Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1987
|
|
|
- Daniel Elwin Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diabetologia (1987) 30: Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1987 Assessment of islet cell viability using fluorescent dyes H. L. Bank Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina, USA Summary. A rapid fluorometfic method has been developed to evaluate the viability of isolated islet cells. The assay differentiates between viable and nonviable cells by the simultaneous use of the inclusion and exclusion dyes acridine orange and propidium iodide. When viewed by fluorescent microscopy, viable cells fluoresce green, while nonviable cells fluoresce bright red. Although the acridine orange and propidium iodide assay measures membrane integrity, the results of this assay correlate with other measures of cell viability. Compared to trypan blue exclusion, this assay is easier to read, more stable, and has fewer staining artifacts. The assay enables the rapid estimation of the viability of a population of islet cells prior to time-consuming experiments rather than retrospectively. This assay can also be used with intact islets. Stained islets can be divided into three distinct groups: green fluorescing islets contain insulin, red fluorescing islets contain little or no insulin and a third class of islets containing some non-viable cells fluoresce red, green, and yellow. The yellow colour is due to the superimposition of red and green fluorescing cells. Key words: Islet viability, fluorochromes, B cells, acridine orange, propidium iodide, trypan blue exclusion, membrane integrity. A reliable method for rapidly determining the viability of isolated islet cells would be useful in studies on transplantation, cryopreservation, insulin release, and biosynthesis. Functional assays to determine insulin content or release and morphological assays including histochemistry or electron microscopy are time-consuming and expensive for routine viability assays. An alternative approach uses inclusion and/or exclusion dyes to test the integrity of the plasma membrane. Several fluorometric dyes were tested as indicators of membrane integrity. Fluorescein diacetate (FDA) has been used as a fluorometric assay of cell viability. FDA is a nonpolar ester which passes through plasma membranes and is hydrolysed by intracellular esterases to produce free fluorescein. The polar fluorescein is confined within cells with an intact plasma membrane and can be observed under appropriate excitation conditions [1-4]. However, staining of islet cells with FDA results in high background fluorescence. This fluorescence is presumably due to extracellular hydrolysis of the FDA or to fluorescein that leaked through damaged membranes. Acridine orange (AO) is a membrane-permeable, monovalent, cationic dye [5, 6] which binds to nucleic acids. A low concentration of AO causes a green fluorescence, while a high concentration causes a red fluo- rescence. Propidium iodide (PI) is impermeable to intact plasma membranes, but it easily penetrates the plasma membrane of dead or dying cells [7] and intercalates with DNA or RNA forming a bright red fluorescent complex [8-11]. Both intracellular and extracellular background fluorescence is minimal after staining with optimal concentrations of these dyes. A combination of low concentrations of AO and PI was evaluated as a viability assay for islet cell suspensions. This combination of fluorochromes permits the simultaneous observation of cells with intact and with compromised plasma membranes [12]. However, any new assays must be compared with classical assays of cell "viability". In this report the AO/PI assay is compared to the traditional trypan blue exclusion assay. The stability, cytotoxicity, and reproducibility of the assay was evaluated on isolated islet cells derived from adult rat. In addition, the assay was applied to islet cells derived from mice, dogs and neonatal humans and to isolated intact rat islets. Materials and methods All National Institute of Health and institutional Animal Research Committee guidelines for the welfare of research animals were followed. Long Evans Hooded (LEH) male rats ( g) were fast-
2 H. L. Bank: Fluorescent islet cell viability assay ed for 12 to 18 h before the isolation of the islets. Pancreatic islets of Langerhans were isolated using the collagenase isolation procedure described previously [13, 14]. A single step, 11% Ficoll (LSM, Bionetics Lab, Litton, Kensington, Md, USA) separation was used to separate islets from the tissue digest [14]. The islets were collected at the buffer/ficoll interface, and washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Rat islets were dissociated with gentle and repeated pipetting or with additional collagenase and incubation for 3-5 rain at 37 ~ followed by gentle pipetting. Adult mouse, rat and canine islets as well as human neisidioblastic neonatal islets were isolated according to previously described methods [15-17] and dissociated as described above. Isolated islet cells were placed in PBS buffer containing 0.2% (w/v) trypan blue (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) or a combination of AO (Sigma, St. Louis, Mo, USA) and PI (Sigma) in PBS buffer. Stained cells were examined using a 10X/0.4 NA Wild Fluotar phase contrast lens on an inverted Wild M40 microscope equipped for phase contrast and epi-illumination fluorescent microscopy. An FITC fiker set (Ex490 : Em510) permitted the simultaneous visualization of green and red fluorescing cells. Since high concentrations of many dyes are toxic to cells, a serial dilution of AO and PI was made over the concentration range