QUESTIONSHEET 1. (b)name two specific types of gene mutation and give two examples of gene mutation.
|
|
|
- Claude Clark
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 QUESTIONSHEET 1 New variations may sometimes arise because of mutation. This may be gene mutation or chromosomal mutation. (a) Briefly distinguish between gene and chromosomal mutations. [3] (b)name two specific types of gene mutation and give two examples of gene mutation. Type 1:... Type 2:... Examples:... [4] (c) What is Down s syndrome? (d)when mutations occur they usually cause discontinuous variation. However, continued gene mutation can lead to continuous variation. Explain how this is so. TOTAL / 11
2 QUESTIONSHEET 2 The flow diagram below illustrates the evolution of modern Bread Wheat, Triticum aestivum which has occured during the last 10,000 years. Modern Bread Wheat has arisen by polyploidy occuring between ancient cultivated wheats and wild species. Triticum monococcum (Einkorn wheat) 2n = 14 AA X Sterile F 1 hybrid 2n=14 AB Restitution nucleus Triticum dicoccum (Emmer wheat) 4n = 28 ABAB Agropyron sp. (Wild goat grass) 2n = 14 BB X Triticum aestivum (Modern bread wheat) 6n = 42 ABDABD Triticum tauschii 2n = 14 DD Sterile F 1 hybrid 3n = 21 ABD Restitution nucleus (a) (i) What is meant by the term polyploidy? The type of polyploidy illustrated above involves hybridisation. What name is given to this type of polyploidy? [1] (iii)what do the letters A, B and D indicate? [1] (iv) What is a restitution nucleus? (Contimued...)
3 QUESTIONSHEET 2 CONTINUED (b) Unlike other forms of speciation which are gradual, polyploidy can produce new species within one generation. Explain why this is so. [3] (c) (i) Polyploid plants have evolutionary advantage since they possess hybrid vigour. What is meant by hybrid vigour? [3] Einkorn wheat was cultivated by Neolithic humans and Emmer wheat by ancient Iranian peoples. Suggest two advantages you think Modern bread wheat may have over the ancient breeds? 1:... 2:... TOTAL / 14
4 QUESTIONSHEET 3 Suggest mechanisms to explain the following. (a) The emergence and establishment of new strains of DDT-resistant mosquitoes. [4] (b)the emergence of antibiotic strains of bacteria among many different bacterial species. [4] (c) The sudden emergence of fertility in a sterile F 1 hybrid. TOTAL / 10
5 QUESTIONSHEET 4 (a) What is background radiation and why is it present? (b)distinguish alpha, beta and gamma radiation and say which is least likely to cause mutation. [4] (c) Name two chemical mutagens. 1:... 2:... (d)(i) The damage caused by radiation to the genetic material is cumulative. What does this mean? [1] A sample of Drosophila (fruit flies) was irradiated with X-rays giving a dose of 5 Sieverts (a measure of radiation dose). The mutation rate of a specific gene was found to be increased by 2%. What would the expected percentage mutation rate be after a radiation dose of 12.5 Sieverts? Show your working. (e) (i) List three types of gene mutation. Answer:... 1:... 2:... 3:... [1] List three types of chromosome mutation where chromosome structure is altered. 1:... 2:... 3:... [1] TOTAL / 13
6 QUESTIONSHEET 5 The picture below shows human chromosomes obtained by karyotyping. (a) (i) Describe the process of karyotyping. [4] In humans karyotyping is usually carried out after amniocentesis. What is amniocentesis? [3] (Continued...)
7 QUESTIONSHEET 5 CONTINUED (b)(i) Does the karyotype above represent a full set of human chromosomes? Explain your answer. A mutation is shown in the above karyotype. Label it on the drawing, name it and explain how could it have happened. Name:... How it happened: [4] (iii) What was the sex of the individual from which the karyotype was taken? Explain your answer. Sex:... Explanation: TOTAL / 15
8 QUESTIONSHEET 6 The drawings below show the appearance of normal human red cells and red cells from an individual with sickle cell anaemia. The condition is caused by a mutant recessive gene.in the homozygous condition it causes sickle cell anaemia which has serious disabling effects on sufferers, while in the heterozygous condition it causes sickle cell trait which is harmless and gives resistance against infection by malarial parasites. The abnormal gene also changes the permeability of red cell membranes so that the red cells lose potassium ions. normal red cells sickle cells (a) The mutation affects the amino acid sequence of the β-globin chain of haemoglobin. The normal amino acid sequence, together with the mrna and DNA bases which code for the sequence are shown below. amino acid sequence: valine /histidine /leucine /threonine /proline /glutamic acid /glutamic acid mrna codons: GUA CAU CUC ACU CCA GAA GAA DNA bases: CAT GTA GAG TGA GGT CTT CTT (i) If the base marked with an arrow was changed to A (adenine) what would be the effect on the amino acid sequence of the globin? Explain your answer. What will be the probable effect is this change in amino acid sequence on the structure of the haemoglobin? Explain your answer.... (iii) Name this type of gene mutation.... [1] (b) The sickle cell haemoglobin is known as haemoglobin S. This type of haemoglobin is found mainly in individuals who live in the malarial belts of the world or in their descendents. Suggest and explain why this is so.... [4] TOTAL / 10
9 QUESTIONSHEET 7 Cystic fibrosis is the most common recessive genetic disorder in the UK Caucasian population with an overall birth frequency of about 1 in It is characterised by severe respiratory problems and inadequate pancreatic function, caused by accumulation of sticky mucus.there is no cure at present but improved treatments can now increase the life expectancy to about 30 years, death usually being due to respiratory failure. Males with CF are usually sterile. Cystic fibrosis is due to a mutation in the gene encoding the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator(cftr). This protein regulates transport of chloride across cell membranes. The mutant gene is recessive and heterozygotes do not exhibit symptoms. The mutant gene occurs in about 4% of the population and usually arises by deletion of three adjacent nucleotides. (a) (i) Explain how the deletion could occur and influence the effectiveness of the CFTR gene.... [4] Name two other types of gene mutation. 1:... 2:... (b)(i) By means of a genetic diagram show the probability of two carrier parents producing a CF child. Probability:... [5] What would be the expected % incidence of cystic fibrosis in the population? Explain your answer.... [4] (iii) Since cystic fibrosis is a lethal condition,why does its allele persist in the population?... [1] (c) Suggest two treatments for cystic fibrosis. 1:... 2:... TOTAL / 18
10 QUESTIONSHEET 8 About 80% of the world s coffee is obtained from Coffea arabica. The genus Coffea contains about 100 species of small evergreen seed producing trees, with a basic diploid chromosome number of 2n = 22. These species are generally outbreeding. The seeds are the coffee beans that can be processed and ground for use. Coffea arabica, however, is a tetraploid with 2n = 44 and it is generally inbreeding, a habit which, in this case, provides considerable advantages. (a) (i) Explain how the tetraploid condition could have arisen in Coffea arabica.... [4] Coffea arabica is genetically isolated from its closely related species and ancestral species, with which it cannot successfully interbreed. Explain why this is so. (b)suggest four reasons why the inbreeding habit of Coffea arabica has been advantageous. 1:... 2:... 3:... 4:... [4] TOTAL / 11
