Development of Mesonephros and Metanephros in Phalange Stage Embryo of Leaf Nosed Bat Hipposideros speoris (Schnider); Chiroptera, Mammalia
|
|
|
- Dale Lewis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 World Journal of Zoology 10 (3): , 2015 ISSN IDOSI Publications, 2015 DOI: /idosi.wjz Development of Mesonephros and Metanephros in Phalange Stage Embryo of Leaf Nosed Bat Hipposideros speoris (Schnider); Chiroptera, Mammalia Patil Kishor Gopal and Janbandhu Kishor Sukhadeo Department of Zoology, Government Institute of Science, R T Road, Civil Lines, Nagpur (M S) India Abstract: At early phalange stages of Hipposideros speoris the mesonephri differentiated into Bowman s capsules; mesonephric tubules with very wide lumina lined by the cuboidal epithelial cells, open into a very narrow mesonephric duct. The metanephric protuberances increase in diameter than the mesonephros. In the metanephros the primary collecting tubules originate from the central wide renal pelvis and terminate as ampullae at the outer surface, below the collagenous capsule. The dense metanephrogenic mesoderm around the ampullae becomes gradually transformed into the renal tubules, which differentiate into the renal corpuscles and further develop into the Bowman s capsule deep in the metanephros. Large amount of the loose metanephrogenic mesoderm observed around the tubules. The ureter originates from the central renal pelvis and emerges out from the kidney through the wide hilus. The late phalange stage is characterized by further differentiation and increase in size of the metanephros than the mesonephros. The metanephric Bowman s capsules and the uriniferous tubules undergo further differentiation in the middle region of the metanephros. Key words: Bat Kidney Mesonephros Metanephros Renal Tubule INTRODUCTION Van der Stricht [2] examined the structural relationship between the sclerotomes and mesonephric The origin of excretory system from the intermediate plaques at 21 somite stage of Rhinolophus hipposideros mesoderm appears at early embryonic stages. In mammals and an older embryos of Nyctalus [= Vesperugo] the development of three stages of excretory system viz., noctula. He noticed that the sclerotomes and pronephros (anterior embryonic kidney), mesonephros mesonephric plaques bear bimetameric relationship for (middle embryonic kidney) and metanephros (posterior each sclerotomes at the cranial end. This pattern was not embryonic kidney) appear in succession. The consistent in the older embryos of N. noctula. Sperber mesonephros implies the existence of pronephros and [3] observed typical fetal furrows on the surface of metanephros and the metanephros develops later and fetal kidneys from Myotis (Kidney 1.0 mm in length) become the permanent functional kidney. Pronephri the and Plecotus. No cortical and medullary zones were most primitive organs is an exceedingly transitory differentiated at this stage of development. structures appears and degenerated in the early Patil and Janbandhu [4, 5] described relationship embryonic stages in birds and mammals; while its of protein and glycogen activity in the prenatal and functional role has been replace temporarily by the postnatal kidneys of Rousettus leschenaulti, Megaderma mesonephros. In early embryonic stages of mammals the lyra lyra and Hipposideros speoris with structural mesonephros attain a considerable degree of development development and functional physiology by using and are believe to be involved on the elimination of histochemical methods. They examined the high protein nitrogenous waste. All the three types of excretory organ and glycogen activity in the cortical region, which are the paired structures and are concerned in collecting decreases in the medulla and further decreases in the waste [1]. region of the papilla in general. Corresponding Author: Patil Kishor Gopal, Department Of Zoology, Government Institute Of Science, R T Road, Civil Lines, Nagpur (M S) India. 181
