4/30/2008. Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg
|
|
|
- Julianna Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence Based Management 1
2 Definition the complaint of suprapubic pain related to bladder filling, accompanied by other symptoms such as increased daytime and night time frequency, in the absence of proven urinary infection or other obvious pathology. Abrams PH, Cardozo L, Fall M et al: The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the standardisation subcommittee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodynam 2002; 21: 167, Epidemiology Considerable variability among studies regarding incidence and prevalence First population based study in Helsinky (1975): Prevalence in women 18.1 / 100,000 Both sexes 10.6 /100,000 Incidence in females 1.2 per 100,000 2
3 More recent studies suggest Prevalence likely higher 197 women per 100,000 population (from physician-assigned assigned diagnosis) (Clemens et al, 2005) 450 women per 100,000 population (from validated symptom questionnaire) (Roberts, 2003) 865 women per 100,000 population (from patient self-report) roughly 236,000 to > 1 million American women EPIDEMIOLOGY Prevalence estimates per 100,000 United States: 35-24,000 Netherlands: 7 Finland: Japan: 1.2 Female to male ratio = 5:1 Economic cost of disease ~ $427 million Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg
4 ETIOLOGY Likely multifactorial Many theories Role of infection Little data to support the role of infectious etiology Bacterial cystitis may be the first step leading to a low level inflammatory response Unlikely that active infection is involved in the ongoing pathological process or that antibiotics have a role in treatment 4
5 Immune/neuroimmune mechanisms Excessive release of sensory nerve neurotransmitters and mast cell inflammatory mediators propagation of symptoms Inflammation altered nerve growth factor content morphological changes in sensory and motor neurons long-term symptoms after inflammation subsides. Role of Mast Cells Histamine release in tissue causes pain, hyperemia and fibrosis a high number of activated mast cells have been seen in the bladder of patients with PBS/IC could contribute to failure of epithelialization of the bladder surface following injury by 2 potential mechanisms: 1) inhibition of epithelial cell replication 2) interference with epithelial cell spreading, thus resulting in the leaky epithelium found in some cases. 5
6 Leaky Epithelium GAG layer functions as a permeability and anti- adherence barrier Patients with IC have a lower excretion of urinary uronic acid and GAGS than normals, possibly due to a leaky transitional epithelium that might be absorbing these substances to surfaces. Increased mucosal permeability is non-specific and a consequence of bladder inflammation Neurogenic inflammation Activation of sensory nerves neuropeptides such as substance P, neurokinin A neurogenic inflammation. 6
7 Consolidating theories Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg Nervous system and IC Repetitious activation of C fibers results in a progressive build-up up of the magnitude of the electrical response recorded in the second order dorsal horn neurons. wind-up phenomenon persistent NMDA receptor activation cause spinal cord cells to undergo trophic changes, and the pain resulting from subsequent stimulation becomes exaggerated and prolonged. 7
8 DIAGNOSIS Diagnostic approaches vary widely No general agreement on a diagnostic algorithm Heavy reliance on other aspects of the NIDDK criteria NIDDK criteria Based on consensus among a group of researchers who wanted to define strict, homogenous criteria for patient recruitment into research trials Not meant to define the disease, but rather to ensure comparability between that groups of patients research studies 8
9 NIDDK Criteria T o b e d i a g n o s e d w it h i n t e r s t i t i a l c y s t i t i s, p a t i e n t s m u s t h a v e e it h e r g l o m e r u l a t i o n s o n c y s t o s c o p i c e x a m i n a t i o n o r a c l a s s i c H u n n e r u l c e r, a n d t h e y m u s t h a v e e i t h e r p a i n a s s o c i a t e d w it h t h e b l a d d e r o r u r i n a r y u r g e n c y. A n e x a m i n a t io n f o r g l o m e r u l a t i o n s s h o u ld b e u n d e r t a k e n a f t e r d i s t e n t io n o f t h e b l a d d e r u n d e r a n e s t h e s i a t o 8 0 t o c m H 2 O f o r 1 t o 2 m i n u t e s. T h e b l a d d e r m a y b e d is t e n d e d u p t o t w o t i m e s b e f o r e e v a l u a t i o n. T h e g l o m e r u l a t i o n s m u s t b e d i f f u s e - p r e s e n t i n a t l e a s t t h r e e q u a d r a n t s o f t h e b l a d d e r - a n d t h e r e m u s t b e a t l e a s t 1 0 g l o m e r u l a t i o n s p e r q u a d r a n t. T h e g lo m e r u l a t i o n s m u s t n o t b e a l o n g t h e p a t h o f t h e c y s t o s c o p e ( t o e l i m i n a t e a r t i f a c t f r o m c o n t a c t i n s t r u m e n t a t i o n ). T h e p r e s e n c e o f a n y o n e o f t h e f o l lo w i n g e x c l u d e s a d i a g n o s i s o f i n t e r s t i t i a l c y s t i t i s : 1. B l a d d e r c a p a c i t y o f g r e a t e r t h a n m L o n a w a k e c y s t o m e t r y u s i n g e it h e r a g a s o r l i q u i d f i l l i n g m e d i u m 2. A b s e n c e o f a n i n t e n s e u r g e t o v o id w i t h t h e b l a d d e r f i l l e d t o m L o f g a s o r m L o f l i q u i d f i l l i n g m e d i u m 3. T h e d e m o n s t r a t i o n o f p h a s i c i n v o l u