MANAGEMENT OF GASTROINTESTINAL ASPECTS IN SSC
|
|
|
- Sabina McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MANAGEMENT OF GASTROINTESTINAL ASPECTS IN SSC A. MANAGEMENT OF INCONTINENCE 1. Establish diagnosis Assess frequency, enquire dietary and fluid intake Determine pattern if any or precipitating factors eg access to toilets, mobility issues related to SSc Assess urge faecal incontinence, passive leakage, sensation of incomplete evacuation, post-defaecation soiling Assess consequences eg perianal pruritus/soreness Assess impact of symptoms on lifestyle/quality of life Physical examination to include PR for anal tone, ability to squeeze anal sphincter voluntarily Core investigations may include rigid sigmoidoscopy and direct visualisation with colonoscopy if red flag features are present 2. Identify and underlying contributory factors A history of anal sphincter injury including obstetric history (parity, difficult delivery, large birth weight and associated complications) and other perianal surgical procedures should be evaluated Rectal prolapse, third-degree haemorrhoids or urinary incontinence SSc-GI issues eg diarrhoea (See link) Consider drugs that may exacerbate faecal incontinence and loose stools including calcium channel blockers, SSRIs, sildenafil, magnesium-containing antacids, tricyclics 3. Based on baseline assessment, initial management may include Patient education with advice on dietary modification, address access to toilet at work, review medications that may contribute to FI and prescribe anti-diarrhoeal drugs for those with loose stools and faecal incontinence Generic advice is provided. Prescribe anti-diarrhoeal drugs, Loperamide hydrochloride should be first drug of choice, introduced at very low dose and to escalate as tolerated until desired stool consistency is reached. Syrup preparation may be used for doses less than 2 mg. Codeine phosphate may be used as alternative. 1
2 4.If patients remain symptomatic, consider referral for specialist investigations Anorectal physiology/manometry (Thoua 2011) Endoanal US especially those with obstetric history. Referral to specialist GI centre may be necessary If these investigations are not available, MRI, endovaginal US and perineal US should be considered. Defaecating proctogram may be considered as indicated 5. Specialist management Patient-focus and practical management Address toilet access issues Modify dietary and fluid intake pelvic floor muscle training, bowel retraining, biofeedback, specialist dietary assessment and management, anal plugs (for people who can tolerate them), Rectal irrigation Coping strategies with advice on emotional and psychological support are important Continence products with choice of disposable body-worn pads and disposable bed pads may be necessary Surgical approaches may be considered Consider a trial of temporary sacral nerve stimulation and proceed to implantation if successful. These patients should be assessed and managed at a specialist centre that has experience of performing this procedure. Sphincter augmentation with bioprothestic device may be considered in specialist units. NICE has published guidelines on management of faecal incontinence in adults. Further details are available on 2
3 B. MANAGEMENT OF ABDOMINAL PAIN AND DISTENSION 1. Ascertain contributing factors including warning signs of true obstruction and other acute abdominal events such as sigmoid volvulus, diabetes 2. Identify dominant symptom: Small bowel bacterial overgrowth, Gastroparesis 3. Based on initial clinical assessment, appropriate investigations should be instituted Plain Xray to assess features of bowel obstruction Further investigations are undertaken, if indicated, to evaluate both upper and lower GI symptoms; for example, endoscopy for upper GI symptoms, US for biliary causes, CT to exclude other intraabdominal pathologies 4. Clinical assessment and investigations will guide management and this may include a trial of empiral antibiotics for presumed bacterial overgrowth. The choice of antibiotics is governed by local guidelines, and these may include Doxycycline and Ciprofloxacin. 5. If these initial steps fail to control the symptoms, these patients should be referred for specialist assessment. Specific investigations are undertaken as indicated Hydrogen breath test Gastric emptying test (Marie 2012) Oesophageal/ Antro-duodenal manometry?? 5. Treatment Practical patient-focussed approaches These should address anxiety and depression with professional counselling. Dietary modification includes formal dietitian review dietary balance, meal size and timing of meals. Probiotics may be helpful in selected patients (Frech 2011) Lifestyle factors such as smoking and alcohol may delay gastric emptying Pharmacological agents Prokinetics eg Domperidone, Metoclopramide and low-dose Erythromycin, somatostatin analogues such as Octreotide (Nikou 2007) A trial of rotating antibiotics for SBO without breath test is justifiable. These may include Ciprofloxacin,.. Enteral support may be required Trial of nasogastric or nasojejunal feeding leading to PEG/PEJ feeding. If enteral nutrition is poorly tolerated because of pain, bloating or recurrent abdominal injection, longterm parenteral nutrition may be necessary (Brown 2008). Colonoscopic decompression may be considered in selected patients?? 3