2 In mammals the secretion of hypertonic urine is shows the metanephric protuberance and the related with the functional activity within the loop of mesonephros. The metanephros consists of outer dense Henle. In the uriniferous tubules the urine formation metanephrogenic mesoderm around the developing mainly involves glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption ampullae and the central loose metanephrogenic and tubular secretion. The glomerular filtration appears to mesoderm surrounding the primary collecting tubules. be a passive process, without any cellular activity. In The mesonephric Bowman s capsule encloses the most of the mammals about 80-85% of the glomerular glomerulus along with glomerular cells, which are is filtrate is reabsorbed through tubular active reabsorption surrounded by the lumen lined by flattened epithelial [6]. The large number of convolutions of the proximal cells. The convoluted mesonephric tubules with lumen tubules in the thick cortex of the kidney of P. lined by the cuboidal epithelial cells open into the hermaphroditus hermaphroditus are an indication that mesonephric duct with wide lumen lined by the cuboidal the proximal convoluted tubule is also the longer part of epithelial cells. The mesonephric tubules are embedded in the uriniferous tubule. the mesonephric mesoderm. There is some species specific differentiation of the The embryo of H. speoris with a body mass g excretory organs during development. In this report the and CR length of 8.5mm is characterized by the development of mesonephros and metanephros at development of metanephros (permanent kidney) which phalange stages of embryonic development in is not yet differentiated into a cortex and a medulla. The Hipposideros speoris are described as a mammalian kidneys exhibit the primary collecting tubules originating example. from the central wide renal pelvis and terminating as ampullae below the collagenous capsule in each fetal MATERIALS AND METHODS furrow at the outer surface. The dense metanephrogenic mesoderm around the ampullae becomes gradullay The report is based on the examination of transformed into the renal tubules. The renal tubules mesonephros and metanephros at the phalange stages of become differentiated into renal corpuscles, which further development from 7 preserved embryos of Leaf Nosed Bat develop into the Bowman s capsules deep in the Hipposideros speoris. The pregnant females of metanephros. In the differentiating Bowman s capsules, Hipposederos speoris were previously collected from the glomeruli with few glomerular cells surrounded by the underground dilapidated dark rooms of Ballarshah fort, lumen lined by the flattened epithelial cells are present. Maharashtra, India. The embryos at phalange stage of Large amount of loose metanephrogenic tissue is development were selected; their body weight (taken by observed around the tubules and the long ureter which the electronic weighing balance) and crown rump length originates from the central renal pelvis and emerges out of (CR) were recorded and then fixed in 10% buffer Formalin the kidney through a wide hilus. for 24 hours for histological study. The embryos washed The embryo with CR length 11.5mm and body mass overnight in running tap water and dehydrated by 0.009g, show increased differentiating metanephri than the passing through different grades of ethyl alcohol, cleared mesonephri. At this stage of development, mesonephric in xylene and embedded in paraffin (58-60 C). The tubules with wide lumina and narrow collecting ducts are sections of embryos were cut at 5-7µm with the help of observed in the mesonephros. The mesonephros consists rotary microtome. For routine histological observations of the well differentiaed Bowman s capsules and the the sections were stained with Haematoxylin-Eosin mesonephric tubules opening into the mesonephric duct. technique. The sections containing mesonephros and Mesonephros shows the afferent glomerular vessel metanephros were selected and observed under light entering the glomerulus and the efferent glomerular vessel microscope. The measurements of different parts of emerging out from the glomerulus. mesonephros and metanephros were calculated with the In the embryo with a body mass g and a CR help of ocular micrometer scale. length of 11.5mm the Bowman s capsules and the uriniferous tubules undergo further differentiation in the RESULTS middle region of the kidney. Note: The details and measurements of various The prenatal embryo of Hipposederos speoris at components of mesonephros and metanephros are given early phalange stage with a body mass g (CR 8mm) in Table 1, 2A and 2B. 182
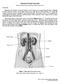
