The Preventive Effect of Atorvastatin on Paraquat-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in the Rats
|
|
|
- Lucas Ryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin Adv Pharm Bull, 2014, 4(x), x-x doi: /apb Research Article The Preventive Effect of Atorvastatin on Paraquat-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in the Rats Mohammad Javad Khodayar 1,2 *, Milad Kiani 1, Ali Asghar Hemmati 1, Anahita Rezaie 3, Mohammad Rahim Zerafatfard 1, Mohammad Reza Rashidi Nooshabadi 1, Mehdi Goudarzi 1 1 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, School of Pharmacy, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran. 2 Toxicology Research Center, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran. 3 Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Shahid Chamran University, Ahvaz, Iran. Article History: Received: 29 September 2013 Revised: 1 February 2014 Accepted: 1 February 2014 Available Online: 2 Feb Keywords: Paraquat Pulmonary fibrosis Atorvastatin Rat Abstract Purpose: Pulmonary fibrosis is a potentially lethal inflammatory disease and there has been no effective medication for this progressive disease up to now. As a model, different therapeutic approaches have been applied for paraquat-induced pulmonary injury and fibrosis. Atorvastatin besides cholesterol-lowering effects possesses anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties. The current study was designed to investigate the preventive antifibrotic effects of atorvastatin on paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Methods: The rats were randomly divided into five experimental groups. Group I, control group (saline), group II received a single oral dose of 20 mg/kg paraquat with no treatment and III, IV and V groups received atorvastatin at the doses of 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg/day orally one week before and three weeks after paraquat administration, respectively. The rats were sacrificed 21 days after paraquat. Lung hydroxyproline and serum levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) were determined and lung indices and semi-quantitative histopathological changes were evaluated. Results: Paraquat could significantly increase the serum MDA and lung hydroxyproline levels. Elevated content of tissue hydroxyproline and serum levels of malondialdehyde induced by paraquat, attenuated by atorvastatin at the doses of 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg. Furthermore, histopathological findings and the amount of lung indices showed the beneficial preventive role of atorvastatin in rat pulmonary fibrosis induced by paraquat. Conclusion: In conclusion, the present data show that atorvastatin alleviate the toxic effects of paraquat under the experimental circumstances and may be a useful agent in cases who are in contact or poisoned with paraquat. Introduction Pulmonary fibrosis may result from a variety of acute and chronic lung disorders. The great accumulation of matrix proteins such as collagen produced by fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, thicken and damage alveolar walls and reduce elasticity, widening of interstitial matrix and development of lung fibrosis. 1 Although specific treatments for fibrotic lung diseases are not yet available, control and prevention of inflammatory events might delay progress of the fibrotic events. Corticosteroids are usually administered to control the inflammation in fibrotic lungs; however, the useful effects of these agents are not well established. 2 The progression of pulmonary fibrosis is closely related to a complicated network consisting of many cytokines, chemical mediators, growth factors and biophysical peptides derived from inflammatory immune cells, alveolar type II cells and endothelial cells. 3 Paraquat (C12 H14 N2), a bipyridyl and non-selective quaternary nitrogen herbicide, is commonly used all around the world. Paraquat a highly toxic herbicide causes fatal pulmonary damage. Although liver, kidney, heart and central nervous system are affected, lung damage and pulmonary fibrosis are the most widespread injuries and the usual causes of death. Lung tissue and particularly the type II pneumocytes accumulate paraquat by a selective and active polyamine uptake procedure. 4,5 The mechanism of paraquat toxicity has not been fully understood. The main potential mechanism is producing the superoxide radicals. 6,7 The chemical cascades leading to the reduction of paraquat and the generation of free radicals and lipid peroxidation may create lethal lesions associated with intra-alveolar fibrosis resulting in lung failure. 8,9 The pulmonary toxicity of paraquat occurs in two different phases. The first is a damage and demolition of alveolar epithelial cells causing edema and hemorrhage. The second is to infiltrate myofibroblasts into the alveolar spaces and septa and differentiation in fibroblasts by producing *Corresponding author: Mohammad Javad Khodayar, Tel: , khodayar-mj@ajums.ac.ir 2014 The Authors. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, as long as the original authors and source are cited. No permission is required from the authors or the publishers.
2 Khodayar et al. collagen. 10,11 At present no specific antidote or effective treatment is proposed for paraquat toxicity and poisoning. Since there are no known pharmacological antidote for paraquat, the management of paraquat poisoning has been predominantly limited either to decrease its absorption or to increase its elimination. 12 Currently different treatment strategies that prevent or reverse the lipid peroxidation at the cellular level and reduce the pulmonary collagen synthesis had been reported. 13,14 Statins, which are HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, belong to a class of drugs that lowers the level of cholesterol in the blood. Statins may have also antifibrotic function. Statins block hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzymea reductase (HMG-CoA reductase), which takes part in liver synthesis of cholesterol. Recent research shows that statins reduce inflammation. Reduction of inflammation by statins is independent of statins ability to reduce cholesterol. Furthermore, anti-inflammatory effects of statins can be seen as early as two weeks after starting statin treatment. 15,16 In recent years, several studies have shown these positive effects of statins to be due both to their lipid lowering and to anti-inflammatory effect. 17 Positive results in experimental efforts have been obtained through the anti-inflammatory efficacy of statins in numerous respiratory disease models such as smokinginduced emphysema, asthma, Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF), pulmonary hypertension, acute lung injury and lung transplantation. Materials and Methods Animals Thirty female Sprague Dawley rats, 8 weeks old, weighting 200±25 g were purchased from the experimental research center, medical science university of Jundishapur (Iran, Ahvaz). Rats were housed in a specific cage in 24 h light/dark cycle and allowed with free access to water and food. All the ethical issues were considered based on the Ahvaz Medical University Ethical Protocols (AMUEP) on animal experiments. Reagents Atorvastatin was obtained from Exir pharmaceutical manufacturing company (Borujerd, Iran). Paraquat (methyl viologen) and other chemicals were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St Louis, MO, USA). Experiment Protocols To investigate whether atorvastatin modulates paraquatinduced pulmonary fibrosis, the rats were randomly divided into five experimental groups (six rats in each group). Group I, control group (saline), group II received a single oral dose of 20 mg/kg paraquat with no treatment and III, IV and V groups received atorvastatin at the doses of 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg/day orally one week before and three weeks after paraquat administration, respectively. The rats were sacrificed 21 days after paraquat. Body Weight and Lung Index In the course of the experiment, the body weight of rats was measured every 7 days. After sacrifice, the lung index was expressed as the ratio of wet lung weight (mg) to body weight (g). Lipid peroxidation assay The serum malondialdehyde (MDA) levels as a measurement of oxidative stress were determined by the method described by Hemmati. 