ESTIMATION OF GLOMERULAR SIZE BY MICROMETRY IN MIDGESTATIONAL PERIOD
|
|
|
- Melanie Lorin Paul
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Research Article ESTIMATION OF GLOMERULAR SIZE BY MICROMETRY IN MIDGESTATIONAL PERIOD Suvarna A. Gulanikar * 1, G.A. Shroff 2, A.R. kharkar 3, V.S.Mandhana 4. ABSTRACT Introduction: Changes in glomerular size play an important role in the initiation and progression of various glomerulopathies. There are few anatomical reports on the fetal glomerular size than on adult human renal glomerulus. Therefore, our study conducted, with an aim to estimate an average glomerular diameter in cortical zones of the kidney during 14 th to the 28 th weeks of gestation, to define periods of their most intensive growth, and to record differences of glomerular size between different cortical zones. Materials and Methods: Thirty normal human fetuses without any congenital anomalies in midgestational period ranging from 14 to 28 weeks were selected for the study. The glomerular diameters were evaluated in hematoxylin and eosin-stained microscopic sections of the kidneys by micrometry in outer, middle, and inner zones of renal cortex. Average diameter was calculated in different groups and relation of them in all three zones of the cortex was analysed. Results: The results showed that outer cortex glomerulus were smallest with the average diameter of ±7.20 to 63.5±7.33 µm. At the deeper level, size of glomerulus increased. In the intermediate cortex average size of glomerulus is ± to ± 9.37 µm. and the deepest juxta medullary glomerulus were largest in size with the average diameter of 94.61±14.18 to ± Conclusion: The present study concluded that smallest diameter of glomerulus was seen in outer cortex, while the largest one in inner cortex. In all the age groups [14-28 weeks] the glomerular diameter remained nearly same in each zone of the cortex. The Changes in glomerular size played an important role in the initiation and progression of various glomerulopathies. The importance of this study lies in determining the average glomerular diameter, which could be used as baseline values for studies of glomerular diseases. It may be possible to define the pathological changes in fetal kidney based on the present study. KEY WORDS: Glomerulus, Cortex, Micrometry, Glomerulopathies. International Journal of Anatomy and Research, Int J Anat Res 2016, Vol 4(1): ISSN DOI: *1 Assistant Professor, Dept. Of Anatomy, MGM Medical college, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. 2,3 Professor, Dept. Of Anatomy, MGM Medical college, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. 4 Associate Professor, Dept. Of Anatomy, MGM Medical college, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. Address for Correspondence: Dr. Suvarna A. Gulanikar, Assistant Professor, Dept. Of Anatomy, MGM Medical college, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. suvarnagulanikar@gmail.com Access this Article online Quick Response code Web site: International Journal of Anatomy and Research ISSN DOI: /ijar Received: 17 Dec 2015 Accepted: 06 Jan 2016 Peer Review: 17 Dec 2015 Published (O): 31 Jan 2016 Revised: None Published (P): 31 Jan 2016 INTRODUCTION With an advent of modern technology and equipments for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in the field of medical sciences, it becomes imperative to have sound knowledge of the basic human morphology and developmental anatomy. Early prenatal diagno-sis and the importance of genetic counselling are of great interest for evaluation of normal fetus anatomy. Changes in glomerular size play an important role in the initiation and progression of various Int J Anat Res 2016, 4(1): ISSN
2 glomerulopathies. Estimation of glomerular size in the normal kidney provides baseline values for studies of glomerular diseases. Bertram J F et al. (1995) States that the highly specialized architecture of the renal glomerulus is altered in a variety of disease states. Glomerular enlargement precedes glomerulosclerosis in idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), diabetic nephropathy, obesityrelated glomerulopathy, HIV nephropa-thy, reflux nephropathy, pre-eclampsia, sickle cell nephropathy and transplant glomerulopathy. Morphometric methods, including stereological methods, have been widely used to analyze these changes in both animal and human glomeruli [1]. There are few anatomical reports on the fetal glomerular size than on adult human renal glomerulus. The objective of the present study was to calculate an average glomerular diameter in cortical zones of the kidney during midgestational period, to define periods of their most intensive growth, and to record differences of glomerular size between different cortical zones. Nephrogenesis during kidney development involves reciprocal molecular signalling between cells of the metanephric mesenchyme and epithelial cells at the tips of the ureteric branches [2]. The formation of nephrons lasts from week 9 to week 44 after conception, with each newly formed nephron opposed to the periphery of each renal lobe. Consequently, the earliest formed glomeruli are located centrally. Approximately 70 75% of the nephrons are found in the outer and midportions of the renal cortex [3]. Inner cortical (juxtamedullary) nephrons form first, while the most superficial outer cortical nephrons form last. In fetal kidneys, juxtamedullary glomeruli have been reported to be larger than outer cortical glomeruli [4]. Souster and Emery et al. (1980) [2] have shown that initially the glomerular size increases rapidly, while the difference between size of juxtamedullary and superficial glomeruli tapering progressively and disappearing after the age of 3 years [4]. Olivetti and co-workers et al. (1980) found a linear transcortical gradient of glomerular diameters in both young and old rats, with a mean volume of juxtamedullary renal glomeruli twice that of subcapsular glomeruli [5]. According to Arataki et al. (1926), the glomeruli