of ,500 p~mol/1 and the fluorochromes were tested on freshly isolated rat islet cells to determine the useful concentration range for each fluoroehrome. Low concentrations of AO (0.67 p.mol/1) and PI (75 ~mol/l) were used for the AO/PI assay because they resulted in a bright cellular fluorescence while minimizing extracellular fluorescence. Once the optimal staining conditions for AO/PI were determined, this assay was compared to the trypan blue dye exclusion assay performed under "optimal conditions". Dissociated rat islet cells were stained with AO/PI for 60 min and the percentage of cells which fluoresced green were compared with the percentage of the same population of cells which excluded trypan blue after 5 rain. To determine if the dyes were toxic, dissociated rat islet cells were exposed to either AO/PI or trypan blue for 60 and 5 rain, and the mean viabilities were compared. After exposure to the fluorochromes, the cells were placed in the dark at room temperature. Cell counts of trypan blue or AO/PI stained islet cells were made after 5 and 60 rain. At least 100 cells were counted per replicate, and a minimum of 3 replicates were counted per experiment to determine the mean percent viable cells. To determine if the AO/PI assay could be applied to islet cells isolated from other species, dissociated cells from adult mouse, adult dog, and human neonatal islets were observed after staining with AO/PI or trypan blue for 5 or 60 min. To assay the viability of intact islets, individual islets were placed into separate wells of a 96 well microtiter plate, and stained with AO/PI. Staining time and dye concentration was identical to that described above. Each islet was classified according to its fluorescent colours. The criteria used for islet selection were: type A (> 90% green), type B (40-60% green), or type C (>90% red). To confirm the interpretation that live islet ceils fluoresce green, and dead islet cells fluoresce red, dissociated islet ceils were stained for 5 min with AO/PI and photographed with fluorescence microscopy. Next the islets were washed free of AO/PI, stained for 5 min with trypan blue, and rephotographed with phase contrast microscopy. Statistical analysis An unpaired Student's t-test was used to test for differences between the means. All experiments on rat cells were repeated three times with three replicates per experiment. To determine if the AO/PI assay was reproducible, the within-assay coefficients of variation (CV%) were determined in the 6 separate experiments. Table 1. Effect of fluorochrome concentrations on rat islet cells Concentration Fluorescence [gmol/l] AO a pi b Background Cells Background Cells 0.67 clear green clear no uptake 1.5 clear green clear no uptake 10 clear green clear no uptake 20 clear red clear no uptake 40 green red clear no uptake 90 green red clear no uptake 190 green red clear no uptake 390 green red clear no uptake 780 green red clear no uptake green red red red green red red red green red red red green red red red a Acridine Orange (AO) enters live cells and fluoresces green at low dye concentrations. At concentrations > 20 pomol/l, the intracellular fluorescence undergoes a metachromatic shift from green to red. At AO concentrations >40 lxmol/1, an intense green extracellular background obscured the fluorescent cells, b Propidium Iodide (PI) stains the nuclei of dead and dying cells bright red. At concentrations > 1,560 Ixmol/1, both background and cellular staining was an intense red. At concentrations <780 Ixmol/1, viable cells excluded dye and the background fluorescence was minimal Results Table 1 shows the effects of varying either acridine orange or propidium iodide concentrations on intracellular and extracellular fluorescence in rat islet cell preparations. When these cells were exposed to > 20 txmol/1 AO, an intracellular metachromatic shift from green to red fluorescence was observed. At AO concentrations > 40 [xmol/l islet cells were more difficult to recognise against a bright green background of extracellular fluorescence. At a concentration of 0.67 gmol/l AO, islet cells fluoresced a bright green colour with very little extracellular fluorescence. When high concentrations of propidium iodide were used, alone, (>_ 1560 ~tmol/1) resulted in a bright red extracellular fluorescence (Table 1). At lower dye concentrations extracellular fluorescence was progressively reduced, and fluorescent cells were discernable. At a concentration of 75 p.mol/1 PI [12], dead and dying islet cells fluoresced a bright red colour with a low extracellular fluorescence. Table 2 compares AO/PI and trypan blue staining of dissociated rat islet cells. There was no significant difference between AO/PI and trypan blue viability estimates at 5 min (p > 0.05). The AO/PI assay was not cytotoxic to dissociated rat islet cells, since the 5 and 60 rain viability remained constant (p > 0.05). The AO/ PI assay was stable with time (p > 0.05) while the trypan blue assay was not. In addition to being an accurate, non-toxic, and stable assay, the AO/PI assay is reproducible. Replicate counts were similar as shown by small interassay 813
3 814 H.L. Bank: Fluorescent islet cell viability assay
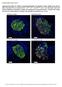