18 Values obtained were compared with a series of standard Solutions (1, 1, 3, 3- tetraethoxypropane). The serum samples were obtained by collecting 1ml blood from the left ventricle, centrifuging at 1000g for 5min, and diluting 20 times with phosphate buffer solution (ph = 7.4). Results were expressed as µmol/l. Histopathological examination Rat lungs on day 21 after paraquat administration were inflated with a buffered 10% formalin solution for 24 h and embedded in paraffin. Sections (3 µm) were stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histological examination. The Ashcroft score was used for semiquantitative assessment of fibrotic changes. The severity of fibrotic changes in each histological section of the lung was assessed as the mean score of severity from observing microscopic fields. Twenty five fields in each rat lung section were analyzed. After examination of the whole fields of the section, the mean of the scores from all fields was considered as the fibrotic score. The entire lung section was reviewed at a magnification of 100. A score ranging from zero (normal lung) to eight (total fibrosis) was assigned. The mean score of all fields was taken as a fibrosis score of that lung section. Criteria for grading pulmonary fibrosis were as follows: A grade 0 normal lung; 1=minimal fibrosis thickening of alveolar or bronchial walls; 2 3=moderate thickening of the walls without obvious damage to the lung architecture; 4 5= increased fibrosis with definite damage to lung architecture and formation of fibrotic bands or small fibrotic mass; 6 7=severe distortion of structure and large fibrotic are as; honeycomb lung was placed in this category and grade 8 indicates a total fibrotic change of the field. The mean score of all fields was taken as the fibrosis score of that lung section. 19 Hydroxyproline assay The lung hydroxyproline of the left lung was measured using a colorimetric assay on day 21 after paraquat. 20 In brief, the minced left lung lobes were homogenized in 6 molar HCl and hydrolyzed for five hours at 130 C. The ph was adjusted to with NaOH, and the sample volume was adjusted to 30 ml with distilled water. The sample solution (1.0 ml) was mixed with 1.0 ml of chloramine T solution (0.05 mol/l), and then 2 Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2014, 4(x), x-x
3 Atorvastatin prevent paraquat pulmonary fibrosis the mixture was incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes. When 1.0 ml of 20% dimethyl benzaldehyde solution was added, the mixture was incubated at 60 C for 20 minutes. The absorbance of each sample at 550 nm was measured. The results were calculated as mg hydroxyproline per g wet lung weight using hydroxyproline standards. Statistical analysis Data were expressed as mean±sem. Statistical analysis was carried out by analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey s post hoc tests. All analyses were made using the SPSS version 16 and the probability value of less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Results Lung indices The lung index (wet lung weight/body weight) in the control group was significantly lower compared with the paraquat group on day 28. However, the rats received atorvastatin (10 and 20 mg/kg) significantly lower lung index compared with the paraquat group (Figure 1). Figure 2. Effect of pretreatment with atorvastatin at the doses of 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg on hydroxyproline content in the lungs of rats with pulmonary fibrosis. Each column represents mean ± SEM of hydroxyproline; a significant increase of hydroxyproline in paraquat group in comparison with the control group ( # P< 0.05); a significant decrease of hydroxyproline in atorvastatin groups in comparison with the paraquat group (*P< 0.05 and ***p<0.001). The analysis of oxidative stress marker A significant rise was observed in MDA level in serum of rat exposed to paraquat which is an index of lipid peroxidation, when compared with the control group (#p < 0.001). As shown in Figure 3, the decrease in MDA level was observed in pretreated rats by atorvastatin (*p<0.05 and ***p<0.001). Figure 1. Effect of atorvastatin pretreatment at the doses of 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg on lung index of rats in paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Each column represents mean lung index ± SEM. # A significant increase of the lung index in the paraquat group in comparison with the control group (P< 0.05).* A significant decrease of the lung index in atorvastatin groups at the doses of 10 and 20 mg/kg in comparison with the paraquat group (P< 0.05). Assessment of lung fibrosis by measurement of hydroxyproline Lung fibrosis was assessed by measuring the hydroxyproline content in lungs as an index of collagen accumulation. A comparison of hydroxyproline contents among the 5 groups was shown in Figure 2. Paraquat treatment produced a significant increase in the hydroxyproline levels. This increment was prevented by atorvastatin. The light microscopic findings Photomicrographic evaluation of pulmonary fibrosis by infiltration of fibroblast, inflammatory cells and extracellular matrix showed grade 0 for control and grade 8 more prominent for paraquat group. The rat pretreated by atorvastatin showed grade 6-7 for the dose of 10 mg/kg of atorvastatin and grade 4-5 more evident for the lung photomicrographs in the dose of 20 and 40 mg/kg of atorvastatin (Figure 4). Discussion This study inquired whether pretreatment and continuing treatment with atorvastatin might attenuate pulmonary fibrosis following paraquat administration in rat. Because inflammation and fibrosis are the two determinants of the development of pulmonary fibrosis, potentially beneficial anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects of atorvastatin on paraquat induced pulmonary fibrosis were measured. In this study, atorvastatin had the following effects in paraquatinduced pulmonary fibrosis as a popular model of human pulmonary fibrosis: (a) attenuating the increase of inflammatory cells and hydroxyproline and collagen content in lung tissue, (b) alleviation of paraquatinduced increases in the MDA levels that may be through an increase in antioxidant enzyme activities in Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2014, 4(x), x-x 3
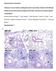
4 Khodayar et al. the damaged lung tissue of rats. Antioxidant treatments have been extensively investigated in human IPF and paraquat-induced lung fibrosis in rat. The rational for this approach presumes that the progressive fibrosis that characterized IPF results from chronic persistent inflammation. The existence of chronic inflammation in lung tissue ultimately leads fibrosis. However, aggressive suppression of this inflammation will block the subsequent accumulation of matrix proteins such as collagen formation, proliferation of fibroblasts and recruitment of inflammatory cells. Reduced MDA level of rats pretreated with atorvastatin may be suggest the antioxidant activity of the drug. It has been reported that statins exert anti-inflammatory effects in numerous tissues via the activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), which regulates important cellular functions, such as glucose and lipid catabolism, cellular differentiation, proliferation and survival Anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic activity of atorvastatin has been viewed as a promising therapeutic target for bladder cancer. 24 Furthermore, the effects of statins, namely of atorvastatin, seem to be potentiated by cycloxygenase (COX) -2 inhibitors. 