tissue: the SomoInsight Study. Radiology 2015; 274: [5] Parris T, Wakefild D and Frimmer H. Real world performance of screening breast ultrasound following enactment of Connecticut Bill 458. Breast J 2013; 19: [6] Chen L, Chen Y, Diao XH, Fang L, Pang Y, Cheng AQ, Li WP and Wang Y. Comparative study of automated breast 3-D ultrasound and handheld B-mode ultrasound for differentiation of benign and malignant breast masses. Ultrasound Med Biol 2013; 39: [7] Elston CW, Ellis IO and Pinder SE. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. Crit Rew Oncol Hematol 1999; 31: [8] Hussein MR, Abd-Elwahed SR and Abdulwahed AR. Alterations of estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors and c-erbb2 oncogene protein expression in ductal carcinomas of breast cancer. Cell Biol Int 2008; 32: [9] Candelaria RP, Hwang L, Bouchard RR and Whitman GJ. Breast ultrasound: current concepts. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 2013; 34: [10] Jiang J, Chen YQ, Xu YZ, Chen ML, Zhu YK, Guan WB and Wang XJ. Correlation between three-dimensional ultrasound features and pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. Eur Radiol 2014; 24: [11] Tavassoli FA and Devilee P. WHO Pathology and Genetics tumors of the breast and femal genital organ. 3rd edition. Lyon: IARC Press; 2003; pp. 10. [12] Tan T, Platel B, Huisman H, Sánchez CI, Mus R and Karssemeijer N. Computer-aided lesion diagnosis in automated 3-D breast ultrasound using coronal spiculation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2012; 31: [13] Rotten D, Levaillant JM and Zerat L. Analysis of normal breast tissue and of solid breast masses using three-dimensional ultrasound mammography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1999; 14: [14] Kalmantis K, Dimitrakakis C, Koumpis Ch, Tsigginou A, Papantoniou N, Mesogitis S and Antsaklis A. The contribution of three-dimensional power Doppler imaging in the preoperative assessment of breast tumors: a preliminary report. Obstet Gynecol Int 2009; 2009: [15] Lin X, Wang J, Han F, Fu J and Li A. Analysis of eighty-one cases with breast lesions using automated breast volume scanner and comparison with handheld ultrasound. Eur J Radio 2012; 81: [16] Chen DR and Lai HW. Three-dimensional ultrasonography for breast malignancy detection. Expert Opin Med Diagn 2011; 5: [17] Rotten D, Levaillant JM, Constancis E, Collet Billon A, Le Guerinel Y and Rua P. Threedimensional imaging of solid breast tumors with ultrasound: preliminary data and analysis Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):
9 of its possible contribution to the understanding of the standard two-dimensional sonographic images. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1991; 1: [18] Cianfrocca M and Goldstein LJ. Prognostic and predictive factors in early-stage breast cancer. Oncologist 2004; 9: [19] Evans AJ, Pinder SE, James JJ, Ellis IO and Cornford E. Is mammographic spiculation an independent, good prognostic factor in screening-detected invasive breast cancer? AJR Am J Roentgenol 2006; 187: [20] Irshad A, Leddy R, Pisano E, Baker N, Lewis M, Ackerman S and Campbell A. Assessing the role of ultrasound in predicting the biological behavior of breast cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2013; 200: [21] Lamb PM, Perry NM, Vinnicombe SJ and Wells CA. Correlation between ultrasound characteristics, mammographic findings and histological grade in patients with invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Clin Radio 2000; 55: [22] Xu G, Han T, Yao MH, Xie J, Xu HX and Wu R. Three-dimensional ultrasonography for the prediction of breast cancer prognosis. J BUON 2014; 19: [23] Yaghan R, Stanton PD, Robertson KW, Going JJ, Murray GD and McArdle CS. Oestrogen receptor status predicts local recurrence following breast conservation surgery for early breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 1998; 24: [24] Krizmanich-Conniff KM, Paramagul C, Patterson SK, Helvie MA, Roubidoux MA, Myles JD, Jiang K and Sabel M. Triple receptor-negative breast cancer: imaging and clinical characteristics. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2012; 199: [25] Cooke T, Reeves J, Lannigan A and Stanton P. The value of the human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2) as a prognostic marker. Eur J Cancer 2001; 37: S3-10. [26] Li BJ, Zhu ZH, Wang JY, Hou JH, Zhao JM, Zhang PY, Yao GY, Wang X, Long H, Yang MT and Rong TH. Expression correlation of Ki67 to P53, VEGF, and C-erbB-2 genes in breast cancer and their clinical significance. Ai Zheng 2004; 23: [27] Kim SH, Seo BK, Lee J, Kim SJ, Cho KR, Lee KY, Je BK, Kim HY, Kim YS and Lee JH. Correlation of ultrasound findings with histology, tumor grade, and biological markers in breast cancer. Acta Oncol 2008; 47: Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):
Original Article Relation between qualitative and quantitative 3-dimensional ultrasound and ki-67 expression in breast cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):18538-18542 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012561 Original Article Relation between qualitative and quantitative 3-dimensional ultrasound and ki-67 expression in breast
