Is Urethral Pain Syndrome Really Part of Bladder Pain Syndrome?
|
|
|
- Lisa Mills
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review ISSN (Print) / ISSN: (Online) Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1): Is Urethral Pain Syndrome Really Part of Bladder Pain Syndrome? Sung Tae Cho Department of Urology, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea Urethral pain syndrome is a symptom complex that includes dysuria, urinary urgency, frequency, nocturia, and persistent or intermittent urethral and/or pelvic pain in the absence of proven infection. Bladder pain syndrome is a clinical diagnosis, based primarily on chronic symptoms of pain from the bladder and/or pelvis associated with urinary urgency or frequency in the absence of identified cause for the symptoms. To date, the term, urethral pain syndrome, remains to be unclear in referring to a distinct subgroup of bladder pain syndrome. However, these two syndromes share many similarities, except the organ of pain. This review is intended to summarize the current state of literature with regard to similar pathophysiology and possible interrelations between urethral pain syndrome and bladder pain syndrome. Keywords: Cystitis, interstitial; Urinary bladder; Urethra Copyright 2017, Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and Inflammation. All rights reserved. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Received: 24 March, 2017 Revised: 10 April, 2017 Accepted: 10 April, 2017 Correspondence to: Sung Tae Cho Department of Urology, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, 1 Singil-ro, Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul 07441, Korea Tel: , Fax: cst326@paran.com INTRODUCTION The term urethral syndrome was used in 1965 by Gallagher et al. [1]. In 2002, the term urethral pain syndrome was implemented by the International Continence Society (ICS) to delineate the occurrence of recurrent episodic urethral pain, usually on voiding, with daytime frequency and nocturia, in the absence of proven infection. It is often common for dyspareunia to also be described. Regardless of the symptoms, the lack of evidence of urinary tract infection or other obvious pathologies is essential [2]. Due to these nonspecific symptoms, there are often overlaps with disease pictures, such as interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) or the overactive bladder (OAB). As such, some authors describe the urethral syndrome as an early form of IC [3]. In the current guidelines of the European Association of Urology (EAU), urethral pain syndrome is considered to be a part of the complex of chronic pelvic pain [4]. Urethral pain syndrome and BPS have a lot in common, except the organ of pain. To aid in understanding the possible relationship between these two syndromes, we summarized both syndromes and presented evidence-based information on whether additional similarities with regard to pathophysiology exist between these two syndromes. URETHRAL PAIN SYNDROME Urethral pain syndrome is a symptom complex that includes dysuria, urinary urgency, frequency, nocturia, and persistent or intermittent urethral and/or pelvic pain in the absence of proven infection [2]. The diagnosis implies a specific duration of symptoms, a minimum of six months [5]. The exact etiology is unknown; however, infectious and psychogenic factors, urethral spasms, early IC, hypoestrogenism, squamous metaplasia, as well as gynecological 22
2 Sung Tae Cho. Urethral Pain Syndrome of BPS 23 risk factors are discussed [6]. There is now evidence that the microscopic paraurethral glands connected to the distal third of the urethra in the prevaginal space are homologous to the prostate. They stain histologically for prostate-specific antigen and, like the prostate, are subject to infection and cancer. Some researchers have theorized that inflammation of the female prostate (Skene glands and the paraurethral glands) may explain the causes of urethral pain syndrome [7]. The diagnosis is mainly based on symptoms. However, it is important to rule out other conditions, including paraurethral pathology, bladder cancer, atrophic urethral changes, and vaginitis [5]. The incidence and prevalence of this condition is not well known thus far due to the lack of consensus in the method of diagnoses. In several studies, 15-30% of women who presented with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) were diagnosed with urethral pain syndrome [8,9]. Most of these patients are women aged 20 to 30 years and 50 to 60 years. Contrary to the earlier definition, urethral pain syndrome may also occur in men, but less frequently [6,10]. This condition is more common in Caucasians than other races [5]. As a result of these nonspecific symptoms, patients with urethral pain syndrome often enter into urological care after long-term suffering and repeated treatment [6,11]. INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The first known modern documentation of a condition resembling IC appeared in the early 19th century. Philip Syng Physick described an inflammatory condition of the bladder with an ulcer producing the same symptoms as a bladder stone in 1808 [12]. He expanded this concept to include chronic frequency, urgency, and pain syndrome, occurring in the absence of demonstrable etiology, which was called the tic douloureux of the bladder in 1836 [12,13]. This may represent the first description of IC. Fifty years later, Skene used the term IC to describe an inflammation that had destroyed the mucous membrane partly or wholly and extended to the muscular parietes in 1887 [14]. However, because of the distinctive clinical characterization of the syndrome, the physician who is always remembered and quoted is Guy Hunner [13]. Early in the 20th century, he described a symptom complex of bladder pain associated with distinguishing cystoscopic feature of mucosal lesions as the elusive ulcer, which was later termed Hunner s ulcer. For several years, this finding was the hallmark of IC, and urologists would look for ulcers but failed to make the diagnosis in their absence [13]. The Interstitial Cystitis Association (ICA), established in 1984, succeeded in gaining the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) s interest in the research for this field [15]. In an effort to define IC, the NIDDK held a workshop in August 1987, at which point in time, the consensus diagnostic criteria were established for the diagnosis of IC [16]. After the pilot studies to test for the criteria, they were revised at the follow-up NIDDK workshop in 1988 [15,16]. These criteria were specifically designed for the basic and clinical research purposes, but not as a diagnostic tool for the clinician (Table 1) [17]. PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME The ICS has been standardizing the terminology of lower urinary tract diseases. In 2002, for the first time, the ICS defined IC, calling it a painful bladder syndrome (PBS), delineating it as: the complaint of suprapubic pain related to bladder filling, accompanied by other symptoms, such as increased daytime and night-time