of rats continue to increase in number and size until the age of 100 days [6]. Tsuda et al. (1943) described that in all cases the central glomeruli had a greater diameter than the peripheral ones, in some cases twice as great, as but never more than this [7]. Shimada K. et al. (1993) states that, The glomeruli were arranged in the uniform fashion on the medullary ray with the smallest in the most superficial cortex and the largest in the juxtamedullary zone. The superficial glomeruli remained at the surprisingly same size up to birth. Juxtamedullary glomeruli showed no significant differences before birth, either [8]. Dakovic-Bjelakovic M. et al. (2006) studied on changes of glomerular size during different gestational ages and concluded that superficial glomeruli had the smallest diameter, while juxtamedullary glomeruli were the largest. The average glomerular diameter increased during intrauterine development in all zones, most intensive in the X lunar month [37-40 weeks]. There was a significant difference of the glomeruli between different cortical zones in the young foetuses. Such significant difference receded as gestational age increased [9]. Tank K. C. et al. (2012) showed in their study that histologically the glomeruli were arranged in such a way that the smallest in the most superficial cortex and the largest in the juxtamedullary zone. The mean glomerular size in the outer, middle, and inner zone of the cortex was 43.8 µ, 51.5 µ, and 59.7µ respectively, and it remained nearly same in a particular zone of cortex at different weeks of fertilization from 12 to 36 weeks of fertilization [10]. Number of glomeruli increases gradually between 10 th and 18 th of gestation and then increases rapidly until 32 weeks then an upper limit is reached. At term nephron formation is complete, with each kidney containing about 2 millions of nephrons [11]. Once glomerular production is brought about to a halt, it never resumes subsequently. Increase Int J Anat Res 2016, 4(1): ISSN
3 in kidney size is the result of increasing length of tubules and associated increase in blood vessels and connective tissues [12]. MATERIALS AND METHODS Thirty human fetal kidneys were studied in the present study. Thirty aborted fetuses of midgestational age without any congenital anomaly were collected from the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology MGM medical college, Aurangabad after taking written permission of parents. Each specimen fetus was tagged with an identification number. The proper fixation of fetus was done with 10% formalin solution for 2 to 3 days. Macrodissection was done to extract both kidneys enblock. Only normal kidneys were included in the study. The associated fat, fascia, nerves and other unwanted tissues were removed from the dissected fetal kidneys. The kidneys were kept in 10% formalin for 24 hours and then processed for dehydration, clearing, embedding. Then paraffin blocks were prepared. Tissue blocks were, serially sectioned in a transverse plane parallel to the long axis of the kidney. 7 µm thick sections were taken using a rotary microtome. After affixing sections on glass slides, tissue was stained with Haematoxylin- Eosin (H&E) and Masson s trichrome stain. All specimens, divided into 8 groups according to gestational age of the fetus for the purpose of histomorphometrical study of glomerulus. Group 1-14 weeks, Group 2-16 weeks, Group 3-18 weeks, Group 4-20 weeks, Group 5-22 weeks, Group 6-24 weeks, Group 7-26 weeks and Group 8-28 weeks. Method used for Micrometry [11]: Micrometry is a two-dimensional quantitative method that uses a gauge with a calibrated micrometer for the measurement of objects under microscopic observation. The Micrometer has two parts, a stage micrometer and an eyepiece reticle. The use of a stage micrometer to check the divisions and measurements on the eyepiece reticle is the best way to achieve this calibration. Stage Micrometer (fig. 1): A Stage Micrometer is a microscope slide with a finely divided scale marked on the surface. The scale is of a known true length and used for calibration of optical systems with eyepiece reticle patterns. Eyepiece Reticle (fig. 1): A linear measurement scale fitted into one eyepiece of the light microscope. The eyepiece scale is called as the reticle. This eyepiece reticle is interchangeable. The reticle is used to measure any plantar dimension in a microscope field, since the ocular can be rotated in any direction and the object of interest can be repositioned with the stage manipulators. The present study used the micrometer for micrometry. The divisions and measurements on the eyepiece reticle are used to achieve the calibration. Fig. 1: Stage Micrometer and Eyepiece Reticle. Conversion Factor: To get the conversion factor, we calibrated the microscope and its associated reticle with a stage micrometer. The following was the procedure: 1. Select normal or lowest magnification. 2. Ensure the eyepiece reticle is in sharp focus, 2. Place the stage micrometer on microscope stage. 3. Adjust position and focus so the stage scale is clearly visible, 4. Rotate the eyepiece reticle and position the stage in the field of view so that the two scales appear parallel, one positioned above the other 5. Adjust the alignment of the scales so that the zero values correspond. With the zero values aligned, the stage micrometer scale will either appear longer than the eyepiece scale or alternatively it may appear the same length or shorter than the eyepiece scale. In the present study the conversion factor calculated as given below. The stage scale appears shorter than the eyepiece scale: Note how many eyepiece divisions match the full length of the stage micrometer scale. Using a Stage Micrometer with 100 divisions of 0.1mm, which is the total Int J Anat Res 2016, 4(1): ISSN