11 QUESTIONSHEET 9 Read through the following passage concerning grapefruit (Citrus paradisii) and then answer the questions below. Grape fruit originated on the island of Barbados in the middle of the 1700s. It arose as a result of hybridisation between the orange (Citrus sinensis) and the pummelo (Citrus grandis). Grape fruit have apomictic seeds, meaning that the seeds develop without being fertilised. Red ruby grapefruit arose in Texas in the 1920s as a result of mutation in a white-fleshed variety. (a) Describe what is meant by the term hybridisation in the passage above. (b) Suggest why the grapefruit reproduces by apomictic seeds.... (c) What will the consequences be to the grapefruit of having apomictic seeds?... (d) What type of mutation would have produced the ruby variety?... TOTAL / 9
12 QUESTIONSHEET 10 The nectarine arose as a single gene mutation in a peach which caused the development of a smooth skin instead of the fuzzy skin of a peach. (a) Explain what is meant by the term single gene mutation. (b)(i) Name two conditions in humans that are caused by single gene mutations Describe the genetic basis of Down s syndrome in humans. TOTAL / 8
13 QUESTIONSHEET 11 The graph below shows the effect of mother s age on the incidence of children born with Down s syndrome. Incidence of Down s syndrome per 1000 births Age of mother/years (a) (i) Describe the trend in the incidence of Down s syndrome shown in the graph. Suggest a reason for the change in the incidence of Down s syndrome.... [1] (iii) Down s syndrome is also known as trisomy 21, Edward s syndrome is trisomy 18 and Patau s syndrome is trisomy 13. Describe how these trisomies may arise. (b) Women over 40 years of age are advised to have the chromosomes of the fetus examined. Suggest how this could be done. TOTAL / 10
14 QUESTIONSHEET 12 Carefully study chromosomes A and B. Chromosome B differs from chromosome A due to a chromosomal mutation. A B (a) (i) Name the type of chromosomal mutation that has occured.... [1] Draw an arrow ( ) under chromosome B to show the mutated region. [1] (b) Chromosome B is from a human and chromosome A is the equivalent chromosome from a chimpanzee. (i) How do the chromosomes show that humans and chimpanzees are closely related genetically, almost certainly sharing some common ancestry in their evolutionary history? Altogether there are nine similar mutations altering the genotypes of man and chimpanzees. At what stage in the evolutionary history of these species did the mutations probably occur?... [1] TOTAL / 6
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level * 37031 33241* BIOLOGY 9700/41 Paper 4 Structured Questions A2 Core October/November 2009 2 hours Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level * 37031 33241* BIOLOGY 9700/41 Paper 4 Structured Questions A2 Core October/November 2009 2 hours Candidates
Meiosis I. Meiosis II. In each empty circle, write the number of chromosomes that would be found in the cell. (1)
 1. The diagram shows stages of meiosis in a human testis. Each circle represents a cell. 46 Meiosis I Meiosis II (a) In each empty circle, write the number of chromosomes that would be found in the cell.
1. The diagram shows stages of meiosis in a human testis. Each circle represents a cell. 46 Meiosis I Meiosis II (a) In each empty circle, write the number of chromosomes that would be found in the cell.
Human Genetic Disorders
 Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Class XII Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Biology
 Question 1: Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for experiment by Mendel. Mendel selected pea plants to carry out his study on the inheritance of characters from parents to offspring. He selected
Question 1: Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for experiment by Mendel. Mendel selected pea plants to carry out his study on the inheritance of characters from parents to offspring. He selected
Genes are found on Chromosomes! Genes are found on Chromosomes! I. Types of Mutations
 Genes are found on Chromosomes! genes and chromosomes are made up of DNA, which is the genetic material for all life on earth genes are found on a specific region on a chromosome; called a locus (loci)
Genes are found on Chromosomes! genes and chromosomes are made up of DNA, which is the genetic material for all life on earth genes are found on a specific region on a chromosome; called a locus (loci)
Genetic Variation Junior Science
 2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
Human Genetic Disorders. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Human Genetic Disorders
 Lesson Overview 14.2 Human Genetic Disorders THINK ABOUT IT Have you ever heard the expression It runs in the family? Relatives or friends might have said that about your smile or the shape of your ears,
Lesson Overview 14.2 Human Genetic Disorders THINK ABOUT IT Have you ever heard the expression It runs in the family? Relatives or friends might have said that about your smile or the shape of your ears,
Lesson Overview. Human Genetic Disorders. Lesson Overview Human Genetic Disorders
 Lesson Overview 14.2 Human Genetic Disorders From Molecule to Phenotype There is a direct connection between molecule and trait, and between genotype and phenotype. In other words, there is a molecular
Lesson Overview 14.2 Human Genetic Disorders From Molecule to Phenotype There is a direct connection between molecule and trait, and between genotype and phenotype. In other words, there is a molecular
Principles of Inheritance and Variation
 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question 1: Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for experiment by Mendel. Answer Mendel selected pea plants to carry out his study on the inheritance of
Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question 1: Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for experiment by Mendel. Answer Mendel selected pea plants to carry out his study on the inheritance of
Mechanisms of Evolution
 Mechanisms of Evolution TEKS 7(F) analyze and evaluate the effects of other evolutionary mechanisms, including genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination Evolution is. For Darwin (1859): Evolution
Mechanisms of Evolution TEKS 7(F) analyze and evaluate the effects of other evolutionary mechanisms, including genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination Evolution is. For Darwin (1859): Evolution
Mutations. A2 Biology For WJEC
 12. Mutation is a change in the amount, arrangement or structure in the DNA of an organism. 13. There are two types of mutations, chromosome mutations and gene mutations. Mutations A2 Biology For WJEC
12. Mutation is a change in the amount, arrangement or structure in the DNA of an organism. 13. There are two types of mutations, chromosome mutations and gene mutations. Mutations A2 Biology For WJEC
REPRODUCTION. NAME.. Page 1. Q1.Figure 1 shows the stages in the transmission of the malaria parasite by mosquitoes to humans.
