Cardiovascular Safety of Incretin Based Therapy
|
|
|
- Gerald Wilson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cardiovascular Safety of Incretin Based Therapy John B. Buse, MD, PhD Verne S. Caviness Distinguished Professor Chief, Division of Endocrinology Executive Associate Dean, Clinical Research University of North Carolina School of Medicine Chapel Hill, NC Disclosures I have been an investigator and/or consultant without any direct financial benefit under contracts between his employer (the University of North Carolina) and the following companies: Amylin Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Andromeda, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Dance Biopharm, Elcelyx Therapeutics Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, GI Dynamics, GlaxoSmithKline, Halozyme Therapeutics, F. Hoffmann- La Roche Ltd., Intarcia Therapeutics, Johnson & Johnson, Lexicon, LipoScience, Medtronic, Merck, Metavention, Novo Nordisk, Orexigen Therapeutics Inc., Osiris Therapeutics Inc., Pfizer Inc., PhaseBio Pharmaceuticals Inc, Quest Diagnostics, Sanofi, Santarus, Scion NeuroStim, Takeda, ToleRx and TransTech Pharma. I am a consultant to PhaseBio Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and have received payments, reimbursement for travel and stock options for that effort.
2 Nathanson MH. Am J Med (183) year History of Anti-hyperglycemic Therapeutics Number of classes of antihyperglycemic agents Phenformin Sulphonylurea Intermediate-acting insulin SGLT-2 inhibitor Bromocriptine-QR Bile acid sequestrant DPP-4 inhibitor GLP-1 receptor agonist Amylinomimetic Basal insulin analogue Glinide Thiazolidinedione Human insulin Alpha-glucosidase inhibitor Rapid-acting insulin analogue Metformin 2 Phenformin withdrawn 0 Soluble insulin Year UGDP, DCCT and UKPDS studies. Buse, JB
3 Targeting the Incretin System Incretin secretion and/or action is arguably impaired in type 2 diabetes Endogenous incretins have very short half-life due to inactivation by DPP-4 : DPP-4 inhibitors (incretin enhancers, oral) Block DPP-4, the enzyme that inactivates endogenous incretin (GLP-1 and GIP) GLP-1 receptor agonists (incretin mimetics, injectable) DPP-4 resistant GLP-1 mimetics, analogs or fusion peptides with longer half-life Drucker DJ, Nauck MA. Lancet. 2006; 368: DPP-4 Inhibitor in vitro Selectivity (Fold Selectivity for DPP-4 vs Other Enzymes) Selectivity QPP/DPP II PEP FAPα DPP-8 DPP-9 Sitagliptin High >5 550 >5 550 >5 550 >2 660 >5 550 Vildagliptin Moderate > Saxagliptin Moderate >50 000? > Alogliptin High > > > > > Linagliptin Moderate > > > Deacon; Diabetes Obes Metab 2011 Adapted from CF Deacon; IDF, Dubai 2011
4 The GLP-1 RA Class: Pharmacokinetic Properties GLP-1 RA Short-acting (<24 hours) Long-acting ( 24 hours) Exenatide BID Lixisenatide* OD * investigational Liraglutide OD Dulaglutide OW Albiglutide OW Exenatide OW GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; GLP-1RA, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; BID, twice daily; OD, once daily; OW, once weekly Individual package inserts. GLP-1 Enzymatic Cleavage, GLP-1 Metabolites, and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Ussher JR and Drucker DJ. Circulation Research. 2014; 114: GLP-1RA = GLP-1 receptor agonists
5 Actions of GLP-1 and GLP-1RA on the Atria and Vasculature Ussher JR and Drucker DJ. Circulation Research. 2014; 114: GLP-1RA = GLP-1 receptor agonists Potential Indirect Cardiovascular Effects of GLP-1RA Ussher JR and Drucker DJ. Circulation Research. 2014; 114: GLP-1RA = GLP-1 receptor agonists
6 A Cardioactive DPP-4 Substrates SDF-1α (1-68) GLP-1 (7-36) BNP (1-32) SP(1-11) NPY (1-36) PYY (1-36) GLP-2 (1-33) GIP (1-42) Progenitor Cell B Blood Vessel BNP (3-32) Kidney GLP-1 (9-36) Heart NPY (3-36) PYY (3-36) Brain DPP-4 Adipose Tissue Ussher, J.R., and Drucker, D. J., Endocrine Reviews Fig DPP4 Inhibitor Mechanisms of Action: Cardiovascular implications Pancreatic Islets Enhance β cell function (GLP-1/GIP) Decrease glucagon (GLP-1) Intestine Decrease lipoprotein production (GLP-1) Cardioprotection? GLP-1 SDF-1 Immune Cells Increase chemotaxis Mulvihill, E., & Drucker D. J., Endo Rev 2014 DPP4 inhibitors Progenitor Cells Increase egress and homing (SDF-1)
7 GLP-1 Receptors Fairly Ubiquitously Expressed Cardiac Myocytes α and β cells CNS, PNS Heart Kidney Lung GI tract Vascular endothelial cells Medial SMCs Vascular endothelium Smooth muscle cells Endocardium Ban et al. Circulation 2008;117: Clinical Cardiovascular Effects of Incretin Based Therapies Hypertension Weight Loss Lipids Heart Rate Cardiovascular Outcomes Ischemia reperfusion injury in AMI Meta-analysis of MACE Cardiovascular Outcome Clinical Trials 14
8 Clinical Cardiovascular Effects of Incretin Based Therapies Hypertension Weight Loss Lipids Heart Rate Cardiovascular Outcomes Ischemia reperfusion injury in AMI Meta-analysis of MACE Cardiovascular Outcome Clinical Trials 15 Liraglutide vs Exenatide: HTN & Lipids Liraglutide Exenatide Estimated Treatment Difference P-value Blood Pressure Systolic BP (mmhg) Diastolic BP (mmhg) Lipid profiles Total cholesterol (mmol/l) LDL cholesterol (mmol/l) VLDL cholesterol (mmol/l) HDL cholesterol (mmol/l) Triglycerides (mmol/l) Free fatty acids (mmol/l) Apolipoprotein B (g/l) Buse et al. Lancet 2009;374:
9 Weight Changes Drucker D. Lancet 2006; 368: Heart Rate and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Astrup et al. Int J Obesity 2011; doi: /ijo
10 Clinical Cardiovascular Effects of Incretin Based Therapies Hypertension Weight Loss Lipids Heart Rate Cardiovascular Outcomes Ischemia reperfusion injury in AMI Meta-analysis of MACE Cardiovascular Outcome Clinical Trials 19 Native GLP-1
11 Native GLP-1: Endothelial Function in Type 2 Diabetes with Stable CAD 7 GLP-1 effect on endothelialdependent vasodilation Change in FMD (%) from baseline * p<0.05 compared with saline (onset and clamp) and with GLP-1 (onset) 0 Control (saline) GLP-1 Data are mean ± SEM. FMD = Flow-Mediated Dilation (endothelial-dependent vasodilation) of brachial artery. Nystrom T et al, Am J Phsiol Endocrinol Metab 2004; 287:E Native GLP-1 limits infarct size in an ischemic rat model of MI Infarct size (%) N=116 *p<0.001 vs. saline and VP Saline DPP-4 inhibitor Native GLP-1 + DPP-4 * Rat model of ischemia In vivo protection against MI Protection abolished by GLP-1 receptor antagonist Native GLP-1 protection mediated by the induction of multiple pro-survival kinases data are mean + SE Bose et al. Diabetes 2005;54:
12 Native GLP-1 improves left ventricular function in high-risk cardiac patients LVEF (%) Baseline p<0.01 Control Post IV GLP-1 Native GLP-1 Regional wall motion score* Baseline p<0.01 Post IV GLP-1 Effect of GLP-1 infusion, in patients with acute MI and high risk of post-mi heart failure, after successful reperfusion (independent of DM status and MI location) Data are mean ± SE; post i.v. GLP-1, post 72-h intravenous GLP-1 infusion; *measures regional systolic function. A decrease in regional wall motion score is beneficial. Nikolaidis et al. Circulation 2004;109:962 5; Moller et al. Am Heart J 2006;151: Summary Pre-CVOT Ussher JR and Drucker DJ. Circulation Research. 2014; 114:
13 DPP-4 Inhibitors DPP-4 Inhibitor Cardiovascular Outcome Trials * Drug Trial Name Identifier Sitagliptin TECOS NCT Alogliptin EXAMINE NCT Saxagliptin SAVOR-TIMI 53 NCT * Accessed April 30, 2013; CV death, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke; Based on renal function; CV death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or unstable angina requiring hospitalization; **CVD or specified diabetes end-organ damage or age 70 years or 2 CRFs ACS=acute coronary syndromes; CRF=cardiovascular risk factors; CVD=cardiovascular disease; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CHF= chronic heart failure; MACE=major adverse cardiovascular events
14 Study Design SAVOR EXAMINE Primary end-point Design Treatment composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal ischemic stroke Multicenter, double blind and randomized Saxagliptin vs placebo in addition to existing antihyperglycemic therapy Alogliptin vs placebo in addition to existing antihyperglycemic therapy Patients Follow-up 2.1 years 18 months Scirica BM, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369: and Circulation. 2014; 130: ; Scirica BM, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369: and Circulation. 2014; 130: ;
15 CV death, MI or ischemic CVA (%) Primary End Point HR 1.00 [ ] P<0.001 (non inferiority) 2y KM Saxagliptin 7.3% Placebo 7.2% Placebo 8212 Saxagliptin Months Scirica BM, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369: and Circulation. 2014; 130: ; Individual End Points 2-year KM rate (%) Placebo (N=8 212) Saxagliptin (N=8 280) HR P-value for superiority CV death ( ) 0.72 MI ( ) 0.52 Ischemic stroke ( ) 0.38 Hosp for cor. revasc ( ) 0.18 Hosp for UA ( ) 0.24 Hosp for heart failure ( ) All-cause mortality ( ) 0.15 Scirica BM, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369: and Circulation. 2014; 130: ;
16 SAVOR-TIMI 53 - Risk of Hospitalization for Heart Failure over Time 4% Saxagliptin Placebo n= HR 1.27 ( ) P=0.007 Hospitalization for Heart Failure 3% 2% 1% HR 1.80 ( ) P= % HR 1.46 ( ) P= % 1.3% 3.5% 2.8% 0.6% Days from Randomization Scirica BM, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369: and Circulation. 2014; 130: ; Study Design White WB, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:
17 Primary End Point White WB, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369: EXAMINE: Primary Endpoint by Components Primary endpoint: CV death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke, No. (%) Alogliptin n=2701 Placebo n= (11.3) 316 (11.8) Hazard Ratio for Alogliptin Group (95% CI) 0.96 ( 1.16)* CV death 89 (3.3) 111 (4.1) Nonfatal MI 187 (6.9) 173 (6.5) Nonfatal stroke 29 (1.1) 32 (1.2) 0.79 (0.60, 1.04) 1.08 (0.88, 1.33) 0.91 (0.55, 1.50) *99% one-sided confidence interval, P<.001 for non-inferiority; P=.32 for superiority White W, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:
18 EXAMINE: Post-hoc Composite Endpoint Inclusive of Hospitalized Heart Failure Composite endpoint inclusive of hospitalized heart failure, No. (%) CV mortality, No. (%) Hospitalization for heart failure, No. (%) Alogliptin n=2701 Placebo n=2679 HR for Alogliptin (95% CI) P-Value 201 (7.4) 207 (7.5) 0.89 (0.82, 1.21) (3.5) 112 (4.2) 0.84 (0.64, 1.10) (3.9) 89(3.3) 1.19 (0.90, 1.58).22 White W on behalf of EXAMINE Investigators at EASD Do Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-IV) Inhibitors Cause Heart Failure? More HF w Placebo More HF w DPP 4i Forest plot separated by cohort and randomized, controlled trial (RCT) based studies. EXAMINE = Examination of Cardiovascular Outcomes With Alogliptin Versus Standard of Care; SAVOR-TIMI 53 = Saxagliptin Assessment of Vascular Outcomes Recorded in... Cliftin P. Clinical Therapeutics, Volume 36, Issue 12, 2014,
19 TECOS: Summary of Study Design 1,2 Patients with T2DM aged 50 years with pre-existing CVD and HbA1c 6.5% 8.0% (48 64 mmol/mol) and dose-stable for 3 months on Metformin, pioglitazone, or sulfonylurea as monotherapy or any dual combination therapy OR Insulin alone or in combination with metformin R Sitagliptin 100 mg once daily a Placebo Additional oral AHA agents or insulin added as part of usual care to target HbA1c goals according to current guidelines V1 Randomization (day 1) V2 M4 V3 M8 AV M12 T M15 Brief visit M18 T M21 AV M24 T M27 Brief visit M30 T M33 AV M36 T M39 Brief visit M42 T M45 AV M48 End of study visit b T2DM = type 2 diabetes mellitus; CVD = cardiovascular disease; HbA 1c = hemoglobin A 1c ; R = randomization; AHA = antihyperglycemic agent; V = visit; M = month; AV = annual visit; T = telephone contact (study participants will also see their usual care physician regularly). a Patients with moderate renal impairment 50 mg once daily (dose dependant on renal function). b Physician visits and telephone contact until completion of the trial 1. Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes with Sitagliptin. University of Oxford Web site. Accessed June 17, Sitagliptin cardiovascular outcome study ( AM1) (TECOS). Accessed June 17, Merck Announces the Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes with Sitagliptin (TECOS) Met Primary Endpoint Kenilworth, N.J., April 27, 2015 Merck (NYSE: MRK), known as MSD outside the United States and Canada, today announced that the Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes with Sitagliptin (TECOS) of Merck s DPP-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, achieved its primary endpoint of non-inferiority for the composite cardiovascular (CV) endpoint. Among secondary endpoints, there was no increase in hospitalization for heart failure in the sitagliptin group versus placebo ,724 participants from 38 countries.... ~3 year follow-up.
