Protective Effects of Tribulus Terrestris L Extract Against Acute Kidney Injury Induced By Reperfusion Injury in Rats
|
|
|
- Rodney Simpson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 KIDNEY DISEASES Protective Effects of Tribulus Terrestris L Extract Against Acute Kidney Injury Induced By Reperfusion Injury in Rats Houshang Najafi, 1 Mohammad Reza Firouzifar, 2 Omid Shafaat, 2 Saeed Changizi Ashtiyani, 3 Nasser Hosseini 4 Original Paper 1 Medical Biology Research Center, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, Kermanshah, Iran 2 Student Research Committee, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran 3 Department of Physiology, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran 4 Department of Medicinal Plants, Faculty of Agriculture and Natural Resources, Arak University, Arak, Iran Keywords. acute kidney injury, reperfusion injury, Tribulus, oxidative stress Introduction. This study aimed to investigate the protective effect of aerial parts of the Tribulus terrestris L extract on acute kidney injury (AKI) induced by ischemia for 30 minutes and reperfusion for 24 hours in rats. Materials and Methods. Ten male Sprague-Dawley rats in the AKI and 10 in the Tribulus terrestris groups received the extract solvent and extract of the plant (11 mg/kg), respectively, for 13 days (oral administration). On day 14, ischemia for 30 minutes and reperfusion for 24 hours were induced on the rats. In the last 6 hours of the reperfusion period (24 hours), urine samples were collected in metabolic cages. At the end of this period, blood samples were also taken to determine plasma urea nitrogen, creatinine, and electrolyte concentrations. The kidney tissues were collected for measuring the level of oxidative stress and histological studies. They were compared with the sham operation group and a control group with normal diet and no operation. Results. In the Tribulus terrestris group, the increase in plasma creatinine and urea nitrogen concentrations was significantly less following reperfusion, and their values reached the same level as that in the sham group. Creatinine clearance and urine osmolarity in the Tribulus terrestris group was higher in comparison with the AKI group, whereas sodium absolute excretion, fractional excretion of potassium, oxidative stress, and cellular damages were less. Conclusions. Oral administration of Tribulus terrestris extract for 2 weeks can decrease kidney functional disturbance, oxidative stress, and cellular damages following reperfusion injury in rats. IJKD 2014;8: INTRODUCTION Tribulus terrestris L is a herb (Zygophyllaceae family) with a wide distribution in the south of Europe, south of Asia, Africa, and north of Australia. In traditional medicine, different parts of Tribulus terrestris are applied to the treatment of hypertension and coronary artery diseases, diabetes and hyperlipidemia, and fungal diseases. 1-5 In addition, it has been shown that Tribulus terrestris possesses diuretic, aphrodisiac, lithontriptic, and antibacterial effects. 6-8 Recent studies have also indicated that Tribulus terrestris extract has antioxidative, apoptosis inhibitory, and vasodilator properties, 9-14 as well as protecting renal epithelial cells against damages due to oxalates and ethylene glycol consumption. 15,16 Various conditions may result in acute kidney injury (AKI), the most common of which is reperfusion injury. Pathophysiological damages due to reperfusion injury include vascular endothelium, 292
2 tubular epithelium, and inflammation These damages through induction of oxidative stress, necrosis, and cellular apoptosis, as well as sustained reduction of renal blood flow (RBF), lead to further damage to kidney function. 17 It has already been proven that Tribulus terrestris extract possesses antioxidant and vasodilator properties, and that it can protect renal epithelial cells. The aim of this study was to investigate the protective effects of Tribulus terrestris extracts against AKI induced by ischemia-reperfusion. MATERIALS AND METHODS Rats In this experimental study, 40 male Sprague- Dawley rats weighing 280 g to 350 g were supplied and divided into 4 groups of 10 each: control (no operation and no injection), sham (sham operation), AKI, and AKI receiving Tribulus terrestris extract (TT). These animals were placed in controlled conditions of temperature (23 ± 2 C) and 12-hour light-dark cycles. They were provided with standard rat food and water ad libitum. Induction