4 C. MANAGEMENT OF GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX 1. Establish diagnosis and determine dominant symptom (Ntoumazios 2006) Assess severity of symptoms (volume regurgitation, nocturnal symptoms) Assess comorbidities: myositis, sicca symptoms and lung fibrosis 2. Investigations should be undertaken Ba swallow/ogd for persistent dysphagia or strictures Consider OGD for odynophagia, persistent iron deficiency anaemia to evaluate candidiasis and gastric antral vascular ectasia 3. Treatment Pharmacological High dose PPI ± H2 receptor blockade (Pakozdi 2009) A majority of patients require a maintenance dose of PPI which may be increased as necessary when symptoms flare. Adjunct prokinetic may be considered if there are features of oesophageal dysmotility Practical patient-focussed management Elevation of head bed Avoid meals for at least three hours prior to bed time Avoid fluid overload with meal Small frequent meals Dietary consideration with avoidance of cold fluid may be helpful Specialist referral Oesophageal manometry and ph studies including impedance for non-acid reflux may be required Surgical intervention such as fundoplication should be avoided as this procedure is unlikely to benefit patients with SSc and may aggravate oesophageal symptoms Candida infection should be considered if symptoms especially odynophagia fail to improve and empirical antifungal treatment may be indicated. 4
5 Barrett s oesophagus will require endoscopic surveillance as per local/national guidelines. Recognition that treating reflux aggressively may prevent further progression of interstitial lung disease in selected patients. 5
6 D.MANAGEMENT OF DIARRHOEA 1. Establish diagnosis and assess severity. Nutritional status should be evaluated using the Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool (MUST) to identify those who are risk of malnourishment and therefore those who may benefit from appropriate nutritional intervention (Elia M 2003, Baron 2009). These include five steps: Step 1 and 2: Gather nutritional measurements (height, weight, BMI, unplanned weight loss over preceding months) Step 3: Consider the effect of scleroderma to the nutritional intake Step 4: Determine the overall risk score of malnutrition. Step 5: Develop care plan using local management guidelines ( Contributory factors including infection in particular C. difficile related to antibiotic use, coeliac disease and small bowel bacterial overgrowth should be addressed(forbess 2011) 2. The following investigations should be considered as indicated Screen for infection with stool microscopy and culture including C. difficile Screen for celiac screen, thyroid function, B12 and folate Specialist referral for further investigations may include Hydrogen Breath test (Marie 2009) Investigate for malabsorption including faecal elastase, SeHCAT for bile malabsorption 4. Treatment Nutrition and dietary consideration as indicated with formal dietitian review Medical therapy Antibiotics for small bowel bacterial overgrowth Symptomatic approaches should only be considered once the contributory causes to diarrhoea are identified. These may include Loperamide,?Trial of Fybogel if overflow. Specific therapies may be required: antibiotics or Rifaximin if available and Cholestyramine for bile-salt diarrhoea (Parodi 2008). Gluten-free diet for coexisting celiac disease 6
7 Trial of pancreatic enzyme supplementation if pancreatic insufficiency Role of fermentable diet in selected cases 7
8 E. MANAGEMENT OF NUTRITIONAL ISSUES AND WEIGHT LOSS 1. Establish contributing causes (active SSc, major organ involvement, underlying neoplasia, depressive illness) 2. Assess severity and risk of malnutrition with MUST score.. ( 3. Investigations Blood tests TFT, FBC, Haematinics, Electrolytes imbalance Imaging CT Abdomen Screening for malnutrition with change in BMI score, weight loss during preceding months and risk stratification Specialist Referral for further management of nutritional assessment 3.Treatments Specific management of this aspect of the disease is governed by the primary cause or contributing factor to weight loss. These are discussed in the other sections. (See link on Diarrhoea, Abdominal pain/distension) Dietician review Oral nutrition support to ensure overall nutrient intake contains a balanced mixture of protein, energy and fibre, electrolytes, vitamins and minerals. Management of associated dysphagia is critical to evaluate the risks and benefits of modified oral nutrition support and/or enteral tube feeding Parenteral feeding ( In those malnourished with inadequate oral or unsafe oral intake with functional and accessible gastrointestinal tract, enteral tube feeding is considered. If there is associated gastric emptying abnormalities, post-pyloric (duodenal or jejunal) feeding is considered. If there is severe non-functional gastrointestinal tract or failure with enteral tube feeding, continuous or cyclical parenteral nutrition is considered These require coordinated multidisciplinary team, which includes input from specialist nutrition nurses, dietitians, GPs, pharmacists and district and/or homecare company nurses Venting gastrostomy may be considered to address abdominal distension 8
9 F.MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION 1. Assessment of each symptom component (urge frequency and difficulty in evacuation). Use of patient diary should be considered. 2. Evaluation of contributory causes such as metabolic, endocrine causes and drugs (antidepressants) Red flags such as features of malignancy must be considered. 3. Basic investigations such as calcium and TFT should be undertaken. Based on initial assessment, appropriate generic advice may be sufficient. Specialist referral for further management may be required 4. Specialist investigations Colonic imaging or direct visualisation with colonoscopy is necessary if there is a change in bowel habit Related issues such as slow colonic transit/evacuation with radiopaque markers need to be addressed Defaecating proctogram to evaluate rectocoele 5. Treatment Dietary manipulation should be considered Adequate fluid intake Adequate fibre. Recommend foods with high fibre content such as fruits, vegetables, high-fibre bread, baked beans and wholegrain breakfast cereals. Do not recommend unprocessed bran which may aggravate bloating and flatulence. Oral/Suppository laxatives such as stimulants in high doses may be required. Prucolapride may be used in difficult cases (NICE guideline Dec 2010). Surgical intervention such as defunctioning stoma should only be undertaken after careful consideration and this should be undertaken at a specialist centre 9
