HISTOGENESIS AND MORPHOGENESIS OF HUMAN LARYNGEAL EPITHELIUM: A PRENATAL STUDY Rachna Magotra 1, Sanjay Raina 2, Shyama K.
|
|
|
- Madison Williamson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HISTOGENESIS AND MORPHOGENESIS OF HUMAN LARYNGEAL EPITHELIUM: A PRENATAL STUDY Rachna Magotra 1, Sanjay Raina 2, Shyama K. Razdan 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Rachna Magotra, Sanjay Raina, Shyama K. Razdan. Histogenesis and Morphogenesis of Human Laryngeal Epithelium: A Prenatal Study. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences 2015; Vol. 4, Issue 28, April 06; Page: , DOI: /jemds/2015/698 ABSTRACT: The anatomy of epithelium of human foetal larynx has not been fully described. In the present study we observed the development of epithelium of human larynx, in 40 fetuses with gestational ages ranging from 75mm C. R. L. (crown rump length) to 220mm C. R. L. (Crown rump length). Tissues were prepared for microtomy by paraffin wax embedding method. Step sections (every fifth) were fixed and stained by Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) and Masson s Trichrome method. In the present study, the entire laryngeal cavity is lined uniformily by respiratory epithelium initially, i. e., ciliated pseudostratified columnar type. Later on the epithelium over the true vocal cords and dorsal surface of the epiglottis changes into stratified squamous type. Besides, there is flattening of epithelium, over the true vocal cords as a result of desquamation. Larynx, though is a common organ to reptiles, amphibians and mammals with function of breathing, sound production and preventing food particles going into the trachea but the advancement of human has make it a very important organ for physicians, paediatricians, otorhinolaryngologists etc. So the knowledge of anatomy of fetal airway and its development is important for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases. Our aim was to study the type of epithelium during different stages of development of human fetal larynx. KEYWORDS: Larynx, Fetus, Epithelium. INTRODUCTION: If one wishes to become acquainted with the structure and form of any organ, there is perhaps no better way than to trace its development, step by step back into the earlier embryonic stage as quoted by Harrison D. F. N. (1) An important and unusual fact about larynx is that phylogenetically it is eons older than those brain and muscle structures, responsible for the language and articulation. (2) Larynx, also called the voice box is a two inch, long tube shaped organ, in the neck. In adult males, it lies opposite third to sixth cervical vertebrae, although it is somewhat higher in children (C1- C4) and adult females. The wall of the larynx consists of mucosa, poorly defined submucosa and series of irregularly shaped cartilages connected by joints of fibroelastic membranes and a group of intrinsic skeletal muscles which act upon the cartilages. The laryngeal epithelium is mainly ciliated pseudostratified (ie., respiratory epithelium), where it covers the inner aspects of the larynx, including the posterior surface of epiglottis. However, over the vocal cords, it is nonkeratinised stratified squamous which protects the tissue from the effects of the considerable mechanical stresses acting on the surface of the vocal cords. According to the various controversial studies conducted on larynx, there was tremendous interest in, what type of cell composes the mucus membrane of larynx? Where is the epithelium squamous and where is it ciliated? Does squamous epithelium occurs in the area of the larynx in which it is present because of a functional or pathological transition or does it begin to differentiate in the embryo as part of an orderly process of development? J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol.4/ Issue 28/ Apr 06, 2015 Page 4816
2 These questions generated tremendous interest and were debated by every laryngologist HOPP, E. S (1955). (3) According to HOPP, E. S. (1955), (3) epithelium of the larynx differentiates in a definite pattern throughout embryonic life to achieve its adult appearance, a process called as physiological metaplasia. The embryonic epithelium of the true vocal cord becomes cuboidal and then stratified squamous. Scanning and thorough study of the available literature thus reveals vast controversy and a difference of opinion regarding the embryogenesis and histogenesis of epithelium of human fetal larynx. The present study has been undertaken to enable us to study the pattern of development of epithelium of human fetal larynx and compare the results so obtained with those of the earlier studies. MATERIAL AND METHODS: The present study was carried out on 40 human foetuses ranging from 75 mm C. R. L. to 220 mm C. R. L. The foetuses were collected from operation theatres, labour rooms and obstetric wards of Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics of Government Medical College, Jammu. Government Hospital, Gandhi Nagar Jammu and various Nursing homes operating in and around Jammu city. The fetuses were obtained as the byproducts of still births and abortions which were either induced or natural or from hystrotomy procedures. Specimens having any type of congenital malformations were not taken up for the present study. Foetuses were preserved in 10% formalin and their crown lump length was measured with a vernier calliper. Assessment of the age of the foetuses was done, according to the rule described by Hamilton, Boyd and Mossman. (4) (Table -1). Out of 40 foetuses dissected 15 foetuses were female and 25 were male. Two paramedian incisions were given on the anterior surface of the neck, skin was removed and larynx was removed enbloc along with epiglottis and some part of base of tongue. The tissues was fixed in 10% formalin for 7 to 10 days and prepared for microtomy by paraffin wax embedding method. 7 micron thick step sections (every 5 th ) were taken for fixation and staining. Staining was done by Harris Haematoxylin and Eosin stain (H and E) and Massons s Trichrome stain. OBSERVATIONS: The human foetuses were divided into four groups (Table 2). Group- I (75mm- 125mm C. R. L.). Nine foetuses were dissected in this group. The lining epithelium of the entire laryngeal cavity is pseudostratified columnar and the cells appear to be arranged in several layers as their nuclei are situated at different levels. In the present study, the cilia are seen on the epithelial surface lining the ventricular cavity at 112 mm C. R. L. Basement membrane is visible separating the surface epithelium from the underlying connective tissue of lamina propria (Fig-1) The epithelium lining the true vocal cords appear to be similar to the one lining the entire ventricular cavity. Goblet cells seen occasionally in few foetal specimen. Group-II ( mm C. R. L.) Eleven foetuses were dissected in this group. Well-formed epithelium lines the whole of the ventricular cavity which is of same type ie., ciliated pseudostratified columnar or respiratory type. The epithelium shows proximo- distal developmental gradient which means that the development of the epithelium in the proximal part of the ventricular cavity is advanced as compared to its distal end (Fig. 2). There is change of epithelium lining the true vocal J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol.4/ Issue 28/ Apr 06, 2015 Page 4817
3 cords i. e. from ciliated pseudostratified columnar type to stratified squamous epithelium. Occasional goblet cells may be seen in few foetuses. Group-III (146mm-168mm C. R. L.) Eight foetuses were dissected in this group. The ventricular cavity is uniformily lined by ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium except the true vocal folds and the dorsal surface of the epiglottis which shows stratified squamous epithelium on them (Fig. 3). Well ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium is observed on the laryngeal surface of the epiglottis in the ventricle. In the true vocal cords, diminished height of the stratified squamous epithelium is observed as a result of desquamation Goblet cells are more in number in the lower part of the laryngeal mucosa as compared to the previous group (Fig. 4). Group-IV (170mm-220mm C. R. L.) Twelve foetuses were dissected in this group showing same features as the previous group as regards its lining epithelium. Stratified squamous epithelium of the true vocal folds appears flattened now due to desquamation. Goblet cells have increased in number and are more abundant in the lower part of the laryngeal ventricle and are well developed and well recognised by 21 st week of intrauterine life (Fig. 5). DISCUSSION: In the present study, the emphasis is laid on the epithelium of developing human larynx. The present study shows pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium lining the ventricular cavity uniformly in all the four groups starting from 12 wks of foetus except the true vocal folds and anterior surface of epiglottis where the lining epithelium is of stratified squamous variety. This finding is similar to the finding of Hopp, ES (1955) (3) and Meena Negi and Chandrama Anand (1987). (5) This study shows flattening of stratified squamous epithelium of the vocal folds due to desquamation which is especially marked in group 3 and 4 foetuses. This observation is consistent with the observation made by Nakashima et al (1981) (6) who observed diminished height of stratified squamous epithelial cells of true vocal folds. These findings were further supported by similar findings of Hopp E. S. (1955) (3) who observed same changes of foetus of 30wks intrauterine life and by those of Meena Negi and Chandrama Anand (1987) (5) who observed them at the 17 wks of