20 GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Liraglutide in Mice: Survival and Infarct Size after AMI Liraglutide-200 Liraglutide-75 Placebo Sham operation 100 Overall Survival Survival (%) Days n=60 per group AMI: acute myocardial infarction Noyan-Ashraf, Drucker et al. Diabetes 2009;58: Infarct size 28 days post MI (%) *
21 Exenatide Infusion as an Adjunct to 1º Angioplasty in ST-segment Elevation MI Occluded Coronary Artery Reperfusion Conventional PPCI Reperfusion injury PPCI + iv exenatide 15 min 6 hrs Reperfusion injury Drug Lønborg et al. European Heart Journal 2011; /eurheartj/ehr309 Method- Salvage Index MR: acute phase MR: 3 mdr. post-stemi Salvage Index: Area at Risk - Infarct Area at Risk X 100% Lønborg et al. European Heart Journal 2011; /eurheartj/ehr309
22 Outcomes MRI Infarct size/area at risk 50 Exenatide Placebo Percentage P= P= P= All infarctions Anterior location Non-anterior location Lønborg et al. European Heart Journal 2011; /eurheartj/ehr309 Outcomes MRI Salvage index 15% 19% Exenatide Placebo Percentage P=0.003 P=0.023 P= All infarctions Anterior location Non-anterior location Lønborg et al. European Heart Journal 2011; /eurheartj/ehr309
23 Risk of Primary MACE and Secondary CV Endpoints with Exenatide BID Relative to Pooled Comparators Ratner R et al. Cardiovascular Diabetology 2011; 10:22 45 Integrated Meta-Analysis of Liraglutide for Adjudicated MACE Marso et al. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res 2011;8:
24 GLP-1 Receptor Agonist: Cardiovascular Outcome Trial * Drug Study Name Study Population Primary Outcome Dose n Duration (y) End Date Identifier Lixisenatide ELIXA T2D and ACS (within >180 days) MACE 20 mg qd ~ NCT * Accessed April 30, 2013; CV death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or unstable angina requiring hospitalization ACS=acute coronary syndromes; MACE=major adverse cardiovascular events 47 Sanofi Announces Top-Line Results for CV Outcome Study of Lixisenatide PARIS, March 19, 2015 /PRNewswire/ -- Sanofi announced today top-line results of the Phase IIIb ELIXA cardiovascular outcomes study, which compared lixisenatide to placebo in a high-risk population* of adults with type 2 diabetes evaluating cardiovascular safety. The study showed that lixisenatide was non-inferior, although not superior, to placebo for cardiovascular safety. ELIXA full results will be presented Monday, June 8, 2015, at the American Diabetes Association 75th Scientific Sessions in Boston by the ELIXA steering committee, chaired by Dr. Marc Pfeffer.... Lixisenatide is not approved in the United States. * ~6000 participants, eligible within 180 days post-acs, ~4 years follow-up html. And Both accessed April 12, 2015
25 CVOT in Type 2 Diabetes Katz P, et al. Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research 2014; 11: Summary GLP-1 effects in preclinical and clinical settings suggest intermediate term cardiovascular (CV) benefits. DPP-4 inhibitors have broad potential to affect CV mechanisms and events. CV outcomes trials suggest CV safety in high risk patients Congestive heart failure (CHF) hospitalizations increased with saxagliptin, trends with alogliptin. Preliminary results from a sitagliptin trial suggests no increased risk. GLP-1 receptor agonists in preclinical and clinical setting suggests intermediate term CV benefits. Preliminary results with lixisenatide (not FDA approved) suggest neither harms nor benefits Many more studies will be reported over the next few years. Studies targeting lower risk patients may have greater potential to demonstrate benefits.
Can We Reduce Heart Failure by Treating Diabetes? CVOT Data on SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1Receptor Agonists
 Can We Reduce Heart Failure by Treating Diabetes? CVOT Data on SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1Receptor Agonists Robert R. Henry, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Diego Relevant Conflict
Can We Reduce Heart Failure by Treating Diabetes? CVOT Data on SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1Receptor Agonists Robert R. Henry, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Diego Relevant Conflict
Update on Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcome Trials
 Update on Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcome Trials Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Update on Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcome Trials Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Novel anti-diabetic therapies
 Prof. Manfredi Rizzo, MD, PhD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF INTERNAL MEDICINE School of Medicine University of Palermo, Italy & ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF INTERNAL MEDICINE School of Medicine University of South
Prof. Manfredi Rizzo, MD, PhD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF INTERNAL MEDICINE School of Medicine University of Palermo, Italy & ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF INTERNAL MEDICINE School of Medicine University of South
Terapia con agonisti GLP1 e outcome cardiovascolare. Edoardo Mannucci
 Terapia con agonisti GLP e outcome cardiovascolare Edoardo Mannucci Conflitti di interessi Negli ultimi due anni, E. Mannucci ha ricevuto compensi per relazioni e/o consulenze da: Abbott, AstraZeneca,
Terapia con agonisti GLP e outcome cardiovascolare Edoardo Mannucci Conflitti di interessi Negli ultimi due anni, E. Mannucci ha ricevuto compensi per relazioni e/o consulenze da: Abbott, AstraZeneca,
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
 ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials Tom Blevins MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials 2018 Tom Blevins MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas Speaker Disclosure Dr. Blevins has disclosed that he has received grant support
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials 2018 Tom Blevins MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas Speaker Disclosure Dr. Blevins has disclosed that he has received grant support
Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk: the role of GLP-1
 Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk: the role of GLP-1 Dr Isidora Kitsou-Mylona, PhD Novo Nordisk Regional Medical Advisor Business Area Africa, Gulf & India Disclaimer I am an employee of Novo Nordisk
Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk: the role of GLP-1 Dr Isidora Kitsou-Mylona, PhD Novo Nordisk Regional Medical Advisor Business Area Africa, Gulf & India Disclaimer I am an employee of Novo Nordisk
Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP
 Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research InsAtute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research InsAtute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Incretin-based Therapies for Type 2 Diabetes Comparisons Between Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors
 Incretin-based Therapies for Type 2 Diabetes Comparisons Between Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors Timothy Bailey, MD, FACE, CPI Director, AMCR Institute,
Incretin-based Therapies for Type 2 Diabetes Comparisons Between Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors Timothy Bailey, MD, FACE, CPI Director, AMCR Institute,
GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle. Dr Bernard SAMIA. KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration
 GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle Dr Bernard SAMIA KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email: kcardiacs@gmail.com Web: www.kenyacardiacs.org Disclosures I have
GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle Dr Bernard SAMIA KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email: kcardiacs@gmail.com Web: www.kenyacardiacs.org Disclosures I have
Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes. Rury R. Holman, FMedSci NIHR Senior Investigator 11 th February 2013
 Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes Rury R. Holman, FMedSci NIHR Senior Investigator 11 th February 2013 Residual Vascular Risk in People with Diabetes 2 Analyses based on 530,083 participants
Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes Rury R. Holman, FMedSci NIHR Senior Investigator 11 th February 2013 Residual Vascular Risk in People with Diabetes 2 Analyses based on 530,083 participants
La lezione dei trials di safety cardiovascolare. Edoardo Mannucci
 La lezione dei trials di safety cardiovascolare Edoardo Mannucci Conflitti di interessi Negli ultimi due anni, E. Mannucci ha ricevuto compensi per relazioni e/o consulenze da: Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer
La lezione dei trials di safety cardiovascolare Edoardo Mannucci Conflitti di interessi Negli ultimi due anni, E. Mannucci ha ricevuto compensi per relazioni e/o consulenze da: Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer
Medical therapy advances London/Manchester RCP February/June 2016
 Medical therapy advances London/Manchester RCP February/June 2016 Advances in medical therapies for diabetes mellitus Duality of interest: The speaker or institutions with which he is associated has received
Medical therapy advances London/Manchester RCP February/June 2016 Advances in medical therapies for diabetes mellitus Duality of interest: The speaker or institutions with which he is associated has received
No Increased Cardiovascular Risk for Lixisenatide in ELIXA
 ON ISSUES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES JUNE 2015 Coverage of data from ADA 2015, June 5 9 in Boston, Massachusetts No Increased Cardiovascular Risk for Lixisenatide in ELIXA First Cardiovascular
ON ISSUES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES JUNE 2015 Coverage of data from ADA 2015, June 5 9 in Boston, Massachusetts No Increased Cardiovascular Risk for Lixisenatide in ELIXA First Cardiovascular
Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy
 Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 7, 2012 VanderbiltHeart.com Outline
Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 7, 2012 VanderbiltHeart.com Outline
GLP-1 agonists. Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK
 GLP-1 agonists Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What do GLP-1 agonists do? Physiology of postprandial glucose regulation Meal ❶ ❷ Insulin Rising plasma
GLP-1 agonists Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What do GLP-1 agonists do? Physiology of postprandial glucose regulation Meal ❶ ❷ Insulin Rising plasma
Du gusts is megl che one. Edoardo Mannucci
 Du gusts is megl che one Edoardo Mannucci Conflitti di interessi Negli ultimi due anni, E. Mannucci ha ricevuto compensi per relazioni e/o consulenze da: Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli
Du gusts is megl che one Edoardo Mannucci Conflitti di interessi Negli ultimi due anni, E. Mannucci ha ricevuto compensi per relazioni e/o consulenze da: Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli
LEADER Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes
 LEADER Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes Presented at DSBS seminar on mediation analysis August 18 th Søren Rasmussen, Novo Nordisk. LEADER CV outcome study To determine the effect
LEADER Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes Presented at DSBS seminar on mediation analysis August 18 th Søren Rasmussen, Novo Nordisk. LEADER CV outcome study To determine the effect
CV outcomes Studies and Implications for diabetes management. Seraj Abualnaja, MD, FRCPC Consultant Interventional cardiologist DSFH
 CV outcomes Studies and Implications for diabetes management Seraj Abualnaja, MD, FRCPC Consultant Interventional cardiologist DSFH Case 49 y female with the following medical problems DM typ2 Hypertension
CV outcomes Studies and Implications for diabetes management Seraj Abualnaja, MD, FRCPC Consultant Interventional cardiologist DSFH Case 49 y female with the following medical problems DM typ2 Hypertension
LATE BREAKING STUDIES IN DM AND CAD. Will this change the guidelines?