4 H. L. Bank: Fluorescent islet cell viability assay Table 2. Stability of trypan blue and AO/P1 a stained rat islet cells Experiment Time Trypan blue AO/PI (rain) 1 5 b 80.4 c 80.7 c 60 a , a Acridine orange (0.67 gmol/l) and propidium iodide (75 9mol/1) in PBS buffer, b After 5 min of exposure there was no significant difference between the number of cells which excluded trypan blue or fluoresced green after exposure to AO/PI. c The mean percent of cells + SE with an intact plasma membrane after staining, d There was no change in the number of cells which fluoresced green after 5 or 60 rain exposure to AO/PI (p > 0.05). The number of positively stained cells increased between 5 and 60 min of exposure to trypan blue (p < 0.05) Table 3. Viability of rat, mouse, dog and human islet cells stained with trypan blue or AO/PP Species Time Trypan blue AO/PI (min) Rat 5 b 85, c c 60 d 56, _+ 2.8 Mouse 5 86, Dog _ _ 5.7 Human _ a Acridine orange (0.67 p~mol/1) and propidium iodide (75 p~mol/l) in PBS buffer, b Regardless of species, there was no significant difference between the number of cells which stained blue after exposure to trypan blue for 5 rain and the number of cells which fluoresced green after exposure to AO/PI for 5 or 60 min (p >0.05). c The mean percent of cells + SE with an intact plasma membrane after staining (3 replicate samples), a A significant increase occurred in the number of cells which stained blue after exposure to trypan blue for 5 min and 60 min (p < 0.05) coefficients of variations (CV%) for 6 separate experiments (5.3%, 3.2%, 2.6%, 2.9%, 6.2%, 4.3%). When the assay was tested on three other species - human, canine, murine - the results with AO/PI and trypan blue were similar. The number of green fluorescing cells after 5 or 60 rain exposure to AO/PI were similar to the number of cells excluding trypan blue after 5 rain exposure to the dye (p > 0.05). However the number of trypan blue stained cells increased over the same time interval regardless of species tested (p < 0.05, Table 3). The fluorescent images of intact islets result from the fluorescence of its component cells. The islets can be classified into three basic groups; type A islets have a relatively uniform green fluorescence. In freshly isolated islets, a few peripheral yellow or red pancreatic acinar cells are often seen. Type B islets have many distinct yellow-coloured cells while type C islets fluoresce uniformly red (Fig. 1). Discussion Chromogenic inclusion dyes such as neutral red and exclusion dyes such as trypan blue are commonly used to assay the membrane integrity of numerous cell types [18-20]. However, these dyes have a limited usefulness for evaluating islet cells [12]. Our results agree with "previous reports that the percentage of cells stained with trypan blue increases with time [22-25]. The constraints of a 5-10 min window of stability for trypan blue limits the number of samples that can be stained at a single time. The combination of AO/PI permits the observation of intact and damaged cells simultaneously. The similarity of the results of the AO/PI assay and the trypan blue assay indicates that the AO/PI assay is at least as sensitive as the classic dye exclusion test for cell viability. Cells with intact vs compromised plasma membranes are easily discriminated using the AO/PI assay (green vs red). The AO/PI assay [5] gives similar results to the trypan blue assay (using 5 min staining time) [6]; produces quantitatively reliable results [8]; the proportion of AO stained cells remains constant after exposure to the dye for at least 60 min [9]; the dyes are not cytotoxic to islet cells for at least 1 h [10]; the assay is precise (low within-assay coefficient of variation) [11]. The AO/PI assay is capable of simultaneously visualizing live and dead cells in intact islets. Since live cells fluoresce a bright green and dead cells fluoresce a bright red the assay is sensitive enough to detect individual dead cells within an islet composed of thousands of living cells. In our laboratory, the primary use of the assay is to rapidly sample the viability of a population of islets prior to the onset of a time-consuming experiment. This screening assay allows a judgment to be made on the condition of a population of islets prior to experiments. 815 Fig.la-d. Four low power light micrographs showing the appearance of freshly isolated islets viewed by phase contrast (a, c) and the same field of islets viewed by fluorescent microscopy (b, c). The small bright spots in the fluorescent micrographs correspond to the intense red staining of the propidium iodide poskive (dead) cells. The diffusely stained regions correspond to the AO stained (live) cells. Despite the similar appearance of a and c in bright field or phase contrast, the damaged islets are readily distinguished after AO/PI staining (b vs d). All photographs were taken with a 10X objective and photographically enlarged to 600 diameters (bar= 10 ~mol/1)
5 816 The conformation that the fluorescent colours are related to the physiological condition of intact islets will be reported separately [21]. Briefly, the insulin content of green type A islets are identical to untreated islets and these islets have normal ultrastructural morphology. Red type C islets had little or no insulin and showed disrupted cell membranes and no cytoplasmic granules when viewed by electron microscopy. Yellow type C islets had an intermediate insulin content and heterogenous ultrastructural appearance. The appearance of cells stained with AO/PI is comparable to cells stained with fluorescein diacetate and ethidium bromide (the FDA/EB assay), but AO has the advantage that the pattern of fluorescence reveals nuclear morphology. This allows identification and exclusion of contaminating leukocytes, such as eosinophils and polymorphonuclear neutrophils, from the count of viable islet cells. An additional application of the AO/PI assay is testing the viability of mononuclear cells. For example, this laboratory recently reported excellent agreement between the AO/PI assay results and the blastogenic potential of lymphocytes as well as the ability