Role of pathogenic auto-antibody production by Toll-like receptor 9 of B cells in active systemic lupus erythematosus
|
|
|
- Rachel Patrick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
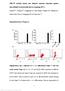
1 Rheumatology Advance Access published December, 7 Rheumatology 7; of doi:.93/rheumatology/kem37 Role of pathogenic auto-antibody production by Toll-like receptor 9 of cells in active systemic lupus erythematosus S. Nakano, S. Morimoto, J. Suzuki, K. Nozawa, H. Amano, Y. Tokano and Y. Takasaki Objectives. Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) is a pattern-associated receptor functioning in innate immunity that may be involved in the recognition of self-antigens and the production of pathogenic auto-antibodies. Therefore, we examined the expression of TLR9 in systemic lupus erythematosus () to determine whether TLR9 is involved in the production of pathogenic auto-antibodies. Methods. cells were collected from patients with active, and subjected to analysis of the TLR9 molecule using flow cytometry fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) and TLR9 mrna by reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. cells were stimulated with CpG-ODN, and subsequent cytokine and anti-dsdna antibody production was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Results. The expression and mrna level of TLR9 on cells was up-regulated in patients, and disease activity index (DAI) and CH were correlated with TLR9 expression on CDþ cells. Moreover, TLR9 CpG interaction enhanced the production of anti-dsdna antibody and IL-. Conclusions. The present study demonstrated that higher expression of TLR9 on peripheral blood cells from patients with active was significantly correlated with CH and DAI to TLR9, and induced the production of anti-dsdna antibody and IL- by TLR9 CpG ligation. These results suggest that an abnormality of innate immunity plays a crucial role in the pathology of, and that blockade of CpG TLR9 interaction may be a new therapeutic approach for. KEY WORDS:, cells, Toll-like receptor 9, CpG-DNA, Anti-dsDNA antibody, IL-, DAI, CH, Innate immunity. Introduction Autoimmune diseases are associated with various immunological abnormalities, such as an increased number of activated cells and auto-antibody production, and in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus () -cell hyperactivity is a central feature [, ]. Although it is considered that autoimmune disease is mainly related to acquired immunity, a recent study has shown that some abnormality of the innate system may also be involved [3]. The Toll-like receptor (TLR) contributes to innate immunity, and its gene has been cloned in humans. The human TLR has subunits, each recognizing a different causative factor [, ]. When these causative factors react with TLR, MyD present in the cytoplasmic compartment is activated, and nuclear localization of nuclear factor-kappa is promoted. This in turn leads to production of inflammatory cytokines such as tumour necrosis factor- or interleukin- (IL-) []. TLR9 is present only in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pdcs) and cells, and is a receptor for microbial CpG-DNA []. It recognizes a single-stranded CpG motif, consisting of unmethylated CpG dinucleotides flanked by particular bases and it is not generally present in mammalian cells, including those of humans [, 7]. However, our previous study has shown that methylation of DNA is decreased in patients with, suggesting that CpG-DNA is related to the pathogenesis []. Furthermore, a recent study has shown that anti-dna auto-antibody production is impaired in TLR9 gene-knockout lupus-prone mice [9]. However, it has not been clarified whether TLR9 contributes directly to the pathogenesis or clinical features of human. cells play an important role in auto-regulation of humoral immune responses, and cells from patients with active and from lupus-prone mice have an intrinsic tendency to over-react Department of Rheumatology and Internal Medicine, Juntendo University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. Submitted May 7; revised version accepted November 7. Correspondence to: S. Nakano, Department of Rheumatology and Internal Medicine, Juntendo University School of Medicine, -- Hongo, unkyo-ku, Tokyo 3-, Japan. soubey@med.juntendo.ac.jp to immunological stimulation during anti-genemic challenge. This has led to a novel hypothesis regarding therapeutic approaches that might interfere with the development and progression of []. Since TLR9 recognizes unmethylated CpG motifs characteristic of bacterial DNA and is involved in the immediate response to a wide range of microbial organisms, cells may, in addition to their role as antibody-producing cells during the adaptive immune response, respond to pathogens in a manner associated with the innate branch of immune defence. Inducible expression of TLR9 in cells may thus provide a link between the innate and adaptive branches of the immune system []. Furthermore, it has been reported that CpG-ODN can enhance TLR9 mrna expression in activated human cells []. In addition, it has been reported that TLR9 controls anti-dna autoantibody production in murine lupus [9]. In the present study, we examined the level of TLR9 expression on peripheral blood cells from patients with active and its correlation with clinical parameters. We also investigated whether CpG ligation of TLR9 is involved in pathogenic auto-antibody production in active. Patients and methods Patients We obtained samples of peripheral blood from 9 patients (Table ), age- and sex-matched healthy s and patients with rheumatoid arthritis () as a disease control. Informed consent was obtained from all patients and healthy s. Eleven blood samples were drawn from patients before treatment. Eight patients had been receiving steroid therapy with prednisolone at mg/day. All patients fulfilled the 997 revised criteria of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) [3]. Disease activity in the patients was assessed using the ACR disease activity index (DAI) []. Cell preparation For isolation of peripheral blood cells, ml of peripheral blood was labelled with l of anti-human CD antibody coupled of ß The Author 7. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ritish Society for Rheumatology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org Downloaded from at Pennsylvania State University on April,