10 References Thoua NM, Schizas A, Forbes A, Denton CP, Emmanuel AV. Internal anal sphincter atrophy in patients with systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) Sep;50(9): The authors reported that in a series of patients with SSc including asymptomatic patients, anorectal manometry and endoanal ultrasound is helpful in detection of atrophy of internal anal sphincter and this may be amenable to neuromodulation. NICE document on Management of Faecal Incontinence in Adults Frech TM, Khanna D, Maranian P, Frech EJ, Sawitzke AD, Murtaugh MA. Probiotics for the treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated gastrointestinal bloating/ distention. Clin Exp Rheumatol Mar-Apr;29(2 Suppl 65):S22-5. Nikou GC, Toumpanakis C, Katsiari C, Charalambopoulos D, Sfikakis PP.Treatment of small intestinal disease in systemic sclerosis with octreotide: a prospective study in seven patients. J Clin Rheumatol Jun;13(3): Parenteral somatostatin analogue appeared to be helpful and well-tolerated in patients who failed prokinetic agents and its effect may be apparent as early as the first month. Brown M, Teubner A, Shaffer J, Herrick AL. Home parenteral nutrition--an effective and safe long-term therapy for systemic sclerosis-related intestinal failure. Rheumatology (Oxford) Feb;47(2): Home parenteral nutrition when well-supported by a specialised nutrition unit and trained specialist nurses may be used successfully in a selected group of patients with minimal risk of line infections. Ntoumazios SK, Voulgari PV, Potsis K, Koutis E, Tsifetaki N, Assimakopoulos DA. Esophageal involvement in scleroderma: gastroesophageal reflux, the common problem. Semin Arthritis Rheum Dec;36(3): This review reports that oesophageal involvement is frequent and various diagnostic procedures have been used including oesophageal manometry, 24-hour ambulatory ph, and endoscopy. Most treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux requires regular use of proton pump inhibitors in addition to behavioural modification. Surgical intervention is rarely used Pakozdi A, Wilson H, Black CM, Denton CP. Does long term therapy with lansoprazole slow progression of oesophageal involvement in systemic sclerosis? Clin Exp Rheumatol May-Jun;27(3 Suppl 54):5-8. The authors reported in a small series of patients that lansoprazole may suppress gastrooesophageal symptoms but longer-term studies are required to investigate its effect on progression of gastro-oesophageal motility. Forbess LJ, Gordon JK, Doobay K, Bosworth B, Davids ML, Spiera R. Prevalence of Coeliac Antibodies in patients with Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum 2011; 63 Suppl 10:
11 Marie I, Ducrotté P, Denis P, Menard JF, Levesque H. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) Oct;48(10): This study suggests that presence of diarrhoea and constipation is predictive of small bowel bacterial overgrowth but eradication of bacterial overgrowth was only achieved in about half of those patients who reported significant benefit with antibiotic therapy. Parodi A, Sessarego M, Greco A, Bazzica M, Filaci G, Setti M, Savarino E, Indiveri F, Savarino V, Ghio M. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients suffering from scleroderma: clinical effectiveness of its eradication. Am J Gastroenterol May;103(5): This study suggests that intestinal dysmotility is a risk factor for small bowel bacterial overgrowth. Significant improvement was reported in more than 70% of patients treated with Rifaximin for 10 days. Elia M: Screening for Malnutrition: A Multidisciplinary Responsibility. Development and Use of the Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool (MUST) for Adults. Malnutrition Advisory Group (MAG), a Standing Committee of BAPEN. Redditch, Worcs.: BAPEN; Baron M, Hudson M, Steele R; Canadian Scleroderma Research Group. Malnutrition is common in systemic sclerosis: results from the Canadian scleroderma research group database. J Rheumatol Dec;36(12): MUST score identified a high number of patients with SSc at risk of malnutrition in particular among those with abdominal distension and evidence of malabsorption. NICE document on Nutrition Support in Adults NICE document on Prucolapride for the treatment of Chronic Constipation in Women. Dec
Clinical problems related to GI involvement in SSc
 Clinical problems related to GI involvement in SSc Incontinence Abdominal pain/distension Gastro-oesophageal Diarrhoea Weight loss/al Issues Constipation Management of incontinence Establish diagnosis
Clinical problems related to GI involvement in SSc Incontinence Abdominal pain/distension Gastro-oesophageal Diarrhoea Weight loss/al Issues Constipation Management of incontinence Establish diagnosis
Guide to managing Gastrointestinal Pelvic Radiation Disease (PRD) using Algorithm V7 (January 2011)
 Guide to managing Gastrointestinal Pelvic Radiation Disease (PRD) using Algorithm V7 (January 2011) This algorithm is particularly designed to help clinical nurse specialists working in conjunction with
Guide to managing Gastrointestinal Pelvic Radiation Disease (PRD) using Algorithm V7 (January 2011) This algorithm is particularly designed to help clinical nurse specialists working in conjunction with
Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma
 Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma Dr. Shamaila Butt Gastroenterology Research Registrar GI Physiology unit University College Hospital London GI manifestations in Scleroderma Oesophagus
Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma Dr. Shamaila Butt Gastroenterology Research Registrar GI Physiology unit University College Hospital London GI manifestations in Scleroderma Oesophagus
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction. Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield
 GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
Constipation. Information for adults. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus.