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):18538-18542 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012561 Original Article Relation between qualitative and quantitative 3-dimensional ultrasound and ki-67 expression in breast
Topic Exploration Report
 Topic Exploration Report Topic explorations are designed to provide a high-level briefing on new topics submitted for consideration by Health Technology Wales. The main objectives of this report are to:
Topic Exploration Report Topic explorations are designed to provide a high-level briefing on new topics submitted for consideration by Health Technology Wales. The main objectives of this report are to:
Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions. Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea
 Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea Not so benign lesions? Imaging abnormalities(10% recall) lead to diagnostic evaluation,
Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea Not so benign lesions? Imaging abnormalities(10% recall) lead to diagnostic evaluation,
The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
Breast pathology. 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University
 Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (13):
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (13): 5925-5929 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Study on the correlation between ultrasonic imaging features in breast cancer and the expression of ER, PR, HER-2 and nm23.
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (13): 5925-5929 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Study on the correlation between ultrasonic imaging features in breast cancer and the expression of ER, PR, HER-2 and nm23.
Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule
 Original Article Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule Xuan Zhang*, Hong-Hong Yan, Jun-Tao Lin, Ze-Hua Wu, Jia Liu, Xu-Wei Cao, Xue-Ning Yang From
Original Article Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule Xuan Zhang*, Hong-Hong Yan, Jun-Tao Lin, Ze-Hua Wu, Jia Liu, Xu-Wei Cao, Xue-Ning Yang From
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients
 236 Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients Mingfian Yang Hao Long Jiehua He Xi Wang Zeming Xie Department of Thoracic Oncology, Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou
236 Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients Mingfian Yang Hao Long Jiehua He Xi Wang Zeming Xie Department of Thoracic Oncology, Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9497-9501 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Analysis of relevant risk factor and recurrence prediction model construction of thyroid cancer after surgery. Shuai Lin 1#,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9497-9501 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Analysis of relevant risk factor and recurrence prediction model construction of thyroid cancer after surgery. Shuai Lin 1#,
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound
 Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
Original Article Ultrasonographic characteristics and BI-RADS-US classification of BRCA1 mutation-associated breast cancer in Guangxi, China
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(2):2411-2416 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002834 Original Article Ultrasonographic characteristics and BI-RADS-US classification of BRCA1 mutation-associated breast cancer
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(2):2411-2416 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002834 Original Article Ultrasonographic characteristics and BI-RADS-US classification of BRCA1 mutation-associated breast cancer
ELIZABETH CEDARS DR. KOREY HOOD Available September 29
 ELIZABETH CEDARS DR. KOREY HOOD Available September 29 Title and Investigators Optimizing Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer: Using Surgeon-performed Ultrasound to Predict Extrathyroidal Extension of
ELIZABETH CEDARS DR. KOREY HOOD Available September 29 Title and Investigators Optimizing Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer: Using Surgeon-performed Ultrasound to Predict Extrathyroidal Extension of
Clinical and pathological portraits of axillary presentation breast cancer and effects of preoperative systemic therapy
 Case Series Clinical and pathological portraits of axillary presentation breast cancer and effects of preoperative systemic therapy Ling Xu 1*, Fang Li 1,2*, Yinhua Liu 1, Xuening Duan 1, Jingming Ye 1,
Case Series Clinical and pathological portraits of axillary presentation breast cancer and effects of preoperative systemic therapy Ling Xu 1*, Fang Li 1,2*, Yinhua Liu 1, Xuening Duan 1, Jingming Ye 1,
IBCM 2, April 2009, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
 Preoperative diagnosis and treatment planning in breast cancer The pathologist s perspective L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia Locarno, Switzerland IBCM 2, 23-25 April 2009, Sarajevo, Bosnia
Preoperative diagnosis and treatment planning in breast cancer The pathologist s perspective L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia Locarno, Switzerland IBCM 2, 23-25 April 2009, Sarajevo, Bosnia
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR
 BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging?
 Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICO-IMAGING STUDY OF INVASIVE DUCTAL BREAST CARCINOMAS CORRELATED TO HORMONAL RECEPTORS AND HER2/NEU ONCOPROTEIN
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICO-IMAGING STUDY OF INVASIVE DUCTAL BREAST CARCINOMAS CORRELATED TO HORMONAL RECEPTORS AND HER2/NEU ONCOPROTEIN
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Basement membrane in lobule.
 Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Proliferative Breast Disease: implications of core biopsy diagnosis. Proliferative Breast Disease
 Proliferative Breast Disease: implications of core biopsy diagnosis Jean F. Simpson, M.D. Breast Pathology Consultants, Inc. Nashville, TN Proliferative Breast Disease Must be interpreted in clinical and
Proliferative Breast Disease: implications of core biopsy diagnosis Jean F. Simpson, M.D. Breast Pathology Consultants, Inc. Nashville, TN Proliferative Breast Disease Must be interpreted in clinical and
Invasive Papillary Breast Carcinoma
 410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
BARC/2013/E/019 BARC/2013/E/019. AUDIT OF MAMMOGRAPHY PERFORMED IN OUR HOSPITAL by Surita Kantharia Medical Division
 BARC/2013/E/019 BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF MAMMOGRAPHY PERFORMED IN OUR HOSPITAL by Surita Kantharia Medical Division BARC/2013/E/019 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF
BARC/2013/E/019 BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF MAMMOGRAPHY PERFORMED IN OUR HOSPITAL by Surita Kantharia Medical Division BARC/2013/E/019 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF
Current Imaging Diagnosis of the Breast Tumors
 Breast Cancer Current Imaging Diagnosis of the Breast Tumors JMAJ 45(6): 258 264, 2002 Tokiko ENDO Director of the Department of Radiology, National Nagoya Hospital Abstract: Breast masses include the
Breast Cancer Current Imaging Diagnosis of the Breast Tumors JMAJ 45(6): 258 264, 2002 Tokiko ENDO Director of the Department of Radiology, National Nagoya Hospital Abstract: Breast masses include the
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography
 Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update Stuart J. Schnitt, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Papillary Lesions of the Breast
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update Stuart J. Schnitt, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Papillary Lesions of the Breast
Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: A report of nine cases and a review of the literature
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 1753-1758, 2015 Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: A report of nine cases and a review of the literature YIZI CONG *, GUANGDONG QIAO *, HAIDONG ZOU, JUN LIN, XINGMIAO WANG,
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 1753-1758, 2015 Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: A report of nine cases and a review of the literature YIZI CONG *, GUANGDONG QIAO *, HAIDONG ZOU, JUN LIN, XINGMIAO WANG,
Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided. CNB) versus mammograph-guided biopsy for suspicious microcalcifications. without definite breast mass
 Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
DIAGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF CHANGES IN SERUM HUMAN EPIDIDYMIS EPITHELIAL SECRETORY PROTEIN 4 AND CARBOHYDRATE ANTIGEN 125 IN ENDOMETRIAL CARCINOMA
 Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2018, 34: 785 DIAGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF CHANGES IN SERUM HUMAN EPIDIDYMIS EPITHELIAL SECRETORY PROTEIN 4 AND CARBOHYDRATE ANTIGEN 125 IN ENDOMETRIAL CARCINOMA PATIENTS JING-LI
Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2018, 34: 785 DIAGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF CHANGES IN SERUM HUMAN EPIDIDYMIS EPITHELIAL SECRETORY PROTEIN 4 AND CARBOHYDRATE ANTIGEN 125 IN ENDOMETRIAL CARCINOMA PATIENTS JING-LI
Complex cystic breast lesions, which are defined as lesions
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Value of Ultrasonographic Features for Assessing Malignant Potential of Complex Cystic Breast Lesions Jin-Peng Yao, MD, Yu-Zhi Hao, MD, Qing Chang, MD, Cheng-Yun Geng, MD, Yu Chen, MD,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Value of Ultrasonographic Features for Assessing Malignant Potential of Complex Cystic Breast Lesions Jin-Peng Yao, MD, Yu-Zhi Hao, MD, Qing Chang, MD, Cheng-Yun Geng, MD, Yu Chen, MD,
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING
 OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant
 Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant
 Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma
 http://dx.doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.1.66 KMJ Case Report Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma Jeong Hyun Oh 1, Taek Sang Kim 1, Hyun Yul Rhew 1, Bong Kwon Chun
http://dx.doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.1.66 KMJ Case Report Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma Jeong Hyun Oh 1, Taek Sang Kim 1, Hyun Yul Rhew 1, Bong Kwon Chun
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine
 Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Neuroendocrine differentiation in pure type mammary mucinous carcinoma is associated with favorable histologic and immunohistochemical parameters
 & 2004 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/04 $25.00 www.modernpathology.org Neuroendocrine differentiation in pure type mammary mucinous carcinoma is associated with favorable histologic and immunohistochemical
& 2004 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/04 $25.00 www.modernpathology.org Neuroendocrine differentiation in pure type mammary mucinous carcinoma is associated with favorable histologic and immunohistochemical
Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients
 BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, December 2015. Vol. 12(3), 2221-2225 Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients S.M. Hosseini¹, H. Shahbaziyan
BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, December 2015. Vol. 12(3), 2221-2225 Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients S.M. Hosseini¹, H. Shahbaziyan
Does elastography change the indication to biopsy? IBDC
 Does elastography change the indication to biopsy? A LEXANDRA A THANASIOU, M D DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY CURIE INSTITUTE PARIS, FRANCE IBDC Ultrasound Detected Cancers Physician-performed ultrasound increases
Does elastography change the indication to biopsy? A LEXANDRA A THANASIOU, M D DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY CURIE INSTITUTE PARIS, FRANCE IBDC Ultrasound Detected Cancers Physician-performed ultrasound increases
Rare types of breast carcinoma
 Open Med. 2015; 10: 92-96 Research Article Open Access Daiva Gudaviciene*, Laura Steponaviciene, Raimundas Meskauskas, Giedre Smailyte, Eduardas Aleknavicius Rare types of breast Abstract: Breast cancer
Open Med. 2015; 10: 92-96 Research Article Open Access Daiva Gudaviciene*, Laura Steponaviciene, Raimundas Meskauskas, Giedre Smailyte, Eduardas Aleknavicius Rare types of breast Abstract: Breast cancer
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Original Article Diagnosis significance of single high frequency ultrasonography and mammography and their combined examination on breast cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(2):3713-3718 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0032065 Original Article Diagnosis significance of single high frequency ultrasonography and mammography and their combined examination
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(2):3713-3718 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0032065 Original Article Diagnosis significance of single high frequency ultrasonography and mammography and their combined examination
NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY
 A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
Breast Cancer. What is breast cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form
 S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass
 Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer 2 The So Called Pre-Neoplastic Lesions and Carcinoma In Situ
 Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Risk Factor and Etiological Agents... 2 1.3 The Concept of the Windows of Susceptibility to Carcinogenesis... 5
Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Risk Factor and Etiological Agents... 2 1.3 The Concept of the Windows of Susceptibility to Carcinogenesis... 5
04/10/2018. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast INTRADUCTAL PAPILLOMA
 Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Date of Preparation: December 8, 2017 A. GENERAL INFORMATION. 1. Name: Eun Sook KO Citizenship: Republic of Korea
 Date of Preparation: December 8, 2017 A. GENERAL INFORMATION 1. Name: Eun Sook KO 2. Email: mathilda0330@gmail.com 3. Citizenship: Republic of Korea B. EDUCATIONAL & TRAINING BACKGROUND Degree Institution
Date of Preparation: December 8, 2017 A. GENERAL INFORMATION 1. Name: Eun Sook KO 2. Email: mathilda0330@gmail.com 3. Citizenship: Republic of Korea B. EDUCATIONAL & TRAINING BACKGROUND Degree Institution
Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal
 Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated. FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia.
 DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated BENIGN BREAST DISORDERS (Essential Surg 2 nd Ed, pp 540) FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia. Fibroadenosis is the distortion
DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated BENIGN BREAST DISORDERS (Essential Surg 2 nd Ed, pp 540) FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia. Fibroadenosis is the distortion
Breast Pathology. Breast Development
 Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Interpretation of Breast Pathology in the Era of Minimally Invasive Procedures
 Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine Jacksonville Medical Director, UF Health Breast Center Chief of Pathology
Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine Jacksonville Medical Director, UF Health Breast Center Chief of Pathology
Prognostic importance of ultrasound BI-RADS classification in breast cancer patients
 Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2015, 45(5) 411 415 doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyv018 Advance Access Publication Date: 10 February 2015 Original Article Original Article Prognostic importance of ultrasound
Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2015, 45(5) 411 415 doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyv018 Advance Access Publication Date: 10 February 2015 Original Article Original Article Prognostic importance of ultrasound
Feasibility of using negative ultrasonography results of axillary lymph nodes to predict sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients
 Received: 21 April 2018 Revised: 14 May 2018 DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1606 Accepted: 14 May 2018 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Feasibility of using negative ultrasonography results of axillary lymph nodes to predict sentinel
Received: 21 April 2018 Revised: 14 May 2018 DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1606 Accepted: 14 May 2018 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Feasibility of using negative ultrasonography results of axillary lymph nodes to predict sentinel
Toru Nakamura 1, Takashi Fukutomi 1, Hitoshi Tsuda 2, Sadako Akashi-Tanaka 1, Kaneyuki Matsuo 1, Chikako Shimizu 1 and Kunihisa Miyakawa 3
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2000;30(10)453 457 Changes in Findings of Mammography, Ultrasonography and Contrast-enhanced Computed Tomography of Three Histological Complete Responders with Primary Breast Cancer Before
Jpn J Clin Oncol 2000;30(10)453 457 Changes in Findings of Mammography, Ultrasonography and Contrast-enhanced Computed Tomography of Three Histological Complete Responders with Primary Breast Cancer Before
Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti. Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS
 Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS Histological diversity of breast adenocarcinomas Different histological types are defined according to specific
Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS Histological diversity of breast adenocarcinomas Different histological types are defined according to specific
Aims and objectives. Page 2 of 10
 Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences
 SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER April 2013 Vol.56 No.4: 335 340 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4435-y Risk factors of recurrence in small-sized, node negative breast cancer in young women: a retrospective
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER April 2013 Vol.56 No.4: 335 340 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4435-y Risk factors of recurrence in small-sized, node negative breast cancer in young women: a retrospective
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Breast Pathology Evening Specialty Conference Case #4. Clinical Case: Pathologic Features
 Breast Pathology Evening Specialty Conference Case #4 K.P. Siziopikou, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Director of Breast Pathology and Breast Pathology Fellowship Program Northwestern University Feinberg
Breast Pathology Evening Specialty Conference Case #4 K.P. Siziopikou, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Director of Breast Pathology and Breast Pathology Fellowship Program Northwestern University Feinberg
Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM)
 Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-1237 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: N. Seo 1, H. H. Kim
Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-1237 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: N. Seo 1, H. H. Kim
Atypical And Suspicious Categories In Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology Of The Breast
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. III (October. 216), PP 57-61 www.iosrjournals.org Atypical And Suspicious Categories in
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. III (October. 216), PP 57-61 www.iosrjournals.org Atypical And Suspicious Categories in
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours
 Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance
 Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance Anne Moore, MD Medical Oncology Syed Hoda, MD Surgical Pathology The pathologist is central to the team approach needed to manage the patient with breast
Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance Anne Moore, MD Medical Oncology Syed Hoda, MD Surgical Pathology The pathologist is central to the team approach needed to manage the patient with breast
Xiaohuan Pan 1,2 *, Xinguan Yang 1,2 *, Jingxu Li 1,2, Xiao Dong 1,2, Jianxing He 2,3, Yubao Guan 1,2. Original Article
 Original Article Is a 5-mm diameter an appropriate cut-off value for the diagnosis of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ on chest computed tomography and pathological examination?
