Quantitative analysis of the terminal branches of facial nerve in fresh frozen head and neck specimens
|
|
|
- Iris Stewart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 73, No. 1, pp DOI: /FM Copyright 2014 Via Medica ISSN Quantitative analysis of the terminal es of facial nerve in fresh frozen head and neck specimens M.F. Sargon 1, O. Ogretmenoglu 2, C. Gunenc Beser 1, Y. Karaoglan 1, B. Ercakmak 1, H.M. Hayran 1, M. Hayran 3, U.B. Kasirga 1 1 Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey 2 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Faculty of Medicine, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey 3 Department of Preventive Oncology, Faculty of Medicine, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey [Received 2 August 2013; Accepted 26 August 2013] Background: The first aim of this study was the quantification of nerve fibres found in terminal es of facial nerve and the second aim was the ultrastructural analysis of these terminal es in order to observe their ultrastructural differences, if present. In the examination of literature; we could not find any studies related to this subject. Materials and methods: Four fresh frozen head and neck specimens were used and the dissections were done bilaterally. Therefore; totally 8 samples were examined. The samples were prepared according to routine transmission electron microscopic tissue preparation technique. The semi-thin sections were examined under light microscope by camera lucida. In every sample, the quantitative analysis was performed in 5 different areas in an area of 0.01 mm 2 and statistical analysis was done. Secondly; the ultrastructural appearance of these terminal es were examined under transmission electron microscope. Results: In the quantitative analysis of terminal es of facial nerve in an area of 0.01 mm 2 ; the least number of nerve fibres were found in temporal es and the highest number were detected in cervical es. In transmission electron microscopic examination, no significant difference was found in between these es. In the statistical analysis; statistically significant differences were obtained in between the temporal and buccal, marginal mandibular, cervical es; zygomatic and marginal mandibular, cervical es; buccal and marginal mandibular, cervical es; marginal mandibular and cervical es. Conclusions: These numerical data will have an importance during the nerve repair process of terminal es of facial nerve in various injuries. (Folia Morphol 2014; 73, 1: 24 29) Key words: facial nerve, quantitative analysis, ultrastructure, fresh frozen, human, head, neck Address for correspondence: M.F. Sargon, MD, PhD, Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Hacettepe University, Ankara, 06100, Turkey, tel: , fax: , mfsargon@hacettepe.edu.tr This study was presented in the XII th European Joint Congress of Clinical Anatomy in Lisbon, (June 26 29, 2013) as an oral presentation. 24
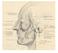
2 M.F. Sargon et al. Examination of facial nerve terminal es Figure 1. Photograph showing temporal (t), zygomatic (z), buccal (b), marginal mandibular (m) and cervical (c) es of facial nerve. INTRODUCTION The facial nerve emerges from the base of the skull at the stylomastoid foramen and then enters the parotid gland. Within the substance of the gland; it es into the temporofacial and cervicofacial trunks just behind the retromandibular vein. The trunks further to form a parotid plexus. Five main terminal es which are the temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular and cervical rami arise from the plexus and diverge within the gland. These terminal es leave the parotid gland by its anteromedial surface and they supply the muscles of facial expression [4, 17]. The terminal es of the facial nerve are very thin and in formalin fixed cadavers, it is very difficult to find them. Secondly; for transmission electron microscopic examination of these es; fresh or fresh frozen human samples are necessary. Therefore; in this study, they were examined in fresh frozen head and neck specimens. The first aim of this study was the quantification of nerve fibres found in the terminal es of facial nerve and the second aim was the ultrastructural analysis of these terminal es in order to observe their ultrastructural differences, if present. In the examination of literature; we could not find any studies related to this subject. MATERIALS AND METHODS In the study, 4 fresh frozen head and neck specimens were used and the dissections were done bilaterally. Therefore; totally 8 samples were examined from each terminal. Two of the head and neck specimens were male (ages 70 and 81 years) and 2 of them were female (ages 68 and 70 years). All procedures were approved by the Ethical Committee of Hacettepe University, Faculty of Medicine and the study was conducted in the gross anatomy dissection laboratory of Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Hacettepe University. Dissection At the beginning of the dissection; a lazy S incision was made in the preauricular area. Following the incision; the skin and soft tissues were removed and the facial nerve trunk was observed. Then; the nerve trunk was followed and 5 terminal es (temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular and cervical rami) were found when they were leaving the parotid gland by its anteromedial surface (Fig. 1). From this region; tissue samples were taken for quantitative analysis and transmission electron microscopic examination. Tissue preparation The facial nerve terminal samples were put into 2.5% glutaraldehyde for 24 h for primary fixation. Then, these samples were washed with Sorenson s Phosphate Buffer solution (ph: 7.4) and they were post-fixed in 1% osmium tetroxide for 2 h. After post-fixation, they were washed with the same buffer. Following this procedure; the tissue samples were dehydrated in increasing concentrations of alcohol 25