 REPRODUCTION. Thornton College NAME.. Q.Figure shows the stages in the transmission of the malaria parasite by mosquitoes to humans. Figure (a) Where in the mosquito does Stage 2 happen? Draw a ring around
REPRODUCTION. Thornton College NAME.. Q.Figure shows the stages in the transmission of the malaria parasite by mosquitoes to humans. Figure (a) Where in the mosquito does Stage 2 happen? Draw a ring around
Lesson Overview. Human Genetic Disorders. Lesson Overview Human Genetic Disorders
 Lesson Overview 14.2 Human Genetic Disorders THINK ABOUT IT Have you ever heard the expression It runs in the family? Relatives or friends might have said that about your smile or the shape of your ears,
Lesson Overview 14.2 Human Genetic Disorders THINK ABOUT IT Have you ever heard the expression It runs in the family? Relatives or friends might have said that about your smile or the shape of your ears,
Each person has a unique set of characteristics, such as eye colour, height and blood group.
 1 of 51 2 of 51 What is inheritance? 3 of 51 Each person has a unique set of characteristics, such as eye colour, height and blood group. A person s characteristics are determined by a combination of the
1 of 51 2 of 51 What is inheritance? 3 of 51 Each person has a unique set of characteristics, such as eye colour, height and blood group. A person s characteristics are determined by a combination of the
PRINCIPLE OF INHERITANCE AND
 29 CHAPTER 5 PRINCIPLE OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. All genes located on the same chromosome: a. Form different groups depending upon their relative distance b. Form one linkage
29 CHAPTER 5 PRINCIPLE OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. All genes located on the same chromosome: a. Form different groups depending upon their relative distance b. Form one linkage
State the number of chromosomes which would be present in the cells labelled A, Band C.
 M N&ll!Iif..t _ class lviarks DO NOT WRITE IN TIllS MARGIN. The diagram below represents stages in the production of human sperm. (a) Name the type of cell division that produces sex cells. (b) State the
M N&ll!Iif..t _ class lviarks DO NOT WRITE IN TIllS MARGIN. The diagram below represents stages in the production of human sperm. (a) Name the type of cell division that produces sex cells. (b) State the
Below are the sections of the DNA sequences of a normal hemoglobin gene and the mutated gene that causes sickle cell disease.
 Sickle Cell Analysis Directions: Read the information below to complete the two tables. A person with sickle-cell disease has the genotype: Hb s Hb s. People who have this condition have two abnormal genes,
Sickle Cell Analysis Directions: Read the information below to complete the two tables. A person with sickle-cell disease has the genotype: Hb s Hb s. People who have this condition have two abnormal genes,
Genetics, Mendel and Units of Heredity
 Genetics, Mendel and Units of Heredity ¾ Austrian monk and naturalist. ¾ Conducted research in Brno, Czech Republic from 1856-1863 ¾ Curious about how traits were passed from parents to offspring. Gregor
Genetics, Mendel and Units of Heredity ¾ Austrian monk and naturalist. ¾ Conducted research in Brno, Czech Republic from 1856-1863 ¾ Curious about how traits were passed from parents to offspring. Gregor
Genetics Practice Test. A. phenylketonuria B. Tay-Sachs C. hemophilia D. color blindness
 Name: ate: 1. Which statement best describes a cloned population?. It is usually produced by sexual reproduction.. The individual organisms usually have varying N sequences.. There are usually no variations
Name: ate: 1. Which statement best describes a cloned population?. It is usually produced by sexual reproduction.. The individual organisms usually have varying N sequences.. There are usually no variations
PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION
 CHAPTER 5 PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION POINTS TO REMEMBER Allele : Various or slightly different forms of a gene, having same position on chromosomes. Phenotype : The observable or external
CHAPTER 5 PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION POINTS TO REMEMBER Allele : Various or slightly different forms of a gene, having same position on chromosomes. Phenotype : The observable or external
What is the inheritance pattern (e.g., autosomal, sex-linked, dominant, recessive, etc.)?
 Module I: Introduction to the disease Give a brief introduction to the disease, considering the following: the symptoms that define the syndrome, the range of phenotypes exhibited by individuals with the
Module I: Introduction to the disease Give a brief introduction to the disease, considering the following: the symptoms that define the syndrome, the range of phenotypes exhibited by individuals with the
Genetics 275 Examination February 10, 2003.