 LATE BREAKING STUDIES IN DM AND CAD Will this change the guidelines? Objectives 1. Discuss current guidelines for prevention of CHD in diabetes. 2. Discuss the FDA Guidance for Industry regarding evaluating
LATE BREAKING STUDIES IN DM AND CAD Will this change the guidelines? Objectives 1. Discuss current guidelines for prevention of CHD in diabetes. 2. Discuss the FDA Guidance for Industry regarding evaluating
Early treatment for patients with Type 2 Diabetes
 Israel Society of Internal Medicine Kibutz Hagoshrim, June 22, 2012 Early treatment for patients with Type 2 Diabetes Eduard Montanya Hospital Universitari Bellvitge-IDIBELL CIBERDEM University of Barcelona
Israel Society of Internal Medicine Kibutz Hagoshrim, June 22, 2012 Early treatment for patients with Type 2 Diabetes Eduard Montanya Hospital Universitari Bellvitge-IDIBELL CIBERDEM University of Barcelona
In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American Diabetes Association requires the following disclosure to the participants:
 In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American Diabetes Association requires the following disclosure to the participants: Entity Activity Financial Consideration Comments Novo Nordisk
In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American Diabetes Association requires the following disclosure to the participants: Entity Activity Financial Consideration Comments Novo Nordisk
Diabetic Management of the Cardiac Patient
 Diabetic Management of the Cardiac Patient Dr Peter A Senior BMedSci MBBS PhD FRCP(E) Associate Professor, Director Division of Endocrinology, University of Alberta Disclosures Grants/Research Support:
Diabetic Management of the Cardiac Patient Dr Peter A Senior BMedSci MBBS PhD FRCP(E) Associate Professor, Director Division of Endocrinology, University of Alberta Disclosures Grants/Research Support:
Clinical Relevance of Blood Pressure Lowering Effect of Modern Antidiabetic Drugs
 Clinical Relevance of Blood Pressure Lowering Effect of Modern Antidiabetic Drugs Professor Guntram Schernthaner Medical University of Vienna, Austria guntram.schernthaner@meduniwien.ac.at Agenda Glucose
Clinical Relevance of Blood Pressure Lowering Effect of Modern Antidiabetic Drugs Professor Guntram Schernthaner Medical University of Vienna, Austria guntram.schernthaner@meduniwien.ac.at Agenda Glucose
Beyond A1C. Non-glycemic Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Olga Astapova MD, PhD Luis Chavez MD URMC Endocrinology Fellows
 Beyond A1C Non-glycemic Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Olga Astapova MD, PhD Luis Chavez MD URMC Endocrinology Fellows Disclosures No conflicts of interest. Learning Objectives 1. Understand the physiological
Beyond A1C Non-glycemic Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Olga Astapova MD, PhD Luis Chavez MD URMC Endocrinology Fellows Disclosures No conflicts of interest. Learning Objectives 1. Understand the physiological
Cardiovascular Impact of Medications for Treating Type 2 Diabetes
 Friday CME Breakfast Lecture Cardiovascular Impact of Medications for Treating Type 2 Diabetes Thomas Blevins, MD Endocrinologist, Private Practice Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas Educational
Friday CME Breakfast Lecture Cardiovascular Impact of Medications for Treating Type 2 Diabetes Thomas Blevins, MD Endocrinologist, Private Practice Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas Educational
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities
 The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
LEADER and EMPA-REG. John Buse, MD, PhD. University of North Carolina School of Medicine Chapel Hill, NC, USA. Duality of Interest Declaration
 1 LEADER and EMPA-REG John Buse, MD, PhD University of Nth Carolina School of Medicine Chapel Hill, NC, USA Duality of Interest Declaration I rept the following potential duality/dualities of interest
1 LEADER and EMPA-REG John Buse, MD, PhD University of Nth Carolina School of Medicine Chapel Hill, NC, USA Duality of Interest Declaration I rept the following potential duality/dualities of interest
Multi-factor approach to reduce cardiovascular risk in diabetes
 Multi-factor approach to reduce cardiovascular risk in diabetes Prof. Nicola Napoli, MD PhD Division of Endocrinology and Diabetes Università Campus Bio-Medico di Roma Washington University in St Louis
Multi-factor approach to reduce cardiovascular risk in diabetes Prof. Nicola Napoli, MD PhD Division of Endocrinology and Diabetes Università Campus Bio-Medico di Roma Washington University in St Louis
original article Is insulin the most effective injectable antihyperglycaemic therapy?
 Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 17: 145 151, 2015. 2014 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Is insulin the most effective injectable antihyperglycaemic therapy?
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 17: 145 151, 2015. 2014 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Is insulin the most effective injectable antihyperglycaemic therapy?
