Congenital dilatation of the large and segmental intrahepatic bile ducts (Caroli s disease) in two Golden retriever littermates
|
|
|
- Andrea Williamson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
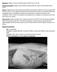
1 Clinical communication Kliniese mededeling Congenital dilatation of the large and segmental intrahepatic bile ducts (Caroli s disease) in two Golden retriever littermates R D Last a*, J M Hill b, M Roach b and T Kaldenberg c ABSTRACT Two, sibling, male Golden retriever puppies, 13 weeks of age, were presented with congenital biliary cysts of the liver involving both hepatic and segmental bile ducts, as well as bilateral polycystic kidney disease. Ultrasonography of the livers of both pups demonstrated segmental cystic lesions that were contiguous with the bile ducts. Histopathology revealed cystic ectatic bile duct hyperplasia and dysplasia with variable portal fibrosis in the liver, while in the kidneys there were radially arranged, cylindrically dilated cysts of the collecting ducts, which extended through the medulla and cortex. This pathology was compatible with that of congenital dilatation of the large and segmental bile ducts (Caroli s disease) described in humans, dogs and rats. In humans Caroli s disease has an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, while in rats activation of the MEK5/ERK cascade initiates the biliary dysgenesis of Caroli s disease in this species. However, the exact mode of inheritance and pathogenesis of Caroli s disease in dogs is as yet unknown. Previous reports on congenital hepatic cystic diseases of the dog have described Caroli s disease like lesions in various breeds, but these are believed to be the 1st reported cases in the Golden retriever breed. Key words: Caroli s syndrome, congenital, ductal plate abnormality, Golden retriever, dog, polycystic kidney disease, segmental biliary cysts. Last R D, Hill J M, Roach M, Kaldenberg T Congenital dilatation of the large and segmental intrahepatic bile ducts (Caroli s disease) in two Golden retriever littermates. Journal of the South African Veterinary Association (2006) 77(4): (En.). Vetdiagnostix Veterinary Pathology Services, PO Box 13624, Cascades, 3202 South Africa. INTRODUCTION Congenital cystic liver diseases are a complex and confusing group of presumed heritable disorders, in which there is actual or potential cystic dilatation of elements of the bile ducts and are often accompanied by renal lesions, especially cysts of renal tubular origin 3,6,13,16,18,19,20. These conditions have only recently been classified in the veterinary literature 23. Although these various cystic entities have quite distinct histomorphological features they all appear to represent an anomalous development of intrahepatic bile ducts 2,7,11,13,17,19,23. Embryological development of the intrahepatic bile ducts is from bipotential liver progenitor cells associated with the primitive mesenchyme around portal veins forming the ductal plate 5,7,21,23,25. Remodelling of ductal a Vetdiagnostix Veterinary Pathology Services, PO Box 13624, Cascades, 3202 South Africa. b Westville Veterinary Hospital, PO Box 31, Westville, 3630 South Africa. c Village Veterinary Hospital, 2 St Mary s Road, Kloof, 3640 South Africa. *Author for correspondence. vetdiagnostix@futurenet.co.za Received: May Accepted October: plates with formation of intrahepatic bile ducts, follows the outgrowth of portal veins from the hilus to liver periphery 7,23,25. Malformation, persistence of, or lack of remodelling of this embryonic double-layered sleeve of cells (ductal plate) results in altered architecture of this system of ducts (ductal plate malformations) and the different levels at which these malformations occur are thought to be linked to the type of disease condition which develops 2,3,9,17 20,23. Two main groups of congenital intrahepatic bile duct abnormalities have been described in humans namely diseases characterised by atresia of intrahepatic bile ducts, eventually complicated by fibrosis, and those characterised by ectasia of intrahepatic bile ducts with a variable degree of fibrosis (fibrocystic diseases) 2,3,5,7,13,21. In the 1st group extrahepatic bile duct atresia and paucity of interlobular bile ducts are recognised. In the 2nd group, autosomal recessive or childhood type of polycystic kidney disease, von Meyenburg complexes (microhamartomas), Caroli s disease and congenital hepatic fibrosis are found 2,3,7,21. In autosomal recessive or childhood type of polycystic kidney disease malformations of the ductal plate occurs at the level of the interlobular bile ducts, while von Meyenburg complexes (microhamartomas) are ductal plate malformations of embryological vestiges of small interlobular ducts which have failed to undergo involution 7,11,17,21. Caroli s disease represents ductal plate abnormalities of the large intrahepatic bile ducts with insufficient resorption of ductal plates resulting in segmental enlargement and ectatic dilatation of primitive bile ducts, which retain communication with the biliary tree 13,17,21. Congenital hepatic fibrosis is thought to arise from ductal plate malformation of interlobular bile ducts, but where there is a concurrent destructive cholangiopathy resulting in scarring fibrosis 7. The World Small Animal Veterinary Associations Liver Standardization Group has only recently proposed the nomenclature for the classification of biliary abnormalities in animals 23. As in humans two main groups are described namely biliary atresia and congenital cystic disease of the liver. Biliary atresia is considered extremely rare in animals and has only been documented in dogs, lambs and calves 10,23. Included under congenital cystic diseases are congenital dilatation of the large and segmental bile ducts (Caroli s disease), juvenile polycystic disease/congenital hepatic fibrosis and adult polycystic disease which includes Von Meyenburg complexes 23. Among domestic animals congenital hepatic cystic conditions have been documented in all domestic species, with multiple congenital cysts derived from bile ducts being noted in dogs, cats, rats and swine 10,23. Congenital cystic diseases of the liver are frequently associated with polycystic kidney disease in all species 3,11,17,20,23. Caroli s disease is a distinct subgroup of biliary tree anomalies stemming from ductal plate remodelling at the level of the large intrahepatic bile ducts characterised by non-obstructive, segmental, ectatic dilatations of the large intrahepatic bile ducts and often accompanied by diffuse cylindrical dilatation of collecting ducts of Tydskr.S.Afr.vet.Ver. (2006) 77(4):