Original Article Is a 5-mm diameter an appropriate cut-off value for the diagnosis of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ on chest computed tomography and pathological examination?
FIBROEPITHELIAL LESIONS
 DEFINITIONS FIBROEPITHELIAL LESIONS Suzanne Moore FIBROADENOMA- A discrete benign tumour showing evidence of connective tissue and epithelial proliferation- WHO Fibrous stromal element of these tumours
DEFINITIONS FIBROEPITHELIAL LESIONS Suzanne Moore FIBROADENOMA- A discrete benign tumour showing evidence of connective tissue and epithelial proliferation- WHO Fibrous stromal element of these tumours
Immunohistochemical studies (ER & Ki-67) in Proliferative breast lesions adjacent to malignancy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. IV. (Mar. 2014), PP 84-89 Immunohistochemical studies (ER & Ki-67) in Proliferative
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. IV. (Mar. 2014), PP 84-89 Immunohistochemical studies (ER & Ki-67) in Proliferative
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS
 1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
Significance and prognosis of epithelial cadherin expression in invasive breast carcinoma
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 16: 1659-1665, 2018 Significance and prognosis of epithelial cadherin expression in invasive breast carcinoma LIANG YANG, XIAO WEN WANG, LI PING ZHU, HONG LI WANG, BIN WANG, QIAN ZHAO
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 16: 1659-1665, 2018 Significance and prognosis of epithelial cadherin expression in invasive breast carcinoma LIANG YANG, XIAO WEN WANG, LI PING ZHU, HONG LI WANG, BIN WANG, QIAN ZHAO
Tumour markers in breast carcinoma correlate with grade rather than with invasiveness
 doi: 10.1054/ bjoc.2001.1995, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on http://www.bjcancer.com Tumour markers in breast carcinoma correlate with grade rather than with invasiveness F Wärnberg
doi: 10.1054/ bjoc.2001.1995, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on http://www.bjcancer.com Tumour markers in breast carcinoma correlate with grade rather than with invasiveness F Wärnberg
Biomedical Research 2014; 25(3): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2014; 25(3): 321-326 ISSN 0970-938X http://www.biomedres.info The logistic regression analysis of ultrasonographic features in differential diagnosis of cervical lymph nodes metastasis
Biomedical Research 2014; 25(3): 321-326 ISSN 0970-938X http://www.biomedres.info The logistic regression analysis of ultrasonographic features in differential diagnosis of cervical lymph nodes metastasis
Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology. Report. Key Questions. Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help:
 Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report Key Questions Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help: Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report 1. Is this
Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report Key Questions Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help: Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report 1. Is this
Dense Breasts, Get Educated
 Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression
 Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Case Report A case of matrix-producing carcinoma of the breast with micoglandular adenosis and review of literature
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(7):8568-8572 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0010093 Case Report A case of matrix-producing carcinoma of the breast with micoglandular adenosis and review of literature
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(7):8568-8572 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0010093 Case Report A case of matrix-producing carcinoma of the breast with micoglandular adenosis and review of literature
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography
 Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(5) : 229-233 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography M Muttarak, S Pojchamarnwiputh,
Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(5) : 229-233 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography M Muttarak, S Pojchamarnwiputh,
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013
 Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Journal of Ningxia Medical University. Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI b 500 s / mm s / mm 2
 786 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 34 8 2012 8 1674-6309 2012 08-0786 - 04 MRI 1 2 2 2 2 1 1. 750002 2. 750004 MR Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI 27 38 DWI2 b 500 s / mm 2 1000 s / mm 2 Apparent
786 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 34 8 2012 8 1674-6309 2012 08-0786 - 04 MRI 1 2 2 2 2 1 1. 750002 2. 750004 MR Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI 27 38 DWI2 b 500 s / mm 2 1000 s / mm 2 Apparent
Breast Cancer. What is breast cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