3 Fig. 1: Potrait of the prenatal embryo of H. speoris at early phalange stage with a body mass g (CR 8mm). e: eye; er: ear; f: fore limb; h: hind limb; t: tail-bud. Fig. 2: Part of section to show the metanephric protuberance and the mesonephros. The metanephros consists of outer dense metanephrogenic mesoderm around the developing ampullae (thick arrows) and the central loose metanephrogenic mesoderm surrounding the primary collecting tubules (thin arrows). In the mesonephros the Bowman s capsule encloses the glomerulus along with glomerular cells, which are is surrounded by the lumen lined by flattened epithelial cells (arrowheads). The highly convoluted mesonephric tubules with wide lumen lined by the cuboidal epithelial cells open into the mesonephric duct (m) with wide lumen lined by the cuboidal epithelial cells. The mesonephric tubules are embedded in the mesonephric mesoderm. g: gonad; m: mesonephric duct; : mesonephric glomerulus; : mesonephric tubule. Figs. 3-4: Midsagittal sections of the right (Fig. 3) and left (Fig. 4) developing metanephri of the embryo (Fig. 1) showing the collagenous capsule (cap) forming the outer covering of the kidney. The primary collecting tubules (thick arrows) originate from the renal pelvis (rp) and terminate as ampullae (arrowheads) below the capsule forming the furrows at the outer boundary. The ampullae are surrounded by the dense metanephrogenic tissue, from which develop the renal tubules (long arrows) lying lateral to the ampullae. The differentiating renal tubules are transformed into the renal corpuscles (thin arrow) which gradually develop into the differentiating Bowman s capsule ( ) deep in the loose metanephrogenic mesoderm. The ureter (ur) emerges out from the metanephros at the hilus (Fig. 3). ad: adrenal. 183
4 Fig. 5: Potrait of the prenatal female embryo of H. speoris with a body mass 0.009g and CR length 11.5 mm. e:eye; er: ear; f: fore limb; h: hind limb; t: tail bud. Fig. 6: Section to show the mesonephric Bowman s capsule (thick arrow), mesonephric tubules (thin arrows) and mesonephric duct (arrowhead) in the mesonephros. The developing metanephros shows the primary collecting tubules (long arrows) terminating as ampullae ( ) surrounded by dense metanephrogenic mesoderm at the outer surface. g: gonad; ur: ureter. Fig. 7: Lateral view of the prenatal male embryo of H. speoris (CR length 11.5 mm) with a body mass e: eye; f: fore limb; h: hind limb; p: pinna; t: tail-bud. Fig. 8: Midsagittal section of the left kidney of the prenatal embryo of H. speoris shown in figure 7. Note that at this stage of development still there is no differentiation of the metanephric tissue into cortex and medulla. At the outer boundary of the kidney in each foetal furrow (thin arrows) the ampullae are seen below the collagenous capsule. The primary collecting tubules (long arrows) originate from the renal pelvis (rp). The ureter (ur) leads to the exterior through the wide hilus ad: adrenal. Table 1: Measurements of different parts of Mesonephros at Phalange stage of development Hipposideros speoris (in µm). Sr. No CR length 9.5mm 11.5mm 11.5mm Body Mass g g g. Mesonephros at T.S. 451 x x x 322 Mesonephric Bowman s Capsule External Diameter Diameter of Glomerulus Lumenal Diameter Mesonephric Tubule External Diameter Luminal Diameter Epithelial cells Height / Shape 10.7 Cuboidal 7.1 Cuboidal 7.1 Cuboidal Mesonephric Duct External Diameter Luminal Diameter Epithelial cells Height / Shape 10.7 Cuboidal 9 Cuboidal 7.1 Cuboidal 184
5 Table 2A: Measurements of different parts of Bowman s Capsule in the Metanephros at the phalange stage of development of Hipposideros speoris (in m) Bowman s Capsule Glomerular Cells Capsular Epithelium External Diameter of Glomerular Diameter Nuclear Shape Nuclear S N CR in mm Diameter Glomerulus Lumen of Cell Diameter of Cells Height Diameter Squamosal Squamosal Squamosal Squamosal Table 2B: Measurements of different parts of Metanephros at the phalange stage of development of Hipposideros speoris (in µm) Epithelial cells Metanephric Component Sr. No. External Diameter Luminal Diameter Shape Height Nuclear Diameter Ureter Cuboidal Cuboidal Cuboidal Renal Pelvis Cuboidal Cuboidal Cuboidal Primary Collecting Tubule Cuboidal Cuboidal Cuboidal Cuboidal Straight Collecting Tubules Cuboidal Cuboidal Cuboidal Cuboidal Ampulla Columnar Columnar Columnar Columnar Renal Tubule Columnar Columnar Columnar Columnar Renal Corpuscle Columnar Columnar Columnar Columnar (Sr. No. 1: Embryo of CR length 8.00mm, Body Mass g. TS of Metanephros (Left) 0.885x0.515mm; Sr. No. 2: Embryo of CR length 8.50mm, Body Mass g. TS of Metanephros (Right) 