2 the kidney 3,6,9,13,17,20,21. Some authors in the human literature reserve the term Caroli s disease for those rare cases in which there is only segmental ectatic dilatation of large intrahepatic ducts, whereas the term Caroli s syndrome is applied to the more common form of the disease, where the bile duct dilatation is accompanied by portal fibrosis, although controversies and overlap of classifications exist,6,7,12,13,16,18,20,3 In the current veterinary nomenclature there is no splitting of these entities with the term Caroli s disease being applied to conditions characterised by congenital dilatation of the large and segmental bile ducts 23. In human patients with Caroli s there is usually biliary stasis that results in biliary lithiasis, cholangitis, cholangiohepatitis, hepatic abscesses and portal hypertension, with onset in childhood or early adult life 3,12,17,20,21. In both dogs and humans the term Caroli s disease refers to the liver pathology, although many cases also have concurrent polycystic renal disease characterised by radially arranged, cylindrically dilated cysts of the collecting ducts, which extended through the medulla and cortex 9,16,18,19,23. In humans there is an association between these congenital cystic liver diseases and inherited polycystic kidney diseases with inheritance patterns placed in 3 basic categories namely autosomal dominant or adult type of polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), autosomal recessive or childhood type of polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) and Caroli s disease with autosomal recessive inheritance, with von Meyenberg complexes being associated with ADPKD, while congenital hepatic fibrosis is linked to ARPKD 3,6,8,9,12,16, In dogs polycystic hepatic and renal disease resembling ARPKD of childhood have been previously described in young Cairn terriers and West highland white terrier puppies, associated with severe disease in the 1st week of life 9,14,15,24. A single dog in a series of 7 animals with different types of hepatorenal polycystic disease, reported in 1985, had lesions compatible with Caroli s disease 24. A recent report documents a series of 8 young dogs, including 3 Collies, 2 Frisian stabyhouns, 2 Jack Russell terriers and 1 mixed breed dog, with congenital dilatation of the intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts and diffuse cystic kidney disease, consistent with Caroli s disease described in humans 9. To the best of the authors knowledge this report is believed to be the 1st documenting lesions consistent with congenital dilatation of the large and segmental bile ducts (Caroli s disease) in the Golden retriever breed. Fig. 1: Liver. On the caudal aspect of the liver, which has been reflected cranially, multiple, segmental, dilated, saccular, bile ducts (arrows) are present. CASE HISTORY Clinical history Two, male, Golden retriever puppies, 13 weeks of age, originating from the same litter, were presented to 2 separate clinical practices for examination. These 2 animals were emaciated with one weighing only 6.3 kg. Appetite was reported as good and 1 pup was alert and playful, while the other was reported to be quiet and subdued. Abdominal palpation was performed in both cases with lobulated abdominal masses in the region of the kidneys being reported. In-house serum chemistry analysis (Vetscan Abaxis Model ) on the depressed dog revealed the following: Urea 8.69 mmol/ (reference range: 2 9 mmol/ ) and Creatinine 144 µmol/ (reference range: µmol/ ). Cystocentesis was performed on both animals. Urine SGs of and 1.010, respectively, were found with a trace of protein, while the urine sediment analyses were unremarkable. Abdominal ultrasound findings in both pups were similar, with small amounts of free fluid noted in the abdominal cavity (ascites). Multiple, small to large, round, irregular cystic spaces were observed throughout the liver in both dogs, and these cysts were observed to be contained within the biliary tree communicating with bile ducts. These segmentally, ecstatically dilated cysts, were restricted to the intrahepatic biliary radicles, with no involvement of extrahepatic bile ducts. No evidence of bile duct obstruction was noted. The normal architecture of both kidneys in the two dogs was disturbed with poor cortico-medullary distinction and hyper-echoic areas in the renal medulla. Following these ultrasound examinations, both owners elected euthanasia for the respective puppies. The veterinarians involved in these cases obtained owners consent to harvest liver and renal tissues for histopathological examination. Gross examination of the livers revealed multiple, segmental, ecstatically dilated bile ducts (Fig. 1) while renal pathology was characterised by fine radially arranged cysts, which extend from the medulla through the cortex (Fig. 2). Renal and liver samples for histopathological examination were placed into 10 % buffered formalin. Histopathology Histological examination of liver sections from both pups revealed distortion of hepatic architecture due to cystic ectatic bile duct dilatation. This was associated with portal fibrosis, which extended along the hepatic lobule limiting plate with portal-to-portal linking in some areas (Fig. 3). The dilated bile ducts were lined by columnar epithelium and in some instances contained pink-staining proteinaceous material (Fig. 4). In some areas bulbar infoldings of bile duct epithelium into the lumenal space and transductal bridge formation was noted (Fig. 5). Renal histopathology was characterised by radially arranged, cylindrically dilated cysts lined by cuboidal epithelium, which extended through the medulla and cortex (Fig. 6). Interstitial fibrosis was evident between the cystically dilated collecting ducts. DISCUSSION According to current veterinary nomenclature for morphological characterisation of hepatic pathology, Caroli s disease of the dog is classified as a congenital dilatation of the large and segmental Jl S.Afr.vet.Ass. (2006) 77(4):
