J. 0. AKINOSI, B.D.s., F.D.S.R.C.S.
|
|
|
- Eleanor McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 British Journal of Oral Surgery 15 ( ) A NEW APPROACH TO THE MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK J. 0. AKINOSI, B.D.s., F.D.S.R.C.S. Department of Oral Surgery and Pathology, College of Medicine, Lagos University, P.M.B , Lagos Summary. A new method for the block anaesthesia of the oral branches of the mandibular nerve is described. Only one penetration of the oral mucosa is made in this injection at a site which is relatively painless and which results in a more rapid onset of anaesthesia. This method is also of value when trismus or ankylosis is present and is free of common complications. Introduction Conventional methods for achieving an inferior alveolar nerve block are relatively easy. These techniques, however, rely on the presence and identification of certain anatomical landmarks such as the teeth, the mucosal elevation due to the pterygomandibular raphe and the apex of the buccal pad of fat. Difficulties may be experienced in edentulous patients, in cases where the raphe is not prominent and particularly in cases where opening is limited. Anatomical variations in the shape and size of the mandible may make accurate localisation of the mandibular fossa difficult. The width of the ascending rami and their divergance determine the position of the mandibular foramen and this varies from one individual to another. As a result of these variations coupled with operator-mediated errors, a failure rate of at least 5 per cent is to be expected when the conventional method is used (Bremer, 1952; Gow-Gates, 1973). Inaddition to the above, failure to achieve anaesthesia may be due to a number of other factors which include inadequate dosage of anaesthetic solution and the presence of supplementary innervations, which may together raise the failed inferior dental anaesthesia rate to over 15 per cent (Northop, 1949). As a result of these deficiences, various other methods which claim superiority over the conventional methods have been described for the inferior dental nerve injection (Gow-Gates, 1973; Cannel1 & Cannon, 1976; Rood, 1976). This communication describes a technique which is markedly less painful and which even though it cannot claim a higher efficacy rate over other methods is remarkable because of its ease of administration and the more rapid onset of anaesthesia, faster than in most methods as yet described. In addition, this method has the added advantage that it can easily be employed in cases in which the jaw opening is limited. Materials and Method The materials required for this injection are in no way different from those normally used for giving the inferior dental block injection. They include the standard cartridge syringe with a 27 g disposable long needle (about 3.5 cm or 13 in length) a cartridge of 2 per cent local anaesthetic solution containing 1: adrenaline, a pair of Spencer Wells artery forceps, a surface anaesthetic spray and a container and applicator for a suitable antiseptic solution. (Received 16 December 1976; accepted 14 January 1977) 83
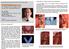
2 84 BRITISH JOURNAL OF ORAL SURGERY FIG. 1. Young patient receiving the injection. Note the relaxed appearance. FIG. 2. Outline of area of lip and face which became numb following injection.
3 MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK 85 auriculotemporal n. inferior ahreolar n.. lingual n., FIG. 3. A schematic diagram showing the relationship of the main branches of the mandibular nerve and the relationship of the needle during injection. The patient is seated in a semi-reclining position with the head, neck and shoulders well supported. When the mouth is open, the pterygo-mandibular elevation of the oral mucosa can be easily identified extending from the retromolar area of the mandible upwards and backwards to join the tissues immediately posterior to the upper third molar. The cheek is then freely distended using the fingers of the left hand and the mucosa immediately buccal and distal to the upper third molar is wiped with a 0.5 per cent chlorhexidine tincture or any other suitable antiseptic. A few seconds later the area is dried and a small amount of a surface anaesthetic solution is sprayed into the area and in about one minute the patient is ready for his injection. The dentist stands in front and to the right of the patient. The teeth are closed to aid relaxation of the cheek muscles which are then well distended for good vision. The needle is positioned at the level of the maxillary marginal gingivae and with the barrel parallel to the maxillary occlusal plane, the syringe is then advanced and the needle then penetrates the tissues in the embrasure between the vertical ramus and maxillary tuberosity (Fig. 1). Between 2.5 cm and 3 cm of the needle is buried in the tissues at this site and about 1.5 cc to 2 cc of anaesthetic solution is slowly deposited. The needle at this point lies in the pterygo-mandibular space having passed through the buccinator muscle. It is in close relationship with the main branches of the mandibular nerve in this situation and are easily reached by diffusion of the anaesthetic solution. The needle is then slowly withdrawn. Results When correctly given, the patient experiences altered sensations in the tongue and lip from about 40 seconds after the injection and surgical anaesthesia is obtained in about 14 minutes. The anaesthesia involves the sensory divisions of the mandibular nerve excepting the auriculotemporal branch. The branches which are affected are the