4 length of the scale equal to 1000 µm. So, 1 division is equal to 10 µm. Selected objective magnifications 4X: The full length of the stage micrometer scale covered 29 divisions of the reticle. So the first 29 divisions of the reticle scale are 0.1mm long which is equal to 100 divisions the full length of the reticle scale equals 1000 µm. So each reticle division is equivalent to (1000/29) = 34.5µm. For an eyepiece reticle with 100 divisions, each division will measure 34.5 µm at the stage for this magnification. Selected objective magnification 10 X: The stage scale now covers 79 divisions of the reticle scale. For an eyepiece reticle with 100 divisions, each division will measure [1000/79] = 12.7ìm at the stage for this magnification. Therefore, we can apply these conversion factors to state what each division of the eyepiece reticle is measuring for a selected magnification. 4X - 1 division = µm 10X - 1 division = 12.7 µm If the stage scale appears longer than the eyepiece scale: Count the number of eyepiece reticle divisions that cover the stage micrometer scale. The Conversion Factor: A Stage Micrometer with 100 divisions in 0.1mm having a total length of 0.1m.m. Selected objective magnification 40 X: The full length of the reticle scale only spans the first 30.5 divisions of the stage scale. We know that 100 divisions of stage scale are equal 0.1 mm = 1000 µm. And 1 division =10 µm. So 33.5 divisions of stage scale equals to 305 µm, which is equivalent to 100 divisions of eyepiece reticle. So 1 division of the reticle scale will measure [305/100] =3. 05 µm. The conversion factor is: 40X - 1 division = µm Histomorphometry of glomerulus: In each histological section the renal cortex was divided into three evenly spaced zones, Outer zone (superficial glomeruli), middle zone, and inner zone (juxtamedullary glomeruli). Outer cortical glomeruli were within 3-4 glomerular diameters of the capsule, while juxtamedullary glomeruli were within 3-4 glomerular diameters of the corticomedullary junction. The diameters of individual glomeruli from each zones of the cortex from each group were measured by using ocular micrometer [8]. [fig 2] For measurement of glomerular diameter five random approximately circular glomeruli from each zone of the cortex were analysed. Two fetal kidney samples were studied in each group of gestational week. Total ten glomerular diameters were measured in each cortical zone in different groups. Average diameter of the three cortical zones was analysed and compared with the other studies. The data obtained showed specific rate of growth of fetal kidney in different gestational ages. Fig. 2 : Measuring diameter of Glomeruli- Diameter of glomerulus= = 88.9 µm. RESULTS 10 X- [14 weeks, middle cortex] 10 X- [14 weeks, middle cortex] After staining with H and E and Masson s trichrome stains the following things were observed. Glomerular Size: With the help of micrometry we calculated the diameters of individual glomeruli from outer, middle and inner zones of the cortex. These observations suggest that Glomeruli in the superficial cortical zone had the lowest Int J Anat Res 2016, 4(1): ISSN
5 Table 1: Relation of glomerular size in outer middle and inner cortex with gestational age of fetus. Gestational age [In weeks] Outer cortex average diameter that is 55.88±7.20 to 63.5±7.33 µm. In the intermediate cortex average size of glomerulus is ± to ± 9.37 µm. and the deepest juxta medullary glomerulus were largest in size that is 94.61±14.18 to ± In present study, the period of intensive growth is between weeks of gestation, while the size of the glomeruli in a particular zone does not significantly alter with different gestational age groups. Middle cortex Inner cortex [In µm] ±SD [In µm] ±SD [In µm] ±SD ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ±14.18 Graph 1: Relation of glomerular size in outer, middle and inner cortex with gestational age of fetus. Gestational Age [In weeks] Average outer glomrular Diameter [In µm ] DISCUSSION Dakovic-Bjelakovic M et al. (2006) [9] states that the average glomerular diameter in the outer zone continually increased from IV lunar month [13-16 weeks] ( / mm) to X lunar month [37-40 weeks ] ( / mm), with highly significant correlation with gestational age (r=0. 755; p<0.01). In the intermediate zone diameter increased from / mm (IV lunar month) to / mm (X lunar month) with low linear correlation with gestational age (r=0. 161). Juxtamedullary glomeruli were the biggest ones with their average diameter, during the IV LM ranged from / mm to / mm. In the IV and V lunar months [13 20 weeks] of gestation, there was a significant difference (p<0.01; p<0.05) between the average glomerular diameter in the different zones of the kidney cortex. Tsuda et al. (1943) [7] stated that in all cases the central glomeruli have a greater diameter Table 2: Comparison of average Glomerular diameter at outer middle and inner cortex with the study of Tank K.C et al. [10]. Average middle glomerular Diameter [In µm ] Average Inner Glomerular Diameter [in µm ] Tank K.C et al. Present Tank K.C. Present Tank K.C. Present [10] study et al. [10] study et al. [10] study Int J Anat Res 2016, 4(1): ISSN
6 than the peripheral ones as high as twice. Robert L. Vernier et al. (1962) [12] observed that glomeruli of all stages of maturity from the most primitive to the mature, adult type of glomerulus were founded in the renal cortex of fetuses of all ages. Glomerular maturation was noted to proceed progressively from about 1 1/2 months (origin of metanephros) to about 35 weeks of gestation. Shimada K et al. (1993) [8] reported that the glomeruli were arranged in the uniform fashion on the medullary ray with the smallest in the most superficial cortex and the largest in the Juxtamedullary zone According to Tank K. C. et al. (2012) [10] the glomeruli are smallest in the most superficial cortex and the largest in the juxtamedullary zone. The mean glomerular size remained nearly same in a particular zone of cortex at different weeks of fertilization from 12 to 36 weeks of fertilization. The present results correlate all the above workers study. It observes smallest diameter glomerulus in outer cortex, while