 Genetics 275 Examination February 10, 2003. Do all questions in the spaces provided. The value for this examination is twenty marks (20% of the grade for the course). The value for individual questions
Genetics 275 Examination February 10, 2003. Do all questions in the spaces provided. The value for this examination is twenty marks (20% of the grade for the course). The value for individual questions
Section 4 Genetics and heredity
 1 Section 4 Genetics and heredity Chapter 21 Cell division, chromosomes and genes Page 182 1. a Gametes are reproductive cells. (i) Plants. The male gametes are the pollen nuclei and are produced in the
1 Section 4 Genetics and heredity Chapter 21 Cell division, chromosomes and genes Page 182 1. a Gametes are reproductive cells. (i) Plants. The male gametes are the pollen nuclei and are produced in the
Pedigree Analysis. Genetic disorders. Dominant inheritance. Recessive inheritance. Autosomal vs. sex-linked traits. X-linked recessive inheritance
 Genetic disorders 4.2 Errors During Meiosis 5.3 Following Patterns of Human nheritance Pedigree Analysis 2005 Lee Bardwell Autosomal vs. sex-linked traits Autosomal traits are caused by genes on autosomes
Genetic disorders 4.2 Errors During Meiosis 5.3 Following Patterns of Human nheritance Pedigree Analysis 2005 Lee Bardwell Autosomal vs. sex-linked traits Autosomal traits are caused by genes on autosomes
Human Genetic Mutations
 Human Genetic Mutations 2 Main Types of Mutations 1.) Chromosomal Mutations 2.) Gene Mutations What are chromosomes? Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one chromosome from each parent. The chromosomes
Human Genetic Mutations 2 Main Types of Mutations 1.) Chromosomal Mutations 2.) Gene Mutations What are chromosomes? Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one chromosome from each parent. The chromosomes
Human Inheritance. Use Target Reading Skills. Patterns of Human Inheritance. Modern Genetics Guided Reading and Study
 Human Inheritance This section explains some patterns of inheritance in humans. It also describes the functions of the sex chromosomes and the relationship between genes and the environment. Use Target
Human Inheritance This section explains some patterns of inheritance in humans. It also describes the functions of the sex chromosomes and the relationship between genes and the environment. Use Target
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS-Please type your awesome answers on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What is an X-linked inheritance pattern? Use a specific example to explain the role of the father and mother in
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS-Please type your awesome answers on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What is an X-linked inheritance pattern? Use a specific example to explain the role of the father and mother in
Genetic diagrams show the genotype and phenotype of the offspring of two organisms. The different generation are abbreviated like so:
 Genetics 2 Genetic Diagrams and Mendelian Genetics: Genetic diagrams show the genotype and phenotype of the offspring of two organisms. The different generation are abbreviated like so: P parent generation
Genetics 2 Genetic Diagrams and Mendelian Genetics: Genetic diagrams show the genotype and phenotype of the offspring of two organisms. The different generation are abbreviated like so: P parent generation
Patterns of Inheritance
 1 Patterns of Inheritance Bio 103 Lecture Dr. Largen 2 Topics Mendel s Principles Variations on Mendel s Principles Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Sex Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Genes 3 Experimental
1 Patterns of Inheritance Bio 103 Lecture Dr. Largen 2 Topics Mendel s Principles Variations on Mendel s Principles Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Sex Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Genes 3 Experimental
Chapter 11 Gene Expression
 Chapter 11 Gene Expression 11-1 Control of Gene Expression Gene Expression- the activation of a gene to form a protein -a gene is on or expressed when it is transcribed. -cells do not always need to produce
Chapter 11 Gene Expression 11-1 Control of Gene Expression Gene Expression- the activation of a gene to form a protein -a gene is on or expressed when it is transcribed. -cells do not always need to produce
What You ll Learn. Genetics Since Mendel. ! Explain how traits are inherited by incomplete dominance
 Genetics Since Mendel GLE 0707.4.4 Predict the probable appearance of offspring based on the genetic characteristics of the parents. What You ll Learn! Explain how traits are inherited by incomplete dominance!
Genetics Since Mendel GLE 0707.4.4 Predict the probable appearance of offspring based on the genetic characteristics of the parents. What You ll Learn! Explain how traits are inherited by incomplete dominance!
The Origin of Species
 Chapter 24 The Origin of Species PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 24 The Origin of Species PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
- Aya Alomoush. - Talal Al-Zabin. - Belal Azab. 1 P a g e
 24 - Aya Alomoush - Talal Al-Zabin - Belal Azab 1 P a g e 1) Features of autosomal dominant inheritance: A) Vertical transmission: direct transmission from grandparent to parent to child without skipping
24 - Aya Alomoush - Talal Al-Zabin - Belal Azab 1 P a g e 1) Features of autosomal dominant inheritance: A) Vertical transmission: direct transmission from grandparent to parent to child without skipping
Guided Notes: Simple Genetics
 Punnett Squares Guided Notes: Simple Genetics In order to determine the a person might inherit, we use a simple diagram called a o Give us of an offspring having particular traits Pieces of the Punnett
Punnett Squares Guided Notes: Simple Genetics In order to determine the a person might inherit, we use a simple diagram called a o Give us of an offspring having particular traits Pieces of the Punnett
EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663]
![EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663]](/thumbs/87/96059079.jpg) EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] Student Class Date 1. A particular peach tree produces peaches that are more resistant to disease than other peaches. What method would reproduce these EXACT
EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] Student Class Date 1. A particular peach tree produces peaches that are more resistant to disease than other peaches. What method would reproduce these EXACT
Genetics 1. Down s syndrome is caused by an extra copy of cshromosome no 21. What percentage of
 Genetics 1. Down s syndrome is caused by an extra copy of cshromosome no 21. What percentage of offspring produced by an affected mother and a normal father would be affected by this disorder? (2003) 1)
Genetics 1. Down s syndrome is caused by an extra copy of cshromosome no 21. What percentage of offspring produced by an affected mother and a normal father would be affected by this disorder? (2003) 1)
Ch 4: Mendel and Modern evolutionary theory
 Ch 4: Mendel and Modern evolutionary theory 1 Mendelian principles of inheritance Mendel's principles explain how traits are transmitted from generation to generation Background: eight years breeding pea
Ch 4: Mendel and Modern evolutionary theory 1 Mendelian principles of inheritance Mendel's principles explain how traits are transmitted from generation to generation Background: eight years breeding pea
Genetics. by their offspring. The study of the inheritance of traits is called.
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Unit B2, B2.7. Cell division and inheritance. Stage 1. Ovary. Cell Q. Cell P. Cell R. Cell S. 7 Embryo A B C
 Cell division and inheritance 1. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released from the ovary at the same time.
Cell division and inheritance 1. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released from the ovary at the same time.