of Ischemia-Reperfusion Ischemia-reperfusion was used as the model of inducing AKI. In the AKI and TT groups, the rats were first anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital (50 mg/kg to 60 mg/kg) and a longitudinal incision was made in the linea alba. Then, the arteries and veins of both kidneys were simultaneously clamped for 30 minutes. After the 30-minute period, obstruction was removed and the surgical area was sutured with 3-zero silk. The rats were returned to the cages to spend the 24-hour reperfusion period. During this period, they had free access to water and food. The same protocol was followed for the sham group; however, no occlusion was done. The control group did not go through anesthesia or any operation. Extraction Method Tribulus terrestris was obtained from pharmaceutical plants farm of Arak University. Then, aerial parts of the plant were dried in shade and its extract was obtained through the percolation method. The solvent used for extracting was 70% ethanol. After filtering, the resulting extract was concentrated through rotavapor and dried in freeze drier. 20 Study Protocol The rats in the AKI and TT groups received the extract solvent and Tribulus terrestris extract at 11 mg/kg dose of body weight, respectively (a total volume of 5 ml through gavage), for 13 days. 21 At the beginning of day 14, they underwent surgery and ischemia (30 minutes) as well as reperfusion for 24 hours. Then at the beginning of the last 6 hours of the reperfusion period, the rats were transferred to a metabolic cage and their urine samples were collected. At the end of this period, the rats were anesthetized again and blood samples were obtained from their descending aorta. Next, the amount of oxidative stress in the right kidney was measured and the left kidney was extracted for histological studies. The rats in the sham group received the solvent of Tribulus terrestris extract and underwent the same procedure. The control group, however, received a normal diet without operation and underwent measurements. Measurements Plasma creatinine and urea nitrogen concentrations were measured by an RA-1000 autoanalyzer (Technicon, Tarry Town, USA). An EasyLyte (Medica, Bedford, USA) was used for measurement of sodium and potassium concentrations in urine and plasma samples, while urine and plasma osmolarity were measured using an osmometer (Osmomat 010, Gonotec, Germany). For evaluation of the status of oxidative stress, malondialdehyde and ferric reducing/antioxidant power (FRAP) values in kidney tissue samples were measured. These parameters were measured as explained in our previous studies, through Ohkawa and Benzie methods, respectively. 25,26 The removed segments of the kidneys were fixed in 10% formalin and placed in paraffin to be studied histologically. After providing slides stained with hematoxylin-eosin, the following were measured: the degree of renal histopathological damages in terms of increase in Bowman space, decrease in the number of erythrocytes in glomerular capillaries, tubular cells necrosis and their exfoliation into tubular lumens, vacuole formation within the cells, vascular congestion, and intratubular proteinaceous casts Statistical Analysis All data were presented as mean ± standard error of mean. For analyzing data on kidney 293
3 function parameters and oxidative stress values, the 1-way analysis of variance and the Duncan post hoc test were used. The comparison of total histopathological scores between the groups was made using the nonparametric the Kruskal-Wallis and the Mann-Whitney tests. A P value less than.05 was considered as the level of significance. RESULTS For evaluating the induction of reperfusion injury, plasma creatinine and urea nitrogen concentrations were determined, which did not differ between the sham and control groups (Table 1). Ischemia for 30 minutes and reperfusion for 24 hours resulted in increases in plasma creatinine (2.9 times) and urea nitrogen (3.3 times) concentrations in the AKI group compared with the sham group (P <.001). However, plasma creatinine and urea nitrogen concentrations in the TT group significantly decreased in comparison with the AKI group (P <.001), and creatinine concentration value reached the same level as that in the sham group. Reperfusion in the AKI group increased the absolute excretion of sodium and fractional excretion of potassium by 2.6 and 4.9 times, respectively, in comparison with the sham group (P <.001). Administration