the largest one in inner cortex. In all the groups [14-28 weeks] of the present study, all stages of maturation of glomerulus are seen. The glomerular diameter remains nearly same in different zones of the cortex, which supports the observation of Tank K. C et al. [10]. However, not follow the results of Dakovic-Bjelakovic M et al. [9]. Average glomerular diameters in outer, middle and inner zones of the cortex are comparable with the study of Tank K.C et al. [10]. It is possible to analyse functional maturation of fetal kidney with the help of glomerular diameter in different zones of the cortex. CONCLUSION The present study showed the significant difference of the size of glomeruli between different cortical zones with the presence of the smallest diameter glomerulus in outer cortex, and the largest in the inner juxtaglomerular cortex. The period of intensive growth is between weeks of gestation, while the size of the glomeruli in a particular zone does not significantly alter with different gestational age groups. The present study indicate that the micrometry of fetal glomerulus constitute an important tool which could extract as much information as possible from tissue specimens and set objective criteria for the definition of glomerular disease. It can complement molecular data with information on quantity that are amenable to statistical evaluation. It may be possible to analyse functional maturity of fetal kidney with the help of change in glomerular diameter, which could be used as baseline values for studies of glomerular diseases. Conflicts of Interests: None REFERENCES [1]. Bertram J F. Analyzing renal glomeruli with the new stereology. Int Rev Cytol. 1995;161: [2]. Clark AT, Bertram JF. Molecular regulation of nephron endowment. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:F485- F497.[PubMed] [3]. Moore L, Williams R, Staples A. Glomerular dimensions in children under 16 years of age. J. Pathol. 1993;171: [4]. Souster LP, Emery JL. The sizes of renal glomeruli in fetuses and infants. J. Anat. 1980;130: [5]. Olivetti G, Anversa P, Melissari M, LoodAV. Morphometry of the renal corpuscle during postnatal growth and compensatory hypertrophy. Kidney Int. 1980;17: [6]. Arataki M. On the postnatal growth of the kidney, with special reference to the number and size of the glomeruli (albino rat). Am. J. Anat. 1926;36: [7]. Tsuda. Histologic investigation of fetal kidney, Jap J.Obst.Gynec.1943;17: [8]. Shimda K., Hosokawa S., Tohda A. Histological study of fetal kidneys. Development of nephrons according to gestational weeks. Nippon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi. 1993;84(12): [9]. Dakovic-Bjelakovic M. et al. Changes of glomerular size during fetal kidney development.s RP. Arh. Celok. Lek. 2006;134(1-2): [10]. Tank K.C.,Saiyad S. S.,Pandya A. M., Akbari U. J. Dangar K. P. A study of histogenesis of human fetal kidney, Int. J. of Biol. Med Res. 2012;3(1): [11]. Todd J.C. Clinical Diagnosis by Laboratory Methods, Philadelphia, PA, W.B. Saunders Company, 1979 [12]. Robert L. Vernier. Studies of human fetal kidney :1 Development of glomerulus. Jour. Of Peadiatrics. 1962;60(5); How to cite this article: Suvarna A. Gulanikar, G.A. Shroff, A.R. kharkar, V.S.Mandhana. ESTIMATION OF GLOMERULAR SIZE BY MICROMETRY IN MIDGESTATIONAL PERIOD. Int J Anat Res 2016;4(1): DOI: / ijar Int J Anat Res 2016, 4(1): ISSN
Histological differentiation of human fetal kidney
 Original Research Article Histological differentiation of human fetal kidney Mamatha Hosapatnaa 1, Hemalatha Bangera 2, Anne D Souza 3, Aswin Das 4, Supriya 4, Antony Sylvan D Souza 5, Vrinda Hari Ankolekar
Original Research Article Histological differentiation of human fetal kidney Mamatha Hosapatnaa 1, Hemalatha Bangera 2, Anne D Souza 3, Aswin Das 4, Supriya 4, Antony Sylvan D Souza 5, Vrinda Hari Ankolekar
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
[ 331 ] THE LATE INTRAUTERINE AND POSTNATAL DEVELOP- MENT OF HUMAN RENAL GLOMERULI
![[ 331 ] THE LATE INTRAUTERINE AND POSTNATAL DEVELOP- MENT OF HUMAN RENAL GLOMERULI [ 331 ] THE LATE INTRAUTERINE AND POSTNATAL DEVELOP- MENT OF HUMAN RENAL GLOMERULI](/thumbs/85/92705171.jpg) [ 331 ] THE LATE INTRAUTERINE AND POSTNATAL DEVELOP- MENT OF HUMAN RENAL GLOMERULI BY MORAG S. MACDONALD* AND JOHN L. EMERY Department of Pathology, The Children's Hospital, Sheffield When examining a
[ 331 ] THE LATE INTRAUTERINE AND POSTNATAL DEVELOP- MENT OF HUMAN RENAL GLOMERULI BY MORAG S. MACDONALD* AND JOHN L. EMERY Department of Pathology, The Children's Hospital, Sheffield When examining a
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM
 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM cortex Medulla DEMO SLIDE BOX 172 (450-E001-H-76). Kidney, horse. the inner medulla medullary rays, Uriniferous tubules expand both the cortex and medulla corticomedullary
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM cortex Medulla DEMO SLIDE BOX 172 (450-E001-H-76). Kidney, horse. the inner medulla medullary rays, Uriniferous tubules expand both the cortex and medulla corticomedullary
The functional anatomy of the urinary system. Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic
 The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
~~I li~jllwl t... ~i d.. ud...!j.i..:.jj..u_,. ~I.:,.o \\- oo ~~1.:,-o L::...l_,
 Qatar Univ. Sci. J. (1993), 13(2): 264-270 PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE GUINEA PIG KIDNEY QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE MORPHOLOGY By ZEINAB M. A. EL GOHARY Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, University
Qatar Univ. Sci. J. (1993), 13(2): 264-270 PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE GUINEA PIG KIDNEY QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE MORPHOLOGY By ZEINAB M. A. EL GOHARY Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, University
HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FOETAL PITUITARY AT VARIOUS GESTATIONAL AGES S. Babu Rao * 1, G. Geetha vani 2, V. Subhadra Devi 3.
