Cytokines sing the blues: inflammation and the pathogenesis of depression
|
|
|
- Derek Harper
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review TRENDS in Immunology Vol.27 No.1 Jnury 26 Cytokines sing the blues: inflmmtion nd the pthogenesis of depression Chrles L. Rison, Lucile Cpuron nd Andrew H. Miller Deprtment of Psychitry nd Behviorl Sciences, Emory University School of Medicine, 11 Woodruff Circle, Suite 4, Atlnt, GA 3322, USA Incresing mounts of dt suggest tht inflmmtory responses hve n importnt role in the pthophysiology of depression. Depressed ptients hve been found to hve higher levels of proinflmmtory cytokines, cute phse proteins, chemokines nd cellulr dhesion molecules. In ddition, therpeutic dministrtion of the cytokine interferon- leds to depression in up to 5% of ptients. Moreover, proinflmmtory cytokines hve been found to interct with mny of the pthophysiologicl domins tht chrcterize depression, including neurotrnsmitter metbolism, neuroendocrine function, synptic plsticity nd behvior. Stress, which cn precipitte depression, cn lso promote inflmmtory responses through effects on sympthetic nd prsympthetic nervous system pthwys. Finlly, depression might be behviorl byproduct of erly dptive dvntges conferred by genes tht promote inflmmtion. These findings suggest tht trgeting proinflmmtory cytokines nd their signling pthwys might represent novel strtegy to tret depression. So much is lost from the lives of people who suffer with mjor depression tht it ws perhps nturl for initil discoveries regrding mood disorders nd immunity to focus on yet nother loss in this cse, diminished functioning of the humorl nd cellulr rms of the cquired immune response [1]. Nevertheless, dt mssed over the pst 15 yers hve led to drmtic prdigm shift in which the erly focus on immunosuppression hs been subsumed within, nd supplnted by, n incresing recognition tht depressive disorders might be best chrcterized s conditions of immune ctivtion, especilly hyperctivity of innte immune inflmmtory responses. This profound chnge in our view of depression nd immunity hs not occurred in isoltion but rther is prt of lrger scientific movement built round n incresing pprecition tht inflmmtory processes re centrl to the pthogenesis of severl modern mldies, including crdiovsculr disese, dibetes nd cncer [2 4]. Indeed, much of the recent work linking depression with inflmmtion hs been prompted by the serch for potentil shred etiologicl mechnisms tht might explin the striking Corresponding uthor: Miller, A.H. (mill2@emory.edu). Avilble online 28 November 25 co-morbidity between these medicl illnesses nd mjor depression [5]. Evidence for incresed inflmmtion in depression Ptients with mjor depression who re otherwise mediclly helthy hve been repetedly observed to hve ctivted inflmmtory pthwys, s mnifested by incresed proinflmmtory cytokines, incresed cutephse proteins nd incresed expression of chemokines nd dhesion molecules [6 22]. Incresed serum nd/or plsm concentrtions of interleukin (IL)-6 nd/or C-rective protein hve been most frequently observed [6 15,17,19,2], lthough elevtions in IL-1-b nd tumor necrosis fctor (TNF)- hve lso been described, both in the peripherl blood circultion nd in the centrl nervous system (CNS; in prticulr, in the cerebrospinl fluid) [1,12,15 17,21,23 26]. In ddition to C-rective protein, other cute-phse proteins found to be elevted include - 1-cid glycoprotein, -1-ntichymotrypsin nd hptoglobin [11,15,22]. Incresed levels of chemokines nd dhesion molecules, including humn mcrophge chemottrctnt protein-1 (MCP-1), soluble intrcellulr dhesion molecule-1 (sicam-1) nd E-selectin, hve lso been described [18]. Although most studies hve compred inflmmtory mrkers in depressed versus nondepressed subjects, severl hve reported positive correltions between plsm concentrtions of vrious inflmmtory meditors nd depressive symptom severity [6,7,26]. Finlly, nscent literture suggests tht functionl llelic vrints of the genes for IL-1b nd TNF- increse the risk for depression nd re ssocited with reduced responsiveness to ntidepressnt therpy [27,28]. The ssocition between depression nd inflmmtion is pprent cross the dult lifespn [8,1,11,18] nd is evident even in the context of mild depressive symptoms tht do not meet criteri for mjor depression [29]. Indeed, even single depression-relted symptoms such s ftigue, insomni nd nger nd/or hostility hve been ssocited with evidence of inflmmtory ctivtion in otherwise helthy individuls [29 32]. Inflmmtion hs generlly been mesured t single time point; however, recent study found tht bnorml IL-6 production is pprent cross the circdin cycle in ptients with mjor depression [6]. In ddition to findings in mediclly helthy subjects, depression nd depressive symptoms (including ftigue nd cognitive dysfunction) hve been ssocited with inflmmtory mrkers in severl medicl illnesses, /$ - see front mtter Q 25 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:1.116/j.it
2 Review TRENDS in Immunology Vol.27 No.1 Jnury including crdiovsculr disese [33,34], cncer [9,35,36] nd postvirl infection [25,3]. Questions nd controversies: does ssocition imply cuslity? Although severl studies support the ide tht inflmmtory processes contribute to the pthogenesis of mjor depression, other studies hve filed to find n ssocition between the two [37,38] nd, in some cses, ssocitions hve been ttenuted or obvited when potentil mediting or moderting fctors (e.g. body mss index, gender or personlity) hve been included in the nlyses [8,13,14,39]. Some positive studies hve filed to find correltion between inflmmtion nd depressive severity [12,25] or hve found disprte nd occsionlly opposite correltions for different proinflmmtory meditors [7,12,16,26,34]. These inconsistencies indicte tht strong pronouncements bout the role of the immune system in depression might be premture nd suggest tht inflmmtion contributes to some, but not ll, cses of depression. Consistent with this, wide rnge of inflmmtory ctivity is typiclly observed within ny given smple of depressed subjects, nd ssocitions between inflmmtion nd groups of depressed subjects re often ccounted for by subset of individuls t the upper rnge of cytokine production nd/or relese [11]. Moreover, individul symptoms, especilly sleep disturbnce [4], hve been reported to contribute disproportiontely to the ssocition between depression nd inflmmtion. These points of controversy suggest venues of future reserch, including clrifiction of fctors most closely ssocited with immune ctivtion. Pthophysiologicl mechnisms: immunologicl pthwys to psychopthology A rich neuropsychitric literture ttests to fundmentl mechnisms tht conspire to cuse the syndrome of mjor depression. At neurobiologicl level, ltertions in neurotrnsmitter function involving serotonin, norepinephrine nd dopmine re well known to induce depression nd re primry trgets for currently vilble psychophrmcologicl (ntidepressnt) tretments [41]. Abnormlities in neuropeptide function re lso believed to contribute. Indeed, hypersecretion of the neuropeptide hormone corticotrophin-relesing hormone (CRH) hs been relibly demonstrted in depressed ptients [42]. CRH is the primry regultor of the hormonl response to stress [ctivtion of the hypothlmic pituitry drenl (HPA) xis nd the sympthetic nervous system]. Hypersecretion of CRH is considered to be the crucil biologicl substrte of the well-known link between psychosocil stress nd depression [42]. In ddition, the well-chrcterized hyperctivity of the HPA xis nd sympthetic nervous system in depression is believed to be secondry to CRH hyperctivity, in prt becuse of impired negtive regultion of CRH by glucocorticoids [43]. Altered CRH regultion by glucocorticoids is thought to be result of ltertions in the functioning of the glucocorticoid receptor [44]. Chnges in regionl brin ctivity hve lso been documented in depression nd involve bnorml metbolic ctivity in the prefrontl cortex nd ltered dopmine metbolism in the bsl gngli (cudte) [45,46]. There hs lso been incresing interest in the role of neurl plsticity in depression, with specil emphsis on fctors tht influence neuronl growth nd survivl [47]. At the interfce between immunology nd behvior Given the primry fctors tht re ssocited with the pthophysiology of depression, it is intriguing tht peripherlly relesed inflmmtory cytokines cn ccess the brin nd influence ll of the relevnt pthophysiologicl domins (Figure 1). Becuse of the lrge size of cytokines nd their resultnt inbility to redily penetrte the blood brin brrier, ttention hs been pid to routes by which cytokines ccess the brin, including (i) entry through leky regions in the blood brin brrier, such s the circumventriculr orgns; (ii) binding to cytokinespecific trnsport molecules expressed on brin endothelium nd (iii) ctivtion of vgl fferent fibers which trnsmit cytokine signls to specific brin nuclei, such s the nucleus of the solitry trct, which then serves s rely sttion to other brin nuclei, including the prventriculr nucleus in the hypothlmus [48] (Figure 1c). Once in the brin, there is CNS cytokine network tht is mde up of cells (neurons nd glil elements) tht not only produce cytokines nd express cytokine receptors, but lso mplify cytokine signls, which in turn cn hve profound effects on neurotrnsmitter nd CRH function, s well s on behvior [43,49]. For exmple, studies in lbortory nimls provide compelling evidence tht inflmmtory cytokines induce syndrome of sickness behvior tht hs mny overlpping fetures with mjor depression, including nhedoni (n inbililty to experience plesure), norexi, impired sleep nd reduced locomotor ctivity [49]. Consistent with the pthophysiology of depression, these cytokine-induced behviorl chnges re ssocited with ltertions in the metbolism of serotonin, norepinephrine nd dopmine in brin regions essentil to the regultion of emotion, including the limbic system (mygdl, hippocmpus nd nucleus ccumbens), s well s the regultion of psychomotor function nd rewrd, including the bsl gngli [5,51]. In ddition to effects on neurotrnsmitter metbolism, inflmmtory cytokines hve profound stimultory effects on HPA xis hormones s well s CRH (mrna nd protein), in both the hypothlmus nd the mygdl, brin region tht hs n importnt role in fer nd nxiety [52 54]. These effects re, in lrge prt, medited by rich network of cytokines nd their receptors within HPA xis tissues which fcilitte the integrtion of cytokine signls [53]. Downstrem cytokine signl trnsduction pthwys, including mitogen-ctivted protein kinses (MAPKs) nd nucler fctor kb (NF-kB), lso disrupt glucocorticoid receptor signling [55,56], nd thus might contribute to ltered glucocorticoid-medited feedbck regultion of both CRH nd further proinflmmtory cytokine relese. In ddition, ctivtion of p38 MAPKs might contribute to ltertions in neurotrnsmitter function through effects on the serotonin trnsporter [57]. Induction of NF-kB in the brin following peripherl cytokine (IL-1) exposure hs been shown to medite mny of the behviorl effects of IL-1, including socil