Chapter 28 Modern Mendelian Genetics
 Chapter 28 Modern Mendelian Genetics (I) Gene-Chromosome Theory Genes exist in a linear fashion on chromosomes Two genes associated with a specific characteristic are known as alleles and are located on
Chapter 28 Modern Mendelian Genetics (I) Gene-Chromosome Theory Genes exist in a linear fashion on chromosomes Two genes associated with a specific characteristic are known as alleles and are located on
Review for Meiosis and Genetics Unit Test: Theory
 Review for Meiosis and Genetics Unit Test: Theory 1. What is a karyotype? What stage of mitosis is the best for preparing karyotypes? a karyotype is a picture of all of the chromosomes in a cell, organized
Review for Meiosis and Genetics Unit Test: Theory 1. What is a karyotype? What stage of mitosis is the best for preparing karyotypes? a karyotype is a picture of all of the chromosomes in a cell, organized
Figure 1: Transmission of Wing Shape & Body Color Alleles: F0 Mating. Figure 1.1: Transmission of Wing Shape & Body Color Alleles: Expected F1 Outcome
 I. Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance As early cytologists worked out the mechanism of cell division in the late 1800 s, they began to notice similarities in the behavior of BOTH chromosomes & Mendel s
I. Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance As early cytologists worked out the mechanism of cell division in the late 1800 s, they began to notice similarities in the behavior of BOTH chromosomes & Mendel s
BIO113 Exam 2 Ch 4, 10, 13
 BIO113 Exam 2 Ch 4, 10, 13 See course outline for specific reading assignments Study notes and focus on terms and concepts The images in the textbook are useful CELLS (pg. 37) The basic unit of life living
BIO113 Exam 2 Ch 4, 10, 13 See course outline for specific reading assignments Study notes and focus on terms and concepts The images in the textbook are useful CELLS (pg. 37) The basic unit of life living
Chapter 02 Mendelian Inheritance
 Chapter 02 Mendelian Inheritance Multiple Choice Questions 1. The theory of pangenesis was first proposed by. A. Aristotle B. Galen C. Mendel D. Hippocrates E. None of these Learning Objective: Understand
Chapter 02 Mendelian Inheritance Multiple Choice Questions 1. The theory of pangenesis was first proposed by. A. Aristotle B. Galen C. Mendel D. Hippocrates E. None of these Learning Objective: Understand
Meiosis and Genetics
 Meiosis and Genetics Humans have chromosomes in each cell What pattern do you notice in the human karyotype (a technique that organizes chromosomes by type and size)? Humans are diploid 1 Gametes are produced
Meiosis and Genetics Humans have chromosomes in each cell What pattern do you notice in the human karyotype (a technique that organizes chromosomes by type and size)? Humans are diploid 1 Gametes are produced
(a) Similarity between different species (b) Diversity within a species
 Fig. 24-1 Fig. 24-2 (a) Similarity between different species (b) Diversity within a species Fig. 24-2a (a) Similarity between different species Fig. 24-2b (b) Diversity within a species Fig. 24-3 EXPERIMENT
Fig. 24-1 Fig. 24-2 (a) Similarity between different species (b) Diversity within a species Fig. 24-2a (a) Similarity between different species Fig. 24-2b (b) Diversity within a species Fig. 24-3 EXPERIMENT
Lesson Overview Human Chromosomes
 Lesson Overview 14.1 Human Chromosomes Human Genome To find what makes us uniquely human, we have to explore the human genome, which is the full set of genetic information carried in our DNA. This DNA
Lesson Overview 14.1 Human Chromosomes Human Genome To find what makes us uniquely human, we have to explore the human genome, which is the full set of genetic information carried in our DNA. This DNA
EEB 122b FIRST MIDTERM
 EEB 122b FIRST MIDTERM Page 1 1 Question 1 B A B could have any slope (pos or neg) but must be above A for all values shown The axes above relate individual growth rate to temperature for Daphnia (a water
EEB 122b FIRST MIDTERM Page 1 1 Question 1 B A B could have any slope (pos or neg) but must be above A for all values shown The axes above relate individual growth rate to temperature for Daphnia (a water
Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7
 Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 20 Q. Cystic fibrosis is a disease which affects in 600 babies. (a) What are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis? (3) Two parents with normal
Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 20 Q. Cystic fibrosis is a disease which affects in 600 babies. (a) What are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis? (3) Two parents with normal
Untitled Document. 1. Which of the following is the template for the production of RNA within a cell? A. DNA B. ATP C. protein D.
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following is the template for the production of RNA within a cell? A. DNA B. ATP C. protein D. carbohydrate 2. Which sequence of DNA bases would pair with the ones shown in
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following is the template for the production of RNA within a cell? A. DNA B. ATP C. protein D. carbohydrate 2. Which sequence of DNA bases would pair with the ones shown in
Genetics: CH9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Genetics: CH9 Patterns of Inheritance o o Lecture note Directions Highlight Key information (10-30% of most slides) My Thoughts: Questions, comments, additional information, connections to prior knowledge,
Genetics: CH9 Patterns of Inheritance o o Lecture note Directions Highlight Key information (10-30% of most slides) My Thoughts: Questions, comments, additional information, connections to prior knowledge,
GENE EXPRESSION. Individuality & Mutations
 GENE EXPRESSION Individuality & Mutations I. Are all genes turned on in all cells? The answer is NO! Every body cell contains your DNA (genetic make-up) Cells use only genes specific for function EX. Red
GENE EXPRESSION Individuality & Mutations I. Are all genes turned on in all cells? The answer is NO! Every body cell contains your DNA (genetic make-up) Cells use only genes specific for function EX. Red
Answers to Practice Items
 nswers to Practice Items Question 1 TEKS 6E In this sequence, two extra G bases appear in the middle of the sequence (after the fifth base of the original). This represents an insertion. In this sequence,
nswers to Practice Items Question 1 TEKS 6E In this sequence, two extra G bases appear in the middle of the sequence (after the fifth base of the original). This represents an insertion. In this sequence,
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12
 NTIONL SENIOR CERTIFICTE GRDE 12 LIFE SCIENCES P1 FEBRURY/MRCH 2009 MRKS: 150 TIME: 2½ hours This question paper consists of 17 pages. Life Sciences/P1 2 INSTRUCTIONS ND INFORMTION Read the following instructions
NTIONL SENIOR CERTIFICTE GRDE 12 LIFE SCIENCES P1 FEBRURY/MRCH 2009 MRKS: 150 TIME: 2½ hours This question paper consists of 17 pages. Life Sciences/P1 2 INSTRUCTIONS ND INFORMTION Read the following instructions
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over Why? Double crossovers
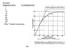 Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Ch. 23 The Evolution of Populations
 Ch. 23 The Evolution of Populations 1 Essential question: Do populations evolve? 2 Mutation and Sexual reproduction produce genetic variation that makes evolution possible What is the smallest unit of
Ch. 23 The Evolution of Populations 1 Essential question: Do populations evolve? 2 Mutation and Sexual reproduction produce genetic variation that makes evolution possible What is the smallest unit of
Genetics All somatic cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes 22 pairs of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes Genes contained in each pair of chromosomes
 Chapter 6 Genetics and Inheritance Lecture 1: Genetics and Patterns of Inheritance Asexual reproduction = daughter cells genetically identical to parent (clones) Sexual reproduction = offspring are genetic
Chapter 6 Genetics and Inheritance Lecture 1: Genetics and Patterns of Inheritance Asexual reproduction = daughter cells genetically identical to parent (clones) Sexual reproduction = offspring are genetic
Biology 2C03: Genetics What is a Gene?