3 Folia Morphol., 2014, Vol. 73, No. 1 Table 1. The mean number of myelinated nerve fibres of temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular and cervical es of facial nerve counted under 200 magnification, in a constant area of 0.01 mm 2 using camera lucida (The myelinated nerve fibres were counted in 5 different areas in an area of 0.01 mm 2 during the quantitative analysis of each specimen and the mean values for each specimen were given) Specimen no. Temporal Zygomatic Buccal Marginal mandibular Cervical Mean ± ± ± ± ± 0.41 series. After dehydration, the tissues were washed with propylene oxide and embedded in epoxy resin embedding media. Quantitative analysis The semi-thin sections, about 2 µm in thickness, were cut with a glass knife on a LKB-Nova ultramicrotome (LKB-Produkter AB, Bromma, Sweden). These semi-thin sections were stained with methylene blue and they were examined under the camera lucida of a Nikon Optiphot (Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) light microscope by the same researcher for quantitative analysis. The myelinated nerve fibres of the temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular and cervical rami were counted in areas of 0.01 mm 2 under 200 magnification by using a camera lucida. Parts of myelinated nerve fibres located at the lower and left hand edges were included in the counting, whereas those at the upper and right hand edges were not recorded [12 14]. From every specimen, one semi-thin section was taken by the ultramicrotome. In each semi-thin section, the myelinated nerve fibres were counted in 5 different areas in an area of 0.01 mm 2 during the quantitative analysis (Table 1). The statistical analyses were done by using Repeated Measures Analysis of Variance. Secondly, the ultrastructural appearance of these terminal es were examined under transmission electron microscope. Transmission electron microscopic examination For transmission electron microscopic examination; trimming was done to the tissue blocks and their ultrathin sections which were about 60 nm in thickness were taken by the same ultramicrotome. These ultra-thin sections were stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate and they were examined under Jeol JEM 1200 EX (Tokyo, Japan) transmission electron microscope. The electron micrographs of the specimens were taken by the same microscope. RESULTS In the study, the terminal es of facial nerve were examined in 8 specimens obtained from 4 fresh frozen human head and necks bilaterally (Figs. 2A E). From every specimen, 1 semi-thin section was taken by the ultramicrotome and the myelinated nerve fibres were counted in 5 different areas in an area of 0.01 mm 2 during the quantitative analysis of each specimen. The mean numbers of myelinated nerve fibres of temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular and cervical es of facial nerve counted under 200 magnification, in a constant area of 0.01 mm 2 using camera lucida are given in Table 1. In the quantitative analysis of these terminal es, the least number of myelinated nerve fibres in an area of 0.01 mm 2 were found in temporal es and the highest number were detected in cervical es (Table 1). Statistical analyses using Repeated Measures Analysis of Variance revealed that the cervical had the highest number of nerve fibres followed by marginal mandibular with statistically significant differences (all p < 0.001). Also, the buccal had more fibres than the temporal (p = 0.008). In the statistical analyses, there were significant differences between the 26
4 M.F. Sargon et al. Examination of facial nerve terminal es A D B E C Figure 2. Photomicrographs showing the myelinated nerve fibres in the temporal (A), zygomatic (B), buccal (C), marginal mandibular (D) and cervical (E) es of facial nerve (stained with methylene blue, bar represents 15 µm). temporal and buccal, marginal mandibular, cervical es; zygomatic and marginal mandibular, cervical es; buccal and marginal mandibular, cervical es; marginal mandibular and cervical es. In the transmission electron microscopic examination of the terminal es of facial nerve, no ultrastructural differences were detected. The sizes, shapes and ultrastructural appearances of these myelinated nerve fibres did not show any marked difference between the groups (Figs. 3A, B). psychological disorders. Additionally, the anatomy of facial nerve is very complicated and may show variations among ethnic groups. This variance may explain the diverse facial expressions and animations between these groups [6, 10]. These variations in facial nerve anatomy are well documented in the literature. Katz and Catalano [7] performed 100 parotidectomies and classified the terminal ing pattern of facial nerve into 5 groups. In all of the cases, the main trunk was divided into a larger frontozygomatic and smaller cervicofacial sections. Tzafetta and Terzis [19] made 10 fresh cadaveric hemifacial dissections and demonstrated great variability in ing pattern of the facial nerve and innervation of the mimetic muscles by facial nerve. Davis et al. [3] studied the DISCUSSION Facial expression is an exclusively controlled trait and dysfunction of this nerve may lead to physical and 27
5 Folia Morphol., 2014, Vol. 73, No. 1 A B Figure 3. Electron micrographs showing the myelinated nerve fibres (m) in the buccal (A) and cervical (B) es of facial nerve. No ultrastructural differences were detected in between the terminal es of facial nerve (stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, bar represents 5 µm). ing patterns of facial nerve and described 6 different patterns in 350 hemifacial dissections. The most common type was a single connection between the frontozygomatic and cervicofacial divisions, with a connecting loop between the zygomatic and buccal es. Farahvash et al. [6] examined the extratemporal facial nerve and its es in 42 hemifacial dissections in fresh cadavers. The results of their study confirmed the variable ing pattern of the extratemporal facial nerve. Erbil et al. [5] studied the close relationship between the parotid duct and the buccal and zygomatic es of facial nerve in 10 cadavers. During their morphometric measurements, the reference points used for surgery of this region were taken into consideration as the landmarks for these measurements. In the literature; there are many studies related to the number of terminal es of facial nerve. Baker and Conley [2] observed that the cervical division of the extratemporal facial nerve had three to 5 es. From these es; 1 of them was buccal, 3 of them were marginal mandibular and 1 of them was cervical. Kim et al. [8] and Lineweaver et al. [9] have reported a high percentage of 2 and 3 ed marginal mandibular nerves. In the study of Farahvash et al. [6], a single marginal mandibular was seen in 95.7% of the cadavers. Al-Hayani [1] studied the marginal mandibular of facial nerve post mortem in 50 human subjects. This was found to be presented by 1 (32%), 2 (40%) es and 3 (28%) es. Mizia et al. [11] measured the histological structure of human median nerve by using the computer-assisted image analysis method. The number of nerve bundles in this nerve varied from 13 to 38 and in the motor of the median nerve from 4 to 14. The mean cross- -sectional area of the median nerve at the level of Carpal tunnel was found to be 0.19 cm 2. There are only a very few studies related to the quantitative analysis of facial nerve especially in humans. Shimozawa [15] performed a fibre count analysis on the motor root of the mouse facial nerve with electron microscope in 6 mice. On an average, 