of Tribulus terrestris extract in the TT group caused significant decreases in the absolute excretion of sodium and fractional excretion of potassium levels compared with those in the AKI group, in a way that they were not significantly different from their corresponding values in the sham group (Table 1). Figure 1 shows that renal reperfusion injury decreased creatinine clearance in the AKI group by 65% in comparison with that in the sham group (P <.01), whereas administration of Tribulus terrestris extract in the TT group increased it by 1.9 times as compared with the AKI group (P <.05). Figure 1. Mean levels of creatinine clearance and urine osmolality after the reperfusion period in rats with induced acute kidney injury (AKI) with and without pretreatment with saline (AKI) or Tribulus terrestris (TT), compared with rats in the sham operation and control groups. *P <.01 in comparison with the sham group P <.05 in comparison with the AKI group P <.001 in comparison with the sham group P <.001 in comparison with the AKI group Table 1. Effects of Oral Administration of Tribulus Terresteris (TT) Extract on Kidney Function Parameters After Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion Animal Groups Parameters Control Sham AKI TT Plasma creatinine, mg/dl 0.86 ± ± ± 0.14* 1.00 ± 0.06 Plasma urea nitrogen, mg/dl ± ± ± 1.90* ± 2.60 Absolute excretion of sodium, mmol/min.kg body weight 4.20 ± ± ± 1.60* 3.10 ± 0.24 Fractional excretion of potassium, % ± ± ± 9.03* ± 3.60 *P <.001 in comparison with the sham group P <.001 in comparison with the AKI group P <.01 in comparison with the sham group P <.01 in comparison with the AKI group 294
4 In addition, urine osmolarity in the AKI group decreased to less than its corresponding value in the sham group (P <.001). Administration of Tribulus terrestris extract in the TT group significantly increased urine osmolarity compared with the AKI group (P <.001), as such it reached the same level as the sham group (Figure 1). Tissue malondialdehyde in the sham group was 8.5 ± 1.1 nmol/g kidney weight (Figure 2), which increased to 34.3 ± 2.3 nmol/g in the AKI group (P <.001). Although treatment with Tribulus terrestris extract could decrease malondialdehyde value to 20.1 ± 2.9 nmol/g (P <.01), it was still 2.3 times more than that in the sham group (P <.01). Moreover, tissue FRAP in the sham group was 12.5 ± 1.6 µmol/g kidney weight that decreased to 6.4 ± 0.8 µmol/g following reperfusion (P <.01). In the TT group, FRAP level was 11.8 ± 1.5 µmol/g that was significantly higher than its corresponding value in the AKI group (Figure 2). As Table 2 shows, in the cortical region of the kidneys, the Bowman space increased (grade 5) and the number of erythrocytes decreased in the glomerular capillaries (grades 5) and the cells were vacuolated (grade 4) in the AKI group. In addition, cells in the proximal tubule walls and the thick ascending limb of loop of Henle were damaged (grades 3 and 2, respectively). All these damages were partially improved with treatment with Tribulus terrestris in the TT group (Figure 3). In the external medulla, reperfusion induced damage in the tubular segments of Pars Recta (S3) and the thick ascending limb of loop of Henle (grade 3), vascular congestion (grade 5), and intratubular proteinaceous casts (grade 4). All these damages decreased in the TT group as compared with the AKI group (Figure 4). In the internal medulla, the values for vascular congestion and intratubular proteinaceous casts in the TT group relatively decreased as compared with the AKI group (Table 2). The total histopathologic score in the AKI Table 2. Histopathologic Scores in Rats With Oral Administration of Tribulus Terresteris (TT) Extract After Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion Figure 2. Mean levels of renal tissue malondialdehyde and ferric reducing/antioxidant power (FRAP) after the reperfusion period in rats with induced acute kidney injury (AKI) with and without pretreatment with saline (AKI) or Tribulus terrestris (TT), compared with rats in the sham operation and control groups. *P <.001 in comparison with the sham group P <.01 in comparison with the sham group P <.01 in comparison with the AKI group Animal Groups Histopathology Sham AKI TT Cortex Bowman space enlargement 0 V I Proximal tubule injury 0 III I Thick ascending limb injury 0 II I Reduced number of erythrocytes in 0 V II glomerular capillaries Intracellular vacuolization 0 IV I Outer medulla Pars recta (S3) injury 0 III I Thick ascending limb injury 0 III I Vascular congestion 0 V II Intratubular proteinaceous casts 0 IV II Inner medulla Vascular congestion 0 III II Intratubular proteinaceous casts 0 IV I Total histopathologic score 0 41* 15* *P <.001 in comparison with the sham group P <.01 in comparison with the AKI group 295