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) Agonists Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol
 Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) Agonists Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medicaid P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) Agonists Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medicaid P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed
Preventing Serious Health Consequences of Type 2 Diabetes
 Preventing Serious Health Consequences of Type 2 Diabetes The Evidence Hertzel C. Gerstein MD MSc FRCPC Professor and Population Health Institute Chair in Diabetes Research McMaster University and Hamilton
Preventing Serious Health Consequences of Type 2 Diabetes The Evidence Hertzel C. Gerstein MD MSc FRCPC Professor and Population Health Institute Chair in Diabetes Research McMaster University and Hamilton
Diabetes and Heart Failure: The Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors
 22 nd Annual Heart Failure 2018 Symposium Diabetes and Heart Failure: The Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHFSA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA Division
22 nd Annual Heart Failure 2018 Symposium Diabetes and Heart Failure: The Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHFSA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA Division
CANVAS Program Independent commentary
 CANVAS Program Independent commentary Cliff Bailey Aston University, Birmingham, UK 2017 Disclosures and disclaimers Clifford J Bailey CJB has attended advisory boards, undertaken ad hoc consultancy, received
CANVAS Program Independent commentary Cliff Bailey Aston University, Birmingham, UK 2017 Disclosures and disclaimers Clifford J Bailey CJB has attended advisory boards, undertaken ad hoc consultancy, received
DR. SUBHASH K. WANGNOO
 Photograph DR. SUBHASH K. WANGNOO M.D, D.M, FRCP (London) Senior Consultant, Endocrinologist & Diabetologist Apollo Centre for Obesity, Diabetes and Endocrinology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, Sarita Vihar,
Photograph DR. SUBHASH K. WANGNOO M.D, D.M, FRCP (London) Senior Consultant, Endocrinologist & Diabetologist Apollo Centre for Obesity, Diabetes and Endocrinology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, Sarita Vihar,
Current principles of diabetes management
 Current principles of diabetes management Prof. Martin Haluzík, MD, DSc. 3 Department of Medicine, General University Hospital and 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic
Current principles of diabetes management Prof. Martin Haluzík, MD, DSc. 3 Department of Medicine, General University Hospital and 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic
3/8/2011. Julie M. Sease, Pharm D, BCPS, CDE Associate Professor of Pharmacy Practice Presbyterian College School of Pharmacy
 Summarize revisions to the 2011 American Diabetes Association clinical practice guidelines. Evaluate bromocriptine as a therapeutic option in the management of type 2 diabetes. Compare and contrast the
Summarize revisions to the 2011 American Diabetes Association clinical practice guidelines. Evaluate bromocriptine as a therapeutic option in the management of type 2 diabetes. Compare and contrast the
Practical Strategies for the Clinical Use of Incretin Mimetics CME/CE. CME/CE Released: 09/15/2009; Valid for credit through 09/15/2010
 Practical Strategies for the Clinical Use of Incretin Mimetics CME/CE Robert R. Henry, MD Authors and Disclosures CME/CE Released: 09/15/2009; Valid for credit through 09/15/2010 Introduction Type 2 diabetes
Practical Strategies for the Clinical Use of Incretin Mimetics CME/CE Robert R. Henry, MD Authors and Disclosures CME/CE Released: 09/15/2009; Valid for credit through 09/15/2010 Introduction Type 2 diabetes
01/09/2017. Outline. SGLT 2 inhibitor? Diabetes Patients: Complex and Heterogeneous. Association between diabetes and cardiovascular events
 MICROVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS Incidence of outcome g 1 Cardioprotective Effects of SGLT2s Relevant for Which T2 Diabetes Patient? SGLT 2 inhibitor? 58 year old, waist circumference 5 cm, PMH: IHD On statin,
MICROVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS Incidence of outcome g 1 Cardioprotective Effects of SGLT2s Relevant for Which T2 Diabetes Patient? SGLT 2 inhibitor? 58 year old, waist circumference 5 cm, PMH: IHD On statin,
Case Studies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials
 Case Studies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials Louis Kuritzky MD Clinical Assistant Professor Emeritus Department of Community Health and Family Medicine College of Medicine
Case Studies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials Louis Kuritzky MD Clinical Assistant Professor Emeritus Department of Community Health and Family Medicine College of Medicine
Soo LIM, MD, PHD Internal Medicine Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
 Soo LIM, MD, PHD Internal Medicine Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Agenda Association between Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Importance of HbA1c Management esp. High risk patients
Soo LIM, MD, PHD Internal Medicine Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Agenda Association between Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Importance of HbA1c Management esp. High risk patients
Drug Class Monograph
 Drug Class Monograph Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drugs: alogliptin, alogliptin/metformin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin),
Drug Class Monograph Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drugs: alogliptin, alogliptin/metformin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin),
Cardiovascular Benefits of Two Classes of Antihyperglycemic Medications
 Cardiovascular Benefits of Two Classes of Antihyperglycemic Medications Nathan Woolever, Pharm.D., Resident Pharmacist Pharmacy Grand Rounds November 6 th, 2018 Franciscan Healthcare La Crosse, WI 2017
Cardiovascular Benefits of Two Classes of Antihyperglycemic Medications Nathan Woolever, Pharm.D., Resident Pharmacist Pharmacy Grand Rounds November 6 th, 2018 Franciscan Healthcare La Crosse, WI 2017
Drug Class Monograph
 Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drug Class Monograph Drugs: alogliptin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin), Jentadueto (linagliptin/metformin),
Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drug Class Monograph Drugs: alogliptin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin), Jentadueto (linagliptin/metformin),
Cardiovascular Outcomes With Newer Diabetes Drugs: Results From The EMPA-REG and LEADER Trials
 Cardiovascular Outcomes With Newer Diabetes Drugs: Results From The EMPA-REG and LEADER Trials Rajiv Roy, MD Endocrinology Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group Background Between 1990 and 2010: Incidence of
Cardiovascular Outcomes With Newer Diabetes Drugs: Results From The EMPA-REG and LEADER Trials Rajiv Roy, MD Endocrinology Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group Background Between 1990 and 2010: Incidence of
Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital
 Targeting the Incretins System: Can it Improve Our Ability to Treat Type 2 Diabetes? Darshi Sunderam, MD Darshi Sunderam, MD Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital Age-adjusted Percentage
Targeting the Incretins System: Can it Improve Our Ability to Treat Type 2 Diabetes? Darshi Sunderam, MD Darshi Sunderam, MD Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital Age-adjusted Percentage
Cardiologists and HbA1c: Novel Diabetes Drugs and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes
 Biomarkers 2018 Cardiologists and HbA1c: Novel Diabetes Drugs and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHFSA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA Division
Biomarkers 2018 Cardiologists and HbA1c: Novel Diabetes Drugs and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHFSA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA Division
Diabetes update - Diagnosis and Treatment
 Diabetes update - Diagnosis and Treatment Eugene J Barrett, MD,PhD Madge Jones Professor of Medicine Director, University of Virginia Diabetes Center Disclosures - None Case 1 - Screening for Diabetes
Diabetes update - Diagnosis and Treatment Eugene J Barrett, MD,PhD Madge Jones Professor of Medicine Director, University of Virginia Diabetes Center Disclosures - None Case 1 - Screening for Diabetes
Updates in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Management: Are You Making the Link?
 Updates in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Management: Are You Making the Link? Denise Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS AQ Cardiology 1 Erika Hellenbart, PharmD, BCPS 2 Jennifer D Souza, PharmD, CDE, BC ADM
Updates in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Management: Are You Making the Link? Denise Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS AQ Cardiology 1 Erika Hellenbart, PharmD, BCPS 2 Jennifer D Souza, PharmD, CDE, BC ADM
Diabetes Management in CAD Patients. Stuart R. Chipkin, MD Research Professor School of Public Health and Health Sciences University of Massachusetts
 Diabetes Management in CAD Patients Stuart R. Chipkin, MD Research Professor School of Public Health and Health Sciences University of Massachusetts Disclosure Stuart R. Chipkin, MD, FACE Nothing to disclose
Diabetes Management in CAD Patients Stuart R. Chipkin, MD Research Professor School of Public Health and Health Sciences University of Massachusetts Disclosure Stuart R. Chipkin, MD, FACE Nothing to disclose
Can Treating Diabetes with SGLT2 inhibitors Prevent Heart Failure?