3 26 Review TRENDS in Immunology Vol.27 No.1 Jnury 26 Depression ACTH PVN Pituitry Dorsl vgl complex 5HT DA CRH (d) (i) (ii) BDNF (iii) NTS Senso ry vgus (c) Stress Adrenl glnd Glucocorticoids (f) Motor vgus (e) Sympthetic NE ACh αar nd βar α7nachr TNF IL-1 IL-6 (b) Inflmmtion Pro-inflmmtory cytokines Chemokines Adhesion molecules Acute phse rectnts GR NFκB (g) JNK ERK p38 TLR () Mcrophge Infection, tissue dmge or destruction Figure 1. Stress immune interctions nd depression. () Activtion of NF-kB through Toll-like receptors (TLR) during immune chllenge leds to n inflmmtory response including (b) the relese of the proinflmmtory cytokines TNF-, IL-1 nd IL-6. (c) These cytokines, in turn, ccess the brin vi leky regions in the blood brin brrier, ctive trnsport molecules nd fferent nerve fibers (e.g. sensory vgus), which rely informtion through the nucleus trctus solitrius (NTS) [48]. (d) Once in the brin, cytokine signls prticipte in pthwys (indicted in ornge) known to be involved in the development of depression, including: (i) ltered metbolism of relevnt neurotrnsmitters such s serotonin (5HT) nd dopmine (DA) [5,51]; (ii) ctivtion of CRH in the prventriculr nucleus (PVN) nd the subsequent production nd/or relese of ACTH nd glucocorticoids (cortisol) [52,53] nd (iii) disruption of synptic plsticity through ltertions in relevnt growth fctors [e.g. brin-derived neurotrophic fctor (BDNF)] [59,6]. (e) Exposure to environmentl stressors promotes ctivtion of inflmmtory signling (NF-kB) through incresed outflow of proinflmmtory sympthetic nervous system responses [relese of norepinephrine (NE), which binds to (AR) nd b (bar) drenoceptors] (ornge). (f) Stressors lso induce withdrwl of inhibitory motor vgl input [relese of cetylcholine (ACh), which binds to the 7 subunit of the nicotinic cetylcholine receptor (7nAChR)] (blue) [73,77]. (g) Activtion of the mitogen ctivted protein kinse pthwys, including p38 nd Jun mino-terminl kinse (JNK), inhibit the function of glucocorticoid receptors (GR), thereby relesing NF-kB from negtive regultion by glucocorticoids relesed s result of the HPA xis in response to stress (blue) [55,56]. withdrwl nd decresed food intke [58]. NF-kB induction in the brin lso might contribute to ltertions in neuronl growth nd survivl, especilly through the induction of nitric oxide (e.g. vi inducible nitric oxide synthse, inos) nd, ultimtely, oxidtive stress, which hs been shown to lter promoter function for severl genes centrl to synptic plsticity [59,6]. Finlly, humns who re dministered cytokines exogenously for infectious diseses nd cncer show ltered function in brin regions relevnt to the development of depressive symptoms [54]. Interferon-: clinicl model of cytokine-induced depression To study the effects of innte immune cytokines on behvior in humns, severl investigtors hve seized upon the profound clinicl observtion tht high percentge of ptients who re dministered the cytokine interferon (IFN)- for the tretment of infectious diseses or cncer develop behviorl syndrome tht is strikingly similr to mjor depression (Figure 2). IFN- is potent inducer of proinflmmtory cytokines, including IL-6 nd, to lesser extent, IL-1 b nd TNF- [54]. Substntiting the fct tht the IFN--induced behviorl syndrome is indeed depression s encountered in other venues (e.g. mentl helth clinics) is tht IFN--induced depression: (i) is responsive to tretment with stndrd ntidepressnt therpy [61]; (ii) is ssocited with ltertions in serotonin metbolism, in prt relted to incresed ctivity of the metbolic enzyme indolemine 2,3, dioxygense, which degrdes tryptophn to kynurenine, which is then
4 Review TRENDS in Immunology Vol.27 No.1 Jnury () (b) (c) (d) ACC ACTH (pg ml 1 ) Cortisol (µg dl 1 ) Time following IFN-α injection (hr) b b MADRS score (d26) Trp (d d26) Free of mjor depression (%) Weeks of IFN-α therpy (e) fmri signl (ACC) Loction errors TRENDS in Immunology Figure 2. IFN-: modeling of cytokine-induced depression. Therpeutic dministrtion of IFN- is ssocited with depression in 3 5% of ptients, depending on the dose [61,62]. IFN--induced depression is ssocited with pthophysiologicl chnges tht overlp with those found in mediclly helthy depressed ptients, including ctivtion of neuroendocrine (HPA xis) pthwys (), ltertions in neurotrnsmitter metbolism (b), responsiveness to ntidepressnt tretment (c) nd ltertions in brin circuitry relevnt to informtion processing (d). () The initil injection of IFN- to ptients with mlignnt melnom is ssocited with mrked induction of ACTH nd cortisol, which ws significntly higher in ptients who eventully developed depression (blue) thn in those who never becme depressed during IFN- tretment (red)., significntly different from hours; P!.1; b, significnt difference between groups, P!.1. (b) The reltionship between the severity of depressive symptoms [s mesured by the Montgomery Asberg Depression Rting Scle (MADRS)] nd chnges in plsm tryptophn (TRP) concentrtions during IFN- therpy for cncer. TRP is the primry mino cid precursor of serotonin, mjor regultor of limbic brin circuitry tht subserves emotion. Decreses in TRP were significntly correlted (RZK.5, P!.5) with increses in depression severity scores during IFN- tretment. (c) Ptients who received the serotonin reuptke inhibitor proxetine, commonly used ntidepressnt, before nd during IFN- therpy for mlignnt melnom (red tringles), were significntly more likely to remin free of depression during IFN- dministrtion thn plcebo-treted control group (blck squres). (d) Significntly greter ctivtion (yellow nd ornge) of the dorsl ACC, s mesured by functionl mgnetic resonnce imging (fmri) during tsk of visuosptil ttention ws found in IFN--treted ptients compred with controls. (e) A significnt liner reltionship ws found between ctivtion of the ACC nd the number of tsk-relted errors in IFN--treted ptients (red strs) but not in control subjects (blck tringles). Incresed ACC ctivtion in response to reltively low tsk error rtes hs been ssocited with cognitive styles tht predispose to nxiety nd depression, suggesting tht IFN--induced chnges in ACC function might represent cognitive pthwy to psychopthology [65]. Reproduced, with permission, from () Ref. [63], (b) Ref. [62], (c) Ref. [61] nd (d,e) Ref. [65]. metbolized to quinolinic cid [62]; nd (iii) is ssocited with ltertions in CRH function s mnifested by n exggerted drenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) nd cortisol response to the first dministrtion of IFN- in ptients who ultimtely develop depression [63]. In ddition, using positron emission tomogrphy, IFN- hs been shown to lter metbolic ctivity in the bsl gngli [64], possibly representing disruption of bsl gngli circuitry involving dopmine nd subserving hedonic tone (i.e. the cpcity to experience plesure nd rewrd), s well s psychomotor speed. IFN- hs lso been found to lter fundmentl informtion processing in the dorsl prt of the nterior cingulte cortex (ACC), s reveled by functionl mgnetic resonnce imging. In comprison with control subjects, IFN--treted ptients exhibited incresed ACC ctivity in response to tsk with low error rte, possibly representing n incresed sensitivity to negtive events or conflict [65]. Similr ltertions hve been demonstrted in popultions t risk for mood nd nxiety disorders, including subjects with high-trit nxiety, neuroticism nd obsessive compulsive disorder. Tken together, these dt demonstrte tht cytokine (IFN-) dministrtion to humns replictes multiple pthologies centrl to depression, thereby providing support for the notion tht endogenous cytokines tht medite innte immune responses cn contribute to the stte of depression. Stress nd immunity: crucil link in the cytokine depression chin Inflmmtion is the sine qu non of pthology, so it is understndble tht proinflmmtory cytokines might contribute to depression in the context of medicl illness, thus potentilly ccounting for the five tenfold greter prevlence of depression in individuls with wide rnge of medicl disorders [5]. Nevertheless, it is not s redily pprent wht might drive incresed inflmmtion in ptients with mjor depression who re presumbly physiclly helthy. One possibility is the impct of stress on the immune response (Figures 1 nd 3). Psychologicl stress is common risk fctor for the development of mjor depression in every culture exmined, nd most initil episodes of mjor depression re preceded by n identifible stressor [66]. Consistent with the notion tht stress might provide link between depression nd inflmmtion, incresing dt indicte tht psychologicl stress ctivtes proinflmmtory cytokines nd their signling pthwys in the periphery nd CNS. In lbortory nimls, vriety of psychologicl stressors (e.g. restrint, open-field exposure or socil isoltion) increse concentrtions of proinflmmtory cytokines, including IL-1b nd TNF-, in brin regions involved in emotionl regultion, s well s in the periphery [6,67]. Moreover, behviorl chnges induced in rodents by socil isoltion cn be reversed by intrcerebroventriculr dministrtion of the soluble IL-
5 28 Review TRENDS in Immunology Vol.27 No.1 Jnury 26 Divorce S t r e s s Nturl disster Poverty Interpersonl conflict Berevement Job loss Genetics Mjor depression Pst experience Infection Autoimmune disorder Cncer Tissue trum I n f l m m t i o n Chemotherpy Surgery TRENDS in Immunology Figure 3. Acute nd chronic immune nd inflmmtory processes, combined with relevnt contributions from immunogenetics (such s polymorphisms in cytokine genes) nd pst immune experiences (such s prior infections nd vccintion history) (ornge) interct with cute nd chronic stressors combined with relevnt contributions from psychitric genetics (such s polymorphisms in neurotrnsmitter trnsporter genes) nd pst emotionl experiences (such s dversity in erly life) (yellow) to promote the syndrome of mjor depression (brown). A dignosis of mjor depression is bsed on the presence of five of the following symptoms: depressed mood, nhedoni, ftigue, guilt nd/or worthlessness, suicidl idetion, impired concentrtion nd/or memory, psychomotor retrdtion nd/or gittion nd disturbnces of sleep or ppetite. Symptoms must persist for t lest two weeks nd cuse significnt functionl impirment [91]. 1 receptor ntgonist (IL-1r) [68]. Proinflmmtory cytokine ctivtion lso ppers to medite other stressrelted biochemicl chnges in the brin. For exmple, TNF- is required for the production of nitric oxide within the CNS following immobiliztion stress [6], nd IL-1-b hs key role in the inhibition of the expression of brinderived neurl growth fctor in the hippocmpus of rts following socil isoltion [69]. Consistent with these findings is the fct tht stress-induced neuronl cell loss in rodents is linked to incresed concentrtions of TNF- nd NF-kB [6]. In humns, cute stress (e.g. lbortory stressor) nd chronic stress (including lck of socil support) hve both been ssocited with incresed production nd/or relese of proinflmmtory cytokines nd decreses in ntiinflmmtory cytokines such s IL-1 [7 72]. Recent work indictes tht psychosocil stress lso ctivtes NFkB in peripherl blood mononucler cells of helthy volunteers [73]. Interestingly, stress-induced ctivtion of proinflmmtory cytokines might provide some insight into the decreses in cquired immune responses found in both stress nd depression. For exmple, stress-induced decreses in the IgM nd IgG ntibody responses to immuniztion with keyhole limpet hemocynin were found to be ttenuted significntly if rts were pretreted with IL-1r [74]. Combined with dt suggesting tht TNF- cn significntly disrupt T-cell signling, these findings suggest tht overctivtion of innte immune responses following stress nd during depression might come t the expense of decresed cellulr nd humorl cquired immune responses [43]. Stress system ctivtion might promote cytokine production through severl mechnisms (Figure 1). Despite suppressing certin immune processes, ctivtion of the sympthetic nervous system hs been linked in severl studies to proinflmmtory ctivtion in the periphery, which might, in turn, influence inflmmtory processes in the CNS [43]. For exmple, stress-induced ctivtion of NF-kB in peripherl blood mononucler cells ppers to be dependent on norepinephrine nd cn be brogted by 1-drenoceptor blockde [73]. Similrly, b- drenoceptor stimultion hs been shown to increse gene expression nd protein production of TNF-, IL-1b nd IL- 6 in myocrdil cells [75], nd chronic b-blockde reduces plsm levels of IL-6 in concert with symptomtic improvement in ptients with congestive hert filure [76]. Vgl withdrwl in response to stress might lso promote inflmmtion, given the evidence tht vgl ctivity inhibits NFkB ctivtion (nd the relese of TNF from mcrophges) vi cholinergic signling through the -7 subunit of the nicotinic cetylcholine receptor [77]. Indeed, decresed vgl tone, s mnifested by reduced hert rte vribility, hs been ssocited with incresed inflmmtory mrkers in women with coronry rtery disese [78]. Stress nd depression hve both been ssocited with reduced hert rte vribility [79]. Finlly, chronic stress promotes the development of glucocorticoid resistnce, which hs been ssocited with incresed cytokine production nd which might lso relese the sympthetic nervous system from inhibitory control, further promoting inflmmtory ctivtion [43]. Evolutionry perspectives The reltionship between depression nd ctivtion of innte immune responses might hve its roots in the evolutionry dvntges of behviorl repertoire tht enbles diversion of crucil energy resources to the metbolic demnds of fever during times of pthogen exposure. In ddition, pthophysiologicl chnges centrl to depression might protect inflmmtory responses from negtive regultion by neuroendocrine (glucocorticoid) responses [48,8] (Box 1). Thus, depression might hve been necessry behviorl ccoutrement to erly, endogenous ntibiotic strtegies tht hve been rendered unnecessry in modern times. Tretment implictions Becuse prdigm shifts within medicine re judged (finlly) by their clinicl utility, it is encourging tht importnt tretment implictions hve lredy emerged from our nscent understnding of the role of inflmmtion in the pthogenesis of mjor depression. Indeed, dt incresingly suggest tht inflmmtory processes contribute to the therpeutic effects of the currently vilble ntidepressnts nd could provide trgets for novel phrmcologicl nd nonphrmcologicl tretment strtegies.