5 Tribulus Terrestris L Against Acute Kidney Injury Najafi et al Figure 3. A to C, Bowman space widening in the sham, acute kidney injury, and Tribulus terrestris groups, respectively. D to F, Outer medulla for tubular cells necrosis in the sham, acute kidney injury, and Tribulus terrestris groups, respectively (hematoxylin-eosin, 400). Figure 4. A to C, Outer medulla showing intratubular casts in the sham, acute kidney injury, and Tribulus terrestris groups, respectively. D to F, Outer medulla showing vascular congestion in the sham, acute kidney injury, and Tribulus terrestris groups, respectively (hematoxylin-eosin, 400). group was 41, while with treatment with Tribulus terrestris extract it was significantly lower in the TT group (P <.01). DISCUSSION This study showed that the oral administration 296 of Tribulus terrestris extract decreases histological damages, oxidative stress, and as a result, improves kidney function following bilateral renal ischemia for 30 minutes and reperfusion for 24 hours. In the AKI group, creatinine clearance as the index of glomerular filtration rate significantly decreased,
6 which caused significant increase in plasma creatinine and urea nitrogen concentrations. Several studies have shown that renal reperfusion injury by intrarenal vasoconstriction and increasing the bonding molecules leads to linking leukocytes, platelets, and erythrocytes to each other and permanent reduction in RBF during the reperfusion period. 17,27 In the present study, the decreased number of erythrocytes in glomerular capillaries and vascular congestion in medullae verified that. Reduction in RBF together with increased pressure in the Bowman space and increased back leak through the damaged epithelial layer of tubules result in significant decreases of glomerular filtration rate in AKI. 17 Various studies have shown that Tribulus terrestris fruit extract has vasodilator properties. 1,14 In their study on rats, Sharifi and coworkers reported that consumption of Tribulus terrestris fruit extract led to vasodilatations through reducing the activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme. 14 Other studies have shown that Tribulus terrestris extract through increasing nitric oxide release from vascular endothelium and its hyperpolarization as well as its direct effect leads to vasodilatation. 1,28,29 Thus, it seems that Tribulus terrestris extract can resolve the vasoconstriction due to renal reperfusion injury, due to its inhibitory effect on the activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme, stimulation of nitric oxide release from vascular endothelium, hyperpolarization of the vascular smooth muscles, and its direct effect, and as a result, improve plasma parameters, such as creatinine and urea nitrogen. Histological study showed that following reperfusion injury, the degree of damage to cells in the tubules walls, and their exfoliation into the lumens along the proximal tubules and the thick ascending limb significantly increased. During ischemia, severe reduction of adenosine triphosphate results in the complete loss of cell metabolic activity. This leads to the development of mitochondrial damage, increased production of reactive oxygen species, and increased concentration of intracellular calcium, which result in disruption of proteins, DNA, and cell membrane, through activating phospholipases, proteases, endonucleases, and lipid and protein peroxidation, that induce and develop damage to cells and stimulate inflammation. 17,30,31 Zhang and colleagues indicated that Tribulus terrestris extract reduced oxidative stress and cell apoptosis in heart muscles of rats following reperfusion injury. 