 Biology 2C03: Genetics What is a Gene? September 9 th, 2013 Model Organisms - E. coli - Yeast - Worms - Arabodopsis - Fruitflie - Mouse What is a Gene? - Define, recognize, describe and apply Mendel s
Biology 2C03: Genetics What is a Gene? September 9 th, 2013 Model Organisms - E. coli - Yeast - Worms - Arabodopsis - Fruitflie - Mouse What is a Gene? - Define, recognize, describe and apply Mendel s
Chapter 15 Review Page 1
 hapter 15 Review Page 1 1 ased on the results of this cross, you determine that the allele for round eyes is linked to the allele for no tooth. round eyes are dominant to vertical eyes, and the absence
hapter 15 Review Page 1 1 ased on the results of this cross, you determine that the allele for round eyes is linked to the allele for no tooth. round eyes are dominant to vertical eyes, and the absence
MR. DALLINGA S BIOLOGY
 MR. DALLINGA S BIOLOGY Gregor Mendel Facts Born July 22 nd 1822 in Czechoslovakia A region of Austria. Today is Czech republic. Life of Poverty Entered a monastery to get an education The monastery was
MR. DALLINGA S BIOLOGY Gregor Mendel Facts Born July 22 nd 1822 in Czechoslovakia A region of Austria. Today is Czech republic. Life of Poverty Entered a monastery to get an education The monastery was
5Which one of the following occurs in meiosis, but not mitosis?
 Practice Questions: 1Humans possess: a. 22 pairs of sex chromosomes and 1 pair of autosomes b. 23 pairs of autosomes c. equal numbers of autosomes and sex chromosomes d. 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair
Practice Questions: 1Humans possess: a. 22 pairs of sex chromosomes and 1 pair of autosomes b. 23 pairs of autosomes c. equal numbers of autosomes and sex chromosomes d. 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair
The Living Environment Unit 3 Genetics Unit 11 Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity-class key. Name: Class key. Period:
 Name: Class key Period: Chapter 11 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Topic: Recessive Genetic Disorders Objective: Describe some recessive human genetic disorders. _recessive_ alleles are
Name: Class key Period: Chapter 11 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Topic: Recessive Genetic Disorders Objective: Describe some recessive human genetic disorders. _recessive_ alleles are
IB BIO I Genetics Test Madden
 Name Date Multiple Choice 1. What does the genotype X H X h indicate? A. A co-dominant female B. A heterozygous male C. A heterozygous female D. A co-dominant male 2. A pure breeding tall plant with smooth
Name Date Multiple Choice 1. What does the genotype X H X h indicate? A. A co-dominant female B. A heterozygous male C. A heterozygous female D. A co-dominant male 2. A pure breeding tall plant with smooth
By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' CHAPTER CONCEPT NOTES
 Chapter Notes- Genetics By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' 1 CHAPTER CONCEPT NOTES Relationship between genes and chromosome of diploid organism and the terms used to describe them Know the terms Terms
Chapter Notes- Genetics By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' 1 CHAPTER CONCEPT NOTES Relationship between genes and chromosome of diploid organism and the terms used to describe them Know the terms Terms
NOTES: : HUMAN HEREDITY
 NOTES: 14.1-14.2: HUMAN HEREDITY Human Genes: The human genome is the complete set of genetic information -it determines characteristics such as eye color and how proteins function within cells Recessive
NOTES: 14.1-14.2: HUMAN HEREDITY Human Genes: The human genome is the complete set of genetic information -it determines characteristics such as eye color and how proteins function within cells Recessive
PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION
 PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION Genetics Genetics is a branch of biology dealing with inheritance and variation of characters from parents of offspring. Inheritance Process by which characters
PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION Genetics Genetics is a branch of biology dealing with inheritance and variation of characters from parents of offspring. Inheritance Process by which characters
Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes
 Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes 5.6 Explain how nondisjunction can result in whole chromosomal abnormalities. (Module 5.10) 5.7 Describe the inheritance patterns for strict dominant
Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes 5.6 Explain how nondisjunction can result in whole chromosomal abnormalities. (Module 5.10) 5.7 Describe the inheritance patterns for strict dominant
Friday, January 4. Bell Work:
 Friday, January 4 Bell Work: Red green colorblindness is an X linked trait and is recessive. A male who is normal marries a woman who is a carrier, what is the phenotypic ratio of their offspring? 1 Genetic
Friday, January 4 Bell Work: Red green colorblindness is an X linked trait and is recessive. A male who is normal marries a woman who is a carrier, what is the phenotypic ratio of their offspring? 1 Genetic
Review. 1) A huge molecule made up of amino acids (adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine)
 Mutations Review 1) A huge molecule made up of amino acids (adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine) DNA 2) A process that produces the sex cells with half the chromosomes of a body cell Meiosis 3) Strands
Mutations Review 1) A huge molecule made up of amino acids (adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine) DNA 2) A process that produces the sex cells with half the chromosomes of a body cell Meiosis 3) Strands
Patterns in Inheritance. Chapter 10
 Patterns in Inheritance Chapter 10 What you absolutely need to know Punnett Square with monohybrid and dihybrid cross Heterozygous, homozygous, alleles, locus, gene Test cross, P, F1, F2 Mendel and his
Patterns in Inheritance Chapter 10 What you absolutely need to know Punnett Square with monohybrid and dihybrid cross Heterozygous, homozygous, alleles, locus, gene Test cross, P, F1, F2 Mendel and his
The Meaning of Genetic Variation
 Activity 2 The Meaning of Genetic Variation Focus: Students investigate variation in the beta globin gene by identifying base changes that do and do not alter function, and by using several CD-ROM-based
Activity 2 The Meaning of Genetic Variation Focus: Students investigate variation in the beta globin gene by identifying base changes that do and do not alter function, and by using several CD-ROM-based
Ch 8 Practice Questions
 Ch 8 Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What fraction of offspring of the cross Aa Aa is homozygous for the dominant allele?