25 These data suggest the role of inflammation in lung fibrosis and the putative relevance of preventive strategies based on antiinflammatory activity, such as demonstrated by atorvastatin in the present study. This observation may have significance for the present study because of pathobiological similarity between high altitude pulmonary edema and paraquat-induced lung fibrosis in which free radical formation may play an important role. Possible mechanism of the preventive role of atorvastatin on high altitude pulmonary edema seems to be its free radical scavenging activity. Figure 3. Effect of pretreatment with atorvastatin at the doses of 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg on serum MDA of rats with pulmonary fibrosis. Each column represents mean MDA ± SEM; a significant increase of MDA in paraquat group in comparison with the control group ( # P< 0.05); a significant decrease of MDA in atorvastatin treated groups in comparison with the paraquat group (*P< 0.05 and ***p<0.001). Conclusion The findings of the current study illustrate that paraquat administration resulted in lung fibrosis in rats via increased oxidative stress and atorvastatin significantly prevented the fibrosis events through its potent free radical scavenging and antioxidant properties. The data suggest that atorvastatin is a highly promising agent in protecting early lung tissue damage induced by paraquat exposure or in the treatment of IPF. Acknowledgments This paper was extracted from Milad Kiani's Pharm.D thesis that was submitted in the School of Pharmacy of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences and financially supported by a grant of Toxicology Research Center of this university. Conflict of Interest There is no conflict of interest to be reported. Figure 4.The figures are representatives of the lungs from animals in each treatment group. Lung tissues were stained 21 days after administration of paraquat in saline with H&E. Appearance of rat lungs in different groups: (A) control (B) paraquat (C) paraquat treated with 10 mg/kg atorvastatin (D) paraquat treated with 20 mg/kg atorvastatin and (E) paraquat treated with 40 mg/kg atorvastatin. Lung paranchyma of control is well-preserved and intact. Extensive interstitial infiltration and fibrosis showing in group (B). A marked prevention of the paraquat-induced histological changes was seen in the rat lungs in groups (D) and (E). 4 Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2014, 4(x), x-x
5 Atorvastatin prevent paraquat pulmonary fibrosis References 1. Green FH. Overview of pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2002;122(6 Suppl):334S-9S. 2. Kroegel C, Mock B, Hengst U, Reissig A. Interferongamma-1b: therapeutic option in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Respiration 2004;71(6): Yao HW, Zhu JP, Zhao MH, Lu Y. Losartan attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Respiration 2006;73(2): Rose MS, Smith LL, Wyatt I. Evidence for energydependent accumulation of paraquat into rat lung. Nature 1974;252(5481): Forman HJ, Aldrich TK, Posner MA, Fisher AB. Differential paraquat uptake and redox kinetics of rat granular pneumocytes and alveolar macrophages. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1982;221(2): Smith LL. The toxicity of paraquat. Adverse Drug React Acute Poisoning Rev 1988;7(1): Aldrich TK, Fisher AB, Cadenas E, Chance B. Evidence for lipid peroxidation by paraquat in the perfused rat lung. J Lab Clin Med 1983;101(1): Carre P, Leophonte P. Cytokines and pulmonary fibroses. Rev Mal Respir 1993;10(3): Melchiorri D, Reiter RJ, Sewerynek E, Hara M, Chen L, Nistico G. Paraquat toxicity and oxidative damage. Reduction by melatonin. Biochem Pharmacol 1996;51(8): Vijeyaratnam GS, Corrin B. Experimental paraquat poisoning: a histological and electron-optical study of the changes in the lung. J Pathol 1971;103(2): Smith LL, Rose MS. A comparison of the effects of paraquat and diquat on the water content of rat lung and the incorporation of thymidine into lung DNA. Toxicology 1977;8(2): Suntres ZE, Hepworth SR, Shek PN. Protective effect of liposome-associated alpha-tocopherol against paraquat-induced acute lung toxicity. Biochem Pharmacol 1992;44(9): Shahar E, Keidar I, Hertzeg E, Barzilay Z. Effectiveness of vitamin E and colchicine in amelioration of paraquat lung injuries using an experimental model. Isr J Med Sci 1989;25(2): Kojima S, Miyazaki Y, Honda T, Kiyozumi M, Shimada H, Funakoshi T. Effect of L-cystine on toxicity of paraquat in mice. Toxicol Lett 1992;60(1): Lardizabal JA, Deedwania PC. Benefits of statin therapy and compliance in high risk cardiovascular patients. Vasc Health Risk Manag 2010;6: Tousoulis D, Charakida M, Stefanadi E, Siasos G, Latsios G, Stefanadis C. Statins in heart failure. Beyond the lipid lowering effect. Int J Cardiol 2007;115(2): Greenwood J, Steinman L, Zamvil SS. Statin therapy and autoimmune disease: from protein prenylation to immunomodulation. Nat Rev Immunol 2006;6(5): Hemmati AA, Nazari Z, Samei M. A comparative study of grape seed extract and vitamin E effects on silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 2008;21(4): Ashcroft T, Simpson JM, Timbrell V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J Clin Pathol 1988;41(4): Woessner JF Jr. The determination of hydroxyproline in tissue and protein samples containing small proportions of this imino acid. Arch Biochem Biophys 1961;93: Balakumar P, Mahadevan N. Interplay between statins and PPARs in improving cardiovascular outcomes: a double edged sword? Br J Pharmacol 2012;165(2): Paumelle R, Blanquart C, Briand O, Barbier O, Duhem C, Woerly G, et al. Acute antiinflammatory properties of statins involve peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor-alpha via inhibition of the protein kinase C signaling pathway. Circ Res 2006;98(3): Moraes LA, Piqueras L, Bishop-Bailey D. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and inflammation. Pharmacol Ther 2006;110(3): Mansure JJ, Nassim R, Kassouf W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in bladder cancer: a promising therapeutic target. Cancer Biol Ther 2009;8(7): Zheng X, Cui XX, Avila GE, Huang MT, Liu Y, Patel J, et al. Atorvastatin and celecoxib inhibit prostate PC-3 tumors in immunodeficient mice. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13(18 Pt 1): Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2014, 4(x), x-x 5
European Respiratory Society Annual Congress. Presented at: of new drugs for respiratory diseases. Barcelona, Spain, September 7-11, 2013 Page 1
 PBI-4050, a novel first-in-class anti-fibrotic compound, reduces lung fibrosis in the bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis model: a comparative study with pirfenidone Presented at: Thematic Poster Session:
PBI-4050, a novel first-in-class anti-fibrotic compound, reduces lung fibrosis in the bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis model: a comparative study with pirfenidone Presented at: Thematic Poster Session:
Green tea extract Its potential protective effect on bleomycin induced lung injuries in rats
 Green tea extract Its potential protective effect on bleomycin induced lung injuries in rats Azza H. EL-Medany, Jamila EL-Medany The interest in the use of plant extracts in the treatment of several diseases
Green tea extract Its potential protective effect on bleomycin induced lung injuries in rats Azza H. EL-Medany, Jamila EL-Medany The interest in the use of plant extracts in the treatment of several diseases
Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II
 Pathobasic Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II Spasenija Savic Prince Pathology Program Systematic approach to surgical lung biopsies with ILD Examples (chronic ILD): Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: UIP,
Pathobasic Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II Spasenija Savic Prince Pathology Program Systematic approach to surgical lung biopsies with ILD Examples (chronic ILD): Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: UIP,
Disclosures. Traditional Paradigm. Overview 4/17/2010. I have relationships with the following organizations and companies:
 Disclosures Pharmacological Therapy for ILD What to Use and How to Use It Harold R Collard MD Interstitial Lung Disease Program University of California San Francisco (UCSF) I have relationships with the
Disclosures Pharmacological Therapy for ILD What to Use and How to Use It Harold R Collard MD Interstitial Lung Disease Program University of California San Francisco (UCSF) I have relationships with the
Ebrahim Abbasi Oshaghi 1,2
 1 2 Flaxseed normalized antioxidant status and also changed ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes expression in diabetic rat Fatemeh Mirzaei 1,Mona Pourjafarr 1, Seyyed Alireza Vafaei 1, Rezvan Mostoli 1, Ebrahim Abbasi
1 2 Flaxseed normalized antioxidant status and also changed ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes expression in diabetic rat Fatemeh Mirzaei 1,Mona Pourjafarr 1, Seyyed Alireza Vafaei 1, Rezvan Mostoli 1, Ebrahim Abbasi
7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY. 7.1 Introduction
 268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
CONSEQUENCES OF METHYL MERCURY EXPOSURE ON LUNG HISTO-ARCHITECTURE IN RAT Y. Nagamalleswari 1, V. Reddy Dhyana 2, V. Karunasri 3 and P.