10 They showed that Tribulus terrestris extract resulted in the reduction of proapoptotic proteins such as Bax and caspase-3 through activating protein kinase C and increased the level of Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic protein. They also stated that Tribulus terrestris extract reduced oxidative stress in heart muscles. Hence, Tribulus terrestris extract maybe exerts sedative effects on cellular damages and oxidative stress in kidney tissues (as in heart muscles) through a similar mechanism or other mechanisms that need to be investigated in future studies. CONCLUSIONS Overall, it can be concluded that Tribulus terrestris extract increases RBF during the reperfusion phase through its vasodilatory effects, which in turn, returns glomerular filtration rate to its normal level. As a result, it leads to relative improvement of the plasma parameters indicative of kidney function. In addition, through reduction of cell destructive damages and oxidative stress, Tribulus terrestris can prevent the development and progression of cellular damages. Clearly, determining the exact mechanism of each of these effects in kidney requires further investigation. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors would like to thank the Research Deputy of Arak University of Medical Sciences and the administrative assistant of Students Research Committee for considering and approving research project No 410. CONFLICT OF INTEREST None declared. REFERENCES 1. Phillips OA, Mathew KT, Oriowo MA. Antihypertensive and vasodilator effects of methanolic and aqueous extracts of Tribulus terrestris in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;104: Amin A, Lotfy M, Shafiullah M, Adeghate E. The protective effect of Tribulus terrestris in diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1084: Chu S, Qu W, Pang X, Sun B, Huang X. [Effect of saponin from Tribulus terrestris on hyperlipidemia]. Zhong Yao Cai. 2003;26: Zhang JD, Cao YB, Xu Z, et al. In vitro and in vivo antifungal activities of the eight steroid saponins from Tribulus terrestris L. with potent activity against 297
7 fluconazole-resistant fungal pathogens. Biol Pharm Bull. 2005;28: Adimoelja A. Phytochemicals and the breakthrough of traditional herbs in the management of sexual dysfunctions. Int J Androl. 2000;23 Suppl 2: Kianbakht S, Jahaniani F. Evaluation of antibacterial activities of Tribulus terrestris L. growing in Iran. Iran J Pharmacol Ther. 2003;2: Abbasoglu U, Tosun F. Antimicrobial activity of Tribulus terrestris L. growing in Turkey. Hacettepe Universitesi Eczacilik Fakultesi Dergisi. 1994;14: Al-Bayati FA, Al-Mola HF. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of different parts of Tribulus terrestris L. growing in Iraq. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2008;9: Kavitha P, Ramesh R, Bupesh G, Stalin A, Subramanian P. Hepatoprotective activity of Tribulus terrestris extract against acetaminophen-induced toxicity in a freshwater fish (Oreochromis mossambicus). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011;47: Zhang S, Li H, Yang SJ. Tribulosin protects rat hearts from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010;31: Kadry H, Abou BL, El GO, Temraz A. Antioxidant activity of aerial parts of Tribulus alatus in rats. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2010;23: Zhang S, Li H, Yang SJ. Tribulosin suppresses apoptosis via PKC epsilon and ERK1/2 signaling pathway during hypoxia/reoxygenation in neonatal rat ventricular cardiac myocytes. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2011;13: Wang SS, Ji YS, Li H, Yang SJ. [Mechanisms of gross saponins of Tribulus terrestris via activating PKCepsilon against myocardial apoptosis induced by oxidative stress]. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2009;44: Chinese. 14. Sharifi AM, Darabi R, Akbarloo N. Study of antihypertensive mechanism of Tribulus terrestris in 2K1C hypertensive rats: role of tissue ACE activity. Life Sci. 2003;73: Aggarwal A, Tandon S, Singla SK, Tandon C. Diminution of oxalate induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury and inhibition of calcium oxalate crystallization in vitro by aqueous extract of Tribulus terrestris. Int Braz J Urol. 2010;36: Kamboj P, Aggarwal M, Puri S, Singla SK. Effect of aqueous extract of Tribulus terrestris on oxalate-induced oxidative stress in rats. Indian J Nephrol. 2011;21: Clarkson MR, Friedewald JJ, Eustace JA, Rabb H. Acute kidney injury. In: Brenner BM, Livine SA, editors. Brenner & Rectore s the kidney. 8th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; p Thadhani R, Pascual M, Bonventre JV. Acute renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1996;334: Sutton TA, Fisher CJ, Molitoris BA. Microvascular endothelial injury and dysfunction during ischemic acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2002;62: Bonakdaran A, Falah Hosseini H, Khalighi Sigaroudi F, Ahvazi M. Investigation of the hypoglycemic effect of Tribulus terrestris extract on diabetic rats. J Med Plant. 