0.966x0.805mm; Sr. No. 3: Embryo of CR length 11.5mm, Body Mass g. TS of Metanephros (Left) 1.175x0.563mm; Sr. No. 4: Embryo of CR length 11.5mm, Body Mass g. TS of Metanephros (Left) 1.369x0.805mm) DISCUSSION kidney. Embryologically the tubules of all three organs arise from intermediate mesoderm which looses its original Three types of paired excretory organs, pronephros, connection with the somites [1]. mesonephros and metanephros develop in succession The well differentiated mesonephros is observed at during the embryogenesis of vertebrates. In mammals the the early phalange stages of development of the pronephros and mesonephros are transitory excretory Hipposederos speoris. The mesonephri occurs as a paired organs while the metanephros is the permanent functional protuberance of intermediate mesoderm on either side of 185
6 the dorsal aorta. In the mesonephric protuberance the the metanephros of adult [9] and postnatal sucklings [10] differentiating mesonephric corpuscles enclosing the the renal tubules are well differentiated histologically into glomerular capillaries are observed. Adjacent to the the Bowman s capsules, the proximal and distal mesonephric corpuscles are seen a few developing convolutated tubules in the cortex. The medulla comprises mesonephric tubules which open into the mesonephric the network of large collecting tubules and the very duct. narrow loops of Henle with lumen. In the large papilla At early phalange stages (1. with a body mass collecting ducts with wide lumen open into the wide calyx; g and CR length 8mm and 2. body mass 0.009g and few collecting tubules and the thin loop of Henle are also CR length 8.5mm) the metanephric protuberances increase observed in the papilla. in diameter than the mesonephros. In the metanephros the At late phalange stages of the developing primary collecting tubules originate from the central wide metanephros shows the differentiation of the renal tubles, renal pelvis and terminate as ampullae at the outer surface, renal corpuscles, Bowman s capsules and the below the collagenous capsule. The dense differentiating uriniferous tubules. The branches of renal metanephrogenic mesoderm around the ampullae becomes vessels observed anterior to the ureter at the region of the gradually transformed into the renal tubules, which renal pelvis. The surface of the foetal kidneys of Myotis differentiate into the renal corpuscles, which further and Plecotus show the presence of furrows [3]. Similar develop into the Bowman s capsule deep in the furrows are observed in on the outer surfaces of metanephros. Large amount of the loose metanephrogenic differentiating embryonic kidneys of H. speoris; which are mesoderm is observed around the tubules. The ureter due to the termination of the collecting tubules as originates from the central renal pelvis and emerges out ampullae embedded in the peripheral tissue under the from the kidney through the wide hilus. collagenous capsule. The phalange stage of H. speoris (at CR length of The metanephros is covered by a thick collagenous 11.5mm and body masses 0.009g and g) is capsule, the kidneys are bean shaped, but the right kidney characterized by further differentiation and increase in size is broader at its anterior pole. Such a variation in the of the metanephros than the mesonephros. The structure of the two kidneys has also been reported in metanephric Bowman s capsules and the uriniferous Pipstrellus jaranicus [11] where the right kidney is tubules undergo further differentiation in the middle shorter and thicker than the left because of its close region of the metanephros. At this stage in H. speoris the association with the liver. No differentiation of cortical mesonephros consists of mesonephric tubules with very and medullary tissues was noticed in the metanephros at wide lumina lined by the cuboidal epithelial cells which this stage [3, 12]. The length of renal tubules suggests open into a very narrow mesonephric duct. The that they are adapted to develop into the long loop of development and structure of the mesonephros are similar Henle of uriniferous tubules [13]. The length of loop of to that in other vertebrates and the metanephros is similar Henle is directly proportional to the medullary thickness to that in other mammals [1]. [14, 15] which is an adaptation to conserve more water In Megaderma lyra lyra at phalange stage of from the filtrate. embryonic development the metanephri, the differentiating renal tubules, renal corpuscles and the REFERENCES Bowman s capsules were examined [7]. The characteristic cavity of renal pelvis surrounded by the thick 1. Patten, B.M., The Urogenital System, Chapter metanephrogenic tissue in the centre of the metanephros XIX. In: Human Embryology, 3d. ed., McGraw-Hill as seen in M. lyra lyra was not observed in the phalange Book Company. New York, pp: \ stage of H. speoris. 