84.9% of the total nerve fibres were myelinated and 14.6% were unmyelinated. In another study, Shimozawa [16] made a fibre count analysis on the facial nerve trunk distal to the geniculate ganglion in 7 mice. On an average, 93% of the total nerve fibres were myelinated and 6.3% were unmyelinated. A quantitative study of nerve fibres in the human facial nerve was done by Thurner et al. [18] in 7 patients. In 2 of these cases, the facial nerve fibres were counted at 5 different levels. The total number of myelinated nerve fibres in the facial nerve varied from 7500 to 9370 and the total number of myelinated nerve fibres in the intermediate nerve varied between 3120 and CONCLUSIONS According to our knowledge, there is no study in the literature examining the quantification of nerve fibres found in terminal es of facial nerve. Secondly, we also performed ultrastructural analysis in these terminal es in order to observe their ultrastructural differences. However, we could not find any ultrastructural differences in between these es. Although the injuries of the terminal es of facial nerve are very common and they may lead to physical and psychological disorders, there is no study in the literature performing the quantitative analysis of them. Additionally, these numerical data will have an importance during the nerve repair process of terminal es of facial nerve in various injuries. 28
6 M.F. Sargon et al. Examination of facial nerve terminal es Acknowledgements We would like to send our special thanks to the cadaver bodies that were used in our research study. References 1. Al-Hayani A (2007) Anatomical localisation of the marginal mandibular of the facial nerve. Folia Morphol, 66: Baker DC, Conley J (1979) Avoiding facial nerve injuries in rhytidectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg, 64: Davis RA, Anson BJ, Budinger JM, Kurth LR (1956) Surgical anatomy of the facial nerve and parotid gland based upon a study of 350 cervicofacial halves. Surg Gynecol Obstet, 102: Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM (2005) Gray s anatomy for students. Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, Philadelphia, p Erbil KM, Uz A, Hayran M, Mas N, Senan S, Tuncel M (2007) The relationship of the parotid duct to the buccal and zygomatic es of the facial nerve; an anatomical study with parameters of clinical interest. Folia Morphol, 66: Farahvash MR, Yaghoobi A, Farahvash B, Farahvash Y, Abiyaneh SH (2013) The extratemporal facial nerve and its es: analysis of 42 hemifacial dissections in fresh Persian (Iranian) cadavers. Aesthetic Surg J, 33: Katz AD, Catalano P (1987) The clinical significance of the various anastomotic es of the facial nerve: report of 100 patients. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 113: Kim DI, Nam SH, Nam YS, Lee KS, Chung RH, Han SH (2009) The marginal mandibular of the facial nerve in Koreans. Clin Anat, 22: Lineweaver W, Rhoton A, Habal MB (1997) Microsurgical anatomy of the facial nerve. J Craniofac Surg, 8: Marsh AA, Elfenbein HA, Ambady N (2003) Nonverbal accents : cultural differences in facial expressions of emotion. Psychol Sci, 14: Mizia E, Tomaszewski KA, Lis GJ, Goncerz G, Kurzydlo W (2012) The use of computer-assisted image analysis in measuring the histological structure of the human median nerve. Folia Morphol, 71: Sargon MF, Mas N, Şenan S, Özdemir B, Çelik HH, Cumhur M (2003) Quantitative analysis of myelinated axons of commissural fibres in the rat brain. Anat Histol Embryol, 32: Sargon MF, Celik HH, Kapakin S, Basar R, Aksit MD (2004) Quantitative analysis of myelinated axons of commissural fibres in the cat brain. Neurosciences, 9: Sargon MF, Çelik HH, Akşit MD, Karaağaoğlu E (2007) Quantitative analysis of myelinated axons of corpus callosum in the human brain. Int J Neurosci, 117: Shimozawa A (1975) Quantitative studies on the motor root of the mouse facial nerve. An electron-microscopic study. Acta Anat, 92: Shimozawa A (1976) Quantitative studies on the mouse facial nerve trunk distal to the geniculate ganglion. An electron-microscopic study. Acta Anat, 95: Standring S: Editor in Chief (2005) Gray s anatomy. 39 th Ed. Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp Thurner KH, Egg G, Spoendlin H, Schrott-Fischer A (1993) A quantitative study of nerve fibres in the human facial nerve. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 250: Tzafetta K, Terzis JK (2010) Essays on the facial nerve. Part I. Microanatomy. Plast Reconstr Surg, 125:
Sacrificing the buccal branch of the facial nerve during parotidectomy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sacrificing the buccal branch of the facial nerve during parotidectomy Muthuswamy Dhiwakar, MS, FRCS,* Zubair A. Khan, MS Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Kovai Medical
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sacrificing the buccal branch of the facial nerve during parotidectomy Muthuswamy Dhiwakar, MS, FRCS,* Zubair A. Khan, MS Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Kovai Medical
Development of the myelin sheath of the hypogastric nerves in a human foetus aged 23 weeks
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 63, No. 3, pp. 289 301 Copyright 2004 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Development of the myelin sheath of the hypogastric nerves in a human
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 63, No. 3, pp. 289 301 Copyright 2004 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Development of the myelin sheath of the hypogastric nerves in a human
Anatomical localisation of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 66, No. 4, pp. 307 313 Copyright 2007 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Anatomical localisation of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 66, No. 4, pp. 307 313 Copyright 2007 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Anatomical localisation of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial
Functional components
 Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Morphometric Analysis of the Human Trigeminal Nerve
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 78(2-3): 49-54, August. 2001 Morphometric Analysis of the Human Trigeminal Nerve By Hiromitsu EZURE, Noboru GOTO, Naoko NONAKA, Jun GOTO and Hiroaki TANI Department of Anatomy,
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 78(2-3): 49-54, August. 2001 Morphometric Analysis of the Human Trigeminal Nerve By Hiromitsu EZURE, Noboru GOTO, Naoko NONAKA, Jun GOTO and Hiroaki TANI Department of Anatomy,
Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report
 Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
be very thin and variable. Facial nerve branches that exit the parotid gland are deep to the SMAS.