n t a r y b l a d d e r c o n t r a c t i o n s o n c y s t o m e t r y u s i n g t h e f i l l r a t e j u s t d e s c r i b e d 4. D u r a t i o n o f s y m p t o m s l e s s t h a n 9 m o n t h s 5. A b s e n c e o f n o c t u r i a 6. S y m p t o m s r e l i e v e d b y a n t i m i c r o b i a l a g e n t s, u r i n a r y a n t i s e p t ic a g e n t s, a n t ic h o l i n e r g i c a g e n t s, o r a n t i s p a s m o d i c a g e n t s 7. A f r e q u e n c y o f u r i n a t i o n w h i l e a w a k e o f l e s s t h a n 8 t i m e s p e r d a y 8. A d i a g n o s is o f b a c t e r i a l c y s t i t i s o r p r o s t a t it is w i t h i n a 3 - m o n t h p e r i o d 9. B l a d d e r o r u r e t e r a l c a l c u l i 1 0. A c t i v e g e n it a l h e r p e s 1 1. U t e r i n e, c e r v i c a l, v a g i n a l, o r u r e t h r a l c a n c e r 1 2. U r e t h r a l d i v e r t ic u l u m 1 3. C y c lo p h o s p h a m i d e o r a n y t y p e o f c h e m i c a l c y s t it is 1 4. T u b e r c u l o u s c y s t i t i s 1 5. R a d i a t i o n c y s t i t i s 1 6. B e n ig n o r m a l i g n a n t b l a d d e r t u m o r s 1 7. V a g i n i t i s 1 8. A g e y o u n g e r t h a n 1 8 y e a r s Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg NIDDK Criteria - Criticisms ICDB study accumulated data on 424 pt with IC. Entry criteria were much more symptom driven than those promulgated for research studies Fully 90% of expert clinicians agreed that patients diagnosed with IC by those criteria in the ICDB indeed had the disorder. 60% of patients deemed to have IC by these experienced clinicians would not have met NIDDK research criteria. 9
10 NIDDK Criteria - Criticisms More recent studies challenge the need for cystoscopy for diagnosis 39-60% of patients have minimal reduction in capacity, minimal or scant glomerulations, and no consistent urine marker or bladder biopsy findings. 8.7% of patients in the IC database had normal cystoscopy Glomerulations are not specific for IC and may be just a response to distention after a prolonged period of under filling rather than a pathological process. Pts. with symptoms of less than 9 months duration could still have IC Pathology Way to exclude other diagnoses No pathognomonic picture No consistent findings Great variation within the same patients pathologic findings 10
11 Associations among Pathologic Features and Patient Symptoms Night-Time Frequency Mast cell count in lamina propria on tryptase stain Complete loss of urothelium Granulation tissue in lamina propria Vascular density in lamina propria Urinary Urgency Percentage of submucosal granulation tissue Urinary Pain Percentage of mucosa denuded of urothelium Percentage of submucosal hemorrhage Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg KCL Test Comparing the sensory nerve provocative ability of sodium versus potassium using a 0.4 M KCl solution Pain and provocation of symptoms constitutes a positive test. Not valid for diagnosis of IC (Chambers et al, 1999) A 36% false-positive rate in asymptomatic men (Yilmaz et al, 2004) 11
12 KCL test (continued) Up to 25% of patients meeting the NIDDK criteria will have a negative KCl test (Parsons et al, 1998) May be positive in overactive bladder, radiation cystitis and urinary tract infection How does one make the diagnosis? Three consensus panels concluded that the diagnosis is suspected on the basis of history, physical examination, and laboratory tests, including negative urinalysis, negative urine culture, negative cytology, and possibly cystoscopy findings. Nickel JC: Interstitial cystitis: the paradigm shifts: international consultations on interstitial cystitis. Rev Urol 2004; 6:
13 Antiproliferative Factor Frizzled-related related peptide growth inhibitor Produced by the urothelium of patients with IC. Found in bladder urine but not in renal pelvic urine High APF has been linked to IC patients with many racial backgrounds Zhang CO, Li ZL, Shoenfelt JL, Kong CZ, Chai TC, Erickson DR, Peters KM, Rovner ES, Keay S. Comparison of APF activity and epithelial growth factor levels in urine from Chinese, African-American, American, and white American patients with interstitial cystitis. Urology May;61(5): Keay SK, Szekely Z, Conrads TP, Veenstra TD, Barchi JJ Jr, Zhang CO, Koch KR, Michejda CJ.An antiproliferative factor from interstitial cystitis patients is a frizzled 8 protein-related related sialoglycopeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A Aug 10;101(32): Antiproliferative Factor APF seems to have role in increasing cell permeability induces reversible inhibition of HB- EGF production and normal bladder epithelial cell proliferation Keay S, Zhang CO, Shoenfelt JL, Chai TC. Decreased in vitro proliferation of bladder epithelial cells from patients with interstitial ystitis. Urology Jun;61(6): Zhang CO, Wang JY, Koch KR, Keay S. Regulation of tight junction proteins and bladder epithelial paracellular permeability by an antiproliferative factor from patients with interstitial cystitis. J Urol Dec;174(6):