3 intrahepatic bile ducts 23. By contrast, some current human classifications distinguish between Caroli s disease (simple/classic type) and Caroli s syndrome (associated with congenital hepatic fibrosis) 3,6,7,12,17,18,20. Caroli s disease is the term used to describe cases in which there is only segmental ectatic dilatation of large intrahepatic ducts, whereas the term Caroli s syndrome is applied to the more common form of the disease where the bile duct dilatation is accompanied by portal fibrosis 3,6,7,12,17,18,20. The degree of portal fibrosis is not used as a criterion for sub-categorisation in the dog and all currently reported cases in this species fall within the category of congenital dilatation of the large and segmental intrahepatic bile ducts identical to Caroli s disease, as proposed by the World Small Animal Veterinary Associations Liver Standardization Group 9,14,15,23,24. In rats the pathology reported most closely resembles the Caroli s syndrome with congenital hepatic fibrosis as described in humans 3,18,19. Segmental cystic dilatation of bile ducts due to ductal plate malformation, is central in the pathogenesis of Caroli s disease and the hepatic histopathology of these pups with bulbar protrusions of the bile duct epithelium into duct lumens, as well as bridge formation across the lumen, are typical of the bile duct dysplasia expected with ductal plate malformations 3,6,9,19,20. The renal histopathology of radial cylindrical dilatation of collecting ducts was also consistent with that described in dogs, humans and rats with Caroli s disease, which is distinctly different to the renal pathology of adult ADPKD in humans, Persian and Persian-cross cats 8,9,16,18,19. In human patients with Caroli s there is usually concurrent biliary stasis and this together with the fact that cysts communicate with the rest of the biliary tree, results in varying degrees of acute and chronic ascending cholangitis with periductal fibrosis, biliary lithiasis, cholangiohepatitis, hepatic abscesses and portal hypertension 6,12,13,17,20,21. Although no active inflammation was observed histologically in the bile ducts of the pups described in this report, an accumulation of pink-staining proteinaceous material was noted, which raises the level of suspicion for possible biliary stasis in these 2 animals. However, cholangiohepatitis, hepatic abscesses or biliary liths (bile stones) were not observed in this instance or reported in any of the previous documented cases of Caroli s disease in dogs 9,14,15,23,24. Although considered a rare autosomal recessive inherited disease in humans, Fig. 2: Kidney. Fine, radially arranged, dilated ducts, extending through the cortex and medulla (arrows). The surface of the kidney is irregular, imparting a multilobular appearance (arrowhead). Fig. 3: Liver. Distortion of hepatic architecture due to proliferation of dilated bile ducts (arrowhead). Portal fibrosis extends along the hepatic lobule limiting plate (arrow), accentuating lobulation. Haematoxylin-Eosin, 100. Fig. 4: Liver. Dilated bile ducts lined by columnar epithelium (arrow) and some contain luminal proteinaceous material (arrowhead). Haematoxylin-Eosin, Tydskr.S.Afr.vet.Ver. (2006) 77(4):
4 Fig. 5: Liver. Bulbar infoldings (arrows) of bile duct epithelium into the dilated luminal space of a dilated duct, attempting transductal bridge formation suggestive of a ductal plate abnormality. Haematoxylin-Eosin, 200. Caroli s is commonly associated with morbidity related to the complications of choledocholithiasis (common), cholangitis, cholangiohepatitis, hepatic abscessation, bacteraemia, septicaemia, pancreatitis resulting from stone passage, portal hypertension and bile duct neoplasia 4,6,11,13,17,20,21. In those cases with concurrent polycystic renal disease there maybe adverse effects on renal function including reduction in glomerular filtration rates, hypertension and impaired urinary concentration with resultant urinary tract infections, nephritis and eventually end stage renal disease 1,11,22,26. In most instances clinical symptoms arising from these complications occur in young adults, with the average age of patients at diagnosis being 22 years, although Caroli s disease can occur in young children and there is a sex predilection for females 6,17,20. Clinical pathological hepatic function tests may or may not be abnormal but are non specific from a diagnostic perspective, with raised alkaline phosphatase levels and bilirubinemia being documented 17. Although congenital dilatation of bile ducts in dogs is believed to be an inherited condition, the exact mode of inheritance remains undetermined 9,23. Unlike humans Fig. 6: Kidney cortex and medulla. Radially arranged, dilated collecting ducts extending through the cortex and medulla (arrows). Haematoxylin-Eosin, 100. bile stones have not been documented with Caroli s disease in dogs and cholangitis in canines is usually mild or not reported 9,14,15,23,24. Most cases have been in young dogs of only a few months of age with no sex predilection, animals usually presenting with polyuria/polydipsia, apathy, vomiting and less frequently icterus and ascites 9. Raised, fasting, serum bile acid concentrations and alkaline phosphatase activity in plasma are the most consistent liver function test abnormalities reported in dogs with Caroli s disease 9,23. While Caroli s disease represents an in-utero ductal plate abnormality of the large intrahepatic bile ducts in all species, the pathogenesis of this biliary dysgenesis has only been characterised in the rat, where over-expression of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases in the MEK5/ERK5 cascade have been linked to proliferation of biliary epithelial cells 19. Diagnostic imaging techniques of abdominal ultrasonography and radiography are considered the primary diagnostic tools, with demonstration of contiguity between the hepatic cystic lesions and intrahepatic bile ducts being considered paramount in the diagnosis of Caroli s disease 9,17,22,23. Other imaging procedures such as nuclear scintigraphy, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have also been successfully applied as diagnostic procedures in humans 1,9,17,22. Histopathology of liver and renal biopsies have high diagnostic specificity when interpreted in conjunction with diagnostic imaging and clinical parameters 6,9,20,23. In the two cases described in this report the owners opted for euthanasia and therefore no further follow up on possible progression of the clinical syndrome, pathology or clinical pathology parameters could be made. In humans various treatment modalities are employed including drainage procedures of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC), sphincterotomy for biliary drainage and bile stone removal, hepatic lobectomy for cases restricted to a single lobe, internal surgical bypass of the biliary tree in diffuse forms of the disease, but ultimately liver transplantation is frequently required 17. In almost all of the cases of Caroli s disease reported in dogs the animals have been euthanased at the time of diagnosis and little has been attempted in the way of therapy in this species 9. Investigation into the parentage of the pups in this report revealed that this had been the 1st mating between this particular sire and bitch. There were 5 pups in the Jl S.Afr.vet.Ass. (2006) 77(4):
