Role of Toll-like Receptors in the Activation
|
|
|
- Toby Park
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Role of Toll-like Receptors in the Activation of Natural Killer T (NKT) lymphocytes HOST PATHOGEN CROSS TALK Annecy, Les Pensières September 24-26, 2007 Institut Pasteur de Lille Inserm 547 (Prof M. Capron) «Innate Immunity and Immunoregulation»
2 Ag MHC I/II peptide TCR Ag presenting cell (APC) (dendritic cell, ) Conventional T lymphocyte (CD4 +, CD8 + ) Ag CD1 (glyco)lipid TCR APC Lipid-reactive T lymphocyte
3 Invariant Natural Killer T cells (inkt cells) NK1.1 Ly49 NKT * Express markers found on NK cells and on T lymphocytes TCR CD1d * Very conserved TCR Invariant TCR :V 14-J 1818 segment/ chains (inkts) APC * Recognized exogenous or self lipid Ags restricted by the CD1d molecules alpha-galactosylceramide l l ( -GalCer) as a canonical lli ligand ceramide Polar head (carbohydrate(s)) Glycosphingolipide * Rapid production of IFN- and/or IL-4 Strong impact on innate and acquired immune responses Benefical : infectious diseases, cancer Detrimental : auto-immune and inflammatory diseases
4 Factors involved in the activation/orientation of auto-reactive inkt cells during stress conditions IL-4 Flexibility IFN- APC/iNKT cell cross-talk NKT TCR CD1d Nature of the endogenous lipids APC Nature of the co-factors produced Stress (infection, inflammation)
5 Mechanisms by which inkt cells become activated during infection Exogenous (microbial) vs self lipid Ags Mycobacteria Leishmania Sphingomonas Ehrlichia Borrelia Exogenous Ag Il-12 (1) CD1d TcR Innate and adaptive responses pathogen (2) Innate sensors (TLR4) DC CD40 CD86 Endogenous Ag (still unknown)
6 Do diverse TLR signals in conventional DCs differentially stimulate inkt cells? 4 4 2, 5 7/8, 9 3 TLRs? TRIF APC NKT 0 peptidoglycan dsrnas ssrnas dscpg-rich DNA Cell surface Endosome/lysosome
7 TLR4, TLR7 and TLR9-stimulated DCs activate inkt cells TLR agonists + washing 48 hrs ELISA BMDC Sorted CD5 + NK1.1 + liver cells TLR member 9 7/8 4 2/1 2/6 3 5
8 inkt cell activation requires CD1d and soluble co-factors CpG stimulation and fixation with paraformaldehyde Co-factors? TLR7 TLR9 CD1d TCR Lipid(s)? inkt
9 IL-12 is not involved in inkt cell activation in response to DC/CpG agonists + Neutralizing Abs washing BMDC WT or IL-12p40 -/-
10 inkt cell activation in response to CpG ODN-treated DCs requires type I IFN Neutralizing Abs BMDC NKT cells (WT, IFNAR -/- )
11 IFN I TLR9? CD1d TCR inkt De novo synthesis of self ligands following TLR9 stimulation?
12 NB-DGJ N-butyl-deoxygalactonojirimycin GalNAcT Ceramide Cer Glucosyl Tf Glc-Cer Lactosylcer synthase Lac-Cer GlcNAcT Cer Glc-Cer Gal-Glc-Cer (Lac Cer) GA2 Gal T GM3 GM3 S igb3 Gb3 Lc3 o-series a-series Gangliosides (iso)globo-series (Neo)lacto-series inkt cell activation requires de novo synthesis of -linked GlcCer N-butyl-deoxygalactonojirimycin 48 hrs before CpG ODN stimulation
13 Lipids are generated in CpG ODN-stimulated DCs to activate inkt cells NS or CpG ODN + BMDC Lipid extraction Total lipids + BMDC 12 hrs Washing +/- IFN type I Same data with R848/DC
14 Charged glucosylseramide (s) is (are) involved in inkt cell activation NS or CpG ODN + BMDC Lipid extraction Neutral Total lipids + Charged BMDC 12 hrs Washing +/- IFN type I +/- base treated (NaOH): eliminates all lipids excepted GSLs +/- ceramide glycanase treated: eliminates GSLs