 Original Research Article HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FOETAL PITUITARY AT VARIOUS GESTATIONAL AGES S. Babu Rao * 1, G. Geetha vani 2, V. Subhadra Devi 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research,
Original Research Article HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FOETAL PITUITARY AT VARIOUS GESTATIONAL AGES S. Babu Rao * 1, G. Geetha vani 2, V. Subhadra Devi 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research,
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
(From the Institute of Pathology, Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and the Department of Zoology, Yale University, New Haven) Method
 THE EFFECT OF UNILATERAL NEPHRECTOMY ON THE SENILE ATROPHY OF THE KIDNEY IN THE WHITE RAT BY ROBERT A. MOORE, M.D.,* A~ LOUIS M. HELLMAN (From the Institute of Pathology, Western Reserve University, Cleveland,
THE EFFECT OF UNILATERAL NEPHRECTOMY ON THE SENILE ATROPHY OF THE KIDNEY IN THE WHITE RAT BY ROBERT A. MOORE, M.D.,* A~ LOUIS M. HELLMAN (From the Institute of Pathology, Western Reserve University, Cleveland,
Microscopic Anatomy of Inferior Medullary Velum Of Cerebellum
 32 J Anat. Soc. India 51(1) 32-34 (2002) Microscopic Anatomy of Of Cerebellum Arora, N.K. Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Chandigarh INDIA. Abstract. A study of the inferior medullary
32 J Anat. Soc. India 51(1) 32-34 (2002) Microscopic Anatomy of Of Cerebellum Arora, N.K. Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Chandigarh INDIA. Abstract. A study of the inferior medullary
The Egyptian journal of hospital medicine (2009)vol.,36:
 The Egyptian journal of hospital medicine (2009)vol.,36: 468-482 QUANTITATIVE AND HISTOCHEMICAL STUDY ON THE ADRENAL MEDULLA IN POST NATAL PERIOD OF ALBINO RAT Wagieh k.baiomy; Abdel-mawgood Anas; Mamdooh
The Egyptian journal of hospital medicine (2009)vol.,36: 468-482 QUANTITATIVE AND HISTOCHEMICAL STUDY ON THE ADRENAL MEDULLA IN POST NATAL PERIOD OF ALBINO RAT Wagieh k.baiomy; Abdel-mawgood Anas; Mamdooh
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus. With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs
 Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Histomorphometric Changes of Pancreatic Islets with Advancing Age A Postmortem Study in A Bangladeshi Male Population
 Histomorphometric Changes of Pancreatic Islets with Advancing Age A Postmortem Study in A Bangladeshi Male Population Shahriah S, 1 Nurunnabi ASM, 2* Begum GN, 3 Kabir R 4 1 Department of Anatomy, Z. H.
Histomorphometric Changes of Pancreatic Islets with Advancing Age A Postmortem Study in A Bangladeshi Male Population Shahriah S, 1 Nurunnabi ASM, 2* Begum GN, 3 Kabir R 4 1 Department of Anatomy, Z. H.
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017, 2706 2711 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE MICROANATOMICAL FEATURES OF THE RENAL CORTEX IN EMU (Dromaius novaehollandiae)
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017, 2706 2711 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE MICROANATOMICAL FEATURES OF THE RENAL CORTEX IN EMU (Dromaius novaehollandiae)
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences HISTOGENESIS OF MESODERMAL COMPONENTS OF HUMAN FETAL THYMUS ABSTRACT
 Research Article Cytology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 HISTOGENESIS OF MESODERMAL COMPONENTS OF HUMAN FETAL THYMUS BASHIR KHAN *1 AND SANOBAR SHAIKH 2 1 Department of
Research Article Cytology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 HISTOGENESIS OF MESODERMAL COMPONENTS OF HUMAN FETAL THYMUS BASHIR KHAN *1 AND SANOBAR SHAIKH 2 1 Department of
Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor
 Vet. Pathol. 12: 1-5 (1975) Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor C.H. LAMAR and D.C. VAN SICKLE School of Veterinary Medicine, Purdue University,
Vet. Pathol. 12: 1-5 (1975) Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor C.H. LAMAR and D.C. VAN SICKLE School of Veterinary Medicine, Purdue University,
Urinary Anatomy. Lab 40. Kidneys. Nephrons. Renal Corpuscle
 Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
LECTURE 4. Anatomy of the urinary and genital organs.
 LECTURE 4 Anatomy of the urinary and genital organs. SKELETOTOPY OF THE KIDNEYS Left kidney upper pole of the kidney - ThXI lower pole of the kidney LIII Right kidney is located on the half vertebra
LECTURE 4 Anatomy of the urinary and genital organs. SKELETOTOPY OF THE KIDNEYS Left kidney upper pole of the kidney - ThXI lower pole of the kidney LIII Right kidney is located on the half vertebra
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
Thyroid Follicles and Parenchyma are Found to Increase with Advancing age during the first 50 years of life in Bangladeshi People
 Thyroid Follicles and Parenchyma are Found to Increase with Advancing age during the first 50 years of life in Bangladeshi People Nurunnabi ASM 1, Mahbub S 2, Shahriah S 3, Begum GN 4, Ara S 5 Abstract
Thyroid Follicles and Parenchyma are Found to Increase with Advancing age during the first 50 years of life in Bangladeshi People Nurunnabi ASM 1, Mahbub S 2, Shahriah S 3, Begum GN 4, Ara S 5 Abstract
Age related muscle texture variation between Cobb-500 and Ross broiler strain
 J. Bangladesh Agril. Univ. 8(2): 265 269, 2010 ISSN 1810-3030 Age related muscle texture variation between Cobb-500 and Ross broiler strain M. T. Rahaman 1, M. S. Rahman 1, M. F. Hoque 2 and N. H. Parvez
J. Bangladesh Agril. Univ. 8(2): 265 269, 2010 ISSN 1810-3030 Age related muscle texture variation between Cobb-500 and Ross broiler strain M. T. Rahaman 1, M. S. Rahman 1, M. F. Hoque 2 and N. H. Parvez
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
LECTURE ON THE URINARY SYSTEM
 LECTURE ON THE URINARY SYSTEM (Uropoetic System) AN OVERVIEW Dr HAMIADJI THE URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance
LECTURE ON THE URINARY SYSTEM (Uropoetic System) AN OVERVIEW Dr HAMIADJI THE URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance
Ordering Physician. Collected REVISED REPORT. Performed. IgG IF, Renal MCR. Lambda IF, Renal MCR. C1q IF, Renal. MCR Albumin IF, Renal MCR
 RenalPath Level IV Wet Ts IgA I Renal IgM I Renal Kappa I Renal Renal Bx Electron Microscopy IgG I Renal Lambda I Renal C1q I Renal C3 I Renal Albumin I Renal ibrinogen I Renal Mayo Clinic Dept. of Lab
RenalPath Level IV Wet Ts IgA I Renal IgM I Renal Kappa I Renal Renal Bx Electron Microscopy IgG I Renal Lambda I Renal C1q I Renal C3 I Renal Albumin I Renal ibrinogen I Renal Mayo Clinic Dept. of Lab
Not all renal stem cell niches are the same: anatomy of an evolution
 eissn: 2281-0692 Journal of Pediatric and Neonatal Individualized Medicine 2016;5(2):e050225 doi: 10.7363/050225 Received: 2015 Sept 11; revised: 2015 Dec 21; accepted: 2016 Mar 01; published online: 2016