2 of S. Nakano et al. TALE. Profile of patients with No. Gender Age a Dose of steroid b DAI Duration c Clinical manifestation Female 9 Nephritis Female 7 Arthritis, rash 3 Female 7 Pancytopenia Female 3 Leucopenia Female 3 Leucopenia Female Arthritis 7 Male 3 Nephritis Female 3 7 Arthritis 9 Female Nephritis Female 3 3 Nephritis Female 3 Arthritis Male 3 7 Thrombocytopenia 3 Female 3 9 Rash Female 3 9 Arthritis Female 7 3 Arthritis Female 3 3 NP 7 Female 9 NP Female Arthritis 9 Male 3 Nephritis Treatment after the initial analysis: Ten of the patients (nos,, ) were receiving middle-dose steroid therapy (. mg/kg/day prednisolone), two of the patients (nos 9 and ) were receiving high-dose oral steroid therapy ( mg/kg/day prednisolone) and six patients (nos 3, 7, 9) were receiving steroid pulse therapy ( mg methylprednisolone i.v. for 3 days). NP: neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. a Age (mean S.D.): 33.. yrs old. b Prednisolone dose (mg/day) (mean S.D.):.. mg/day. c Duration of the disease (mean S.D.):..9 months. Shows treated with steroids before the analysis. with colloidal paramagnetic microbeads (Miltenyi iotech, ergisch-gladbach, Germany) and isolated using AutoMACS (Miltenyi iotech). cells were isolated at a purity of >93%, as assessed by flow cytometric analysis. TLR9 mrna analysis Total RNA was isolated from cells using an RNeasy Mini kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA). Real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed in a single l reaction volume containing l of One-step RT- PCR SYR Green Master Mix (Applied iosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) with. l of AmpliTaq Gold DNA polymerase (Applied iosystems),. l of MultiScribe reverse transcriptase (Applied iosystems), nm forward and reverse primers for TLR9 ( -ATGGGTTTCTGCCGC and 3 - GAAGAGATGCCGCAGG) or -actin ( -GGACTT CGAGCAAGAGATG and 3 -AGCACTGTGTTGGCGTACA) and g of RNA. TLR9 was measured with an AI PRISM 7 Sequence Detection System (Applied iosystems). TLR9 levels were normalized to -actin for each. Flow cytometric analysis We carried out cell surface staining by adding l of anti-human CD, CD and CD antibody (PharMingen, San Diego, CA, USA) conjugated with PE to the cells ( /ml), and incubating them for 3 min on ice. For intracellular staining, we used Intraprep TM (eckman Coulter, Miami, FL, USA) for fixation and membrization. Then, intracellular staining was performed with l of anti-human TLR9 antibody (C93) (Imgenex, San Diego, CA, USA) conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), and incubated for 3 min in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions. Two-colour analysis was then performed using FacsAria (ecton Dickinson, Mountain View, CA, USA). Detection of anti-dsdna antibody and cytokine Isolated cells differentiated for 3 days were re-plated in 9-well round-bottom plates at cells/well, then stimulated with, ODN ( M) and ODN ( M). Complete (CM) consisted of RPMI- containing L-alanyl-Lglutamine dipeptide supplemented with % fetal calf serum (FCS; ICN iomedicals, Inc.), M -ME (Sigma) and antibiotics (penicillin U/ml, streptomycin g/ml, GICO RL). The stimulatory CpG-ODNs were ODN ( -TCGTCGTTTTGTCGTTTTGTCGTT-3 ) and ODN ( -GGGGGACGATCGTCGGGGG-3 ) []. Anti-dsDNA antibody (io-rad) and cytokine (IL-, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) concentrations were quantified by enzyme-liked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed using the Mann Whitney U-test and Pearson s correlation coefficient. Statistical significance was defined as a P-value of <.. Results Expression of TLR9 on cells from active We first examined the expression of TLR9 mrna on cells from patients with active, and found that this was higher than on cells from healthy s and disease controls (P <.) (Fig. A and ). We then examined the surface expression of TLR9 on cells, but none was detected on cells from any of the three groups. We then examined intracellular expression of TLR9 in cells, and found that this was strikingly and significantly (P <.) higher in CD þ cells from patients than in those from healthy controls and disease controls by mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) (Fig. C and D). Next, we examined the relationship between TLR9 expression on CD þ cells from patients with active and disease activity. The intracellular expression of TLR9 was significantly (P <.) lower in patients whose disease activity had decreased after treatment (Fig. ). However, the expression of TLR9 mrna on cells from patients with active was not significantly decreased. Moreover, we investigated the relationship between the expression of TLR9 on cells from patients with active and laboratory parameters (DAI, anti-dsdna antibody, CH), and found significant correlations with DAI (Fig. 3A) (P <., R ¼.99) and CH by MFI (Fig. 3) (P <., R ¼.3). However, there was no significant correlation between the expression of TLR9 mrna and anti-dsdna antibody. CpG induces anti-dsdna antibody and IL- production We next investigated whether TLR9 CpG interaction was related to activity and its activation. ODN enhanced the expression of TLR9 on cells from patients with active, and was correlated with production of anti-dsdna antibody (Fig. A) (P <.). Moreover, IL- production was significantly increased (Fig. ; P <.) by ODN ligation. Discussion In the present study, we demonstrated that higher expression of TLR9 on peripheral blood cells from patients with active was significantly correlated with CH and DAI to TLR9, and induced anti-dsdna antibody and IL- production by TLR9 CpG ligation. Although a recent study has shown that apoptosis via TLR9 on cells may play a role in the pathogenesis of [], our present study demonstrated that production of anti-dsdna antibody is related to pathogenesis through ligation of CpG to TLR9 on cells. Since the TLR9 molecule is produced by mrna and usually exists in the cytoplasm, it is difficult to examine by flow cytometric analysis. Using cytoplasmic staining and RT-PCR, the present study confirmed that the expression of TLR9 was Downloaded from at Pennsylvania State University on April,