 The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report
 SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
Co-Innervation of Triceps Brachii Muscle with Variant Branch of Ulnar Nerve
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.22126-17.2 Received: 23.11.2017 / Accepted: 07.02.2018 Published Online: 26.02.2018 Turk Neurosurg, 2018 Original Investigation Co-Innervation of Triceps Brachii Muscle with
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.22126-17.2 Received: 23.11.2017 / Accepted: 07.02.2018 Published Online: 26.02.2018 Turk Neurosurg, 2018 Original Investigation Co-Innervation of Triceps Brachii Muscle with
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
Anatomical variations of the median nerve distribution and communication in the arm
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 63, No. 3, pp. 313 318 Copyright 2004 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Anatomical variations of the median nerve distribution and communication
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 63, No. 3, pp. 313 318 Copyright 2004 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Anatomical variations of the median nerve distribution and communication
Differentiation of the facial-vestibulocochlear ganglionic complex in human embryos of developmental stages 13 15
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 3, pp. 167 173 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Differentiation of the facial-vestibulocochlear ganglionic complex
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 3, pp. 167 173 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Differentiation of the facial-vestibulocochlear ganglionic complex
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich)
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 552 556 Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q N. Imanishi a, *, H. Nakajima b, T. Minabe c, H. Chang d,
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 552 556 Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q N. Imanishi a, *, H. Nakajima b, T. Minabe c, H. Chang d,
Temple and Postauricular Dissection in Face and Neck Lift Surgery
 Temple and Postauricular Dissection in Face and Neck Lift Surgery Topic Joo Heon Lee 1, Tae Suk Oh 2, Sung Wan Park 3, Jae Hoon Kim 3, Tanvaa Tansatit 4 1 Area88 Plastic Surgery Clinic, Seoul; 2 Department
Temple and Postauricular Dissection in Face and Neck Lift Surgery Topic Joo Heon Lee 1, Tae Suk Oh 2, Sung Wan Park 3, Jae Hoon Kim 3, Tanvaa Tansatit 4 1 Area88 Plastic Surgery Clinic, Seoul; 2 Department
Revisiting the Topographic Anatomy of the Marginal Mandibular Branch of Facial Nerve Relating to the Surgical Approach
 Facial Surgery Revisiting the Topographic Anatomy of the Marginal Mandibular Branch of Facial Nerve Relating to the Surgical Approach Aesthetic Surgery Journal 2016, Vol 36(9) 977 982 2016 The American
Facial Surgery Revisiting the Topographic Anatomy of the Marginal Mandibular Branch of Facial Nerve Relating to the Surgical Approach Aesthetic Surgery Journal 2016, Vol 36(9) 977 982 2016 The American
Anatomical Study of Pectoral Nerves and its Implications in Surgery
 DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8631.4545 Anatomy Section Original Article Anatomical Study of Pectoral Nerves and its Implications in Surgery Prakash KG 1, Saniya K 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: This anatomical study
DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8631.4545 Anatomy Section Original Article Anatomical Study of Pectoral Nerves and its Implications in Surgery Prakash KG 1, Saniya K 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: This anatomical study
Variations of median nerve and musculocutaneous nerve: Cadeveric study
 Original article: Variations of median nerve and musculocutaneous nerve: Cadeveric study 1Dr.VaishaliBondge*, 2 Dr. Ashok Khade, 3 Dr. P.H.Shingare 1Assistant Professor, Grant Medical College, Mumbai,
Original article: Variations of median nerve and musculocutaneous nerve: Cadeveric study 1Dr.VaishaliBondge*, 2 Dr. Ashok Khade, 3 Dr. P.H.Shingare 1Assistant Professor, Grant Medical College, Mumbai,
The Subzygomatic Triangle: Rapid, minimally invasive identification of the masseteric nerve for facial ACCEPTED
 Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Advance Online Article DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318290f6dc The Subzygomatic Triangle: Rapid, minimally invasive identification of the masseteric nerve for facial reanimation
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Advance Online Article DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318290f6dc The Subzygomatic Triangle: Rapid, minimally invasive identification of the masseteric nerve for facial reanimation
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
A Rare Case of Bilateral Jugular Venous Malformation
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2013;3(2):326-330 A Rare Case of Bilateral Jugular Venous Malformation Prasanna LC, Alva R, D Souza AS, Bhat KMR Department of Anatomy, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University,
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2013;3(2):326-330 A Rare Case of Bilateral Jugular Venous Malformation Prasanna LC, Alva R, D Souza AS, Bhat KMR Department of Anatomy, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University,
The study of arterial anastomoses in the region of the alveolar process and the anterior maxilla wall in foetuses
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp. 65 69 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The study of arterial anastomoses in the region of the alveolar process
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp. 65 69 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The study of arterial anastomoses in the region of the alveolar process
Clinical Study Open Reduction of Subcondylar Fractures Using a New Retractor
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 2011, Article ID 421245, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/421245 Clinical Study Open Reduction of Subcondylar Fractures Using a New Retractor Akira Sugamata, 1 Naoki Yoshizawa,
Plastic Surgery International Volume 2011, Article ID 421245, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/421245 Clinical Study Open Reduction of Subcondylar Fractures Using a New Retractor Akira Sugamata, 1 Naoki Yoshizawa,
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta.
 Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
EXTRATEMPORAL FACIAL NERVE ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS IN CADAVERS AT KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL MORTUARY
 EXTRATEMPORAL FACIAL NERVE ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS IN CADAVERS AT KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL MORTUARY MUTAHI FRANCIS THUKU DEPARTMENT OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY, ORAL PATHOLOGY AND ORAL MEDICINE,
EXTRATEMPORAL FACIAL NERVE ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS IN CADAVERS AT KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL MORTUARY MUTAHI FRANCIS THUKU DEPARTMENT OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY, ORAL PATHOLOGY AND ORAL MEDICINE,
Computer-assisted assessment of the histological structure of the human sural nerve
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 73, No. 3, pp. 292 297 DOI: 10.5603/FM.2014.0046 Copyright 2014 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Computer-assisted assessment of the histological
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 73, No. 3, pp. 292 297 DOI: 10.5603/FM.2014.0046 Copyright 2014 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Computer-assisted assessment of the histological
The relative position of the inferior alveolar nerve in cadaveric hemi-mandibles
 SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 9 (1): 49-53 (2005) The relative position of the inferior alveolar nerve in cadaveric hemi-mandibles V. Saralaya and K. Narayana Department of Anatomy, Centre for Basic Sciences,
SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 9 (1): 49-53 (2005) The relative position of the inferior alveolar nerve in cadaveric hemi-mandibles V. Saralaya and K. Narayana Department of Anatomy, Centre for Basic Sciences,
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
Anatomy Paper 2 Exam
 Anatomy Paper 2 Exam Monday, 4 Head Office: Level 9, 51 Druitt Street, Sydney NSW 2000, Australia Ph: +61 2 9268 9777 Fax: +61 2 9268 9799 Email: ranzcr@ranzcr.edu.au New Zealand Office: Floor 6, 142 Lambton
Anatomy Paper 2 Exam Monday, 4 Head Office: Level 9, 51 Druitt Street, Sydney NSW 2000, Australia Ph: +61 2 9268 9777 Fax: +61 2 9268 9799 Email: ranzcr@ranzcr.edu.au New Zealand Office: Floor 6, 142 Lambton
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
A study on structural variations of the parotid glands
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Jayamma C et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3790-3794 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151444
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Jayamma C et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3790-3794 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151444
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Unmyelinated fibers in the trigeminal motor root. Possible relationship to the results of trigeminal rhizotomy
 J Neurosurg 49:538-543, 1978 Unmyelinated fibers in the trigeminal motor root Possible relationship to the results of trigeminal rhizotomy RONALD F. YOUNG, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, University of
J Neurosurg 49:538-543, 1978 Unmyelinated fibers in the trigeminal motor root Possible relationship to the results of trigeminal rhizotomy RONALD F. YOUNG, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, University of
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Face and Scalp 解剖學科鄭授德
 Face and Scalp 解剖學科鄭授德 本教材之圖片取自於 1 Gray s Anatomy for Students, 3rd ed, 2015, by Drake, Vogl, and Mitchell 2 Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed, 2014, by Moore, Dalley, and Agur 3 Clinically Oriented
Face and Scalp 解剖學科鄭授德 本教材之圖片取自於 1 Gray s Anatomy for Students, 3rd ed, 2015, by Drake, Vogl, and Mitchell 2 Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed, 2014, by Moore, Dalley, and Agur 3 Clinically Oriented
Original Research Article
 STUDY OF VARIATION IN THE HIGH DIVISION OF SCIATIC NERVE AND ITS RELATIONSHIP WITH THE PIRIFORMIS MUSCLE Dr. Rupali Shastrakar, Dr. Manisha Nakhate, Dr. V. G. Sawant Dr. D. Y. Patil School of Medicine,
STUDY OF VARIATION IN THE HIGH DIVISION OF SCIATIC NERVE AND ITS RELATIONSHIP WITH THE PIRIFORMIS MUSCLE Dr. Rupali Shastrakar, Dr. Manisha Nakhate, Dr. V. G. Sawant Dr. D. Y. Patil School of Medicine,
High Variability of Facial Muscle Innervation by Facial Nerve Branches: A Prospective Electrostimulation Study
 The Laryngoscope VC 206 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. High Variability of Facial Muscle Innervation by Facial Nerve Branches: A Prospective Electrostimulation Study
The Laryngoscope VC 206 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. High Variability of Facial Muscle Innervation by Facial Nerve Branches: A Prospective Electrostimulation Study
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
Anatomical Landmarks to Avoid Injury to the Great Auricular Nerve During Rhytidectomy
 Facial Surgery Anatomical Landmarks to Avoid Injury to the Great Auricular Nerve During Rhytidectomy Todd Lefkowitz, MD; Ron Hazani, MD; Saeed Chowdhry, MD; Josh Elston, BS; Michael J. Yaremchuk, MD; and
Facial Surgery Anatomical Landmarks to Avoid Injury to the Great Auricular Nerve During Rhytidectomy Todd Lefkowitz, MD; Ron Hazani, MD; Saeed Chowdhry, MD; Josh Elston, BS; Michael J. Yaremchuk, MD; and
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Thin basement membrane nephropathy cannot be diagnosed reliably in deparaffinized, formalin-fixed tissue
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2007) 22: 1228 1232 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfl838 Advance Access publication 3 February 2007 Technical Note Thin basement membrane nephropathy cannot be diagnosed reliably in deparaffinized,
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2007) 22: 1228 1232 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfl838 Advance Access publication 3 February 2007 Technical Note Thin basement membrane nephropathy cannot be diagnosed reliably in deparaffinized,
Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies. No Disclosures or Conflicts of Interest. Anatomy 10/4/2013
 Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies Daniel G. Deschler, MD Director: Division of Head and Neck Surgery Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary Massachusetts General Hospital Professor Harvard Medical School
Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies Daniel G. Deschler, MD Director: Division of Head and Neck Surgery Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary Massachusetts General Hospital Professor Harvard Medical School