eissn: 2281-0692 Journal of Pediatric and Neonatal Individualized Medicine 2016;5(2):e050225 doi: 10.7363/050225 Received: 2015 Sept 11; revised: 2015 Dec 21; accepted: 2016 Mar 01; published online: 2016
41B. Metabolism produces wastes that must be eliminated from the body. This. Renal System Physiology: Computer Simulation
 41B E X E R C I S E Renal System Physiology: Computer Simulation O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define the following terms: glomerulus, glomerular capsule, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, nephron, proximal convoluted
41B E X E R C I S E Renal System Physiology: Computer Simulation O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define the following terms: glomerulus, glomerular capsule, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, nephron, proximal convoluted
******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY
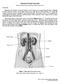 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
IN the kidneys of a wide variety of animals the second convoluted tubule
 Further Observations on the Glomerular Root of the Vertebrate Kidney BY J. F. A. McMANUS (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford) With five Text-figures INTRODUCTION IN the kidneys
Further Observations on the Glomerular Root of the Vertebrate Kidney BY J. F. A. McMANUS (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford) With five Text-figures INTRODUCTION IN the kidneys
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
The Histogenesis Of Islets In the Human Fetal Pancreas
 23 J Anat. Soc. India 51(1) 23-26 (2002) The Histogenesis Of Islets In the Human Fetal Pancreas Gupta, V., Garg, K., Raheja, S., Choudhry, R. and Tuli, A. Department of Anatomy, Lady Hardinge Medical College,
23 J Anat. Soc. India 51(1) 23-26 (2002) The Histogenesis Of Islets In the Human Fetal Pancreas Gupta, V., Garg, K., Raheja, S., Choudhry, R. and Tuli, A. Department of Anatomy, Lady Hardinge Medical College,
Histomorphometric Study of the Glomeruli of the Kidney in Bangladeshi Population
 Article Histomorphometric Study of the Glomeruli of the Kidney in Bangladeshi Population Fatema Johora 1, Abu Sadat Mohammad Nurunnabi 2, Sunjida Shahriah 3, Rukshana Ahmed 4, Shamim Ara 5 Abstract Background:
Article Histomorphometric Study of the Glomeruli of the Kidney in Bangladeshi Population Fatema Johora 1, Abu Sadat Mohammad Nurunnabi 2, Sunjida Shahriah 3, Rukshana Ahmed 4, Shamim Ara 5 Abstract Background:
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Morphometry and Histogenesis of Human Foetal Pancreas Sujatha Manupati 1, Raju Sugavasi 2*,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Morphometry and Histogenesis of Human Foetal Pancreas Sujatha Manupati 1, Raju Sugavasi 2*,
Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow and Their Control.
 Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow and Their Control. Chapter 26 Yanal A Shafagoj. MD. PhD Lecture-1 Introduction 31/3/2015 1 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine
Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow and Their Control. Chapter 26 Yanal A Shafagoj. MD. PhD Lecture-1 Introduction 31/3/2015 1 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM
 AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
IN normal male fowls, four developmental stages of spermatogenetic activity
 Development of the Testis Tubule in the Fowl By GAMAL A. R. KAMAR (From the Animal Production Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt) With three plates (figs. 1-3) SUMMARY Three
Development of the Testis Tubule in the Fowl By GAMAL A. R. KAMAR (From the Animal Production Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt) With three plates (figs. 1-3) SUMMARY Three
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats
 Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
POSTNATAL GROWTH OF THE LUNG
 Thorax (1962). 1, 329. BY M. S. DUNNILL* From the Department of Medicine, Columbia University, and the Cardiopulmonary Laboratory, Bellevue Hospital, New York There are two opposed views on the problem
Thorax (1962). 1, 329. BY M. S. DUNNILL* From the Department of Medicine, Columbia University, and the Cardiopulmonary Laboratory, Bellevue Hospital, New York There are two opposed views on the problem
On Three Cases of the Genuine Accessory Suprarenal
 Dept. of Anat., Tokyo Med. and Dent. Univ. (Chief: Prof. T. KIRINO). On Three Cases of the Genuine Accessory Suprarenal Bodies in Man. In the course of studies on the ZUCKERKANDL's paraganglia, by careful
Dept. of Anat., Tokyo Med. and Dent. Univ. (Chief: Prof. T. KIRINO). On Three Cases of the Genuine Accessory Suprarenal Bodies in Man. In the course of studies on the ZUCKERKANDL's paraganglia, by careful
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys II. Nephron Unit and Urine Formation
 URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced
 Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART
 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART 1 DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Urinary System Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body Regulates water, electrolyte, and ph
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART 1 DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Urinary System Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body Regulates water, electrolyte, and ph
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Development of Mesonephros and Metanephros in Phalange Stage Embryo of Leaf Nosed Bat Hipposideros speoris (Schnider); Chiroptera, Mammalia
 World Journal of Zoology 10 (3): 181-187, 2015 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2015 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2015.10.3.94126 Development of Mesonephros and Metanephros in Phalange Stage Embryo of Leaf
World Journal of Zoology 10 (3): 181-187, 2015 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2015 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2015.10.3.94126 Development of Mesonephros and Metanephros in Phalange Stage Embryo of Leaf
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Histomorphometric Study of the Proportion of Different Zones of Adrenal Cortex A Postmortem Study
 Article Histomorphometric Study of the Proportion of Different Zones of Adrenal Cortex A Postmortem Study Dilruba Siddiqua 1, Abu Sadat Mohammad Nurunnabi 2, Fatema Johora 3, Hasna Hena 4, Sunjida Shahriah
Article Histomorphometric Study of the Proportion of Different Zones of Adrenal Cortex A Postmortem Study Dilruba Siddiqua 1, Abu Sadat Mohammad Nurunnabi 2, Fatema Johora 3, Hasna Hena 4, Sunjida Shahriah
Development of the Urinary System. 3 Distinct Embryonic Kidney Structures
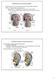 Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
