Aqueous Bark Extract of Cinnamomum Zeylanicum: A Potential Therapeutic Agent for Streptozotocin- Induced Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) Rats
|
|
|
- Job Carroll
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Halder et al Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research June 2012; 11 (3): Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, Nigeria. All rights reserved. Research Article Available online at Aqueous Bark Extract of Cinnamomum Zeylanicum: A Potential Therapeutic Agent for Streptozotocin- Induced Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) Rats Syed A Hassan 1*, Ritu Barthwal 2, Maya S Nair 2 and Syed S Haque 1 Department of Biotechnology, Institute of Life Sciences, University of Hyderabad Campus, Hyderabad, 2 Molecular Biophysics Laboratory, Department of Biotechnology, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee, 3 Department of Clinical Biochemistry, Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna, India. Abstract Purpose: To investigate the anti-diabetic, hepatoprotective and lipid homeostatic activity of Cinnamomum zeylanicum aqueous bark extract on streptozotocin (STZ)-induced type-i diabetic rats. Methods: The animals were divided into three groups (n = 6). of normal rats; streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats; and diabetic rats treated with 200 mg/kg of the aqueous bark extract, respectively. Treatment was via the oral route for 15 days. Various biochemical parameters, including lipid profile and glycogen biosynthesis were analysed. Similarly, differential regulation and expression of glucose homeostatic enzymes were evaluated in order to validate the anti-diabetic activity of the extract. Results: Total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), LDL-cholesterol (LDL) and VLDL-cholesterol (VLDL) levels decreased significantly (p < 0.05) in the diabetic animals by 12.5, 23.86, and 20 %, respectively, compared to their initial values. The extract increased HDL-cholesterol (HDL) and tissue glycogen levels by 25.0 and %, respectively, in diabetic rats. Similarly, differential regulation and expression of glucose homeostatic enzymes, namely, glucokinase (GK), glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase), phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6- PDH) and Insulin II (Ins II), showed significant improvement upon extract treatment in STZ-induced diabetic rats. Conclusion: These results demonstrate the anti-diabetic, and hypolipidemic activities of Cinnamomum zeylanicum aqueous bark extract in diabetic rats. Keywords: Streptozotocin, Type 1 diabetes mellitus, Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Glucose homeostasis, Hypoglycemia, Lipid homeostasis. Received: 31 August 2011 Revised accepted: 23 April 2012 *Corresponding author: asif_srmcbt@yahoo.com; Tel: Trop J Pharm Res, June 2012;11 (3): 429
2 INTRODUCTION During the last decades of the 20 th century, there was an increase in the incidence of Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) with several million people already affected around the globe. A variety of factors, ranging from immune dysregulation to environmental triggers have been suggested as contributing to this increasing trend [1,2]. In spite of the introduction of new potential treatments, diabetes and related complications continue to be a major medical problem. The possibility of strong side effects associated with the current pre-clinical protocols developed in rodents is a major concern and unacceptable in humans [3]. Recently, the role of herbal remedies has come into focus due to the side effects associated with current protocols in the treatment and containment of diabetes and its associated complications. More than 400 plants with glucose-lowering effects are known in India [4], some of which have been tested and their active components are being isolated. Thus, there is continuing search for new anti-diabetic drugs. Cinnamon is one of the traditional herbs used as a remedy for diabetes. Cinnamon tree (Cinnamomum zeylanicum B. Lauraceae) is a native of South-west Asia, including Sri Lanka, and the bark is sold in powder, scrapings and branches. Cinnamon extract has also been shown to enhance glucose utilization in vivo in a dose-dependent manner, as well as potentiates insulinstimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of IR-β, insulin receptor-1 (IRS-1) and Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) association with phosphotidyl inositol-3 kinase (PI 3-kinase), without affecting their protein content in skeletal muscle [5]. Cinnamon extract has a regulatory role in a type-2 diabetic animal model (C57BIKsj db/db). It was found to reduce blood glucose in a dose-dependent manner, as well as triglyceride, total cholesterol and intestinal α- glycosidase activity, but enhances serum insulin and HDL-cholesterol levels. It also shows blood glucose-suppressing effect by improving insulin sensitivity or slowing absorption of carbohydrates in the small intestine [6]. Widespread achievement of therapeutic glycemic targets remains an elusive goal for type-1 diabetic subjects. To date, only one study of the role of cinnamon in glycemic control among adolescents with type-1 diabetes has been reported [7]. In this context, the aim of the present study was to investigate new and strong evidence of the hypolipidemic and anti-diabetic activity of Cinnamomum zeylanicum aqueous bark extract in STZ-induced type-1 diabetic rats. EXPERIMENTAL Plant material Cinnamon bark was purchased from an ayurvedic store in Kannur, Kerala, India in December The plant material was identified as per Auyervada literature, by a local expert in herbal gardens, and confirmed by Dr. H.S. Dhaliwal, Professor of Plant Biotechnology, Department of Biotechnology, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, India. Preparation of the bark extract Cinnamon bark (~500 g) was thoroughly powdered and kept airtight in cool, dry and dark conditions. Approximately 50 g was placed in a soxhlet apparatus and extracted in aqueous medium for 60 h. The extract was concentrated in a rotary evaporator at reduced pressure to give a yield of 10 % which was then lyophilized (ScanVac CoolSafe Freeze Drying Tm ) and used for further studies. Experimental animals The study was conducted on 26 male Wistar rats, 8-10 weeks old, weighing g, and purchased from the animal facility centre Trop J Pharm Res, June 2012;11 (3): 430
3 at NIPER, Chandigarh, India. They were housed in colony cages (maximum 5 rats/cage) at an ambient temperature of 25 ± 2 C with 12 h/12 h light/dark cycle. The rats were fed normal diet purchased from commercial vendors and were randomly divided into three groups (n = 6): Group 1 (untreated, control); Group 2 (streptozotocininduced diabetic); and Group 3 streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats treated with the extract. The rats were acclimatized for a period of a further 2-3 weeks in the new environment prior to initiation of the experiment. The animals were deprived of food at least 16 h but were allowed free access to drinking water. All the experiments were performed as per the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee which also gave approval for the tests (registration number: 563/02/a/CPCSEA), and the national guidelines of Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals, as applicable. The animals were handled according to the standard protocols for the use of laboratory animals [8]. Induction of diabetes mellitus A freshly prepared solution of streptozotocin (65 mg/kg body weight) in 0.1M citrate buffer (ph 4.5) was injected intraperitoneally to the overnight fasted rats. The rats in the control group were injected with sodium citrate buffer (vehicle). Fasting blood glucose (FBG) was evaluated at the time of induction of diabetes while postprandial glucose (PPG) was checked regularly until stable hyperglycemia was achieved. The rats having marked hyperglycemia (FBG > 250 mg/dl) were selected for the study as stable hyperglycemic animals [9]. Serum preparation Serum was prepared following routine procedure. Briefly, blood samples were withdrawn from retro orbital sinus using nonheparinised capillary tubes, collected in dried centrifuge tubes and allowed to clot. Serum was separated from the clot by centrifugation for five min at 800 x g in a fixed rotor centrifuge at room temperature. The serum was collected carefully using a Pasteur pipette and kept at -20 C until enzyme analysis. Determination of lipid profile and tissue glycogen Total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and triglyceride (TG) levels in serum were determined according