2. Van der Strict, O., Le mésonéphros chez le The megachiropteran fruit bat Rousettus Chauve-souris. C.R. Assoc. Anat. Suppl., 15: leischenaulti exhibits similar structural development in 3. Sperber, I., Studies on the mammalian kidney. the mesonephric as well as metanephric components Zool. Bidr. Uppsala, 22: \ during the embryonic development [8]. The dimentions of 4. Patil, K.G. and K.S. Janbandhu, Protein and the different parts of differentiating renal tubules are vary Glycogen Histochemistry in Prenatal and Postnatal in the bats M. lyra lyra, R. leischenaulti and H. speoris; Kidney of Rousettus leschenaulti (Desmarest) may be related with the varying size of the embryos of Chiroptera, Mammalia. J. Golden Research Thoughts, same developmental stages in these species. In H. speoris 1(3):
7 5. Patil, K.G. and K.S. Janbandhu, Carbohydrate 10. Patil, K.G., Renal Morphology of Postnatal Histochemistry in the Kidneys of Postnatal Sucklings Suckling of Hipposideros speoris (Schnider), of Indian False Vampire Megaderma lyra lyra Chiroptera; Mammalia. International Journal of Life (Geoffroy) and Indian Leaf Nosed Bat Hipposideros Sciences, 1(1): speoris (Schnider), Chiroptera; Mammalia. Indian 11. Shew, T., Anatomy of the excretory and the Streams Research Journal, 1(10): \ reproductive system of the bat, Pipistrellus tralatitius. 6. Patil, K.G., K.S. Janbandhu and A.V. Ramteke, Science Shanghai, 16: Renal Morphology of Indian Palm Civet Paradoxurus 12. Rosenbaum, R.M., Urinary System. In: Biology hermaphroditus hermaphroditus (Schrater); Order- of bats, (W.A. Wimsatt,Ed.) Acad. Press, New York, Carnivora, Mammalia. Hislopia Journal, 3(2): pp: Patil, K.G., K.B. Karim and K.S. Janbandhu, Gerhardt, U., Zur Morphologie der Säugeniere. Metanephros Structure at Phalange Stage of Verh. Deut. Zool. Ges., 21: Embryonic Development in Indian False Vampire 14. Bankir, L. and C. de Rouffignac, Urinary Megaderma lyra lyra (Geoffroy) Chiroptera, concentrating ability: insights from comparative Mammalia. Global Journal of Science, Engineering anatomy. Amer J. Physiol., 249: R643-R666. and Technology, 1: Beuchat, C.A., The scaling of concentrating 8. Patil, K.G., K.B. Karim and K.S. Janbandhu, ability in mammals. In: New Insights in Vertebrate Development of Mesonephros and Metanephros in Kidney Function, (J. A. Brown, R.J. Balment and J.C. Indian Fruit Bat Rousettus leschenaulti (Desmarest), Rankin, eds). Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, Family- Pteropodidae, Chiroptera, Mammalia. pp: International Journal of Biotechnology and Biosciences, 2(2): Patil, K.G. and K.S. Janbandhu, Morphology and Histoarchitectural Observations on the Renal Organs of Indian Leaf Nosed Bat Hipposideros speoris, Order- Chiroptera, Mammalia (Schnider). International Journal of Biotechnology and Biosciences, 2(1):
Structure ofmetanephrosat Term Embryo Stage of Megaderma lyra lyra (Geoffroy) Chiropteran, Mammalian
 World Journal of Zoology 8 (2): 192-197, 2013 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2013.8.2.7328 Structure ofmetanephrosat Term Embryo Stage of Megaderma lyra lyra (Geoffroy)
World Journal of Zoology 8 (2): 192-197, 2013 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2013.8.2.7328 Structure ofmetanephrosat Term Embryo Stage of Megaderma lyra lyra (Geoffroy)
Kishor G. patil and kishor s. janbandhu. Research Papers
 Vol1,IssueIII/Dec; 11pp1-4 Kishor G patil and kishor s janbandhu ISSN:-2249-894X Research Papers R R Developmental Stages of Metanephros in Indian False Vampire Megaderma lyra lyra (Geoffroy) Chiroptera,
Vol1,IssueIII/Dec; 11pp1-4 Kishor G patil and kishor s janbandhu ISSN:-2249-894X Research Papers R R Developmental Stages of Metanephros in Indian False Vampire Megaderma lyra lyra (Geoffroy) Chiroptera,
Histological Structure of Kidney at Term Stage of Embryonic Development in Leaf Nosed Bat Hipposideros speoris (Schnider), Chiropteran; Mammalian