3 Expression of TLR9 in 3of A. TLR9 7 3 TLR9 mrna/β-actin mrna ratio C Counts.. Pre-Tx ** Post-Tx (n = 9) FIG.. Decreased expression of TLR9 on cells from active patients after treatment. Post-treatment expression of TLR9 on cells from active patients. The MFI of TLR9 in post-treatment patients was significantly lower than that before treatment ( P <.). Pre-Tx: pre-treatment; Post-Tx: post-treatment. Fluorescence intensity TLR9 on CD cells D b actin T cell T cell FIG.. Expression of TLR9 on cells from active patients and healthy s. (A) Expression of TLR9 mrna in active patients was significantly higher than in healthy individuals ( P <.). ars show the mean S.D. () TLR9 or -actin samples ( l) were used as template for RT-PCR. The products were electrophoresed on % Tris base, boric acid and EDTA (TE) agarose gels containing. g/ml ethidium bromide and visualized under ultraviolet (UV). Negative control was l of total RNA isolated from CD þ T cells. (C) Representative staining pattern of TLR9 on peripheral cells from a healthy, a patient with active and a patient with. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stained with monoclonal antibodies against TLR9 and CD. (D) TLR9 molecule in cells from patients with active and healthy controls was analysed by flow cytometry. The MFI of TLR9 in active patients was significantly higher than that in healthy s and disease controls ( P <.). increased on cells from patients with active, and that this was correlated with disease activity. These results suggest that innate immunity might play a role in the pathogenesis of through TLR9 on cells. TLR induced the expression of co-stimulatory molecules, as represented by CD and CD, and the expression of TLR9 was correlated with that of CD on cells (data not shown). Since the expression of CD on cells is commonly increased in active, it is possible that the increased expression of TLR9 induces the initial activation of cells. It has been suggested that TLR9 expression on cells plays a role in pathogenesis through the induction of anti-dsdna antibody. As described previously, the ligand of TLR9 is CpG that is a product of abnormal methylation of DNA, and commonly recognized in. A previous study has shown that methylation of DNA is decreased in patients, suggesting that CpG-DNA is related to the pathogenesis of []. Our present study showed that production of anti-dsdna antibody occurred through ligation of CpG to TLR9 on cells from patients with active. Although the mechanism responsible for production Downloaded from at Pennsylvania State University on April,
4 of S. Nakano et al. A 3 3 Anti ds-dna antibody IgG [IU/ml] 3 A * ODN DAI ODN (n = 9) (P<., R=.99) ODN ODN (: n =, : n = ) of anti-dsdna antibody is heterogeneous, we think that the interaction between CpG and TLR9 plays a pivotal role. The production of anti-dsdna antibody may not be induced directly by CpG, but may require various processes including the differentiation of cells. In order to investigate this issue, we examined various cytokines in the culture supernatant. Surprisingly, we found that IL- production from patients with active cells was increased by stimulation with CpG. Although it has recently been established that IL- is a regulatory cytokine, it was originally reported to be a factor inducing antibody production in certain diseases, especially. Indeed, injection of an IL- blocking antibody has been reported to suppress disease activity in lupus mice [7]. Futhermore, it has been reported that cells from patients produce IL- [], and that this cytokine induces the production of anti-dsdna antibody [7]. Abnormality of DNA methylation easily induces the transcription of mrna from DNA, and it has been shown previously that this abnormality commonly occurs in []. This finding suggests that the abnormal methylation induces increased transcription of the TLR9 gene, and that the CpG produced as a result reacts with the highly expressed TLR9. The role of innate immunity in autoimmune disease is still unclear. We have demonstrated that expression of TLR9 on cells is increased in human, and that this increased expression is closely related to disease activity. We suggest that abnormality of innate immunity also plays a crucial role in the 3 IL- [pg/ul] pathology of, and that blockade of CpG TLR9 interaction may be a promising new therapeutic approach for. Acknowledgements We are grateful to D. Douglas for assistance in preparing the manuscript. Disclosure statement: The authors have declared no conflicts of interest. References * ODN ODN Rheumatology key messages ODN ODN (: n =, : n = ) FIG.. TLR9 CpG ligation enhances production of anti-dsdna antibody and IL- from cells of patients. (A) ODN enhanced the expression of TLR9 on cells and was correlated with higher production of anti-dsdna antibody (P <.). () IL- production was significantly increased (P <.) by ODN ligation. Isolated cells were stimulated with, ODN ( M) or ODN ( M). IL- and anti-dsdna antibody production was measured by ELISA. : healthy. CH (n = 9) (P<., R=.3) FIG. 3. Correlation between TLR9 molecule and active cells from active. (A) Correlation between MFI of TLR9 and DAI on cells from patients with active (P <., R ¼.99). () Correlation between MFI of TLR9 and CH on cells from patients with active (P <., R ¼.3). The expression and mrna level of TLR9 on cells up-regulated in patients. TLR9 expression is strongly associated with activity of. In function, cells were activated interacting to CpG-DNA. Chan OT, Madaio MP, Shlomchik MJ. The central and multiple roles of cells in lupus pathogenesis. Immunol Rev 999;9:7. Fernandez-Gutierrez, de Miguel S, Morado C, Hernandez-Garcia C, anares A, Jover JA. Defective early T and T-dependent cell activation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 99;7:3. 3 Anders HJ. A Toll for lupus. Lupus ;:7. Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol ;:99. Downloaded from at Pennsylvania State University on April,