4 86 BRITISH JOURNAL OF ORAL SURGERY inferior alveolar, the lingual and the long buccal nerves. The area of anaesthesia obtained is similar to that achieved when conventional methods are used (Fig. 2). Surgical anaesthesia is obtainable in the mandibular teeth from the third molar to the canine on the injected side and simple surgical procedures such as dental extractions and soft tissue surgery in the buccal or lingual sulcus as well as in the lower lip can be performed without pain. Of a total of 100 consecutive injections given to patients requiring routine mandibular extractions only seven were unsuccessful at the first attempt and of these, five were successful at the second attempt. This injection technique, which can be called the tuberosity approach to the mandibular nerve, is based on a knowledge of the anatomy of the pterygo-mandibular space. The lingual nerve passes upwards and backwards through the space a little in front of the inferior dental nerve. The two nerves are joined by the long buccal nerve which arises from the cheek and buccal mucoperiosteum and crosses the anterior border of the ascending ramus to traverse the upper part of the pterygo-mandibular space. In this upper part, the three trunks come to lie in close proximity suitable for simultaneous injection (Fig. 3). This technique of injection has many advantages over the old method. The patient is less likely to be apprehensive since the injection is not made into the throat and particularly as he is not required to open his mouth fully. The tissues in the retromolar area of the maxilla are rather lax when the mouth is in the semi-open or closed position and the penetration of the needle is, therefore, relatively painless. A further advantage is the rather loose areolar tissue deep in the space into which the solution is easily accommodated without pain. The average patient is rather afraid of injections particularly when several injections have to be given. The old method for the injection of branches of the mandibular nerve involves three separate manoeuvres one for each nerve and at least two separate needle pricks. The technique described here has the important advantage that only one prick of the needle is required together with a more rapid onset of analgesia. The dental surgeon should feel safer giving this injection since neither his equipment nor his finger lie between the patient s teeth and are, therefore, unlikely to be bitten should the patient suddenly find himself in a mood for vengeance. The conventional technique is often unsuitable for anaesthetising the area of the lower third molar particularly in the presence of acute alveolar abscess or a pericoronitis in this area. This is because inflammatory changes may extend to the injection site and trismus may be present limiting adequate mandibular opening. The use of the tuberosity approach would allow surgical procedures to be carried out in these circumstances. Last, but by no means least of the advantages, is the relative safety of the needle in this area from the danger of fractures. Difficulties may be experienced with this method when either a deformity exists or a tumour is present in the area of the maxillary tuberosity. The absence of teeth in the upper quadrant may also create some problems, but this can always be overcome by the utilisation of the alveolar ridge in place of the gum margin. When dealing with children, short needles (3.175 cm) should be used. This technique has not been found reliable in children as it has been in adults, but this may be due to the difficulty experienced in estimating the depth to which the needle should penetrate in the growing child. Although this injection has been in use in our clinic for over four years, not a single significant complication has so far been recorded. Post-anaesthetic infection has not
5 MANDIBULAR NERVE BLOCK 87 occurred in any of our cases. This may be explained by the relative cleanliness of the tuberosity area when compared with the corresponding mandibular site. Acknowledgements I thank Mrs T. M. Lawal for her secretarial assistance, the staff of the Medical Illustration Unit, Lagos University Teaching Hospital, for the photographs and the Medical Artist, London Hospital Dental School, for Figure 3. Bremer, G. (1952). Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, 36, 321. Cannell, H. & Cannon, P. D. (1976). British Dental Journal, 141, 48. Gow-Gates, G. A. E. (1973). Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, 36, 321. Northop, P. M. (1949). Journal of the American Dental Association, 38, 444. Rood, J. P. (1976). British Dental Journal, 140, 413.