Original Article Analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer and thyroid nodules
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):14424-14429 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021975 Original Article Analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer and
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):14424-14429 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021975 Original Article Analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer and
Benign Breast Disease and Breast Cancer Risk
 Benign Breast Disease and Breast Cancer Risk Jean F. Simpson, M.D. Vanderbilt University Nashville, Tennessee December 1, 2011 Nashville Nashville Lebanon 1 Cedars of Lebanon State Park The American University
Benign Breast Disease and Breast Cancer Risk Jean F. Simpson, M.D. Vanderbilt University Nashville, Tennessee December 1, 2011 Nashville Nashville Lebanon 1 Cedars of Lebanon State Park The American University
It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue
 59 Breast cancer 1 It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue including both early stages which are potentially curable, and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) which is usually incurable. Most breast
59 Breast cancer 1 It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue including both early stages which are potentially curable, and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) which is usually incurable. Most breast
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE. Jonathan I. Epstein
 INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer
 Elmer ress Original Article World J Oncol. 2017;8(3):71-75 A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer Hui Hu a, Wei Wei a, Xin Yi a, Ling Xin
Elmer ress Original Article World J Oncol. 2017;8(3):71-75 A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer Hui Hu a, Wei Wei a, Xin Yi a, Ling Xin
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Basal phenotype: a powerful prognostic factor in small screen-detected invasive breast cancer with long-term follow-up ...
 21 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Basal phenotype: a powerful prognostic factor in small screen-detected invasive breast cancer with long-term follow-up A J Evans, E A Rakha, S E Pinder, A R Green, C Paish and I O Ellis...
21 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Basal phenotype: a powerful prognostic factor in small screen-detected invasive breast cancer with long-term follow-up A J Evans, E A Rakha, S E Pinder, A R Green, C Paish and I O Ellis...
Research on the correlation between ultrasonographic features of breast cancer and expressions of ER, CD34 and p53
 JBUON 2018; 23(2): 372-377 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Research on the correlation between ultrasonographic features of breast
JBUON 2018; 23(2): 372-377 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Research on the correlation between ultrasonographic features of breast
Clinical Study on Prognostic Factors and Nursing of Breast Cancer with Brain Metastases
 Clinical Study on Prognostic Factors and Nursing of Breast Cancer with Brain Metastases Ying Zhou 1#, Kefang Zhong 1#, Fang Zhou* 2 ABSTRACT This paper aims to explore the clinical features and prognostic
Clinical Study on Prognostic Factors and Nursing of Breast Cancer with Brain Metastases Ying Zhou 1#, Kefang Zhong 1#, Fang Zhou* 2 ABSTRACT This paper aims to explore the clinical features and prognostic
Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide
 Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide Breast Cancer - Understanding Your Pathology Report Pathology Reports can be overwhelming. They contain scientific terms that are unfamiliar and might be a bit
Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide Breast Cancer - Understanding Your Pathology Report Pathology Reports can be overwhelming. They contain scientific terms that are unfamiliar and might be a bit
Table of contents. Page 2 of 40
 Page 1 of 40 Table of contents Introduction... 4 1. Background Information... 6 1a: Referral source for the New Zealand episodes... 6 1b. Invasive and DCIS episodes by referral source... 7 1d. Age of the
Page 1 of 40 Table of contents Introduction... 4 1. Background Information... 6 1a: Referral source for the New Zealand episodes... 6 1b. Invasive and DCIS episodes by referral source... 7 1d. Age of the
Prediction of Lymph Node Involvement in Patients with Breast Tumors Measuring 3 5 cm in a Middle-Income Setting: the Role of CancerMath
 DOI 10.1007/s00268-014-2752-3 BRIEF ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC REPORT Prediction of Lymph Node Involvement in Patients with Breast Tumors Measuring 3 5 cm in a Middle-Income Setting: the Role of CancerMath E.
DOI 10.1007/s00268-014-2752-3 BRIEF ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC REPORT Prediction of Lymph Node Involvement in Patients with Breast Tumors Measuring 3 5 cm in a Middle-Income Setting: the Role of CancerMath E.