6 Review TRENDS in Immunology Vol.27 No.1 Jnury Box 1. Evolutionry impertives for the depression inflmmtion link The discovery tht depression shres n underlying physiology with inflmmtion nd stress system ctivtion provides novel perspective on why vulnerbility genes for mjor depression might hve been retined in the humn gene pool despite the negtive impct of depression on morbidity nd mortlity. Although current dptive theories focus on the potentil benefits of depressive symptoms themselves (i.e. serving s signls to increse id from, or decrese competition with, others), viewing depression s requisite behviorl counterprt of immune ctivtion suggests tht the high prevlence of mood disorders cme bout not s result of providing hidden socil benefits but becuse these disorders re pleiotropiclly linked to genes tht directly, or indirectly, promote enhnced inflmmtory responses nd, hence, survivl in times of stress. Despite posing risk for depression, such llelic vrints might hve simultneously improved overll fitness by incresing resistnce to pthogen ssult before the dvent of modern snittion nd ntibiotic therpy [48]. Consistent with this hypothesis is the observtion tht mny symptoms of depression (e.g. psychomotor retrdtion, ftigue nd nhedoni) promote the conservtion of essentil energy resources tht re dptive in the context of subserving the metbolic demnds of endogenous ntibiotic strtegies such s fever [48]. The benefits of heightened inflmmtory ctivity in response to infection might lso help to explin common neuroendocrine bnormlity found in mjor depression. In hierrchicl socil species (including humns), psychosocil stress in mles is frequently ccounted for by dominnce struggles in which the risk of wounding, especilly in subordintes, is high. This presents individuls with the prdox of needing HPA xis ctivtion (nd the relese of glucocorticoids) to provide energy for the stressful encounter, while voiding the incresed dnger of wound infection presented by glucocorticoid-induced immunosuppression. Studies using socil disruption prdigm in rodents suggest tht this impsse is resolved through the induction of glucocorticoid resistnce, which correltes with ssumption of subordinte behviorl profile following defet nd with the number of wounds received in fighting with ggressive intruder mice [8]. Interestingly, depression in humns is highly ssocited with both socil defet (especilly in mles) nd with endocrine nd immune tissue resistnce to glucocorticoids. These considertions suggest tht, rther thn hrboring hidden dptive fetures, mjor depression is disese fueled in the modern world by n evolutionry mismtch between current conditions nd our ncestrl environment. This lso suggests surprising hypothesis: to the degree tht inflmmtory processes re rendered less essentil by culturl inventions (i.e. improved medicines or lws ginst physicl violence), genes tht promote mjor depression should decrese in frequency s the survivl benefits of immune ctivtion become outweighed by disdvntges, including n incresed risk of mjor depression in the context of psychologicl stress. Consistent with their bility to meliorte cytokineinduced depression [61], ntidepressnts hve been shown in nimls nd humns to inhibit the production nd/or relese of proinflmmtory cytokines nd to stimulte the production of nti-inflmmtory cytokines (such s IL-1) [81]. These effects might contribute to therpeutic efficcy, given recent dt tht ntidepressnt-like effects of desiprmine in the forced swim test (n niml model frequently used to evlute ntidepressnt efficcy) depend on the bility of the drug to inhibit CNS production of TNF- [82]. In humns, vriety of ntidepressnt strtegies (including mediction, electroconvulsive shock therpy nd psychotherpy) pper to ttenute inflmmtory ctivity in concert with improvements in depressive symptoms, suggesting tht reductions in inflmmtion might contribute to tretment response [16,17,19,23,24,83]. An inflmmtory perspective on depression lso provides novel insights into indequcies in our current tretment options. For exmple, ptients with history of nonresponse to ntidepressnts hve been found to exhibit incresed plsm concentrtions of IL-6 nd cute-phse proteins when compred with tretmentresponsive ptients [2,22]. Similrly, ptients with evidence of incresed inflmmtory ctivity before tretment hve been reported to be less responsive to ntidepressnts, lithium or sleep deprivtion ( potent short-term mood elevtor) [17,21,22,84]. Moreover, work by our group nd by others suggests tht in the context of cytokine exposure, ntidepressnts might only ddress selected symptom domins (e.g. depressed mood nd nxiety), while leving severl symptoms reltively unffected (e.g. ftigue or psychomotor slowing) [85,86]. Interestingly, this pttern of symptom response hs lso been observed in the ntidepressnt tretment of mediclly helthy ptients with depression [87]. These observtions suggest tht inhibition of proinflmmtory cytokine signling represents vible strtegy for the tretment of depression, especilly in ptients with evidence of incresed inflmmtory ctivity before therpy who might be less likely to respond to conventionl gents. In support of this ide, studies in lbortory nimls demonstrte tht cytokine-induced sickness syndromes (which overlp symptomticlly with depression) cn be meliorted or reversed by dministering specific cytokine ntgonists (e.g. IL-1r) or ntiinflmmtory cytokines (e.g. IL-1) directly into the brin [68,88]. Moreover, cytokine ntgonists pper to hve ntidepressnt-like effects, even in the bsence of n immune chllenge. For exmple, in rodents intrcerebroventriculr dministrtion of IL-1r prevents memory deficits following the psychologicl stress of socil isoltion [68], nd ntibodies to TNF- demonstrte ntidepressnt effects on the forced swim test when dministered vi the intrcerebroventriculr route [82]. In humns, ntgonists of TNF- (i.e. etnercept, infliximb) hve been reported to reduce depressive symptoms in the context of treting vriety of utoimmune conditions [89,9]. Interestingly, in these ptients, improvements in mood often pper to precede improvements in the underlying disese stte. Conclusion A gret mount of compelling dt suggest tht inflmmtory innte immune responses might contribute to the development of depression, in prt through complex interctions with stress-responsive pthwys involving the neuroendocrine nd utonomic nervous systems. The role of the immune system in the pthophysiology of depression probbly derives from evolutionry impertives, nd presents intriguing nd unique therpeutic
7 3 Review TRENDS in Immunology Vol.27 No.1 Jnury 26 opportunities to expnd the tretment trgets for this disbling nd common disorder. References 1 Herbert, T.B. nd Cohen, S. (1993) Depression nd immunity: metnlytic review. Psychol. Bull. 113, Wellen, K.E. nd Hotmisligil, G.S. (25) Inflmmtion, stress, nd dibetes. J. Clin. Invest. 115, Willerson, J.T. nd Ridker, P.M. (24) Inflmmtion s crdiovsculr risk fctor. Circultion 19 (21, Suppl 1), II2 1 4 Li, Q. et l. (25) Inflmmtion-ssocited cncer: NF-kppB is the lynchpin. Trends Immunol 26, Evns, D.L. et l. (25) Mood disorders in the mediclly ill: scientific review nd recommendtions. Biol. Psychitry 58, Alesci, S. et l. (25) Mjor depression is ssocited with significnt diurnl elevtions in plsm interleukin-6 levels, shift of its circdin rhythm, nd loss of physiologicl complexity in its secretion: clinicl implictions. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metb. 9, Miller, G.E. et l. (22) Clinicl depression nd inflmmtory risk mrkers for coronry hert disese. Am. J. Crdiol. 9, Bouhuys, A.L.et l. (24) Potentil psychosocil mechnisms linking depression to immune function in elderly subjects. Psychitry Res. 127, Musselmn, D.L. et l. (21) Higher thn norml plsm interleukin- 6 concentrtions in cncer ptients with depression: preliminry findings. Am. J. Psychitry 158, Khl, K.G. et l. (25) Bone minerl density, mrkers of bone turnover, nd cytokines in young women with borderline personlity disorder with nd without comorbid mjor depressive disorder. Am. J. Psychitry 162, Tiemeier, H. et l. (23) Inflmmtory proteins nd depression in the elderly. Epidemiology 14, Schltter, J. et l. (24) Monocytic prmeters in ptients with dysthymi versus mjor depression. J. Affect. Disord. 78, Ford, D.E. nd Erlinger, T.P. (24) Depression nd C-rective protein in US dults. Arch. Intern. Med. 164, Dnner, M. et l. (23) Assocition between depression nd elevted C-rective protein. Psychosom. Med. 65, Mes, M. (1999) Mjor depression nd ctivtion of the inflmmtory response system. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 461, Levine, J. et l. (1999) Cerebrospinl cytokine levels in ptients with cute depression. Neuropsychobiology 4, Lnquillon, S. et l. (2) Cytokine production nd tretment response in mjor depressive disorder. Neuropsychophrmcology 22, Rjgopln, S. et l. (21) Abnorml brchil rtery flow-medited vsodiltion in young dults with mjor depression. Am. J. Crdiol. 88, Sluzewsk, A. et l. (1995) Interleukin-6 serum levels in depressed ptients before nd fter tretment with fluoxetine. Ann. N. Y. Acd. Sci. 762, Mes, M. et l. (1997) Incresed serum IL-6 nd IL-1 receptor ntgonist concentrtions in mjor depression nd tretment resistnt depression. Cytokine 9, Mikov, O. et l. (21) Incresed serum tumor necrosis fctor lph concentrtions in mjor depression nd multiple sclerosis. Eur. Neuropsychophrmcol. 11, Sluzewsk, A. et l. (1997) Chnges in cute-phse proteins during lithium potentition of ntidepressnts in refrctory depression. Neuropsychobiology 35, Tuglu, C. et l. (23) Incresed serum tumor necrosis fctor-lph levels nd tretment response in mjor depressive disorder. Psychophrmcology (Berl.) 17, Hestd,K.A. et l. (23) Rised plsm levels of tumor necrosis fctor lph in ptients with depression. J. ECT 19, Owen, B.M. et l. (21) Rised levels of plsm interleukin-1bet in mjor nd postvirl depression. Act Psychitr. Scnd. 13, Thoms, A.J. et l. (25) Increse in interleukin-1bet in lte-life depression. Am. J. Psychitry 162, Yu, Y.W. et l. (23) Assocition study of the interleukin-1 bet (C- 511T) genetic polymorphism with mjor depressive disorder, ssocited symptomtology, nd ntidepressnt response. Neuropsychophrmcology 28, Jun, T.Y. et l. (23) Possible ssocition between -G38A tumour necrosis fctor-lph gene polymorphism nd mjor depressive disorder in the Koren popultion. Psychitr. Genet. 