to the instructions of the manufacturer (Transasia Bio Medical Limited, Himachal Pradesh, India). For the determination of very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) and low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, Friedwald s formulae was used which gives: VLDL cholesterol as triglyceride/5, and LDL cholesterol as total cholesterol (VLDL + HDL cholesterol). The assessment of tissue glycogen from liver was carried out by the method of Sadasivam [10]. The liver was homogenized in hot 80 % ethanol to a tissue concentration of 100 mg/ml and then centrifuged at 8000 x g for 20 min. The residue was collected and allowed to dry over a hot water bath. To the residue, 5 ml of distilled water and 6 ml of 52 % perchloric acid was added, and the mixture subjected to extraction at 0 o C for 20 min. The mixture was centrifuged at 8000 x g for 15 min. The supernatant (0.2 ml) was transferred to a graduated test tube and the volume made up to 1ml with distilled water. Graded standards were prepared using 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1.0 ml of the working standard and the volume of each of these made up to 1ml with distilled water. To each of the test tubes, 4 ml of anthrone reagent was added. The tubes were heated in a boiling water bath and then allowed to cool to room temperature. The intensity of the green to dark green colour of the solution generated was recorded spectrophotometrically at 630 nm. The amount of glycogen was computed from calibration (standard) curve derived from standard glucose solution. The amount of glycogen in the tissue sample was expressed in µg/mg tissue. Trop J Pharm Res, June 2012;11 (3): 431
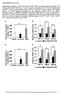
4 Semi-quantitative reverse transcriptasepolymerase chain reaction RT PCR Total RNA were extracted from treated and diabetic rat liver and pancreas, respectively using GenElute TM Mammalian Total RNA Miniprep Kit (Sigma-Aldrich, U.S.A). The isolated RNA samples were quantified, equal amounts of which were reverse transcribed with the aid of the RT PCR kit (Bangalore Genei, Bangalore, India) according to manufacturer s instructions. PCR was performed by denaturing at 94 C for 60 s, annealing at various temperatures (depending on primer pairs) and by extension at 72 C for 60 s; 35 additional cycles were used for amplification. The primer pairs used for analysis were: GK-F5 -CAGACAGTC- CTCACCTGCAA-3,GK-R5 TTTGTCTTCAC- GCTCCACTG-3 ;G6Pase-F5 -ACCCTGGTA- GCCCTGTCTTT-3, G6Pase-R5 -ACTCATT- ACACGGGCTGGTC-3 ; Ins II-F5 -CTGTG- GATCCGCTTCCTG-3,Ins II-R5 -AGAGAGA- GCAGATGCTGGTG-3 ; PEPCK-F5 -ATACG- GTGGGAACTCACTGC-3,PEPCK-R5 -ACC- CCCATCACTTGTCTCAG-3 ; Gapdh-F5 - AGACAGCCGCATCTTCTTGT-3, Gapdh- R5 -TACTCAGCACCAGCATCACC-3. PCR product of β-actin gene, using β-actin-f5 - CAGCGGAACCGCTCATTGCCAATGG-3, β- Actin-R5 -TCACCCACACTGTGCCCCATCT- ACGA-3 primers, was used as internal standard. The PCR products were then separated on 2 % agarose gel and visualized in a gel documentation system (Bio Rad, USA). The intensity of the bands on gels was converted into a digital image with a gel analyzer. Statistical analysis All values are presented as mean ± SEM (standard error of mean). Statistical significance was evaluated by independent two-population t-test using Origin software (Origin Lab Corporation, USA), version 6.1. P < 0.05 was taken as indicative of significant difference. RESULTS Lipid profile There was a significant reduction (p <0.05) of 12.5, 23.86, and 20 % in TC, TG, LDLcholesterol and VDL-cholesterol levels, respectively, whereas a significant (p <0.05) increase of HLD-cholesterol in diabetic rats by 25 %, as compared to their initial values (Table 1). Glycogen level in liver Tissue glycogen content showed a significant increase (p < 0.05) of %, after oral administration of the extract in STZ-induced diabetic rats (Table 1). Gene expression profile As shown in Fig. 1, a marked change in Table 1: Serum lipid levels and tissue glycogen content following administration of C. zeylanicum aqueous bark extract to streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Group TC (mg/dl) Normal 141±3.8 HDLC (mg/dl) Serum lipid level Tissue glycogen content (µg/g) LDL TG VLDL (mg/dl) (mg/dl) (mg/dl) 78± ±3.7 23± ± ±2.1 Diabetic 208± ± ±7.2 35± ± ±1.5 Treated 182±4.7* 25±3.8* 134±6.6* 28±0.6* 44.3±3.4* 32.0±2.8* Each value is mean S.E.M., n = 6; * statistically significant different compared to diabetic group (p < 0.05). Trop J Pharm Res, June 2012;11 (3): 432
5 expression profile of mrna for all the glucose hepatic regulatory enzymes was observed in diabetic treated groups (Group 3). The hepatic level of glucokinase and glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase increased 2-fold in treated diabetic rats while pancreatic insulin II expression increased several-fold, compared to untreated diabetic rats. Furthermore, there was a clear reduction in the expression patterns of gluconeogenic enzymes, G6Pase and PEPCK, by almost 2-fold, compared to diabetic rats (Group 2). In contrast, hepatic β- Actin showed uniform expression in all the groups - normal, diabetic and treated animals. Fig 1: RT-PCR analysis of (A) liver mrna expression of alpha actin, (B) liver mrna expression of glucokinase, (C) liver mrna expression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, (D) liver mrna expression of glucose-6-phosphatase, (E) liver mrna expression of phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase, and (F) pancreas mrna expression of Insulin II, before and after treatment of extract in diabetic rats. Note: M, N, D and T denote DNA ladder, normal, diabetic and treated diabetic samples of RNA from liver and pancreas, respectively DISCUSSION Streptozotocin has been shown to induce free radical production and cause tissue injury. The pancreas is especially susceptible to the action of streptozotocin-induced free radical damage. It was reported earlier that cinnamon extract is capable of acting as a free radical scavenger in vitro [11]. A single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (65 mg/kg) induced damage that mimicked insulin-dependent diabetic (T1DM) conditions to a great extent. The present study was designed to determine the lipid profile, tissue glycogen content and glycolytic, gluconeogenic gene expression profile in both diabetic (control) and treated rats. In order to understand the molecular mechanism of action of Cinnamomum zeylanicum aqueous extract as antidiabetogenic agent, the expression level of glucokinase, glucose-6-phosphatase, glucose -6-phosphate dehydrogenase, Insulin II and phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase was analyzed. These enzymes are directly linked to glucose homeostasis and production of glycogen. Glucokinase is involved in the phosphorylation step of glucose during glycolysis. This enzyme was significantly reduced in the liver of diabetic rats and this may be the reason for the decrease in the utilization of glucose and increased blood glucose level [12]. The extract-treated diabetic rats showed increased activity of glucokinase that may lead to activation of glycolysis and increased utilization of glucose for energy production. Glucokinase that that leads to a reduction in the expression of G6Pase and PEPCK in response to extract treatment provides an additional clue to its role in carbohydrate metabolism [13]. The extract-treated diabetic rats showed increased expression of insulin II, compared to diabetic control. This is another possible reason for the normal blood glucose levels in extract-treated diabetic group. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6- PDH) is the key enzyme for maintaining normal blood sugar level. Streptozotocininduced type-1 diabetes also develops due to reduction of G-6-PDH activity in the liver which obstructs glucose utilization via pentose phosphate pathway as this enzyme activity is under insulin stimulation [14]. The Trop J Pharm Res, June 2012;11 (3): 433