5 Expression of TLR9 in of Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T et al. A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature ;:7. Krieg AM. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA and their immune effects. Annu Rev Immunol ;:79. 7 Krieg AM, Yi AK, Matson S et al. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA trigger direct -cell activation. Nature 99;37: 9. Sekigawa I, Okada M, Ogasawara H, Kaneko H, Hishikawa T, Hashimoto H. DNA methylation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 3;:79. 9 Christensen SR, Kashgarian M, Alexopoulou L, Flavell, Akira S, Shlomchik MJ. Toll-like receptor 9 controls anti-dna autoantibody production in murine lupus. J Exp Med ;:3 3. Grammer AC, Lipsky PE. cell abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 3;(Suppl. ):S 7. Viau M, Zouali M. -lymphocytes, innate immunity, and autoimmunity. Clin Immunol ;:7. Cognasse F, Acquart S, eniguel L et al. Differential production of immunoglobulin classes and subclasses by mucosal-type human -lymphocytes exposed in vitro to CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. Clin Chem Lab Med ;3: 3. 3 Hochberg MC. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 997;:7. ombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz M, Caron D, Chang CH. Derivation of the DAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in. Arthritis Rheum 99;3:3. Krug A, Rothenfusser S, Hornung V et al. Identification of CpG oligonucleotide sequences with high induction of IFN-alpha/beta in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol ;3: 3. Papadimitraki ED, Choulaki C, Koutala E et al. Expansion of toll-like receptor 9-expressing cells in active systemic lupus erythematosus: implications for the induction and maintenance of the autoimmune process. Arthritis Rheum ;:3. 7 Ishida H, Muchamuel T, Sakaguchi S, Andrade S, Menon S, Howard M. Continuous administration of anti-interleukin antibodies delays onset of autoimmunity in NZ/ W F mice. J Exp Med 99;79:3. Miret C, Font J, Molina R et al. Relationship of oncogenes (sfas, cl-) and cytokines (IL-, alpha-tnf) with the activity of systemic lupus erythematosus. Anticancer Res ;:33 9 Downloaded from at Pennsylvania State University on April,
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
1. TLR. TLR Toll-like receptors. Toll Toll-like receptor, TLR TLR TLR TLR. type I TLR TLR. Toll
 54pp.145 152 2004 1. TLR T B TLR Toll-like receptors TLR TLR I IFN TLR T B B T Toll NF- B 1996 565-0871 3-1 TEL 06-6879-8303 FAX 06-6879-8305 E-mail uemattsu@biken.osaka-u.ac.jp Toll Toll-like receptor,
54pp.145 152 2004 1. TLR T B TLR Toll-like receptors TLR TLR I IFN TLR T B B T Toll NF- B 1996 565-0871 3-1 TEL 06-6879-8303 FAX 06-6879-8305 E-mail uemattsu@biken.osaka-u.ac.jp Toll Toll-like receptor,
Antibodies for human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells studies Dendritics SAS, 60 avenue Rockefeller, F Lyon
 Antibodies for human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells studies Dendritics SAS, 60 avenue Rockefeller, F-69008 Lyon www.dendritics.net Human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells (PDCs) are considered the main sentinels
Antibodies for human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells studies Dendritics SAS, 60 avenue Rockefeller, F-69008 Lyon www.dendritics.net Human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells (PDCs) are considered the main sentinels
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms
 TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
Horizon 2020 Programme. SFS-01b Tackling losses from terrestrial animal diseases
 Horizon 2020 Programme SFS-01b-2014 Tackling losses from terrestrial animal diseases Strengthening Animal Production and Health through the Immune Response Project ID: 633184 D12.1 Age related innate responses
Horizon 2020 Programme SFS-01b-2014 Tackling losses from terrestrial animal diseases Strengthening Animal Production and Health through the Immune Response Project ID: 633184 D12.1 Age related innate responses
Apoptosis of lymphocytes in SLE: the level, correlation with dosage prednisolone and lymphocyte phenotypes
 Apoptosis of lymphocytes in SLE: the level, correlation with dosage prednisolone and lymphocyte phenotypes ABDELMAROUF MOHIELDEIN 1, NATALIA BELUSHKINA 2, ULIANA PETROVA 3. 1,2 Department of Biochemistry,
Apoptosis of lymphocytes in SLE: the level, correlation with dosage prednisolone and lymphocyte phenotypes ABDELMAROUF MOHIELDEIN 1, NATALIA BELUSHKINA 2, ULIANA PETROVA 3. 1,2 Department of Biochemistry,
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
Autoimmunity. Autoimmunity arises because of defects in central or peripheral tolerance of lymphocytes to selfantigens
 Autoimmunity Autoimmunity arises because of defects in central or peripheral tolerance of lymphocytes to selfantigens Autoimmune disease can be caused to primary defects in B cells, T cells and possibly
Autoimmunity Autoimmunity arises because of defects in central or peripheral tolerance of lymphocytes to selfantigens Autoimmune disease can be caused to primary defects in B cells, T cells and possibly
Application of genetic signatures to clinical care of lupus
 Application of genetic signatures to clinical care of lupus Dr Durga Prasanna Misra MD, MRCP(UK), DM Assistant Professor Department of Clinical Immunology, JIPMER, Puducherry. LAYOUT Genetics of lupus
Application of genetic signatures to clinical care of lupus Dr Durga Prasanna Misra MD, MRCP(UK), DM Assistant Professor Department of Clinical Immunology, JIPMER, Puducherry. LAYOUT Genetics of lupus
Vasoactive intestinal peptide inhibits IFN-α secretion and modulates the immune function of plasmacytoid dendritic cells
 Excerpt from MACS&more Vol 12 1/21 Vasoactive intestinal peptide inhibits IFN-α secretion and modulates the immune function of plasmacytoid dendritic cells Dorit Fabricius 1, 2,, M. Sue O Dorisio 1, 2,
Excerpt from MACS&more Vol 12 1/21 Vasoactive intestinal peptide inhibits IFN-α secretion and modulates the immune function of plasmacytoid dendritic cells Dorit Fabricius 1, 2,, M. Sue O Dorisio 1, 2,
Supplemental Information. T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism
 Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection
 Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
Correlation between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index, C3, C4 and Anti-dsDNA Antibodies
 Original Article Correlation between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index, C3, C4 and Anti-dsDNA Antibodies Col K Narayanan *, Col V Marwaha +, Col K Shanmuganandan #, Gp Capt S Shankar
Original Article Correlation between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index, C3, C4 and Anti-dsDNA Antibodies Col K Narayanan *, Col V Marwaha +, Col K Shanmuganandan #, Gp Capt S Shankar
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Introduction. Key-Words: - SLE, apoptosis, lymphocyte phenotypes, prednisolone, dsdna autoantibodies, flow cytometry.