Oral Surgery. Basic Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia. A variety of techniques used in administration and deposition of local anesthesia:
 Oral Surgery Lecture: 9 Dr. Saif Saadedeen Basic Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia A variety of techniques used in administration and deposition of local anesthesia: 1. Topical anesthesia 2. Infiltration
Oral Surgery Lecture: 9 Dr. Saif Saadedeen Basic Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia A variety of techniques used in administration and deposition of local anesthesia: 1. Topical anesthesia 2. Infiltration
Fundamentals of technique Types of local anaesthesia Topical or surface anaesthesia
 Fundamentals of technique The importance of a quiet, confident, and friendly manner towards all patients so physical comfort is also essential for the co-operation of the patient and the ease of operation
Fundamentals of technique The importance of a quiet, confident, and friendly manner towards all patients so physical comfort is also essential for the co-operation of the patient and the ease of operation
MANDIBULAR LOCAL ANAESTHESIA A CLINICAL COMPARISION OF THREE TECHNIQUES
 International International Multidisciplinary Multidisciplinary e-journal e Journal / Dr.Neeta Mohanty. Dr.Susant ISSN Mohant(74-83) 2277-4262 MANDIBULAR LOCAL ANAESTHESIA A CLINICAL COMPARISION OF THREE
International International Multidisciplinary Multidisciplinary e-journal e Journal / Dr.Neeta Mohanty. Dr.Susant ISSN Mohant(74-83) 2277-4262 MANDIBULAR LOCAL ANAESTHESIA A CLINICAL COMPARISION OF THREE
Techniques of local anesthesia in the mandible
 Techniques of local anesthesia in the mandible The technique of choice for anesthesia of the mandible is the block injection and this is attributed to the absence of the advantages which are present in
Techniques of local anesthesia in the mandible The technique of choice for anesthesia of the mandible is the block injection and this is attributed to the absence of the advantages which are present in
LOCAL ANESTHESIA IN PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of local anesthesia in pediatric dentistry must be made in conjunction
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of local anesthesia in pediatric dentistry must be made in conjunction
DEVELOPING ANALOGUE/SUBTITUTE FOR THE MANDIBULAR DENTURE BEARING AREA. Dr Muhammad Rizwan Memon FCPS Assistant Professor
 DEVELOPING ANALOGUE/SUBTITUTE FOR THE MANDIBULAR DENTURE BEARING AREA Dr Muhammad Rizwan Memon FCPS Assistant Professor Crest of Residual Ridge Buccal Shelf Shape of supporting structure Mylohyoid Ridge
DEVELOPING ANALOGUE/SUBTITUTE FOR THE MANDIBULAR DENTURE BEARING AREA Dr Muhammad Rizwan Memon FCPS Assistant Professor Crest of Residual Ridge Buccal Shelf Shape of supporting structure Mylohyoid Ridge
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Upper arch. 1Prosthodontics. Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi. Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth
 1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
6610 NE 181st Street, Suite #1, Kenmore, WA
 660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
Figure (2-6): Labial frenum and labial notch.
 The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
Mandibular and Maxillary Anesthesia
 Mandibular and Maxillary Anesthesia Uses of the Conduction Technique JACK H. SELTSAM, D.D.S., M.D., Los Angeles THE ARMAMENTARIUM of a surgeon who operates on the head and neck should include the ability
Mandibular and Maxillary Anesthesia Uses of the Conduction Technique JACK H. SELTSAM, D.D.S., M.D., Los Angeles THE ARMAMENTARIUM of a surgeon who operates on the head and neck should include the ability
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Oral cavity landmarks
 By: Dr. Ahmed Rabah Oral cavity landmarks The knowledge of oral anatomy and physiology will help the operator and provides enough landmarks to act as positive guide during denture construction. This subject
By: Dr. Ahmed Rabah Oral cavity landmarks The knowledge of oral anatomy and physiology will help the operator and provides enough landmarks to act as positive guide during denture construction. This subject
IDC COURSE BASIC LOCAL DENTAL ANESTHESIA LULU F. SCHAEFER LT, DC, USN
 IDC COURSE BASIC LOCAL DENTAL ANESTHESIA LULU F. SCHAEFER LT, DC, USN Lulu.F.Schaefer.mil@mail.mil LOCAL ANESTHETIC AND ARMAMENTARIUM Aspirating syringe Needle Local Anesthetic Carpules LOCAL ANESTHETIC
IDC COURSE BASIC LOCAL DENTAL ANESTHESIA LULU F. SCHAEFER LT, DC, USN Lulu.F.Schaefer.mil@mail.mil LOCAL ANESTHETIC AND ARMAMENTARIUM Aspirating syringe Needle Local Anesthetic Carpules LOCAL ANESTHETIC
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
King's College Hospital Dental School, London, S.E. 5.
 OSTECTOMY AT THE MANDIBULAR SYMPHYSIS J. H. SOWRAY, B.D.S., F.D.S.R.C.S. (Eng.), L.R.C.P., M.R.C.S. and R. HASKELL, M.B., B.S., F.D.S.R.C.S. (Eng.). King's College Hospital Dental School, London, S.E.