14 Antiproliferative Factor Sensitivity and specificity of increased APF activity in IC has been postulated to be 94 and 95% Could be used to gauge response to treatment improvement in APF activity noted after hydrodistention and neuromodulation. Erickson DRet al. Changes in urine markers and symptoms after bladder distention for interstitial cystitis. J Urol Feb;177(2): Chai TC, Zhang C, Warren JW, Keay S. Percutaneous sacral third nerve root neurostimulation improves symptoms and normalizes urinary HB- EGF levels and antiproliferative activity in patients with interstitial cystitis. Urology May;55(5):643-6 Keay SK, Zhang CO, Shoenfelt J, Erickson DR, Whitmore K, Warren JW, Marvel R, Chai T. Sensitivity and specificity of antiproliferative factor, heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor, and epidermal growth factor as urine markers for interstitial cystitis. is. Urology Jun;57(6 Suppl 1): Prevalence of urine antiproliferative factor activity in interstitial cystitis patients and control groups Groups No. Pos/Total No. (%) Pts: interstitial cystitis 206/219 (94) Controls: Asymptomatic 10/113 (9) Overactive bladder 2/32 (6) Bacterial cystitis 7/58 (12) Microscopic hematuria 2/19 (10) Stress incontinence 1/10 (10) Neurogenic bladder 0/11 (0) Benign prostatic hyperplasia 1/14 (7) Nonbacterial prostatitis 1/16 (6) Vulvovaginitis 0/12 (0) Miscellaneous 1/16 (6) (adapted from Keay S, Zhang CO, Marvel R et al: Antiproliferative factor, heparin-binding pidermal growth factor-like growth factor, and epidermal growth factor: sensitive and specific urine markers for interstitial cystitis. Urology 2001; 57: 104) 14
15 Symptoms urinary urgency (57-98%), daytime frequency (84-97%), pain (66-94%) nocturia (44-90%) pain with voiding/dysuria (71-98%) suprapubic pain (39-71%) perineal pain (25-56%) 56%) patient sensation of bladder spasms (50-74%) pubic pressure (60-71%) dyspareunia (46-80%) Depression (55-67%) Teichman JMH, Parsons CL: Contemporary clinical presentation interstitial cystitis. Urology 2007; 69 (supp 4A): Clinical Symptom Scales Three published PBS/IC symptom questionnaires: University of Wisconsin IC Scale, O'Leary-Sant IC Symptom Index and IC problem Index, Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Scale. 15
16 The University of Wisconsin IC Scale Includes seven PBS/IC symptom items captures severity of symptom expression IC patients do NOT score higher than controls (Porru et al, 2005) Addresses some QOL issues Easy to implement Not validated for identification or diagnosis of PBS/IC O'Leary-Sant IC Symptom Index subjected to test-retest reliability analysis validated by administration to IC patients and asymptomatic controls centered on three questions related to urgency/frequency and one on bladder- associated pain 16
17 Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Scale Includes questions that directly reflect a wide variety of the symptoms One third of the questions address pelvic pain A large study utilizing the PUF questionnaire has concluded that up to 23% of American females have PBS/IC (Parsons et al, 2002a) Face validity and utility in question. THERAPY 17
18 THERAPY Conservative Hydrodistention Oral therapy Intravesicle therapy Neuromodulation Surgery Conservative Approach A single trial with empirical course of antibiotics maybe warranted Doxycycline has been reported to have an efficacy of up to 70% in relieving / improving symptoms in a prospective cohort analysis (Burkhard et al, 2004) Repeat courses of antibiotics not recommended in absence of negative cultures. 18
19 Conservative Approach Patient education and empowerment Timed voiding and behavioral modification therapy Stress reduction, exercise, warm tub baths (No RCT evidence) Dietary Modifications Elaborate dietary restrictions are unsupported by any literature. Anecdotal association of IC with many acidic foods. The only placebo-controlled controlled dietary study, while small, failed to demonstrate a relationship between diet and symptoms (Fisher et al, 1993). 19
20 Hydrodistention Perform an initial cystoscopic examination Obtain urine for cytology Distend the bladder for 1 to 2 minutes at a pressure of 80 cm H2O. Bladder is emptied and then refilled A look for glomerulations or ulceration. A therapeutic hydraulic distension follows for another 8 minutes. Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg Hydrodistention Therapeutic responses in patients with a bladder capacity under anesthesia of less than 600 cc were excellent in 26% and fair in 29% compared to 12% excellent and 43% fair in patients with larger bladder capacities. Most favorable responses were extremely brief, with the exceptional patient noting improvement for 6 months. Hanno PM, Wein AJ: Conservative therapy of interstitial cystitis. Semin Urol 1991;9:
21 Hydrodistention Allows for staging of the disease, giving the clinician some idea of the capacity with which conservative therapies may work. A capacity with the patient under anaesthesia of less than 200 cc would not bode well for the likelihood of success of medical therapy Allows for identification of Hunner s ulcers. Oral Therapy Tricyclic antidepressants Antihistamines Sodium Pentosan Polysulfate Analgesics 21
22 Oral Therapy Table Some Oral Medications That Have Been Used for Treatment of PBS/IC Drug Randomized Control Trial % Success Yes 42% Amitriptyline Antibiotic regimens Yes 48% Anticholinergics and antispasmodics No Anecdotal Azathioprine No 50% Benzydamine Yes 0% Chloroquine derivatives No 50% Cimetidine Yes 65% Cortisone and other steroids No 80% Cyclosporine No 90% Doxycycline No 71% Gabapentin No Anecdotal Hormones No Anecdotal Hydroxyzine Yes 31% L-Arginine Yes Not effective Methotrexate No 50% Misoprostol No 48% Montelukast No 90% Nalmefene Yes Not effective Narcotic analgesics No Anecdotal Nifedipine No 87% Phenazopyridine No Anecdotal Quercetin No 92% Sodium pentosan polysulfate Yes 33% Suplatast tosylate Yes Pending publication Vitamin E No Anecdotal AUA Update Series, Lesson 9: Volume 25, 2006 Tricyclic Antidepressants Amitriptyline has been the staple of oral therapy Mechanism of action: central and peripheral anticholinergic actions block the active transport system in the presynaptic nerve ending that is responsible for the reuptake of the released amine neurotransmitters serotonin and noradrenaline sedatives, an action that occurs presumably on a central basis but perhaps is related to their antihistaminic properties 22