 Apoptosis of lymphocytes in SLE: the level, correlation with dosage prednisolone and lymphocyte phenotypes ABDELMAROUF MOHIELDEIN 1, NATALIA BELUSHKINA 2, ULIANA PETROVA 3. Abstract: - Introduction SLE
Apoptosis of lymphocytes in SLE: the level, correlation with dosage prednisolone and lymphocyte phenotypes ABDELMAROUF MOHIELDEIN 1, NATALIA BELUSHKINA 2, ULIANA PETROVA 3. Abstract: - Introduction SLE
Autoimmune Diseases. Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic
 Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with
 Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens
 How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
DISCLOSURE. Relevant relationships with commercial entities none. Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none
 AUTOIMMUNITY DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential bias N/A MODULE
AUTOIMMUNITY DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential bias N/A MODULE
York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
Pathogenesis of lupus apoptosis clearance and regulation of self tolerance. Durga Prasanna Misra
 Pathogenesis of lupus apoptosis clearance and regulation of self tolerance Durga Prasanna Misra Format Apoptosis Apoptosis in SLE Decreased apoptosis of autoreactive cells Increased apoptosis Defective
Pathogenesis of lupus apoptosis clearance and regulation of self tolerance Durga Prasanna Misra Format Apoptosis Apoptosis in SLE Decreased apoptosis of autoreactive cells Increased apoptosis Defective
DNA vaccine, peripheral T-cell tolerance modulation 185
 Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity
 Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity B cell development in health and disease: B-lymphocytes or B cells, and the antibodies they produce, are crucial mediators of humoral immunity, providing
Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity B cell development in health and disease: B-lymphocytes or B cells, and the antibodies they produce, are crucial mediators of humoral immunity, providing
IMMUNOTOOLS: EFFECT OF NOTCH-DEFICIENT MACROPHAGES TO AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE WIPAWEE WONGCHANA
 IMMUNOTOOLS: EFFECT OF NOTCH-DEFICIENT MACROPHAGES TO AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE 22-02-2017 WIPAWEE WONGCHANA WHAT DO YOU SEE? Allergy Ref: http://carrington.edu/blog/medical/vaccines/smallpox-andsmallpox-vaccine/
IMMUNOTOOLS: EFFECT OF NOTCH-DEFICIENT MACROPHAGES TO AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE 22-02-2017 WIPAWEE WONGCHANA WHAT DO YOU SEE? Allergy Ref: http://carrington.edu/blog/medical/vaccines/smallpox-andsmallpox-vaccine/
IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, TNF- ELISA. 1 Candida albicans ,,,, C. albicans., Clonetics BioWhittaker 5% CO 2. TLD-0142, TLD-0143, 37 C, 3,
 Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. Vol. 45, 131 136, 2004 ISSN 0916 4804,,.,,.,,,, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, TNF- ELISA., IL-8, IL-8, TNF-, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-.,,,,,.,. key word: cytokine, keratinocyte, ELISA enzyme-linked
Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. Vol. 45, 131 136, 2004 ISSN 0916 4804,,.,,.,,,, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, TNF- ELISA., IL-8, IL-8, TNF-, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-.,,,,,.,. key word: cytokine, keratinocyte, ELISA enzyme-linked
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Original Article. Abstract
 Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of antinuclear antibodies and anti-double stranded DNA antibodies in patients of systemic lupus erythematosus presenting with dermatological features Attiya Tareen*,
Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of antinuclear antibodies and anti-double stranded DNA antibodies in patients of systemic lupus erythematosus presenting with dermatological features Attiya Tareen*,
T. Xing*, L. Zhong*, G. Qiu, L. Huang and Z. Peng
 Evolution of CD4 + CD25 hi T cell subsets in Aspergillus-infected liver transplantation recipients reduces the incidence of transplantation rejection via upregulating the production of anti-inflammatory
Evolution of CD4 + CD25 hi T cell subsets in Aspergillus-infected liver transplantation recipients reduces the incidence of transplantation rejection via upregulating the production of anti-inflammatory
APRIL is increased in serum of patients with brain glioblastoma multiforme
 276 Eur. Cytokine Netw., Vol. 17 n 4, December 06, 276-80 APRIL is increased in serum of patients with brain glioblastoma multiforme Joanna Iłżecka 1, Marek Iłżecki 2 1 Department of Neurology, Medical
276 Eur. Cytokine Netw., Vol. 17 n 4, December 06, 276-80 APRIL is increased in serum of patients with brain glioblastoma multiforme Joanna Iłżecka 1, Marek Iłżecki 2 1 Department of Neurology, Medical
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by. activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b
 Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Bachelor of Chinese Medicine ( ) AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
 Bachelor of Chinese Medicine (2002 2003) BCM II Dr. EYT Chan February 6, 2003 9:30 am 1:00 pm Rm 134 UPB AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES 1. Introduction Diseases may be the consequence of an aberrant immune response,
Bachelor of Chinese Medicine (2002 2003) BCM II Dr. EYT Chan February 6, 2003 9:30 am 1:00 pm Rm 134 UPB AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES 1. Introduction Diseases may be the consequence of an aberrant immune response,
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Environmental factors including drugs. Jyoti Ranjan Parida
 Environmental factors including drugs Jyoti Ranjan Parida Scheme of presentation Pathogenesis of autoimmune disease Evidence for environmental influence Environmental factors Proposed -Role of Sunlight
Environmental factors including drugs Jyoti Ranjan Parida Scheme of presentation Pathogenesis of autoimmune disease Evidence for environmental influence Environmental factors Proposed -Role of Sunlight
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/23854 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Marel, Sander van der Title: Gene and cell therapy based treatment strategies
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/23854 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Marel, Sander van der Title: Gene and cell therapy based treatment strategies
Significance of Anti-C1q Antibodies in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus as A Marker of Disease Activity and Lupus Nephritis
 THE EGYPTIAN JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY Vol. 23 (1), 2016 Page: 00-00 Significance of Anti-C1q Antibodies in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus as A Marker of Disease Activity and Lupus Nephritis 1
THE EGYPTIAN JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY Vol. 23 (1), 2016 Page: 00-00 Significance of Anti-C1q Antibodies in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus as A Marker of Disease Activity and Lupus Nephritis 1
Generation of monocytederived Dendritic Cells (modcs)
 monocytederived Dendritic (modcs) Application Note Background Dendritic (DCs) are so called because of their characteristic cell surface projections that resemble the dendrites of neurons (see Fig 1 and
monocytederived Dendritic (modcs) Application Note Background Dendritic (DCs) are so called because of their characteristic cell surface projections that resemble the dendrites of neurons (see Fig 1 and
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/366/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Viral entry route determines how human plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce type I interferons Daniela Bruni, Maxime
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/366/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Viral entry route determines how human plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce type I interferons Daniela Bruni, Maxime
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors Presented by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-10780-00 Outline Introduction Cytokines Transcription
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors Presented by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-10780-00 Outline Introduction Cytokines Transcription
Supplemental Figure 1. IL-3 blockade with Fab CSL362 depletes plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pdcs), but not basophils, at higher doses.