frequency, in the absence of proven urinary infection or other obvious pathology [18,19]. The ICS reserves the diagnosis of IC as a specific diagnosis that requires confirmation by typical cystoscopic and histological features. This definition may miss 36% of patients, primarily because it confines the pain to a suprapubic location and mandates a relationship of pain to bladder filling [18]. This disorder, despite confusion, came to be known as PBS/IC or IC/PBS. BLADDER PAIN SYNDROME The European Society for the Study of Interstitial Cystitis (ESSIC) proposed a new definition and another name change from IC/PBS to BPS alone. The ESSIC paper, published in 2008, proposed the following definition: Chronic (six months or more) pelvic pain, pressure or discomfort perceived to be related to the urinary bladder accompanied by at least one other urinary symptom like persistent urge to void or urinary frequency. Confusable diseases as the cause of the symptoms must be excluded [20]. ESSIC also introduced a new classification system of BPS types and a list of confusable diseases. BPS is indicated
3 24 Sung Tae Cho. Urethral Pain Syndrome of BPS Table 1. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) revised the criteria for interstitial cystitis in 1988 To be included as IC, patients must have either glomerulations on cystoscopic examination or a classic Hunner s ulcer, and they must have either pain associated with the bladder or urinary urgency. Examination for glomerulations should occur after distension of the bladder under anesthesia to cmh 2O for 1-2 min. The bladder may be distended up to two times before evaluation. The glomerulations must be diffuse present in at least 3 quadrants of the bladder and there must be at least 10 glomerulations per quadrant. The glomerulations must not be along the path of the cystoscope (to eliminate artifact from contact instrumentation). The presence of any one of the following will exclude the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis: 1. Bladder capacity of greater than 350 ml on awake cystometry using either a gas or liquid filling medium 2. Absence of an intense urge to void with the bladder filled to 100 ml of gas or 150 ml of water during cystometry, using a fill rate of ml/min 3. The demonstration of phasic involuntary bladder contractions on cystometry using the fill rate described above 4. Duration of symptoms less than 9 months 5. Absence of nocturia 6. Symptoms relieved by antimicrobials, urinary antiseptics, anticholinergics, or antispasmodics 7. A frequency of urination while awake of less than eight times per day 8. A diagnosis of bacterial cystitis or prostatitis within a 3-month period 9. Bladder or lower ureteral calculi 10. Active genital herpes 11. Uterine, cervical, vaginal, or urethral cancer 12. Urethral diverticulum 13. Cyclophosphamide or any type of chemical cystitis 14. Tuberculous cystitis 15. Radiation cystitis 16. Benign or malignant bladder tumors 17. Vaginitis 18. Age less than 18 years Adapted from Bladder pain syndrome (Interstitial Cystitis) and related disorders. In: Campbell-Walsh urology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; p [17]. by two symbols: The first corresponds to cystoscopy with hydrodistention (CHD) findings (1, 2, or 3, indicating increasing grade of severity), and the second to biopsy findings (A, B, and C, indicating increasing grade of pathologic severity) [20]. Although neither CHD nor bladder biopsy was prescribed as an essential part of the evaluation, categorizing patients in terms of whether they have undergone the procedure with results, made it possible to follow patients with similar findings and study each identified cohort to compare the natural history, prognosis, and response to therapy [20]. The definition of ESSIC is a clinically useful one, and changes made since its original iteration have likely made it more sensitive and inclusive [21]. The panel of the Society for Urodynamics and Female Urology (SUFU) produced a slightly different definition for IC/BPS in 2008: An unpleasant sensation (pain, pressure, discomfort), perceived to be related to the urinary bladder, associated with LUTS for more than six weeks, in the absence of infection or other identifiable causes [22]. The SUFU definition was adopted in the guidelines of the American Urological Association (AUA) in 2011, along with the nomenclature IC/BPS, without differentiating between the two [23]. HYPERSENSITIVE BLADDER SYNDROME Homma [24] proposed that frequency/urgency syndrome is characterized by frequency (frequent voiding) and urgency (strong desire to void). It is an inclusive term that incorporates OAB, hypersensitive bladder syndrome (HBS), and other conditions that are associated with frequency and urgency. Urgency in OAB is characterized by a sudden onset and/or fear of leakage, while urgency in HBS is characterized by persistent nature and is associated with the fear of pain. OAB-wet is a subgroup of OAB, while PBS is a subgroup of HBS with pain. IC is one of the diseases manifested by frequency/urgency and overlapping with HBS and PBS [24,25]. A clinical guideline and algorism for IC and HBS has been developed by a group of East Asian (Japan, Korea, and Taiwan) urologists as a revised form of the Japanese guideline for IC [26]. This East-Asian guideline defines IC as a disease of the urinary bladder diagnosed by three following conditions: 1) a characteristic complex of LUTS, 2) bladder pathology, such as Hunner s ulcer and bladder bleeding after overdistention, and 3) exclusions of confusable diseases. The characteristic symptom complex is termed, HBS, which is defined as bladder hypersensitivity, usually associated with urinary frequency, with or without
4 Sung Tae Cho. Urethral Pain Syndrome of BPS 25 bladder pain. For the definite diagnosis of IC, cystoscopy or hydrodistention is crucial; HBS is the diagnosis when IC is suspected, but not confirmed by the 3 requirements. NEW PARADIGM The paradigm change has resulted in altering what was originally considered a bladder disease (IC) to a chronic pain syndrome (BPS). IC/BPS is now viewed not only through the paradigm of chronic pain syndrome manifesting through bladder-related symptoms, but as a syndrome that may not only isolated to the bladder alone [17]. There may be many causes of chronic pelvic pain. When a cause cannot be determined, the condition is characterized as pelvic pain syndrome. If it can be distinguished as urologic, it is further categorized by the organ system. A urologic pain syndrome can sometimes be further differentiated based on the site of perceived pain. These pain syndromes include bladder, urethra, prostate, testicular, and epididymal pain syndromes. The types of BPS can be further defined as IC or simply categorized by ESSIC criteria [17,22]. URETHRA AND BLADDER PATHOPHYSIOLOGY IN PAIN SYNDROME IC/BPS is a chronic disease characterized by prolonged duration of symptoms of pelvic or perineal pain, thinning of the bladder epithelium, and various voiding symptoms, such as nocturia, increased urinary frequency, and urgency. In terms of pain, suprapubic or bladder