OSTECTOMY AT THE MANDIBULAR SYMPHYSIS J. H. SOWRAY, B.D.S., F.D.S.R.C.S. (Eng.), L.R.C.P., M.R.C.S. and R. HASKELL, M.B., B.S., F.D.S.R.C.S. (Eng.). King's College Hospital Dental School, London, S.E.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity. Dr. Faghih
 Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
IMPRESSION MAKING (IN COMPLETE DENTURES)
 IMPRESSION MAKING (IN COMPLETE DENTURES) DR ZURYATI AB GHANI BDS (WALES), Grad Dip Clin Dent (Adelaide), Doctor in Clinical Dentistry (prosthodontics), Adelaide, FRACDS 17.06.2007 Impressions An impression
IMPRESSION MAKING (IN COMPLETE DENTURES) DR ZURYATI AB GHANI BDS (WALES), Grad Dip Clin Dent (Adelaide), Doctor in Clinical Dentistry (prosthodontics), Adelaide, FRACDS 17.06.2007 Impressions An impression
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE. Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic
 MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic Introduction A number of injection techniques are available to aid in providing clinically adequate anesthesia of the teeth and soft and hard
MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic Introduction A number of injection techniques are available to aid in providing clinically adequate anesthesia of the teeth and soft and hard
Arrangement of the artificial teeth:
 Lecture Prosthodontic Dr. Osama Arrangement of the artificial teeth: It s the placement of the teeth on a denture with definite objective in mind or it s the setting of teeth on temporary bases. Rules
Lecture Prosthodontic Dr. Osama Arrangement of the artificial teeth: It s the placement of the teeth on a denture with definite objective in mind or it s the setting of teeth on temporary bases. Rules
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Local Anesthesia and Dental Splinting
 Local Anesthesia and Dental Splinting Brian Bast DMD, MD Associate Clinical Professor Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Sensory Nerve Fascicular Pattern of the Inferior Alveolar Nerve. Svane.
Local Anesthesia and Dental Splinting Brian Bast DMD, MD Associate Clinical Professor Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Sensory Nerve Fascicular Pattern of the Inferior Alveolar Nerve. Svane.
Maxillary LA: Techniques. Ra ed Salma BDS, MSc, JBOMFS, MFDRCSI
 Maxillary LA: Techniques Ra ed Salma BDS, MSc, JBOMFS, MFDRCSI dr.raedsalma@riyadh.edu.sa https://sites.google.com/a/riyadh.edu.sa/raed/ LA Options for the Maxilla Infiltration Submucosal Supraperiosteal
Maxillary LA: Techniques Ra ed Salma BDS, MSc, JBOMFS, MFDRCSI dr.raedsalma@riyadh.edu.sa https://sites.google.com/a/riyadh.edu.sa/raed/ LA Options for the Maxilla Infiltration Submucosal Supraperiosteal
Mandibular Block. Passé? Is the Dr. Stanley F. Malamed. All Rights Reserved
 Is the Mandibular Block Passé? 1 Stanley F. Malamed, DDS Dentist Anesthesiologist Emeritus Professor of Dentistry Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of U.S.C. Los Angeles, CA, USA Stanley F. MALAMED, DDS
Is the Mandibular Block Passé? 1 Stanley F. Malamed, DDS Dentist Anesthesiologist Emeritus Professor of Dentistry Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of U.S.C. Los Angeles, CA, USA Stanley F. MALAMED, DDS
TASKS. 2. Apply a disclosing agent to make the plaque visible.