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 2, 2017, 1095 1099 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) CONSEQUENCES OF METHYL MERCURY EXPOSURE ON LUNG HISTO-ARCHITECTURE IN RAT Y.
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 2, 2017, 1095 1099 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) CONSEQUENCES OF METHYL MERCURY EXPOSURE ON LUNG HISTO-ARCHITECTURE IN RAT Y.
Restrictive lung diseases
 Restrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases are diseases that affect the interstitium of the lung. Interstitium of the lung is the very thin walls surrounding the alveoli, it s formed of epithelium
Restrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases are diseases that affect the interstitium of the lung. Interstitium of the lung is the very thin walls surrounding the alveoli, it s formed of epithelium
B reast cancer is the most common cancer among women and also the second leading
 Original Article Caspian J Intern Med 2017; 8(4):264-268 DOI: 10.22088/cjim.8.4.264 Mostafa Taherkhani (MSc) 1, 2 Soleiman Mahjoub (PhD) *2, 3 Dariush Moslemi (MD) 4 Ahmad Karkhah (MD) 2 1. Student Research
Original Article Caspian J Intern Med 2017; 8(4):264-268 DOI: 10.22088/cjim.8.4.264 Mostafa Taherkhani (MSc) 1, 2 Soleiman Mahjoub (PhD) *2, 3 Dariush Moslemi (MD) 4 Ahmad Karkhah (MD) 2 1. Student Research
Hesperidin. Keep Health, Keep Happiness
 Hesperidin Kang-Hui Keep Health, Keep Happiness Table of Contents 01 Brief Introduction 03 Functions 02 Technical Description 04 Experimental Data 05 Product Application 06 Highlights Brief Introduction
Hesperidin Kang-Hui Keep Health, Keep Happiness Table of Contents 01 Brief Introduction 03 Functions 02 Technical Description 04 Experimental Data 05 Product Application 06 Highlights Brief Introduction
C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate. than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Short-Term Doxorubicin Treatment
 Original Article C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate Acta Cardiol Sin 2012;28:236 240 Heart Failure & Cardiomyopathy C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Original Article C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate Acta Cardiol Sin 2012;28:236 240 Heart Failure & Cardiomyopathy C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy
i-bodies a new class of protein therapeutics to treat fibrosis
 i-bodies a new class of protein therapeutics to treat fibrosis BIOSHARES JULY 2017 Sam Cobb, CEO and Managing Director AdAlta Limited (ASX:1AD) s.cobb@adalta.com.au Disclaimer Investment in AdAlta is subject
i-bodies a new class of protein therapeutics to treat fibrosis BIOSHARES JULY 2017 Sam Cobb, CEO and Managing Director AdAlta Limited (ASX:1AD) s.cobb@adalta.com.au Disclaimer Investment in AdAlta is subject
5/9/2015. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Original Article TLR4 contributes to mechanical ventilation induced lung injury in the rabbits
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4700-4704 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0040416 Original Article TLR4 contributes to mechanical ventilation induced lung injury in the rabbits Hongmei Zhang 1, Pei
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4700-4704 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0040416 Original Article TLR4 contributes to mechanical ventilation induced lung injury in the rabbits Hongmei Zhang 1, Pei
Dynamic changes of found in inflammatory zone 1 protein and mrna expression in the lung with experimental pulmonary fibrosis of the rat
 Acta Physiologica Sinica, August 25, 2005, 57 (4): 493-497 http://www.actaps.com.cn 493 FIZZ1 mrna 1 2, * 1 1 1 430022 2 430030 FIZZ1 (found in inflammatory zone 1) (5 mg/kg ) HE Masson FIZZ1 mrna (1)
Acta Physiologica Sinica, August 25, 2005, 57 (4): 493-497 http://www.actaps.com.cn 493 FIZZ1 mrna 1 2, * 1 1 1 430022 2 430030 FIZZ1 (found in inflammatory zone 1) (5 mg/kg ) HE Masson FIZZ1 mrna (1)
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung
 IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia. Nitra and the Gangs.
 Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
For unclear reasons, only about 40% of patients with calcific aortic stenosis also have coronary
 Αθηροσκλήρωση και ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας. Οµοιότητες και διαφορές Ν. Μεζίλης Κλινική «Άγιος Λουκάς» Ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας: Μία ακόµα µορφή αθηρωµάτωσης; Some observations
Αθηροσκλήρωση και ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας. Οµοιότητες και διαφορές Ν. Μεζίλης Κλινική «Άγιος Λουκάς» Ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας: Μία ακόµα µορφή αθηρωµάτωσης; Some observations
Introduction. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats
 Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Micro-Anatomical Effect Of Tahitian Noni Dietary Supplement On The Heart Of Caffeine-Treated SpragueDawley Rats
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 2 Micro-Anatomical Effect Of Tahitian Noni Dietary Supplement On The Heart Of Caffeine-Treated SpragueDawley Rats R Bassey, O Yama, A Osinubi,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 2 Micro-Anatomical Effect Of Tahitian Noni Dietary Supplement On The Heart Of Caffeine-Treated SpragueDawley Rats R Bassey, O Yama, A Osinubi,
An amino acid for a healthy heart
 AOR CODE: AOR04054 Premium Arginine An amino acid for a healthy heart A natural nitric oxide precursor Protects the heart from high blood sugar levels Helps in cellular energy production Gluten Free Vegan
AOR CODE: AOR04054 Premium Arginine An amino acid for a healthy heart A natural nitric oxide precursor Protects the heart from high blood sugar levels Helps in cellular energy production Gluten Free Vegan
Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded
 BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
2.5. AMPK activity
 Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
HEPATIC CELL INJURY BY ETHINYL OESTRADIOL ESTROGEN Pandey Govind a*, Pandey S.P. b and Madhuri S. c
 Research Article HEPATIC CELL INJURY BY ETHINYL OESTRADIOL ESTROGEN Pandey Govind a*, Pandey S.P. b and Madhuri S. c a* Ex-Professor & Head of Pharmacology (Pharmacy), presently Officer-In-Charge of Rinder
Research Article HEPATIC CELL INJURY BY ETHINYL OESTRADIOL ESTROGEN Pandey Govind a*, Pandey S.P. b and Madhuri S. c a* Ex-Professor & Head of Pharmacology (Pharmacy), presently Officer-In-Charge of Rinder
To determine the effect of over-expression and/or ligand activation of. PPAR / on cell cycle, cell lines were cultured as described above until ~80%
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell cycle analysis To determine the effect of over-expression and/or ligand activation of PPAR / on cell cycle, cell lines were cultured as described above until ~80%
Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell cycle analysis To determine the effect of over-expression and/or ligand activation of PPAR / on cell cycle, cell lines were cultured as described above until ~80%
CTD-related Lung Disease
 13 th Cambridge Chest Meeting King s College, Cambridge April 2015 Imaging of CTD-related Lung Disease Dr Sujal R Desai King s College Hospital, London Disclosure Statement No Disclosures / Conflicts of
13 th Cambridge Chest Meeting King s College, Cambridge April 2015 Imaging of CTD-related Lung Disease Dr Sujal R Desai King s College Hospital, London Disclosure Statement No Disclosures / Conflicts of
A. Incorrect! The alveolus is where gas exchange takes place. B. Correct! Surfactant is the lipid-rich material that permits lung inflation.
 Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Oxidative Stress Unify the Pathophysiological Mechanism of Experimental Hypertension and Diabetes of Spontaneously Hypertensive Stroke-Prone Rats
 Oxidative Stress Unify the Pathophysiological Mechanism of Experimental Hypertension and Diabetes of Spontaneously Hypertensive Stroke-Prone Rats Stenio Fiorelli¹, Camille F França¹, Carlos Alberto Basílio
Oxidative Stress Unify the Pathophysiological Mechanism of Experimental Hypertension and Diabetes of Spontaneously Hypertensive Stroke-Prone Rats Stenio Fiorelli¹, Camille F França¹, Carlos Alberto Basílio
Original paper. Abstract. Abdullah S. Asia 1*, Al-Mahdi A. Modar 2, Hadi M. Ali 3
 Original paper Frequency Of Potential Adverse Effects Of A Semisynthetic Statin (Simvastatin) Compared To A Synthetic Statin (Atorvastatin) Used To Reduce Cardiovascular Risk For Patients In Basra 1*,
Original paper Frequency Of Potential Adverse Effects Of A Semisynthetic Statin (Simvastatin) Compared To A Synthetic Statin (Atorvastatin) Used To Reduce Cardiovascular Risk For Patients In Basra 1*,
Case 4 History. 58 yo man presented with prox IP joint swelling 2 months later pain and swelling in multiple joints Chest radiograph: bi-basilar
 Case 4 History 58 yo man presented with prox IP joint swelling 2 months later pain and swelling in multiple joints Chest radiograph: bi-basilar basilar infiltrates suggestive of pulmonary fibrosis Open
Case 4 History 58 yo man presented with prox IP joint swelling 2 months later pain and swelling in multiple joints Chest radiograph: bi-basilar basilar infiltrates suggestive of pulmonary fibrosis Open
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Aslı Korkmaz* and Prof. Dr. Dürdane Kolankaya**
 The possible protective effects of some flavonoids that found honey by experimental ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) induced nitrosative damage in kidney of male rats Assoc. Prof. Dr. Aslı Korkmaz* and Prof.
The possible protective effects of some flavonoids that found honey by experimental ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) induced nitrosative damage in kidney of male rats Assoc. Prof. Dr. Aslı Korkmaz* and Prof.
Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction Gocmen Gokhan 1 *, Gonul O 1, Oktay NS 2, Pisiriciler R 2 and Goker
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction Gocmen Gokhan 1 *, Gonul O 1, Oktay NS 2, Pisiriciler R 2 and Goker
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Rock et al. 10.1073/pnas.1117988108 Fig. S1. Heterogeneity of stromal cells in normal and fibrotic mouse lungs. Sections of normal mouse lungs (A and D) and fibrotic lungs collected
Supporting Information Rock et al. 10.1073/pnas.1117988108 Fig. S1. Heterogeneity of stromal cells in normal and fibrotic mouse lungs. Sections of normal mouse lungs (A and D) and fibrotic lungs collected
MUCINAC 600 Tablets (Acetylcysteine)
 Published on: 10 Jul 2014 MUCINAC 600 Tablets (Acetylcysteine) Composition MUCINAC 600 Tablets Each effervescent tablet contains: Acetylcysteine 600 mg Dosage Form Oral Tablet Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics
Published on: 10 Jul 2014 MUCINAC 600 Tablets (Acetylcysteine) Composition MUCINAC 600 Tablets Each effervescent tablet contains: Acetylcysteine 600 mg Dosage Form Oral Tablet Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics
Fish Skin Grafts Promote Superior Cell Ingrowth Compared to Amnion Allografts, Human Cadaver Skin and Mammalian Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
 Fish Skin Grafts Promote Superior Cell Ingrowth Compared to Amnion Allografts, Human Cadaver Skin and Mammalian Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Christopher L. Winters, DPM American Health Network Indianapolis,
Fish Skin Grafts Promote Superior Cell Ingrowth Compared to Amnion Allografts, Human Cadaver Skin and Mammalian Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Christopher L. Winters, DPM American Health Network Indianapolis,
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
INFLUENCE OF MELATONIN ON ARSENIC MEDIATED PANCREATIC DAMAGE IN SWISS ALBINO MICE
 INFLUENCE OF MELATONIN ON ARSENIC MEDIATED PANCREATIC DAMAGE IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DIMPLE DAMORE Bhavan s Sheth R.A.College of Science, Gujarat University, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India INTRODUCTION Arsenic
INFLUENCE OF MELATONIN ON ARSENIC MEDIATED PANCREATIC DAMAGE IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DIMPLE DAMORE Bhavan s Sheth R.A.College of Science, Gujarat University, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India INTRODUCTION Arsenic
New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma
 July 2016 New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma Contributed by: Laurel Rose, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Medicine,
July 2016 New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma Contributed by: Laurel Rose, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Medicine,
Catechins Green Tea Clones GMB4 Inhibit Inflammation Process of Atherosclerosis Through Decreasing TNF-Α Levels. *
 J. Islamic Pharm. Vol. 01 (01) 2016 28 Catechins Green Tea Clones GMB4 Inhibit Inflammation Process of Atherosclerosis Through Decreasing TNF-Α Levels Erna Susanti *1, Febiyanti Suratno 2 1 Pharmacy and
J. Islamic Pharm. Vol. 01 (01) 2016 28 Catechins Green Tea Clones GMB4 Inhibit Inflammation Process of Atherosclerosis Through Decreasing TNF-Α Levels Erna Susanti *1, Febiyanti Suratno 2 1 Pharmacy and
Regenerative Medicine for Sclerotic Disorders
 Regenerative Medicine Regenerative Medicine for Sclerotic Disorders JMAJ 7(7): 3 37, Toshikazu NAKAMURA rofessor, Division of Molecular Regenerative Medicine, Course of Advanced Medicine, Osaka University
Regenerative Medicine Regenerative Medicine for Sclerotic Disorders JMAJ 7(7): 3 37, Toshikazu NAKAMURA rofessor, Division of Molecular Regenerative Medicine, Course of Advanced Medicine, Osaka University
Relationship between Energy Expenditure Related Factors and Oxidative Stress in Follicular Fluid
 Original Article Relationship between Energy Expenditure Related Factors and Oxidative Stress in Follicular Fluid Abstract This study evaluated the impact of body mass index (BMI), total calorie intake
Original Article Relationship between Energy Expenditure Related Factors and Oxidative Stress in Follicular Fluid Abstract This study evaluated the impact of body mass index (BMI), total calorie intake
EFFECT OF STRESS ON LIPID PEROXIDATION
 EFFECT OF STRESS ON LIPID PEROXIDATION Bindu.M.P Effect of different types of stress on lipid metabolism and antioxidant status in albino rats Thesis. Amala cancer hospital and research centre,university
EFFECT OF STRESS ON LIPID PEROXIDATION Bindu.M.P Effect of different types of stress on lipid metabolism and antioxidant status in albino rats Thesis. Amala cancer hospital and research centre,university
EXPERIMENTAL PLEURAL EMPYEMA PATHOLOGIC CHANGES
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 2, pp 61-65, 2005 Copyright 2005 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1312-1723 Original Contribution EXPERIMENTAL PLEURAL EMPYEMA PATHOLOGIC