of macrophages to secrete lysozyme [22]. This AO/PI assay is not designed as a quantitative 9 replacement for more traditional assays such as glucose sensitive insulin release. Rather, this assay enables the investigator to estimate the viability of a preparation of islet cells prior to time-consuming experiments rather than retrospectively. In conclusion, the AO/PI assay was used to visualize live and dead islet cells simultaneously. AO stains the live cells green while PI stains dead cells red. A major advantage of the AO/PI assay is that viability can be assessed even 60 min after staining and yield reproducible results. The AO/PI assay can be used to determine the viability of isolated rat islet cells, and preliminary studies show that similar results with islet cells isolated from adult rat, murine, canine, and neonatal neisidoblastic human islets. Acknowledgements. I wish to acknowledge the technical assistance of Dr. P.Moore and Ms R.Didiyk, Drs. G.Bright and A.J.Garvin for providing the human neonatal pancreatic tissue, Dr. B. Loadholt for his comments and assistance in the statistical analyses of the data and Ms M.Jackson-Gegan for her editorial comments. Research supported in part by NIH grant OK References 1. Edidin M (1970) A rapid, quantitative fluorescence assay for cell damage by cytotoxic antibodies. J Immunol 104: Molar LR, Trounson AO (1980) The use of fluorescein diacetate to assess embryo viability in the mouse. J Reprod Fertil 58: Rotman B, Papermaster BW (1966) Membrane properties of living mammalian cells as studied by enzymatic hydrolysis of fluorogenic esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 55: Bank HL (1980) Viability of frozen rat granulocytes and granulocyte precursors. Cryobiology 17: Pantazis CG, Kniker WT (1979) Assessment of blood leukocyte H. L. Bank: Fluorescent islet cell viability assay microbial killing by using a new fluorochrome microassay. J Reticuloendothel Soc 26: West SS (1969) Fluorescence microspectrophotometry of supravitally stained cells. In: Pollister AW (ed) Physical techniques in biological research, 2nd ed, Vol 3 c. Academic Press, New York, pp Kapuscinski J, Darzynkiewicz Z, Melamed MR (1983) Interactions of acridine orange with nucleic acids. Properties of complexes of acridine orange with single stranded ribonucleic acid. Biochem Pharmacol 32: Waring M (1975) Ethidium and propidium. In: Corcoran JW, Hahn FE (eds) Antibiotics III. Mechanism of action of antimicrobial and antitumor agents. Springer, New York, pp Yeh C-JG, Hsi B-L, Faulk WP (1981) Propidium iodide as a nuclear marker in immunofluorescence, II. Use with cellular identification and viability studies. J Immunol Methods 43: Tanke HJ, Van der Linden PWG, Langerak J (1982) Alternative fluorochromes to ethidium bromide for automated read out of cytotoxicity tests. J Immunol Methods 52: Jacobs DB, Pipho C (1983) Use of propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry to measure antibody-mediated cytotoxicity: resolution of complement-sensitive and resistant target cells. J Immunol Methods 62: Moore PL, Didyk R, Bank HL (1985) The rapid assessment of viability of isolated islets of Langerhans with fluorescent dyes: relationship between fluorescent images and insulin content. J Cell Biol 101: 247a 13. Lacy PE, Walker MM, link CJ (1972) Perifusion of isolated rat islets in vitro: participation of the microtubular system in the biphasic release of insulin. Diabetes 21 : Bank HL, Davis RF, Emerson D (1979) Cryogenic preservation of isolated rat islets of Langerhans: effect of cooling and warming rates. Diabetologia 16: Gray DW, McShane P, Grant A, Morris PJ (1984) A method for isolation of islets of Langerhans from the human pancreas. Diabetes 33: Gotoh M, Maki T, Kiyoizumi T, Satomi T, Monaco AP 0985) An improved method for isolation of mouse pancreatic islets. Transplantation 40: Horaguchi A, Merrell RC (1981) Preparation of viable islet cells from dogs by a new method. Diabetes 30: Hutz RJ, DeMayo FJ, Dukelow WR (1985) The use of vital dyes to assess embryonic viability in the hamster, Mesocricetus Auratu. Stain Technol 60: Dolan MF (1965) Viability assays - a critique. Fed Proc 24 [Suppl]: $ Klebe RJ (1984) Rapid cloning of mammalian cells with honeycomb cloning plates and nonlethal vital stains. In Vitro 20: Bank HL (1988) The rapid assessment of islet viability with Acridine orange and propidium iodide, In Vitro 24 (in press) 22. Taylor M J, Bank HL, Benton MJ (1987) Selective destruction of leukocytes by freezing as a potential means of modifying tissue immunogenicity: membrane integrity of Lymphocytes and Macrophages. Cryobiology 24: Albright BL, Selinger DS, Reed WP (1979) Use of vital stains to study bacterial adherence to epithelial cells. Stain Technol 54: Black L, Berenbaum MC (1964) Factors affecting the dye exclusion test for cell viability. F, xp Cell Res 35: Tennant JR (1964) Evaluation of the trypan blue technique for determination of cell viability. Transplantation 2: Received: 4 May 1987 and in revised form: 11 August 1987 Dr. Harvey Bank Department of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC USA
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
 The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets. A.N.Balamurugan
 Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets A.N.Balamurugan Human Islets Functional Mass Preservation 18-25 min 10 min 8-12 min 10-15 min 45-60 min pancreas in chamber 37º Sub-Optimal
Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets A.N.Balamurugan Human Islets Functional Mass Preservation 18-25 min 10 min 8-12 min 10-15 min 45-60 min pancreas in chamber 37º Sub-Optimal