 TASKS EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS Personal protective equipment Assortment of nylon, soft-bristled toothbrushes Assortment of dental Floss, waxed and nonwaxed Disclosing solution Face mirror 3. Demonstrate
TASKS EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS Personal protective equipment Assortment of nylon, soft-bristled toothbrushes Assortment of dental Floss, waxed and nonwaxed Disclosing solution Face mirror 3. Demonstrate
Types of Anaesthesia for dermal and lip fillers at Simply Fox
 Types of Anaesthesia for dermal and lip fillers at Simply Fox The Juvederm range we use contains lidocaine- a local anaesthetic, however this does not work instantly as the needle is inserted, it is mixed
Types of Anaesthesia for dermal and lip fillers at Simply Fox The Juvederm range we use contains lidocaine- a local anaesthetic, however this does not work instantly as the needle is inserted, it is mixed
Local Anesthesia Review and Update. Dr. Julius N. Manz NMDHA Scientific Session 2013
 Local Anesthesia Review and Update Dr. Julius N. Manz NMDHA Scientific Session 2013 Disclosure I am not paid by, nor do I hold any financial interest in any of the devices or materials being presented
Local Anesthesia Review and Update Dr. Julius N. Manz NMDHA Scientific Session 2013 Disclosure I am not paid by, nor do I hold any financial interest in any of the devices or materials being presented
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
The Anatomical Study of the Sinew String Observed on the Buccal Mucosa of Mandibular Second Molar and Posterior of Retromolar Pad
 The Anatomical Study of the Sinew String Observed on the Buccal Mucosa of Mandibular Second Molar and Posterior of Retromolar Pad Seiichiro Someya Vol.28 No.1-2 combined edition: 14-20, 2008 (Japanese)
The Anatomical Study of the Sinew String Observed on the Buccal Mucosa of Mandibular Second Molar and Posterior of Retromolar Pad Seiichiro Someya Vol.28 No.1-2 combined edition: 14-20, 2008 (Japanese)
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera
 PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy. Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali
 Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Arrangement of posterior artificial teeth Standardized parameters Curve of Wilson Curve of Spee
 . Arrangement of posterior artificial teeth Posterior teeth are set up in tight centric occlusion. The mandibular teeth are set in the wax occlusion rim over the residual ridge in their ideal buccolingual
. Arrangement of posterior artificial teeth Posterior teeth are set up in tight centric occlusion. The mandibular teeth are set in the wax occlusion rim over the residual ridge in their ideal buccolingual
Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve
 19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
An anatomical study of a muscle bun Title from the medial pterygoid muscle. Cranio : the journal of craniomandi Journal 15(4):
 An anatomical study of a muscle bun Title from the medial pterygoid muscle Author(s) Abe, S; Iida, T; Ide, Y; Saitoh, C Cranio : the journal of craniomandi Journal 15(4): 341-344 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/1097
An anatomical study of a muscle bun Title from the medial pterygoid muscle Author(s) Abe, S; Iida, T; Ide, Y; Saitoh, C Cranio : the journal of craniomandi Journal 15(4): 341-344 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/1097
Providing effective pain control is one of the
 Is the mandibular nerve block passé? Stanley F. Malamed, DDS Providing effective pain control is one of the most important aspects of dental care. Patients rate a dentist who does not hurt and one who
Is the mandibular nerve block passé? Stanley F. Malamed, DDS Providing effective pain control is one of the most important aspects of dental care. Patients rate a dentist who does not hurt and one who
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Patient information leaflet about Lower Wisdom Teeth (3 rd Molars)
 Patient information leaflet about Lower Wisdom Teeth (3 rd Molars) This leaflet is designed to give you more information about what the issues are with wisdom teeth, what treatment options may be given,
Patient information leaflet about Lower Wisdom Teeth (3 rd Molars) This leaflet is designed to give you more information about what the issues are with wisdom teeth, what treatment options may be given,
Muscles of mastication [part 1]
![Muscles of mastication [part 1] Muscles of mastication [part 1]](/thumbs/76/73586850.jpg) Muscles of mastication [part 1] In this lecture well have the muscles of mastication, neuromuscular function, and its relationship to the occlusion morphology. The fourth determinant of occlusion is the
Muscles of mastication [part 1] In this lecture well have the muscles of mastication, neuromuscular function, and its relationship to the occlusion morphology. The fourth determinant of occlusion is the
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
Set the patient in up right position. For mandibular impression the dentist stand in front of the patient
 Set the patient in up right position For mandibular impression the dentist stand in front of the patient For maxillary impression the dentist stand behind the patient Denture retention relies on a number
Set the patient in up right position For mandibular impression the dentist stand in front of the patient For maxillary impression the dentist stand behind the patient Denture retention relies on a number
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois Phone: Fax:
 Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Parotid Gland. Parotid Gland. Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible. Medial pterygoid.
 Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Complete denture impressions
 Lec.5 Complete denture impressions د. غسان الطائي Dental Impression: a negative imprint of an oral structure used to produce a positive replica of the structure to be used as a permanent record or in the
Lec.5 Complete denture impressions د. غسان الطائي Dental Impression: a negative imprint of an oral structure used to produce a positive replica of the structure to be used as a permanent record or in the
Concepts of occlusion Balanced occlusion. Monoplane occlusion. Lingualized occlusion. Figure (10-1)
 Any contact between teeth of opposing dental arches; usually, referring to contact between the occlusal surface. The static relationship between the incising or masticatory surfaces of the maxillary or
Any contact between teeth of opposing dental arches; usually, referring to contact between the occlusal surface. The static relationship between the incising or masticatory surfaces of the maxillary or
Lips and labial mucosa
 Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the
Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Vertical relation: It is the amount of separation between the maxilla and
 Vertical relations Vertical relation: It is the amount of separation between the maxilla and the mandible in a frontal plane. Vertical dimension: It is the distance between two selected points, one on
Vertical relations Vertical relation: It is the amount of separation between the maxilla and the mandible in a frontal plane. Vertical dimension: It is the distance between two selected points, one on
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔. 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機
 Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
THE APPLIED ANATOMY OF THE PTERYGOMANDIBULAR SPACE. B. C. W. BAgKnR AND P. L. DAVIES Department of Anatomy, University of Sydney.