 The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
Irritable bowel syndrome in adults
 Irritable bowel syndrome in adults NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised Welcome In February 2008, NICE published a clinical guideline on
Irritable bowel syndrome in adults NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised Welcome In February 2008, NICE published a clinical guideline on
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation. Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class
 Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, and Nutritional Challenges in FA
 Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, and Nutritional Challenges in FA Sarah Jane Schwarzenberg, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition June 29, 2014 GI problems in FA 5% have gastrointestinal tract
Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, and Nutritional Challenges in FA Sarah Jane Schwarzenberg, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition June 29, 2014 GI problems in FA 5% have gastrointestinal tract
Faecal Incontinence: Assessment and Management
 Mrs PK; 56 yrs; Married; 2 children Faecal Incontinence: Assessment and Management Professor Marc A Gladman MBBS DFFP PhD MRCOG FRCS (UK) FRACS Professor of Colorectal Surgery >10 years of incontinence
Mrs PK; 56 yrs; Married; 2 children Faecal Incontinence: Assessment and Management Professor Marc A Gladman MBBS DFFP PhD MRCOG FRCS (UK) FRACS Professor of Colorectal Surgery >10 years of incontinence
Amyloidosis & the GI Tract
 Amyloidosis & the GI Tract John O. Clarke, M.D. Director, Esophageal Program Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University john.clarke@stanford.edu 2017 Topics to cover 1) Patterns of GI
Amyloidosis & the GI Tract John O. Clarke, M.D. Director, Esophageal Program Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University john.clarke@stanford.edu 2017 Topics to cover 1) Patterns of GI
Biofeedback for pouch dysfunction. Brigitte Collins, Lead Nurse BSc (Hons), MSc GI Nursing, Dip/ Hypnotherapy
 Biofeedback for pouch dysfunction Brigitte Collins, Lead Nurse BSc (Hons), MSc GI Nursing, Dip/ Hypnotherapy Objectives Awareness of St Marks biofeedback therapy Strategies that may help pouch dysfunction
Biofeedback for pouch dysfunction Brigitte Collins, Lead Nurse BSc (Hons), MSc GI Nursing, Dip/ Hypnotherapy Objectives Awareness of St Marks biofeedback therapy Strategies that may help pouch dysfunction
Pelvic Floor Disorders. Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon
 Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
CHRONIC DIARRHEA DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) DEFINITION: *LOOSE, WATERY STOOLS *MORE THAN 3 TIMES A DAY *FOR MORE THAN 4 WEEKS
 DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (403) 270-7479 CHRONIC DIARRHEA DEFINITION: *LOOSE, WATERY STOOLS *MORE THAN 3 TIMES A DAY *FOR MORE
DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (403) 270-7479 CHRONIC DIARRHEA DEFINITION: *LOOSE, WATERY STOOLS *MORE THAN 3 TIMES A DAY *FOR MORE
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University
 CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST
 COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
Tertiary, regional and local pelvic floor service providers: the future. model? Andrew Williams
 Tertiary, regional and local pelvic floor service providers: the future Andrew Williams model? Pelvic Floor Unit Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust Background 23% women suffer at least one pelvic
Tertiary, regional and local pelvic floor service providers: the future Andrew Williams model? Pelvic Floor Unit Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust Background 23% women suffer at least one pelvic
Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Mustafa Giaffer March 2017
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Mustafa Giaffer March 2017 Introduction First described in 1771. 50% of patients present
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Mustafa Giaffer March 2017 Introduction First described in 1771. 50% of patients present
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
GI Complications in heds and HSD
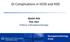 GI Complications in heds and HSD Qasim Aziz PhD, FRCP Professor in Neurogastroenterology Neurogastroenterology Group GUT = Gastrointestinal (GI) tract Oesophagus / gullet Gastro-oesophageal junction Stomach
GI Complications in heds and HSD Qasim Aziz PhD, FRCP Professor in Neurogastroenterology Neurogastroenterology Group GUT = Gastrointestinal (GI) tract Oesophagus / gullet Gastro-oesophageal junction Stomach
June By: Reza Gholami
 ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction. Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Gastroenterology and Feeding Issues in Fanconi Anemia
 Gastroenterology and Feeding Issues in Fanconi Anemia Sarah Jane Schwarzenberg, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition August 12, 2012 GI problems in FA 5% have gastrointestinal tract
Gastroenterology and Feeding Issues in Fanconi Anemia Sarah Jane Schwarzenberg, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition August 12, 2012 GI problems in FA 5% have gastrointestinal tract
Fecal incontinence causes 196 epidemiology 8 treatment 196
 Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES
 OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Introduction Mean faecal weight 128 g / cap / day Mean range 51-796 g Absolute range 15-1505 g Main factors affecting mass are caloric intake,
OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Introduction Mean faecal weight 128 g / cap / day Mean range 51-796 g Absolute range 15-1505 g Main factors affecting mass are caloric intake,
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Dr Rex J Polson 17 th January 2018 Overview Description of the condition Discussion of symptoms and investigations that may be required Discussion of management and treatment
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Dr Rex J Polson 17 th January 2018 Overview Description of the condition Discussion of symptoms and investigations that may be required Discussion of management and treatment
Late effects of treatment for colorectal cancer. Claire Taylor Macmillan Nurse Consultant St Mark s Hospital
 Late effects of treatment for colorectal cancer Claire Taylor Macmillan Nurse Consultant St Mark s Hospital The number of people living with cancer is set to double from 2m to 4m by 2030 Source: Maddams
Late effects of treatment for colorectal cancer Claire Taylor Macmillan Nurse Consultant St Mark s Hospital The number of people living with cancer is set to double from 2m to 4m by 2030 Source: Maddams
Gastrointestinal Involvement in Adult Mitochondrial Disease
 Newcastle Mitochondrial Disease Guidelines At a glance guidelines: Gastrointestinal Involvement in Adult Mitochondrial Disease For full guideline visit: http://www.newcastle-mitochondria.com/service/patient-care-guidelines/
Newcastle Mitochondrial Disease Guidelines At a glance guidelines: Gastrointestinal Involvement in Adult Mitochondrial Disease For full guideline visit: http://www.newcastle-mitochondria.com/service/patient-care-guidelines/
When to Refer for OGD and the Work Up of Upper GI Malignancies
 When to Refer for OGD and the Work Up of Upper GI Malignancies Dr Hong Qiantai Registrar, Department of Surgery GP Forum 27 May 2017 38 year old female, non-smoker, BMI 29 Works as investment banker Presents
When to Refer for OGD and the Work Up of Upper GI Malignancies Dr Hong Qiantai Registrar, Department of Surgery GP Forum 27 May 2017 38 year old female, non-smoker, BMI 29 Works as investment banker Presents
Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation
 Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation Linda Nguyen, MD Director, Neurogastroenterology and Motility Clinical Assistant Professor Stanford University Overview Normal bowel function Defining Constipation:
Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation Linda Nguyen, MD Director, Neurogastroenterology and Motility Clinical Assistant Professor Stanford University Overview Normal bowel function Defining Constipation:
PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS. A08/S/d Colorectal: Faecal Incontinence (Adult)
 A08/S/d 2013/14 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR COLORECTAL: FAECAL INCONTINENCE (ADULT) PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service Commissioner Lead Provider
A08/S/d 2013/14 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR COLORECTAL: FAECAL INCONTINENCE (ADULT) PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service Commissioner Lead Provider
Faecal Incontinence Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
Faecal incontinence. Faecal incontinence: the management of faecal incontinence in adults
 Issue date: June 2007 Faecal incontinence Faecal incontinence: the management of faecal incontinence in adults NICE clinical guideline 49 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Acute Care NICE
Issue date: June 2007 Faecal incontinence Faecal incontinence: the management of faecal incontinence in adults NICE clinical guideline 49 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Acute Care NICE
Constipation An Overview. Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment
 CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE SCOPE. Coeliac disease: recognition, assessment and management of coeliac disease
 Appendix B: NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Coeliac disease: recognition, assessment and management of coeliac disease 1.1 Short title Coeliac disease 2 The remit
Appendix B: NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Coeliac disease: recognition, assessment and management of coeliac disease 1.1 Short title Coeliac disease 2 The remit
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE The management of faecal incontinence in adults 1.1 Short title Faecal incontinence 2 Background (a) (b) (c) The National Institute
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE The management of faecal incontinence in adults 1.1 Short title Faecal incontinence 2 Background (a) (b) (c) The National Institute
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
Dr David Rowbotham. The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust NHS
 Dr David Rowbotham The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust NHS Useful Titbits from the World of Gastroenterology David Rowbotham Clinical Director & Consultant Gastroenterologist Dept of Gastroenterology
Dr David Rowbotham The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust NHS Useful Titbits from the World of Gastroenterology David Rowbotham Clinical Director & Consultant Gastroenterologist Dept of Gastroenterology
Survivorship. 15 th October Orla Hynes Dietitian St Thomas Hospital
 Survivorship 15 th October 2016 Orla Hynes Dietitian St Thomas Hospital Survivorship Refers to living with or beyond cancer - What happens to these patients after they have finished their treatment January
Survivorship 15 th October 2016 Orla Hynes Dietitian St Thomas Hospital Survivorship Refers to living with or beyond cancer - What happens to these patients after they have finished their treatment January
SIBO
 SIBO What is it? Small Intestinal Bowel Overgrowth A chronic bacterial infection of the small intestine Caused by bad bacteria such as E Coli and Clostridium migrating to the small intestine There is not
SIBO What is it? Small Intestinal Bowel Overgrowth A chronic bacterial infection of the small intestine Caused by bad bacteria such as E Coli and Clostridium migrating to the small intestine There is not
Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly
 Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly Brian Viviano, D.O. Objectives Understand the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management of GI diseases of the elderly. Differentiate
Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly Brian Viviano, D.O. Objectives Understand the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management of GI diseases of the elderly. Differentiate
Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer. Edmond Sung Consultant Gastroenterologist Lead Clinician for Clinical Nutrition and Endoscopy
 Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer Edmond Sung Consultant Gastroenterologist Lead Clinician for Clinical Nutrition and Endoscopy Overview The pancreas and nutrition Nutrition screening - can we do this well?
Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer Edmond Sung Consultant Gastroenterologist Lead Clinician for Clinical Nutrition and Endoscopy Overview The pancreas and nutrition Nutrition screening - can we do this well?
GUIDANCE ON THE INDICATIONS FOR DIAGNOSTIC UPPER GI ENDOSCOPY, FLEXIBLE SIGMOIDOSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY
 Position Statement produced by BSG, AUGIS and ACPGBI GUIDANCE ON THE INDICATIONS FOR DIAGNOSTIC UPPER GI ENDOSCOPY, FLEXIBLE SIGMOIDOSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY Introduction In 2011 the Independent Practice
Position Statement produced by BSG, AUGIS and ACPGBI GUIDANCE ON THE INDICATIONS FOR DIAGNOSTIC UPPER GI ENDOSCOPY, FLEXIBLE SIGMOIDOSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY Introduction In 2011 the Independent Practice
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints. Jennifer Curtis, MD
 A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection
 Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection The University of Nottingham John Atherton Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham, UK Community management of dyspepsia
Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection The University of Nottingham John Atherton Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham, UK Community management of dyspepsia
A quick guide for health professionals
 A quick guide for health professionals Background Most cancer survivors will not have any long-term lower GI consequences of their cancer or its treatment. However, some will develop problems including
A quick guide for health professionals Background Most cancer survivors will not have any long-term lower GI consequences of their cancer or its treatment. However, some will develop problems including
Opinion statement. Introduction. Scleroderma (D Khanna, Section Editor)
 Current Treatment Options in Rheumatology (2015) 1:82 105 DOI 10.1007/s40674-014-0005-0 Scleroderma (D Khanna, Section Editor) Management of Gastrointestinal Involvement in Scleroderma Vivek Nagaraja,
Current Treatment Options in Rheumatology (2015) 1:82 105 DOI 10.1007/s40674-014-0005-0 Scleroderma (D Khanna, Section Editor) Management of Gastrointestinal Involvement in Scleroderma Vivek Nagaraja,
Drossman Gastroenterology 55 Vilcom Center Drive Boyd Hall, Suite 110 Chapel Hill, NC 27514
 Drossman Gastroenterology 55 Vilcom Center Drive Boyd Hall, Suite 110 Chapel Hill, NC 27514 Normal Gastrointestinal Motility and Function "Motility" is an unfamiliar word to many people; it is used primarily
Drossman Gastroenterology 55 Vilcom Center Drive Boyd Hall, Suite 110 Chapel Hill, NC 27514 Normal Gastrointestinal Motility and Function "Motility" is an unfamiliar word to many people; it is used primarily
DOES ENTERAL NUTRITION CAUSE DIARRHOEA & LOOSE STOOLS?