5 litter with only these 2 pups being submitted for veterinary examination. Two pups died at birth, the 2 reported here were euthanased and the remaining pup has been reported to be normal. Previous mating of this sire to the full sister of this bitch produced a normal litter. It was the 1st litter of this bitch and she has not been bred since. These are believed to be the 1st reports of pathology compatible with congenital dilatation of the bile ducts identical to Caroli s disease in the Golden retriever breed. REFERENCES 1. Asplin J R, Coe F L 1998 Disorders of the kidney and urinary tract. In Fauci A S, Braunwald E, Isselbacher K J, Wilson J D, Martin J B, Kasper D I, Hauser S L, Longo D L (eds) Harrison s principles of internal medicine (14th edn). McGraw-Hill, New York: Awasthi A, Das A, Srinivasan R, Joshi K 2004 Morphological and immunohistochemical analysis of ductal plate malformation: correlation with fetal liver. Histopathology 45: Bettini G, Mandrioli L, Morini M 2003 Bile duct dysplasia and congenital hepatic fibrosis associated with polycystic kidney (Caroli syndrome) in a rat. Veterinary Pathology 40: Bockhorn M, Malago M, Lang H, Nadalin S, Paul A, Saner F, Frilling A, Broelsch C E 2006 The role of surgery in Caroli s disease. Journal of the American College of Surgeons 202: Chandra R S, Stocker J T 1992 The liver gallbladder and biliary tract. In Stocker J T, Dehner L P (eds) Pediatric pathology. J B Lippincott, Philadelphia: Crawford J M 1999 The liver and biliary tract. In Cotran R S, Kumar V, Collins T (eds) Robbins pathological basis of disease (6th edn). W B Saunders, Philadelphia: Desmet V J 1998 Ludwig symposium on biliary disorders part 1. Pathogenesis of ductal plate abnormalities. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 73: Eaton K A, Biller D S, DiBartola S P, Radin M J, Wellman M L 1997 Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in persian and persian-cross cats. Veterinary Pathology 34: Gorlinger S, Rothuizen J, Bunch S, van den Ingh T S G A M 2003 Congenital dilatation of the bile ducts (Caroli s disease) in young dogs. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 17: Kelly W R The liver and biliary system. In Jubb K V F, Kennedy P C, Palmer N (eds) Pathology of domestic animals (4th edn). Academic Press, San Diego: Longmire W P, Mandiola S A, Gordon H E Congenital cystic disease of the liver and biliary system. Annals of Surgery 174: Madjov R, Chervenkov P, Madjova V, Balev B 2005 Caroli s disease. Report of 5 cases and review of literature. Hepatogastroenterology 52: McGee J O The liver and biliary system. In McGee J O, Isaacson P G, Wright N A (eds) Oxford textbook of pathology: principles of pathology Vol. 2A. Oxford University Press, New York: McKenna S C, Carpenter J L 1980 Polycystic disease of the kidney and liver in the Cairn terrier. Veterinary Pathology 17: McAloose D, Casal M, Patterson D F, Dambach D M 1998 Polycystic kidney and liver disease in two related West Highland white terrier litters. Veterinary Pathology 35: Rennke H 1999 The kidney. In Cotran R S, Kumar V, Collins T (eds) Robbins pathological basis of disease (6th edn). W B Saunders, Philadelphia: Romano W J 2002 Caroli disease. In Brandon J C, Coombs B D, Dachman A H, Krasny R M, Lin E C (eds) E-medicine continuing education. Online: emedicine. com/radio/topic131.htm (accessed 1 August 2006) 18. Sanzen T, Harada K, Yasoshima M, Kawamura Y, Ishibashi M, Nakanuma Y 2001 Polycystic kidney rat is a novel animal model of Caroli s disease associated with congenital hepatic fibrosis. American Journal of Pathology 158: Sato Y, Harada K, Kizawa K, Sanzen T, Furubo S, Yasoshima M, Ozaki S, Ishibashi M, Nakanuma Y 2005 Activation of the MEK5/ERK5 cascade is responsible for biliary dysgenesis in a rat model of Caroli s disease. American Journal of Pathology 166: Saul S H Masses of the liver. In Sternberg S S (ed.), Diagnostic surgical pathology Vol. 2 (3rd edn). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia: Scheuer P J, Lefkowitch J H 2006 Liver biopsy interpretation (7th edn). Elsevier-Saunders, Philadelphia: 53 84, Sung J M, Huang J J, Lin X Z, Ruaan M K, Lin C Y, Chang T T, Shu H F, Chow N H 1992 Caroli s disease and congenital hepatic fibrosis associated with polycystic kidney disease. A case presenting with acute focal bacterial nephritis. Clinical Nephrology 38: Van den Ingh T S G A M, Cullen J M, Twedt D C, Van Winkle T V, Desmet V J, Rothuizen J 2006 Morphological Classification of biliary disorders of the canine and feline liver. In WSAVA Standards for clinical and histological diagnosis of canine and feline liver disease. Elsevier-Saunders, Edinburgh: Van den Ingh T S G A M,Rothuizen J 1985 Congenital cystic diseases of the liver in seven dogs. Journal of Comparative Pathology 95: Volvier W, Wilson R A, Larson A M, Ostrow J D 2006 The liver and biliary system. In The gut course (HUB10551): on-line syllabus. University of Washington Division of Gastroenterology. Online: uwgi.org/gut/liver_02.asp (accessed 1 August 2006) 26. Zerres K, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Deget F, Holtkamp U, Brodehl J, Geisert J, Scharer K 1996 Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease in 115 children: clinical presentation, course and influence of gender. Acta Paediatrica 85: Tydskr.S.Afr.vet.Ver. (2006) 77(4):
Congenital Disorders of the Canine and Feline Biliary Tree