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1813 1819 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS IN PRENATAL BUFFALO (Bubalus
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1813 1819 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS IN PRENATAL BUFFALO (Bubalus
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Anatomical Study of the Facial Nerve
 World Journal of Zoology 10 (4): 267-273, 2015 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2015 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2015.10.4.9627 Anatomical Study of the Facial Nerve 1 1 1 2 Khalid M.S. Al-Shaikh, Mohammed
World Journal of Zoology 10 (4): 267-273, 2015 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2015 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2015.10.4.9627 Anatomical Study of the Facial Nerve 1 1 1 2 Khalid M.S. Al-Shaikh, Mohammed
The functional anatomy of hip abductors
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp. 98 103 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The functional anatomy of hip abductors A. Al-Hayani Department of Anatomy,
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp. 98 103 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The functional anatomy of hip abductors A. Al-Hayani Department of Anatomy,
THE SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE CERVICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE FACIAL NERVE. Biology and Anatomy, University of Shefield
 British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981), 19, 171-179 @ The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00260171$02.00 THE SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE CERVICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE FACIAL NERVE HAITHEM
British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981), 19, 171-179 @ The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00260171$02.00 THE SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE CERVICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE FACIAL NERVE HAITHEM
Determination and classification of cutaneous innervation of dorsum of the foot in fetal cadavers
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is a provisional PDF only. Copyedited and fully formatted version will be made available soon. ONLINE FIRST ISSN: 0015-5659 e-issn: 1644-3284 Determination and classification
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is a provisional PDF only. Copyedited and fully formatted version will be made available soon. ONLINE FIRST ISSN: 0015-5659 e-issn: 1644-3284 Determination and classification
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Original article Journal of International Medicine and Dentistry 2014; 1 (1): 10-18
 Original article JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share ISSN 2350-045X Study of variations in medial sural cutaneous nerve, lateral sural cutaneous nerve and peroneal
Original article JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share ISSN 2350-045X Study of variations in medial sural cutaneous nerve, lateral sural cutaneous nerve and peroneal
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
Comparison of one-stage free gracilis muscle flap with two-stage method in chronic facial palsy*
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 21, No.2, August 2007. pp. 63-70 Comparison of one-stage free gracilis muscle flap with two-stage method in chronic facial palsy*
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 21, No.2, August 2007. pp. 63-70 Comparison of one-stage free gracilis muscle flap with two-stage method in chronic facial palsy*
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
A rare bilateral varaiation in renal vascular pedicle
 Case Report: A rare bilateral varaiation in renal vascular pedicle *Anshu Mishra, *Parmatma Prasad Mishra, **Gyan Prakash Mishra *Department of Anatomy, Integral Institute of Medical Sciences and Research,
Case Report: A rare bilateral varaiation in renal vascular pedicle *Anshu Mishra, *Parmatma Prasad Mishra, **Gyan Prakash Mishra *Department of Anatomy, Integral Institute of Medical Sciences and Research,
Abnormal Pattern Of Brachial Plexus Formation: An Original Case Report. K Oluyemi, O Adesanya, D Ofusori, C Okwuonu, V Ukwenya, F Om'iniabohs, B Odion
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 4 Number 2 Abnormal Pattern Of Brachial Plexus Formation: An Original Case Report K Oluyemi, O Adesanya, D Ofusori, C Okwuonu, V Ukwenya, F Om'iniabohs,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 4 Number 2 Abnormal Pattern Of Brachial Plexus Formation: An Original Case Report K Oluyemi, O Adesanya, D Ofusori, C Okwuonu, V Ukwenya, F Om'iniabohs,
R,;habdomyosarcoma, the most common
 Fine-structural classification of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma Arnold J. Kroll Six cases of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma were studied with the electron microscope. Tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) could be classified
Fine-structural classification of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma Arnold J. Kroll Six cases of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma were studied with the electron microscope. Tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) could be classified
Use of Semithin Sections Embedded in a Water-Miscible Methacrylate. for Light Microscopy of Central Nerve Tissues
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 66 (2-3): 145-152, August, 1989 Use of Semithin Sections Embedded in a Water-Miscible Methacrylate for Light Microscopy of Central Nerve Tissues By Yasukazu NAGATO, Masaki SEKIGUCHI,
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 66 (2-3): 145-152, August, 1989 Use of Semithin Sections Embedded in a Water-Miscible Methacrylate for Light Microscopy of Central Nerve Tissues By Yasukazu NAGATO, Masaki SEKIGUCHI,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve. The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions
 Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
STUDY OF VARIATIONS IN THE ORIGIN OF AXILLARY NERVE FROM THE POSTERIOR CORD OF BRACHIAL PLEXUS AND ITS CLINICAL IMPORTANCE
 Original Research Article STUDY OF VARIATIONS IN THE ORIGIN OF AXILLARY NERVE FROM THE POSTERIOR CORD OF BRACHIAL PLEXUS AND ITS CLINICAL IMPORTANCE Suman Tiwari * 1, Jyothi N Nayak 2 ABSTRACT International
Original Research Article STUDY OF VARIATIONS IN THE ORIGIN OF AXILLARY NERVE FROM THE POSTERIOR CORD OF BRACHIAL PLEXUS AND ITS CLINICAL IMPORTANCE Suman Tiwari * 1, Jyothi N Nayak 2 ABSTRACT International
DO ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENTS OF THE HAND IMPACT THE HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN MEDIAN NERVE AT THE LEVEL OF THE CARPAL TUNNEL?