 DOES ENTERAL NUTRITION CAUSE DIARRHOEA & LOOSE STOOLS? Geoffrey Axiak M.Sc. Nursing (Manchester), B.Sc. Nursing, P.G. Dip. Nutrition & Dietetics, Dip. Public Management, Cert. Clinical Nutrition (Leeds)
DOES ENTERAL NUTRITION CAUSE DIARRHOEA & LOOSE STOOLS? Geoffrey Axiak M.Sc. Nursing (Manchester), B.Sc. Nursing, P.G. Dip. Nutrition & Dietetics, Dip. Public Management, Cert. Clinical Nutrition (Leeds)
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS
 INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE ENTERAL FEEDING TOLERANCE. IS IT WORTH IT? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA)
 STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE ENTERAL FEEDING TOLERANCE. IS IT WORTH IT? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION OF ENTERAL FEEDING INTOLERANCE Gastrointestinal feeding intolerance are usually defined as: High gastric
STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE ENTERAL FEEDING TOLERANCE. IS IT WORTH IT? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION OF ENTERAL FEEDING INTOLERANCE Gastrointestinal feeding intolerance are usually defined as: High gastric
Incidence of Colorectal Cancers- Australia. Anterior Resection 5/23/2018. What spurs us to investigate?
 Incidence of Colorectal Cancers- Australia 17,000 Colorectal cancers in 2018 20% of Colorectal cancers are in the Rectum 12.3% of all new cancers Anterior Resection Syndrome (ARS) Lisa Wilson. Colorectal
Incidence of Colorectal Cancers- Australia 17,000 Colorectal cancers in 2018 20% of Colorectal cancers are in the Rectum 12.3% of all new cancers Anterior Resection Syndrome (ARS) Lisa Wilson. Colorectal
Clinical guideline Published: 23 February 2008 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg61
 Irritable bowel syndrome in adults: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 23 February 2008 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg61 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Irritable bowel syndrome in adults: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 23 February 2008 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg61 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Objectives. Identify age-related changes in the gastrointestinal tract
 The Primary Care Physician s Approach to Gastrointestinal Complaints in the Elderly Brian Viviano, D.O. Medical Associates of Erie Objectives Identify age-related changes in the gastrointestinal tract
The Primary Care Physician s Approach to Gastrointestinal Complaints in the Elderly Brian Viviano, D.O. Medical Associates of Erie Objectives Identify age-related changes in the gastrointestinal tract
Diet what helps? Lindsey Allan Macmillan Oncology Dietitian Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford
 Diet what helps? Lindsey Allan Macmillan Oncology Dietitian Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford Diet and cancer Diet and cancer Nutrition research Lack of funding RCTs Low quality Small sample sizes
Diet what helps? Lindsey Allan Macmillan Oncology Dietitian Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford Diet and cancer Diet and cancer Nutrition research Lack of funding RCTs Low quality Small sample sizes
Guidelines NICE, not NICE and the Daily Mail. Dr Andy Poullis Consultant Gastroenterologist
 Guidelines NICE, not NICE and the Daily Mail 2018 Dr Andy Poullis Consultant Gastroenterologist Coeliac IBS Gall bladder polyps PEI PPI Who to test for Coeliac persistent unexplained abdominal or gastrointestinal
Guidelines NICE, not NICE and the Daily Mail 2018 Dr Andy Poullis Consultant Gastroenterologist Coeliac IBS Gall bladder polyps PEI PPI Who to test for Coeliac persistent unexplained abdominal or gastrointestinal
A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence
 Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2000, 279- A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence Christine Norton, MA, RN, and Sonya Chelvanayagam, MSc, RN Abstract Fecal incontinence
Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2000, 279- A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence Christine Norton, MA, RN, and Sonya Chelvanayagam, MSc, RN Abstract Fecal incontinence
Biofeedback Therapy A nurse led management service for functional bowel disorders
 Biofeedback Therapy A nurse led management service for functional bowel disorders Brigitte Collins Lead Nurse BSc, MSc GI Nursing, Dip/Hypnotherapy St Marks Hospital Is biofeedback necessary? Conservative
Biofeedback Therapy A nurse led management service for functional bowel disorders Brigitte Collins Lead Nurse BSc, MSc GI Nursing, Dip/Hypnotherapy St Marks Hospital Is biofeedback necessary? Conservative
Western Health Specialist Clinics Access & Referral Guidelines
 Gastroenterology Specialist Clinics at Western Health: Western Health provides the following Specialist Clinics for patients who require assessment and management of Gastroenterology / Hepatology conditions.