H. M. Carleton, Lecturer in Histology, University of Oxford. (From the Department of Physiology.) INTRODUCTORY.
 Note on the Comparative Effects on Tissues of Isotonic Saline and Distilled Water when used as Solvents for Mercuric Chloride and Formol in Histological Fixation. By H. M. Carleton, Lecturer in Histology,
Note on the Comparative Effects on Tissues of Isotonic Saline and Distilled Water when used as Solvents for Mercuric Chloride and Formol in Histological Fixation. By H. M. Carleton, Lecturer in Histology,
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
The Urinary System PART A
 15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen. Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang
 Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang Abstract Although tissue engineering of artificial organs such as skin or cartilage
Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang Abstract Although tissue engineering of artificial organs such as skin or cartilage
The Golgi Element in the Cells of the Firstand Second Convoluted Tubules of the Cat Kidney.
 The Golgi Element in the Cells of the Firstand Second Convoluted Tubules of the Cat Kidney. By J. F. A. McManus, Major, R.C.A.M.C. With 5 Text-figures. CONTENTS. PREFACE 97 LITERATURE 97 MATERIALS AND
The Golgi Element in the Cells of the Firstand Second Convoluted Tubules of the Cat Kidney. By J. F. A. McManus, Major, R.C.A.M.C. With 5 Text-figures. CONTENTS. PREFACE 97 LITERATURE 97 MATERIALS AND
A morphometric study of the Pedicles of dry human typical lumbar vertebrae
 Original article: A morphometric of the Pedicles of dry human typical lumbar vertebrae Dhaval K. Patil 1 *, Pritha S. Bhuiyan 2 1Resident, Department of Anatomy, Seth G S Medical College, Parel, Mumbai-400012,
Original article: A morphometric of the Pedicles of dry human typical lumbar vertebrae Dhaval K. Patil 1 *, Pritha S. Bhuiyan 2 1Resident, Department of Anatomy, Seth G S Medical College, Parel, Mumbai-400012,
nevertheless, the arteriae rectee (subsequently called art. rect. verse) were completely injected. He gave figures "drawn as accurately as possible
 THE COURSE OF THE BLOOD OF THE RENAL ARTERY. BY J. N. LANGLEY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THERE are many accounts of the blood flow through the kidney. A few only need here be mentioned.
THE COURSE OF THE BLOOD OF THE RENAL ARTERY. BY J. N. LANGLEY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THERE are many accounts of the blood flow through the kidney. A few only need here be mentioned.
Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal
 Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Chapter 25: Urinary System
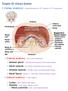 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
HISTOGENESIS AND MORPHOGENESIS OF HUMAN LARYNGEAL EPITHELIUM: A PRENATAL STUDY Rachna Magotra 1, Sanjay Raina 2, Shyama K.
 HISTOGENESIS AND MORPHOGENESIS OF HUMAN LARYNGEAL EPITHELIUM: A PRENATAL STUDY Rachna Magotra 1, Sanjay Raina 2, Shyama K. Razdan 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Rachna Magotra, Sanjay Raina, Shyama K. Razdan.
HISTOGENESIS AND MORPHOGENESIS OF HUMAN LARYNGEAL EPITHELIUM: A PRENATAL STUDY Rachna Magotra 1, Sanjay Raina 2, Shyama K. Razdan 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Rachna Magotra, Sanjay Raina, Shyama K. Razdan.
Lab 2: Investigating Variation Across Spatial Scales
 Lab 2: Investigating Variation Across Spatial Scales What are scales and variation in a biological context? The world around us displays incredible diversity across many scales. Today s lab investigates
Lab 2: Investigating Variation Across Spatial Scales What are scales and variation in a biological context? The world around us displays incredible diversity across many scales. Today s lab investigates
Histobiometrical Study of the Ocular Muscles of Japanese Fetuses.
 Histobiometrical Study of the Ocular Muscles of Japanese Fetuses. V. Size of Muscle Fibres. By Akira Hayashi. From the Department of Anatomy, Keio University, Tokyo. With 10 Text-figures. Contents. I.
Histobiometrical Study of the Ocular Muscles of Japanese Fetuses. V. Size of Muscle Fibres. By Akira Hayashi. From the Department of Anatomy, Keio University, Tokyo. With 10 Text-figures. Contents. I.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Variations in the Appearance of Human Elastic Cartilage
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
Impact of Intramedullary Reaming Depth on Establishing Femoral Canal Axis in the Sagittal Plane
 Impact of Intramedullary Reaming Depth on Establishing Femoral Canal Axis in the Sagittal Plane Yifei Dai, Ph.D., Dwight Todd. Zimmer Inc, Warsaw, IN, USA. Disclosures: Y. Dai: 3A; zimmer inc. 4; zimmer
Impact of Intramedullary Reaming Depth on Establishing Femoral Canal Axis in the Sagittal Plane Yifei Dai, Ph.D., Dwight Todd. Zimmer Inc, Warsaw, IN, USA. Disclosures: Y. Dai: 3A; zimmer inc. 4; zimmer
Effect of methotrexate (mtx) administration on spermatogenesis: an experimental on animal model
 Effect of methotrexate (mtx) administration on spermatogenesis: an experimental on animal model S Shrestha, 1 S Dhungel, 1 AK Saxena, 2 S Bhattacharya 1 and D Maskey 1 1 Department of Anatomy, B. P. Koirala
Effect of methotrexate (mtx) administration on spermatogenesis: an experimental on animal model S Shrestha, 1 S Dhungel, 1 AK Saxena, 2 S Bhattacharya 1 and D Maskey 1 1 Department of Anatomy, B. P. Koirala
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Outline the functional anatomy, and the physiological factors, that determine oxygen delivery to the renal medulla.