6 expression of G-6-PDH increased after oral administration of the extract. These results clearly show the vibrant role of the extract in restoring the glucose homeostasis in STZinduced diabetic rats. Cardiovascular diseases are listed as the cause of death in 65 % of people suffering from diabetes [15]. Since lipid abnormalities accompanied with premature atherosclerosis are the major cause of cardiovascular diseases in diabetic patients, an ideal treatment for diabetes, in addition to glycemic control, should seek to achueve a favorable lipid profile. There was a significant decrease in TC, LDL, VLDL and TG levels as well as enhancement of the cardioprotective lipid, HDL, by 25 % in diabetic rats following extract treatment (Table 1). Increase in HDLcholesterol is associated with a decrease in coronary risk and most of the drugs that decrease total cholesterol also decrease HDL-cholesterol [16]. In the present study, the extract not only decreased total cholesterol but also enhanced HDLcholesterol significantly. High levels of TC and, more importantly, LDL cholesterol are major coronary risk factors [17]. Administration of the extract to diabetic rats lowered TC and LDL cholesterol by 12.5 and 15 %, respectively. This is remarkable as diabetes is associated with coronary complications which constitute the major cause of morbidity and deaths in diabetic subjects. Biochemical studies suggest that TG itself is independently related to coronary heart disease [18] and most of the antihypercholesterolemic drugs do not decrease TG levels but the extract lowered it by 23.9 % after treatment. The level of glycemic control is the major determinant of very low density lipoprotein and triglyceride concentrations [19]; improved glycemic control following extract treatment also resulted in decreased levels of serum VLDL and total triglyceride. This progressive change in lipid profile of the treated diabetic rats sheds some light on the mode of action of the extract as a positive stimulator of lipid homeostasis in streptozotocin-induced type-i diabetic rats. Glycogen is the primary intracellular storable form of glucose and its levels in liver is a direct reflection of insulin activity. Since streptozotocin causes selective destruction of β-cells of islets of Langerhans, resulting in marked decrease in insulin levels, it could be predicted that glycogen levels in liver decrease as the influx of glucose in the liver is inhibited in the absence of insulin [20]. Our study showed that the extract significantly improved hepatic glycogen levels in treated diabetic rats. This suggest thats one of the possible ways the extract exerts its effect is by improving the process of glycogenesis in liver. CONCLUSION The aqueous bark extract of C. zeylanicum exhibits strong hypolipidemic activity in addition to its role in glucose homeostasis in diabetic animals. We believe that our findings brings forth new and strong evidence that the bark extract, if used as a glucose homeostatic agent, may also reverse dyslipidemia associated with type-1 diabetes and prevent cardiovascular complications which are prevalent in diabetic patients. Thus, there is need for further investigation of this extract with a view to the development of potent phytomedicine for type-1 diabetes mellitus from Cinnamomum zeylanicum. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Financial assistance to one of the authors, Syed Asif Hassan, in the form of a research fellowship from Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India, is gratefully acknowledged. REFERENCES 1. Gale EA. Spring harvest? Reflections on the rise of Type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2005; 48: Trop J Pharm Res, June 2012;11 (3): 434
7 2. Peng H, Hagopian W. Environmental factors in the development of Type 1 diabetes. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2006; 7: Von Herrath MG, Nepom GT. Lost in translation: barriers to implementing clinical immunotherapeutics for autoimmunity. J Exp Med 2005; 202 (9): Grover JK, Yadav S, Vats V. Medicinal plants of India with anti-diabetic potential. J Ethnopharmacol 2002; 81: Qin B, Nagasaki M, Ren M, Bajotto G, Oshida Y, Sato Y. Cinnamon extract (traditional herb) potentiates in vivo insulin regulated glucose utilization via enhancing insulin signaling in rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pr 2003; 62: Kim HSH, Choung SY. Anti-diabetic effect of cinnamon extract on blood glucose in db/db rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2006; 104: Justin AA, Samuel JC, Todd AM, Kevin MC. The Effect of Cinnamon on A1C among Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007; 30: National Institute of Health, USA. Public health service policy on humane care and use of laboratory animals; Kenneth KW, Youming H. Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Models UNIT 5.47 in Mice and Rats, Current Protocols in Pharmacology, 2008; Sadasivam S, Manikam A. Carbohydrates. In: Sadasivam S; Manickam A. Methods in biochemistry. New Delhi: New Age International Pvt. Ltd. 1996; pp Mathew S, Abraham TE. Studies on the antioxidant activities of cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum) bark extracts, through various in vitro models. Food Chem 2006; 94: Vestergaard H. Studies of gene expression and activity of hexokinase, phosphofructokinase and glycogen synthase in human skeletal muscle in states of altered insulin-stimulated glucose metabolism. Dan Med Bull 1999; 46: Bhavna S, Viswanath G, Rajani S, Partha R. Effects of flavonoid-rich extract from seeds of Eugenia jambolana (L.), on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in diabetic mice Food Chem 2008; 110: Ugochukw, NH, Babady N.E. Antihyperglycemic effect of aqueous and ethanolic extract of Gongronema latifolium leaves on glucose and glycogen metabolism in liver of normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Life Sci 2003; 73: Geiss LS, Herman WH, Smith PJ. Diabetes in America. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda; pp Wilson PWF. High density lipoprotein, low density lipoprotein and coronary heart disease. Am J Cardiol 1990; 66: 7A 10A. 17. National Cholesterol Education Program Expert Panel. Second report of the expert panel on detection, evaluation and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults Circulation. 1994; 89: Bainton D, Miller NE, Botton CH, Yarnell JWG, Suretman PM, Baker IA, Lewis B, Elwood PC. Plasma triglycerides and high density Lipoprotein cholesterol as predictors of ischemic heart disease in British man. Brit Heart J 1992; 68: Taskinen MR. Beltz WF, Harper I. Effects of noninsulin dependent diabetes mellitus on VLDL triglyceride and apolipoprotein B metabolism: studies before and after sulfonylurea therapy. Diabetes 1986; 35: Golden S, Wals PA, Okakima F. Glycogen synthesis by hepatocytes from diabetic rats. Biochem J 1979; 182 (3): Trop J Pharm Res, June 2012;11 (3): 435
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
Metabolic integration and Regulation
 Metabolic integration and Regulation 109700: Graduate Biochemistry Trimester 2/2016 Assistant Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla kpanida@sut.ac.th School of Chemistry Suranaree University of Technology 1 Overview
Metabolic integration and Regulation 109700: Graduate Biochemistry Trimester 2/2016 Assistant Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla kpanida@sut.ac.th School of Chemistry Suranaree University of Technology 1 Overview
Ebrahim Abbasi Oshaghi 1,2
 1 2 Flaxseed normalized antioxidant status and also changed ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes expression in diabetic rat Fatemeh Mirzaei 1,Mona Pourjafarr 1, Seyyed Alireza Vafaei 1, Rezvan Mostoli 1, Ebrahim Abbasi
1 2 Flaxseed normalized antioxidant status and also changed ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes expression in diabetic rat Fatemeh Mirzaei 1,Mona Pourjafarr 1, Seyyed Alireza Vafaei 1, Rezvan Mostoli 1, Ebrahim Abbasi
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2009) I VESTIGATIO OF A TIHYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF MORUS IGRA O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I STREPTOZOTOCI DIABETIC RATS
 I VESTIGATIO OF A TIHYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF MORUS IGRA O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I STREPTOZOTOCI DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2, Ahmad R. Gohari 2*, Mojgan Yazdanpanah 2, Abbass
I VESTIGATIO OF A TIHYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF MORUS IGRA O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I STREPTOZOTOCI DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2, Ahmad R. Gohari 2*, Mojgan Yazdanpanah 2, Abbass
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2009) Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Gliclazide and Mexiletine in Rats
 Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Gliclazide and Mexiletine in Rats K. Abedulla Khan 1, S. Satyanarayana 2, K. Eswar Kumar 2, K. Pavan Kumar 1, K. Anupama 1 1 Sultan-ul-uloom College of pharmacy, Banjarahills,
Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Gliclazide and Mexiletine in Rats K. Abedulla Khan 1, S. Satyanarayana 2, K. Eswar Kumar 2, K. Pavan Kumar 1, K. Anupama 1 1 Sultan-ul-uloom College of pharmacy, Banjarahills,
What systems are involved in homeostatic regulation (give an example)?