15 What happens in vivo? Can DC/CpG activate inkt cells in vivo? Functional relevance?
16 CpG ODN/DCs activate inkt cells in vivo NS/DCs -GC/DCs CpG ODN/DCs Gated TCR + /TT + liver cells NS/DCs -GalCer/DCs CpG ODN/DCs CD4 Isotype control IFN-
17 CpG ODN/DCs activate inkt cells in vivo to protect mice against B16 melanoma B16F10 (5 x10 5 ) Day 0 Day 14 NS/DCs -GalCer/DCs CpG ODN/DCs Sacrifice
18 Self lipids (charged -linked glucosylceramides) are generated in CpG ODN-stimulated DCs to activate inkt cells, in concert with IFN type I IFN I TLR9 CD1d TCR Charged GSL(s) inkt «NKT1» phenotype Paget et al. Immunity (in Press) Relevant during infection? Nature of the self glycolipid?
19 Relevance during viral/bacterial infection? DNA viruses (HSV, MCMV, ) Intracellular bacteria DAI cytosol DNA sensors Invading dsdna TLR9 endosome Type I INF Glycolipid synthesis Activation of inkt/nk cell pathway
20 Yellow Fever (YF) virus 17D activates inkt cells through DCs YF17D 1 MOI + washing 48 hrs ELISA BMDC Sorted inkt cells * *
21 Impact of TLR activation on glycolipid synthesis n=6 Ceramide (Cer) GlcCer Glc 1-1Cer Ugcg B4galnt1 GA2 GalNAc 1-4Gal 1-4Glc 1-1Cer LacCer B4galt6 Gal 1-4Glc 1-1Cer B3gnt5 LC3 GlcNAc 1-3Gal 1-4Glc 1-1Cer St3gal5 A3galt2 A4galt GM3 NeuNAc 2-3Gal 1-4Glc 1-1Cer igb3 Gal 1-3Gal 1-4Glc 1-1Cer Gb3 Gal 1-4Gal 1-4Glc 1-1Cer Ganglio-series (o, a, b,c) Charged GSLs Isoglobo-series Globo-series (Neo)lacto series Neutral GSLs
22 Ganglioside pathway St3gal5 St8sia1 St8sia5 LacCer GM3 GD3 GT3 Cer Cer Cer Cer B4galnt1 GA2 GM2 GD2 GT2 Cer Cer Cer Cer B3galt4 GA1 GM1a GD1b GT1c Cer Cer Cer Cer St3gal1/2/4 GM1b GD1a GT1b GQ1c Cer Cer Cer Cer St8sia5 GD1c GT1a GQ1b GP1c Cer Cer Cer Cer n = 6 o-series a-series b-series c-series St: sialyltransferase Glucose 1,3Gal 2,3NeuAc 2,8NeuAc 1,4GalNAc Towards the quest for the ligand(s)
23 Inserm 547 Oxford Univ F. Platt A. Speak Hôpital Necker/CNRS ML Leite de Moraes CNRS, Orléans C. Paget B. Ryffel T. Mallevaey J. Fontaine D. Torrès IPP/IPL C. Vendeville G. Barba-Spaeth C. Faveeuw J. Dubuisson
Invariant natural killer T cells recognize lipid self-antigen induced by microbial danger signals
 Supplementary Information: Invariant natural killer T cells recognize lipid self-antigen induced by microbial danger signals Patrick J. Brennan 1,5, Raju V.V. Tatituri 1,5, Manfred Brigl 1, Edy Y. Kim
Supplementary Information: Invariant natural killer T cells recognize lipid self-antigen induced by microbial danger signals Patrick J. Brennan 1,5, Raju V.V. Tatituri 1,5, Manfred Brigl 1, Edy Y. Kim
a1 Ceramide Website: Phone: +1 (404)
 α-galactosylceramide (α-galcer) or the common name of KRN7000 was isolated from an extract of the Okinawan marine sponge Agelas mauritianus. The Alpha-GalCer structure consist of a galactose combined with
α-galactosylceramide (α-galcer) or the common name of KRN7000 was isolated from an extract of the Okinawan marine sponge Agelas mauritianus. The Alpha-GalCer structure consist of a galactose combined with
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
2. Innate immunity 2013
 1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
GANGLIOSIDES for Neuroscience Research
 GANGLIOSIDES for Neuroscience Research STANDARDS & MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES Gangliosides GANGLIOSIDE AND GLYCOLIPID STANDARDS purified PURIFIED NATURAL GANGLIOSIDES Cat. # Description Size GANGLIOSIDE A PATH
GANGLIOSIDES for Neuroscience Research STANDARDS & MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES Gangliosides GANGLIOSIDE AND GLYCOLIPID STANDARDS purified PURIFIED NATURAL GANGLIOSIDES Cat. # Description Size GANGLIOSIDE A PATH
General information. Cell mediated immunity. 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon. Anytime after class.