pain is prominent. However, many patients report different and/or additional sites, particularly in the urethra, genitalia, and lower back [27,28]. Although the cause of BPS is usually unknown, there is a body of evidence supporting the involvement of bladder urothelial abnormalities in these illnesses [29,30]. Parsons showed that a leaky dysfunctional epithelium and subsequent diffusion of potassium into the tissue may be responsible for the pelvic pain [10]. These altered the paradigms in the generation of frequency, urgency, and pelvic pain. After all, urethral pain syndrome and BPS have all been shown to have epithelial leak and potassium sensitivity, uniting these syndromes into one disease, lower urinary tract dysfunction epithelium (LUDE) [10,31]. LUDE can affect the bladder, urethra, labia or vaginal introitus in women, and the prostatic ducts and urethra in men. Because patients with LUDE may experience pain in one or more locations throughout the pelvis in any combination, it is important for physicians to avoid making a diagnosis solely based on the site of pain. A useful diagnostic tool is the intravesical potassium sensitivity test, which detects the abnormal epithelial permeability of LUDE [32]. There is also evidence that the urothelium in the region of the urethra may play a role in continence and sensation. It has been suggested that symptoms of pain that arise from the lower urinary tract might originate principally from the bladder neck and proximal urethra [33]. The bladder neck and proximal urethral contain the largest density of bladder nerves, and the epithelial cells that line the surface show neuronal-like properties [34]. Thus urethral epithelialneural interactions could lead to a urethral instability influencing the storage and voiding reflexes, and resulting in symptoms of urgency and pain [34,35]. CONCLUSIONS Urethral pain syndrome is an occurrence of recurrent episodic urethral pain usually on voiding with frequency and nocturia. BPS is chronic pelvic pain, pressure, or discomfort often exacerbated by bladder filling, and associated with urinary frequency. Seemingly, two different syndromes that would usually seem nothing like one another have much in common when it comes to the new paradigm and pathophysiology. Chronic pelvic pain can have multiple causes, including many types of urologic pain syndromes. In broad terms, urologic pain syndrome encompasses urethral pain syndrome and BPS. Pain arising from the lower urinary tract may originate from the bladder neck and proximal urethra, and LUDE can affect tissues of the bladder and urethra. Even if controversies still remain, urethral pain syndrome can be a part of BPS. Further basic science and clinical research in this area is needed to better understand the pathophysiology of these syndromes. CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
5 26 Sung Tae Cho. Urethral Pain Syndrome of BPS REFERENCES 1. Gallagher DJ, Montgomerie JZ, North JD. Acute infections of the urinary tract and the urethral syndrome in general practice. Br Med J 1965;1: Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Grifftihs D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology in lower urinary tract function: report from the standardisation sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Urology 2003;61: Stamm WE, Running K, McKevitt M, Counts GW, Turck M, Holmes KK. Treatment of the acute urethral syndrome. N Engl J Med 1981;304: Engeler DS, Baranowski AP, Dinis-Oliveira P, Elneil S, Hughes J, Messelink EJ, et al. The 2013 EAU guidelines on chronic pelvic pain: is management of chronic pelvic pain a habit, a philosophy, or a science? 10 years of development. Eur Urol 2013;64: Kaur H, Arunkalaivanan AS. Urethral pain syndrome and its management. Obstet Gynecol Surv 2007;62:348-51; quiz Dreger NM, Degener S, Roth S, Brandt AS, Lazica DA. [Urethral pain syndrome: fact or fiction--an update]. Urologe A 2015;54: German. 7. Gittes RF, Nakamura RM. Female urethral syndrome. A female prostatitis? West J Med 1996;164: Gurel H, Gurel SA, Atilla MK. Urethral syndrome and associated risk factors related to obstetrics and gynecology. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1999;83: Tait J, Peddie BA, Bailey RR, Arnold EP, Russell GL, Bishop VA, et al. Urethral syndrome (abacterial cystitis)--search for a pathogen. Br J Urol 1985;57: Parsons CL. The role of a leaky epithelium and potassium in the generation of bladder symptoms in interstitial cystitis/overactive bladder, urethral syndrome, prostatitis and gynaecological chronic pelvic pain. BJU Int 2011;107: Burkhard FC, Blick N, Hochreiter WW, Studer UE. Urinary urgency and frequency, and chronic urethral and/or pelvic pain in females. Can doxycycline help? J Urol 2004;172: Parsons JK, Parsons CL. The historical origins of interstitial cystitis. J Urol 2004;171: Fall M, Logadottir Y, Peeker R. Interstitial cystitis is bladder pain syndrome with Hunner's lesion. Int J Urol 2014;21 Suppl 1: Skene AJC. Diseases of the bladder and urethra in women. 2nd ed. New York: William Wood; Meijlink JM. Interstitial cystitis and the painful bladder: a brief history of nomenclature, definitions and criteria. Int J Urol 2014;21 Suppl 1: Gillenwater JY, Wein AJ. Summary of the National Institute of Arthritis, Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases Workshop on Interstitial Cystitis, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, August 28-29, J Urol 1988;140: Hanno PM. Bladder pain syndrome (Interstitial Cystitis) and related disorders. In: Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA, editors. Campbell-Walsh urology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; p Warren JW, Meyer WA, Greenberg P, Horne L, Diggs C, Tracy JK. Using the International Continence Society's definition of painful bladder syndrome. Urology 2006;67: ; discussion Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn 2002;21: van de Merwe JP, Nordling J, Bouchelouche P, Bouchelouche K, Cervigni M, Daha LK, et al. Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: an ESSIC proposal. Eur Urol 2008;53: Mouracade P, Lang H, Jacqmin D, Saussine C. [Using the intersitital cystitis new diagnostic criteria in daily practice: about 156 patients]. Prog Urol 2008;18: French. 22. Hanno P, Dmochowski R. Status of international consensus on interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome/painful bladder syndrome: 2008 snapshot. Neurourol Urodyn 2009;28: Hanno PM, Burks DA, Clemens JQ, Dmochowski RR, Erickson D, Fitzgerald MP, et al. AUA guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J Urol 2011;185: Homma Y. Lower urinary tract symptomatology: its definition and confusion. Int J Urol 2008;15: Nordling J, Fall M, Hanno P. Global concepts of bladder pain syndrome (interstitial cystitis). World J Urol 2012;30: Homma Y, Ueda T, Tomoe H, Lin AT, Kuo HC, Lee MH, et al. Clinical guidelines for interstitial cystitis and hypersensitive bladder syndrome. Int J Urol 2009;16: Warren JW, Langenberg P, Greenberg P, Diggs C, Jacobs S, Wesselmann U. Sites of pain from interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. J Urol 2008;180: FitzGerald MP, Brensinger C, Brubaker L, Propert K; ICDB Study Group. What is the pain of interstitial cystitis like? Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 2006;17: Cho YS. Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder pain syndrome: a urologic mystery. Int Neurourol J 2016;20: Keay SK, Birder LA, Chai TC. Evidence for bladder urothelial pathophysiology in functional bladder disorders. Biomed Res Int 2014;2014: Parsons CL, Bullen M, Kahn BS, Stanford EJ, Willems JJ. Gynecologic presentation of interstitial cystitis as detected by intravesical potassium sensitivity. Obstet Gynecol 2001;98: Parsons CL. Interstitial cystitis and lower urinary tract symptoms in males and females-the combined role of potassium and epithelial dysfunction. Rev Urol 2002;4 Suppl 1:S49-55.