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
GLYCOGEN BEFORE THE LAB YOU HAVE TO READ ABOUT:
 GLYCGEN BEFRE THE LAB YU HAVE T READ ABUT:. Glycogen structure. 2. Glycogen synthesis and degradation (reactions with structural formulas and enzymes). 3. The role of glycogen in liver and muscles. INTRDUCTIN
GLYCGEN BEFRE THE LAB YU HAVE T READ ABUT:. Glycogen structure. 2. Glycogen synthesis and degradation (reactions with structural formulas and enzymes). 3. The role of glycogen in liver and muscles. INTRDUCTIN
EVALUATION OF ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF TRIUMFETTA PILOSA ROTH IN STREPTOZOTOCIN- INDUCED DIABETIC RATS
 EVALUATION OF ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF TRIUMFETTA PILOSA ROTH IN STREPTOZOTOCIN- INDUCED DIABETIC RATS * D Ramakrishna 1, G Vidyasagar 2, K Pavan Kumar 1, I Madhusudhana Reddy 3, VSS S Gupta Atyam 4 1
EVALUATION OF ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF TRIUMFETTA PILOSA ROTH IN STREPTOZOTOCIN- INDUCED DIABETIC RATS * D Ramakrishna 1, G Vidyasagar 2, K Pavan Kumar 1, I Madhusudhana Reddy 3, VSS S Gupta Atyam 4 1
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies
 Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies Gene symbol Forward primer Reverse primer ACC1 5'-TGAGGAGGACCGCATTTATC 5'-GCATGGAATGGCAGTAAGGT ACLY 5'-GACACCATCTGTGATCTTG
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies Gene symbol Forward primer Reverse primer ACC1 5'-TGAGGAGGACCGCATTTATC 5'-GCATGGAATGGCAGTAAGGT ACLY 5'-GACACCATCTGTGATCTTG
2.5% of all deaths globally each year. 7th leading cause of death by % of people with diabetes live in low and middle income countries
 Lipid Disorders in Diabetes (Diabetic Dyslipidemia) Khosrow Adeli PhD, FCACB, DABCC Head and Professor, Clinical Biochemistry, The Hospital for Sick Children, University it of Toronto Diabetes A Global
Lipid Disorders in Diabetes (Diabetic Dyslipidemia) Khosrow Adeli PhD, FCACB, DABCC Head and Professor, Clinical Biochemistry, The Hospital for Sick Children, University it of Toronto Diabetes A Global
ANTIHYPERGLYCEMIC ACTIVITY OF METHANOLIC EXTRACT OF MADHUCA LONGIFOLIA BARK
 1 Departments of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, 2 Pharmacology, 3 Pharmacognosy B. Pharmacy College, Rampura, Kakanpur, Godhara, Dist. Panchmahal, Gujarat, India Original Research Article Received: July 9,
1 Departments of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, 2 Pharmacology, 3 Pharmacognosy B. Pharmacy College, Rampura, Kakanpur, Godhara, Dist. Panchmahal, Gujarat, India Original Research Article Received: July 9,
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics
 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.3 Issue 4 Oct-Dec-2014 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access Anti-diabetic
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.3 Issue 4 Oct-Dec-2014 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access Anti-diabetic
Antihyperglycemic Activity of Trianthema Portulacastrum Plant in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats
 Antihyperglycemic Activity of Trianthema Portulacastrum Plant in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats A. Shyam Sunder a *, G. Rajyalakshmi b, A. Bharath b, and Y. Rajeshwar a a S.R. College of Pharmacy,
Antihyperglycemic Activity of Trianthema Portulacastrum Plant in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats A. Shyam Sunder a *, G. Rajyalakshmi b, A. Bharath b, and Y. Rajeshwar a a S.R. College of Pharmacy,
Clinical abstracts. Diabetes
 Clinical abstracts Diabetes Antidiabetic Activity Of Aloes: Preliminary Clinical & Experimental Observations Ghannam N; Kingston M; Al-Meshaal IA; Tariq M; Parman NS; Woodhouse N Horm Res 24(4):288-94
Clinical abstracts Diabetes Antidiabetic Activity Of Aloes: Preliminary Clinical & Experimental Observations Ghannam N; Kingston M; Al-Meshaal IA; Tariq M; Parman NS; Woodhouse N Horm Res 24(4):288-94
18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM. Pancreatic secretions ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Insulin
 18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM ISLETS OF LANGERHANS Some pancreatic functions have already been discussed in the digestion section. In this one, the emphasis will be placed on the endocrine function
18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM ISLETS OF LANGERHANS Some pancreatic functions have already been discussed in the digestion section. In this one, the emphasis will be placed on the endocrine function
Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Integration of Metabolism
 Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN-C THERAPY ON HYPERGLYCEMIA, HYPERLIPIDEMIA AND NON HIGH DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN LEVEL IN TYPE 2 DIABETES
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2013 Varikasuvu Seshadri Reddy et al., 2013 Review Article ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 2, No. 1, January 2013 2013 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN-C
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2013 Varikasuvu Seshadri Reddy et al., 2013 Review Article ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 2, No. 1, January 2013 2013 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN-C
HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTION OF THE FLAVONOID FRACTION OF ARTOCARPUS HETEROPHYLLUS LEAF
 42 Research Paper ISSN 0189-6016 2006 Afr. J. Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines www.africanethnomedicines.net HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTION OF THE FLAVONOID FRACTION OF ARTOCARPUS HETEROPHYLLUS
42 Research Paper ISSN 0189-6016 2006 Afr. J. Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines www.africanethnomedicines.net HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTION OF THE FLAVONOID FRACTION OF ARTOCARPUS HETEROPHYLLUS
Effects of Shaddock (Citrus maxima) Fruit Juice on Glucose Tolerance and Lipid Profile in Type-II Diabetic Rats
 Chem Sci Trans., 2013, 2(1), 19-24 Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2013.244 ISSN/E-ISSN: 2278-3458/2278-3318 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effects of Shaddock (Citrus maxima) Fruit Juice on Glucose Tolerance
Chem Sci Trans., 2013, 2(1), 19-24 Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2013.244 ISSN/E-ISSN: 2278-3458/2278-3318 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effects of Shaddock (Citrus maxima) Fruit Juice on Glucose Tolerance
Multiple choice: Circle the best answer on this exam. There are 12 multiple choice questions, each question is worth 3 points.
 CHEM 4420 Exam 4 Spring 2015 Dr. Stone Page 1 of 6 Name Use complete sentences when requested. There are 120 possible points on this exam. Therefore there are 20 bonus points. Multiple choice: Circle the
CHEM 4420 Exam 4 Spring 2015 Dr. Stone Page 1 of 6 Name Use complete sentences when requested. There are 120 possible points on this exam. Therefore there are 20 bonus points. Multiple choice: Circle the
Anti diabetic activity of Zizipus mauritiana Lam. In streptozotocin induced Diabetic Rats and its comparison with some standard flavonoids
 Research Paper Anti diabetic activity of Lam. In streptozotocin induced Diabetic Rats and its comparison with some standard flavonoids Bhargava Amit * and Rana A.C. 1 *B. N. College of Pharmacy, Udaipur
Research Paper Anti diabetic activity of Lam. In streptozotocin induced Diabetic Rats and its comparison with some standard flavonoids Bhargava Amit * and Rana A.C. 1 *B. N. College of Pharmacy, Udaipur
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences REVIEW ARTICLE PHARMACOLOGY A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON THE ANTIDIABETIC EFFECT OF NELUMBO NUCIFERA AND GLIMEPIRIDE IN STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS POLURU
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences REVIEW ARTICLE PHARMACOLOGY A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON THE ANTIDIABETIC EFFECT OF NELUMBO NUCIFERA AND GLIMEPIRIDE IN STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS POLURU
Plasma fibrinogen level, BMI and lipid profile in type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertension
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
Open Access RESEARCH. Danish Ahmed 1*, Vikas Kumar 1, Amita Verma 1, Girija Shankar Shukla 3 and Manju Sharma 2,4*
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1059-7 RESEARCH Antidiabetic, antioxidant, antihyperlipidemic effect of extract of Euryale ferox salisb. with enhanced histopathology of pancreas, liver and kidney in streptozotocin
DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1059-7 RESEARCH Antidiabetic, antioxidant, antihyperlipidemic effect of extract of Euryale ferox salisb. with enhanced histopathology of pancreas, liver and kidney in streptozotocin
METABOLISM CATABOLIC Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins
 Index: - Overview: Catabolism and Anabolism. Few concepts:, NADPH. - Overview: Metabolism glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. - Table summary: Principal anabolic and catabolic pathways, and their main
Index: - Overview: Catabolism and Anabolism. Few concepts:, NADPH. - Overview: Metabolism glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. - Table summary: Principal anabolic and catabolic pathways, and their main
al, JGTPS, 2015, Vol. 6(4):
 ISSN- 2230-7346 Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com PHARMACOGNOSTICAL AND PHYTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF AEGLEE MARMELOS FOR ANTI DIABETIC ACTIVITY ABSTRACT Suresh
ISSN- 2230-7346 Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com PHARMACOGNOSTICAL AND PHYTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF AEGLEE MARMELOS FOR ANTI DIABETIC ACTIVITY ABSTRACT Suresh
BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes
 BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is, after heart disease and cancer, the third leading cause of death in the west. Insulin is either not secreted in sufficient
BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is, after heart disease and cancer, the third leading cause of death in the west. Insulin is either not secreted in sufficient
Toxicity, Acute and Longterm Anti-Diabetic Profile of Methanolic Extract of Leaves of Pterocarpus Marsupium on Alloxan Induced Diabetic Albino Rats
 2016; 5(7): 90-94 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2016; 5(7): 90-94 2016TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 12-05-2016 Accepted: 13-06-2016 Behara Chandra Rekha PG student, Department of Pharmacology, Gandhi Medical
2016; 5(7): 90-94 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2016; 5(7): 90-94 2016TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 12-05-2016 Accepted: 13-06-2016 Behara Chandra Rekha PG student, Department of Pharmacology, Gandhi Medical
HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTIVITY OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACT OF ACTINIOPTERIS DICHOTOMA BEDD IN NORMAL AND STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS
 e - ISSN - 2348-2206 Print ISSN - 2348-2192 European Journal of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ejmbb HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTIVITY OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACT OF ACTINIOPTERIS
e - ISSN - 2348-2206 Print ISSN - 2348-2192 European Journal of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ejmbb HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTIVITY OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACT OF ACTINIOPTERIS
Link download full of Test Bank for Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition by Voet
 Link download full of Test Bank for Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition by Voet http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-fundamentals-ofbiochemistry-4th-edition-by-voet/ Chapter 16: Glycogen
Link download full of Test Bank for Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition by Voet http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-fundamentals-ofbiochemistry-4th-edition-by-voet/ Chapter 16: Glycogen
ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF KOVAI KIZHANGU CHOORANAM IN ALLOXAN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS ABSTRACT
 ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF KOVAI KIZHANGU CHOORANAM IN ALLOXAN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS P. PARTHIBAN 1, RAVIKUMAR 1, J. ANBU *2 AND ASHWINI ANJANA 2 1 Department of Medicine, Govt. Siddha College, Arumbakkam,
ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF KOVAI KIZHANGU CHOORANAM IN ALLOXAN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS P. PARTHIBAN 1, RAVIKUMAR 1, J. ANBU *2 AND ASHWINI ANJANA 2 1 Department of Medicine, Govt. Siddha College, Arumbakkam,
Glycogen Metabolism. BCH 340 lecture 9
 Glycogen Metabolism BC 340 lecture 9 Structure of glycogen Glycogen is homopolysaccharide formed of branched D-glucose units The primary glycosidic bond is 1-4-linkage Each branch is made of 6-12 glucose
Glycogen Metabolism BC 340 lecture 9 Structure of glycogen Glycogen is homopolysaccharide formed of branched D-glucose units The primary glycosidic bond is 1-4-linkage Each branch is made of 6-12 glucose
Therapeutic effect of flavonoid rich extract of apricots on high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemia in rabbits
 Therapeutic effect of flavonoid rich extract of apricots on high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemia in rabbits in rabbits TOOBA LATEEF Assistant Professor Department of Biochemistry Jinnah University for
Therapeutic effect of flavonoid rich extract of apricots on high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemia in rabbits in rabbits TOOBA LATEEF Assistant Professor Department of Biochemistry Jinnah University for
IMPACT OF NATUAL ANTIOXIDANT ON REDUCTION OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN HYPERGLYCEMIC RAT FED GERMINATED PIGEON PEA DIET
 IMPACT OF NATUAL ANTIOXIDANT ON REDUCTION OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN HYPERGLYCEMIC RAT FED GERMINATED PIGEON PEA DIET UCHEGBU NNEKA NKECHI DEPARTMENT OF FOOD TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY,
IMPACT OF NATUAL ANTIOXIDANT ON REDUCTION OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN HYPERGLYCEMIC RAT FED GERMINATED PIGEON PEA DIET UCHEGBU NNEKA NKECHI DEPARTMENT OF FOOD TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY,
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF TRIGONELLA FOENUM-GRACEUM ON DIABETES MELLITUS: EFFECT ON LIPID CONCENTRATION IN BLOOD OF MALE SWISS ALBINO MICE
 THE SIGNIFICANCE OF TRIGONELLA FOENUM-GRACEUM ON DIABETES MELLITUS: EFFECT ON LIPID CONCENTRATION IN BLOOD OF MALE SWISS ALBINO MICE Garima Nigam *, ArpitaAwasthi # *Research Scholar, Centre for Biotechnological
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF TRIGONELLA FOENUM-GRACEUM ON DIABETES MELLITUS: EFFECT ON LIPID CONCENTRATION IN BLOOD OF MALE SWISS ALBINO MICE Garima Nigam *, ArpitaAwasthi # *Research Scholar, Centre for Biotechnological
Chapter 10. Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002
 Chapter 10 Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002 Chapter 10: Integration and Control of Metabolism Press the space bar or click the mouse
Chapter 10 Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002 Chapter 10: Integration and Control of Metabolism Press the space bar or click the mouse
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11464 Supplemental Figure S1. The expression of Vegfb is increased in obese and diabetic mice as compared to lean mice. a-b, Body weight and postprandial blood
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11464 Supplemental Figure S1. The expression of Vegfb is increased in obese and diabetic mice as compared to lean mice. a-b, Body weight and postprandial blood
Carbohydrate. Metabolism
 Carbohydrate Metabolism Dietary carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, sucrose, lactose Mouth salivary amylase Summary of Carbohydrate Utilization Utilization for energy (glycolysis) ligosaccharides and disaccharides
Carbohydrate Metabolism Dietary carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, sucrose, lactose Mouth salivary amylase Summary of Carbohydrate Utilization Utilization for energy (glycolysis) ligosaccharides and disaccharides
A Study to Show Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia as a Risk Factor for Macrovascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetis Mellitus
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/21 A Study to Show Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia as a Risk Factor for Macrovascular Complications in Bingi Srinivas
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/21 A Study to Show Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia as a Risk Factor for Macrovascular Complications in Bingi Srinivas
Integration Of Metabolism
 Integration Of Metabolism Metabolism Consist of Highly Interconnected Pathways The basic strategy of catabolic metabolism is to form ATP, NADPH, and building blocks for biosyntheses. 1. ATP is the universal
Integration Of Metabolism Metabolism Consist of Highly Interconnected Pathways The basic strategy of catabolic metabolism is to form ATP, NADPH, and building blocks for biosyntheses. 1. ATP is the universal
The Pharmaceutical and Chemical Journal, 2018, 5(4): Research Article
 , 2018, 5(4):50-55 Available online www.tpcj.org Research Article ISSN: 2349-7092 CODEN(USA): PCJHBA Role of Ginger as Bioenhancer in the Treatment of Diabetes Ashoka Shenoy M*, Arshad Mohamed, A R Shabaraya
, 2018, 5(4):50-55 Available online www.tpcj.org Research Article ISSN: 2349-7092 CODEN(USA): PCJHBA Role of Ginger as Bioenhancer in the Treatment of Diabetes Ashoka Shenoy M*, Arshad Mohamed, A R Shabaraya
Welcome and Introduction
 Welcome and Introduction This presentation will: Define obesity, prediabetes, and diabetes Discuss the diagnoses and management of obesity, prediabetes, and diabetes Explain the early risk factors for
Welcome and Introduction This presentation will: Define obesity, prediabetes, and diabetes Discuss the diagnoses and management of obesity, prediabetes, and diabetes Explain the early risk factors for
Integrative Metabolism: Significance
 Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Chapter 18. Diet and Health
 Chapter 18 Diet and Health Risk Factors and Chronic Diseases Interrelationships among Chronic Diseases Chronic Disease Heart Disease and Stroke Hypertension Cancer Diabetes The Formation of Plaques in
Chapter 18 Diet and Health Risk Factors and Chronic Diseases Interrelationships among Chronic Diseases Chronic Disease Heart Disease and Stroke Hypertension Cancer Diabetes The Formation of Plaques in
THE GLUCOSE-FATTY ACID-KETONE BODY CYCLE Role of ketone bodies as respiratory substrates and metabolic signals
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1981), 53, 131 THE GLUCOSE-FATTY ACID-KETONE BODY CYCLE Role of ketone bodies as respiratory substrates and metabolic signals J. C. STANLEY In this paper, the glucose-fatty acid cycle
Br. J. Anaesth. (1981), 53, 131 THE GLUCOSE-FATTY ACID-KETONE BODY CYCLE Role of ketone bodies as respiratory substrates and metabolic signals J. C. STANLEY In this paper, the glucose-fatty acid cycle
Lipid Profile Analysis of Aircrew
 Original Article Lipid Profile Analysis of Aircrew Sampath S *, Richa + ABSTRACT Most laboratories including all our Armed Forces Centers, estimate Low Density Lipoproteins Cholestorol (LDL-C) levels with
Original Article Lipid Profile Analysis of Aircrew Sampath S *, Richa + ABSTRACT Most laboratories including all our Armed Forces Centers, estimate Low Density Lipoproteins Cholestorol (LDL-C) levels with
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nayef Karadsheh
 number 13 Done by Asma Karameh Corrected by Saad hayek Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis This lecture covers gluconeogenesis with aspects of: 1) Introduction to glucose distribution through tissues.