intrauterine life. The present study reveals respiratory type of epithelium that is ciliated pseudo stratified columnar type lining the laryngeal surface of epiglottis in the ventricular cavity. This is in accordance with the findings of Meena Negi and Chandrama Anand (1987) (5) however Kooli. H. et al (2001) (7) differed by observing that the laryngeal surface of the epiglottis has keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium in 60%, and respiratory type in 44%. In the present study the cilia are observed from 16 wks of gestation. This observation is contrary to the observation of Nakashima T. et al (1981) (6) who reported the appearance of first cilia in larynx in 12wks fetus. Our observations do not coincide with the observations of Meena Negi and Chandrama Anand (1987) (5) who observed cilia at 15wks of intrauterine life. SUMMARY: The present study shows the development of the laryngeal epithelium in 40 human foetuses ranging from 75 mm CRL to 220 mm CRL. The entire laryngeal cavity is lined initially uniformally by the respiratory epithelium that is ciliated pseudostratified columnar type. Later on the epithelium over the true vocal cords and dorsal surface of the epiglottis changes into the stratified squamous type. Besides there is flattening of the epithelium over the true vocal cords as a result of desquamation. J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol.4/ Issue 28/ Apr 06, 2015 Page 4818
4 REFERENCES: 1. Harrison, D. F. N.; (1995) (Donald Frederickn Norris): The anatomy and Physiology of the Mammalian Larynx/DFN Harrison. Published by the Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge, the Pitt Building, Trumpington street, Cambridge CB2 IRP ISBN (hardback). Pg Aronson, A. E; Bless, D. M; Petty B. E; (1928): In clinical voice disorders, 4 Th edition Published by Thieme Medical Publishers, United States of America pg 1-2 ISBN S. 3. Hopp, E. S., (1955): The development of the epithelium of the larynx; in laryngoscope Vol. 65, Pg Hamilton, W. J. and Mossman, H. W.; (1978): Hamiton, Boyd and Mossman; s Embryology, 4 th edition. Published by Macmillan London. Pg Meena Negi and Chandrama Anand (1987): Histology and Histo-chemical studies on developing human larynx in J. Ant. Soc, India, Vol. 36 No. 1. Pg Nakashima, T., Makishima, K., Komiyama, S., Takeda, K. And Hiroto, I.: (1981): local Immune system in the developing Fetal Larynx in the Laryngoscope, 91: Pg Kooli, H., Zhioua, A., Zekris, Najeh D., Jaafoura, M. H., and Ferjaoui, M., Histology of Larynx; Rev. Laryngol otol Rhinol (Bord) 2001; 122 (5). Pg FIGURE 1: BASEMENT MEMBRANE (A), PSEUDOSTRATIFIEDCOLUMNAR EPITHELIUM (B), SHOWING CILIA (C) IN 115 mm C. R. LENGTH FETUS H & E X 400. Fig. 1 J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol.4/ Issue 28/ Apr 06, 2015 Page 4819
5 FIGURE 2: PROXIMO DISTAL (A & B) DIFFERENTIATION OFEPITHELIUM OF LARYNGEAL CAVITY (C) SEEN IN135 mm C. R. LENGTH FETUS MASSON STRICHROME X100. Fig. 2 FIGURE 3: TRUE VOCAL FOLD SHOWING STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM (A) LINING VENTRICULAR CAVITY (B) IN 158 mm C. R. LENGTH FETUS H&E X400. Fig. 3 FIGURE 4: WELL ESTABLISHED GOBLET CELL (B) IN CILIATED PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM (A) IN 168 mm C. R. LENGTH FETUS MASSON S TRICHROME X400. Fig. 4 J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol.4/ Issue 28/ Apr 06, 2015 Page 4820
6 FIGURE 5: NUMEROUS GOBLET CELLS (A) PRESENT IN EPITHELIAL LINING (B) OF LARYNGEAL CAVITY SEEN IN 172 mm C. R. LENGTH FETUS H&E X400. Fig. 5 Age of the Embryo /fetus Crown Rump length (C. R. L.) in mm 32 days 5 mm days 5mm +1mm per day 56 days onwards Calculated age of fetus at 55 days +1. 5mm per day TABLE 1 Group No. Crown- Rump Length (C. R. L.) in mm Number of Fetuses I 75 to II 128 to III 146 to IV 170 to TABLE 2 AUTHORS: 1. Rachna Magotra 2. Sanjay Raina 3. Shyama K. Razdan PARTICULARS OF CONTRIBUTORS: 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Jammu. 2. Demonstrator, Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Jammu. FINANCIAL OR OTHER COMPETING INTERESTS: None 3. Ex HOD & Professor, Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Jammu. NAME ADDRESS ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Dr. Rachna Magotra, 242/7 Channi Himmat, Jammu drmagotrarachna@gmail.com < Date of Submission: 12/03/2015. Date of Peer Review: 13/03/2015. Date of Acceptance: 23/03/2015. Date of Publishing: 03/04/2015. J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol.4/ Issue 28/ Apr 06, 2015 Page 4821
Upper Respiratory Histology
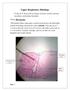 Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Histogenesis of Human Foetal Lung: A Light Microscopic Study.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 9, Issue 2 (Jul.- Aug. 2013), PP 01-08 Histogenesis of Human Foetal Lung: A Light Microscopic Study.