 UCSD Hawaii 2017 Symposium Can Treating Diabetes with SGLT2 inhibitors Prevent Heart Failure? Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA Division of Cardiology
UCSD Hawaii 2017 Symposium Can Treating Diabetes with SGLT2 inhibitors Prevent Heart Failure? Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA Division of Cardiology
Side Effects of: GLP-1 agonists DPP-4 inhibitors SGLT-2 inhibitors. Bryce Fukunaga PharmD April 25, 2018
 Side Effects of: GLP-1 agonists DPP-4 inhibitors SGLT-2 inhibitors Bryce Fukunaga PharmD April 25, 2018 Objectives For each drug class: Identify the overall place in therapy Explain the mechanism of action
Side Effects of: GLP-1 agonists DPP-4 inhibitors SGLT-2 inhibitors Bryce Fukunaga PharmD April 25, 2018 Objectives For each drug class: Identify the overall place in therapy Explain the mechanism of action
DPP-4 inhibitor use and risk of diabetic retinopathy: a new safety issue of a safe drug Nam Hoon Kim
 DPP-4 inhibitor use and risk of diabetic retinopathy: a new safety issue of a safe drug Nam Hoon Kim Endocrinology of Metabolism, Korea University College of Medicine Conflict of interest disclosure None
DPP-4 inhibitor use and risk of diabetic retinopathy: a new safety issue of a safe drug Nam Hoon Kim Endocrinology of Metabolism, Korea University College of Medicine Conflict of interest disclosure None
Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better?
 Blood glucose (mmol/l) Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better? Disclosures Dr Kennedy has provided CME, been on advisory boards or received travel or conference support from:
Blood glucose (mmol/l) Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better? Disclosures Dr Kennedy has provided CME, been on advisory boards or received travel or conference support from:
sitagliptin, 25mg, 50mg and 100mg film-coated tablets (Januvia ) SMC No. (1083/15) Merck Sharp and Dohme UK Ltd
 sitagliptin, 25mg, 50mg and 100mg film-coated tablets (Januvia ) SMC No. (1083/15) Merck Sharp and Dohme UK Ltd 07 August 2015 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
sitagliptin, 25mg, 50mg and 100mg film-coated tablets (Januvia ) SMC No. (1083/15) Merck Sharp and Dohme UK Ltd 07 August 2015 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
Diabete: terapia nei pazienti a rischio cardiovascolare
 Diabete: terapia nei pazienti a rischio cardiovascolare Giorgio Sesti Università Magna Graecia di Catanzaro Cardiovascular mortality in relation to diabetes mellitus and a prior MI: A Danish Population
Diabete: terapia nei pazienti a rischio cardiovascolare Giorgio Sesti Università Magna Graecia di Catanzaro Cardiovascular mortality in relation to diabetes mellitus and a prior MI: A Danish Population
Newer Diabetes Treatments Drug Class Update with New Drug Evaluation: Semaglutide and Ertugliflozin
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Dapagliflozin in combination therapy for the Final scope Remit/appraisal objective To appraise the clinical and
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Dapagliflozin in combination therapy for the Final scope Remit/appraisal objective To appraise the clinical and
INCRETIN-BASED DRUGS: MARKETS FOR DIABETES THERAPIES AND DEVELOPING TREATMENTS
 INCRETIN-BASED DRUGS: MARKETS FOR DIABETES THERAPIES AND DEVELOPING TREATMENTS PHM162A February 2015 Kim Lawson Project Analyst ISBN: 1-62296-047-5 BCC Research 49 Walnut Park, Building 2 Wellesley, MA
INCRETIN-BASED DRUGS: MARKETS FOR DIABETES THERAPIES AND DEVELOPING TREATMENTS PHM162A February 2015 Kim Lawson Project Analyst ISBN: 1-62296-047-5 BCC Research 49 Walnut Park, Building 2 Wellesley, MA
Learning and Earning with Gateway Professional Education CME/CEU Webinar Series. Diabetes Update July 6, :00pm 1:00pm
 Learning and Earning with Gateway Professional Education CME/CEU Webinar Series Diabetes Update July 6, 2017 12:00pm 1:00pm Jennifer Pennock Holst, MD Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism AHN Center for
Learning and Earning with Gateway Professional Education CME/CEU Webinar Series Diabetes Update July 6, 2017 12:00pm 1:00pm Jennifer Pennock Holst, MD Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism AHN Center for
Multiple Factors Should Be Considered When Setting a Glycemic Goal
 Multiple Facts Should Be Considered When Setting a Glycemic Goal Patient attitude and expected treatment effts Risks potentially associated with hypoglycemia, other adverse events Disease duration Me stringent
Multiple Facts Should Be Considered When Setting a Glycemic Goal Patient attitude and expected treatment effts Risks potentially associated with hypoglycemia, other adverse events Disease duration Me stringent
Pharmacology Updates. Quang T Nguyen, FACP, FACE, FTOS 11/18/17
 Pharmacology Updates Quang T Nguyen, FACP, FACE, FTOS 11/18/17 14 Classes of Drugs Available for the Treatment of Type 2 DM in the USA ### Class A1c Reduction Hypoglycemia Weight Change Dosing (times/day)
Pharmacology Updates Quang T Nguyen, FACP, FACE, FTOS 11/18/17 14 Classes of Drugs Available for the Treatment of Type 2 DM in the USA ### Class A1c Reduction Hypoglycemia Weight Change Dosing (times/day)
New Strategies for Cardiovascular Risk reduction in Diabetes
 New Strategies for Cardiovascular Risk reduction in Diabetes Dr. Godwin LEUNG Tat Chi MB ChB(HK), MRCP (UK), FHKCP, FHKAM (Medicine) FRCP (Glasg), FACC Specialist in Cardiology % event as first CV event
New Strategies for Cardiovascular Risk reduction in Diabetes Dr. Godwin LEUNG Tat Chi MB ChB(HK), MRCP (UK), FHKCP, FHKAM (Medicine) FRCP (Glasg), FACC Specialist in Cardiology % event as first CV event
MOA: Long acting glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist
 Alexandria Rydz MOA: Long acting glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist Increases glucose dependent insulin secretion Decreases inappropriate glucagon secretion Increases β- cell growth and replication
Alexandria Rydz MOA: Long acting glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist Increases glucose dependent insulin secretion Decreases inappropriate glucagon secretion Increases β- cell growth and replication
Glucose Control and Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease
 Glucose Control and Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Dr Peter A Senior BMedSci MBBS PhD FRCP(E) Associate Professor, Director Division of Endocrinology, University of Alberta Diabetes Update+, March
Glucose Control and Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Dr Peter A Senior BMedSci MBBS PhD FRCP(E) Associate Professor, Director Division of Endocrinology, University of Alberta Diabetes Update+, March
Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes
 Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes Genetics, environment, and lifestyle (obesity, inactivity, poor diet) Impaired fasting glucose Decreased β-cell
Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes Genetics, environment, and lifestyle (obesity, inactivity, poor diet) Impaired fasting glucose Decreased β-cell
Drug Class Review Newer Diabetes Medications and Combinations
 Drug Class Review Newer Diabetes Medications and Combinations Final Update 2 Report July 2016 The purpose reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness and harms