number 13 Done by Asma Karameh Corrected by Saad hayek Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis This lecture covers gluconeogenesis with aspects of: 1) Introduction to glucose distribution through tissues.
Metabolism of cardiac muscle. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Cardiovascular system, 2013
 Metabolism of cardiac muscle Dr. Mamoun Ahram Cardiovascular system, 2013 References This lecture Mark s Basic Medical Biochemistry, 4 th ed., p. 890-891 Hand-out Why is this topic important? Heart failure
Metabolism of cardiac muscle Dr. Mamoun Ahram Cardiovascular system, 2013 References This lecture Mark s Basic Medical Biochemistry, 4 th ed., p. 890-891 Hand-out Why is this topic important? Heart failure
Dr. Ranjit Kumar. Scientist I Mahavir Cancer Institute & Research Centre, Phulwarisharif, Patna (Bihar), India
 Dr. Ranjit Kumar Scientist I Mahavir Cancer Institute & Research Centre, Phulwarisharif, Patna (Bihar), India Diabetes is a global epidemic and, according to the International Diabetes Federation, one
Dr. Ranjit Kumar Scientist I Mahavir Cancer Institute & Research Centre, Phulwarisharif, Patna (Bihar), India Diabetes is a global epidemic and, according to the International Diabetes Federation, one
TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 1
 BIOO RESEARCH PRODUCTS Glucose Assay Kit Manual Catalog #: 5611-01 BIOO Scientific Corp. 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 Product Description... 1 Procedure Overview... 1 Required Materials
BIOO RESEARCH PRODUCTS Glucose Assay Kit Manual Catalog #: 5611-01 BIOO Scientific Corp. 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 Product Description... 1 Procedure Overview... 1 Required Materials
Experiment 1. Isolation of Glycogen from rat Liver
 Experiment 1 Isolation of Glycogen from rat Liver Figure 35: FIG-2, Liver, PAS, 100x. Note the presence of a few scattered glycogen granules (GG). Objective To illustrate the method for isolating glycogen.
Experiment 1 Isolation of Glycogen from rat Liver Figure 35: FIG-2, Liver, PAS, 100x. Note the presence of a few scattered glycogen granules (GG). Objective To illustrate the method for isolating glycogen.
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2009)
 INFLUENCE OF METHANOLIC EXTRACT OF SYZYGIUM CUMINI SEEDS ON THE ACTIVITY OF GLICLAZIDE IN NORMAL AND ALLOXAN-INDUCED DIABETIC RATS SK Mastan 1 *, T Bhavya Latha 2, T Sri Latha 3, A Srikanth 2, G Chaitanya
INFLUENCE OF METHANOLIC EXTRACT OF SYZYGIUM CUMINI SEEDS ON THE ACTIVITY OF GLICLAZIDE IN NORMAL AND ALLOXAN-INDUCED DIABETIC RATS SK Mastan 1 *, T Bhavya Latha 2, T Sri Latha 3, A Srikanth 2, G Chaitanya
By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
 Resveratrol could partly improve the crosstalk between canonical β-catenin/wnt and FOXO pathways in coronary artery disease patients with metabolic syndrome: A case control study By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Resveratrol could partly improve the crosstalk between canonical β-catenin/wnt and FOXO pathways in coronary artery disease patients with metabolic syndrome: A case control study By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Hypoglycemic Activity of Seerankottai Thiravam (Semicarpus Anacardium. Linn) in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats
 Research Article Hypoglycemic Activity of Seerankottai Thiravam (Semicarpus Anacardium. Linn) in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats P. Parthiban 1, K. Kanagavalli 1, P. Sathiya Rajeswaran 2, J. Anbu 3, A. Chinnasamy
Research Article Hypoglycemic Activity of Seerankottai Thiravam (Semicarpus Anacardium. Linn) in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats P. Parthiban 1, K. Kanagavalli 1, P. Sathiya Rajeswaran 2, J. Anbu 3, A. Chinnasamy
ENERGY FROM INGESTED NUTREINTS MAY BE USED IMMEDIATELY OR STORED
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
 Normal Glucose Metabolism What is Diabetes Mellitus? When the amount of glucose in the blood increases, After a meal, it triggers the release of the hormone insulin from the pancreas. Insulin stimulates
Normal Glucose Metabolism What is Diabetes Mellitus? When the amount of glucose in the blood increases, After a meal, it triggers the release of the hormone insulin from the pancreas. Insulin stimulates
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1
 CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1 web 2017 József Mandl Strategy of metabolism 1 Strategy of metabolism to extract energy ( hydrogen ) from the environment to store the energy excess to store hydrogen CH 3 O 2
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1 web 2017 József Mandl Strategy of metabolism 1 Strategy of metabolism to extract energy ( hydrogen ) from the environment to store the energy excess to store hydrogen CH 3 O 2
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 05 Page May 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.193 Lipid Profile as Early Predictor of Complication
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.193 Lipid Profile as Early Predictor of Complication
(de novo synthesis of glucose)
 Gluconeogenesis (de novo synthesis of glucose) Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the biosynthesis of new glucose. The main purpose of gluconeogenesis is to maintain the constant blood Glc concentration.
Gluconeogenesis (de novo synthesis of glucose) Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the biosynthesis of new glucose. The main purpose of gluconeogenesis is to maintain the constant blood Glc concentration.
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2011) Antihyperlipidemic Activity of Rimonabant on High Cholesterol Diet Induced Hyperlipidemia in Rats
 Antihyperlipidemic Activity of Rimonabant on High Cholesterol Diet Induced Hyperlipidemia in Rats Arshad Ali oorani 1*, Gaurav Dwivedi 1 and M. K. Kale 2 1 Department of Pharmacology, Mandsaur Institute
Antihyperlipidemic Activity of Rimonabant on High Cholesterol Diet Induced Hyperlipidemia in Rats Arshad Ali oorani 1*, Gaurav Dwivedi 1 and M. K. Kale 2 1 Department of Pharmacology, Mandsaur Institute
Research Article GALLIC ACID AND FLAVONOID ACTIVITIES OF AMARANTHUS GANGETICUS
 ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 238 Research Article GALLIC ACID AND FLAVONOID ACTIVITIES OF AMARANTHUS GANGETICUS G. Jyoti Jain 1* and S. Ramachandra Setty 2 1 Department of Pharmacology,
ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 238 Research Article GALLIC ACID AND FLAVONOID ACTIVITIES OF AMARANTHUS GANGETICUS G. Jyoti Jain 1* and S. Ramachandra Setty 2 1 Department of Pharmacology,
EFFECT OF DYKURE A POLYHERBAL FORMULATION ON TYPE-I AND TYPE-II DIABETES
 EFFECT OF DYKURE A POLYHERBAL FORMULATION ON TYPE-I AND TYPE-II DIABETES Address for Correspondence: Harshul Parikh a, R. Balaraman b Prof. R. Balaraman Pharmacy Department Faculty of Tech. & Engg., The
EFFECT OF DYKURE A POLYHERBAL FORMULATION ON TYPE-I AND TYPE-II DIABETES Address for Correspondence: Harshul Parikh a, R. Balaraman b Prof. R. Balaraman Pharmacy Department Faculty of Tech. & Engg., The
Estimation of glucose in blood serum
 Estimation of glucose in blood serum Enzymatic estimation of glucose uses a reagent containing two enzymes and a chromogen. Glucose oxidase catalyses the oxidation of glucose to gluconolactone with the
Estimation of glucose in blood serum Enzymatic estimation of glucose uses a reagent containing two enzymes and a chromogen. Glucose oxidase catalyses the oxidation of glucose to gluconolactone with the
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART D Metabolism Chemical reactions necessary to maintain
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART D Metabolism Chemical reactions necessary to maintain
By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1
 By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Gluconeogenesis is the process of converting noncarbohydrate precursors to glucose or glycogen. The major substrates are the glucogenic amino acids, and lactate, glycerol, and propionate.