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 9, Issue 2 (Jul.- Aug. 2013), PP 01-08 Histogenesis of Human Foetal Lung: A Light Microscopic Study.
PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ Epithelia Simple epithelia Stratified epithelia Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified Stratified squamous - non keratinized - keratinized
PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ Epithelia Simple epithelia Stratified epithelia Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified Stratified squamous - non keratinized - keratinized
The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review
 Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Epithelium tissue system
 Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
TISSUES TYPES. CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions
 Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions
 Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Tissue: is a group of cells that serve the same function, they are surrounded by extra cellular matrix. The 4 basic types of tissue: 1. epithelial
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Tissue: is a group of cells that serve the same function, they are surrounded by extra cellular matrix. The 4 basic types of tissue: 1. epithelial
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
Objectives. Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology. Function of the Lungs/Heart. The lung is for gas exchange. Failure of the Lungs/Heart
 Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Dr. Abeer.c.Yousif. Histology -2 nd stage. What is histology?
 What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES
 Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface
 Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface always has one exposed (apical) surface Some surfaces are smooth & slick, others may have: microvilli fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane; increase
Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface always has one exposed (apical) surface Some surfaces are smooth & slick, others may have: microvilli fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane; increase
Anatomy PHL 212. Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan. -
 Anatomy PHL 212 Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor College of Pharmacy (Female Section) Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University Al kharj / Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Email :- da.hassan@psau.edu.sa 1 Anatomy
Anatomy PHL 212 Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor College of Pharmacy (Female Section) Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University Al kharj / Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Email :- da.hassan@psau.edu.sa 1 Anatomy
Epithelial Tissue. Functions include: 1. Protection 4. Absorption 2. Secretion 5. Filtration 3. Sensory reception
 Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Respiratory System Structures and Gas Exchange
 A. Respiratory medium the oxygen source 1. Air 2. Water Respiratory Medium Organism Cellular Respiration O 2 CO 2 B. Respiratory surface the structure where exchange of gases with the surrounding environment
A. Respiratory medium the oxygen source 1. Air 2. Water Respiratory Medium Organism Cellular Respiration O 2 CO 2 B. Respiratory surface the structure where exchange of gases with the surrounding environment
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Prepared By Student. Dania Abed Al-majeed. Rahma Raad Hanna. Balqees Mohammed Aasim. Dania Hisham. Rasha Rafiee
 Prepared By Student Rahma Raad Hanna Balqees Mohammed Aasim Dania Hisham Dania Abed Al-majeed Rasha Rafiee Epithelia Epithelia can be derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm -ectoderm gives rise to
Prepared By Student Rahma Raad Hanna Balqees Mohammed Aasim Dania Hisham Dania Abed Al-majeed Rasha Rafiee Epithelia Epithelia can be derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm -ectoderm gives rise to
Bio & 241 A&P Unit 1 / Lecture 3
 Bio & 241 A&P Unit 1 / Lecture 3 Tissues All body tissues arise from three fundamental embryonic tissues. Endoderm: forms epithelial tissues lining internal organs such as the GI tract Mesoderm: connective
Bio & 241 A&P Unit 1 / Lecture 3 Tissues All body tissues arise from three fundamental embryonic tissues. Endoderm: forms epithelial tissues lining internal organs such as the GI tract Mesoderm: connective
Basic Tissue Types and Functions
 Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Please refer back to the slides as these are extra notes only. Slide 2 -The Larynx is a Box of cartilage.
 [ANATOMY #3] 1 بسم رلاهللا Please refer back to the slides as these are extra notes only. Slide 2 -The Larynx is a Box of cartilage. -The lower border of c6 is the lower border of cricoid cartilage. -The
[ANATOMY #3] 1 بسم رلاهللا Please refer back to the slides as these are extra notes only. Slide 2 -The Larynx is a Box of cartilage. -The lower border of c6 is the lower border of cricoid cartilage. -The
Chapter 4 Histology: The study of body tissues
 Chapter 4 Histology: The study of body tissues https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zwxm2a0tfxm Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues = groups of cells with similar structure and
Chapter 4 Histology: The study of body tissues https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zwxm2a0tfxm Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues = groups of cells with similar structure and
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
MH1001 Larynx, Monkey, H&E
 MH1001 Larynx, Monkey, H&E - False vocal fold : ciliated pseuodostratified columnar epithelium - True vocal fold : nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium vocalis muscle, vocal ligament - Thyroid
MH1001 Larynx, Monkey, H&E - False vocal fold : ciliated pseuodostratified columnar epithelium - True vocal fold : nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium vocalis muscle, vocal ligament - Thyroid
TISSUE. A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS
 TISSUE A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelium Composed of a layer of cells. Lines
TISSUE A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelium Composed of a layer of cells. Lines
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet
 Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelial Tissue. By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: different types of epithelial membranes.