23 Amitriptyline RCT, intent to treat N = 50 (44 women, 6 men) Methods: randomized to amitriptyline (25) versus placebo (25) prospectively treated for 4 months with a self-titration protocol that allowed them to escalate drug dosage in 25 mg increments in 1 week-intervals (maximum dosage 100 mg). primary outcome parameter.: change from baseline in the O Leary-Sant IC symptom and problem index secondary outcome parameters: functional bladder capacity and frequency (48-hour voiding log), and intensity of pain and urgency (visual analog scales) 23
24 statistically significant change in the symptom score statistically significant improvement of pain and urgency intensity compared with placebo Amitriptyline Anticholinergic side effects were reported by all except 2 patients in the amitriptyline group (92%) and by 5 patients in the placebo group (21%). Mouth dryness was the most frequent side effect reported in the amitriptyline group (79%). 24
25 Van Ophoven A, Hertle L.. Long-term results of amitriptyline treatment for interstitial cystitis. J Urol Nov;174(5): Prospective cohort analysis N= 94 Methods = patients stratified in 2 groups : IC with NIDDK IC without NIDDK (characteristic symptoms) Mean Follow up = 19 months Results: response rate = 64% (60 patients). mean dose = 55 mg (range 12.5 to 150) Side effects in 79 patients (84%) (dry mouth 79%, weight gain59%). therapeutic result was excellent or good in 43 (46%). dropout rate = 31% (29 patients) Non response to treatment was the primary reason for dropout in all cases, while side effects contributed to dropout in 25 (86%). Improvement in the various IC symptoms was statistically significant compared with baseline. Antihistamines Stems from mast cell theory of IC In some uncontrolled studies, hydroxizine showed symptomatic improvement by up to 30%. No significant response to hydroxizine was found in an NIDDK placebo-controlled controlled trial (Sant et al, 2003). Cimetidine, an H2 antagonist, showed efficacy in double blind, placebo controlled trial. (Thilagarajah et al, 2001) 25
26 Sodium Pentosan Polysulfate Its use stems from an attempt to correct a defect in the epithelial permeability barrier, the GAG layer, of the bladder a heparin analogue available in an oral formulation 3% to 6% excreted into the urine Contradictory reports of efficacy in literature. Sodium Pentosan Polysulfate Two placebo controlled multicenter trials in the United States were published. In the initial study overall improvement of greater than 25% was reported by 28% of the PPS treated group versus 13% in the placebo group. (Mullholand et al, 1990) In the latter study the respective figures were 32% on drug versus 16% on placebo. (Parsons et al, 1993) Mulholland SG, Hanno P, Parsons CL et al: Pentosan polysulfate sodium for therapy of interstitial cystitis. A double- blind placebo controlled clinical study. Urology 1990; 35: : 552. Parsons CL, Benson G, Childs SJ et al: A quantitatively controlled method to study prospectively interstitial cystitis and demonstrate the efficacy of pentosanpolysulfate. J Urol 1993; 150: :
27 Sodium Pentosan Polysulfate A recent NIDDK study looking at PPS and hydroxyzine, alone and in combination, compared to placebo failed to show a statistically significant response to either medication. Sant GR, Propert KJ, Hanno PM et al: A pilot clinical trial of oral pentosan polysulfate and oral hydroxyzine in patients with interstitial cystitis. J Urol 2003; 170: : 810. Cyclosporine Versus Pentosan Polysulfate randomized comparative study N = of 64 IC patients diagnosed by NIDDK criteria Methods: randomized in a1:1 ratio to cyclosporine A (Sandimmun Neoral ) or to pentosan polysulfate sodium (bene-arzneimittel GmbH, Munich, Germany) treatment for 6 months. endpoints : daily micturation frequeny, voided volume, number of nocturia episodes, O Leary-Sant symptom and problem indexes, visual analogue scale for pain and subjective global response assessment. Results: CyA was found to be superior on all parameters at 6 months. more adverse events noted in the cyclosporine arm. Sairanen J, Tammela TL, Leppilahti M, Multanen M, Paananen I, Lehtoranta K, Ruutu M.Cyclosporine A and pentosanpolysulfate sodium for the treatment of interstitial cystitis: a randomized comparative study. J Urol Dec;174(6):
28 Intravesicle Therapy remains a mainstay of treatment in the therapeutic armamentarium of IC DMSO Mainstay of intravesicle treatment Pharmacologic properties: membrane penetration enhanced drug absorption anti-inflammatory inflammatory action analgesic action collagen dissolution muscle relaxation mast cell histamine release 28
29 DMSO Success rate of up to 70% noted in prospective studies done in 1970 s most patients ultimately required re- treatment or further therapy with other modalities Patients with bladder instability do not respond Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg Heparin Mechanism of action: mimic the activity of the bladder's own mucopolysaccharide lining anti-inflammatory inflammatory effects inhibit fibroblast proliferation, angiogenesis, and smooth muscle cell proliferation. 29