By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Gluconeogenesis is the process of converting noncarbohydrate precursors to glucose or glycogen. The major substrates are the glucogenic amino acids, and lactate, glycerol, and propionate.
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
Lowers Blood Sugar Naturally
 Lowers Blood Sugar Naturally Scientific Studies Have Proven That These Eleven Natural Ingradients Normalise Blood Sugar Momordica charantia Gymnema sylvestre Pterocarpus marsupium Salacia Reticulata Curcuma
Lowers Blood Sugar Naturally Scientific Studies Have Proven That These Eleven Natural Ingradients Normalise Blood Sugar Momordica charantia Gymnema sylvestre Pterocarpus marsupium Salacia Reticulata Curcuma
Research Article Anti hyperlipidemic Activity of Costus Igneus in Triton X- 100 Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats
 Research Article Anti hyperlipidemic Activity of Costus Igneus in Triton X- 100 Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats Nimmy Chacko*, Shastry CS, Prerana shetty, Prasanna Shyamma, Ullas D souza and Patel Maulika
Research Article Anti hyperlipidemic Activity of Costus Igneus in Triton X- 100 Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats Nimmy Chacko*, Shastry CS, Prerana shetty, Prasanna Shyamma, Ullas D souza and Patel Maulika
EFFECT OF LYCOPENE IN TOMATO SOUP AND TOMATO JUICE ON THE LIPID PROFILE OF HYPERLIPIDEMIC SUBJECTS
 EFFECT OF LYCOPENE IN TOMATO SOUP AND TOMATO JUICE ON THE LIPID PROFILE OF HYPERLIPIDEMIC SUBJECTS Nora Vigasini, Assistant Professor, Department of Home Science, Women s Christian College, Chennai, noravigas@gmail.com
EFFECT OF LYCOPENE IN TOMATO SOUP AND TOMATO JUICE ON THE LIPID PROFILE OF HYPERLIPIDEMIC SUBJECTS Nora Vigasini, Assistant Professor, Department of Home Science, Women s Christian College, Chennai, noravigas@gmail.com
Murugan M. et al / Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Vol. 1 (2), 2009, 69-73
 ISSN:0975-5772 Murugan M. et al / Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Vol. 1 (2), 2009, 69-73 Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activity of leaves of Mucuna pruriens in alloxan induced diabetic
ISSN:0975-5772 Murugan M. et al / Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Vol. 1 (2), 2009, 69-73 Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activity of leaves of Mucuna pruriens in alloxan induced diabetic
0.40. Biochemistry of Carbohydrates
 0.40 Biochemistry of Carbohydrates Biochemistry of Carbohydrates ATP ADP Glycolysis The Breakdown of Glucose Primary Energy Source of Cells Central Metabolic Pathway All Reactions Occur in Cytoplasm Two
0.40 Biochemistry of Carbohydrates Biochemistry of Carbohydrates ATP ADP Glycolysis The Breakdown of Glucose Primary Energy Source of Cells Central Metabolic Pathway All Reactions Occur in Cytoplasm Two
Human LDL ELISA Kit. Innovative Research, Inc.
 Human LDL ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2582 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports cholesterol from the liver to tissues where it is incorporated into cell membranes.
Human LDL ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2582 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports cholesterol from the liver to tissues where it is incorporated into cell membranes.
Lipid Concentration And The Extent Of Their Peroxidation In Nigerian Hypertensives
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 8 Number 1 Lipid Concentration And The Extent Of Their Peroxidation In Nigerian Hypertensives P Igbinaduwa, B Igbinaduwa, I Oforofuo Citation P Igbinaduwa,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 8 Number 1 Lipid Concentration And The Extent Of Their Peroxidation In Nigerian Hypertensives P Igbinaduwa, B Igbinaduwa, I Oforofuo Citation P Igbinaduwa,
Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes
 Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes Genetics, environment, and lifestyle (obesity, inactivity, poor diet) Impaired fasting glucose Decreased β-cell
Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes Genetics, environment, and lifestyle (obesity, inactivity, poor diet) Impaired fasting glucose Decreased β-cell
IMPROVED SHELF LIFE OF BELL CAPSICUM FRUITS BY MANIPULATION OF THE ACTIVITIES OF GLYCOSIDASES THROUGH HEAT TREATMENT
 IMPROVED SHELF LIFE OF BELL CAPSICUM FRUITS BY MANIPULATION OF THE ACTIVITIES OF GLYCOSIDASES THROUGH HEAT TREATMENT B.H. JAGADEESH, T.N. PRABHA AND K. SRINIVASAN* Department of Biochemistry and Nutrition,
IMPROVED SHELF LIFE OF BELL CAPSICUM FRUITS BY MANIPULATION OF THE ACTIVITIES OF GLYCOSIDASES THROUGH HEAT TREATMENT B.H. JAGADEESH, T.N. PRABHA AND K. SRINIVASAN* Department of Biochemistry and Nutrition,
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2009) HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF PHOEBE LA CEOLATA O ALLOXA -I DUCED DIABETIC MICE
 HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF PHOEBE LA CEOLATA O ALLOXA -I DUCED DIABETIC MICE SEMWAL DK 1 *, RAWAT U 1, SEMWAL R 2, SINGH K 3, SINGH R 3, SAINI B 3, KRISHAN P 3, SINGH M 4 1 Department of Chemistry, University
HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF PHOEBE LA CEOLATA O ALLOXA -I DUCED DIABETIC MICE SEMWAL DK 1 *, RAWAT U 1, SEMWAL R 2, SINGH K 3, SINGH R 3, SAINI B 3, KRISHAN P 3, SINGH M 4 1 Department of Chemistry, University
Major Pathways in Carbohydrate Metabolism
 Major Pathways in Carbohydrate Metabolism 70 Stage 1: Digestion of Carbohydrates In Stage 1, the digestion of carbohydrates Begins in the mouth where salivary amylase breaks down polysaccharides to smaller
Major Pathways in Carbohydrate Metabolism 70 Stage 1: Digestion of Carbohydrates In Stage 1, the digestion of carbohydrates Begins in the mouth where salivary amylase breaks down polysaccharides to smaller
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. R 2 GlcNAcβ1 4GlcNAcβ1 Asn
 GlycoProfile II Enzymatic In-Solution N-Deglycosylation Kit Product Code PP0201 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description Glycosylation is one of the most common posttranslational
GlycoProfile II Enzymatic In-Solution N-Deglycosylation Kit Product Code PP0201 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description Glycosylation is one of the most common posttranslational
Effect of D-400, an Ayurvedic Herbal Formulation on Experimentally-induced Diabetes Mellitus
 [Phytotherapy Research (1996): (10), 433-435] Effect of D-400, an Ayurvedic Herbal Formulation on Experimentally-induced Diabetes Mellitus Mitra, S.K., Gopumadhavan, S. and Muralidhar, T.S. R&D Centre,
[Phytotherapy Research (1996): (10), 433-435] Effect of D-400, an Ayurvedic Herbal Formulation on Experimentally-induced Diabetes Mellitus Mitra, S.K., Gopumadhavan, S. and Muralidhar, T.S. R&D Centre,
Oil Palm Phenolics and Diabetes: Lessons from the Nile Rat
 Oil Palm Phenolics and Diabetes: Lessons from the Nile Rat Julia Bolsinger, Andrzej Pronczuk, Ravigadevi Sambanthamurthi, KC Hayes Hayes Laboratory and MPOB 5/21/213 The Nile grass rat (Arvicanthis niloticus)