Drug Class Review Newer Diabetes Medications and Combinations Final Update 2 Report July 2016 The purpose reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness and harms
Top HF Trials to Impact Your Practice
 Top HF Trials to Impact Your Practice Biykem Bozkurt, MD, FACC The Mary and Gordon Cain Chair & Professor of Medicine Medical Care Line Executive, DeBakey VA Medical Center, Director, Winters Center for
Top HF Trials to Impact Your Practice Biykem Bozkurt, MD, FACC The Mary and Gordon Cain Chair & Professor of Medicine Medical Care Line Executive, DeBakey VA Medical Center, Director, Winters Center for
Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2. Insulin Secretion. The Importance of BP and Glucose Control
 Insulin Secretion Management of Type 2 Diabetes DG van Zyl Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2 % reduction 0-5 -10-15 -20-25 -30-35 -40 The Importance of BP and Glucose Control Effects of tight
Insulin Secretion Management of Type 2 Diabetes DG van Zyl Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2 % reduction 0-5 -10-15 -20-25 -30-35 -40 The Importance of BP and Glucose Control Effects of tight
Disclosure. Learning Objectives. Case. Diabetes Update: Incretin Agents in Diabetes-When to Use Them? I have no disclosures to declare
 Disclosure Diabetes Update: Incretin Agents in Diabetes-When to Use Them? I have no disclosures to declare Spring Therapeutics Update 2011 CSHP BC Branch Anar Dossa BScPharm Pharm D CDE April 20, 2011
Disclosure Diabetes Update: Incretin Agents in Diabetes-When to Use Them? I have no disclosures to declare Spring Therapeutics Update 2011 CSHP BC Branch Anar Dossa BScPharm Pharm D CDE April 20, 2011
Navigating the New Options for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Navigating the New Options for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Associate Professor Mark Kennedy Department of General Practice, University of Melbourne Chair, Primary Care Diabetes Society of
Navigating the New Options for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Associate Professor Mark Kennedy Department of General Practice, University of Melbourne Chair, Primary Care Diabetes Society of
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim
 Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Drug Class Update with New Drug Evaluation: Non-insulin Diabetes Treatments (SGLT-2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists)
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Type 2 diabetes & Cardiovascular disease. update. Barcelona, March 15th 2018
 Type 2 diabetes & Cardiovascular disease update Barcelona, March 15th 2018 Francesc Xavier Cos Claramunt Sant Martí de Provençals. Head of Innovation and Health in Barcelona city Assoc.ProfUniversitatAutonomade
Type 2 diabetes & Cardiovascular disease update Barcelona, March 15th 2018 Francesc Xavier Cos Claramunt Sant Martí de Provençals. Head of Innovation and Health in Barcelona city Assoc.ProfUniversitatAutonomade
egfr > 50 (n = 13,916)
 Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Review of FDA Guidance on Cardiovascular Outcomes for Diabetes Medication Trials and Application to Clinical Management
 Katherine S. O Neal Pharm.D., MBA, BCACP, CDE, BC-ADM, AE-C Associate Professor The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center College of Pharmacy Department of Internal Medicine Oklahoma City, OK Member,
Katherine S. O Neal Pharm.D., MBA, BCACP, CDE, BC-ADM, AE-C Associate Professor The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center College of Pharmacy Department of Internal Medicine Oklahoma City, OK Member,
Oral Agents. Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK
 Oral Agents Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What would your ideal diabetes drug do? Effective in lowering HbA1c No hypoglycaemia No effect on weight/ weight
Oral Agents Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What would your ideal diabetes drug do? Effective in lowering HbA1c No hypoglycaemia No effect on weight/ weight
NEWS BRIEFING Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Moderated by: Robert Eckel, MD University of Colorado
 NEWS BRIEFING Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Moderated by: Robert Eckel, MD University of Colorado 1 EMBARGO POLICY All recordings are for personal use only and not for rebroadcast online or in any
NEWS BRIEFING Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Moderated by: Robert Eckel, MD University of Colorado 1 EMBARGO POLICY All recordings are for personal use only and not for rebroadcast online or in any
GLP-1 RECEPTOR AGONIST SHOULD I TRY IT? VERONICA BRADY, PHD, BC-ADM, CDE PROJECT ECHO JUNE 21, 2018
 GLP-1 RECEPTOR AGONIST SHOULD I TRY IT? VERONICA BRADY, PHD, BC-ADM, CDE PROJECT ECHO JUNE 21, 2018 SOMETHING TO CONSIDER IF YOU COULD PRESCRIBE A MEDICATION FOR YOUR PATIENT WITH DIABETES THAT: DECREASED
GLP-1 RECEPTOR AGONIST SHOULD I TRY IT? VERONICA BRADY, PHD, BC-ADM, CDE PROJECT ECHO JUNE 21, 2018 SOMETHING TO CONSIDER IF YOU COULD PRESCRIBE A MEDICATION FOR YOUR PATIENT WITH DIABETES THAT: DECREASED
Update on Agents for Type 2 Diabetes
 Update on Agents for Type 2 Diabetes This presentation will: Outline the clinical considerations in the selection of pharmacotherapy for type 2 diabetes, including degree of A1C lowering achieved, patient-specific
Update on Agents for Type 2 Diabetes This presentation will: Outline the clinical considerations in the selection of pharmacotherapy for type 2 diabetes, including degree of A1C lowering achieved, patient-specific
IDF Regions and global projections of the number of people with diabetes (20-79 years), 2013 and Diabetes Atlas -sixth Edition: IDF 2013
 IDF Regions and global projections of the number of people with diabetes (20-79 years), 2013 and 2035 Diabetes Atlas -sixth Edition: IDF 2013 Diabetes Atlas -sixth Edition: IDF 2013 Chronic complications
IDF Regions and global projections of the number of people with diabetes (20-79 years), 2013 and 2035 Diabetes Atlas -sixth Edition: IDF 2013 Diabetes Atlas -sixth Edition: IDF 2013 Chronic complications
Current Updates & Challenges In Managing Diabetes in CVD
 Current Updates & Challenges In Managing Diabetes in CVD Preventive Cardiovascular Conference 2016 Instituit Jantung Negara 12 th November 2016 Nor Azmi Kamaruddin Diabetes Clinic Department of Medicine
Current Updates & Challenges In Managing Diabetes in CVD Preventive Cardiovascular Conference 2016 Instituit Jantung Negara 12 th November 2016 Nor Azmi Kamaruddin Diabetes Clinic Department of Medicine
New and Emerging Therapies for Type 2 DM
 Dale Clayton MHSc, MD, FRCPC Dalhousie University/Capital Health April 28, 2011 New and Emerging Therapies for Type 2 DM The science of today, is the technology of tomorrow. Edward Teller American Physicist
Dale Clayton MHSc, MD, FRCPC Dalhousie University/Capital Health April 28, 2011 New and Emerging Therapies for Type 2 DM The science of today, is the technology of tomorrow. Edward Teller American Physicist
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Cardiovascular outcome studies with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists what will REWIND add?