 2011-2-21 Outline the functional anatomy, and the physiological factors, that determine oxygen delivery to the renal medulla. Oxygen delivery = Blood flow CaO 2 Where Blood flow determined by (arterial
2011-2-21 Outline the functional anatomy, and the physiological factors, that determine oxygen delivery to the renal medulla. Oxygen delivery = Blood flow CaO 2 Where Blood flow determined by (arterial
STUDIES ON HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF THE ABDOMEN ON ADULT WORKER BEES (APIS MELLIFERA CARPATHICA)
 STUDIES ON HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF THE ABDOMEN ON ADULT WORKER BEES (APIS MELLIFERA CARPATHICA) Petruţ T. 1, D. Condur 1, N. Velicu 1, V. Călin 1 1 Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Spiru Haret, 9-11 Energeticienilor
STUDIES ON HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF THE ABDOMEN ON ADULT WORKER BEES (APIS MELLIFERA CARPATHICA) Petruţ T. 1, D. Condur 1, N. Velicu 1, V. Călin 1 1 Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Spiru Haret, 9-11 Energeticienilor
Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome
 J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
Role of Flutamide on Testosterone Induced Prostatic Hyperplasia in Long Evans Rats
 Bangladesh Journal of Anatomy January 2010, Vol. 8 No. 1 pp. 16-20 Role of Flutamide on Testosterone Induced Prostatic Hyperplasia in Long Evans Rats Md. Atiar Rahman 1, Humaira Naushaba 2, Jesmin Akter
Bangladesh Journal of Anatomy January 2010, Vol. 8 No. 1 pp. 16-20 Role of Flutamide on Testosterone Induced Prostatic Hyperplasia in Long Evans Rats Md. Atiar Rahman 1, Humaira Naushaba 2, Jesmin Akter
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
Dr. Mahmud Abuauba MBChB, DCH, MD, PhD Consultant Pediatrician & pediatric Nephrologist Assistant Professor of Pediatrician
 RENAL BLOOD SUPPLY & FLOW Dr. Mahmud Abuauba MBChB, DCH, MD, PhD Consultant Pediatrician & pediatric Nephrologist Assistant Professor of Pediatrician Zawia Kidney Center 5 th May 2018 برعاية مركز عالج
RENAL BLOOD SUPPLY & FLOW Dr. Mahmud Abuauba MBChB, DCH, MD, PhD Consultant Pediatrician & pediatric Nephrologist Assistant Professor of Pediatrician Zawia Kidney Center 5 th May 2018 برعاية مركز عالج
Formation of Urine: Formation of Urine
 The Urinary outflow tract: monitors and regulates extra-cellular fluids excretes harmful substances in urine, including nitrogenous wastes (urea) returns useful substances to bloodstream maintain balance
The Urinary outflow tract: monitors and regulates extra-cellular fluids excretes harmful substances in urine, including nitrogenous wastes (urea) returns useful substances to bloodstream maintain balance
Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL)
 Original Research Article Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) Sridhar Reddy Erugula 1, P. Sujatha 2, Ayesha Sameera 3, B. Suresh Reddy 4, Jesudass Govada 5, G. Sudhakar 6, Kandukuri
Original Research Article Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) Sridhar Reddy Erugula 1, P. Sujatha 2, Ayesha Sameera 3, B. Suresh Reddy 4, Jesudass Govada 5, G. Sudhakar 6, Kandukuri
JINNAH SINDH MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
 MODULE TITLE INTRODUCTION TARGET STUDENTS DURATION MODULE OUTCOMES Spiral -1 Renal and Excretory-1 Module The Renal and Excretory-1 Module is designed to help the learners understand how the urinary system
MODULE TITLE INTRODUCTION TARGET STUDENTS DURATION MODULE OUTCOMES Spiral -1 Renal and Excretory-1 Module The Renal and Excretory-1 Module is designed to help the learners understand how the urinary system
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach
 Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology
 Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
Fine structural appearances of glomerular capillaries in a case of malignant hypertension
 J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 579-583 Fine structural appearances of glomerular capillaries in a case of malignant hypertension R. F. MACADAM From the University Department of Pathology, Western Infirmary,
J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 579-583 Fine structural appearances of glomerular capillaries in a case of malignant hypertension R. F. MACADAM From the University Department of Pathology, Western Infirmary,
Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
ASSESSMENT OF RELIABILITY OF VARIOUS CRITERIA USED IN ADULT HIP BONE SEX DIFFERENTIATION
 Original Research Article ASSESSMENT OF RELIABILITY OF VARIOUS CRITERIA USED IN ADULT HIP BONE SEX DIFFERENTIATION Vivek K Nirmale * 1, Mohammad Laeeque 2, Chaya V. Diwan 3. ABSTRACT International Journal
Original Research Article ASSESSMENT OF RELIABILITY OF VARIOUS CRITERIA USED IN ADULT HIP BONE SEX DIFFERENTIATION Vivek K Nirmale * 1, Mohammad Laeeque 2, Chaya V. Diwan 3. ABSTRACT International Journal
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
SEASONAL CHANGES IN HISTOLOGYOF THE THYROID GLAND CALOTIS VERSICOLOR
 SEASONAL CHANGES IN HISTOLOGYOF THE THYROID GLAND CALOTIS VERSICOLOR M. D. Kulkarni And A. H. Shinde Department of Zoology Yashwantrao Chavan Arts & Science College, Mangrulpir Dist. Washim. (Received
SEASONAL CHANGES IN HISTOLOGYOF THE THYROID GLAND CALOTIS VERSICOLOR M. D. Kulkarni And A. H. Shinde Department of Zoology Yashwantrao Chavan Arts & Science College, Mangrulpir Dist. Washim. (Received
Muscle tissue. 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue.
 Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