 General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Technical Report. Structural Analysis of Glycosphingolipids by LC-IT-TOF-MS. Abstract:
 C146-E268 Technical Report Structural Analysis of Glycosphingolipids by LC-T-TF-MS Akemi Suzuki 1, Jin-ichi nokuchi 2, Masakazu Nagafuku 2, Hideshi Fujiwake 3, Yoshikatsu Umemura 3 Abstract: A method for
C146-E268 Technical Report Structural Analysis of Glycosphingolipids by LC-T-TF-MS Akemi Suzuki 1, Jin-ichi nokuchi 2, Masakazu Nagafuku 2, Hideshi Fujiwake 3, Yoshikatsu Umemura 3 Abstract: A method for
Invariant NKT cells reduce the immunosuppressive activity of influenza A virus induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells in mice and humans
 Research article Invariant NKT cells reduce the immunosuppressive activity of influenza A virus induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells in mice and humans Carmela De Santo, 1 Mariolina Salio, 1 S. Hajar
Research article Invariant NKT cells reduce the immunosuppressive activity of influenza A virus induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells in mice and humans Carmela De Santo, 1 Mariolina Salio, 1 S. Hajar
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas
 Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Chapter 6. Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes
 Chapter 6 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Generation of T-cell Receptor Ligands T cells only recognize Ags displayed on cell surfaces These Ags may be derived from pathogens that replicate within
Chapter 6 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Generation of T-cell Receptor Ligands T cells only recognize Ags displayed on cell surfaces These Ags may be derived from pathogens that replicate within
Macrophage Activation & Cytokine Release. Dendritic Cells & Antigen Presentation. Neutrophils & Innate Defense
 Macrophage Activation & Cytokine Release Dendritic Cells & Antigen Presentation Neutrophils & Innate Defense Neutrophils Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) are recruited to the site of infection where they
Macrophage Activation & Cytokine Release Dendritic Cells & Antigen Presentation Neutrophils & Innate Defense Neutrophils Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) are recruited to the site of infection where they
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms
 TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Role of Marginal Zone B Lymphocytes in Invariant NKT Cell Activation
 This information is current as of June 27, 2018. Role of Marginal Zone B Lymphocytes in Invariant NKT Cell Activation Emilie Bialecki, Christophe Paget, Josette Fontaine, Monique Capron, François Trottein
This information is current as of June 27, 2018. Role of Marginal Zone B Lymphocytes in Invariant NKT Cell Activation Emilie Bialecki, Christophe Paget, Josette Fontaine, Monique Capron, François Trottein
TechNotes. Gangliosides. 1. Applications
 TechNotes Gangliosides Gangliosides are a large group of sialylated glycosphingolipids that are widely expressed in mammalian tissues. Gangliosides are found in most tissues of the body, but they are particularly
TechNotes Gangliosides Gangliosides are a large group of sialylated glycosphingolipids that are widely expressed in mammalian tissues. Gangliosides are found in most tissues of the body, but they are particularly
Glycans linked to lipids and lipid precursors
 Glycobiology BCMB 8130 Clinical Correlations! -sign up for 1st and 2nd choice (1/2)! *********************************! Glycosylation in Diabetes! O-Mannosylation in Human Pathophysiology! Glycoconjugate
Glycobiology BCMB 8130 Clinical Correlations! -sign up for 1st and 2nd choice (1/2)! *********************************! Glycosylation in Diabetes! O-Mannosylation in Human Pathophysiology! Glycoconjugate
Review Article Ganglioside Biochemistry
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Biochemistry Volume 2012, Article ID 506160, 36 pages doi:10.5402/2012/506160 Review Article Ganglioside Biochemistry Thomas Kolter Program Unit Membrane Biology