Oil Palm Phenolics and Diabetes: Lessons from the Nile Rat Julia Bolsinger, Andrzej Pronczuk, Ravigadevi Sambanthamurthi, KC Hayes Hayes Laboratory and MPOB 5/21/213 The Nile grass rat (Arvicanthis niloticus)
HYPOLIPIDEMIC EFFECT OF EXTRACTS FROM ABELMOSCHUS ESCULENTUS L. MALVACEAE ON TYLOXAPOL- INDUCED HYPERLIPIDEMIA IN MICE
 HYPOLIPIDEMIC EFFECT OF EXTRACTS FROM ABELMOSCHUS ESCULENTUS L. MALVACEAE ON TYLOXAPOL- INDUCED HYPERLIPIDEMIA IN MICE Huynh Ngoc Trinh 1, Nguyen Ngoc Quynh 1, Tran T Van Anh 2, Vo Phung Nguyen 1 1 Department
HYPOLIPIDEMIC EFFECT OF EXTRACTS FROM ABELMOSCHUS ESCULENTUS L. MALVACEAE ON TYLOXAPOL- INDUCED HYPERLIPIDEMIA IN MICE Huynh Ngoc Trinh 1, Nguyen Ngoc Quynh 1, Tran T Van Anh 2, Vo Phung Nguyen 1 1 Department
BIOO LIFE SCIENCE PRODUCTS
 BIOO LIFE SCIENCE PRODUCTS FOR REFERENCE PURPOSES This manual is for Reference Purposes Only. DO NOT use this protocol to run your assays. Periodically, optimizations and revisions are made to the kit
BIOO LIFE SCIENCE PRODUCTS FOR REFERENCE PURPOSES This manual is for Reference Purposes Only. DO NOT use this protocol to run your assays. Periodically, optimizations and revisions are made to the kit
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Received on: 08/02/2017 Published on:27/03/2017
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Received on: 08/02/2017 Published on:27/03/2017 Corresponding Author Anuradha VivekanandPhatak, Department of Pharmacology, Dr.BhanubenNanavati College of Pharmacy, Vile Parle (West),
RESEARCH ARTICLE Received on: 08/02/2017 Published on:27/03/2017 Corresponding Author Anuradha VivekanandPhatak, Department of Pharmacology, Dr.BhanubenNanavati College of Pharmacy, Vile Parle (West),
Discussion & Conclusion
 Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Manual (Second edition)
 Reagent for RNA Extraction ISOGENⅡ Manual (Second edition) Code No. 311-07361 Code No. 317-07363 NIPPON GENE CO., LTD. Table of contents I Product description 1 II Product content 1 III Storage 1 IV Precautions
Reagent for RNA Extraction ISOGENⅡ Manual (Second edition) Code No. 311-07361 Code No. 317-07363 NIPPON GENE CO., LTD. Table of contents I Product description 1 II Product content 1 III Storage 1 IV Precautions
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF SWARNA MAKSHIKA BHASMA AS ANTI DIABETIC MEDICINE
 ISSN 2347-2375 UNIQUE JOURNAL OF AYURVEDIC AND HERBAL MEDICINES Available online: www.ujconline.net Research Article AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF SWARNA MAKSHIKA BHASMA AS ANTI DIABETIC MEDICINE Singh Neetu
ISSN 2347-2375 UNIQUE JOURNAL OF AYURVEDIC AND HERBAL MEDICINES Available online: www.ujconline.net Research Article AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF SWARNA MAKSHIKA BHASMA AS ANTI DIABETIC MEDICINE Singh Neetu
Evaluation of the in vitro antioxidant potential of extracts obtained from Cinnamomum zeylanicum barks
 Evaluation of the in vitro antioxidant potential of extracts obtained from Cinnamomum zeylanicum barks Lidiya Georgieva, Dasha Mihaylova Evaluation of the in vitro antioxidant potential of extracts obtained
Evaluation of the in vitro antioxidant potential of extracts obtained from Cinnamomum zeylanicum barks Lidiya Georgieva, Dasha Mihaylova Evaluation of the in vitro antioxidant potential of extracts obtained
EFFECTS OF CAPSICUM FRUTESCENS SUPPLEMENTED DIET ON LIPID PROFILE OF WISTAR RAT.
 EFFECTS OF CAPSICUM FRUTESCENS SUPPLEMENTED DIET ON LIPID PROFILE OF WISTAR RAT. Ekene, N and Erhirhie, O. E Department of Pharmacology, Delta State University, Abraka Correspondence Author: Ekene, N.,
EFFECTS OF CAPSICUM FRUTESCENS SUPPLEMENTED DIET ON LIPID PROFILE OF WISTAR RAT. Ekene, N and Erhirhie, O. E Department of Pharmacology, Delta State University, Abraka Correspondence Author: Ekene, N.,
Week 3, Lecture 5a. Pathophysiology of Diabetes. Simin Liu, MD, ScD
 Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
Final Review Sessions. 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office Hours
 Final Review Sessions 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office ours 3/14 (WED) 9:30 11:30 am (Rebecca) 3/16 (FRI) 9-11 am (Abel) Final ESSENTIALS Posted Lecture 20 ormonal
Final Review Sessions 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office ours 3/14 (WED) 9:30 11:30 am (Rebecca) 3/16 (FRI) 9-11 am (Abel) Final ESSENTIALS Posted Lecture 20 ormonal
Biochemistry of carbohydrates
 Biochemistry of carbohydrates الفريق الطبي األكاديمي Done By: - Hanan Jamal لكية الطب البرشي البلقاء التطبيقية / املركز 6166 6102/ In the last lecture we talked about Pyruvate, pyruvate is a central intermediate;
Biochemistry of carbohydrates الفريق الطبي األكاديمي Done By: - Hanan Jamal لكية الطب البرشي البلقاء التطبيقية / املركز 6166 6102/ In the last lecture we talked about Pyruvate, pyruvate is a central intermediate;
Glucose is the only source of energy in red blood cells. Under starvation conditions ketone bodies become a source of energy for the brain
 Glycolysis 4 / The Text :- Some Points About Glucose Glucose is very soluble source of quick and ready energy. It is a relatively stable and easily transported. In mammals, the brain uses only glucose
Glycolysis 4 / The Text :- Some Points About Glucose Glucose is very soluble source of quick and ready energy. It is a relatively stable and easily transported. In mammals, the brain uses only glucose
2017, Pharmapex USA, A Member of Apex Group of Companies
 2017, Pharmapex USA, A Member of Apex Group of Companies Natural Blood Health Aid uses a proprietary and licensed Virgin Isolate Technology, invented which recreates the Ayurvedic method used in ancient
2017, Pharmapex USA, A Member of Apex Group of Companies Natural Blood Health Aid uses a proprietary and licensed Virgin Isolate Technology, invented which recreates the Ayurvedic method used in ancient
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research. International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 U. Venkatesh et al, IJMPR, 2017, 5(2): 38-42 CODEN (USA): IJMPMW ISSN: 2321-2624 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research
U. Venkatesh et al, IJMPR, 2017, 5(2): 38-42 CODEN (USA): IJMPMW ISSN: 2321-2624 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2009)
 THE EFFECT OF ASTURTIUM OFFICIALE O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Ahmad R. Gohari 2, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2 *, aghi Shahabi Majd 3, Abbass Hadjiakhoondi 2 1- Department of Pharmacology,
THE EFFECT OF ASTURTIUM OFFICIALE O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Ahmad R. Gohari 2, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2 *, aghi Shahabi Majd 3, Abbass Hadjiakhoondi 2 1- Department of Pharmacology,
Natural Approaches to Cholesterol Deregulation
 Most of us have inherited certain physiological weaknesses that may require ongoing attention and as we get older certain issues tend to arise that need specific requirements. Cholesterol Imbalance and
Most of us have inherited certain physiological weaknesses that may require ongoing attention and as we get older certain issues tend to arise that need specific requirements. Cholesterol Imbalance and