 Epithelial Tissue Objectives: By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: n Describe general characteristics of epithelial tissue. n Discuss microscopic structure and distribution of different types
Epithelial Tissue Objectives: By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: n Describe general characteristics of epithelial tissue. n Discuss microscopic structure and distribution of different types
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
EPITHELIUM 3/12/2018 د. درويش بدران د. ماهر الحديدي د.امجد الشطرات و احسان العمري
 EPITHELIUM 1 2 3 1- SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM It is a single layer of flat cells that resembles a tiled floor when viewed from apical surface; centrally located nucleus that is flattened and oval or spherical
EPITHELIUM 1 2 3 1- SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM It is a single layer of flat cells that resembles a tiled floor when viewed from apical surface; centrally located nucleus that is flattened and oval or spherical
UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI
 UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 LEVEL I MID-SEMESTER II EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN NURSING (BScN) AND BACHELOR OF PHARMACY (B.PHARM) MARKING SCHEME HNS101/UPC106:
UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 LEVEL I MID-SEMESTER II EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN NURSING (BScN) AND BACHELOR OF PHARMACY (B.PHARM) MARKING SCHEME HNS101/UPC106:
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Chapter 05. *Lecture Outline. PowerPoints prepared by Melanie Waite-Altringer Biology Faculty Member of Anoka-Ramsey Community College
 Chapter 05 *Lecture Outline *See separate Image PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. PowerPoints prepared by Melanie Waite-Altringer Biology Faculty
Chapter 05 *Lecture Outline *See separate Image PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. PowerPoints prepared by Melanie Waite-Altringer Biology Faculty
Body Tissues Pearson Education, Inc.
 Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Body Tissues. Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure. and function Four primary tissue types:
 Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
يراهظلا( يئلاطلا جيسنلا
 Epithelium النسيج الطالئي )الظهاري( Features of Epithelium Epithelium occurs in the body as a sheet of cells that covers a body surface, lines a cavity, or forms a gland. Coverings, linings, glands. Derived
Epithelium النسيج الطالئي )الظهاري( Features of Epithelium Epithelium occurs in the body as a sheet of cells that covers a body surface, lines a cavity, or forms a gland. Coverings, linings, glands. Derived
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts
 77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Chapter 5. Tissues. 4 Types of Body Tissues. Tissues
 Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Tissue four basic types of tissue Epithelial Tissue Functions of Epithelial Tissue
 Tissue A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar shape and function. Different types of tissues can be found in different organs. In humans, there are four basic types of tissue: 1. Epithelial Tissue
Tissue A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar shape and function. Different types of tissues can be found in different organs. In humans, there are four basic types of tissue: 1. Epithelial Tissue
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Lab Activity 27. Anatomy of the Respiratory System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
BIOH111. o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Biology Histology: Histology: is the study of the tissues of the body. Tissue: group of similar cells combined to perform a common function. The human body is composed of only 4 basic
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Biology Histology: Histology: is the study of the tissues of the body. Tissue: group of similar cells combined to perform a common function. The human body is composed of only 4 basic
Histology. Study of body tissues
 Histology Study of body tissues 2 Introduction to Body Tissues 1. Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function 2. Four major types (4 Cs) a. Epithelial - Cover b. Connective
Histology Study of body tissues 2 Introduction to Body Tissues 1. Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function 2. Four major types (4 Cs) a. Epithelial - Cover b. Connective
Tissues and Structures to Know for the Lab Practical
 Ch. 3 - Cells and Tissues Tissues and Structures to Know for the Lab Practical Miss School, Miss Out! Simple squamous epithelium line and cover; site of diffusion Simple squamous epithelium apical surface
Ch. 3 - Cells and Tissues Tissues and Structures to Know for the Lab Practical Miss School, Miss Out! Simple squamous epithelium line and cover; site of diffusion Simple squamous epithelium apical surface
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System
 Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Histology and development of the respiratory system
 Histology and development of the respiratory system Árpád Dobolyi Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Outline of the lecture 1. Structure of the trachea 2. Histology
Histology and development of the respiratory system Árpád Dobolyi Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Outline of the lecture 1. Structure of the trachea 2. Histology
Introductory Histology Tutorial I
 Introductory Histology Tutorial I Epithelial Tissues Human Anatomy & Physiology I Assembled by Stephen Shoemake {Click mouse to advance} NAVIGATION = returns you to the previous slide. = returns you to
Introductory Histology Tutorial I Epithelial Tissues Human Anatomy & Physiology I Assembled by Stephen Shoemake {Click mouse to advance} NAVIGATION = returns you to the previous slide. = returns you to
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system
 Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
HISTOLOGY. Simple squamal lungs
 HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs
 Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Classification of Tissues
 6 R e v i e w S h e e t Exercise Classification of Tissues NAME LAB TIME/DATE Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group of cells similar to one another in structure that perform
6 R e v i e w S h e e t Exercise Classification of Tissues NAME LAB TIME/DATE Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group of cells similar to one another in structure that perform
Histology 101! !! Name:! Block: Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties!