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 2, pp 61-65, 2005 Copyright 2005 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1312-1723 Original Contribution EXPERIMENTAL PLEURAL EMPYEMA PATHOLOGIC
TEST REPORT & SPECIFIC INFORMATION
 Page 1 (5) Dartsch Scientific GmbHAuf der Voßhardt 25 D-49419 Wagenfeld Firma LuKo Pharm GmbH Mayrwiesstrasse 25-27 A-5300 Hallwang Auf der Voßhardt 25 D-49419 Wagenfeld, Germany Fon: +49 5444 980 1322
Page 1 (5) Dartsch Scientific GmbHAuf der Voßhardt 25 D-49419 Wagenfeld Firma LuKo Pharm GmbH Mayrwiesstrasse 25-27 A-5300 Hallwang Auf der Voßhardt 25 D-49419 Wagenfeld, Germany Fon: +49 5444 980 1322
Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine
 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine 0 \ Second Edition BARRY HALLIWELL Professor of Medical Biochemistry, University of London King's College and JOHN M.C. GUTTERIDGE Senior Scientist, National Institute
Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine 0 \ Second Edition BARRY HALLIWELL Professor of Medical Biochemistry, University of London King's College and JOHN M.C. GUTTERIDGE Senior Scientist, National Institute
Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury
 Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury K. Ran 1, D.-L. Yang 1, Y.-T. Chang 1, K.-M. Duan 2, Y.-W. Ou 2, H.-P. Wang 3 and Z.-J. Li 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology,
Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury K. Ran 1, D.-L. Yang 1, Y.-T. Chang 1, K.-M. Duan 2, Y.-W. Ou 2, H.-P. Wang 3 and Z.-J. Li 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology,
NONE OVERVIEW FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF (UIP) FOR PATHOLOGISTS. IPF = Idiopathic UIP Radiologic UIP Path UIP
 UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates
 Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates Maria Elena Vega, M.D Assistant Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Nothing to
Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates Maria Elena Vega, M.D Assistant Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Nothing to
Cholesterol (blood, plasma, serum)
 1 Cholesterol (blood, plasma, serum) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Cholesterol (plasma; also blood, serum) 1.2 Alternative names 2,15-dimethyl-14-(1,5-dimethylhexyl)tetracyclo[8.7.0.0
1 Cholesterol (blood, plasma, serum) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Cholesterol (plasma; also blood, serum) 1.2 Alternative names 2,15-dimethyl-14-(1,5-dimethylhexyl)tetracyclo[8.7.0.0
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) Assay Kit
 (FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. DO NOT USE IT IN CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS!) High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) Assay Kit (Double reagents) Catalog No: E-BC-K221 Method: Colorimetric method Specification: 96T
(FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. DO NOT USE IT IN CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS!) High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) Assay Kit (Double reagents) Catalog No: E-BC-K221 Method: Colorimetric method Specification: 96T
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University
 Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University INTRODUCTION Diabetic nephropathy (DN) DN is defined as the appearance of persistent clinical albuminuria in an
Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University INTRODUCTION Diabetic nephropathy (DN) DN is defined as the appearance of persistent clinical albuminuria in an
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of mortality from gynecologic malignancies in the industrialized countries and is responsible for
 INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of mortality from gynecologic malignancies in the industrialized countries and is responsible for more deaths than both cervical and endometrial tumours.
INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of mortality from gynecologic malignancies in the industrialized countries and is responsible for more deaths than both cervical and endometrial tumours.
NINTEDANIB MEDIA BACKGROUNDER
 NINTEDANIB MEDIA BACKGROUNDER 1. What is nintedanib? 2. How does nintedanib work? 3. Data overview 4. International treatment guidelines for IPF 1. What is nintedanib? Nintedanib (OFEV a ) is a small molecule
NINTEDANIB MEDIA BACKGROUNDER 1. What is nintedanib? 2. How does nintedanib work? 3. Data overview 4. International treatment guidelines for IPF 1. What is nintedanib? Nintedanib (OFEV a ) is a small molecule
OxiSelect Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 Product Manual OxiSelect Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number STA-343 5 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Oxidative stress is a physiological
Product Manual OxiSelect Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number STA-343 5 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Oxidative stress is a physiological
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(9): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(9):4307-4318 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Histopathological and ultrastructural changes
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(9):4307-4318 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Histopathological and ultrastructural changes
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Angel Coz MD, FCCP, DCE Assistant Professor of Medicine UCSF Fresno November 4, 2017 No disclosures OBJECTIVES Identify current trends and risk factors of ARDS Describe
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Angel Coz MD, FCCP, DCE Assistant Professor of Medicine UCSF Fresno November 4, 2017 No disclosures OBJECTIVES Identify current trends and risk factors of ARDS Describe
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Combined Unclassifiable Interstitial Pneumonia and Emphysema: A Report of Two Cases
 CASE REPORT Combined Unclassifiable Interstitial Pneumonia and Emphysema: A Report of Two Cases Nobuhiko Nagata 1, Kentaro Watanabe 2, Michihiro Yoshimi 3, Hiroshi Okabayashi 4, Katsuo Sueishi 5, Kentaro
CASE REPORT Combined Unclassifiable Interstitial Pneumonia and Emphysema: A Report of Two Cases Nobuhiko Nagata 1, Kentaro Watanabe 2, Michihiro Yoshimi 3, Hiroshi Okabayashi 4, Katsuo Sueishi 5, Kentaro
Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and
 Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and Dietetics Tehran University of Medical Sciences Honorary Academic
Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and Dietetics Tehran University of Medical Sciences Honorary Academic
HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER
 HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER 6.1 Inti-oduction The structural and functional organization of the liver has been described by hepatic lobule and hepatic acinus models, respectively (Jarvelainen, 2000).