6 Sung Tae Cho. Urethral Pain Syndrome of BPS Birder LA, Andersson KE, Kanai AJ, Hanna-Mitchell AT, Fry CH. Urothelial mucosal signaling and the overactive bladder-ici-rs Neurourol Urodyn 2014;33: Birder LA, de Wachter S, Gillespie J, Wyndaele JJ. Urethral sensation: basic mechanisms and clinical expressions. Int J Urol 2014;21 Suppl 1: McLennan MT, Melick C, Bent AE. Urethral instability: clinical and urodynamic characteristics. Neurourol Urodyn 2001;20:
Interstitial Cystitis:
 Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
In evaluating a patient with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urologists
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
How does interstitial cystitis begin?
 Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence
 BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial cystitis
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21 (Suppl 1), 43 47 doi: 10.1111/iju.12314 Review Article Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21 (Suppl 1), 43 47 doi: 10.1111/iju.12314 Review Article Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS)
 Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
Addendum 1: International Consultation
 Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome and Male Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: How Are They Related?
 Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.15 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):15-21 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.15 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):15-21 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome
 Review Article Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome Gisela Ens, Gustavo L. Garrido Voiding Dysfunction and Urodynamic Section, Division
Review Article Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome Gisela Ens, Gustavo L. Garrido Voiding Dysfunction and Urodynamic Section, Division
In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective?
 Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Original Article. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUCTION
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(3):342-346 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.342 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Phasic Changes in Bladder Compliance
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(3):342-346 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.342 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Phasic Changes in Bladder Compliance
Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores
 DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines
 Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Mr. GIT KAH ANN. Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
 Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Cystoscopic and Histopathologic Patterns in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Cystitis /Painful Bladder Syndrome
 CHRONIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE CYSTITIS /PAINFUL MEDICAL BLADDER JOURNAL SYNDROME VOL., NO., Cystoscopic and Histopathologic Patterns in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Cystitis /Painful Bladder Syndrome Issam
CHRONIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE CYSTITIS /PAINFUL MEDICAL BLADDER JOURNAL SYNDROME VOL., NO., Cystoscopic and Histopathologic Patterns in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Cystitis /Painful Bladder Syndrome Issam
The new International Continence Society
 ROLE OF CYSTOMETRY IN EVALUATING PATIENTS WITH OVERACTIVE BLADDER ADAM J. FLISSER AND JERRY G. BLAIVAS ABSTRACT Overactive bladder (OAB) can be caused by a variety of conditions. We believe that cystometrography
ROLE OF CYSTOMETRY IN EVALUATING PATIENTS WITH OVERACTIVE BLADDER ADAM J. FLISSER AND JERRY G. BLAIVAS ABSTRACT Overactive bladder (OAB) can be caused by a variety of conditions. We believe that cystometrography
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS. Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >60%
 DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
INTRODUCTION. Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction. Aram Kim 1, Kyeong-Ok Hoe 2, Jung Hyun Shin 2, Myung-Soo Choo 2 1
 Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Dr. Aso Urinary Symptoms
 Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France
 A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
32 OBG Management July 2010 Vol. 22 No. 7 obgmanagement.com
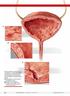 A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
BLADDER HEALTH. Painful Bladder AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
 BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
Chronic pelvic pain-when surgery fails
 Chronic pelvic pain-when surgery fails Sherif Tawfeek FRANZCOG, FRCOG, FICS, MSc, Dip-Endoscopy Consultant in Obstetrics and Gynaecology Senior lecturer at University of Otago Objectives Identify the common
Chronic pelvic pain-when surgery fails Sherif Tawfeek FRANZCOG, FRCOG, FICS, MSc, Dip-Endoscopy Consultant in Obstetrics and Gynaecology Senior lecturer at University of Otago Objectives Identify the common
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
INCONTINENCE. Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation TYPES OF INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE 11/08/2015
 INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 849 853 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence Stefano
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 849 853 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence Stefano
Prostatitis: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria. Michel Pontari IMMPACT-XX Meeting July 13, 2017
 Prostatitis: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria Michel Pontari IMMPACT-XX Meeting July 13, 2017 NIDDK Classification of Prostatitis 1 Type I: Acute Bacterial
Prostatitis: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria Michel Pontari IMMPACT-XX Meeting July 13, 2017 NIDDK Classification of Prostatitis 1 Type I: Acute Bacterial
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
GREAT MEETING FOR CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN AND PAINFUL BLADDER!