 Congenital Disorders of the Canine and Feline Biliary Tree John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP FIATP 1 Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology 2 Embryonic Liver 3 Cytokeratin 7 Ductal Plate
Congenital Disorders of the Canine and Feline Biliary Tree John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP FIATP 1 Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology 2 Embryonic Liver 3 Cytokeratin 7 Ductal Plate
Monosegmental Hepatobiliary Fibropolycystic Disease Mimicking a Mass: Report of Three Cases
 Case Report Gastrointestinal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.54 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):54-60 Monosegmental Hepatobiliary Fibropolycystic Disease Mimicking
Case Report Gastrointestinal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.54 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):54-60 Monosegmental Hepatobiliary Fibropolycystic Disease Mimicking
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, April 2016
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice
 Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice dos Santos R 1, Almeida J 1, Mendes PP 2, Pereira S 3, Borges C 3, Soares E 4. 1) Radiology resident, 2) Radiology
Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice dos Santos R 1, Almeida J 1, Mendes PP 2, Pereira S 3, Borges C 3, Soares E 4. 1) Radiology resident, 2) Radiology
Caroli s disease: magnetic resonance imaging features
 Eur Radiol (2002) 12:2730 2736 DOI 10.1007/s00330-002-1471-6 HEPATOBILIARY PANCREAS France Guy François Cognet Marie Dranssart Jean-Pierre Cercueil Laurent Conciatori Denis Krausé Caroli s disease: magnetic
Eur Radiol (2002) 12:2730 2736 DOI 10.1007/s00330-002-1471-6 HEPATOBILIARY PANCREAS France Guy François Cognet Marie Dranssart Jean-Pierre Cercueil Laurent Conciatori Denis Krausé Caroli s disease: magnetic
Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
 Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
A CASE OF HEPATIC CYST AND HEPATIC LOBE TORSION IN A CHOW-CHOW MALE
 Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LXIII (1) ISSN 2065-1295; ISSN 2343-9394 (CD-ROM); ISSN 2067-3663 (Online); ISSN-L 2065-1295 A CASE OF HEPATIC CYST AND HEPATIC LOBE TORSION IN A CHOW-CHOW
Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LXIII (1) ISSN 2065-1295; ISSN 2343-9394 (CD-ROM); ISSN 2067-3663 (Online); ISSN-L 2065-1295 A CASE OF HEPATIC CYST AND HEPATIC LOBE TORSION IN A CHOW-CHOW
Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
Biliary Atresia. Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s
 Biliary Atresia Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s Biliary Atresia Incidence: 1/8,000-15,000 live births Girls > boys 1.5:1 The most common cause
Biliary Atresia Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s Biliary Atresia Incidence: 1/8,000-15,000 live births Girls > boys 1.5:1 The most common cause
Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
Biliary tract tumors
 Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One. Howard J. Sachs, MD
 Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
Biliary tree dilation - and now what?
 Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst?
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Renal Cystic Disease. Dr H Bierman
 Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg
 Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg Presenting Complaint: Gidget presented after having elevated liver enzymes, patchy alopecia and PU/PD. History: Gidget had been
Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg Presenting Complaint: Gidget presented after having elevated liver enzymes, patchy alopecia and PU/PD. History: Gidget had been
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, March 2017
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst
 Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Jaundice. Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD
 Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz. Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy. History:
 What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XIX, nº 74, pág. 90-107, Abr.-Jun., 2007 Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood Ellen Chung Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Terminology Cyst Polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XIX, nº 74, pág. 90-107, Abr.-Jun., 2007 Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood Ellen Chung Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Terminology Cyst Polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma
 Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology
 Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER & BILIARY TRACT. Lecture 5. Idiopathic & proliferative conditions; diseases of the biliary tract
 PATHOLOGY OF LIVER & BILIARY TRACT Lecture 5 Idiopathic & proliferative conditions; diseases of the biliary tract Enrique Aburto Winter 2015 IX. Diseases of uncertain origin Equine serum hepatitis Idiopathic
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER & BILIARY TRACT Lecture 5 Idiopathic & proliferative conditions; diseases of the biliary tract Enrique Aburto Winter 2015 IX. Diseases of uncertain origin Equine serum hepatitis Idiopathic
Imaging of liver and pancreas
 Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis
 Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
ACG Clinical Guideline: Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Keith D. Lindor, MD, FACG 1, Kris V. Kowdley, MD, FACG 2, and M. Edwyn Harrison, MD 3 1 College of Health Solutions, Arizona State University, Phoenix,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Keith D. Lindor, MD, FACG 1, Kris V. Kowdley, MD, FACG 2, and M. Edwyn Harrison, MD 3 1 College of Health Solutions, Arizona State University, Phoenix,
Associated Terms: Bladder Stones, Ureteral Stones, Kidney Stones, Cystotomy, Urolithiasis, Cystic Calculi
 Associated Terms: Bladder Stones, Ureteral Stones, Kidney Stones, Cystotomy, Urolithiasis, Cystic Calculi The term "ACVS Diplomate" refers to a veterinarian who has been board certified in veterinary surgery.
Associated Terms: Bladder Stones, Ureteral Stones, Kidney Stones, Cystotomy, Urolithiasis, Cystic Calculi The term "ACVS Diplomate" refers to a veterinarian who has been board certified in veterinary surgery.