Ch 8 Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What fraction of offspring of the cross Aa Aa is homozygous for the dominant allele?
HARDY- WEINBERG PRACTICE PROBLEMS
 HARDY- WEINBERG PRACTICE PROBLEMS PROBLEMS TO SOLVE: 1. The proportion of homozygous recessives of a certain population is 0.09. If we assume that the gene pool is large and at equilibrium and all genotypes
HARDY- WEINBERG PRACTICE PROBLEMS PROBLEMS TO SOLVE: 1. The proportion of homozygous recessives of a certain population is 0.09. If we assume that the gene pool is large and at equilibrium and all genotypes
Questions Q1. ) in the box next to your answer. (1) A FF B Ff C ff. D ff (ii) Explain why a person with cystic fibrosis (CF) may lose body mass.
 Questions Q1. Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a recessive genetic disorder. The recessive allele is shown as f and the dominant allele as F. (a) (i) What is the genotype of a person with cystic fibrosis? Put a
Questions Q1. Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a recessive genetic disorder. The recessive allele is shown as f and the dominant allele as F. (a) (i) What is the genotype of a person with cystic fibrosis? Put a
Downloaded from Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation
 Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Genetics: Genetics is a branch of biology which deals with principles of inheritance and its practices. Heredity: It is transmission of traits from one
Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Genetics: Genetics is a branch of biology which deals with principles of inheritance and its practices. Heredity: It is transmission of traits from one
The passing of traits from parents to offspring. The scientific study of the inheritance
 Inheritance The passing of traits from parents to offspring Genetics The scientific study of the inheritance Gregor Mendel -Father of modern genetics -Used peas to successfully identify the laws of heredity
Inheritance The passing of traits from parents to offspring Genetics The scientific study of the inheritance Gregor Mendel -Father of modern genetics -Used peas to successfully identify the laws of heredity
15/12/2011. You and your genes (OCR)
 You and your genes (OCR) Variation Variation is the name given to differences between individuals of the SAME species. Variation is due to GENETIC or ENVIRONMENTAL causes. For example, consider dogs: 1)
You and your genes (OCR) Variation Variation is the name given to differences between individuals of the SAME species. Variation is due to GENETIC or ENVIRONMENTAL causes. For example, consider dogs: 1)
Genetic Disorders. PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders. Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test
 Genetic Disorders PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test Amniocentesis A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus
Genetic Disorders PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test Amniocentesis A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus
Honors Biology Review Sheet to Chapter 9 Test
 Honors Biology Review Sheet to Chapter 9 Test Name Per 1. Label the following flower: sepal, petal, anther, filament, style, ovary, stigma Draw in ovules and label. Color the female structure red and the
Honors Biology Review Sheet to Chapter 9 Test Name Per 1. Label the following flower: sepal, petal, anther, filament, style, ovary, stigma Draw in ovules and label. Color the female structure red and the
Section Objectives: Pedigrees illustrate inheritance. Pedigrees illustrate inheritance
 What You ll Learn You will compare the inheritance of recessive and dominant traits in humans. You will analyze the inheritance patterns of traits with incomplete dominance and codominance. You will determine
What You ll Learn You will compare the inheritance of recessive and dominant traits in humans. You will analyze the inheritance patterns of traits with incomplete dominance and codominance. You will determine
Genetics Practice Test
 Name: ate: 1. Which genetic concept was proposed by Mendel?. chromosome nondisjunction. independent assortment. multiple alleles. sex linkage 4. Mendel s discovery that characteristics are inherited due
Name: ate: 1. Which genetic concept was proposed by Mendel?. chromosome nondisjunction. independent assortment. multiple alleles. sex linkage 4. Mendel s discovery that characteristics are inherited due
Population Genetics Simulation Lab
 Name Period Assignment # Pre-lab: annotate each paragraph Population Genetics Simulation Lab Evolution occurs in populations of organisms and involves variation in the population, heredity, and differential
Name Period Assignment # Pre-lab: annotate each paragraph Population Genetics Simulation Lab Evolution occurs in populations of organisms and involves variation in the population, heredity, and differential
GENETICS - NOTES-
 GENETICS - NOTES- Warm Up Exercise Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. Use the genotype that you came
GENETICS - NOTES- Warm Up Exercise Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. Use the genotype that you came
Mendelian Genetics. Vocabulary. M o l e c u l a r a n d M e n d e l i a n G e n e t i c s
 Mendelian Genetics Vocabulary Genotype: o Capital letter = allele o Lowercase letter = allele o Ex AA, Aa, aa Phenotype: o Ex green, yellow Homozygous: o Homozygous dominant: o Homozygous recessive: Heterozygous:
Mendelian Genetics Vocabulary Genotype: o Capital letter = allele o Lowercase letter = allele o Ex AA, Aa, aa Phenotype: o Ex green, yellow Homozygous: o Homozygous dominant: o Homozygous recessive: Heterozygous:
Natural Selection In Humans (Sickle Cell Anemia)
 Natural Selection In Humans (Sickle Cell Anemia) Background Information Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells Transports oxygen to body tissues Individuals homozygous for the sickle cell allele
Natural Selection In Humans (Sickle Cell Anemia) Background Information Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells Transports oxygen to body tissues Individuals homozygous for the sickle cell allele
Mendelian Genetics & Inheritance Patterns. Multiple Choice Review. Slide 1 / 47. Slide 2 / 47. Slide 4 / 47. Slide 3 / 47. Slide 5 / 47.