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Biochemistry Volume 2012, Article ID 506160, 36 pages doi:10.5402/2012/506160 Review Article Ganglioside Biochemistry Thomas Kolter Program Unit Membrane Biology
Antigen presenting cells
 Antigen recognition by T and B cells - T and B cells exhibit fundamental differences in antigen recognition - B cells recognize antigen free in solution (native antigen). - T cells recognize antigen after
Antigen recognition by T and B cells - T and B cells exhibit fundamental differences in antigen recognition - B cells recognize antigen free in solution (native antigen). - T cells recognize antigen after
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Adaptive Immunity to Bacteria. T cell subsets
 Adaptive Immunity to Bacteria Role of T cells in anti-bacterial host responses. Dr. C. Piccirillo Department of Microbiology & Immunology McGill University T cell subsets MHC I and II -restricted cells
Adaptive Immunity to Bacteria Role of T cells in anti-bacterial host responses. Dr. C. Piccirillo Department of Microbiology & Immunology McGill University T cell subsets MHC I and II -restricted cells
The Innate Immune Response
 The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
Molecular Events Underlying Cell-Associated HIV Transmission. Rahm Gummuluru Boston University School of Medicine Department of Microbiology
 Molecular Events Underlying Cell-Associated HIV Transmission Rahm Gummuluru Boston University School of Medicine Department of Microbiology HIV Dendritic Cell Interactions Robust virus replication in dendritic
Molecular Events Underlying Cell-Associated HIV Transmission Rahm Gummuluru Boston University School of Medicine Department of Microbiology HIV Dendritic Cell Interactions Robust virus replication in dendritic
Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
CD40L TCR IL-12 TLR-L
 CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
Adaptive Immune System
 Short Course on Immunology Adaptive Immune System Bhargavi Duvvuri Ph.D IIIrd Year (Immunology) bhargavi@yorku.ca Supervisor Dr.Gillian E Wu Professor, School of Kinesiology and Health Sciences York University,
Short Course on Immunology Adaptive Immune System Bhargavi Duvvuri Ph.D IIIrd Year (Immunology) bhargavi@yorku.ca Supervisor Dr.Gillian E Wu Professor, School of Kinesiology and Health Sciences York University,
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response
 chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy
 Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
11/25/2017. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS BARRIER DEFENSES INNATE IMMUNITY OF VERTEBRATES
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
A Comparison of Ganglioside Content and Distribution. Tumor Tissue
 A Comparison of Ganglioside Content and Distribution in Normal Murine Neural Tissue and Murine Neural Tumor Tissue Sourav Sengupta under the direction of Dr. Thomas N. Seyfried and Ms. Dia Banerjee Department
A Comparison of Ganglioside Content and Distribution in Normal Murine Neural Tissue and Murine Neural Tumor Tissue Sourav Sengupta under the direction of Dr. Thomas N. Seyfried and Ms. Dia Banerjee Department
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, MBIM 650/720 - Fall TOPIC: Antigen Processing, MHC Restriction, & Role of Thymus Lecture 12
 COURSE: Medical Microbiology, MBIM 650/720 - Fall 2008 TOPIC: Antigen Processing, MHC Restriction, & Role of Thymus Lecture 12 FACULTY: Dr. Mayer Office: Bldg. #1, Rm B32 Phone: 733-3281 Email: MAYER@MED.SC.EDU
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, MBIM 650/720 - Fall 2008 TOPIC: Antigen Processing, MHC Restriction, & Role of Thymus Lecture 12 FACULTY: Dr. Mayer Office: Bldg. #1, Rm B32 Phone: 733-3281 Email: MAYER@MED.SC.EDU
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
Antigen processing and presentation Processing Proteins: the MHC. The exogenous (class II) pathway Glycolipids and carbohydrates: CD1.