13, Surez, E.C. et l. (24) Enhnced expression of cytokines nd chemokines by blood monocytes to in vitro lipopolyscchride stimultion re ssocited with hostility nd severity of depressive symptoms in helthy women. Psychoneuroendocrinology 29, vn der Ven, A. et l. (23) Herpes viruses, cytokines, nd ltered hemostsis in vitl exhustion. Psychosom. Med. 65, Irwin, M. et l. (24) Nocturnl proinflmmtory cytokine-ssocited sleep disturbnces in bstinent Africn Americn lcoholics. Brin Behv. Immun. 18, Surez, E.C. et l. (22) The reltion of ggression, hostility, nd nger to lipopolyscchride-stimulted tumor necrosis fctor (TNF)- lph by blood monocytes from norml men. Brin Behv. Immun. 16, Lespernce, F. et l. (24) The ssocition between mjor depression nd levels of soluble intercellulr dhesion molecule 1, interleukin-6, nd C-rective protein in ptients with recent cute coronry syndromes. Am. J. Psychitry 161, Miller, G.E. et l. (25) Reltion of depressive symptoms to C-rective protein nd pthogen burden (cytomeglovirus, herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Brr virus) in ptients with erlier cute coronry syndromes. Am. J. Crdiol. 95, Bower, J.E. et l. (22) Ftigue nd proinflmmtory cytokine ctivity in brest cncer survivors. Psychosom. Med. 64, Meyers, C.A. et l. (25) Cognitive impirment, ftigue, nd cytokine levels in ptients with cute myelogenous leukemi or myelodysplstic syndrome. Cncer 14, Hck, M. et l. (1999) Plsm levels of cytokines nd soluble cytokine receptors in psychitric ptients upon hospitl dmission: effects of confounding fctors nd dignosis. J. Psychitr. Res. 33, Steptoe, A. et l. (23) Lck of ssocition between depressive symptoms nd mrkers of immune nd vsculr inflmmtion in middle-ged men nd women. Psychol. Med. 33, Miller, G.E. et l. (23) Pthwys linking depression, diposity, nd inflmmtory mrkers in helthy young dults. Brin Behv. Immun. 17, Motivl, S.J. et l. (25) Inflmmtory mrkers nd sleep disturbnce in mjor depression. Psychosom. Med. 67, Szbo, S.T. et l. (24) Neurotrnsmitters, receptors, signl trnsduction, nd second messengers in psychitric disorders. In Textbook of Psychophrmcology (Schtzberg, A.F. nd Nemeroff, C.B., eds), pp. 3 52, Americn Psychitric Publishing 42 Owens, M.J. nd Nemeroff, C.B. (1991) Physiology nd phrmcology of corticotropin-relesing fctor. Phrmcol. Rev. 43, Rison, C.L. nd Miller, A.H. (23) When not enough is too much: the role of insufficient glucocorticoid signling in the pthophysiology of stress-relted disorders. Am. J. Psychitry 16, Printe, C.M. nd Miller, A.H. (21) Glucocorticoid receptors in mjor depression: relevnce to pthophysiology nd tretment. Biol. Psychitry 49, Mrtinot, M. et l. (21) Decresed presynptic dopmine function in the left cudte of depressed ptients with ffective flttening nd psychomotor retrdtion. Am. J. Psychitry 158, Drevets, W.C. (21) Neuroimging nd neuropthologicl studies of depression: implictions for the cognitive-emotionl fetures of mood disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 11, Dumn, R.S. (24) Depression: cse of neuronl life nd deth? Biol. Psychitry 56, Mier, S.F. nd Wtkins, L.R. (1998) Cytokines for psychologists: implictions of bidirectionl immune-to-brin communiction for understnding behvior, mood, nd cognition. Psychol. Rev. 15, Dntzer, R. (24) Cytokine-induced sickness behviour: neuroimmune response to ctivtion of innte immunity. Eur. J. Phrmcol. 5,
8 Review TRENDS in Immunology Vol.27 No.1 Jnury Go, H.M. et l. (22) Microglil ctivtion-medited delyed nd progressive degenertion of rt nigrl dopminergic neurons: relevnce to Prkinson s disese. J. Neurochem. 81, Dunn, A.J. et l. (1999) Effects of cytokines on cerebrl neurotrnsmission. Comprison with the effects of stress. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 461, Besedovsky, H.O. nd del Rey, A. (1996) Immune-neuro-endocrine interctions: fcts nd hypotheses. Endocr. Rev. 17, Silvermn, M.N. et l. (25) Immune modultion of the hypothlmic-pituitry-drenl (HPA) xis during virl infection. Virl Immunol. 18, Cpuron, L. nd Miller, A.H. (24) Cytokines nd psychopthology: lessons from interferon-lph. Biol. Psychitry 56, Wng, X. et l. (24) Interleukin-1 lph-induced ctivtion of p38 mitogen-ctivted kinse inhibits glucocorticoid receptor function. Mol. Psychitry 9, McKy, L.I. nd Cidlowski, J.A. (1999) Moleculr control of immune/inflmmtory responses: interctions between nucler fctor-kpp B nd steroid receptor-signling pthwys. Endocr. Rev. 2, Zhu, C.B. et l. (25) p38 MAPK ctivtion elevtes serotonin trnsport ctivity vi trfficking-independent, protein phosphtse 2A-dependent process. J. Biol. Chem. 28, Ndjr, A. et l. Inctivtion of the cerebrl NFkppB pthwy inhibits interleukin-1bet-induced sickness behvior nd c-fos expression in vrious brin nuclei. Neuropsychophrmcology (in press) 59 Lu, T. et l. (24) Gene regultion nd DNA dmge in the geing humn brin. Nture 429, Mdrigl, J.L. et l. (22) The increse in TNF-lph levels is implicted in NF-kppB ctivtion nd inducible nitric oxide synthse expression in brin cortex fter immobiliztion stress. Neuropsychophrmcology 26, Musselmn, D.L. et l. (21) Proxetine for the prevention of depression induced by high-dose interferon lf. N. Engl. J. Med. 344, Cpuron, L. et l. (22) Assocition between decresed serum tryptophn concentrtions nd depressive symptoms in cncer ptients undergoing cytokine therpy. Mol. Psychitry 7, Cpuron, L. et l. (23) Assocition of exggerted HPA xis response to the initil injection of interferon-lph with development of depression during interferon-lph therpy. Am. J. Psychitry 16, Juengling, F.D. et l. (2) Prefrontl corticl hypometbolism during low-dose interferon lph tretment. Psychophrmcology (Berl.) 152, Cpuron, L. et l. (25) Anterior cingulte ctivtion nd error processing during interferon-lph tretment. Biol. Psychitry 58, Kendler, K.S. et l. (2) Stressful life events nd previous episodes in the etiology of mjor depression in women: n evlution of the kindling hypothesis. Am. J. Psychitry 157, O Connor, K.A. et l. (23) Peripherl nd centrl proinflmmtory cytokine response to severe cute stressor. Brin Res. 991, Pugh, C.R. et l. (1999) Role of interleukin-1 bet in impirment of contextul fer conditioning cused by socil isoltion. Behv. Brin Res. 16, Brrientos, R.M. et l. (23) Brin-derived neurotrophic fctor mrna downregultion produced by socil isoltion is blocked by intrhippocmpl interleukin-1 receptor ntgonist. Neuroscience 121, Goebel, M.U. et l. (2) Interleukin-6 nd tumor necrosis fctorlph production fter cute psychologicl stress, exercise, nd infused isoproterenol: differentil effects nd pthwys. Psychosom. Med. 62, Deinzer, R. et l. (24) Acute stress effects on locl Il-1bet responses to pthogens in humn in vivo model. Brin Behv. Immun. 18, Mes, M. et l. (1998) The effects of psychologicl stress on humns: incresed production of pro-inflmmtory cytokines nd Th1-like response in stress-induced nxiety. Cytokine 1, Bierhus, A. et l. (23) A mechnism converting psychosocil stress into mononucler cell ctivtion. Proc. Ntl. Acd. Sci. U. S. A. 1, Morsk, A. et l. (22) Elevted IL-1bet contributes to ntibody suppression produced by stress. J. Appl. Physiol. 93, Murry, D.R. et l. (2) Chronic bet-drenergic stimultion induces myocrdil proinflmmtory cytokine expression. Circultion 11, Myer, B. et l. (25) Functionl improvement in hert filure ptients treted with bet-blockers is ssocited with decline of cytokine levels. Int. J. Crdiol. 13, Pvlov, V.A. nd Trcey, K.J. (25) The cholinergic nti-inflmmtory pthwy. Brin Behv. Immun. 19, Jnszky, I. et l. (24) Inflmmtory mrkers nd hert rte vribility in women with coronry hert disese. J. Intern. Med. 256, Kim, C.K. et l. (25) Depressive symptoms nd hert rte vribility in postmenopusl women. Arch. Intern. Med. 165, Avitsur, R. et l. (21) Socil stress induces glucocorticoid resistnce in subordinte nimls. Horm. Behv. 39, Kenis, G. nd Mes, M. (22) Effects of ntidepressnts on the production of cytokines. Int. J. Neuropsychophrmcol. 5, Reynolds, J.L. et l. (24) Brin-derived tumor necrosis fctor-lph nd its involvement in nordrenergic neuron functioning involved in the mechnism of ction of n ntidepressnt. J. Phrmcol. Exp. Ther. 31, Frommberger, U.H. et l. (1997) Interleukin-6-(IL-6) plsm levels in depression nd schizophreni: comprison between the cute stte nd fter remission. Eur. Arch. Psychitry Clin. Neurosci. 247, Benedetti, F. et l. (22) Interleukine-6 serum levels correlte with response to ntidepressnt sleep deprivtion nd sleep phse dvnce. Prog. Neuropsychophrmcol. Biol. Psychitry 26, Cpuron, L. et l. (22) Neurobehviorl effects of interferon-lph in cncer ptients: phenomenology nd proxetine responsiveness of symptom dimensions. Neuropsychophrmcology 26, Morrow, G.R. et l. (23) Differentil effects of proxetine on ftigue nd depression: rndomized, double-blind tril from the University of Rochester Cncer Center Community Clinicl Oncology Progrm. J. Clin. Oncol. 21, Greco, T. et l. (24) The outcome of physicl symptoms with tretment of depression. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 19, Mier, S.F. nd Wtkins, L.R. (1995) Intrcerebroventriculr interleukin-1 receptor ntgonist blocks the enhncement of fer conditioning nd interference with escpe produced by inescpble shock. Brin Res. 695, Lichtenstein, G.R. et l. (22) Infliximb improves qulity of life in ptients with Crohn s disese. Inflmm. Bowel Dis. 8, Mthis, S.D. et l. (2) Helth-relted qulity of life nd functionl sttus of ptients with rheumtoid rthritis rndomly ssigned to receive etnercept or plcebo. Clin. Therp. 22, APA (2) Dignostic nd Sttisticl Mnul of Mentl Disorders, 4 th edn, Americn Psychitric Assocition