 FOLIA MEDICA CRACOVIENSIA Vol. LII, 1 2, 2012: 17 24 PL ISSN 0015-5616 KRZYSZTOF A. TOMASZEWSKI 1, IWONA M. TOMASZEWSKA 2, WOJCIECH KURZYDŁO 3, JANUSZ SKRZAT 1, ALEKSANDRA MATUSZYK 1, MICHAŁ KŁOSIŃSKI
FOLIA MEDICA CRACOVIENSIA Vol. LII, 1 2, 2012: 17 24 PL ISSN 0015-5616 KRZYSZTOF A. TOMASZEWSKI 1, IWONA M. TOMASZEWSKA 2, WOJCIECH KURZYDŁO 3, JANUSZ SKRZAT 1, ALEKSANDRA MATUSZYK 1, MICHAŁ KŁOSIŃSKI
Pichayen Duangthongpon MD*, Chaiwit Thanapaisal MD*, Amnat Kitkhuandee MD*, Kowit Chaiciwamongkol MD**, Vilaiwan Morthong MD**
 The Relationships between Asterion, the Transverse-Sigmoid Junction, the Superior Nuchal Line and the Transverse Sinus in Thai Cadavers: Surgical Relevance Pichayen Duangthongpon MD*, Chaiwit Thanapaisal
The Relationships between Asterion, the Transverse-Sigmoid Junction, the Superior Nuchal Line and the Transverse Sinus in Thai Cadavers: Surgical Relevance Pichayen Duangthongpon MD*, Chaiwit Thanapaisal
The pinealocytes of the human pineal gland: a light and electron microscopic study
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 65, No. 3, pp. 181 187 Copyright 2006 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The pinealocytes of the human pineal gland: a light and electron microscopic
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 65, No. 3, pp. 181 187 Copyright 2006 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The pinealocytes of the human pineal gland: a light and electron microscopic
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
Anatomical variations of brachial plexus: anomalous branching pattern
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gopal K et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Aug;4(8):3376-3380 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20162297
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gopal K et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Aug;4(8):3376-3380 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20162297
A New External Landmark for Mental Foramen
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Jumroon Tungkeeratichai, Thongchai Bhongmakapat, Porncharn Saitongdee, Pisamai Orathai ABSTRACT Purpose: The purpose of this study was to establish a new external landmark of mental foramen
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Jumroon Tungkeeratichai, Thongchai Bhongmakapat, Porncharn Saitongdee, Pisamai Orathai ABSTRACT Purpose: The purpose of this study was to establish a new external landmark of mental foramen
The anatomy of the Berrettini branch: implications for endoscopic carpal tunnel release
 The anatomy of the Berrettini branch: implications for endoscopic carpal tunnel release Zlatko Kolic, M.D., Vladimir Micovic, M.D., Gordana Zamolo, Ph.D., Vesna Golubovic, M.D., Ph.D., Miljenko Uravic,
The anatomy of the Berrettini branch: implications for endoscopic carpal tunnel release Zlatko Kolic, M.D., Vladimir Micovic, M.D., Gordana Zamolo, Ph.D., Vesna Golubovic, M.D., Ph.D., Miljenko Uravic,
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE
 ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE by D. L. Lee ABSTRACT Infective stage larvae of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis are immobilized within
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE by D. L. Lee ABSTRACT Infective stage larvae of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis are immobilized within
Accessory Renal Arteries: A Cadaveric Study
 Accessory Renal Arteries: A Cadaveric Study Bina.K.Katariya 1*, Priyank Bhabhor 2, H.R.Shah 3. 1, 2 Third year resident, 3 Additional Professor, Department of anatomy, B.J.Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat
Accessory Renal Arteries: A Cadaveric Study Bina.K.Katariya 1*, Priyank Bhabhor 2, H.R.Shah 3. 1, 2 Third year resident, 3 Additional Professor, Department of anatomy, B.J.Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat
[1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the
![[1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the [1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the](/thumbs/84/89127006.jpg) 'ca -.101 6II.25:6II.OI8.86 NERVES AND NERVE ENDINGS IN THE VISCERAL PLEURA OF THE CAT. BY A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN. (From the Unit Laboratories, University College Hospital Medical School.) (Received September
'ca -.101 6II.25:6II.OI8.86 NERVES AND NERVE ENDINGS IN THE VISCERAL PLEURA OF THE CAT. BY A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN. (From the Unit Laboratories, University College Hospital Medical School.) (Received September
Yuki Uchida, DDS, PhD,* Yoshio Yamashita, DDS, PhD, Masaaki Goto, DDS, PhD, and Tsunehiko Hanihara, MD, PhD
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:1772-1779, 2007 Measurement of Anterior Loop Length for the Mandibular Canal and Diameter of the Mandibular Incisive Canal to Avoid Nerve Damage When Installing Endosseous Implants
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:1772-1779, 2007 Measurement of Anterior Loop Length for the Mandibular Canal and Diameter of the Mandibular Incisive Canal to Avoid Nerve Damage When Installing Endosseous Implants
Downloaded from umj.umsu.ac.ir at 20: on Friday March 22nd
 * 1391/04/04 1392/02/01.. :... : - - : : Email: sazegargh@mums.ac.ir.( ) () () () (). (). () ... ( ) :(). :() ( ). .. :() ( ). :() ( ) () () ( ) () ().() (). ...... References: 1. Standring S. Grays Anatomy
* 1391/04/04 1392/02/01.. :... : - - : : Email: sazegargh@mums.ac.ir.( ) () () () (). (). () ... ( ) :(). :() ( ). .. :() ( ). :() ( ) () () ( ) () ().() (). ...... References: 1. Standring S. Grays Anatomy
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for
 Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Cutaneous Melanoma: Epidemiology (USA) The Sentinel Node in Head and Neck Melanoma. Cutaneous Melanoma: Epidemiology (USA)
 The Sentinel Node in Head and Neck Melanoma Cutaneous Melanoma: Epidemiology (USA) 6 th leading cause of cancer among men and women 68,720 new cases of invasive melanoma in 2009 8,650 deaths from melanoma
The Sentinel Node in Head and Neck Melanoma Cutaneous Melanoma: Epidemiology (USA) 6 th leading cause of cancer among men and women 68,720 new cases of invasive melanoma in 2009 8,650 deaths from melanoma
COMMUNICATIONS BETWEEN MUSCULOCUTANEOUS NERVE AND MEDIAN NERVE - A STUDY