Gastroenterology Specialist Clinics at Western Health: Western Health provides the following Specialist Clinics for patients who require assessment and management of Gastroenterology / Hepatology conditions.
Home Total Parenteral Nutrition for Adults
 Home Total Parenteral Nutrition for Adults Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.08.007 05/21/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: PPO, HMO, QUEST Integration 05/27/2016 Section: Home
Home Total Parenteral Nutrition for Adults Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.08.007 05/21/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: PPO, HMO, QUEST Integration 05/27/2016 Section: Home
ABDOMINAL PAIN, CHRONIC
 Introduction Incidence Aetiology Clinical Assessment Formulation Investigations Management Prognosis Conclusion References Introduction The generally accepted definition of this condition is three or more
Introduction Incidence Aetiology Clinical Assessment Formulation Investigations Management Prognosis Conclusion References Introduction The generally accepted definition of this condition is three or more
IBS - Definition. Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by:
 IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
CONTINENCE MODULE 3 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION AND FAECAL INCONTINENCE
 CONTINENCE MODULE 3 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION AND FAECAL INCONTINENCE The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative treatment
CONTINENCE MODULE 3 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION AND FAECAL INCONTINENCE The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative treatment
Managing Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes Mellitus. Nathan Landesman, DO FACOI Flint Gastroenterology Associates October 12, 2017
 Managing Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Nathan Landesman, DO FACOI Flint Gastroenterology Associates October 12, 2017 EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES Understand prevalence of gastrointestinal
Managing Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Nathan Landesman, DO FACOI Flint Gastroenterology Associates October 12, 2017 EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES Understand prevalence of gastrointestinal
ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION. Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital
 ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital Accidental Bowel Leakage What Gets the Woman into Your Office 67%
ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital Accidental Bowel Leakage What Gets the Woman into Your Office 67%
Guidelines for the Management of Dyspepsia and GORD. Gastroenterology/ Acute Adult Governance. Drugs and Therapeutics Committee
 Guidelines for the Management of Dyspepsia and GORD Document type: Version: 3.0 Author (name): Author (designation): Validated by Prescribing Dr. G. Lipscomb Date validated October 2015 Ratified by: Date
Guidelines for the Management of Dyspepsia and GORD Document type: Version: 3.0 Author (name): Author (designation): Validated by Prescribing Dr. G. Lipscomb Date validated October 2015 Ratified by: Date
Barrett s Oesophagus Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Barrett s Oesophagus Barrett s Oesophagus is the term used for a pre-cancerous condition where the normal
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Barrett s Oesophagus Barrett s Oesophagus is the term used for a pre-cancerous condition where the normal
Management Challenges of the Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT) in Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) Presented by: Tracy M. Frech, MD, MS April 2016
 Management Challenges of the Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT) in Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) Presented by: Tracy M. Frech, MD, MS April 2016 DISCLOSURES AND COPYRIGHT No financial or ethical conflicts of interest.
Management Challenges of the Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT) in Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) Presented by: Tracy M. Frech, MD, MS April 2016 DISCLOSURES AND COPYRIGHT No financial or ethical conflicts of interest.
PATIENT INFORMATION Anterior Resection After Care
 PATIENT INFORMATION Anterior Resection After Care Anatomy of your bowel Transverse colon Ascending colon Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum Anus Your bowel before your operation The large bowel or colon
PATIENT INFORMATION Anterior Resection After Care Anatomy of your bowel Transverse colon Ascending colon Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum Anus Your bowel before your operation The large bowel or colon
PARENTERAL NUTRITION THERAPY
 UnitedHealthcare Benefits of Texas, Inc. 1. UnitedHealthcare of Oklahoma, Inc. 2. UnitedHealthcare of Oregon, Inc. UnitedHealthcare of Washington, Inc. UnitedHealthcare West BENEFIT INTERPRETATION POLICY
UnitedHealthcare Benefits of Texas, Inc. 1. UnitedHealthcare of Oklahoma, Inc. 2. UnitedHealthcare of Oregon, Inc. UnitedHealthcare of Washington, Inc. UnitedHealthcare West BENEFIT INTERPRETATION POLICY
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children
 Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
University Medical Center at Brackenridge. Gastroenterology Clinic Worksheet
 Gastroenterology Clinic Worksheet 1. GI Bleeding (occult or symptomatic) a. CBC b. Iron, Ferritin b. Medication history 2. Iron Deficiency Anemia and no evident source (if no iron deficiency consider hematological
Gastroenterology Clinic Worksheet 1. GI Bleeding (occult or symptomatic) a. CBC b. Iron, Ferritin b. Medication history 2. Iron Deficiency Anemia and no evident source (if no iron deficiency consider hematological
Recent developments in radiotherapy and management of bowel toxicity
 The Roy al Marsden Recent developments in radiotherapy and management of bowel toxicity Dr Alexandra Taylor Radiotherapy for cervical cancer Historical perspective 1901 First use of radium for cervical
The Roy al Marsden Recent developments in radiotherapy and management of bowel toxicity Dr Alexandra Taylor Radiotherapy for cervical cancer Historical perspective 1901 First use of radium for cervical
Gastrointestinal problems in individuals with CdLS. Peter Gillett Consultant Gastroenterologist RHSC Edinburgh UK Cork 2011
 Gastrointestinal problems in individuals with CdLS Peter Gillett Consultant Gastroenterologist RHSC Edinburgh UK Cork 2011 Major problems Gastro-oesophageal reflux and GORD Swallowing problems and
Gastrointestinal problems in individuals with CdLS Peter Gillett Consultant Gastroenterologist RHSC Edinburgh UK Cork 2011 Major problems Gastro-oesophageal reflux and GORD Swallowing problems and
Faecal incontinence. The management of faecal incontinence in adults. Issued: June NICE clinical guideline 49. guidance.nice.org.