 British Journal of Oral Surgery (I972), xo, 43-55 THE APPLIED ANATOMY OF THE PTERYGOMANDIBULAR SPACE B. C. W. BAgKnR AND P. L. DAVIES Department of Anatomy, University of Sydney. THE pterygomandibular
British Journal of Oral Surgery (I972), xo, 43-55 THE APPLIED ANATOMY OF THE PTERYGOMANDIBULAR SPACE B. C. W. BAgKnR AND P. L. DAVIES Department of Anatomy, University of Sydney. THE pterygomandibular
Overview of Local Anesthesia Techniques
 Chapter 1 Overview of Local Anesthesia Techniques Mohammad Ali Ghavimi, Yosef Kananizadeh, Saied Hajizadeh and Arezoo Ghoreishizadeh Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/59214
Chapter 1 Overview of Local Anesthesia Techniques Mohammad Ali Ghavimi, Yosef Kananizadeh, Saied Hajizadeh and Arezoo Ghoreishizadeh Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/59214
Mandibular ridge changes after adaptation. An issue of shortened dental arch to be considered from changes of soft tissues after unattended tooth loss
 (Journal of Dental Outlook, Vol.110, Vol.6:1021~1027, Japan 2007. An issue of shortened dental arch to be considered from changes of soft tissues after unattended tooth loss Dr. Jiro Abe Abe Dental Clinic
(Journal of Dental Outlook, Vol.110, Vol.6:1021~1027, Japan 2007. An issue of shortened dental arch to be considered from changes of soft tissues after unattended tooth loss Dr. Jiro Abe Abe Dental Clinic
Temporomandibular Joint. Dr Noman ullah wazir
 Temporomandibular Joint Dr Noman ullah wazir Type of Joint TMJ is a Synovial joint between : The condylar head of the mandible. The mandibular fossa of squamous part of temporal bone. The joint cavity
Temporomandibular Joint Dr Noman ullah wazir Type of Joint TMJ is a Synovial joint between : The condylar head of the mandible. The mandibular fossa of squamous part of temporal bone. The joint cavity
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
REDUPLICATION OF THE MOUTH AND MANDIBLE. Groote Schuur Hospital and the Red Cross Hospital, Cape Town, South Africa
 IJHtlsh Journnl of Plaslic NurgeO, (1973), 26, 84-89 REDUPLICATION OF THE MOUTH AND MANDIBLE By D. DaviEs, M.B., Ch.B., F.R.C.S., G. MoRgIso~r, M.B., Ch.B., F.C.S. and B. H. MILLER, B.D.S., F.D.S., Dip.Orth.
IJHtlsh Journnl of Plaslic NurgeO, (1973), 26, 84-89 REDUPLICATION OF THE MOUTH AND MANDIBLE By D. DaviEs, M.B., Ch.B., F.R.C.S., G. MoRgIso~r, M.B., Ch.B., F.C.S. and B. H. MILLER, B.D.S., F.D.S., Dip.Orth.