 Supplemental Figure 1. IL-3 blockade with Fab CSL362 depletes plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pdcs), but not basophils, at higher doses. Percentage of viable (A) pdcs (Sytox Blue-, Lin1-, HLADR+, BDCA2++)
Supplemental Figure 1. IL-3 blockade with Fab CSL362 depletes plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pdcs), but not basophils, at higher doses. Percentage of viable (A) pdcs (Sytox Blue-, Lin1-, HLADR+, BDCA2++)
Protection against Experimental Autoimmune Myocarditis Is Mediated by Interleukin-10-Producing T Cells that Are Controlled by Dendritic Cells
 Liberty University DigitalCommons@Liberty University Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Biology and Chemistry 7-2005 Protection against Experimental Autoimmune Myocarditis Is Mediated
Liberty University DigitalCommons@Liberty University Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Biology and Chemistry 7-2005 Protection against Experimental Autoimmune Myocarditis Is Mediated
Mechanisms of Autontibodies
 Mechanisms of Autontibodies Production in Rheumatic Diseases Eisa Salehi PhD Tehran University of Medical Sciences Immunology Department Introduction Rheumatic diseases: Cause inflammation, swelling, and
Mechanisms of Autontibodies Production in Rheumatic Diseases Eisa Salehi PhD Tehran University of Medical Sciences Immunology Department Introduction Rheumatic diseases: Cause inflammation, swelling, and
Organic dust-induced interleukin-12 production activates T- and natural killer cells
 Eur Respir J 22; 2: 686 69 DOI:.1183/931936.2.222 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 22 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Organic dust-induced interleukin-12 production
Eur Respir J 22; 2: 686 69 DOI:.1183/931936.2.222 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 22 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Organic dust-induced interleukin-12 production
in vitro in vivo [hemagglutinating virus of Japan envelope (HVJ-E)] HVJ-E (Scid) HVJ-E HVJ-E
![in vitro in vivo [hemagglutinating virus of Japan envelope (HVJ-E)] HVJ-E (Scid) HVJ-E HVJ-E in vitro in vivo [hemagglutinating virus of Japan envelope (HVJ-E)] HVJ-E (Scid) HVJ-E HVJ-E](/thumbs/89/98726692.jpg) 57 pp.19-282007 1. [hemagglutinating virus of Japan envelope (HVJ-E)] HVJ-E HVJ-E 60% 80% (Scid) In vitro HVJ-E HVJ(live HVJ) HVJ-E live HVJ IL-6 RT-PCR HVJ-E CD4 + T CD8 + T T (CTL) HVJ-E Foxp3 + CD4
57 pp.19-282007 1. [hemagglutinating virus of Japan envelope (HVJ-E)] HVJ-E HVJ-E 60% 80% (Scid) In vitro HVJ-E HVJ(live HVJ) HVJ-E live HVJ IL-6 RT-PCR HVJ-E CD4 + T CD8 + T T (CTL) HVJ-E Foxp3 + CD4
T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation
 1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
2. Innate immunity 2013
 1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION. Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one. of the most common diseases found in the population.
 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION I.1 Background Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one of the most common diseases found in the population. Based on community survey that is held by PERNEFRI (Perhimpunan
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION I.1 Background Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one of the most common diseases found in the population. Based on community survey that is held by PERNEFRI (Perhimpunan
Lack of association of IL-2RA and IL-2RB polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population
 Lack of association of IL-2RA and IL-2RB polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population J. Zhu 1 *, F. He 2 *, D.D. Zhang 2 *, J.Y. Yang 2, J. Cheng 1, R. Wu 1, B. Gong 2, X.Q. Liu
Lack of association of IL-2RA and IL-2RB polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population J. Zhu 1 *, F. He 2 *, D.D. Zhang 2 *, J.Y. Yang 2, J. Cheng 1, R. Wu 1, B. Gong 2, X.Q. Liu
B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis?