 Faecal incontinence The management of faecal incontinence in adults Issued: June 2007 NICE clinical guideline 49 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg49 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Clinical
Faecal incontinence The management of faecal incontinence in adults Issued: June 2007 NICE clinical guideline 49 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg49 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Clinical
Regaining Bowel Control. Yvette Perston Functional Bowel CNS Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham
 Regaining Bowel Control Yvette Perston Functional Bowel CNS Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham GI Tract Sigmoid Colon and Rectum Anterior Resection What is Anterior Resection Syndrome (LARS)? Disordered
Regaining Bowel Control Yvette Perston Functional Bowel CNS Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham GI Tract Sigmoid Colon and Rectum Anterior Resection What is Anterior Resection Syndrome (LARS)? Disordered
CONTINENCE MODULE 1 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS
 CONTINENCE MODULE 1 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative
CONTINENCE MODULE 1 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative
Gut involvement in PoTS an overview
 Gut involvement in PoTS an overview Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology Case Hx * 28 year old lady presents with a long hx of constipation
Gut involvement in PoTS an overview Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology Case Hx * 28 year old lady presents with a long hx of constipation
What Is Constipation?
 CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
ABDOMINAL PAIN, CHRONIC
 Introduction Incidence Aetiology Clinical Assessment Formulation Investigations Management Prognosis Conclusion References Introduction The generally accepted definition of this condition is three or more
Introduction Incidence Aetiology Clinical Assessment Formulation Investigations Management Prognosis Conclusion References Introduction The generally accepted definition of this condition is three or more
Malnutrition in Adults: Guidelines for Identification and Treatment
 Malnutrition in Adults: Guidelines for Identification and Treatment Signatures (e.g. chair of the ratifying committee and lay member) and date Signature...date Designation: Signature...date Designation
Malnutrition in Adults: Guidelines for Identification and Treatment Signatures (e.g. chair of the ratifying committee and lay member) and date Signature...date Designation: Signature...date Designation
Chapter 34. Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
Medical Report: Digestive System (Gut, Gastro-intestinal) Involvement in Scleroderma
 Medical Report: Digestive System (Gut, Gastro-intestinal) Involvement in Scleroderma Updated January 2019 By Dinesh Khanna, MD, MS Professor of Medicine Director, University of Michigan Scleroderma Program
Medical Report: Digestive System (Gut, Gastro-intestinal) Involvement in Scleroderma Updated January 2019 By Dinesh Khanna, MD, MS Professor of Medicine Director, University of Michigan Scleroderma Program
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications
 15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
Review. Consensus Best Practice pathway of the UK Scleroderma Study Group: gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic sclerosis
 Review Consensus Best Practice pathway of the UK Scleroderma Study Group: gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic sclerosis N. Hansi 1, N. Thoua 2, M. Carulli 3, K. Chakravarty 4, S. Lal 5, A. Smyth
Review Consensus Best Practice pathway of the UK Scleroderma Study Group: gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic sclerosis N. Hansi 1, N. Thoua 2, M. Carulli 3, K. Chakravarty 4, S. Lal 5, A. Smyth
Nutritional Protocol for Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT)
 Nutritional Protocol for Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) Scope This protocol details pre, during and post BMT nutritional assessment and management for all forms of BMT undertaken by OxBMT,
Nutritional Protocol for Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) Scope This protocol details pre, during and post BMT nutritional assessment and management for all forms of BMT undertaken by OxBMT,
PPIs: Good or Bad? 1. Basics of PPIs. Gastric Acid Basics. Outline. Gastric Acid Basics. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI)
 Outline Quick basics on Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) PPIs: Good or Bad? What are potential risks of PPI therapy? How to approach your patients American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) recommendations
Outline Quick basics on Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) PPIs: Good or Bad? What are potential risks of PPI therapy? How to approach your patients American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) recommendations
Bowel Health in Adults
 Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions
 PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DR RONALDA DELACY
 GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DR RONALDA DELACY DEFINITIONS GERD -Involuntary, effortless passage of gastric contents into the oesophagus +/-ejected from the mouth resulting in troublesome symptoms or complications
GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DR RONALDA DELACY DEFINITIONS GERD -Involuntary, effortless passage of gastric contents into the oesophagus +/-ejected from the mouth resulting in troublesome symptoms or complications
MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD) Routine endoscopic investigation of patients of any age, presenting with dyspepsia
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD) Routine endoscopic investigation of patients of any age, presenting with dyspepsia
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
GPMP and TCA Coeliac disease
 MP and TCA Coeliac disease ITEM: prepares MP (721) REVIEWS MP (732) prepared TCA (723) REVIEW TCA (732) PATIENT DETAILS: DETAILS: DATE PREPARED: Does a current management plan or Team care arrangement
MP and TCA Coeliac disease ITEM: prepares MP (721) REVIEWS MP (732) prepared TCA (723) REVIEW TCA (732) PATIENT DETAILS: DETAILS: DATE PREPARED: Does a current management plan or Team care arrangement
Managing constipation in residential care
 Managing constipation in residential care Amanda Lee Lecturer, Hull University ; PhD Candidate, Gastroesophageal cancers Key Points Constipation is a major problem in residential care Early detection and
Managing constipation in residential care Amanda Lee Lecturer, Hull University ; PhD Candidate, Gastroesophageal cancers Key Points Constipation is a major problem in residential care Early detection and