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown. By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi
 Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
Research report for MSc Dent. University of Witwatersrand. Faculty of health science. Dr J Beukes. Student number: h
 Research report for MSc Dent University of Witwatersrand Faculty of health science Dr J Beukes Student number: 9507510h Supervisor: Prof JP Reyneke October 2011 1 1. Title 2. Aim 3. Introduction 4. Objectives
Research report for MSc Dent University of Witwatersrand Faculty of health science Dr J Beukes Student number: 9507510h Supervisor: Prof JP Reyneke October 2011 1 1. Title 2. Aim 3. Introduction 4. Objectives
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
Sensory fibers that innervate the bone, teeth, and soft tissue of the oral cavity. Regional Nerve Blocks for Oral Surgery in Companion Animals
 CE Vol. 24, No. 6 June 2002 V 439 Article #1 (1.5 contact hours) Refereed Peer Review Comments? Questions? Email: compendium@medimedia.com Web: VetLearn.com Fax: 800-556-3288 KEY FACTS Due to its long
CE Vol. 24, No. 6 June 2002 V 439 Article #1 (1.5 contact hours) Refereed Peer Review Comments? Questions? Email: compendium@medimedia.com Web: VetLearn.com Fax: 800-556-3288 KEY FACTS Due to its long
Using the Lucia Jig to take an accurate & reliable centric relation bite registration
 Trimming Instructions Trimming the silicone bite records is an important step to ensure an accurate fit on the model. Trimming eliminates all the interferences so there is no movement once the models are
Trimming Instructions Trimming the silicone bite records is an important step to ensure an accurate fit on the model. Trimming eliminates all the interferences so there is no movement once the models are
ARE YOU NUMB YET? THE ANATOMY OF LOCAL ANESTHESIA PART 2: TECHNIQUES
 Frequency of Failed Anesthetic ARE YOU NUMB YET? THE ANATOMY OF LOCAL ANESTHESIA PART 2: TECHNIQUES Alan W. Budenz, MS, DDS, MBA Dept. of Biomedical Sciences and Vice Chair of Diagnostic Sciences & Services,
Frequency of Failed Anesthetic ARE YOU NUMB YET? THE ANATOMY OF LOCAL ANESTHESIA PART 2: TECHNIQUES Alan W. Budenz, MS, DDS, MBA Dept. of Biomedical Sciences and Vice Chair of Diagnostic Sciences & Services,
Medical NBDE-II. Dental Board Exams Part I.
 Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
How to provide intraoral scans to SomnoMed for the production of SomnoDent device.
 How to provide intraoral scans to SomnoMed for the production of SomnoDent device. KEY QUESTIONS: 1. Where do I send my Case? Send intra-oral scan files (maxilla and mandible in protrusive bite) and an
How to provide intraoral scans to SomnoMed for the production of SomnoDent device. KEY QUESTIONS: 1. Where do I send my Case? Send intra-oral scan files (maxilla and mandible in protrusive bite) and an
THE BIOMECHANICAL BASIS OF RETENTION IN COMPLETE DENTURES
 THE BIOMECHANICAL BASIS OF RETENTION IN COMPLETE DENTURES Factors affecting the retention of dentures Retention is the resistance of the denture to removal along its path of insertion. Strictly speaking,
THE BIOMECHANICAL BASIS OF RETENTION IN COMPLETE DENTURES Factors affecting the retention of dentures Retention is the resistance of the denture to removal along its path of insertion. Strictly speaking,
DEVELOPING ANALOGUE SUBTITUTE FOR THE MAXILLARY DENTURE BEARING AREA. Dr Muhammad Rizwan Memon FCPS Assistant Professor
 DEVELOPING ANALOGUE SUBTITUTE FOR THE MAXILLARY DENTURE BEARING AREA Dr Muhammad Rizwan Memon FCPS Assistant Professor Mucous membrane Residual Ridge Incisive papilla Rugae area Mid palatine raphe Hard
DEVELOPING ANALOGUE SUBTITUTE FOR THE MAXILLARY DENTURE BEARING AREA Dr Muhammad Rizwan Memon FCPS Assistant Professor Mucous membrane Residual Ridge Incisive papilla Rugae area Mid palatine raphe Hard
Elevators. elevators:- There are three major components of the elevator are:-
 Elevators Elevators:- Are exo-levers, instrument designed to elevate or luxate the teeth or roots from their bony socket in close or surgical method of extraction to force a tooth or root along the line
Elevators Elevators:- Are exo-levers, instrument designed to elevate or luxate the teeth or roots from their bony socket in close or surgical method of extraction to force a tooth or root along the line
Development of occlusion
 Development of occlusion The development of dentition is an important part of craniofacial growth as the formation, eruption, exfoliation and exchange of teeth take place during this period. Term occlusion
Development of occlusion The development of dentition is an important part of craniofacial growth as the formation, eruption, exfoliation and exchange of teeth take place during this period. Term occlusion
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY. Lab. Manual. Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics. 3 rd year
 ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY Lab. Manual Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics 3 rd year Department of Fixed and removable prosthetic Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry 2012/2013 Course Instructor Dr.
ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY Lab. Manual Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics 3 rd year Department of Fixed and removable prosthetic Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry 2012/2013 Course Instructor Dr.