 Rheumatology 2005;44(Suppl. 2):ii3 ii7 B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh616 The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of RA is well established,
Rheumatology 2005;44(Suppl. 2):ii3 ii7 B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh616 The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of RA is well established,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Role of JAKs in myeloid cells and autoimmune diseases. Satoshi Kubo, Kunihiro Yamaoka and Yoshiya Tanaka
 131 Mini Review Role of JAKs in myeloid cells and autoimmune diseases Satoshi Kubo, Kunihiro Yamaoka and Yoshiya Tanaka The First Department of Internal Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental
131 Mini Review Role of JAKs in myeloid cells and autoimmune diseases Satoshi Kubo, Kunihiro Yamaoka and Yoshiya Tanaka The First Department of Internal Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION. Impaired TLR9 responses in B cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
 1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 3 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 4 Impaired TLR9 responses in B cells from patients with systemic lupus
1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 3 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 4 Impaired TLR9 responses in B cells from patients with systemic lupus
Cell-mediated Immunity
 Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Toll-like Receptor Signaling
 Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Association of anti-mcv autoantibodies with SLE (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus) overlapping with various syndromes
 International Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol. () pp. 21-214, June 211 Available online http://www.academicjournals.org/ijmms ISSN 2-972 211 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Association
International Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol. () pp. 21-214, June 211 Available online http://www.academicjournals.org/ijmms ISSN 2-972 211 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Association
METHODS Penh. Measurements and ribonuclease protection assay. Intracellular cytokine staining. ELISAs RT-PCR. Lung morphometry.
 METHODS Penh In addition to measurement of APTI, airway hyperresponsiveness to methacholine was also evaluated within 24 hours of the last allergen challenge by means of measurement of Penh (Buxco Electronics,
METHODS Penh In addition to measurement of APTI, airway hyperresponsiveness to methacholine was also evaluated within 24 hours of the last allergen challenge by means of measurement of Penh (Buxco Electronics,
The system Fas/Fas-L in SLE
 The system Fas/Fas-L in SLE NATALIA BELUSHKINA 1, ABDELMAROUF MOHIELDEIN 2, ULIANA PETROVA 3. 1,2 Department of Biochemistry, 3 Deparment of immunology 1 Sechenov Moscow Medical Academy, Research Institute
The system Fas/Fas-L in SLE NATALIA BELUSHKINA 1, ABDELMAROUF MOHIELDEIN 2, ULIANA PETROVA 3. 1,2 Department of Biochemistry, 3 Deparment of immunology 1 Sechenov Moscow Medical Academy, Research Institute
In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion
 - 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, Workflow in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of T
- 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, Workflow in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of T
Original Article Brucella outer membrane protein Omp25 induces microglial cells in vitro to secrete inflammatory cytokines and inhibit apoptosis
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):17530-17535 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0013518 Original Article Brucella outer membrane protein Omp25 induces microglial cells in vitro to secrete inflammatory cytokines
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):17530-17535 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0013518 Original Article Brucella outer membrane protein Omp25 induces microglial cells in vitro to secrete inflammatory cytokines
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Page 1 of 2. Product Information Contents: ezkine Th1 Activation 2 Whole Blood Intracellular Cytokine Kit
 Page 1 of 2 ezkine Th1 Activation 2 Whole Blood Intracellular Cytokine Kit Catalog Number: 8822-6852 RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Staining of human whole blood with
Page 1 of 2 ezkine Th1 Activation 2 Whole Blood Intracellular Cytokine Kit Catalog Number: 8822-6852 RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Staining of human whole blood with
Accepted Manuscript. Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development. Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo
 Accepted Manuscript Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo PII: S0016-5085(18)34974-6 DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.057 Reference: YGAST 62119 To appear
Accepted Manuscript Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo PII: S0016-5085(18)34974-6 DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.057 Reference: YGAST 62119 To appear
The immunomodulatory effect 1,25 (OH)2 D3 on TLR 2 and TLR4 expression on monocytes of patients with type II diabetes mellitus
 Original Article The immunomodulatory effect 1,25 (OH)2 D3 on TLR 2 and TLR4 expression on monocytes of patients with type II diabetes mellitus Eisa Salehi 1, Nasrin Hedayati 1, Sanam Dolati 1, Reza Mirzaei
Original Article The immunomodulatory effect 1,25 (OH)2 D3 on TLR 2 and TLR4 expression on monocytes of patients with type II diabetes mellitus Eisa Salehi 1, Nasrin Hedayati 1, Sanam Dolati 1, Reza Mirzaei
Disclosures. Pathogenesis of Autoimmunity Normal immune response: 11/5/2011. Methotrexate and JUN Pathway Activation in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Methotrexate and JUN Pathway Activation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Disclosures N. Olsen and T. Aune are co-founders of ArthroChip LLC. Nancy J. Olsen Penn State MS Hershey Medical Center Thomas M. Aune Vanderbilt
Methotrexate and JUN Pathway Activation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Disclosures N. Olsen and T. Aune are co-founders of ArthroChip LLC. Nancy J. Olsen Penn State MS Hershey Medical Center Thomas M. Aune Vanderbilt
IL-17 in health and disease. March 2014 PSO13-C051n
 IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
The Power of the ANA. April 2018 Emily Littlejohn, DO MPH
 Emergent Rheumatologic Diseases and Disorders for Primary Care. The Power of the ANA April 2018 Emily Littlejohn, DO MPH Question 1: the ANA test is: A) A screening test with high specificity to diagnose
Emergent Rheumatologic Diseases and Disorders for Primary Care. The Power of the ANA April 2018 Emily Littlejohn, DO MPH Question 1: the ANA test is: A) A screening test with high specificity to diagnose
In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion
 - 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + CD127 dim/- regulatory T cell Workflow isolation, in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation
- 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + CD127 dim/- regulatory T cell Workflow isolation, in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Overview: The immune responses of animals can be divided into innate immunity and acquired immunity.
 GUIDED READING - Ch. 43 - THE IMMUNE SYSTEM NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not be accepted.