 IJCRR Vol 05 issue 08 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 13/03/13 Revised on: 04/04/13 Accepted on: 21/04/13 COMMUNICATIONS BETWEEN MUSCULOCUTANEOUS NERVE AND MEDIAN NERVE - A STUDY Balasubramanian
IJCRR Vol 05 issue 08 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 13/03/13 Revised on: 04/04/13 Accepted on: 21/04/13 COMMUNICATIONS BETWEEN MUSCULOCUTANEOUS NERVE AND MEDIAN NERVE - A STUDY Balasubramanian
Pathological changes in the vagus nerve in diabetes
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1987;50:1449-1453 Pathological changes in the vagus nerve in diabetes and chronic alcoholism Y-P GUO,* J G McLEOD, J BAVERSTOCK From the Department of
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1987;50:1449-1453 Pathological changes in the vagus nerve in diabetes and chronic alcoholism Y-P GUO,* J G McLEOD, J BAVERSTOCK From the Department of
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheets, Distributions Page 1
 Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
An Isolated, Giant Infratemporal Fossa Schwannoma: Removal By Transmandibular Transpterygoid Approach
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 5 Number 2 An Isolated, Giant Infratemporal Fossa Schwannoma: Removal By Transmandibular Transpterygoid Rijuneeta, P Kumar Parida, V Mshesha,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 5 Number 2 An Isolated, Giant Infratemporal Fossa Schwannoma: Removal By Transmandibular Transpterygoid Rijuneeta, P Kumar Parida, V Mshesha,
An Algorithm to Guide Recipient Vessel Selection in Cases of Free Functional Muscle Transfer for Facial Reanimation
 An Algorithm to Guide Recipient Vessel Selection in Cases of Free Functional Muscle Transfer for Facial Reanimation Original Article Francis P Henry, Jonathan I Leckenby, Daniel P Butler, Adriaan O Grobbelaar
An Algorithm to Guide Recipient Vessel Selection in Cases of Free Functional Muscle Transfer for Facial Reanimation Original Article Francis P Henry, Jonathan I Leckenby, Daniel P Butler, Adriaan O Grobbelaar
Morphometric characteristic of thyroid cartilage in Gujarat region: A cadaveric study
 Original Article Morphometric characteristic of thyroid cartilage in Gujarat region: A cadaveric study Shital Patel, Rashmi Bhardwaj, Priyanka Parmar, Vasant H Vaniya Department of Anatomy, Government
Original Article Morphometric characteristic of thyroid cartilage in Gujarat region: A cadaveric study Shital Patel, Rashmi Bhardwaj, Priyanka Parmar, Vasant H Vaniya Department of Anatomy, Government
Indian Journal of Basic & Applied Medical Research; June 2013: Issue-7, Vol.-2, P
 Case Report: An Unusual Formation of the Femoral Nerve - A Case Report 1Dr. Indrajit Gupta, 2 Dr. Sudeshna Majumdar*, 3 Dr. Santanu Bhattacharya, 4 Dr. Seikh Ali Amam, 5Dr. Susmita Ghosh, 6 Dr. Lopamudra
Case Report: An Unusual Formation of the Femoral Nerve - A Case Report 1Dr. Indrajit Gupta, 2 Dr. Sudeshna Majumdar*, 3 Dr. Santanu Bhattacharya, 4 Dr. Seikh Ali Amam, 5Dr. Susmita Ghosh, 6 Dr. Lopamudra
A Cadaveric Anatomical Study of the Levator Aponeurosis and Whitnall s Ligament
 접수번호 : 2008-087 Korean Journal of Ophthalmology 2009;23:183-187 ISSN : 1011-8942 DOI : 10.3341/kjo.2009.23.3.183 A Cadaveric Anatomical Study of the Levator Aponeurosis and Whitnall s Ligament Han Woong
접수번호 : 2008-087 Korean Journal of Ophthalmology 2009;23:183-187 ISSN : 1011-8942 DOI : 10.3341/kjo.2009.23.3.183 A Cadaveric Anatomical Study of the Levator Aponeurosis and Whitnall s Ligament Han Woong
Variations in the formation of supraclavicular brachial plexus among Kenyans
 Original Article Variations in the formation of supraclavicular brachial plexus among Kenyans B.O. Olabu, BSc (Anat), J.A. Ogeng o, BSc (Anat), MBChB, PhD, K.O. Awori, MBChB, MMed (Surg), Dip. (SICOT),
Original Article Variations in the formation of supraclavicular brachial plexus among Kenyans B.O. Olabu, BSc (Anat), J.A. Ogeng o, BSc (Anat), MBChB, PhD, K.O. Awori, MBChB, MMed (Surg), Dip. (SICOT),
HIF-P4H-2 deficiency protects against skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury
 J Mol Med 2015 HIF-P4H-2 deficiency protects against skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury Sara Karsikas; Mikko Myllymäki; Minna Heikkilä; Raija Sormunen; Kari I Kivirikko; Johanna Myllyharju; Raisa
J Mol Med 2015 HIF-P4H-2 deficiency protects against skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury Sara Karsikas; Mikko Myllymäki; Minna Heikkilä; Raija Sormunen; Kari I Kivirikko; Johanna Myllyharju; Raisa
STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP STEP 3 SEPARATE PAROTID GLAND FROM SCM STEP 2 IDENTIFICATON OF GREAT AURICULAR NERVE
 STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP Create a modified Blair Figure 1 or facelift incision. Figure 2 Raise a superficial cervico-fascial flap between the Superficial Musculo Aponeurotic System (SMAS)
STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP Create a modified Blair Figure 1 or facelift incision. Figure 2 Raise a superficial cervico-fascial flap between the Superficial Musculo Aponeurotic System (SMAS)
AN UNUSUAL TORTUOUS BRACHIAL ARTERY AND ITS BRANCHES: HISTOLOGICAL BASIS AND ITS CLINICAL PERSPECTIVE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2014 Ashwini C and Vasantha Kuberappa, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 3, No. 2, April 2014 2014 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved AN UNUSUAL TORTUOUS
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2014 Ashwini C and Vasantha Kuberappa, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 3, No. 2, April 2014 2014 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved AN UNUSUAL TORTUOUS
D."espite numerous anatomic and physiologic
 Trigeminal pathway for afferent fibers from the oculomotor nerves William S. Joffe, Andrew J. Gay, and C. Courtney Antrim Stimulation studies in the cat have shown that the afferent fibers for the oculorespiratory
Trigeminal pathway for afferent fibers from the oculomotor nerves William S. Joffe, Andrew J. Gay, and C. Courtney Antrim Stimulation studies in the cat have shown that the afferent fibers for the oculorespiratory
Intercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida
 JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
Learning Outcomes. The Carotid 20/02/2013. Scalp, Face, Parotid. Layers of the Scalp. The Parotid Gland. The Scalp. The Carotid The Facial Artery
 Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