 Histology 101 Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties Name: Block: "1 Introduction to Tissues Histology Notes Tissue (living fabric) : groups
Histology 101 Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties Name: Block: "1 Introduction to Tissues Histology Notes Tissue (living fabric) : groups
Chapter 4 - Epithelial Tissues
 Chapter 4 - Epithelial Tissues Tissues Definition A group of closely associated cells that work together to perform a specific function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement
Chapter 4 - Epithelial Tissues Tissues Definition A group of closely associated cells that work together to perform a specific function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
Tissues. Definition. A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function.
 Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
Review of Histopathological Changes in the Respiratory Tract of Rat Induced by Inhalation of the Mainstream Smoke of Standard Reference Cigarette 1R4F
 Review of Histopathological Changes in the Respiratory Tract of Rat Induced by Inhalation of the Mainstream Smoke of Standard Reference Cigarette 1R4F A. Teredesai LSRO Meeting, Dec., 13, 2001 Slide 1
Review of Histopathological Changes in the Respiratory Tract of Rat Induced by Inhalation of the Mainstream Smoke of Standard Reference Cigarette 1R4F A. Teredesai LSRO Meeting, Dec., 13, 2001 Slide 1
Tissue: The Living Fabric
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
Anatomy of the Airway
 Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Chapter 3. Cells and Tissues. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types:
Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types:
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues
 Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J TISSUE TYPES M. Spector, Ph.D. and I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. The
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J TISSUE TYPES M. Spector, Ph.D. and I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. The
LECTURE 2 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 LECTURE 2 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Respiratory system - a complex of organs and anatomical structures exercising function of external respiration. Functions of the respiratory system: - Provides the organism
LECTURE 2 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Respiratory system - a complex of organs and anatomical structures exercising function of external respiration. Functions of the respiratory system: - Provides the organism
Structure of the normal rat larynx
 Laboratory Animals (1977) 11, 223-228 223 Structure of the normal rat larynx G. SMITH Grollp Research & Development Centre British-American Tobacco Co. Ltd, Regent's Park Road, SOllthampton, S09 IPE Summary
Laboratory Animals (1977) 11, 223-228 223 Structure of the normal rat larynx G. SMITH Grollp Research & Development Centre British-American Tobacco Co. Ltd, Regent's Park Road, SOllthampton, S09 IPE Summary
The Respiratory System. Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration
 C H A P T E R 22 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of
C H A P T E R 22 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Biology 325 Fall 2003
 Name: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is not one of the primary tissue types? A) germinative tissue B) muscle
Name: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is not one of the primary tissue types? A) germinative tissue B) muscle
Development of Respiratory System. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra
 Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types:
 Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FOETAL PITUITARY AT VARIOUS GESTATIONAL AGES S. Babu Rao * 1, G. Geetha vani 2, V. Subhadra Devi 3.
 Original Research Article HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FOETAL PITUITARY AT VARIOUS GESTATIONAL AGES S. Babu Rao * 1, G. Geetha vani 2, V. Subhadra Devi 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research,
Original Research Article HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FOETAL PITUITARY AT VARIOUS GESTATIONAL AGES S. Babu Rao * 1, G. Geetha vani 2, V. Subhadra Devi 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research,
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