 World Journal of Zoology 8 (2): 206-211, 2013 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2013.8.2.7351 Histological Structure of Kidney at Term Stage of Embryonic Development in Leaf
World Journal of Zoology 8 (2): 206-211, 2013 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2013.8.2.7351 Histological Structure of Kidney at Term Stage of Embryonic Development in Leaf
Functional Adaptations in the Kidney of Chiropteran Hipposideros speoris (Schnider): Mammals
 World Journal of Zoology 9 (1): 38-45, 2014 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2014.9.1.8239 Functional Adaptations in the Kidney of Chiropteran Hipposideros speoris (Schnider):
World Journal of Zoology 9 (1): 38-45, 2014 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2014.9.1.8239 Functional Adaptations in the Kidney of Chiropteran Hipposideros speoris (Schnider):
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
The Urinary System PART A
 15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
The functional anatomy of the urinary system. Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic
 The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY
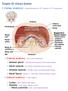
 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Question 1: Solution 1: Question 2: Question 3: Question 4: Class X The Excretory System Biology
 A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal
 Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System
 Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
Chapter 25: Urinary System
 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden
 Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Histology / First stage The Urinary System: Introduction. Kidneys
 The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
Urinary System. J. H. Lue. intermediate mesoderm cloaca coelomic epithelium
 Urinary System J. H. Lue Primordium: intermediate mesoderm cloaca coelomic epithelium 1 3w(18d) 3 w 4w (24d) 4w (26d) 2 Intermediate mesoderm 3 Intermediate mesoderm intermediate mesoderm urogenital ridge
Urinary System J. H. Lue Primordium: intermediate mesoderm cloaca coelomic epithelium 1 3w(18d) 3 w 4w (24d) 4w (26d) 2 Intermediate mesoderm 3 Intermediate mesoderm intermediate mesoderm urogenital ridge
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
Development of the Urinary System. 3 Distinct Embryonic Kidney Structures
 Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Frontal section of human kidney. (Scheme).
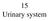 15 Urinary system 15-001 Kidney Cortex Medulla Papilla renalis Medial Lateral Medullary ray Labyrinth Columna renalis Pelvis renalis Calix renalis Ureter Capsula fibrosa Lobus renalis Columna renalis 15-01.
15 Urinary system 15-001 Kidney Cortex Medulla Papilla renalis Medial Lateral Medullary ray Labyrinth Columna renalis Pelvis renalis Calix renalis Ureter Capsula fibrosa Lobus renalis Columna renalis 15-01.
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
The Urinary System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Histological differentiation of human fetal kidney
 Original Research Article Histological differentiation of human fetal kidney Mamatha Hosapatnaa 1, Hemalatha Bangera 2, Anne D Souza 3, Aswin Das 4, Supriya 4, Antony Sylvan D Souza 5, Vrinda Hari Ankolekar
Original Research Article Histological differentiation of human fetal kidney Mamatha Hosapatnaa 1, Hemalatha Bangera 2, Anne D Souza 3, Aswin Das 4, Supriya 4, Antony Sylvan D Souza 5, Vrinda Hari Ankolekar
Lesson 31. Lesson Outline:
 Lesson 31 Lesson Outline: The Urogenital System Urinary System o Embryonic Origins o Phylogenetic Trends Function Urinary Bladder Implications for the Evolution of the Vertebrates o Freshwater or Seawater
Lesson 31 Lesson Outline: The Urogenital System Urinary System o Embryonic Origins o Phylogenetic Trends Function Urinary Bladder Implications for the Evolution of the Vertebrates o Freshwater or Seawater
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM
 AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Filtration Reabsorption Secretion Concentration
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 25 For this lab you will use parts
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 25 For this lab you will use parts
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
Urinary Anatomy. Lab 40. Kidneys. Nephrons. Renal Corpuscle
 Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
LECTURE 4. Anatomy of the urinary and genital organs.