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease
 Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation
 Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Liver Pathology Lab 1. Shannon Martinson, 2017
 Liver Pathology Lab 1 Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 10 year old MC DSH cat History: Inappetence and weight loss Fluid in the abdomen noted on US Esophageal
Liver Pathology Lab 1 Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 10 year old MC DSH cat History: Inappetence and weight loss Fluid in the abdomen noted on US Esophageal
Biliary tract diseases of the liver
 Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
27-Apr-15 1 UAF ANOMALIES OF DEVELOPMENT RENAL SYSTEM - 1 DR. MUHAMMAD TARIQ JAVED UAF UAF
 RENAL SYSTEM - 1 DR. MUHAMMAD TARIQ JAVED Professor, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk RENAL AGENESIS Renal
RENAL SYSTEM - 1 DR. MUHAMMAD TARIQ JAVED Professor, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk RENAL AGENESIS Renal
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013
 Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
Liver. Liver. System examination
 Liver System examination Examine the liver in situ after opening the abdominal cavity examine the liver in context with other changes in the abdominal cavity. The image on the left is of a ruptured liver
Liver System examination Examine the liver in situ after opening the abdominal cavity examine the liver in context with other changes in the abdominal cavity. The image on the left is of a ruptured liver
Multiple Primary Quiz
 Multiple Primary Quiz Case 1 A 72 year old man was found to have a 12 mm solid lesion in the pancreatic tail by computed tomography carried out during a routine follow up study of this patient with adult
Multiple Primary Quiz Case 1 A 72 year old man was found to have a 12 mm solid lesion in the pancreatic tail by computed tomography carried out during a routine follow up study of this patient with adult
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers IMAGING
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers IMAGING
Imaging Guided Biopsy. Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer
 Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US
 Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Case Scenario 1. Discharge Summary
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO
 HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
Anatomy of the biliary tract
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
Biliary Papillomatosis: case report
 Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 407-412 407 Biliary Papillomatosis: case report CHUN-LIN HUANG WEN-PIN CHEN YU-BUN NG JOSEPH HANG LEUNG Department of Medical Imaging, Chiayi Christian Hospital Biliary papillomatosis
Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 407-412 407 Biliary Papillomatosis: case report CHUN-LIN HUANG WEN-PIN CHEN YU-BUN NG JOSEPH HANG LEUNG Department of Medical Imaging, Chiayi Christian Hospital Biliary papillomatosis
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver:
 Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Pediatric Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Potential Therapies
 Pediatric Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Potential Therapies Philip Rosenthal, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics & Surgery University of California, San Francisco DISCLOSURE I have the following financial
Pediatric Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Potential Therapies Philip Rosenthal, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics & Surgery University of California, San Francisco DISCLOSURE I have the following financial
Biliary cancers: imaging diagnosis. Study of 30 cases
 Biliary cancers: imaging diagnosis. Study of 30 cases N Hammoune, S Semlali, M Eddarai, T. Amil, M Zentar, S. El Kandri,, M Benameur,, S Chaouir. Radiology Department. Mohamed V Military Hospital. Rabat-
Biliary cancers: imaging diagnosis. Study of 30 cases N Hammoune, S Semlali, M Eddarai, T. Amil, M Zentar, S. El Kandri,, M Benameur,, S Chaouir. Radiology Department. Mohamed V Military Hospital. Rabat-
Cystic Disease of the Liver Work Up and Management. Louis Ferrari MD, PGY 3 6/9/16 SUNY Downstate Medical Center
 Cystic Disease of the Liver Work Up and Management Louis Ferrari MD, PGY 3 6/9/16 SUNY Downstate Medical Center The Case 73F presents to clinic after diagnostic laparoscopy at OSH. Known liver mass for
Cystic Disease of the Liver Work Up and Management Louis Ferrari MD, PGY 3 6/9/16 SUNY Downstate Medical Center The Case 73F presents to clinic after diagnostic laparoscopy at OSH. Known liver mass for
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree
 A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 1 Normal Liver; Hepatic Injury, Response, and Failure
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 1 Normal Liver; Hepatic Injury, Response, and Failure Shannon Martinson, August 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ WELCOME! Dr Boute is the coordinator Course
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 1 Normal Liver; Hepatic Injury, Response, and Failure Shannon Martinson, August 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ WELCOME! Dr Boute is the coordinator Course
Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses are epithelial invaginations in the gallbladder wall that from as a result of increased gallbladder pressures.
 Anatomy The complexity of the biliary tree can be broken down into much simpler segments. The intrahepatic ducts converge to form the right and left hepatic ducts which exit the liver and join to become
Anatomy The complexity of the biliary tree can be broken down into much simpler segments. The intrahepatic ducts converge to form the right and left hepatic ducts which exit the liver and join to become
Liver pathology findings in infant with Caroli's syndrome
 CASE REPORT Liver pathology findings in infant with Caroli's syndrome 4 OPEN ACCESS Blagica Dukova, Boro Ilievski, Snezana Duganovska, Vladimir Chadikovski, Aco Kostovski ABSTRACT Introduction: Caroli
CASE REPORT Liver pathology findings in infant with Caroli's syndrome 4 OPEN ACCESS Blagica Dukova, Boro Ilievski, Snezana Duganovska, Vladimir Chadikovski, Aco Kostovski ABSTRACT Introduction: Caroli
Percutaneous Removal of Biliary Stone from Anomalous Right Hepatic Duct
 Percutaneous Removal of Biliary Stone from Anomalous Right Hepatic Duct Pages with reference to book, From 94 To 96 Tanveer ul Haq, Mohammed Younus Sheikh, Changes Khan Jadun, M.N. Ahmad, Yousuf H. Husen
Percutaneous Removal of Biliary Stone from Anomalous Right Hepatic Duct Pages with reference to book, From 94 To 96 Tanveer ul Haq, Mohammed Younus Sheikh, Changes Khan Jadun, M.N. Ahmad, Yousuf H. Husen
X-Ray Corner. Imaging Approach to Cystic Liver Lesions. Pantongrag-Brown L. Solitary cystic liver lesions. Hepatic simple cyst (Figure 1)
 THAI J 136 Imaging Approach to Cystic Liver Lesions GASTROENTEROL 2013 X-Ray Corner Imaging Approach to Cystic Liver Lesions Pantongrag-Brown L Cystic liver lesions are common findings in daily practice
THAI J 136 Imaging Approach to Cystic Liver Lesions GASTROENTEROL 2013 X-Ray Corner Imaging Approach to Cystic Liver Lesions Pantongrag-Brown L Cystic liver lesions are common findings in daily practice
Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
Gall bladder cancer. Information for patients Hepatobiliary
 Gall bladder cancer Information for patients Hepatobiliary page 2 of 12 Who will provide my care? You will be cared for by a number of professionals who work together. These professionals will be specialist
Gall bladder cancer Information for patients Hepatobiliary page 2 of 12 Who will provide my care? You will be cared for by a number of professionals who work together. These professionals will be specialist
ROLE OF RADIOLOGY IN INVESTIGATION OF JAUNDICE
 ROLE OF RADIOLOGY IN INVESTIGATION OF JAUNDICE Dr. Sohan kumar sah *, Dr. Liu Sibin, Dr. sumendra raj pandey, Dr. Prakashmaan shah, Dr. Gaurishankar pandit, Dr. Suraj kurmi and Dr. Sanjay kumar jaiswal
ROLE OF RADIOLOGY IN INVESTIGATION OF JAUNDICE Dr. Sohan kumar sah *, Dr. Liu Sibin, Dr. sumendra raj pandey, Dr. Prakashmaan shah, Dr. Gaurishankar pandit, Dr. Suraj kurmi and Dr. Sanjay kumar jaiswal
Cholangiocarcinoma: Radiologic evaluation and interventions
 November 2014 Cholangiocarcinoma: Radiologic evaluation and interventions Colin Nevins, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Initial course and work-up Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
November 2014 Cholangiocarcinoma: Radiologic evaluation and interventions Colin Nevins, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Initial course and work-up Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
Surgical Management of CBD Injury Jin Seok Heo
 Surgical Management of CBD Injury Jin Seok Heo Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea Bile duct injury (BDI) Introduction Incidence
Surgical Management of CBD Injury Jin Seok Heo Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea Bile duct injury (BDI) Introduction Incidence
IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis?