CLASSIFICATIONS. Established in 1994 as a subcommittee of the. Prosthodontic Care Committee
 CLASSIFICATIONS Established in 1994 as a subcommittee of the Prosthodontic Care Committee Committee Members Thomas J. McGarry, DDS, Chair Arthur Nimmo, DDS James F. Skiba, DDS Christopher R. Smith, DDS
CLASSIFICATIONS Established in 1994 as a subcommittee of the Prosthodontic Care Committee Committee Members Thomas J. McGarry, DDS, Chair Arthur Nimmo, DDS James F. Skiba, DDS Christopher R. Smith, DDS
TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH
 Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
 1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
The periodontal ligament (PDL) injection: An alternative to inferior alveolar nerve block
 oral surgery oral medicine oral pathology with secrions endodontics and dental radiology Volume 53. Number 2. February, 1982 oral surgery Editor. ROBERT 6. SHIRA, D.D.S. School qf Dental Medicine, Tufts
oral surgery oral medicine oral pathology with secrions endodontics and dental radiology Volume 53. Number 2. February, 1982 oral surgery Editor. ROBERT 6. SHIRA, D.D.S. School qf Dental Medicine, Tufts
Australian Dental Journal
 Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association REVIEW Australian Dental Journal 2011; 56: 112 121 doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2011.01312.x Applied anatomy of the pterygomandibular
Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association REVIEW Australian Dental Journal 2011; 56: 112 121 doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2011.01312.x Applied anatomy of the pterygomandibular
-Ibrahim Al-Naser. -Dr Al- Muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
-1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
6. Timing for orthodontic force
 6. Timing for orthodontic force Orthodontic force is generally less than 300gm, so early mechanical stability is enough for immediate orthodontic force. There is no actually difference in success rate
6. Timing for orthodontic force Orthodontic force is generally less than 300gm, so early mechanical stability is enough for immediate orthodontic force. There is no actually difference in success rate
Syllabus for International Dental Assistants. Prepare and maintain the dental surgery, instruments, and equipment for clinical dental procedures
 Syllabus for International Dental Assistants UNIT1 Prepare and maintain the dental surgery, instruments, and equipment for clinical dental procedures This section concerns the preparation and maintenance
Syllabus for International Dental Assistants UNIT1 Prepare and maintain the dental surgery, instruments, and equipment for clinical dental procedures This section concerns the preparation and maintenance
Infection of Oral & Maxillofacial Regions. I. Spread of Dental Infection II. Non-Specific Infection III. Specific Infection
 Infection of Oral & Maxillofacial Regions I. Spread of Dental Infection II. Non-Specific Infection III. Specific Infection 1 Spread of Dental Infection 1. Routes of Spread of Infection 2. Factors which
Infection of Oral & Maxillofacial Regions I. Spread of Dental Infection II. Non-Specific Infection III. Specific Infection 1 Spread of Dental Infection 1. Routes of Spread of Infection 2. Factors which
Nose & Mouth OUTLINE. Nose. - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls. - Paranasal Sinuses. - Neurovascular Structures. Mouth. - Oral Cavity & Its Contents
 Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
Development of occlusion:
 : Dr.Issam Aljorani (BDS, MSc. Ortho.) Postnatal development of the dentition When a child is born, mineralization of all the primary tooth crowns is well underway, with this process also beginning in
: Dr.Issam Aljorani (BDS, MSc. Ortho.) Postnatal development of the dentition When a child is born, mineralization of all the primary tooth crowns is well underway, with this process also beginning in
Connect your Scanner to SomnoMed Canada. SOMGauge Protrusive Bite Recording - Manual. Scanning Impressions - Lower and Upper
 IOS Instructions How to create and submit the best scans to SomnoMed Canada for the creation of a custom SomnoDent Sleep Apnea Appliance Its a simple process: STEP 1 Connect your Scanner to SomnoMed Canada
IOS Instructions How to create and submit the best scans to SomnoMed Canada for the creation of a custom SomnoDent Sleep Apnea Appliance Its a simple process: STEP 1 Connect your Scanner to SomnoMed Canada
Variations in the anatomical dimensions of the mandibular ramus and the presence of third molars: its effect on the sagittal split ramus osteotomy
 1 Variations in the anatomical dimensions of the mandibular ramus and the presence of third molars: its effect on the sagittal split ramus osteotomy J. Beukes 1,, J. P. Reyneke 1,2,3,4, P. J. Becker 5,6
1 Variations in the anatomical dimensions of the mandibular ramus and the presence of third molars: its effect on the sagittal split ramus osteotomy J. Beukes 1,, J. P. Reyneke 1,2,3,4, P. J. Becker 5,6