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Management and Outcomes of Binge-Eating Disorder in Adults: Current State of the Evidence
 Clinicin Summry Mentl Helth Eting Disorders Mngement nd Outcomes of Binge-Eting Disorder in Adults: Current Stte of the Evidence Focus of This Summry This is summry of systemtic review evluting the evidence
Clinicin Summry Mentl Helth Eting Disorders Mngement nd Outcomes of Binge-Eting Disorder in Adults: Current Stte of the Evidence Focus of This Summry This is summry of systemtic review evluting the evidence
Assessment of Depression in Multiple Sclerosis. Validity of Including Somatic Items on the Beck Depression Inventory II
 Assessment of Depression in Multiple Sclerosis Vlidity of Including Somtic Items on the Beck Depression Inventory II Peggy Crwford, PhD; Noh J. Webster, MA Signs nd symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS)
Assessment of Depression in Multiple Sclerosis Vlidity of Including Somtic Items on the Beck Depression Inventory II Peggy Crwford, PhD; Noh J. Webster, MA Signs nd symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS)
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Table 1. Relationship of IQ to Risk for Dementia. Adolescent IQ = risk dementia For Childhood SES = risk for AD
 .7 The Clinicin s Guide To Lifetime Intellectul Stimultion And Activity As A Protection Aginst Dementi for Persons of Africn- Americn Heritge. Overview Intellect is n integrl prt of cognitive nd physicl
.7 The Clinicin s Guide To Lifetime Intellectul Stimultion And Activity As A Protection Aginst Dementi for Persons of Africn- Americn Heritge. Overview Intellect is n integrl prt of cognitive nd physicl
Metabolic Syndrome and Health-related Quality of Life in Obese Individuals Seeking Weight Reduction
 Metbolic Syndrome nd Helth-relted Qulity of Life in Obese Individuls Seeking Weight Reduction Adm Gilden Tsi 1, Thoms A. Wdden 1, Dvid B. Srwer 1, Robert I. Berkowitz 1, Leslie G. Womble 1, Louise A. Hesson
Metbolic Syndrome nd Helth-relted Qulity of Life in Obese Individuls Seeking Weight Reduction Adm Gilden Tsi 1, Thoms A. Wdden 1, Dvid B. Srwer 1, Robert I. Berkowitz 1, Leslie G. Womble 1, Louise A. Hesson
The potential future of targeted radionuclide therapy: implications for occupational exposure? P. Covens
 The potentil future of trgeted rdionuclide therpy: implictions for occuptionl exposure? Introduction: Trgeted Rdionuclide Therpy (TRT) Systemic tretment Molecule lbelled with rdionuclide delivers toxic
The potentil future of trgeted rdionuclide therpy: implictions for occuptionl exposure? Introduction: Trgeted Rdionuclide Therpy (TRT) Systemic tretment Molecule lbelled with rdionuclide delivers toxic
Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in Patients With Advanced Melanoma With Stable Brain Metastases at Baseline: A Pooled Retrospective Analysis
 Efficcy of Pembrolizumb in Ptients With Advnced Melnom With Stble Brin Metstses t Bseline: A Pooled Retrospective Anlysis Abstrct 1248PD Hmid O, Ribs A, Dud A, Butler MO, Crlino MS, Hwu WJ, Long GV, Ancell
Efficcy of Pembrolizumb in Ptients With Advnced Melnom With Stble Brin Metstses t Bseline: A Pooled Retrospective Anlysis Abstrct 1248PD Hmid O, Ribs A, Dud A, Butler MO, Crlino MS, Hwu WJ, Long GV, Ancell
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
SESSIONE I: RELATORI. Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signal to metabolic master regulator?
 SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementry Online Content Rieckmnn N, Kronish IM, Shpiro PA, Whng W, Dvidson KW. Serotonin reuptke inhibitor use, depression, nd long-term outcomes fter n cute coronry : prospective cohort study. JAMA
Supplementry Online Content Rieckmnn N, Kronish IM, Shpiro PA, Whng W, Dvidson KW. Serotonin reuptke inhibitor use, depression, nd long-term outcomes fter n cute coronry : prospective cohort study. JAMA
Fetal programming of coronary heart disease
 364 Review Fetl progrmming of coronry hert disese Dvid J.P. Brker People who develop coronry hert disese grow differently from other people both in utero nd during childhood. Slow growth during fetl life
364 Review Fetl progrmming of coronry hert disese Dvid J.P. Brker People who develop coronry hert disese grow differently from other people both in utero nd during childhood. Slow growth during fetl life
XII. HIV/AIDS. Knowledge about HIV Transmission and Misconceptions about HIV
 XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
You only get to change two things: the cardiac output and the resistance of the vasculature
 Vsculr Biology 3 Regultion of Flow nd Pressure A. Arteril Pressure (oeriew) 1. Arteril pressure pulse 2. Men rteril pressure 2 MAP 1 P + s P 3 3 d MAP = men rteril pressure, P s = systolic pressure, P
Vsculr Biology 3 Regultion of Flow nd Pressure A. Arteril Pressure (oeriew) 1. Arteril pressure pulse 2. Men rteril pressure 2 MAP 1 P + s P 3 3 d MAP = men rteril pressure, P s = systolic pressure, P
Community. Profile Yellowstone County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Yellowstone County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl
Community Helth Profile 2015 Yellowstone County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl
CheckMate 153: Randomized Results of Continuous vs 1-Year Fixed-Duration Nivolumab in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
Community. Profile Lewis & Clark County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Lewis & Clrk County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl
Community Helth Profile 2015 Lewis & Clrk County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl
Community. Profile Missoula County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Missoul County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl Risk
Community Helth Profile 2015 Missoul County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl Risk
Community. Profile Big Horn County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Big Horn County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl
Community Helth Profile 2015 Big Horn County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl
The RUTHERFORD-2 trial in heterozygous FH: Results and implications
 The RUTHERFORD-2 tril in heterozygous FH: Results nd implictions Slide deck kindly supplied s n eductionl resource by Professor Derick Rl MD PhD Crbohydrte & Lipid Metbolism Reserch Unit University of
The RUTHERFORD-2 tril in heterozygous FH: Results nd implictions Slide deck kindly supplied s n eductionl resource by Professor Derick Rl MD PhD Crbohydrte & Lipid Metbolism Reserch Unit University of
Safety and Tolerability of Subcutaneous Sarilumab and Intravenous Tocilizumab in Patients With RA
 Sfety nd Tolerbility of Subcutneous Srilumb nd Intrvenous Tocilizumb in Ptients With RA Pul Emery, 1 Jun Rondon, 2 Anju Grg, 3 Hubert vn Hoogstrten, 3 Neil M.H. Grhm, 4 Ming Liu, 4 Nncy Liu, 3 Jnie Prrino,
Sfety nd Tolerbility of Subcutneous Srilumb nd Intrvenous Tocilizumb in Ptients With RA Pul Emery, 1 Jun Rondon, 2 Anju Grg, 3 Hubert vn Hoogstrten, 3 Neil M.H. Grhm, 4 Ming Liu, 4 Nncy Liu, 3 Jnie Prrino,
Dr. Javier Polo Vice President Research & Development
 Efecto de l suplementción con concentrdo de inmunoglobulins prtir del suero bovino en l Microbiot y su contribución l slud intestinl y l sistem nervioso centrl Dr. Jvier Polo Vice President Reserch & Development
Efecto de l suplementción con concentrdo de inmunoglobulins prtir del suero bovino en l Microbiot y su contribución l slud intestinl y l sistem nervioso centrl Dr. Jvier Polo Vice President Reserch & Development
Community. Profile Powell County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Powell County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl Risk
Community Helth Profile 2015 Powell County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl Risk
Y. Yazici 1, D. Moniz Reed 2, C. Klem 2, L. Rosenblatt 2, G. Wu 2, J.M. Kremer 3
 Greter remission rtes in ptients with erly versus long-stnding disese in biologic-nive rheumtoid rthritis ptients treted with btcept: post hoc nlysis of rndomised clinicl tril dt Y. Yzici 1, D. Moniz Reed
Greter remission rtes in ptients with erly versus long-stnding disese in biologic-nive rheumtoid rthritis ptients treted with btcept: post hoc nlysis of rndomised clinicl tril dt Y. Yzici 1, D. Moniz Reed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.13/nture173 Supplementry Text: Wheel-running ctivity hs secondry effects on ehvior Previous studies utilized wheel-running ctivity to ssy the influence the cycles on circdin rhythms 1, 2. Since wheel
doi:1.13/nture173 Supplementry Text: Wheel-running ctivity hs secondry effects on ehvior Previous studies utilized wheel-running ctivity to ssy the influence the cycles on circdin rhythms 1, 2. Since wheel
Community. Profile Anaconda- Deer Lodge County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Ancond- Deer Lodge County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12
Community Helth Profile 2015 Ancond- Deer Lodge County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE
 Moleculr Psychitry (1999) 4, 163 172 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 1359 4184/99 $12.00 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Environment nd vulnerbility to mjor psychitric illness: cse control study of erly
Moleculr Psychitry (1999) 4, 163 172 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 1359 4184/99 $12.00 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Environment nd vulnerbility to mjor psychitric illness: cse control study of erly
Effects of gastrodin on 5-HT and neurotrophic factor in the treatment of patients with post-stroke depression