 CASE REPORT IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Keita Saeki 1, Shigenari Hozawa 1, Naoteru Miyata 1,
CASE REPORT IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Keita Saeki 1, Shigenari Hozawa 1, Naoteru Miyata 1,
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08. Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
 CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
COPYRIGHT: G. Brancatelli
 Fibroysti liver diseases Giuseppe Branatelli University of Palermo Fibroysti liver diseases - definition Group of related lesions of liver and biliary trat Caused by abnormal development of embryologi
Fibroysti liver diseases Giuseppe Branatelli University of Palermo Fibroysti liver diseases - definition Group of related lesions of liver and biliary trat Caused by abnormal development of embryologi
Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma or HCC) Overview
 Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma or HCC) Overview Recent advances in liver cancer care seek to address the rising incidence of liver cancer, which has steadily increased over the past three decades.
Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma or HCC) Overview Recent advances in liver cancer care seek to address the rising incidence of liver cancer, which has steadily increased over the past three decades.
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction
 Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Index. mri.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Angiogenesis, and cancer of prostate, 689 690 Angiography, MR. See MR angiography. Apoptosis, MR imaging of, 637 Apparent diffusion coefficient,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Angiogenesis, and cancer of prostate, 689 690 Angiography, MR. See MR angiography. Apoptosis, MR imaging of, 637 Apparent diffusion coefficient,
Current Management of Biliary Atresia. Janeen Jordan, MD PGY5 Surgery Grand Rounds November 19, 2007
 Current Management of Biliary Atresia Janeen Jordan, MD PGY5 Surgery Grand Rounds November 19, 2007 Overview Etiology and diagnosis Work-up and management History of Kasai Portoenterostomy Studies Advances
Current Management of Biliary Atresia Janeen Jordan, MD PGY5 Surgery Grand Rounds November 19, 2007 Overview Etiology and diagnosis Work-up and management History of Kasai Portoenterostomy Studies Advances
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September Leeds cases
 British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology
 Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in gastroenterology. It includes standards for theoretical
Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in gastroenterology. It includes standards for theoretical
Key words : juvenile adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder, congenital biliary ductal dilatation, anomalous pancreatico-biliary union
 Key words : juvenile adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder, congenital biliary ductal dilatation, anomalous pancreatico-biliary union Table 1 Laboratory data Fig. 1 Abdominal ultrasonography shows marked
Key words : juvenile adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder, congenital biliary ductal dilatation, anomalous pancreatico-biliary union Table 1 Laboratory data Fig. 1 Abdominal ultrasonography shows marked
A CASE REPORT OF SPONTANEOUS BILOMA - AN ENIGMATIC SURGICAL PROBLEM
 A CASE REPORT OF SPONTANEOUS BILOMA - AN ENIGMATIC SURGICAL PROBLEM *Sumanta Kumar Ghosh and Biswajit Mukherjee ESIC Medical College, Joka, Kolkata, India *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Occurrence
A CASE REPORT OF SPONTANEOUS BILOMA - AN ENIGMATIC SURGICAL PROBLEM *Sumanta Kumar Ghosh and Biswajit Mukherjee ESIC Medical College, Joka, Kolkata, India *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Occurrence
Caroli s disease misdiagnosed as intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct
 pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Case Report Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 2015;21:175-179 Caroli s disease misdiagnosed as intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct Dae Hoe Gu, Min Seon Park,
pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Case Report Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 2015;21:175-179 Caroli s disease misdiagnosed as intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct Dae Hoe Gu, Min Seon Park,
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Versus Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Findings in the Postorthotopic Liver Transplant Population Authors: *Ashok Shiani,
Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Versus Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Findings in the Postorthotopic Liver Transplant Population Authors: *Ashok Shiani,
Kidneycentric. Follow this and additional works at:
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker All Kidneycentric 2014 Renal Dysplasia Halana V. Whitehead Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker All Kidneycentric 2014 Renal Dysplasia Halana V. Whitehead Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional
Imaging findings of biliary hamartomas
 Imaging findings of biliary hamartomas Poster No.: C-2475 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Leo, C. Malaspina; Perugia/IT Keywords: Cysts, Education, Ultrasound, MR, CT, Biliary
Imaging findings of biliary hamartomas Poster No.: C-2475 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Leo, C. Malaspina; Perugia/IT Keywords: Cysts, Education, Ultrasound, MR, CT, Biliary
Liver biopsy is integral in the diagnosis and management
 J Vet Intern Med 2015;29:58 62 Histopathologic Variation between Liver s in Dogs S.D. Kemp, K.L. Zimmerman, D.L. Panciera, W.E. Monroe, and M.S. Leib Background: Biopsy of the liver evaluates a small portion
J Vet Intern Med 2015;29:58 62 Histopathologic Variation between Liver s in Dogs S.D. Kemp, K.L. Zimmerman, D.L. Panciera, W.E. Monroe, and M.S. Leib Background: Biopsy of the liver evaluates a small portion
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
The Use of Pancreatoscopy in the Diagnosis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor Lesions of the Pancreas
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S53 S57 The Use of Pancreatoscopy in the Diagnosis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor Lesions of the Pancreas KENJIRO YASUDA, MUNEHIRO SAKATA, MOOSE
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S53 S57 The Use of Pancreatoscopy in the Diagnosis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor Lesions of the Pancreas KENJIRO YASUDA, MUNEHIRO SAKATA, MOOSE
Role of Imaging Methods in Diagnosis of Acute Pancreatitis. Válek V. Radiologická klinika, FN Brno a LF MU v Brně
 Role of Imaging Methods in Diagnosis of Acute Pancreatitis Válek V. Radiologická klinika, FN Brno a LF MU v Brně New Classification: Acute Pancreatitis 2007 revision of Atlanta classification and definitions
Role of Imaging Methods in Diagnosis of Acute Pancreatitis Válek V. Radiologická klinika, FN Brno a LF MU v Brně New Classification: Acute Pancreatitis 2007 revision of Atlanta classification and definitions
What s Your Diagnosis?