 Chapter 18 T cells and the MHC CHAPTER CONTENTS Subpopulations of T cells What T cells recognize Antigen processing and presentation Processing Proteins: the MHC The exogenous (class II) pathway Glycolipids
Chapter 18 T cells and the MHC CHAPTER CONTENTS Subpopulations of T cells What T cells recognize Antigen processing and presentation Processing Proteins: the MHC The exogenous (class II) pathway Glycolipids
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
3/10/14. Ultrastructural organization. Gram Stain. Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation. Gram negative.
 Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
all of the above the ability to impart long term memory adaptive immunity all of the above bone marrow none of the above
 1. (3 points) Immediately after a pathogen enters the body, it faces the cells and soluble proteins of the innate immune system. Which of the following are characteristics of innate immunity? a. inflammation
1. (3 points) Immediately after a pathogen enters the body, it faces the cells and soluble proteins of the innate immune system. Which of the following are characteristics of innate immunity? a. inflammation
Toll-like Receptor Signaling
 Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
White Blood Cells (WBCs)
 YOUR ACTIVE IMMUNE DEFENSES 1 ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE 2! Innate Immunity - invariant (generalized) - early, limited specificity - the first line of defense 1. Barriers - skin, tears 2. Phagocytes - neutrophils,
YOUR ACTIVE IMMUNE DEFENSES 1 ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE 2! Innate Immunity - invariant (generalized) - early, limited specificity - the first line of defense 1. Barriers - skin, tears 2. Phagocytes - neutrophils,
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Time course of immune response
 Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
UMR 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy Chatenay-Malabry. Natura-Brasil. EA Laboratory of Dermatological Research,
 Iuliana Popa 1, Noëlle Remoué 2 and Jacques Portoukalian 3 1 UMR 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy Chatenay-Malabry 2 Natura-Brasil 3 EA 41 69 Laboratory of Dermatological Research, University of Lyon I, Faculty
Iuliana Popa 1, Noëlle Remoué 2 and Jacques Portoukalian 3 1 UMR 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy Chatenay-Malabry 2 Natura-Brasil 3 EA 41 69 Laboratory of Dermatological Research, University of Lyon I, Faculty
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and. Specific. (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell
 There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
Relative sizes of infectious agents
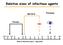 Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Block A: Membrane Biology & Biochemistry. Lipid signalling and sphingolipid function
 Block A: Membrane Biology & Biochemistry Lipid signalling and sphingolipid function 10. - 14.11.2014 Gerhild van Echten-Deckert Tel. 73 2703 E-mail: g.echten.deckert@uni-bonn.de www.limes-institut-bonn.de
Block A: Membrane Biology & Biochemistry Lipid signalling and sphingolipid function 10. - 14.11.2014 Gerhild van Echten-Deckert Tel. 73 2703 E-mail: g.echten.deckert@uni-bonn.de www.limes-institut-bonn.de
Cell Mediated Immunity CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY. Basic Elements of Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI) Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
 Chapter 16 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY Cell Mediated Immunity Also known as Cellular Immunity or CMI The effector phase T cells Specificity for immune recognition reactions TH provide cytokines CTLs do the
Chapter 16 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY Cell Mediated Immunity Also known as Cellular Immunity or CMI The effector phase T cells Specificity for immune recognition reactions TH provide cytokines CTLs do the
Natural Killer T cells and their functions in atherosclerosis and obesity: a therapeutic perspective for cardiovascular diseases
 REVIEW Natural Killer T cells and their functions in atherosclerosis and obesity: a therapeutic perspective for cardiovascular diseases A.M. van de Vrugt 1 and E. Kalkhoven 2 1 Biology of Disease Master
REVIEW Natural Killer T cells and their functions in atherosclerosis and obesity: a therapeutic perspective for cardiovascular diseases A.M. van de Vrugt 1 and E. Kalkhoven 2 1 Biology of Disease Master
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH THE IMMUNE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF HOST DEFENSES The human body contains three lines of against infectious agents (pathogens) 1. Mechanical and chemical boundaries (part of the innate immune system)