30 Heparin No systemic absorption Some SMALL case series showing symptomatic improvement (Parsons, 2000) (Kuo, 2001) Unproven by any placebo-controlled controlled trial. BCG Unclear mechanism of action immunologic and/or anti-inflammatory inflammatory mechanisms have been postulated (Peters et al, 1999) Early small RCT showed high response rate of 60% compared with a 27% placebo response (Peters et al, 1997). Recent large RCT fails to show high response rate. 30
31 BCG RCT N = 265 Participants were randomized to intravesical BCG or intravesical placebo, and received up to 6 instillations within 6 to 10 weeks. F/U WKS Primary outcome: patient reported global response assessment Secondary outcomes: 24-hour voiding diary, pain, urgency, validated IC symptom indexes and adverse events 31
32 RESULTS Response rates for the primary outcome were 12% for placebo and 21% for BCG (p 0.062). No statistical significance reached. Small improvements were observed for all secondary outcomes, some more so with BCG, but these differences were of borderline statistical significance. Although a large number of adverse events were reported in the BCG arm, there was no statistically significant difference between the treatment arms in overall adverse event rates Conclusion Intravesical BCG therapy was reasonably well tolerated but not more effective than placebo in this population of patients with moderate to severe IC. 32
33 Table Some Intravesical Medications That Have Been Used for Treatment of PBS/IC Drug Randomized Controlled Trial % Success Silver nitrate No 60% Clorpactin WCS-90 No 60% Dimethylsulfoxide Yes 70% Bacillus Yes No proven efficacy Calmette-Guérin Resiniferatoxin Yes No proven efficacy Hyaluronic acid Yes No proven efficacy Heparin No 60% Chondroitin sulfate No 33% Lidocaine No 65% Capsaicin No No demonstrated efficacy Oxybutynin No Efficacy suggested Doxorubicin No Anecdotal efficacy Pentosan polysulfate Yes 40% Neuromodulation relieves pain by stimulating myelinated afferents to activate segmental inhibitory circuits patients who do best with this treatment modality are those who have identifiable pain and dysfunction in the pelvic muscles 33
34 Neuromodulation the process Trial stimulation performed with a percutaneous temporary electrode for a 3 to 4-day temporary stimulation period to assess efficacy. S3 nerve is most frequently used. A wire electrode is inserted into the foramen and connected to an external pulse generator If the trial is successful, the patient would be considered for implantation of a permanent neural prosthesis. More recently, a staged procedure has supplanted the traditional percutaneous approach, as the response to stimulation can be better assessed with more accurate lead placement and stability than through the more hit or miss percutaneous lead placement Neuromodulation evidence No RCT evidence A decrease in antiproliferative factor activity and normalization of HB-EGF levels in patients with successful test stimulation (Chai et al, 2000a) In a prospective study of 27 refractory patients, implantation of sacral nerve root stimulator showed improvements in urinary frequency, voided volumes, nocturia and pain after a mean follow up of 14 months. (Commiter, 2003) Sacral neuromodulation can decrease narcotic requirements significantly in refractory PBS/IC (Peters et al, 2004) 34
35 Surgical therapy Reserved for motivated and well-informed patients in the category of extremely severe, unresponsive disease, a group which comprises fewer than 10%. Aimed at increasing the functional capacity of the bladder or diverting the urinary stream. Augmentation (substitution) cystoplasty and urinary diversion with or without cystectomy have been used as a last resort with good results in select patients. AUA Update Series, Lesson 9: Volume 25,
36 CONCLUSIONS Interstitial cystitis is much more common than what was initially thought Once confirmed by other centers, APF may prove to be a useful marker in diagnosis of IC Multiple effective treatment options are available. A step wise approach to management should be used. Thank-you 36
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS. Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >60%
 DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
In evaluating a patient with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urologists
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence
 BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective?
 Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France
 A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
Addendum 1: International Consultation
 Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond
 Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Interstitial Cystitis. Dr. Gerard Testa
 Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS)
 Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
Interstitial cystitis
 Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
Interstitial Cystitis
 Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial Cystitis: Pilot Study Combining Behavioral, Pharmacologic, and Endoscopic Therapies
 Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS)
 31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website:
 Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology
 Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Interstitial Cystitis
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline.
 Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion Criterion non-neurogenic OAB Exclusion Criterion
Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion Criterion non-neurogenic OAB Exclusion Criterion
Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
LLLT FOR INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS USING AN 830 NM GaAlAs DIODE LASER
 LLLT FOR INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS USING AN 830 NM GaAlAs DIODE LASER *Katsumi Sasaki M.D. 1, Toshio Ohshiro M.D. Ph.D. 2, Takafumi Ohshiro M.D. 1, Shunji Fujii M.D. 1, Yuki Taniguchi M.D. 1, and Toshihide
LLLT FOR INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS USING AN 830 NM GaAlAs DIODE LASER *Katsumi Sasaki M.D. 1, Toshio Ohshiro M.D. Ph.D. 2, Takafumi Ohshiro M.D. 1, Shunji Fujii M.D. 1, Yuki Taniguchi M.D. 1, and Toshihide
Functional Bladder Problems
 european urology supplements 6 (2007) 710 716 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Functional Bladder Problems Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler * Department of Urology,
european urology supplements 6 (2007) 710 716 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Functional Bladder Problems Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler * Department of Urology,
Interstitial Cystitis
 J Obstet Gynecol India Vol. 58, No. 1 : January/February 2008 pg 24-31 Review Article Interstitial Cystitis Satpathy Hemant K, Taylor Richert Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, CUMC, Omaha, NE, USA,
J Obstet Gynecol India Vol. 58, No. 1 : January/February 2008 pg 24-31 Review Article Interstitial Cystitis Satpathy Hemant K, Taylor Richert Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, CUMC, Omaha, NE, USA,
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Mini-Reviews. Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review
 J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol (2004) 17:7 11 Mini-Reviews Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review T.F. Mattox, MD, FACOG Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Urogynecology,
J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol (2004) 17:7 11 Mini-Reviews Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review T.F. Mattox, MD, FACOG Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Urogynecology,
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
How does interstitial cystitis begin?
 Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
32 OBG Management July 2010 Vol. 22 No. 7 obgmanagement.com
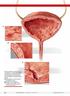 A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
Interstitial and chronic cystitis. Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall?
 Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Management of OAB. Lynsey McHugh. Consultant Urological Surgeon. Lancashire Teaching Hospitals
 Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
Treatment effectiveness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines?
 original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria
original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria
UroToday International Journal. Volume 2 - October 2009
 UroToday International Journal Robert J. Evans, 1 Jeffrey Proctor, 2 Robert M. Moldwin 3 1 Alliance Urology Specialists, Greensboro, NC; 2 Georgia Urology, Cartersville, GA; 3 The Arthur Smith Institute
UroToday International Journal Robert J. Evans, 1 Jeffrey Proctor, 2 Robert M. Moldwin 3 1 Alliance Urology Specialists, Greensboro, NC; 2 Georgia Urology, Cartersville, GA; 3 The Arthur Smith Institute
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
La vescica iperattiva: dalla diagnosi ai nuovi approcci terapeutici
 La Prostata nel Mirino Napoli, 1 dicembre 2016 La vescica iperattiva: dalla diagnosi ai nuovi approcci terapeutici Giorgio Annoni Cattedra e Scuola di Specializzazione in Geriatria Università degli Studi
La Prostata nel Mirino Napoli, 1 dicembre 2016 La vescica iperattiva: dalla diagnosi ai nuovi approcci terapeutici Giorgio Annoni Cattedra e Scuola di Specializzazione in Geriatria Università degli Studi
Efficacy of Interstitial Cystitis Treatments: A Review
 eau-ebu update series 4 (2006) 47 61 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Efficacy of Interstitial Cystitis Treatments: A Review Gilles Karsenty, Walid AlTaweel,
eau-ebu update series 4 (2006) 47 61 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Efficacy of Interstitial Cystitis Treatments: A Review Gilles Karsenty, Walid AlTaweel,
INTRODUCTION. Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction. Aram Kim 1, Kyeong-Ok Hoe 2, Jung Hyun Shin 2, Myung-Soo Choo 2 1
 Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW?
 NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW? *Massimo Lazzeri, 1 Philip Van Kerrebroeck 2 1. Department of Urology, Istituto Clinico Humanitas IRCCS, Humanitas
NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW? *Massimo Lazzeri, 1 Philip Van Kerrebroeck 2 1. Department of Urology, Istituto Clinico Humanitas IRCCS, Humanitas
CYSTISTAT. Hyaluronan Training
 CYSTISTAT Hyaluronan Training HISTORICAL ASPECTS In 1934, Karl Meyer and his assistant, John Palmer, described for the first time the process to isolate a new Glucosa- Amino-Glycan (GAG) from the cows
CYSTISTAT Hyaluronan Training HISTORICAL ASPECTS In 1934, Karl Meyer and his assistant, John Palmer, described for the first time the process to isolate a new Glucosa- Amino-Glycan (GAG) from the cows
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC)
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium
 Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis
 Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis R. J. Evans,*, R. M. Moldwin, N. Cossons, A. Darekar, I. W. Mills and D. Scholfield From the Department
Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis R. J. Evans,*, R. M. Moldwin, N. Cossons, A. Darekar, I. W. Mills and D. Scholfield From the Department
Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome
 Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:395 400 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1252-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome Jennifer T. Anger
Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:395 400 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1252-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome Jennifer T. Anger
2/9/2008. Men Women. Prevalence of OAB. Men: 16.0% Women: 16.9% Prevalence (%) < Age (years)
 Definition Botox for Overactive Bladder Donna Y. Deng Assistant Professor UCSF Department of Urology Urinary urgency With or without urge incontinence Usually with frequency & nocturia International Continence
Definition Botox for Overactive Bladder Donna Y. Deng Assistant Professor UCSF Department of Urology Urinary urgency With or without urge incontinence Usually with frequency & nocturia International Continence
PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA
 PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA E.O. Stakhovsky, PhD, MD, Professor, Head of the Scientific and Research Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Oncourology,
PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA E.O. Stakhovsky, PhD, MD, Professor, Head of the Scientific and Research Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Oncourology,
Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores
 DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
Mr. GIT KAH ANN. Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
 Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Is Urethral Pain Syndrome Really Part of Bladder Pain Syndrome?
 Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.22 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):22-27 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.22 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):22-27 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
 Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23284 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment
Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23284 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial Tahereh Eftekhar 1, Nastaran Teimoory 1, Elahe Miri 1, Abolghasem Nikfallah 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial Tahereh Eftekhar 1, Nastaran Teimoory 1, Elahe Miri 1, Abolghasem Nikfallah 2,
Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF
Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF
Interstitial Cystitis:
 Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive Bladder
 Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 328364, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/328364 Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive
Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 328364, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/328364 Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive
Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information
 Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information Round Rock Jollyville Westlake Central office: Phone 512-231-1444 Fax 512-231-1470 www.urologyteam.com Rev June 2017 What is Interstitial
Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information Round Rock Jollyville Westlake Central office: Phone 512-231-1444 Fax 512-231-1470 www.urologyteam.com Rev June 2017 What is Interstitial
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Corporate Medical Policy File name: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File code: UM.NS.05 Origination: 8/2011 Last Review:
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Corporate Medical Policy File name: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File code: UM.NS.05 Origination: 8/2011 Last Review:
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: percutaneous_tibial_nerve_stimulation_for_voiding_dysfunction
Corporate Medical Policy Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: percutaneous_tibial_nerve_stimulation_for_voiding_dysfunction
Interstitial cystitis (IC), also
 Interstitial cystitis: Algorithm to simplify diagnosis of chronic urinary symptoms By Anita L. Booth, DNP, FNP-BC and Jill Harpst Rodgers, DNP, FNP-BC This pre/post-test study was undertaken to determine
Interstitial cystitis: Algorithm to simplify diagnosis of chronic urinary symptoms By Anita L. Booth, DNP, FNP-BC and Jill Harpst Rodgers, DNP, FNP-BC This pre/post-test study was undertaken to determine
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
03/13/18. A. Symptoms lasting for greater than or equal to 12 months that have resulted to significant impairment in activities of daily living; and
 Reference #: MC/I008 Page: 1 of 5 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) Non-ERISA PreferredOne Community Health Plan
Reference #: MC/I008 Page: 1 of 5 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) Non-ERISA PreferredOne Community Health Plan
BJU International EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME
 EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: BJU-2007-1373
EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: BJU-2007-1373
TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH
 TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH CONTENTS Overactive bladder (OAB) Treatment of OAB Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist (Betmiga ) - Panacea? LASER treatment - a flash in the pan or the
TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH CONTENTS Overactive bladder (OAB) Treatment of OAB Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist (Betmiga ) - Panacea? LASER treatment - a flash in the pan or the
Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults
 Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults Christopher Chapple Professor of Urology Sheffield Teaching Hospitals University of Sheffield Sheffield Hallam University UK 23 rd October 2015 Terminology
Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults Christopher Chapple Professor of Urology Sheffield Teaching Hospitals University of Sheffield Sheffield Hallam University UK 23 rd October 2015 Terminology
Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain
 Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain Prof Dr K. Everaert Functional urology Department of Urology Ghent University Hospital Gent, Belgium Chronic pelvic pain
Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain Prof Dr K. Everaert Functional urology Department of Urology Ghent University Hospital Gent, Belgium Chronic pelvic pain
Infection/Inflammation. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Infection/Inflammation A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Philip C. Bosch*, From the Department of Urology, Palomar Medical
Infection/Inflammation A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Philip C. Bosch*, From the Department of Urology, Palomar Medical
Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
 Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction (Text update March 2009) M. Stöhrer (chairman), B. Blok, D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier- Kastler, P. Denys, G. Kramer, J. Pannek, G. del Popolo, P.
Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction (Text update March 2009) M. Stöhrer (chairman), B. Blok, D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier- Kastler, P. Denys, G. Kramer, J. Pannek, G. del Popolo, P.
Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_
 207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
Objectives. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O. Talbott,* Josephine Davis and Lisa J. Regan
 Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
Introduction. Original Article
 Original Article Test-retest reliability and discriminant validity for the Brazilian version of The Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index and Problem Index and Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Patient
Original Article Test-retest reliability and discriminant validity for the Brazilian version of The Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index and Problem Index and Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Patient
Anticholinergic medication use for female overactive bladder in the ambulatory setting in the United States.