HISTOPL4THOLOG1CAL STUDY OF LIVER 6.1 Inti-oduction The structural and functional organization of the liver has been described by hepatic lobule and hepatic acinus models, respectively (Jarvelainen, 2000).
Supplementary data and figures Thyroid hormone inhibits murine lung fibrosis through improved epithelial mitochondrial function
 Supplementary data and figures Thyroid hormone inhibits murine lung fibrosis through improved epithelial mitochondrial function Guoying Yu 1*, Argyris Tzouvelekis 1,2*, Rong Wang 1,3, Jose D. Herazo-Maya
Supplementary data and figures Thyroid hormone inhibits murine lung fibrosis through improved epithelial mitochondrial function Guoying Yu 1*, Argyris Tzouvelekis 1,2*, Rong Wang 1,3, Jose D. Herazo-Maya
Protein Cleavage Due to Pro-oxidative Activity in Some Spices
 Protein Cleavage Due to Pro-oxidative Activity in Some Spices Sittiwat Lertsiri Department of Biotechnology Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Phayathai, Bangkok 10400 Thailand Kanchana Dumri Department
Protein Cleavage Due to Pro-oxidative Activity in Some Spices Sittiwat Lertsiri Department of Biotechnology Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Phayathai, Bangkok 10400 Thailand Kanchana Dumri Department
Histologic and histomorphometric changes of testis following oral exposure to methyl tertiary-butyl ether in adult rat
 288 Histologic and histomorphometric changes of testis following oral exposure to methyl tertiary-butyl ether in adult rat Gholami, S. 1* ; Ansari-Lari, M. 2 and Khalili, L. 3 1 Department of Basic Sciences,
288 Histologic and histomorphometric changes of testis following oral exposure to methyl tertiary-butyl ether in adult rat Gholami, S. 1* ; Ansari-Lari, M. 2 and Khalili, L. 3 1 Department of Basic Sciences,
Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway (SM04755) as a Potential Topical Scleroderma Treatment
 Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway (SM755) as a Potential Topical Scleroderma Treatment Vishal Deshmukh, PhD, Allison Hood, Yusuf Yazici, MD Disclosures Vishal Deshmukh, Ph.D. o Financial disclosure:
Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway (SM755) as a Potential Topical Scleroderma Treatment Vishal Deshmukh, PhD, Allison Hood, Yusuf Yazici, MD Disclosures Vishal Deshmukh, Ph.D. o Financial disclosure:
IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES
 13 13 IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES Yanni Yu, a Binjie Meng a Guizhou, China SUMMARY: Chondrocytes of rib-cage cartilage from Wistar rats
13 13 IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES Yanni Yu, a Binjie Meng a Guizhou, China SUMMARY: Chondrocytes of rib-cage cartilage from Wistar rats
Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies. Traditional Hypothesis Stress
 3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
Mouse Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Fluorescent Detection Kit
 Mouse Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Fluorescent Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2552 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure H2O2 in
Mouse Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Fluorescent Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2552 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure H2O2 in
Life Needs Energy. The Rules (Laws of Thermodynamics) 1) energy can not be created or destroyed, but it can be changed from one form to another
 Intro to Metabolism Learning Outcomes Explain laws governing energy and energy transfers. Describe enzymes and how they work. Explain what is meant by selectively permeable. Explain the differences between
Intro to Metabolism Learning Outcomes Explain laws governing energy and energy transfers. Describe enzymes and how they work. Explain what is meant by selectively permeable. Explain the differences between
Source Variation in Antioxidant Capacity of Cranberries from Eight U.S. Cultivars
 33 Source Variation in Antioxidant Capacity of Cranberries from Eight U.S. Cultivars Peter J. Schaaf Faculty Sponsors: Margaret A. Maher and Ted Wilson, Departments of Biology/Microbiology ABSTRACT Antioxidants
33 Source Variation in Antioxidant Capacity of Cranberries from Eight U.S. Cultivars Peter J. Schaaf Faculty Sponsors: Margaret A. Maher and Ted Wilson, Departments of Biology/Microbiology ABSTRACT Antioxidants
Antinociceptive Effect of Some Biuret Derivatives on Formalin Test in Mice
 Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2014, 4(2), 179-183 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5681/apb.2014.026 http://apb.tbzmed.ac.ir/ Antinociceptive Effect of Some Biuret Derivatives on Formalin Test in Mice Neda
Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2014, 4(2), 179-183 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5681/apb.2014.026 http://apb.tbzmed.ac.ir/ Antinociceptive Effect of Some Biuret Derivatives on Formalin Test in Mice Neda
Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis
 Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Lecture 19 Summary Gestational Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes. Gestational diabetes;
 Lecture 19 Summary Gestational Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes Gestational diabetes; - Type of diabetes that only develops during pregnancy Usually diagnosed in late pregnancy Causes high blood
Lecture 19 Summary Gestational Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes Gestational diabetes; - Type of diabetes that only develops during pregnancy Usually diagnosed in late pregnancy Causes high blood
The Interaction of Alcohol and Iron-Overload in the in-vivo Regulation of Iron Responsive Genes
 Cantaurus, Vol. 5, -, May 7 McPherson College Division of Science and Technology The Interaction of Alcohol and Iron-Overload in the in-vivo Regulation of Iron Responsive Genes Callie Crist, Elizabeth
Cantaurus, Vol. 5, -, May 7 McPherson College Division of Science and Technology The Interaction of Alcohol and Iron-Overload in the in-vivo Regulation of Iron Responsive Genes Callie Crist, Elizabeth
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz )
 Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz ) Biochemistry Submitted by Marie Havlová on 8. February 2012-0:00 Syllabus of Biochemistry Mechanisms of enzyme catalysis.
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz ) Biochemistry Submitted by Marie Havlová on 8. February 2012-0:00 Syllabus of Biochemistry Mechanisms of enzyme catalysis.
Protective Effects of Celery (Apium graveloens) Seed Extract on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats
 Original Article J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 17, Issu 1; Jan 2015. P:70-76 Protective Effects of Celery (Apium graveloens) Seed Extract on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats I. Javadi (PhD) 1, M.R.