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF HOST DEFENSES The human body contains three lines of against infectious agents (pathogens) 1. Mechanical and chemical boundaries (part of the innate immune system)
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
HLA and antigen presentation. Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol
 HLA and antigen presentation Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol MHC in adaptive immunity Characteristics Specificity Innate For structures shared
HLA and antigen presentation Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol MHC in adaptive immunity Characteristics Specificity Innate For structures shared
Invariant natural killer T cells recognize glycolipids from pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria
 Invariant natural killer T cells recognize glycolipids from pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria 211 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. Yuki Kinjo 1,2,13, Petr Illarionov 3,13, José Luis Vela 1,13,
Invariant natural killer T cells recognize glycolipids from pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria 211 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. Yuki Kinjo 1,2,13, Petr Illarionov 3,13, José Luis Vela 1,13,
Recognition of Lyso-Phospholipids by Human Natural Killer T Lymphocytes
 Recognition of Lyso-Phospholipids by Human Natural Killer T Lymphocytes Lisa M. Fox 1, Daryl G. Cox 2, Jennifer L. Lockridge 1, Xiaohua Wang 1, Xiuxu Chen 1, Louise Scharf 3, David L. Trott 4, Rachel M.
Recognition of Lyso-Phospholipids by Human Natural Killer T Lymphocytes Lisa M. Fox 1, Daryl G. Cox 2, Jennifer L. Lockridge 1, Xiaohua Wang 1, Xiuxu Chen 1, Louise Scharf 3, David L. Trott 4, Rachel M.
Immune response. This overview figure summarizes simply how our body responds to foreign molecules that enter to it.
 Immune response This overview figure summarizes simply how our body responds to foreign molecules that enter to it. It s highly recommended to watch Dr Najeeb s lecture that s titled T Helper cells and
Immune response This overview figure summarizes simply how our body responds to foreign molecules that enter to it. It s highly recommended to watch Dr Najeeb s lecture that s titled T Helper cells and
Immunology. T-Lymphocytes. 16. Oktober 2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Karin Peters,
 Immunology T-Lymphocytes 16. Oktober 2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Karin Peters, karin.peters@rub.de The role of T-effector cells in the immune response against microbes cellular immunity humoral immunity
Immunology T-Lymphocytes 16. Oktober 2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Karin Peters, karin.peters@rub.de The role of T-effector cells in the immune response against microbes cellular immunity humoral immunity
Chapter 10 (pages ): Differentiation and Functions of CD4+ Effector T Cells Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
Identification of Microbes
 Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Micro 204. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier
 Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
Stimulation of Natural Killer T Cells by Glycolipids
 Molecules 2013, 18, 15662-15688; doi:10.3390/molecules181215662 PEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules Review Stimulation of Natural Killer T Cells by Glycolipids Brian L. Anderson
Molecules 2013, 18, 15662-15688; doi:10.3390/molecules181215662 PEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules Review Stimulation of Natural Killer T Cells by Glycolipids Brian L. Anderson
Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology
 By Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology Lecture objectives: At the end of the lecture you should be able to: Enumerate features that characterize acquired immune response
By Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology Lecture objectives: At the end of the lecture you should be able to: Enumerate features that characterize acquired immune response
Figure S2
 Figure S1 Figure S2 Figure S3 Figure S4 Figure S5 Figure S6 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1 Biosynthetic pathway for gangliosides showing activity of GalNAcT and GD3s and the structures of the major
Figure S1 Figure S2 Figure S3 Figure S4 Figure S5 Figure S6 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1 Biosynthetic pathway for gangliosides showing activity of GalNAcT and GD3s and the structures of the major