 Slide 1 / 47 Slide 2 / 47 New Jersey enter for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of
Slide 1 / 47 Slide 2 / 47 New Jersey enter for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of
Page 2. Q1.Figure 1 shows a human body cell. Figure 1. Which part in Figure 1 contains chromosomes? Tick one box. A B C
 Q1.Figure 1 shows a human body cell. Figure 1 (a) Which part in Figure 1 contains chromosomes? Tick one box. A B C (b) Humans have pairs of chromosomes in their body cells. Draw one line from each type
Q1.Figure 1 shows a human body cell. Figure 1 (a) Which part in Figure 1 contains chromosomes? Tick one box. A B C (b) Humans have pairs of chromosomes in their body cells. Draw one line from each type
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level *9622949895* BIOLOGY 9700/21 Paper 2 Structured Questions AS October/November
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level *9622949895* BIOLOGY 9700/21 Paper 2 Structured Questions AS October/November
HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Unit 5: Genetics Notes
 Unit 5: Genetics Notes https://goo.gl/fgtzef Name: Period: Test Date: Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Date Warm-ups 3-4 Mendelian Genetics Notes 5-6 Mendelian Genetics Lets Practice 7 Monohybrid
Unit 5: Genetics Notes https://goo.gl/fgtzef Name: Period: Test Date: Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Date Warm-ups 3-4 Mendelian Genetics Notes 5-6 Mendelian Genetics Lets Practice 7 Monohybrid
40 Bell Work Week 8 5/12 41 Genetic Notes 5/12 42 Bill Nye Video & Questions 5/12
 40 Bell Work Week 8 5/12 41 Genetic Notes 5/12 42 Bill Nye Video & Questions 5/12 1. I am available after school on Wed. and Thurs. this week. 2. Quiz Friday over genetic material 3. Last day to turn in
40 Bell Work Week 8 5/12 41 Genetic Notes 5/12 42 Bill Nye Video & Questions 5/12 1. I am available after school on Wed. and Thurs. this week. 2. Quiz Friday over genetic material 3. Last day to turn in
Warm-Up. Describe an example of a mutation which is beneficial for the individual but deleterious for the individual s offspring.
 Warm-Up Describe an example of a mutation which is beneficial for the individual but deleterious for the individual s offspring. Yesterday s Picture Aa AA aa Some variations (= mutations) are bad for the
Warm-Up Describe an example of a mutation which is beneficial for the individual but deleterious for the individual s offspring. Yesterday s Picture Aa AA aa Some variations (= mutations) are bad for the
When bad things happen to good genes: mutation vs. selection
 When bad things happen to good genes: mutation vs. selection Selection tends to increase the frequencies of alleles with higher marginal fitnesses. Does this mean that genes are perfect? No, mutation can
When bad things happen to good genes: mutation vs. selection Selection tends to increase the frequencies of alleles with higher marginal fitnesses. Does this mean that genes are perfect? No, mutation can
8.1 Genes Are Particulate and Are Inherited According to Mendel s Laws 8.2 Alleles and Genes Interact to Produce Phenotypes 8.3 Genes Are Carried on
 Chapter 8 8.1 Genes Are Particulate and Are Inherited According to Mendel s Laws 8.2 Alleles and Genes Interact to Produce Phenotypes 8.3 Genes Are Carried on Chromosomes 8.4 Prokaryotes Can Exchange Genetic
Chapter 8 8.1 Genes Are Particulate and Are Inherited According to Mendel s Laws 8.2 Alleles and Genes Interact to Produce Phenotypes 8.3 Genes Are Carried on Chromosomes 8.4 Prokaryotes Can Exchange Genetic
Case Study. Malaria and the human genome STUDENT S GUIDE. Steve Cross, Bronwyn Terrill and colleagues. Version 1.1
 STUDENT S GUIDE Case Study Malaria and the human genome Version 1.1 Steve Cross, Bronwyn Terrill and colleagues Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Hinxton Malaria and the human genome Each year, the malaria
STUDENT S GUIDE Case Study Malaria and the human genome Version 1.1 Steve Cross, Bronwyn Terrill and colleagues Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Hinxton Malaria and the human genome Each year, the malaria
Mendelian Genetics and Beyond Chapter 4 Study Prompts
 Mendelian Genetics and Beyond Chapter 4 Study Prompts 1. What is a mode of inheritance? 2. Can you define the following? a. Autosomal dominant b. Autosomal recessive 3. Who was Gregor Mendel? 4. What did
Mendelian Genetics and Beyond Chapter 4 Study Prompts 1. What is a mode of inheritance? 2. Can you define the following? a. Autosomal dominant b. Autosomal recessive 3. Who was Gregor Mendel? 4. What did
End of Course Assessment Review Packet Due: Monday, June 2nd
 Unit 1: 1. Name 5 pieces of evidence that might be obtained at a crime scene that could help solve the crime. 2. Draw a diagram showing the relationship between the following terms: nucleotide, gene, DNA
Unit 1: 1. Name 5 pieces of evidence that might be obtained at a crime scene that could help solve the crime. 2. Draw a diagram showing the relationship between the following terms: nucleotide, gene, DNA
Downloaded from
 5. PRINCIPLE OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type. All genes located on the same chromosome (a) Form different groups depending upon their relative distance
5. PRINCIPLE OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type. All genes located on the same chromosome (a) Form different groups depending upon their relative distance