Original Article J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 17, Issu 1; Jan 2015. P:70-76 Protective Effects of Celery (Apium graveloens) Seed Extract on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats I. Javadi (PhD) 1, M.R.
Lipid Peroxidation Assay
 Package Insert Lipid Peroxidation Assay 96 Wells For Research Use Only v. 1.0 Eagle Biosciences, Inc. 82 Broad Street, Suite 383, Boston, MA 02110 Phone: 866-419-2019 Fax: 617-419-1110 INTRODUCTION Lipid
Package Insert Lipid Peroxidation Assay 96 Wells For Research Use Only v. 1.0 Eagle Biosciences, Inc. 82 Broad Street, Suite 383, Boston, MA 02110 Phone: 866-419-2019 Fax: 617-419-1110 INTRODUCTION Lipid
Off-label use of statins for the prevention of radiation-induced normal tissue damage
 Off-label use of statins for the prevention of radiation-induced normal tissue damage Verena Ziegler, Christian Henninger and Gerhard Fritz Institute of Toxicology, Medical Faculty, Heinrich Heine University
Off-label use of statins for the prevention of radiation-induced normal tissue damage Verena Ziegler, Christian Henninger and Gerhard Fritz Institute of Toxicology, Medical Faculty, Heinrich Heine University
Human Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit
 Human Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2525 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure H₂O₂ in a variety
Human Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2525 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure H₂O₂ in a variety
Using the Ch6diak-Higashi Marker
 A Study of the Origin of Pulmonary Macrophages Using the Ch6diak-Higashi Marker Kent J. Johnson, MD, Peter A. Ward, MD, Gary Striker, MD, and Robin Kunkel, MS Using bone marrow reconstitution techniques
A Study of the Origin of Pulmonary Macrophages Using the Ch6diak-Higashi Marker Kent J. Johnson, MD, Peter A. Ward, MD, Gary Striker, MD, and Robin Kunkel, MS Using bone marrow reconstitution techniques
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Immunological Lung Diseases
 Emphysema and Fibrosis Universitätsklinik für Pneumologie Prof. Thomas Geiser Head Div. of Pulmonary Medicine and Laboratory of Lung Research, MU50 thomas.geiser@insel.ch The healthy lung: The pathway
Emphysema and Fibrosis Universitätsklinik für Pneumologie Prof. Thomas Geiser Head Div. of Pulmonary Medicine and Laboratory of Lung Research, MU50 thomas.geiser@insel.ch The healthy lung: The pathway
Statins in lung disease
 Statins in lung disease Associate Professor Robert Young BMedSc, MBChB, DPhil (Oxon), FRACP, FRCP University of Auckland, New Zealand Smoking and its complications Respiratory COPD Cardiovascular CAD Smoking
Statins in lung disease Associate Professor Robert Young BMedSc, MBChB, DPhil (Oxon), FRACP, FRCP University of Auckland, New Zealand Smoking and its complications Respiratory COPD Cardiovascular CAD Smoking
Influenza A virus infection predisposes hosts to secondary infection with different
 Supplementary information Influenza A virus infection predisposes hosts to secondary infection with different Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes with similar outcome but serotype-specific manifestation.
Supplementary information Influenza A virus infection predisposes hosts to secondary infection with different Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes with similar outcome but serotype-specific manifestation.
Low grade inflammation and cardiovascular disease
 Low grade inflammation and cardiovascular disease Konstantinos Aznaouridis, MD PhD 1 st Department of Cardiology Hippokration Hospital Athens Medical School Atherosclerosis Start from very young To Old
Low grade inflammation and cardiovascular disease Konstantinos Aznaouridis, MD PhD 1 st Department of Cardiology Hippokration Hospital Athens Medical School Atherosclerosis Start from very young To Old
Total Phosphatidic Acid Assay Kit
 Product Manual Total Phosphatidic Acid Assay Kit Catalog Number MET- 5019 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Phosphatidic Acid (PA) is a critical precursor
Product Manual Total Phosphatidic Acid Assay Kit Catalog Number MET- 5019 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Phosphatidic Acid (PA) is a critical precursor
Lung toxicity associated with cyclophosphamide use. Two distinct patterns. [Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996] PMID:
![Lung toxicity associated with cyclophosphamide use. Two distinct patterns. [Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996] PMID: Lung toxicity associated with cyclophosphamide use. Two distinct patterns. [Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996] PMID:](/thumbs/88/115420719.jpg) Amiodarone and Pulmonary Toxicity 06.08.07 1: Pharmacotherapy. 2007 Apr;27(4):616-8. Fatal pulmonary toxicity after a single dose of cyclophosphamide. Gupta S, Mahipal A. University of Connecticut Health
Amiodarone and Pulmonary Toxicity 06.08.07 1: Pharmacotherapy. 2007 Apr;27(4):616-8. Fatal pulmonary toxicity after a single dose of cyclophosphamide. Gupta S, Mahipal A. University of Connecticut Health
Acute and Chronic Lung Disease
 KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
Histopathological Evaluation of Pulmonary Effects of Sodium Dichromate Cr VI in Rats
 IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 9, Issue 4 Ver. II (Apr. 2016), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Histopathological Evaluation of
IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 9, Issue 4 Ver. II (Apr. 2016), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Histopathological Evaluation of
ABSENCE OF AN ADDITIONAL FIBROTIC RESPONSE CAUSED BY OXYGEN IN THE LUNGS OF RATS AFTER THE INTRATRACHEAL ADMINISTRATION OF BLEOMYCIN
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1988), 61, 413-418 ABSENCE OF AN ADDITIONAL FIBROTIC RESPONSE CAUSED BY OXYGEN IN THE LUNGS OF RATS AFTER THE INTRATRACHEAL ADMINISTRATION OF BLEOMYCIN T. S. VENINGA, R. VRIESENDORP, M.
Br. J. Anaesth. (1988), 61, 413-418 ABSENCE OF AN ADDITIONAL FIBROTIC RESPONSE CAUSED BY OXYGEN IN THE LUNGS OF RATS AFTER THE INTRATRACHEAL ADMINISTRATION OF BLEOMYCIN T. S. VENINGA, R. VRIESENDORP, M.
Toll-like receptor 4 promotes fibrosis in bleomycin-induced lung injury in mice
 Toll-like receptor 4 promotes fibrosis in bleomycin-induced lung injury in mice X.X. Li 1,2, D.Y. Jiang 1, X.X. Huang 1, S.L. Guo 1, W. Yuan 1 and H.P. Dai 1 1 Beijing Key Laboratory of Respiratory and
Toll-like receptor 4 promotes fibrosis in bleomycin-induced lung injury in mice X.X. Li 1,2, D.Y. Jiang 1, X.X. Huang 1, S.L. Guo 1, W. Yuan 1 and H.P. Dai 1 1 Beijing Key Laboratory of Respiratory and