 Página 1 de 6 PubMed darifenacin vs solifenacin Display Settings:, Sorted by Recently Added Results: 5 1. Int Urogynecol J. 2013 Oct 25. [Epub ahead of print] Anticholinergic medication use for female
Página 1 de 6 PubMed darifenacin vs solifenacin Display Settings:, Sorted by Recently Added Results: 5 1. Int Urogynecol J. 2013 Oct 25. [Epub ahead of print] Anticholinergic medication use for female
NEUROGENIC BLADDER. Dr Harriet Grubb Dr Alison Seymour Dr Alexander Joseph
 NEUROGENIC BLADDER Dr Harriet Grubb Dr Alison Seymour Dr Alexander Joseph OUTLINE Definition Anatomy and physiology of bladder function Types of neurogenic bladder Assessment and management Complications
NEUROGENIC BLADDER Dr Harriet Grubb Dr Alison Seymour Dr Alexander Joseph OUTLINE Definition Anatomy and physiology of bladder function Types of neurogenic bladder Assessment and management Complications
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease. June 2018
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN
 Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
s r e t n I sititsyc laititsret ystitis Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis In itial Ctsretn IC I sititsyc laititsretni PRODUCT MONOGRAPH
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Intersti t i a l Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Inters IC CONTENTS Interstitial Cystitis: An Overview Introduction... Epidemiology of
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Intersti t i a l Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Inters IC CONTENTS Interstitial Cystitis: An Overview Introduction... Epidemiology of
ABNORMAL EXPRESSION OF MOLECULAR MARKERS FOR BLADDER IMPERMEABILITY AND DIFFERENTIATION IN THE UROTHELIUM OF PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS
 0022-5347/04/1714-1554/0 Vol. 171, 1554 1558, April 2004 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000118938.09119.a5 ABNORMAL EXPRESSION
0022-5347/04/1714-1554/0 Vol. 171, 1554 1558, April 2004 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000118938.09119.a5 ABNORMAL EXPRESSION
Overactive Bladder Syndrome
 Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease. June 2017
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2017 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2017 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Neurogenic bladder. Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder.
 Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Expanding Indications for Neuromodulation
 Urol Clin N Am 32 (2005) 59 63 Expanding Indications for Neuromodulation Andrew J. Bernstein, MD, Kenneth M. Peters, MD* Department of Urology, William Beaumont Hospital, 3535 West 13 Mile Road, Suite
Urol Clin N Am 32 (2005) 59 63 Expanding Indications for Neuromodulation Andrew J. Bernstein, MD, Kenneth M. Peters, MD* Department of Urology, William Beaumont Hospital, 3535 West 13 Mile Road, Suite
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PERCUTANEOUS POSTERIOR TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION (PPTNS) POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PERCUTANEOUS POSTERIOR Clinical criteria used to make utilization review decisions are based on credible scientific evidence published in peer reviewed medical literature generally
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PERCUTANEOUS POSTERIOR Clinical criteria used to make utilization review decisions are based on credible scientific evidence published in peer reviewed medical literature generally
Botulinum Toxin Injection for OAB: Indications & Technique
 Classification of LUTS Botulinum Toxin Injection for OAB: Indications & Technique Sherif Mourad, MD Professor of Urology, Ain Shams University General Secretary of International Continence President of
Classification of LUTS Botulinum Toxin Injection for OAB: Indications & Technique Sherif Mourad, MD Professor of Urology, Ain Shams University General Secretary of International Continence President of
Various Types. Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG
 Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER
 GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER (Limited text update December 21) M. Babjuk, W. Oosterlinck, R. Sylvester, E. Kaasinen, A. Böhle, J. Palou, M. Rouprêt Eur Urol 211 Apr;59(4):584-94 Introduction
GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER (Limited text update December 21) M. Babjuk, W. Oosterlinck, R. Sylvester, E. Kaasinen, A. Böhle, J. Palou, M. Rouprêt Eur Urol 211 Apr;59(4):584-94 Introduction
Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
 Int Urogynecol J (2012) 23:1147 1153 DOI 10.1007/s00192-012-1686-2 REVIEW ARTICLE Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis P. K. Matsuoka & J. M. Haddad
Int Urogynecol J (2012) 23:1147 1153 DOI 10.1007/s00192-012-1686-2 REVIEW ARTICLE Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis P. K. Matsuoka & J. M. Haddad
Pelvic Pain and Interstitial Cystitis: Therapeutic Strategies, Results and Limitations
 EAU Update Series EAU Update Series 2 (2004) 179 186 Pelvic Pain and Interstitial Cystitis: Therapeutic Strategies, Results and Limitations Jørgen Nordling* Department of Urology, Herlev Hospital, University
EAU Update Series EAU Update Series 2 (2004) 179 186 Pelvic Pain and Interstitial Cystitis: Therapeutic Strategies, Results and Limitations Jørgen Nordling* Department of Urology, Herlev Hospital, University
The clinical presentation and diagnosis of ketamineassociated urinary tract dysfunction in Singapore
 Singapore Med J 2015; 56(12): 660-665 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015185 CMEArticle The clinical presentation and diagnosis of ketamineassociated urinary tract dysfunction in Singapore Jacklyn Yek 1, MBBS, MRCS,
Singapore Med J 2015; 56(12): 660-665 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015185 CMEArticle The clinical presentation and diagnosis of ketamineassociated urinary tract dysfunction in Singapore Jacklyn Yek 1, MBBS, MRCS,
Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2
 Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2 1 The Male Health Centre, Oakville, Ontario, Canada 2 Humber River Regional Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2 1 The Male Health Centre, Oakville, Ontario, Canada 2 Humber River Regional Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto,
What is on the Horizon in Drug Therapy for OAB?
 What is on the Horizon in Drug Therapy for OAB? K-E Andersson, MD, PhD Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston Salem, North Carolina Disclosures
What is on the Horizon in Drug Therapy for OAB? K-E Andersson, MD, PhD Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston Salem, North Carolina Disclosures
Introduction. For further information please contact:
 Product Monograph Introduction Teva UK Limited is one of the biggest pharmaceutical companies in the UK. We re proud to be part of the Teva Pharmaceutical Industries group, and we make medicines that help
Product Monograph Introduction Teva UK Limited is one of the biggest pharmaceutical companies in the UK. We re proud to be part of the Teva Pharmaceutical Industries group, and we make medicines that help