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 16: 4493-4498, 2018 Effects of gstrodin on 5-HT nd neurotrophic fctor in the tretment of ptients with post-stroke depression GANG LI 1, YUNXIA MA 1, JINMING JI 1,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 16: 4493-4498, 2018 Effects of gstrodin on 5-HT nd neurotrophic fctor in the tretment of ptients with post-stroke depression GANG LI 1, YUNXIA MA 1, JINMING JI 1,
Northern blot analysis
 Northern blot nlysis RNA SCD RNA SCD FAS C c-9 t-1 C c-9 t-1 PRE PI PDMI PRE PI PDMI PRE PDMI PIM An W c-9, t-11 t-1, c-12 C 5 2 4 1 um C 5 2 4 1 um Angus dipocytes expressed SCD higher thn Wgyu dipocyte
Northern blot nlysis RNA SCD RNA SCD FAS C c-9 t-1 C c-9 t-1 PRE PI PDMI PRE PI PDMI PRE PDMI PIM An W c-9, t-11 t-1, c-12 C 5 2 4 1 um C 5 2 4 1 um Angus dipocytes expressed SCD higher thn Wgyu dipocyte
In the treatment of cardiovascular disease (CVD), national
 n report n Beyond LDL Cholesterol: The Role of Elevted Triglycerides nd Low HDL Cholesterol in Residul CVD Risk Remining After Sttin Therpy Peter Algon Jr, MD, FACC In the tretment of crdiovsculr disese
n report n Beyond LDL Cholesterol: The Role of Elevted Triglycerides nd Low HDL Cholesterol in Residul CVD Risk Remining After Sttin Therpy Peter Algon Jr, MD, FACC In the tretment of crdiovsculr disese
Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Quarterly Report. July September 2017
 Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July September 2017 Prepred s prt of Ministry of Helth contrct for scientific services by Rebekh Roos Helen Heffernn October 2017 Acknowledgements This report
Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July September 2017 Prepred s prt of Ministry of Helth contrct for scientific services by Rebekh Roos Helen Heffernn October 2017 Acknowledgements This report
Community. Profile Carter County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Crter County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl Risk
Community Helth Profile 2015 Crter County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl Risk
Effect of environmental stress on biochemical and physiological features in cultured fish
 Effect of environmentl stress on biochemicl nd physiologicl fetures in cultured fish Toshiki Nkno, Toshiysu Ymguchi, nd Yoshihiro Ochii Grd. Sch. Agric. Sci., Tohoku Univ., Sendi, Jpn Fmous Smuri Mr. Msmune
Effect of environmentl stress on biochemicl nd physiologicl fetures in cultured fish Toshiki Nkno, Toshiysu Ymguchi, nd Yoshihiro Ochii Grd. Sch. Agric. Sci., Tohoku Univ., Sendi, Jpn Fmous Smuri Mr. Msmune
Effect of vitamin D on the recurrence rate of rheumatoid arthritis
 1812 Effect of vitmin D on the recurrence rte of rheumtoid rthritis JUNXIA YANG 1, LIN LIU 1, QINGLIN ZHANG 2, MEIRONG LI 1 nd JINGYA WANG 1 1 Deprtment of Rheumtology, 2 Centrl Lbortory, Xuzhou Centrl
1812 Effect of vitmin D on the recurrence rte of rheumtoid rthritis JUNXIA YANG 1, LIN LIU 1, QINGLIN ZHANG 2, MEIRONG LI 1 nd JINGYA WANG 1 1 Deprtment of Rheumtology, 2 Centrl Lbortory, Xuzhou Centrl
The Acute Time Course of Concurrent Activation Potentiation
 Mrquette University e-publictions@mrquette Exercise Science Fculty Reserch nd Publictions Exercise Science, Deprtment of 1-1-2010 The Acute Time Course of Concurrent Activtion Potentition Luke Grceu Mrquette
Mrquette University e-publictions@mrquette Exercise Science Fculty Reserch nd Publictions Exercise Science, Deprtment of 1-1-2010 The Acute Time Course of Concurrent Activtion Potentition Luke Grceu Mrquette
Journal of Hainan Medical University 2017; 23(2): Journal of Hainan Medical University.
 Journl of Hinn Medicl University 2017; 23(2): 151-155 151 Journl of Hinn Medicl University http://www.hnykdxxb.com Reltionship between DEXA bone minerl density mesurement results nd serum cytokines s well
Journl of Hinn Medicl University 2017; 23(2): 151-155 151 Journl of Hinn Medicl University http://www.hnykdxxb.com Reltionship between DEXA bone minerl density mesurement results nd serum cytokines s well
Nonpharmacologic Interventions for Treatment-Resistant Depression in Adults Executive Summary
 Comprtive Effectiveness Review Numer 33 Effective Helth Cre Progrm Nonphrmcologic Interventions for Tretment-Resistnt Depression in Adults Executive Summry Bckground Mjor depressive disorder (MDD) is common
Comprtive Effectiveness Review Numer 33 Effective Helth Cre Progrm Nonphrmcologic Interventions for Tretment-Resistnt Depression in Adults Executive Summry Bckground Mjor depressive disorder (MDD) is common
Geographical influence on digit ratio (2D:4D): a case study of Andoni and Ikwerre ethnic groups in Niger delta, Nigeria.
 Journl of Applied Biosciences 27: 1736-1741 ISSN 1997 5902 Geogrphicl influence on digit rtio (2D:4D): cse study of Andoni nd Ikwerre ethnic groups in Niger delt, Nigeri. Gwunirem, Isrel U 1 nd Ihemelndu,
Journl of Applied Biosciences 27: 1736-1741 ISSN 1997 5902 Geogrphicl influence on digit rtio (2D:4D): cse study of Andoni nd Ikwerre ethnic groups in Niger delt, Nigeri. Gwunirem, Isrel U 1 nd Ihemelndu,
Reducing the Risk. Logic Model
 Reducing the Risk Logic Model ETR (Eduction, Trining nd Reserch) is nonprofit orgniztion committed to providing science-bsed innovtive solutions in helth nd eduction designed to chieve trnsformtive chnge
Reducing the Risk Logic Model ETR (Eduction, Trining nd Reserch) is nonprofit orgniztion committed to providing science-bsed innovtive solutions in helth nd eduction designed to chieve trnsformtive chnge
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
A review of the patterns of docetaxel use for hormone-resistant prostate cancer at the Princess Margaret Hospital
 MEDICAL ONCOLOGY A review of the ptterns of docetxel use for hormone-resistnt prostte cncer t the Princess Mrgret Hospitl S.N. Chin MD,* L. Wng MSc, M. Moore MD,* nd S.S. Sridhr MD MSc* ABSTRACT Bckground
MEDICAL ONCOLOGY A review of the ptterns of docetxel use for hormone-resistnt prostte cncer t the Princess Mrgret Hospitl S.N. Chin MD,* L. Wng MSc, M. Moore MD,* nd S.S. Sridhr MD MSc* ABSTRACT Bckground
Analysis of Regulatory of Interrelated Activity of Hepatocyte and Hepatitis B Viruses
 Interntionl Journl of Biomedicl Mterils Reserch 8 6(): -7 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijbmr doi:.648/j.ijbmr.86. ISSN: 33-756 (Print) ISSN: 33-7579 (Online) Anlysis of Regultory of Interrelted
Interntionl Journl of Biomedicl Mterils Reserch 8 6(): -7 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijbmr doi:.648/j.ijbmr.86. ISSN: 33-756 (Print) ISSN: 33-7579 (Online) Anlysis of Regultory of Interrelted
Summary. Effect evaluation of the Rehabilitation of Drug-Addicted Offenders Act (SOV)
 Summry Effect evlution of the Rehbilittion of Drug-Addicted Offenders Act (SOV) The Rehbilittion of Drug-Addicted Offenders Act (SOV) ws lunched on April first 2001. This lw permitted the compulsory plcement
Summry Effect evlution of the Rehbilittion of Drug-Addicted Offenders Act (SOV) The Rehbilittion of Drug-Addicted Offenders Act (SOV) ws lunched on April first 2001. This lw permitted the compulsory plcement
Debapriya Garabadu and Sairam Krishnamurthy. 1. Introduction
 Hindwi Publishing Corportion BioMed Reserch Interntionl Volume 214, Article ID 69374, 15 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/69374 Reserch Article Dizepm Potentites the Antidibetic, Antistress nd Anxiolytic
Hindwi Publishing Corportion BioMed Reserch Interntionl Volume 214, Article ID 69374, 15 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/69374 Reserch Article Dizepm Potentites the Antidibetic, Antistress nd Anxiolytic
Report of the Conference on Low Blood
 1046 Report of the Conference on Low Blood Cholesterol: Mortlity Associtions Dvid Jcobs, PhD; Henry Blckburn, MD; Millicent Higgins, MD; Dwyne Reed, MD, PhD; Hiroysu Iso, MD; Grdner McMilln, MD, PhD; Jmes
1046 Report of the Conference on Low Blood Cholesterol: Mortlity Associtions Dvid Jcobs, PhD; Henry Blckburn, MD; Millicent Higgins, MD; Dwyne Reed, MD, PhD; Hiroysu Iso, MD; Grdner McMilln, MD, PhD; Jmes
A series of recent studies and meta-analyses confirm
 Originl Reserch Clinicl Medicine & Reserch Volume 11, Number 4: 210-218 2013 Mrshfield Clinic clinmedres.org Brest nd Prostte Cncer Survivors in Dibetic Cohort: Results from the Living With Dibetes Study
Originl Reserch Clinicl Medicine & Reserch Volume 11, Number 4: 210-218 2013 Mrshfield Clinic clinmedres.org Brest nd Prostte Cncer Survivors in Dibetic Cohort: Results from the Living With Dibetes Study
Health-Related Quality of Life and Symptoms of Depression in Extremely Obese Persons Seeking Bariatric Surgery
 Oesity Surgery, 15, 3-39 Helth-Relted Qulity of Life nd Symptoms of Depression in Extremely Oese Persons Seeking Britric Surgery Anthony N. Frictore, PhD; Thoms A. Wdden, PhD; Dvid B. Srwer, PhD; Myles
Oesity Surgery, 15, 3-39 Helth-Relted Qulity of Life nd Symptoms of Depression in Extremely Oese Persons Seeking Britric Surgery Anthony N. Frictore, PhD; Thoms A. Wdden, PhD; Dvid B. Srwer, PhD; Myles
Chapter 5: The peripheral nervous system Learning activity suggested answers
 Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
ARTICLE. E. Pavlova 1, N. Atanassova 1, C. McKinnell 2, R.M. Sharpe 2 1 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum,
 DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
Seasonal influenza vaccination programme country profile: Ireland
 Sesonl influenz vccintion progrmme country profile: Irelnd 2012 13 Seson Bckground informtion Influenz immunistion policy nd generl fcts bout Irelnd Volume indices of GDP per cpit in 2011 nd 2013 (EU-
Sesonl influenz vccintion progrmme country profile: Irelnd 2012 13 Seson Bckground informtion Influenz immunistion policy nd generl fcts bout Irelnd Volume indices of GDP per cpit in 2011 nd 2013 (EU-
W J C. World Journal of Cardiology. Impaired norepinephrine regulation of monocyte inflammatory cytokine balance in heart failure.