 LECTURE 4 Anatomy of the urinary and genital organs. SKELETOTOPY OF THE KIDNEYS Left kidney upper pole of the kidney - ThXI lower pole of the kidney LIII Right kidney is located on the half vertebra
LECTURE 4 Anatomy of the urinary and genital organs. SKELETOTOPY OF THE KIDNEYS Left kidney upper pole of the kidney - ThXI lower pole of the kidney LIII Right kidney is located on the half vertebra
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Excretion Chapter 29. The Mammalian Excretory System consists of. The Kidney. The Nephron: the basic unit of the kidney.
 Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT. 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys.
 Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Formation of Urine: Formation of Urine
 The Urinary outflow tract: monitors and regulates extra-cellular fluids excretes harmful substances in urine, including nitrogenous wastes (urea) returns useful substances to bloodstream maintain balance
The Urinary outflow tract: monitors and regulates extra-cellular fluids excretes harmful substances in urine, including nitrogenous wastes (urea) returns useful substances to bloodstream maintain balance
Salt and Water Balance and Nitrogen Excretion
 Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys II. Nephron Unit and Urine Formation
 URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
A. Correct! Flushing acids from the system will assist in re-establishing the acid-base equilibrium in the blood.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow and Their Control.
 Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow and Their Control. Chapter 26 Yanal A Shafagoj. MD. PhD Lecture-1 Introduction 31/3/2015 1 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine
Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow and Their Control. Chapter 26 Yanal A Shafagoj. MD. PhD Lecture-1 Introduction 31/3/2015 1 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
THE RENAL / URINARY SYSTEM
 1 THE RENAL / URINARY SYSTEM Definition/Description: The Renal/Urinary system is the body system, which plays a vital role in the maintenance of homeostasis by the following processes: 1. Production of
1 THE RENAL / URINARY SYSTEM Definition/Description: The Renal/Urinary system is the body system, which plays a vital role in the maintenance of homeostasis by the following processes: 1. Production of
Osmoregulation and the Excretory System
 Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Chapter 44. Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Overview: A Balancing Act Physiological systems of animals operate in a fluid environment Relative concentrations of water and solutes must be maintained within
Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Overview: A Balancing Act Physiological systems of animals operate in a fluid environment Relative concentrations of water and solutes must be maintained within
Chapter 13 The Urinary System
 Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
The kidneys are excretory and regulatory organs. By
 exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
Urinary system. Lab-7
 Urinary system Lab-7 Excretion: processes that remove wastes and excess materials from the body Urinary system (kidneys): excretes nitrogenous wastes, excess solutes, and water The Kidneys Regulate Water
Urinary system Lab-7 Excretion: processes that remove wastes and excess materials from the body Urinary system (kidneys): excretes nitrogenous wastes, excess solutes, and water The Kidneys Regulate Water
Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note
![Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note](/thumbs/77/75431210.jpg) Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
URINARY SYSTEM. Urinary System
 URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Urinary system. Aleš Hampl
 Urinary system Aleš Hampl Functions of urinary system 1. Regulating blood volume and pressure 2. Regulating plasma concentrations of sodium, potassium, chloride and other ions 3. Stabilising blood ph 4.
Urinary system Aleš Hampl Functions of urinary system 1. Regulating blood volume and pressure 2. Regulating plasma concentrations of sodium, potassium, chloride and other ions 3. Stabilising blood ph 4.
Histotopography of nephron
 THE URINARY SYSTEM Microscopic structure and development of urinary systém Kidney: nephron structure and function Urinary passages: ureter, urinary bladder, urethra Development of urinary system THE URINARY
THE URINARY SYSTEM Microscopic structure and development of urinary systém Kidney: nephron structure and function Urinary passages: ureter, urinary bladder, urethra Development of urinary system THE URINARY
Development of the Urinary System
 Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