Fluorescein diacetate assessment of embryo viability after ultrarapid freezing of human multipronucleate embryos
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 0 1991 The American Fertility Society l'rintmi on oeid-free paper in U.S.A. Fluorescein diacetate assessment of embryo viability after ultrarapid freezing of human multipronucleate
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 0 1991 The American Fertility Society l'rintmi on oeid-free paper in U.S.A. Fluorescein diacetate assessment of embryo viability after ultrarapid freezing of human multipronucleate
Key words: insulin dependent deabetes mellitus, pancreatic islets, transplantation, cryopreservation, immunomodulat ion
 Key words: insulin dependent deabetes mellitus, pancreatic islets, transplantation, cryopreservation, immunomodulat ion Fig. 1 Number of adult islet all grafts by year performed from 1974 through 1993
Key words: insulin dependent deabetes mellitus, pancreatic islets, transplantation, cryopreservation, immunomodulat ion Fig. 1 Number of adult islet all grafts by year performed from 1974 through 1993
(FITC) or rhodamine blue isothiocyanate (RBITC) for use in mixed egg-transfer experiments. Both FITC and RBITC bind to the zona pellucida
 THE LABELLING OF LIVING RABBIT OVA WITH FLUORESCENT DYES J. W. OVERSTREET Department of Anatomy and International Institute for the Study of Human Reproduction, Columbia University, College of Physicians
THE LABELLING OF LIVING RABBIT OVA WITH FLUORESCENT DYES J. W. OVERSTREET Department of Anatomy and International Institute for the Study of Human Reproduction, Columbia University, College of Physicians
Validation of the Efficacy of a Practical Method for Neutrophils Isolation from Peripheral Blood
 Validation of the Efficacy of a Practical Method for Neutrophils Isolation from Peripheral Blood JONATHAN DEGEL, MASIH SHOKRANI OBJECTIVE: The objectives of this study were to validate the Polymorphprep
Validation of the Efficacy of a Practical Method for Neutrophils Isolation from Peripheral Blood JONATHAN DEGEL, MASIH SHOKRANI OBJECTIVE: The objectives of this study were to validate the Polymorphprep
10/18/2012. A primer in HLA: The who, what, how and why. What?
 A primer in HLA: The who, what, how and why What? 1 First recognized in mice during 1930 s and 1940 s. Mouse (murine) experiments with tumors Independent observations were made in humans with leukoagglutinating
A primer in HLA: The who, what, how and why What? 1 First recognized in mice during 1930 s and 1940 s. Mouse (murine) experiments with tumors Independent observations were made in humans with leukoagglutinating
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Fluorescence Microscopy
 Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
INSTRUCTIONS Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit
 INSTRUCTIONS Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit 88281 Number Description 88281 Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit, contains sufficient reagents to isolate cardiomyocytes from 50 neonatal
INSTRUCTIONS Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit 88281 Number Description 88281 Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit, contains sufficient reagents to isolate cardiomyocytes from 50 neonatal
Cellometer Image Cytometry for Cell Cycle Analysis
 Cellometer Cytometry for Cell Cycle Analysis Importance of Cell Cycle Research Oncology: Since cancer cells often undergo abnormal cell division and proliferation, it is important to understand the cell
Cellometer Cytometry for Cell Cycle Analysis Importance of Cell Cycle Research Oncology: Since cancer cells often undergo abnormal cell division and proliferation, it is important to understand the cell
7-AAD/CFSE Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Assay Kit
 7-AAD/CFSE Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1293 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
7-AAD/CFSE Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1293 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
Using the Ch6diak-Higashi Marker
 A Study of the Origin of Pulmonary Macrophages Using the Ch6diak-Higashi Marker Kent J. Johnson, MD, Peter A. Ward, MD, Gary Striker, MD, and Robin Kunkel, MS Using bone marrow reconstitution techniques
A Study of the Origin of Pulmonary Macrophages Using the Ch6diak-Higashi Marker Kent J. Johnson, MD, Peter A. Ward, MD, Gary Striker, MD, and Robin Kunkel, MS Using bone marrow reconstitution techniques
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
ADVANCED HAEMATOLOGY BATTLE OF THE BANDS. Dennis B. DeNicola, DVM, PhD, DACVP IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. Westbrook, Maine, USA BACKGROUND
 ADVANCED HAEMATOLOGY BATTLE OF THE BANDS Dennis B. DeNicola, DVM, PhD, DACVP IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. Westbrook, Maine, USA BACKGROUND The identification of immature neutrophils (bands, metamyelocytes,
ADVANCED HAEMATOLOGY BATTLE OF THE BANDS Dennis B. DeNicola, DVM, PhD, DACVP IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. Westbrook, Maine, USA BACKGROUND The identification of immature neutrophils (bands, metamyelocytes,
PE Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual KT40001
 PE Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual KT40001 For research use only. Not intended for diagnostic testing. a WuXi AppTec company www.abgent.com.cn PE Annexin-V Apoptosis Detection Kit Product
PE Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual KT40001 For research use only. Not intended for diagnostic testing. a WuXi AppTec company www.abgent.com.cn PE Annexin-V Apoptosis Detection Kit Product
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells.
 Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
ANDROVISION - MORE THAN CASA
 ANDROVISION - MORE THAN CASA AndroVision CASA system with Zeiss AxioScope optics and automated ScanStage Computerized semen analysis AndroVision is a highly precise CASA* system for standardised, interactive
ANDROVISION - MORE THAN CASA AndroVision CASA system with Zeiss AxioScope optics and automated ScanStage Computerized semen analysis AndroVision is a highly precise CASA* system for standardised, interactive
Analysis of the Viability of Umbilical Cord blood Stem Cells. Sachdeva N
 Jsrm/Vol5No.11, 2009 Original Article Analysis of the of Umbilical Cord blood Stem Cells Sachdeva N Dr. Neelam Sachdeva Reader, Department of Zoology, Gargi College, University of Delhi, Siri Fort Road,
Jsrm/Vol5No.11, 2009 Original Article Analysis of the of Umbilical Cord blood Stem Cells Sachdeva N Dr. Neelam Sachdeva Reader, Department of Zoology, Gargi College, University of Delhi, Siri Fort Road,
Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Kit
 Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Kit Catalog Number KA3808 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4
Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Kit Catalog Number KA3808 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4
Computerized semen analysis. Product features. Basic system
 AndroVision - more than CASA AndroVision CASA system with Zeiss AxioScope optics and automated ScanStage Computerized semen analysis AndroVision is a highly precise CASA* system for standardised, interactive
AndroVision - more than CASA AndroVision CASA system with Zeiss AxioScope optics and automated ScanStage Computerized semen analysis AndroVision is a highly precise CASA* system for standardised, interactive
For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples.
 ab14082 500X Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and
ab14082 500X Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and
ab Annexin V- mfluor Blue 570 Detection
 Version 1 Last updated 26 March 2018 ab219914 Annexin V- mfluor Blue 570 Detection Reagent For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of PS exposure in live cells This product is for research use
Version 1 Last updated 26 March 2018 ab219914 Annexin V- mfluor Blue 570 Detection Reagent For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of PS exposure in live cells This product is for research use
Immunology. Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology)
 Host Defenses Overview and Nonspecific Defenses I Immunology Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology) The Nature of Host Defenses 2 3 4 1st line of defense - intact skin mucous membranes
Host Defenses Overview and Nonspecific Defenses I Immunology Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology) The Nature of Host Defenses 2 3 4 1st line of defense - intact skin mucous membranes
Exo-Glow TM Exosome Labeling Kits
 Exo-Glow TM Exosome Labeling Kits Cat# EXOR100A-1 Cat# EXOG200A-1 Cat# EXOC300A-1 User Manual Store kit at -20 o C on receipt Version 8 3/10/2017 A limited-use label license covers this product. By use
Exo-Glow TM Exosome Labeling Kits Cat# EXOR100A-1 Cat# EXOG200A-1 Cat# EXOC300A-1 User Manual Store kit at -20 o C on receipt Version 8 3/10/2017 A limited-use label license covers this product. By use
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit
 Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Supplementary figure legends
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Exposure of CRT occurs independently from the apoptosisassociated loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). (A) HeLa cells treated with MTX
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Exposure of CRT occurs independently from the apoptosisassociated loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). (A) HeLa cells treated with MTX
The use of Fluorescien diacetate to assess embryo viability in the mouse
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/16212435 The use of Fluorescien diacetate to assess embryo viability in the mouse Article in
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/16212435 The use of Fluorescien diacetate to assess embryo viability in the mouse Article in
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Gerasimenko et al..73/pnas.39 SI Materials and Methods Reagents used in this study include Fluo-4/Fura- (Invitrogen), thapsigargin (albiochem), collagenase (Worthington), palmitoleic
Supporting Information Gerasimenko et al..73/pnas.39 SI Materials and Methods Reagents used in this study include Fluo-4/Fura- (Invitrogen), thapsigargin (albiochem), collagenase (Worthington), palmitoleic
BLOOD GRANULOCYTE STAINING WITH ACRIDINE ORANGE
 THE JOURNAL OF HISTOCHEMISTRY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY Copyright 1974 by The Histochemical Society. Inc. Vol. 22. No. 7. pp..26-.v1o. 1974 Printed in L.S.A. BLOOD GRANULOCYTE STAINING WITH ACRIDINE ORANGE CHANGES
THE JOURNAL OF HISTOCHEMISTRY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY Copyright 1974 by The Histochemical Society. Inc. Vol. 22. No. 7. pp..26-.v1o. 1974 Printed in L.S.A. BLOOD GRANULOCYTE STAINING WITH ACRIDINE ORANGE CHANGES
Effect of temperature change of 0.2% chlorhexidine rinse on matured human plaque: an in vivo study.