 What s Your Diagnosis? Courtney S. Wait Signalment: 11 year old FS Labrador Retriever Presenting Complaint/History: The patient presented to the referring DVM for inappetance, vomiting, lethargy, and anorexia.
What s Your Diagnosis? Courtney S. Wait Signalment: 11 year old FS Labrador Retriever Presenting Complaint/History: The patient presented to the referring DVM for inappetance, vomiting, lethargy, and anorexia.
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology
 Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 primary sclerosing cholangitis primary sclerosing cholangitis pdf primary sclerosing cholangitis Diagnosis and Management
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 primary sclerosing cholangitis primary sclerosing cholangitis pdf primary sclerosing cholangitis Diagnosis and Management
4/7/2015. Conflicts of Interest. None Heather Rush
 Heather Rush, APRN, CDE Wendy L Novak Diabetes Care Center Louisville, KY Conflicts of Interest None Heather Rush A conflict of interest exists when an individual is in a position to profit directly or
Heather Rush, APRN, CDE Wendy L Novak Diabetes Care Center Louisville, KY Conflicts of Interest None Heather Rush A conflict of interest exists when an individual is in a position to profit directly or
Diseases of liver. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 4/2/2019. Mob:
 Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Journal of Nephropathology
 www.nephropathol.com DOI: 10.15171/jnp.2017.60 J Nephropathol. 2017;6(4):363-367 Journal of Nephropathology Rapidly progressive nephromegaly in a neonate with autosomal recessive poly cystic kidney disease
www.nephropathol.com DOI: 10.15171/jnp.2017.60 J Nephropathol. 2017;6(4):363-367 Journal of Nephropathology Rapidly progressive nephromegaly in a neonate with autosomal recessive poly cystic kidney disease
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids. Cholestasis
 Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROLOGY C opy ri~ht 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 62. No.3 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE SPLENOMEGALY IN UNCOMPLICATED BILIARY TRACT AND PANCREATIC DISEASE PETER B.
GASTROENTEROLOGY C opy ri~ht 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 62. No.3 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE SPLENOMEGALY IN UNCOMPLICATED BILIARY TRACT AND PANCREATIC DISEASE PETER B.
Fibrosis and Cirrhosis of the Liver
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Fibrosis and Cirrhosis of the Liver Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Fibrosis and Cirrhosis of the Liver Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2000) 15: 1373 1378 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Sonographic pattern of recessive polycystic kidney disease in young adults. Differences from the dominant
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2000) 15: 1373 1378 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Sonographic pattern of recessive polycystic kidney disease in young adults. Differences from the dominant
Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction
 Yamanashi Med. J. 18(4), 67~ 75, 2003 Review Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction Hideki FUJII 1) 1) Department
Yamanashi Med. J. 18(4), 67~ 75, 2003 Review Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction Hideki FUJII 1) 1) Department
Portal Vein in a Patient Undergoing Hepatic Resection
 HPB Surgery, 1997, Vol. 10, pp. 323-327 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1997 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V. Published in
HPB Surgery, 1997, Vol. 10, pp. 323-327 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1997 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V. Published in
Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases
 GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando?
 Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II
 CME Pretest BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II VOLUME 41 1 2015 A pretest is mandatory to earn CME credit on the posttest. The pretest should be completed BEFORE reading the overview. Both tests must be
CME Pretest BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II VOLUME 41 1 2015 A pretest is mandatory to earn CME credit on the posttest. The pretest should be completed BEFORE reading the overview. Both tests must be
Chronic Biliary Disease. Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths
 Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
Case Reports. Intraductal Papillary Cholangiocarcinoma: Case Report and Review of the Literature INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 Case Reports Kongkam K, Rerknimitr R 45 Case Report and Review of the Literature Pradermchai Kongkam, M.D. Rungsun Rerknimitr, M.D. ABSTRACT A case of papillary cholangiocarcinoma is presented. A 64-year-old
Case Reports Kongkam K, Rerknimitr R 45 Case Report and Review of the Literature Pradermchai Kongkam, M.D. Rungsun Rerknimitr, M.D. ABSTRACT A case of papillary cholangiocarcinoma is presented. A 64-year-old