GUIDED READING - Ch. 43 - THE IMMUNE SYSTEM NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not be accepted.
and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the
 Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
ankylosing spondylitis Department of Clinical Immunology, Xijing Hospital, The Fourth Military
 Functional defects in CD4 + CD25 high FoxP3 + regulatory cells in ankylosing spondylitis Huifang Guo 1, 2, 3, Ming Zheng 1, 2, 3, Kui Zhang 1, 3, Fengfan Yang 1, 3, Xin Zhang 1, 3, Qing Han 1, 3, Zhi-Nan
Functional defects in CD4 + CD25 high FoxP3 + regulatory cells in ankylosing spondylitis Huifang Guo 1, 2, 3, Ming Zheng 1, 2, 3, Kui Zhang 1, 3, Fengfan Yang 1, 3, Xin Zhang 1, 3, Qing Han 1, 3, Zhi-Nan
MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Manipulation of immune response Autoimmune diseases & the pathogenic mechanism
 MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Manipulation of immune response Autoimmune diseases & the pathogenic mechanism SCHMAIEL SHIRDEL CONTENT 2 Introduction Autoimmune diseases Classification Involved components Autoimmune
MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Manipulation of immune response Autoimmune diseases & the pathogenic mechanism SCHMAIEL SHIRDEL CONTENT 2 Introduction Autoimmune diseases Classification Involved components Autoimmune
Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel
 Supplementary Figures 1-8 Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel Marc Schmidt 1,2, Badrinarayanan Raghavan 1,2, Verena Müller 1,2, Thomas Vogl 3, György
Supplementary Figures 1-8 Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel Marc Schmidt 1,2, Badrinarayanan Raghavan 1,2, Verena Müller 1,2, Thomas Vogl 3, György
Received 27 October 2004/Returned for modification 7 January 2005/Accepted 2 March 2005
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, May 2005, p. 606 621 Vol. 12, No. 5 1071-412X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cdli.12.5.606 621.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, May 2005, p. 606 621 Vol. 12, No. 5 1071-412X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cdli.12.5.606 621.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
Difference in Cytokine Production and Cell Activation between Adenoidal Lymphocytes and Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes of Children with Otitis Media
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Sept. 2005, p. 1130 1134 Vol. 12, No. 9 1071-412X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cdli.12.9.1130 1134.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Sept. 2005, p. 1130 1134 Vol. 12, No. 9 1071-412X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cdli.12.9.1130 1134.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All
Chapter 4. Estrogen receptor expression in human macrophages
 Chapter 4 Estrogen receptor expression in human macrophages 4.1. Introduction Macrophages respond to estrogen present in their microenvironment and hence should express functional estrogen receptors unless
Chapter 4 Estrogen receptor expression in human macrophages 4.1. Introduction Macrophages respond to estrogen present in their microenvironment and hence should express functional estrogen receptors unless
IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, psoriasis
 IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, inhibits disease development in mouse models of psoriasis Weiwen e Ja Jiang, Fu-Gang Zhu, Dong Yu, Ekambar R. Kandimalla, a a, Nicola La Monica, and Sudhir
IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, inhibits disease development in mouse models of psoriasis Weiwen e Ja Jiang, Fu-Gang Zhu, Dong Yu, Ekambar R. Kandimalla, a a, Nicola La Monica, and Sudhir
Simultaneous comprehensive multiplex autoantibody analysis by CytoBead technology for Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis.
 Simultaneous comprehensive multiplex autoantibody analysis by CytoBead technology for Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis l Assays Indirect Immunofluorescence Goldstandard for Diagnosis of Autoimmune
Simultaneous comprehensive multiplex autoantibody analysis by CytoBead technology for Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis l Assays Indirect Immunofluorescence Goldstandard for Diagnosis of Autoimmune
Index. Index 439. Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305
 Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
Clinical Laboratory. 14:41:00 Complement Component 3 50 mg/dl Oct-18
 Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) Antibody 5.0 IU/mL [0.0-9.0] 18-289-900139 16-Oct-18 Complement Component 3 50 mg/dl 18-289-900139
Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) Antibody 5.0 IU/mL [0.0-9.0] 18-289-900139 16-Oct-18 Complement Component 3 50 mg/dl 18-289-900139
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs
 Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
Supplementary Figures
 MiR-29 controls innate and adaptive immune responses against intracellular bacterial infection by targeting IFN-γ Feng Ma 1,2,5, Sheng Xu 1,5, Xingguang Liu 1, Qian Zhang 1, Xiongfei Xu 1, Mofang Liu 3,
MiR-29 controls innate and adaptive immune responses against intracellular bacterial infection by targeting IFN-γ Feng Ma 1,2,5, Sheng Xu 1,5, Xingguang Liu 1, Qian Zhang 1, Xiongfei Xu 1, Mofang Liu 3,
AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES
 AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (NPSLE) Case presentations and topic discussion The Rheumatology Unit UMMC experience
 Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (NPSLE) Case presentations and topic discussion The Rheumatology Unit UMMC experience References Sanna G, Bertolaccini ML. Neuropsychiatric manifestations
Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (NPSLE) Case presentations and topic discussion The Rheumatology Unit UMMC experience References Sanna G, Bertolaccini ML. Neuropsychiatric manifestations
AUTOIMMUNITY TOLERANCE TO SELF
 AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Resolution of a chronic viral infection after interleukin-10 receptor blockade
 ARTICLE Resolution of a chronic viral infection after interleukin-10 receptor blockade Mette Ejrnaes, 1 Christophe M. Filippi, 1 Marianne M. Martinic, 1 Eleanor M. Ling, 1 Lisa M. Togher, 1 Shane Crotty,
ARTICLE Resolution of a chronic viral infection after interleukin-10 receptor blockade Mette Ejrnaes, 1 Christophe M. Filippi, 1 Marianne M. Martinic, 1 Eleanor M. Ling, 1 Lisa M. Togher, 1 Shane Crotty,
Toll-like receptor-dependent production of IL-12p40 causes chronic enterocolitis in myeloid cell-specific Stat3-deficient mice
 Toll-like receptor-dependent production of IL-12p40 causes chronic enterocolitis in myeloid cell-specific Stat3-deficient mice See the related Commentary beginning on page 1284. Masaya Kobayashi, 1 Mi-Na
Toll-like receptor-dependent production of IL-12p40 causes chronic enterocolitis in myeloid cell-specific Stat3-deficient mice See the related Commentary beginning on page 1284. Masaya Kobayashi, 1 Mi-Na