 Editorial Page 1 of 5 Cardiovascular outcome studies with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists what will REWIND add? Keith C. Ferdinand, Indrajeet Mahata Department of Medicine, Tulane School of Medicine,
Editorial Page 1 of 5 Cardiovascular outcome studies with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists what will REWIND add? Keith C. Ferdinand, Indrajeet Mahata Department of Medicine, Tulane School of Medicine,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Single Technology Appraisal. Canagliflozin in combination therapy for treating type 2 diabetes
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Single Technology Appraisal Canagliflozin in combination therapy for Final scope Remit/appraisal objective To appraise the clinical and cost effectiveness
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Single Technology Appraisal Canagliflozin in combination therapy for Final scope Remit/appraisal objective To appraise the clinical and cost effectiveness
ROLE OF DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE-4 INHIBITOR IN GLYCEMIC CONTROL AND CARDIOVASCULAR MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY
 ROLE OF DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE-4 INHIBITOR IN GLYCEMIC CONTROL AND CARDIOVASCULAR MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY An Article Review By Dr.Shaikh Khalid Anwar, India (PG Diploma in Diabetes, MMSc in Diabetology Student
ROLE OF DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE-4 INHIBITOR IN GLYCEMIC CONTROL AND CARDIOVASCULAR MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY An Article Review By Dr.Shaikh Khalid Anwar, India (PG Diploma in Diabetes, MMSc in Diabetology Student
6/1/2018. Lou Haenel, IV, DO, FACE, FACOI Endocrinology Roper St Francis Charleston, SC THE OMINOUS OCTET: HOW PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND THERAPY MERGE
 Lou Haenel, IV, DO, FACE, FACOI Endocrinology Roper St Francis Charleston, SC THE OMINOUS OCTET: HOW PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND THERAPY MERGE 1 2 3 Sulfonylureas Glipizide Glyburide Glimeperide 4 Metformin Gold
Lou Haenel, IV, DO, FACE, FACOI Endocrinology Roper St Francis Charleston, SC THE OMINOUS OCTET: HOW PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND THERAPY MERGE 1 2 3 Sulfonylureas Glipizide Glyburide Glimeperide 4 Metformin Gold
The Clinical Unmet need in the patient with Diabetes and ACS
 The Clinical Unmet need in the patient with Diabetes and ACS Professor Kausik Ray (UK) BSc(hons), MBChB, MD, MPhil, FRCP (lon), FRCP (ed), FACC, FESC, FAHA Diabetes is a global public health challenge
The Clinical Unmet need in the patient with Diabetes and ACS Professor Kausik Ray (UK) BSc(hons), MBChB, MD, MPhil, FRCP (lon), FRCP (ed), FACC, FESC, FAHA Diabetes is a global public health challenge
Diabetes 2013: Achieving Goals Through Comprehensive Treatment. Session 2: Individualizing Therapy
 Diabetes 2013: Achieving Goals Through Comprehensive Treatment Session 2: Individualizing Therapy Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism
Diabetes 2013: Achieving Goals Through Comprehensive Treatment Session 2: Individualizing Therapy Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism
COMMISSIONING POLICY RECOMMENDATION TREATMENT ADVISORY GROUP Policy agreed by (Vale of York CCG/date)
 Drug, Treatment, Device name ( Vipidia; Takeda) COMMISSIONING POLICY RECOMMENDATION TREATMENT ADVISORY GROUP Policy agreed by (Vale of York CCG/date) Licensed indication To improve glycaemic control in
Drug, Treatment, Device name ( Vipidia; Takeda) COMMISSIONING POLICY RECOMMENDATION TREATMENT ADVISORY GROUP Policy agreed by (Vale of York CCG/date) Licensed indication To improve glycaemic control in
Individualizing Management of T2DM in the Hospital Setting to Reduce Macro and Microvascular Complications
 Individualizing Management of T2DM in the Hospital Setting to Reduce Macro and Microvascular Complications This CME activity is provided by Integrity Continuing Education. This CEU/CNE activity is co-provided
Individualizing Management of T2DM in the Hospital Setting to Reduce Macro and Microvascular Complications This CME activity is provided by Integrity Continuing Education. This CEU/CNE activity is co-provided
The Death of Sulfonylureas? A Review of New Diabetes Medications
 The Death of Sulfonylureas? A Review of New Diabetes Medications Kelly Hoenig, Pharm.D., BCPS Cedar Rapids Family Medicine Residency 2/4/17 Objectives Review GLP-1 Agonists, DPP-IV Inhibitors and SGLT-2
The Death of Sulfonylureas? A Review of New Diabetes Medications Kelly Hoenig, Pharm.D., BCPS Cedar Rapids Family Medicine Residency 2/4/17 Objectives Review GLP-1 Agonists, DPP-IV Inhibitors and SGLT-2
10/27/2011. Challenges in Anti-diabetic Global Drug Development A Shift from Surrogate to Outcome Trials. Disclaimer
 Challenges in Anti-diabetic Global Drug Development A Shift from Surrogate to Outcome Trials Eckhard Leifke, MD PhD Senior Medical Director Takeda Global Research Development Center, Inc. Presentation
Challenges in Anti-diabetic Global Drug Development A Shift from Surrogate to Outcome Trials Eckhard Leifke, MD PhD Senior Medical Director Takeda Global Research Development Center, Inc. Presentation
NEW DIABETES CARE MEDICATIONS
 NEW DIABETES CARE MEDICATIONS James Bonucchi DO, ECNU, FACE Adult Medicine and Endocrinology Specialists Disclosures Speakers bureau Sanofi AZ BI Diabetes Diabetes cost ADA 2017 data Ever increasing disorder.
NEW DIABETES CARE MEDICATIONS James Bonucchi DO, ECNU, FACE Adult Medicine and Endocrinology Specialists Disclosures Speakers bureau Sanofi AZ BI Diabetes Diabetes cost ADA 2017 data Ever increasing disorder.
CONTROLLO GLICEMICO E RISCHIO CARDIOVASCOLARE. AGOSTINO CONSOLI DMSI - Università d Annunzio CHIETI ITALY. sul Paziente ad alto rischio CV*
 CONTROLLO GLICEMICO E RISCHIO CARDIOVASCOLARE AGOSTINO CONSOLI DMSI - Università d Annunzio CHIETI ITALY sul Paziente ad alto rischio CV* Does reducing hyperglycemia protect against cardiovascular risk?
CONTROLLO GLICEMICO E RISCHIO CARDIOVASCOLARE AGOSTINO CONSOLI DMSI - Università d Annunzio CHIETI ITALY sul Paziente ad alto rischio CV* Does reducing hyperglycemia protect against cardiovascular risk?
Content Development Committee
 1 Content Development Committee Cardiologists: Family Physicians: Shaun Goodman, MD, MSc, FRCPC, FACC, FESC, FAHA, FCCS (Chair) Associate Head, Division of Cardiology, St. Michael s Hospital Professor,
1 Content Development Committee Cardiologists: Family Physicians: Shaun Goodman, MD, MSc, FRCPC, FACC, FESC, FAHA, FCCS (Chair) Associate Head, Division of Cardiology, St. Michael s Hospital Professor,
Incredible Incretins Abby Frye, PharmD, BCACP
 Incredible Incretins Abby Frye, PharmD, BCACP Objectives & Disclosures Review the pathophysiology of T2DM and the impact of the incretin system Describe the defining characteristics of the available glucagonlike
Incredible Incretins Abby Frye, PharmD, BCACP Objectives & Disclosures Review the pathophysiology of T2DM and the impact of the incretin system Describe the defining characteristics of the available glucagonlike
HEART FAILURE AND DIABETES MELLITUS: DANGEROUS LIASONS MICHEL KOMAJDA, MD
 HEART FAILURE AND DIABETES MELLITUS: DANGEROUS LIASONS MICHEL KOMAJDA, MD Author affiliations: Department of Cardiology, Hôpital Saint Joseph, Paris, France Address for correspondence: Michel Komajda,
HEART FAILURE AND DIABETES MELLITUS: DANGEROUS LIASONS MICHEL KOMAJDA, MD Author affiliations: Department of Cardiology, Hôpital Saint Joseph, Paris, France Address for correspondence: Michel Komajda,
Causes of death in Diabetes
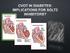 Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