 REVIEW OF THE 42 nd ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS) 15-19 OCTOBER 2012, BEIJING, CHINA GREAT MEETING FOR CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN AND PAINFUL BLADDER! Jane Meijlink This
REVIEW OF THE 42 nd ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS) 15-19 OCTOBER 2012, BEIJING, CHINA GREAT MEETING FOR CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN AND PAINFUL BLADDER! Jane Meijlink This
C. Lowell Parsons UC San Diego Medical Center, Department of Surgery/Urology, La Jolla, CA, USA
 ; 2010 Mini Reviews BLADDER SYMPTOMS CAUSED BY LEAKY EPITHELIUM AND POTASSIUM PARSONS ET AL. BJUI The role of a leaky epithelium and potassium in the generation of bladder symptoms in interstitial cystitis/overactive
; 2010 Mini Reviews BLADDER SYMPTOMS CAUSED BY LEAKY EPITHELIUM AND POTASSIUM PARSONS ET AL. BJUI The role of a leaky epithelium and potassium in the generation of bladder symptoms in interstitial cystitis/overactive
Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
Interstitial Cystitis
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
The Prevalence and Characteristic Differences in Prostatic Calcification between Health Promotion Center and Urology Department Outpatients
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.5.330 Voiding Dysfunction The Prevalence and Characteristic Differences in Prostatic Calcification between Health Promotion Center and Urology Department
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.5.330 Voiding Dysfunction The Prevalence and Characteristic Differences in Prostatic Calcification between Health Promotion Center and Urology Department
The Role of Immunoglobulin E in the Pathogenesis of Ketamine Related Cystitis and Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis: An Immunohistochemical Study
 Pain Physician 2016; 19:E581-E587 ISSN 2150-1149 Prospective Evaluation The Role of Immunoglobulin E in the Pathogenesis of Ketamine Related Cystitis and Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis: An Immunohistochemical
Pain Physician 2016; 19:E581-E587 ISSN 2150-1149 Prospective Evaluation The Role of Immunoglobulin E in the Pathogenesis of Ketamine Related Cystitis and Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis: An Immunohistochemical
Diagnostic approach to LUTS in men. Prof Dato Dr. Zulkifli Md Zainuddin Consultant Urologist / Head Of Urology Unit UKM Medical Center
 Diagnostic approach to LUTS in men Prof Dato Dr. Zulkifli Md Zainuddin Consultant Urologist / Head Of Urology Unit UKM Medical Center Classification of LUTS Storage symptoms Voiding symptoms Post micturition
Diagnostic approach to LUTS in men Prof Dato Dr. Zulkifli Md Zainuddin Consultant Urologist / Head Of Urology Unit UKM Medical Center Classification of LUTS Storage symptoms Voiding symptoms Post micturition
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology
 Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Naoki Wada, Seiji Matsumoto, Masafumi Kita, Kazumi Hashizume and Hidehiro Kakizaki
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (1) 1, 15 1 doi: 1.1111/iju.157 Original Article: Clinical Investigation Decreased urinary nerve growth factor reflects prostatic volume reduction and relief
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (1) 1, 15 1 doi: 1.1111/iju.157 Original Article: Clinical Investigation Decreased urinary nerve growth factor reflects prostatic volume reduction and relief
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms BPH vs OAB FLOW vs VOLUME. Matt T. Rosenberg, MD Family Practice Mid Michigan Health Centers Jackson, Michigan
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms BPH vs OAB FLOW vs VOLUME Matt T. Rosenberg, MD Family Practice Mid Michigan Health Centers Jackson, Michigan 1 Definition of OAB Syndrome or symptom complex defined as urgency,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms BPH vs OAB FLOW vs VOLUME Matt T. Rosenberg, MD Family Practice Mid Michigan Health Centers Jackson, Michigan 1 Definition of OAB Syndrome or symptom complex defined as urgency,
THE ACONTRACTILE BLADDER - FACT OR FICTION?
 THE ACONTRACTILE BLADDER - FACT OR FICTION? Jacob Golomb Department of Urology Chaim Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer NEUROGENIC UNDERACTIVE DETRUSOR Central (complete/incomplete): Spinal cord injury-
THE ACONTRACTILE BLADDER - FACT OR FICTION? Jacob Golomb Department of Urology Chaim Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer NEUROGENIC UNDERACTIVE DETRUSOR Central (complete/incomplete): Spinal cord injury-
CONCLUSIONS. At a median of nearly 3 years after onset, baseline mild IC/PBS was
 BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Prognostic factors for recent-onset interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome John W. Warren *, Daniel J. Clauw and Patricia Langenberg *Department of Medicine, Department of
BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Prognostic factors for recent-onset interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome John W. Warren *, Daniel J. Clauw and Patricia Langenberg *Department of Medicine, Department of
Program and Abstracts
 Program and Abstracts summary INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR THE STUDY OF BPS ESSIC Annual Meeting Philadelphia (USA) 13-15 June 2014 Venue Geary Hall Hahnemann Hospital, Drexel University 230 North Broad Street
Program and Abstracts summary INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR THE STUDY OF BPS ESSIC Annual Meeting Philadelphia (USA) 13-15 June 2014 Venue Geary Hall Hahnemann Hospital, Drexel University 230 North Broad Street
Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults
 Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults Christopher Chapple Professor of Urology Sheffield Teaching Hospitals University of Sheffield Sheffield Hallam University UK 23 rd October 2015 Terminology
Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults Christopher Chapple Professor of Urology Sheffield Teaching Hospitals University of Sheffield Sheffield Hallam University UK 23 rd October 2015 Terminology
Dr. Krithika Doshi. Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical?
 Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical? Dr Kritika Doshi Introduction: Chronic pelvic and urogenital pain syndromes have recently been recognized as a
Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical? Dr Kritika Doshi Introduction: Chronic pelvic and urogenital pain syndromes have recently been recognized as a
Interstitial and chronic cystitis. Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall?
 Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence. Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations
 The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC
 PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC STUDIES: IS THERE VALUE IN PREDICTING POST-OPERATIVE STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN UNDERGOING PROLAPSE SURGERY? Dr K Janse van Rensburg Dr JA van Rensburg INTRODUCTION POP
PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC STUDIES: IS THERE VALUE IN PREDICTING POST-OPERATIVE STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN UNDERGOING PROLAPSE SURGERY? Dr K Janse van Rensburg Dr JA van Rensburg INTRODUCTION POP
A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS)
 31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
The Enlarged Prostate Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 The Enlarged Prostate Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment MAC00031-01 Rev G Financial support for this seminar has been provided by NeoTract, Inc., the manufacturer of the UroLift System. 1 Today s Agenda
The Enlarged Prostate Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment MAC00031-01 Rev G Financial support for this seminar has been provided by NeoTract, Inc., the manufacturer of the UroLift System. 1 Today s Agenda
Summary. Neuro-urodynamics. The bladder cycle. and voiding. 14/12/2015. Neural control of the LUT Initial assessment Urodynamics
 Neuro-urodynamics Summary Neural control of the LUT Initial assessment Urodynamics Marcus Drake, Bristol Urological Institute SAFETY FIRST; renal failure, dysreflexia, latex allergy SYMPTOMS SECOND; storage,
Neuro-urodynamics Summary Neural control of the LUT Initial assessment Urodynamics Marcus Drake, Bristol Urological Institute SAFETY FIRST; renal failure, dysreflexia, latex allergy SYMPTOMS SECOND; storage,
BJUI. Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive bladder
 ; 2010 Lower Urinary Tract PATIENT S PERCEPTION OF INTENSITY OF URGENCY SCALE IN OAB CARTWRIGHT ET AL. BJUI Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive
; 2010 Lower Urinary Tract PATIENT S PERCEPTION OF INTENSITY OF URGENCY SCALE IN OAB CARTWRIGHT ET AL. BJUI Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive
Urinary nerve growth factor levels could be a biomarker for overactive bladder symptom: a meta-analysis
 Urinary nerve growth factor levels could be a biomarker for overactive bladder symptom: a meta-analysis H.C. Qu, S. Yan, X.L. Zhang, X.W. Zhu, Y.L. Liu and P. Wang Department of Urological Surgery, The
Urinary nerve growth factor levels could be a biomarker for overactive bladder symptom: a meta-analysis H.C. Qu, S. Yan, X.L. Zhang, X.W. Zhu, Y.L. Liu and P. Wang Department of Urological Surgery, The
Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks
 1100 Wayne Ave, Suite 825 Silver Spring, MD 20910 301.273.0570 Fax 301.273.0778 info@augs.org www.augs.org Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks ICD 9 ICD 9 Description ICD 10 Code ICD 10 Description
1100 Wayne Ave, Suite 825 Silver Spring, MD 20910 301.273.0570 Fax 301.273.0778 info@augs.org www.augs.org Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks ICD 9 ICD 9 Description ICD 10 Code ICD 10 Description
Overactive bladder can result from one or more of the following causes:
 Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Interstitial Cystitis: Definitions and Confusable Diseases
 Interstitial Cystitis: Definitions and Confusable Diseases ESSIC Meeting 2005 Baden Joop P van de Merwe and Jørgen Nordling This report is the summary of the consensus obtained on definitions and confusable
Interstitial Cystitis: Definitions and Confusable Diseases ESSIC Meeting 2005 Baden Joop P van de Merwe and Jørgen Nordling This report is the summary of the consensus obtained on definitions and confusable
Role of Physiotherapy in the Management of Persistent Pelvic Pain. Brigitte Fung Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital
 Role of Physiotherapy in the Management of Persistent Pelvic Pain Brigitte Fung Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital What is PPP? Chronic Pelvic Pain Pelvic Pain Pelvic Floor/ Pelvic Pain Syndrome Pelvic
Role of Physiotherapy in the Management of Persistent Pelvic Pain Brigitte Fung Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital What is PPP? Chronic Pelvic Pain Pelvic Pain Pelvic Floor/ Pelvic Pain Syndrome Pelvic
Effect of Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Based on the Degree of Obstruction Seen in Urodynamic Study
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.12.840 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Based on the Degree of Obstruction Seen in Urodynamic
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.12.840 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Based on the Degree of Obstruction Seen in Urodynamic
DOWNLOAD OR READ : VOIDING PATTERNS IN YOUNG HEALTHY WOMEN PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : VOIDING PATTERNS IN YOUNG HEALTHY WOMEN PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 voiding patterns in young healthy women voiding patterns in young pdf voiding patterns in young healthy women
DOWNLOAD OR READ : VOIDING PATTERNS IN YOUNG HEALTHY WOMEN PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 voiding patterns in young healthy women voiding patterns in young pdf voiding patterns in young healthy women
Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT
 Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT Hong Sup Kim Konkuk University TURP & MIT TURP : Gold standard MIT TUIP TUNA TUMT HIFU LASER Nd:YAG, ILC, HoLRP, KTP LUTS after TURP and MIT Improved : about 70% Persistent
Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT Hong Sup Kim Konkuk University TURP & MIT TURP : Gold standard MIT TUIP TUNA TUMT HIFU LASER Nd:YAG, ILC, HoLRP, KTP LUTS after TURP and MIT Improved : about 70% Persistent
UP DATE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN ADULT
 UP DATE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN ADULT Yunizaf, MD Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology School of Medicine, University of Indonesia/ Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital
UP DATE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN ADULT Yunizaf, MD Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology School of Medicine, University of Indonesia/ Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital
REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, FEBRUARY 2012
 REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, 24-28 FEBRUARY 2012 Reviewed by Jane Meijlink The EAU Annual Congress 2012 in Paris began with a
REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, 24-28 FEBRUARY 2012 Reviewed by Jane Meijlink The EAU Annual Congress 2012 in Paris began with a
Urodynamic findings in women with insensible incontinence
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
ESSIC 2008 Annual Meeting Rome
 Bladder Pain Syndrome Developing a History Protocol Normal Bladder Function Depends on Suzy, Arul, Andrei, Arvind Integrity of the macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the bladder Central nervous system
Bladder Pain Syndrome Developing a History Protocol Normal Bladder Function Depends on Suzy, Arul, Andrei, Arvind Integrity of the macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the bladder Central nervous system
Management of Female Stress Incontinence
 Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA LEARNING OBJECTIVES DEFINITION. KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer
 MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
Objectives. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
4/30/2008. Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence
PELVIC HEALTH PHYSICAL THERAPY AND THE NURSE PRACTITIONER: WHAT S GOING ON DOWN THERE?
 PELVIC HEALTH PHYSICAL THERAPY AND THE NURSE PRACTITIONER: WHAT S GOING ON DOWN THERE? Kathy Curry, PT, DPT Physical Therapy Today Pelvic Health Physical Therapy () Objectives: Discuss components of pelvic
PELVIC HEALTH PHYSICAL THERAPY AND THE NURSE PRACTITIONER: WHAT S GOING ON DOWN THERE? Kathy Curry, PT, DPT Physical Therapy Today Pelvic Health Physical Therapy () Objectives: Discuss components of pelvic
Kathleen C. Kobashi, MD, FACS Head, Section of Urology and Renal Transplantation Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA
 Kathleen C. Kobashi, MD, FACS Head, Section of Urology and Renal Transplantation Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Advisory Board and/or Speaker Allergan Medtronic Astellas AUA Guidelines
Kathleen C. Kobashi, MD, FACS Head, Section of Urology and Renal Transplantation Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Advisory Board and/or Speaker Allergan Medtronic Astellas AUA Guidelines
Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial Cystitis: Pilot Study Combining Behavioral, Pharmacologic, and Endoscopic Therapies
 Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
Enigma of urethral pain syndrome: Why are there so many ascribed etiologies and therapeutic approaches?
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21, 544 548 doi: 10.1111/iju.12396 Review Article Enigma of urethral pain syndrome: Why are there so many ascribed etiologies and therapeutic approaches?
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21, 544 548 doi: 10.1111/iju.12396 Review Article Enigma of urethral pain syndrome: Why are there so many ascribed etiologies and therapeutic approaches?
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Compassionate and effective management
 IMPACT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE ON QUALITY OF LIFE * Paul Abrams, MD, FRCS ABSTRACT Evaluating the impact of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) on quality of life (QOL) is of paramount importance,
IMPACT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE ON QUALITY OF LIFE * Paul Abrams, MD, FRCS ABSTRACT Evaluating the impact of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) on quality of life (QOL) is of paramount importance,
National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the urinary tract? The urinary tract
Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the urinary tract? The urinary tract
Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Bladder Pain Syndrome Jørgen Nordling Jean-Jacques Wyndaele Joop P. van de Merwe Pierre Bouchelouche Mauro Cervigni Magnus Fall Editors Bladder Pain Syndrome A Guide for Clinicians Editors Jørgen Nordling
Bladder Pain Syndrome Jørgen Nordling Jean-Jacques Wyndaele Joop P. van de Merwe Pierre Bouchelouche Mauro Cervigni Magnus Fall Editors Bladder Pain Syndrome A Guide for Clinicians Editors Jørgen Nordling
Content. Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management
 Prolapse Content Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management Terminology Prolapse Descent of pelvic organs into the vagina Cystocele ant. vaginal wall involving bladder Uterine
Prolapse Content Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management Terminology Prolapse Descent of pelvic organs into the vagina Cystocele ant. vaginal wall involving bladder Uterine
(PDF) PERSISTENT POSTPARTUM URINARY RETENTION: PREVALENCE
 PDF FREQUENT URINATION: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, AND TREATMENT (PDF) PERSISTENT POSTPARTUM URINARY RETENTION: PREVALENCE 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 persistent urge to urinate pdf Frequent urination means having to visit
PDF FREQUENT URINATION: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, AND TREATMENT (PDF) PERSISTENT POSTPARTUM URINARY RETENTION: PREVALENCE 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 persistent urge to urinate pdf Frequent urination means having to visit
4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007)
 4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007) I. Genitourinary Trauma: 1. Goal: The student will be able to demonstrate a basic clinical approach to the management & diagnosis of
4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007) I. Genitourinary Trauma: 1. Goal: The student will be able to demonstrate a basic clinical approach to the management & diagnosis of
Interstitial Cystitis. Dr. Gerard Testa
 Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
REVIEW. International Journal of Surgery
 International Journal of Surgery 11 (2013) 233e237 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect International Journal of Surgery journal homepage: www.theijs.com Review The evil twin syndrome in
International Journal of Surgery 11 (2013) 233e237 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect International Journal of Surgery journal homepage: www.theijs.com Review The evil twin syndrome in
Effect of Desmopressin with Anticholinergics in Female Patients with Overactive Bladder
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2011.52.6.396 Voiding Dysfunction Effect of Desmopressin with Anticholinergics in Female Patients with Overactive Bladder Young Kook Han, Won Ki Lee, Seong Ho Lee, Dae
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2011.52.6.396 Voiding Dysfunction Effect of Desmopressin with Anticholinergics in Female Patients with Overactive Bladder Young Kook Han, Won Ki Lee, Seong Ho Lee, Dae
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice
 Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Neurogenic bladder. Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder.
 Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer
 Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Functional Bladder Problems
 european urology supplements 6 (2007) 710 716 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Functional Bladder Problems Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler * Department of Urology,
european urology supplements 6 (2007) 710 716 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Functional Bladder Problems Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler * Department of Urology,
INVESTIGATION OF LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS IN UROLOGICAL OUTPATIENTS USING ORIGINAL IPSS PLUS POST MICTURITION DRIBBLE QUESTIONNAIRE
 INVESTIGATION OF LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS IN UROLOGICAL OUTPATIENTS USING ORIGINAL IPSS PLUS POST MICTURITION DRIBBLE QUESTIONNAIRE Tadashi Hanail*, Seiji Matsumotol*, Nobutaka Shimizu, Hirotsugu Uemural
INVESTIGATION OF LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS IN UROLOGICAL OUTPATIENTS USING ORIGINAL IPSS PLUS POST MICTURITION DRIBBLE QUESTIONNAIRE Tadashi Hanail*, Seiji Matsumotol*, Nobutaka Shimizu, Hirotsugu Uemural
INJ. Incontinence Pad Usage in Medical Welfare Facilities in Korea. Original Article INTRODUCTION
 Original Article Int Neurourol J 2013;17:186-190 pissn 2093-4777 eissn 2093-6931 International Neurourology Journal Incontinence Pad Usage in Medical Welfare Facilities in Korea Sang Hyub Lee, Ji Soon
Original Article Int Neurourol J 2013;17:186-190 pissn 2093-4777 eissn 2093-6931 International Neurourology Journal Incontinence Pad Usage in Medical Welfare Facilities in Korea Sang Hyub Lee, Ji Soon
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics. Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital 01/02/2018 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms LUTS - one of
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital 01/02/2018 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms LUTS - one of
A REVIEW OF THE ESSIC ANNUAL MEETING 2012, MAY 2012, PORTO, PORTUGAL
 A REVIEW OF THE ESSIC ANNUAL MEETING 2012, 10-12 MAY 2012, PORTO, PORTUGAL Jane Meijlink This year, the ESSIC Annual Meeting was held 10-12 May at the HF Ipanema Park Hotel in the beautiful old city of
A REVIEW OF THE ESSIC ANNUAL MEETING 2012, 10-12 MAY 2012, PORTO, PORTUGAL Jane Meijlink This year, the ESSIC Annual Meeting was held 10-12 May at the HF Ipanema Park Hotel in the beautiful old city of
This Special Report supplement
 ...INTRODUCTION... Overactive Bladder: Defining the Disease Alan J. Wein, MD This Special Report supplement to The American Journal of Managed Care features proceedings from the workshop, Overactive Bladder:
...INTRODUCTION... Overactive Bladder: Defining the Disease Alan J. Wein, MD This Special Report supplement to The American Journal of Managed Care features proceedings from the workshop, Overactive Bladder:
3/20/10. Prevalence of OAB Men: 16.0% Women: 16.9% Prevalence of OAB with incontinence (OAB wet) Men: 2.6% Women: 9.3% Dry. Population (millions) Wet
 1 Prevalence of OAB Men: 16.0% Women: 16.9% Stewart WF, et al. World J Urol. 2003;20:327-336. Prevalence of OAB with incontinence (OAB wet) Men: 2.6% Women: 9.3% Stewart WF, et al. World J Urol. 2003;20:327-336.
1 Prevalence of OAB Men: 16.0% Women: 16.9% Stewart WF, et al. World J Urol. 2003;20:327-336. Prevalence of OAB with incontinence (OAB wet) Men: 2.6% Women: 9.3% Stewart WF, et al. World J Urol. 2003;20:327-336.
As defined by the International Continence Society,
 Validation of the Overactive Bladder Symptom Score Jerry G. Blaivas,* Georgia Panagopoulos, Jeffrey P. Weiss and Chandra Somaroo From the Weill Medical College of Cornell University (JGB, JPW), Lenox Hill
Validation of the Overactive Bladder Symptom Score Jerry G. Blaivas,* Georgia Panagopoulos, Jeffrey P. Weiss and Chandra Somaroo From the Weill Medical College of Cornell University (JGB, JPW), Lenox Hill
Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
Peter K. Sand, M.D. Roger Dmochowski, M.D.
 ANALYSIS OF THE STANDARDISATION OF TERMINOLOGY OF LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION: REPORT FROM THE STANDARDISATION SUB-COMMITTEE OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY Neurourol Urodynam 21: 167-78, 2002
ANALYSIS OF THE STANDARDISATION OF TERMINOLOGY OF LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION: REPORT FROM THE STANDARDISATION SUB-COMMITTEE OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY Neurourol Urodynam 21: 167-78, 2002
Flowmetry/ pelvic floor electromyographic findings in patients with detrusor overactivity
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 41 (3): 521-526, May - June, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0204 Flowmetry/ pelvic floor electromyographic findings in patients with detrusor overactivity Farshid Alizadeh
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 41 (3): 521-526, May - June, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0204 Flowmetry/ pelvic floor electromyographic findings in patients with detrusor overactivity Farshid Alizadeh