2008;7: Martino-Andrade AJ, Morais RN, Spercoski KM, et al. Effects of Tribulus terrestris on endocrine sensitive organs in male and female Wistar rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;127: Ashtiyani SC, Najafi H, Kabirinia K, Vahedi E, Jamebozorky L. Oral omega-3 fatty acid for reduction of kidney dysfunction induced by reperfusion injury in rats. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2012;6: Ashtiyani SC, Najafi H, Firouzifar MR, Shafaat O. Grape seed extract for reduction of renal disturbances following reperfusion in rats. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2013;7: Moosavi SM, Ashtiyani SC, Hosseinkhani S, Shirazi M. Comparison of the effects of L: -carnitine and alphatocopherol on acute ureteral obstruction-induced renal oxidative imbalance and altered energy metabolism in rats. Urol Res. 2010;38: Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem. 1979;95: Benzie IF, Strain JJ. Ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay: direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fluids and modified version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration. Methods Enzymol. 1999;299: Kribben A, Edelstein CL, Schrier RW. Pathophysiology of acute renal failure. J Nephrol. 1999;12 Suppl 2:S142-S Adaikan PG, Gauthaman K, Prasad RN, Ng SC. Proerectile pharmacological effects of Tribulus terrestris extract on the rabbit corpus cavernosum. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2000;29: Arcasoy HB, Erenmemisoglu A, Tekol Y, Kurucu S, Kartal M. Effect of Tribulus terrestris L. saponin mixture on some smooth muscle preparations: a preliminary study. Boll Chim Farm. 1998;137: Millar TM, Phan V, Tibbles LA. ROS generation in endothelial hypoxia and reoxygenation stimulates MAP kinase signaling and kinase-dependent neutrophil recruitment. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;42: Vaziri ND. Causal link between oxidative stress, inflammation, and hypertension. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2008;2:1-10. Correspondence to: Saeed Changizi Ashtiyani, PhD Department of Physiology, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran dr.ashtiyani@arakmu.ac.ir Received April 2013 Revised October 2013 Accepted October 2013 Se Jin Park and Eun-Mi Ahn contributed to this article equally as first authors. 298
Grape Seed Extract for Reduction of Renal Disturbances Following Reperfusion in Rats
 Kidney Diseases Grape Seed Extract for Reduction of Renal Disturbances Following Reperfusion in Rats Saeed Changizi Ashtiyani, 1 Houshang Najafi, 2 Mohammad Reza Firouzifar, 3 Omid Shafaat 3 Original Paper
Kidney Diseases Grape Seed Extract for Reduction of Renal Disturbances Following Reperfusion in Rats Saeed Changizi Ashtiyani, 1 Houshang Najafi, 2 Mohammad Reza Firouzifar, 3 Omid Shafaat 3 Original Paper
Calcium Dobesilate for Prevention of Gentamicin-induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats
 KIDNEY DISEASES Calcium Dobesilate for Prevention of Gentamicin-induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats Mostafa Jafarey, 1 Saeed Changizi Ashtiyani, 2 Houshang Najafi 3 Original Paper 1Student Research Committee,
KIDNEY DISEASES Calcium Dobesilate for Prevention of Gentamicin-induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats Mostafa Jafarey, 1 Saeed Changizi Ashtiyani, 2 Houshang Najafi 3 Original Paper 1Student Research Committee,
Oral Administration of the Aqueous Extract of Rosmarinus Officinalis in Rats Before Renal Reperfusion Injury
 KIDNEY DISEASES Oral Administration of the Aqueous Extract of Rosmarinus Officinalis in Rats Before Renal Reperfusion Injury Saeed Changizi Ashtiyani, 1 Marzieh Zohrabi, 1 Akbar Hassanpoor, 2 Nasser Hosseini,
KIDNEY DISEASES Oral Administration of the Aqueous Extract of Rosmarinus Officinalis in Rats Before Renal Reperfusion Injury Saeed Changizi Ashtiyani, 1 Marzieh Zohrabi, 1 Akbar Hassanpoor, 2 Nasser Hosseini,
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
Introduction. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats
 Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note
![Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note](/thumbs/77/75431210.jpg) Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Excretion Chapter 29. The Mammalian Excretory System consists of. The Kidney. The Nephron: the basic unit of the kidney.
 Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Chapter 44: Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Name Period The steady-state physiological condition that organisms must maintain is termed homeostasis. Osmoregulation and excretion are frequently cited examples of homeostasis and are the central ideas
Name Period The steady-state physiological condition that organisms must maintain is termed homeostasis. Osmoregulation and excretion are frequently cited examples of homeostasis and are the central ideas
Case - Acute Renal Failure
 Case - Acute Renal Failure 73 yo diabetic F w hx of mild HBP but normal renal function develops infection of R foot. Over 1 week fever, chills, inflammation swelling of her R foot and leg. She takes Motrin
Case - Acute Renal Failure 73 yo diabetic F w hx of mild HBP but normal renal function develops infection of R foot. Over 1 week fever, chills, inflammation swelling of her R foot and leg. She takes Motrin
THE EFFECT OF ASCORBIC ACID ON RENAL FUNCTION IN DOGS WITH ISCHEMIA REPERFUSION INJURY
 Nigerian Veterinary Journal 2010 Vol 31(1):66-70 THE EFFECT OF ASCORBIC ACID ON RENAL FUNCTION IN DOGS WITH ISCHEMIA REPERFUSION INJURY KISANI 1 A.I* and AKINRIMADE 2 J.F 1 Department of Veterinary Surgery
Nigerian Veterinary Journal 2010 Vol 31(1):66-70 THE EFFECT OF ASCORBIC ACID ON RENAL FUNCTION IN DOGS WITH ISCHEMIA REPERFUSION INJURY KISANI 1 A.I* and AKINRIMADE 2 J.F 1 Department of Veterinary Surgery
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
In the name of GOD. Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension
 In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY GROSS ANATOMY Location *Bean-shaped *Retroperitoneal *At level of T12 L1 vertebrae. *The right kidney lies slightly inferior to left
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY GROSS ANATOMY Location *Bean-shaped *Retroperitoneal *At level of T12 L1 vertebrae. *The right kidney lies slightly inferior to left
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD, Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD, Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM Kidneys Stabilize the composition of the ECF (electrolyte, H
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD, Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM Kidneys Stabilize the composition of the ECF (electrolyte, H
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY
 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
1. remove: waste products: urea, creatinine, and uric acid foreign chemicals: drugs, water soluble vitamins, and food additives, etc.
 Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury
 Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury K. Ran 1, D.-L. Yang 1, Y.-T. Chang 1, K.-M. Duan 2, Y.-W. Ou 2, H.-P. Wang 3 and Z.-J. Li 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology,
Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury K. Ran 1, D.-L. Yang 1, Y.-T. Chang 1, K.-M. Duan 2, Y.-W. Ou 2, H.-P. Wang 3 and Z.-J. Li 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology,
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
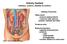 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance
 Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA. Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD. Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA. Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD. Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM Kidneys Stabilize the composition of the ECF (electrolyte,
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA. Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD. Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM Kidneys Stabilize the composition of the ECF (electrolyte,
Osmoregulation. 19 th March 2012
 Osmoregulation 19 th March 2012 1 Outline Body Fluid Regulation Aquatic Animals Marine Bony Fish Freshwater Bony Fish Terrestrial Animals Nitrogenous Waste Products Organs of Excretion Urinary System in
Osmoregulation 19 th March 2012 1 Outline Body Fluid Regulation Aquatic Animals Marine Bony Fish Freshwater Bony Fish Terrestrial Animals Nitrogenous Waste Products Organs of Excretion Urinary System in
Question 1: Solution 1: Question 2: Question 3: Question 4: Class X The Excretory System Biology
 A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
Basic Functions of the Kidneys
 Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Salt and Water Balance and Nitrogen Excretion
 Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
The Excretory System
 The Excretory System The excretory system The excretory system includes the skin, lungs and kidneys which all release metabolic wastes from the body. The kidneys, skin and the lungs are the principle organs
The Excretory System The excretory system The excretory system includes the skin, lungs and kidneys which all release metabolic wastes from the body. The kidneys, skin and the lungs are the principle organs
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
The role of microcirculatory and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsisinduced acute kidney injury (AKI): a. model of sepsis-induced organ dysfunction
 The role of microcirculatory and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsisinduced acute kidney injury (AKI): a model of sepsis-induced organ dysfunction Hernando Gomez, MD Mentors: Michael R. Pinsky, MD John
The role of microcirculatory and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsisinduced acute kidney injury (AKI): a model of sepsis-induced organ dysfunction Hernando Gomez, MD Mentors: Michael R. Pinsky, MD John
Functions of the kidney
 Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM
 AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
Reperfusion Injury: How Can We Reduce It?
 MI/CAD: Practical Question in Management of AMI Patients Reperfusion Injury: How Can We Reduce It? Hyun-Jai Cho, M.D., Ph.D Cardiovascular Center & Department of Internal Medicine Seoul National University
MI/CAD: Practical Question in Management of AMI Patients Reperfusion Injury: How Can We Reduce It? Hyun-Jai Cho, M.D., Ph.D Cardiovascular Center & Department of Internal Medicine Seoul National University
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Contrast Induced Nephropathy
 Contrast Induced Nephropathy O CIAKI refers to an abrupt deterioration in renal function associated with the administration of iodinated contrast media O CIAKI is characterized by an acute (within 48 hours)
Contrast Induced Nephropathy O CIAKI refers to an abrupt deterioration in renal function associated with the administration of iodinated contrast media O CIAKI is characterized by an acute (within 48 hours)
The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion. What are the functions of the urinary system? Maintenance of water-salt and acidbase
 10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
Urinary system. Lab-7
 Urinary system Lab-7 Excretion: processes that remove wastes and excess materials from the body Urinary system (kidneys): excretes nitrogenous wastes, excess solutes, and water The Kidneys Regulate Water
Urinary system Lab-7 Excretion: processes that remove wastes and excess materials from the body Urinary system (kidneys): excretes nitrogenous wastes, excess solutes, and water The Kidneys Regulate Water
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Renal Pharmacology. Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics BIMM118
 Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
shehab Moh Tarek ... ManarHajeer
 3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
Renal-Related Questions
 Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX
 One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Chapter 13 The Urinary System
 Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
** Accordingly GFR can be estimated by using one urine sample and do creatinine testing.
 This sheet includes the lecture and last year s exam. When a patient goes to a clinic, we order 2 tests: 1) kidney function test: in which we measure UREA and CREATININE levels, and electrolytes (Na+,
This sheet includes the lecture and last year s exam. When a patient goes to a clinic, we order 2 tests: 1) kidney function test: in which we measure UREA and CREATININE levels, and electrolytes (Na+,
Class XI Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Biology
 Class XI Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Biology Question 1: Define Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) Glomerular filtration rate is the amount of glomerular filtrate formed in all the
Class XI Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Biology Question 1: Define Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) Glomerular filtration rate is the amount of glomerular filtrate formed in all the
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
Excretory System. Biology 2201
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System. Excretory System
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB
 COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB CG Musso ¹, J Reynaldi¹, N Imperiali ¹, L Algranati ¹, DG Oreopoulos ² Nephrology Department Hospital Italiano
COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB CG Musso ¹, J Reynaldi¹, N Imperiali ¹, L Algranati ¹, DG Oreopoulos ² Nephrology Department Hospital Italiano
Renal Functions: Renal Functions: Renal Function: Produce Urine
 Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