 ISSN: 2278 0211 (Online) Effect of temperature change of 0.2% chlorhexidine rinse on matured human plaque: an in vivo study. Dr. Yashika Jain Senior Lecturer, Institution: SGT Dental College & Hospital,
ISSN: 2278 0211 (Online) Effect of temperature change of 0.2% chlorhexidine rinse on matured human plaque: an in vivo study. Dr. Yashika Jain Senior Lecturer, Institution: SGT Dental College & Hospital,
Muse Assays for Cell Analysis
 Muse Assays for Cell Analysis Multiple Assay Outputs for Cell Analysis Cell Health Cell Signalling Immunology Muse Count & Viability Kit Muse Cell Cycle Kit Muse Annexin V & Dead Cell Kit Muse Caspase
Muse Assays for Cell Analysis Multiple Assay Outputs for Cell Analysis Cell Health Cell Signalling Immunology Muse Count & Viability Kit Muse Cell Cycle Kit Muse Annexin V & Dead Cell Kit Muse Caspase
Ultrarapid freezing of early cleavage stage human embryos and eight-cell mouse embryos*
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1988 The American Fertility Society Printed in U.S.A. Ultrarapid freezing of early cleavage stage human embryos and eight-cell mouse embryos* Alan Trounson, Ph.D.t:!:
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1988 The American Fertility Society Printed in U.S.A. Ultrarapid freezing of early cleavage stage human embryos and eight-cell mouse embryos* Alan Trounson, Ph.D.t:!:
Instructions. Fuse-It-mRNA easy. Shipping and Storage. Overview. Kit Contents. Specifications. Note: Important Guidelines
 Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit
 RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 May 25, 2014 (Cat#: 68FT-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 May 25, 2014 (Cat#: 68FT-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
Supplemental Data. Beck et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
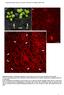 Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypic comparison of the rosette leaves of four-week-old mpk4 and Col-0 plants. A mpk4 vs Col-0 plants grown in soil. Note the extreme dwarfism of the mpk4 plants (white arrows)
Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypic comparison of the rosette leaves of four-week-old mpk4 and Col-0 plants. A mpk4 vs Col-0 plants grown in soil. Note the extreme dwarfism of the mpk4 plants (white arrows)
THE BRITISH JOURN OF VOL. LII OCTOBER, 1971 NO. 5 EXPERIMENTAL PATHOLOGY DISAGGREGATED CELLS OF THE TRANSMISSIBLE VENEREAL TUMOUR OF THE DOG
 Vol. Lll, No. 4 (August, 1971) was issued 2.9.71. THE BRITISH JOURN OF EXPERIMENTAL PATHOLOGY VOL. LII OCTOBER, 1971 NO. 5 A PHENOMENON RESEMBLING OPSONIC ADHERENCE SHOWN BY DISAGGREGATED CELLS OF THE
Vol. Lll, No. 4 (August, 1971) was issued 2.9.71. THE BRITISH JOURN OF EXPERIMENTAL PATHOLOGY VOL. LII OCTOBER, 1971 NO. 5 A PHENOMENON RESEMBLING OPSONIC ADHERENCE SHOWN BY DISAGGREGATED CELLS OF THE
Human Saliva as a Convenient Source of Ribonuclease. By S. BRADBURY
 Human Saliva as a Convenient Source of Ribonuclease 323 By S. BRADBURY (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, University Museum, Oxford) SUMMARY Saliva, heated to 80 C for 10 minutes
Human Saliva as a Convenient Source of Ribonuclease 323 By S. BRADBURY (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, University Museum, Oxford) SUMMARY Saliva, heated to 80 C for 10 minutes
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Interferon γ regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a. Th17 + CD4 + T-cell-mediated GvH disease
 Interferon γ regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a Th17 + CD4 + T-cell-mediated GvH disease Nora Mauermann, Julia Burian, Christophe von Garnier, Stefan Dirnhofer, Davide Germano, Christine Schuett,
Interferon γ regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a Th17 + CD4 + T-cell-mediated GvH disease Nora Mauermann, Julia Burian, Christophe von Garnier, Stefan Dirnhofer, Davide Germano, Christine Schuett,
CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES
 CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES 3.1 HLA TYPING Molecular HLA typing will be performed for all donor cord blood units and patients in the three reference laboratories identified
CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES 3.1 HLA TYPING Molecular HLA typing will be performed for all donor cord blood units and patients in the three reference laboratories identified
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. CXCR4 inhibitors could benefit to HER2 but not to Triple-Negative. breast cancer patients
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CXCR4 inhibitors could benefit to HER2 but not to Triple-Negative breast cancer patients Lefort S. 1,2, Thuleau A. 3, Kieffer Y. 1,2, Sirven P. 1,2, Bieche I. 4, Marangoni E.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CXCR4 inhibitors could benefit to HER2 but not to Triple-Negative breast cancer patients Lefort S. 1,2, Thuleau A. 3, Kieffer Y. 1,2, Sirven P. 1,2, Bieche I. 4, Marangoni E.