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury. Journal Club December 16, 2004
 Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
 The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
Overview of the immune system
 Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
The Immune System. These are classified as the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Innate Immunity
 The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
Innate Immunity. Jan 8 th Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1
 Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM:
 RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: To Distinguish Self from Non-Self Thereby Protecting Us From Our Hostile Environment. Innate Immunity Acquired Immunity Innate immunity: (Antigen nonspecific) defense
RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: To Distinguish Self from Non-Self Thereby Protecting Us From Our Hostile Environment. Innate Immunity Acquired Immunity Innate immunity: (Antigen nonspecific) defense
The regulatory roles of glycosphingolipid-enriched lipid rafts in immune systems
 REVIEW ARTICLE The regulatory roles of glycosphingolipid-enriched lipid rafts in immune systems Hitoshi Nakayama 1,2, Masakazu Nagafuku 3, Akemi Suzuki 3, Kazuhisa Iwabuchi 1,2,4 and Jin-Ichi Inokuchi
REVIEW ARTICLE The regulatory roles of glycosphingolipid-enriched lipid rafts in immune systems Hitoshi Nakayama 1,2, Masakazu Nagafuku 3, Akemi Suzuki 3, Kazuhisa Iwabuchi 1,2,4 and Jin-Ichi Inokuchi
JPEMS Nantes, Basic Immunology Introduction to the immune system Definitions Structure and General Organization
 JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology Introduction to the immune system Definitions Structure and General Organization Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr
JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology Introduction to the immune system Definitions Structure and General Organization Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr
Helminth worm, Schistosomiasis Trypanosomes, sleeping sickness Pneumocystis carinii. Ringworm fungus HIV Influenza
 Helminth worm, Schistosomiasis Trypanosomes, sleeping sickness Pneumocystis carinii Ringworm fungus HIV Influenza Candida Staph aureus Mycobacterium tuberculosis Listeria Salmonella Streptococcus Levels
Helminth worm, Schistosomiasis Trypanosomes, sleeping sickness Pneumocystis carinii Ringworm fungus HIV Influenza Candida Staph aureus Mycobacterium tuberculosis Listeria Salmonella Streptococcus Levels
Introduction to Immune System
 Introduction to Immune System Learning outcome You will be able to understand, at a fundamental level, the STRUCTURES and FUNCTIONS of cell surface and soluble molecules involved in recognition of foreign
Introduction to Immune System Learning outcome You will be able to understand, at a fundamental level, the STRUCTURES and FUNCTIONS of cell surface and soluble molecules involved in recognition of foreign
Antigen processing and presentation. Monika Raulf
 Antigen processing and presentation Monika Raulf Lecture 25.04.2018 What is Antigen presentation? AP is the display of peptide antigens (created via antigen processing) on the cell surface together with
Antigen processing and presentation Monika Raulf Lecture 25.04.2018 What is Antigen presentation? AP is the display of peptide antigens (created via antigen processing) on the cell surface together with
Immunology The innate and adaptive immune systems
 Immunology The innate and adaptive immune systems The immune system is the collection of cells, tissues and molecules that protects the body from numerous pathogenic microbes and toxins in our environment.
Immunology The innate and adaptive immune systems The immune system is the collection of cells, tissues and molecules that protects the body from numerous pathogenic microbes and toxins in our environment.
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS
 TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
Bacterial Diseases IMMUNITY TO BACTERIAL INFECTIONS. Gram Positive Bacteria. Gram Negative Bacteria. Many Infectious agents and many diseases
 IMMUNITY TO BACTERIAL INFECTIONS Chapter 18 Bacterial Diseases Many Infectious agents and many diseases Bacteria can Infect any part of the body Cause disease due to Growth of the microbe in a tissue Produce
IMMUNITY TO BACTERIAL INFECTIONS Chapter 18 Bacterial Diseases Many Infectious agents and many diseases Bacteria can Infect any part of the body Cause disease due to Growth of the microbe in a tissue Produce
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 Concepts. MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally!
 MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity
 Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Sphingolipids in Infectious Diseases
 Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 58, 131-148, 2005 Invited Review Sphingolipids in Infectious Diseases Kentaro Hanada* Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Tokyo
Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 58, 131-148, 2005 Invited Review Sphingolipids in Infectious Diseases Kentaro Hanada* Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Tokyo
Unit 6: Adaptive Immunity. Adaptive Immunity (Humoral Immunity; Cell-Mediated Immunity; Immunodeficiency; Hypersensitivity)
 Unit 6: Adaptive Immunity Adaptive Immunity (Humoral Immunity; Cell-Mediated Immunity; Immunodeficiency; Hypersensitivity) : ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY: AN OVERVIEW OF INNATE AND ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Adaptive Immunity
Unit 6: Adaptive Immunity Adaptive Immunity (Humoral Immunity; Cell-Mediated Immunity; Immunodeficiency; Hypersensitivity) : ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY: AN OVERVIEW OF INNATE AND ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Adaptive Immunity
Defensive mechanisms include :
 Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
Clinical Basis of the Immune Response and the Complement Cascade
 Clinical Basis of the Immune Response and the Complement Cascade Bryan L. Martin, DO, MMAS, FACAAI, FAAAAI, FACOI, FACP Emeritus Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics President, American College of Allergy,
Clinical Basis of the Immune Response and the Complement Cascade Bryan L. Martin, DO, MMAS, FACAAI, FAAAAI, FACOI, FACP Emeritus Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics President, American College of Allergy,
MEDIATED ANTIGEN PRESENTATION
 MECHANISMS OF TGF -INDUCED INHIBITION OF CD1D- MEDIATED ANTIGEN PRESENTATION Jennifer Carrie Ryan Submitted to the faculty of the University Graduate School in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
MECHANISMS OF TGF -INDUCED INHIBITION OF CD1D- MEDIATED ANTIGEN PRESENTATION Jennifer Carrie Ryan Submitted to the faculty of the University Graduate School in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
UNIVERSITA DEGLI STUDI DI MILANO
 UNIVERSITA DEGLI STUDI DI MILANO SCUOLA DI DOTTORATO DI RICERCA IN SCIENZE BIOCHIMICHE, NUTRIZIONALI E METABOLICHE DOTTORATO DI RICERCA IN BIOCHIMICA CICLO XXIII BIO/10 TESI DI DOTTORATO DI RICERCA PLASMA
UNIVERSITA DEGLI STUDI DI MILANO SCUOLA DI DOTTORATO DI RICERCA IN SCIENZE BIOCHIMICHE, NUTRIZIONALI E METABOLICHE DOTTORATO DI RICERCA IN BIOCHIMICA CICLO XXIII BIO/10 TESI DI DOTTORATO DI RICERCA PLASMA
Mechanisms of Autontibodies
 Mechanisms of Autontibodies Production in Rheumatic Diseases Eisa Salehi PhD Tehran University of Medical Sciences Immunology Department Introduction Rheumatic diseases: Cause inflammation, swelling, and
Mechanisms of Autontibodies Production in Rheumatic Diseases Eisa Salehi PhD Tehran University of Medical Sciences Immunology Department Introduction Rheumatic diseases: Cause inflammation, swelling, and
THE. Cutting Edge: Activation by Innate Cytokines or Microbial Antigens Can Cause Arrest of Natural Killer T Cell Patrolling of Liver Sinusoids 1
 THE JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY CUTTING EDGE Cutting Edge: Activation by Innate Cytokines or Microbial Antigens Can Cause Arrest of Natural Killer T Cell Patrolling of Liver Sinusoids 1 Peter Velázquez,* Thomas
THE JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY CUTTING EDGE Cutting Edge: Activation by Innate Cytokines or Microbial Antigens Can Cause Arrest of Natural Killer T Cell Patrolling of Liver Sinusoids 1 Peter Velázquez,* Thomas
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis. Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University
 Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