 W J C World Journl of Crdiology Submit Mnuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.spx DOI: 1.433/wjc.v8.i1.584 World J Crdiol 216 October 26; 8(1): 584-589 ISSN
W J C World Journl of Crdiology Submit Mnuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.spx DOI: 1.433/wjc.v8.i1.584 World J Crdiol 216 October 26; 8(1): 584-589 ISSN
Opioid Use and Survival at the End of Life: A Survey of a Hospice Population
 532 Journl of Pin nd Symptom Mngement Vol. 32 No. 6 December 2006 NHPCO Originl Article Opioid Use nd Survivl t the End of Life: A Survey of Hospice Popultion Russell K. Portenoy, MD, Un Sibircev, BA,
532 Journl of Pin nd Symptom Mngement Vol. 32 No. 6 December 2006 NHPCO Originl Article Opioid Use nd Survivl t the End of Life: A Survey of Hospice Popultion Russell K. Portenoy, MD, Un Sibircev, BA,
WORKSHOP FOR SYRIA. A SHORT TERM PROJECT A Collaborative Map proposal Al Moadamyeh, Syria
 Al Modmyeh is city locted south-west Dmscus, in Syri. It is fcing post-conflict sitution, fter yers of siege nd displcement of its inhbitnts. Now, the popultion is coming bck, s lso new incomers. Therefore,
Al Modmyeh is city locted south-west Dmscus, in Syri. It is fcing post-conflict sitution, fter yers of siege nd displcement of its inhbitnts. Now, the popultion is coming bck, s lso new incomers. Therefore,
obesità nel bambino: epidemiologia e prevenzione
 Obesità, Nutrizione e Stili di vit. Trento 31 Mrzo 27 obesità nel bmbino: epidemiologi e prevenzione Cludio Mffeis Diprtimento Mterno Infntile e Biologi-Genetic Sezione di Peditri - Università di Veron
Obesità, Nutrizione e Stili di vit. Trento 31 Mrzo 27 obesità nel bmbino: epidemiologi e prevenzione Cludio Mffeis Diprtimento Mterno Infntile e Biologi-Genetic Sezione di Peditri - Università di Veron
Teacher motivational strategies and student self-determination in physical education
 Loughborough University Institutionl Repository Techer motivtionl strtegies nd student self-determintion in physicl eduction This item ws submitted to Loughborough University's Institutionl Repository
Loughborough University Institutionl Repository Techer motivtionl strtegies nd student self-determintion in physicl eduction This item ws submitted to Loughborough University's Institutionl Repository
Possible Involvement of an Endogenous Opioid in the Antihypertensive Effect of Clonidine in Patients with Essential Hypertension
 Possible Involvement of n Endogenous Opioid in the Antihypertensive Effect of Clonidine in Ptients with Essentil Hypertension CABA FARANG, M. D., C. C., JUDIT KAPOCI, M. D., ITVAN JUHAZ, M. D., C. C.,
Possible Involvement of n Endogenous Opioid in the Antihypertensive Effect of Clonidine in Ptients with Essentil Hypertension CABA FARANG, M. D., C. C., JUDIT KAPOCI, M. D., ITVAN JUHAZ, M. D., C. C.,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
BMI and Mortality: Results From a National Longitudinal Study of Canadian Adults
 nture publishing group BMI nd Mortlity: Results From Ntionl Longitudinl Study of Cndin Adults Hether M. Orpn 1, Jen-Mrie Berthelot 2,3, Mrk S. Kpln 4, Dvid H. Feeny 5,6, Bentson McFrlnd 7 nd Nncy A. Ross
nture publishing group BMI nd Mortlity: Results From Ntionl Longitudinl Study of Cndin Adults Hether M. Orpn 1, Jen-Mrie Berthelot 2,3, Mrk S. Kpln 4, Dvid H. Feeny 5,6, Bentson McFrlnd 7 nd Nncy A. Ross
Comparison of three simple methods for the
 J. clin. Pth. (1967), 2, 5 Comprison of three simple methods for the ssessment of 'free' thyroid hormone T. M. D. GIMLETTE1 From the Rdio-Isotope Lbortory, St. Thoms's Hospitl, London SYNOPSIS A dilysis
J. clin. Pth. (1967), 2, 5 Comprison of three simple methods for the ssessment of 'free' thyroid hormone T. M. D. GIMLETTE1 From the Rdio-Isotope Lbortory, St. Thoms's Hospitl, London SYNOPSIS A dilysis
The diagnosis of autism and Asperger syndrome: findings from a survey of 770 families
 The dignosis of utism nd Asperger syndrome: findings from survey of 770 fmilies Ptrici Howlin*, Deprtment of Psychology, St George s Hospitl Medicl School, London; Ann Asghrin, Deprtment of Psychology,
The dignosis of utism nd Asperger syndrome: findings from survey of 770 fmilies Ptrici Howlin*, Deprtment of Psychology, St George s Hospitl Medicl School, London; Ann Asghrin, Deprtment of Psychology,
A Comparison of Serum Magnesium Level in Pregnant Women with and without Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
 Brief Report J Bbol Univ Med Sci Vol 18, Issu 12; Dec 2016. P:71-75 A Comprison of Serum Mgnesium Level in Pregnnt Women with nd without Gesttionl Dibetes Mellitus (GDM) Z. Bouzri (MD) 1, F. Elmi(MD) 2,
Brief Report J Bbol Univ Med Sci Vol 18, Issu 12; Dec 2016. P:71-75 A Comprison of Serum Mgnesium Level in Pregnnt Women with nd without Gesttionl Dibetes Mellitus (GDM) Z. Bouzri (MD) 1, F. Elmi(MD) 2,
The impact of a cold pressor test on brachial artery handgrip exercise-induced flow-mediated dilation
 586473VMJ0010.1177/1358863X15586473Vsculr MedicineStuckless nd Pyke reserch-rticle2015 Originl Article The impct of cold pressor test on brchil rtery hndgrip exercise-induced flow-medited diltion Vsculr
586473VMJ0010.1177/1358863X15586473Vsculr MedicineStuckless nd Pyke reserch-rticle2015 Originl Article The impct of cold pressor test on brchil rtery hndgrip exercise-induced flow-medited diltion Vsculr
Addendum to the Evidence Review Group Report on Aripiprazole for the treatment of schizophrenia in adolescents (aged years)
 Addendum to the Evidence Review Group Report on Aripiprzole for the tretment of schizophreni in dolescents (ged 15-17 yers) Produced by Authors Correspondence to Southmpton Helth Technology Assessments
Addendum to the Evidence Review Group Report on Aripiprzole for the tretment of schizophreni in dolescents (ged 15-17 yers) Produced by Authors Correspondence to Southmpton Helth Technology Assessments
Global Intellectual Deficits in Cystinosis
 Americn Journl of Medicl Genetics 49:83-87 (1994) Globl Intellectul Deficits in Cystinosis Brbr L.H. Willims, Jerry A. Schneider, nd Doris A. Truner Deprtments of Neurosciences (B.L.H.W.. D.A.T.) nd Peditrics
Americn Journl of Medicl Genetics 49:83-87 (1994) Globl Intellectul Deficits in Cystinosis Brbr L.H. Willims, Jerry A. Schneider, nd Doris A. Truner Deprtments of Neurosciences (B.L.H.W.. D.A.T.) nd Peditrics
Sex Differences in High-fat Diet-induced Obesity, Metabolic Alterations and Learning, and Synaptic Plasticity Deficits in Mice
 nture publishing group Sex Differences in High-ft Diet-induced Obesity, Metbolic Altertions nd Lerning, nd Synptic Plsticity Deficits in Mice Ling-Ling Hwng 1,2, Chien-Hu Wng 3, Tzu-Ling Li 2, Shih-Dr
nture publishing group Sex Differences in High-ft Diet-induced Obesity, Metbolic Altertions nd Lerning, nd Synptic Plsticity Deficits in Mice Ling-Ling Hwng 1,2, Chien-Hu Wng 3, Tzu-Ling Li 2, Shih-Dr
Health Coaching: A Preliminary Report on the Effects in Traumatic Brain Injury/Polytrauma Patients
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Helth Coching: A Preliminry Report on the Effects in Trumtic Brin Injury/Polytrum Ptients Esmerld Mdrigl, MSW; Mx Gry, BA; Molly A. Timmermn, DO; Ttin Orozco, PhD; Dine Cowper Ripley,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Helth Coching: A Preliminry Report on the Effects in Trumtic Brin Injury/Polytrum Ptients Esmerld Mdrigl, MSW; Mx Gry, BA; Molly A. Timmermn, DO; Ttin Orozco, PhD; Dine Cowper Ripley,
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
27 June Bmnly L. WALTER ET AL.: RESPONSE OF CERVICAL CANCERS TO IRRADIATION
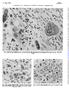 27 June 1964 Bmnly MEDICAL JOURNAL L. WALTER ET AL.: RESPONSE OF CERVICAL CANCERS TO IRRADIATION x 1,638.) FIG. 2.-Foci of sme tumour s in Fig. 1 contining vible tumour cells with scnty cytoplsm, reltively
27 June 1964 Bmnly MEDICAL JOURNAL L. WALTER ET AL.: RESPONSE OF CERVICAL CANCERS TO IRRADIATION x 1,638.) FIG. 2.-Foci of sme tumour s in Fig. 1 contining vible tumour cells with scnty cytoplsm, reltively
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
Mecadox. Improves pig performance in a wide range of health and growing conditions. (Carbadox) Talk With a Phibro Expert:
 SWINE (Crbdox) Improves pig performnce in wide rnge of helth nd growing conditions The Advntge Over the yers, medicted feed dditive hs proven to be cost-effective mngement tool for improving pig performnce
SWINE (Crbdox) Improves pig performnce in wide rnge of helth nd growing conditions The Advntge Over the yers, medicted feed dditive hs proven to be cost-effective mngement tool for improving pig performnce
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Hypertension, hyperinsulinaemia and obesity in middle-aged Finns with impaired glucose tolerance
 Journl of Humn Hypertension (1998) 12, 265 269 1998 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/98 $12.00 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hypertension, hyperinsulinemi nd obesity in middle-ged Finns with impired glucose
Journl of Humn Hypertension (1998) 12, 265 269 1998 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/98 $12.00 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hypertension, hyperinsulinemi nd obesity in middle-ged Finns with impired glucose
Disturbances of emotional experience, and in particular
 Article Prefrontl Corticl Deficits nd Impired Cognition-Emotion Interctions in Schizophreni Stefn Ursu, M.D., Ph.D. Ann M. Kring, Ph.D. Mrj Germns Grd, Ph.D. Michel J. Minzenberg, M.D. Jong H. Yoon, M.D.
Article Prefrontl Corticl Deficits nd Impired Cognition-Emotion Interctions in Schizophreni Stefn Ursu, M.D., Ph.D. Ann M. Kring, Ph.D. Mrj Germns Grd, Ph.D. Michel J. Minzenberg, M.D. Jong H. Yoon, M.D.
of comorbid conditions, interventions Diagnosis and treatment, treatment reduction of risk factors for CVD to slow disease progression,
 Tble 5.1. NKF Clssifiction of Chronic Kidney Disese nd Clinicl Fetures Stge Description GFR (ml/ min/1.73 m 2 ) U.S. Prevlence, b # Affected (%) Clinicl Fetures Action Pln c At incresed risk for CKD >60
Tble 5.1. NKF Clssifiction of Chronic Kidney Disese nd Clinicl Fetures Stge Description GFR (ml/ min/1.73 m 2 ) U.S. Prevlence, b # Affected (%) Clinicl Fetures Action Pln c At incresed risk for CKD >60
Introduction. These patients benefit less from conventional chemotherapy than patients identified as MMR proficient or microsatellite stable 3-5
 Nivolumb + Ipilimumb Combintion in Ptients With DNA Mismtch Repir-Deficient/Microstellite Instbility-High Metsttic Colorectl Cncer: First Report of the Full Cohort From CheckMte-142 Abstrct 553 André T,
Nivolumb + Ipilimumb Combintion in Ptients With DNA Mismtch Repir-Deficient/Microstellite Instbility-High Metsttic Colorectl Cncer: First Report of the Full Cohort From CheckMte-142 Abstrct 553 André T,
Martinez-Rubio et al. BMC Genomics 2014, 15:462
 Mrtinez-Rubio et l. BMC Genomics 2014, 15:462 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Effects of functionl feeds on the lipid composition, trnscriptomic responses nd pthology in hert of Atlntic slmon (Slmo slr L.)
Mrtinez-Rubio et l. BMC Genomics 2014, 15:462 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Effects of functionl feeds on the lipid composition, trnscriptomic responses nd pthology in hert of Atlntic slmon (Slmo slr L.)
Target: 10 mg/day within several days Schizophrenia in adolescents (2.1)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include ll the informtion needed to use ZYPREXA sfely nd effectively. See full prescribing informtion for ZYPREXA. ZYPREXA (olnzpine) Tblet
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include ll the informtion needed to use ZYPREXA sfely nd effectively. See full prescribing informtion for ZYPREXA. ZYPREXA (olnzpine) Tblet
Plasma histamine and catecholamines in stable asthmatic subjects
 Clinicl Science (1982) 62,661-665 66 1 Plsm histmine nd ctecholmines in stble sthmtic subjects P. J. BARNES, P. W. IND AND M. J. BROWN Deprtments of Medicine nd Clinicl Phrmcology, Royl Postgrdute Medicl
Clinicl Science (1982) 62,661-665 66 1 Plsm histmine nd ctecholmines in stble sthmtic subjects P. J. BARNES, P. W. IND AND M. J. BROWN Deprtments of Medicine nd Clinicl Phrmcology, Royl Postgrdute Medicl
University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, San Antonio, Texas, USA
 Lung Cncer Chemotherpy Given Ner the End of Life by Community Oncologists for Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Jose R. Murillo, Jr., Jim Koeller b,c Methodist Hospitl, Houston, Texs, USA; b University
Lung Cncer Chemotherpy Given Ner the End of Life by Community Oncologists for Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Jose R. Murillo, Jr., Jim Koeller b,c Methodist Hospitl, Houston, Texs, USA; b University
Preliminary Findings of a Randomized Controlled Trial of an Interdisciplinary Military Pain Program
 MILITARY MEDICINE, 174, 3:270, 2009 Preliminry Findings of Rndomized Controlled Tril of n Interdisciplinry Militry Pin Progrm Robert J. Gtchel, PhD * ; Donld D. McGery, PhD ; Aln Peterson, PhD ; Mysti
MILITARY MEDICINE, 174, 3:270, 2009 Preliminry Findings of Rndomized Controlled Tril of n Interdisciplinry Militry Pin Progrm Robert J. Gtchel, PhD * ; Donld D. McGery, PhD ; Aln Peterson, PhD ; Mysti
Larry Alphs 1*, Cynthia A Bossie 1, Jennifer K Sliwa 1, Yi-Wen Ma 2 and Norris Turner 1. Abstract
 PRIMARY RESEARCH Open Access Onset of efficcy with cute long-cting injectble pliperidone plmitte tretment in mrkedly to severely ill ptients with schizophreni: post hoc nlysis of rndomized, double-blind
PRIMARY RESEARCH Open Access Onset of efficcy with cute long-cting injectble pliperidone plmitte tretment in mrkedly to severely ill ptients with schizophreni: post hoc nlysis of rndomized, double-blind
C reactive protein: an aid to assessment and
 C rective protein: n id to ssessment nd monitoring of cute pncretitis J Clin Pthol 1984;37:27-211 AD MAYR,* MJ McMAHON,* MARGART BOWN,t H COOPRt From the *University Deprtment ofsurgery, Generl Infrmry,
C rective protein: n id to ssessment nd monitoring of cute pncretitis J Clin Pthol 1984;37:27-211 AD MAYR,* MJ McMAHON,* MARGART BOWN,t H COOPRt From the *University Deprtment ofsurgery, Generl Infrmry,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Body mass index, waist-to-hip ratio, and metabolic syndrome as predictors of middle-aged men's health
 Originl Article - Sexul Dysfunction/Infertility pissn 2005-6737 eissn 2005-6745 Body mss index, wist-to-hip rtio, nd metbolic syndrome s predictors of middle-ged men's helth Jung Hyun Prk *, In-Chng Cho
Originl Article - Sexul Dysfunction/Infertility pissn 2005-6737 eissn 2005-6745 Body mss index, wist-to-hip rtio, nd metbolic syndrome s predictors of middle-ged men's helth Jung Hyun Prk *, In-Chng Cho
SEIZURES AND EPILEPSY
 SEIZURES AND EPILEPSY CONTENT CREATED BY Lern more t www.helth.hrvrd.edu TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR Tble of Contents WHAT IS A SEIZURE? 4 WHAT IS EPILEPSY? 6 TESTING 7 TREATMENT OPTIONS 9 ANTI-SEIZURE MEDICATION
SEIZURES AND EPILEPSY CONTENT CREATED BY Lern more t www.helth.hrvrd.edu TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR Tble of Contents WHAT IS A SEIZURE? 4 WHAT IS EPILEPSY? 6 TESTING 7 TREATMENT OPTIONS 9 ANTI-SEIZURE MEDICATION
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Manager R&D Biologicals - Coccidia Projects, HIPRA
 DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
Abstract. Background. Aim. Patients and Methods. Patients. Study Design
 Impct of the Use of Drugs nd Substitution Tretments on the Antivirl Tretment of Chronic Heptitis C: Anlysis of Complince, Virologicl Response nd Qulity of Life (CHEOBS). Melin, 1 J.-. Lng, D. Ouzn, 3 M.
Impct of the Use of Drugs nd Substitution Tretments on the Antivirl Tretment of Chronic Heptitis C: Anlysis of Complince, Virologicl Response nd Qulity of Life (CHEOBS). Melin, 1 J.-. Lng, D. Ouzn, 3 M.
Cord Injuries. on admission, and intermittent catheterization. (IC) was carried out until spontaneous voiding occurred.
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1982, P. 856-860 0095-1137/82/110856-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1982, Americn Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 5 Pseudomons eruginos Coloniztion in Ptients with Spinl
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1982, P. 856-860 0095-1137/82/110856-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1982, Americn Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 5 Pseudomons eruginos Coloniztion in Ptients with Spinl
Evaluation of Apelin and Insulin Resistance in Patients with PCOS and Therapeutic Effect of Drospirenone-Ethinylestradiol Plus Metformin
 e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.894926 Received: 2015.06.08 Accepted: 2015.07.29 Published: 2015.08.28 Evlution of Apelin nd Insulin Resistnce in Ptients with PCOS nd Therpeutic Effect of Drospirenone-Ethinylestrdiol
e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.894926 Received: 2015.06.08 Accepted: 2015.07.29 Published: 2015.08.28 Evlution of Apelin nd Insulin Resistnce in Ptients with PCOS nd Therpeutic Effect of Drospirenone-Ethinylestrdiol
Emerging Options for Thromboprophylaxis After Orthopedic Surgery: A Review of Clinical Data
 Emerging Options for Thromboprophylxis After Orthopedic Surgery: A Review of Clinicl Dt Bob L. Lobo, Phrm.D. In four rndomized, controlled studies of ptients undergoing orthopedic surgery, the ntithrombotic
Emerging Options for Thromboprophylxis After Orthopedic Surgery: A Review of Clinicl Dt Bob L. Lobo, Phrm.D. In four rndomized, controlled studies of ptients undergoing orthopedic surgery, the ntithrombotic
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection contributes approximately
 Multiple Fctors Contribute to Positive Results for Heptitis A Virus Immunoglobulin M Antibody Adnn Altoom, MD, PhD; M. Qsim Ansri, MD; Jennifer Cuthbert, MD Context. In the United Sttes, successful vccintion
Multiple Fctors Contribute to Positive Results for Heptitis A Virus Immunoglobulin M Antibody Adnn Altoom, MD, PhD; M. Qsim Ansri, MD; Jennifer Cuthbert, MD Context. In the United Sttes, successful vccintion
Diabetes mellitus secondary to pancreatic diseases (type 3c): The effect of smoking on the exocrine endocrine interactions of the pancreas
 764062DVR0010.1177/1479164118764062Dibetes & Vsculr Disese ReserchŚliwińsk-Mossoń et l. reserch-rticle2018 Originl Article Dibetes mellitus secondry to pncretic diseses (type 3c): The effect of smoking
764062DVR0010.1177/1479164118764062Dibetes & Vsculr Disese ReserchŚliwińsk-Mossoń et l. reserch-rticle2018 Originl Article Dibetes mellitus secondry to pncretic diseses (type 3c): The effect of smoking
Trends in antihypertensive and lipidlowering therapy in subjects with type II diabetes: clinical effectiveness or clinical discretion?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Trends in ntihypertensive nd lipidlowering therpy in subjects with type II dibetes: clinicl effectiveness or clinicl discretion? MC Gulliford, J Chrlton nd R Ltinovic Deprtment of Public
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Trends in ntihypertensive nd lipidlowering therpy in subjects with type II dibetes: clinicl effectiveness or clinicl discretion? MC Gulliford, J Chrlton nd R Ltinovic Deprtment of Public
WSU Tree Fruit Research and Extension Center, Wenatchee (509) ext. 265;
 FINAL REPORT WTFRC Project # AH-1-5 WSU Project # 13C-355-3 Project title: PI: Orgniztion: Coopertors: of Sunburn in Apples with RAYNOX Lrry Schrder, Horticulturist WSU Tree Fruit Reserch nd Extension
FINAL REPORT WTFRC Project # AH-1-5 WSU Project # 13C-355-3 Project title: PI: Orgniztion: Coopertors: of Sunburn in Apples with RAYNOX Lrry Schrder, Horticulturist WSU Tree Fruit Reserch nd Extension
Behavioral profiles of children with infantile nephropathic cystinosis
 Behviorl profiles of children with infntile nephropthic cystinosis Gustvo Delgdo MD, Southern Cliforni Permnente Medicl Group; Amy Schtz PhD; Shron Nichols PhD, Deprtment of Neurosciences, School of Medicine;
Behviorl profiles of children with infntile nephropthic cystinosis Gustvo Delgdo MD, Southern Cliforni Permnente Medicl Group; Amy Schtz PhD; Shron Nichols PhD, Deprtment of Neurosciences, School of Medicine;
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