Serafino et al. Thymosin α1 activates complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Figures
 Inhibition of Pulmonary Anti Bacterial Defense by IFN γ During Recovery from Influenza Infection By Keer Sun and Dennis W. Metzger Supplementary Figures d a Ly6G Percentage survival f 1 75 5 1 25 1 5 1
Inhibition of Pulmonary Anti Bacterial Defense by IFN γ During Recovery from Influenza Infection By Keer Sun and Dennis W. Metzger Supplementary Figures d a Ly6G Percentage survival f 1 75 5 1 25 1 5 1
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Blood. Water compartments
 Blood Water compartments 2/8 about 60% of our body is water (young-old, male-female) water is located in compartments, movement is regulated intracellular : extracellular 2:1, i.e. 40:20% interstitial
Blood Water compartments 2/8 about 60% of our body is water (young-old, male-female) water is located in compartments, movement is regulated intracellular : extracellular 2:1, i.e. 40:20% interstitial
Product Datasheet. Ly-6G6C Antibody (NIMP-R14) NB Unit Size: 0.05 mg. Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Publications: 23
 Product Datasheet Ly-6G6C Antibody (NIMP-R14) NB600-1387 Unit Size: 0.05 mg Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Publications: 23 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at:
Product Datasheet Ly-6G6C Antibody (NIMP-R14) NB600-1387 Unit Size: 0.05 mg Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Publications: 23 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at:
- 1 - Cell types Monocytes THP-1 cells Macrophages. LPS Treatment time (Hour) IL-6 level (pg/ml)
 Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit
 Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit Catalog Number KA0716 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit Catalog Number KA0716 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
CryoStor CS2, CS5 and CS10 FREEZE MEDIA
 CryoStor CS2, CS5 and CS10 FREEZE MEDIA Pre-Formulated Serum-Free Protein-Free cgmp Manufactured FDA Master File Sterility, Endotoxin, and Cell-Based Release Testing CryoStor, a series of cell-specific,
CryoStor CS2, CS5 and CS10 FREEZE MEDIA Pre-Formulated Serum-Free Protein-Free cgmp Manufactured FDA Master File Sterility, Endotoxin, and Cell-Based Release Testing CryoStor, a series of cell-specific,
Medical School Histology Basics Introduction to Microscopy. VIBS 289 lab
 Medical School Histology Basics Introduction to Microscopy VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Learn the difference in magnification and resolution Learn about different types of
Medical School Histology Basics Introduction to Microscopy VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Learn the difference in magnification and resolution Learn about different types of
In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay
 Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, in vitro suppression assay and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of
Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, in vitro suppression assay and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of
AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit
 AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3789 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3789 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
SINGLE UV EXCITATION OF HOECHST AND PROPIDIUM IODIDE FOR VIABILITY ASSESSMENT OF RHESUS MONKEY SPERMATOZOA USING FLOW CYTOMETRY
 Archives of Andrology Journal of Reproductive Systems ISSN: 0148-5016 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaan19 SINGLE UV EXCITATION OF HOECHST 33342 AND PROPIDIUM IODIDE
Archives of Andrology Journal of Reproductive Systems ISSN: 0148-5016 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaan19 SINGLE UV EXCITATION OF HOECHST 33342 AND PROPIDIUM IODIDE
MHC Multimer staining (6 colours, with fixation)
 v MH Multimer staining (6 colours, with fixation) Authors M. Odendahl,. Blum,. Busch ate 27-04-2007 Version 1.0 REAGENTS: - PBMs after Ficoll - EMA - Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), ph 7.45 - FAS staining
v MH Multimer staining (6 colours, with fixation) Authors M. Odendahl,. Blum,. Busch ate 27-04-2007 Version 1.0 REAGENTS: - PBMs after Ficoll - EMA - Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), ph 7.45 - FAS staining
2-Deoxyglucose Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 2-Deoxyglucose Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA3753 100 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
2-Deoxyglucose Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA3753 100 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds
 Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds Yuan Zeng, Bingyu Li, Anwar Kalalah, Sang-Jin Suh, and S.S. Ditchkoff Summary Antibiotic activity of ten commercially available odor eliminating
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds Yuan Zeng, Bingyu Li, Anwar Kalalah, Sang-Jin Suh, and S.S. Ditchkoff Summary Antibiotic activity of ten commercially available odor eliminating
ab CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit
 ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Optimization of the Fuse-It-mRNA Protocol for L929 Cells in the µ-plate 24 Well
 Optimization of the Fuse-It-mRNA Protocol for L929 Cells in the µ-plate 24 Well 1. General Information... 1 2. Background... 1 3. Material and Equipment Required... 2 4. Experimental Procedure and Results...
Optimization of the Fuse-It-mRNA Protocol for L929 Cells in the µ-plate 24 Well 1. General Information... 1 2. Background... 1 3. Material and Equipment Required... 2 4. Experimental Procedure and Results...
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Traditional electronic gating strategy for analysing cell death based on A5-FITC and 7-AAD. a, Flow cytometry analysis showing the traditional two-stage electronic gating strategy
Supplementary Figure 1 Traditional electronic gating strategy for analysing cell death based on A5-FITC and 7-AAD. a, Flow cytometry analysis showing the traditional two-stage electronic gating strategy
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors Presented by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-10780-00 Outline Introduction Cytokines Transcription
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors Presented by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-10780-00 Outline Introduction Cytokines Transcription
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy In Vitro Chemoresistance and Chemosensitivity Assays File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: in_vitro_chemoresistance_and_chemosensitivity_assays
Corporate Medical Policy In Vitro Chemoresistance and Chemosensitivity Assays File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: in_vitro_chemoresistance_and_chemosensitivity_assays
ab Lysosome/Cytotoxicity Dual Staining Kit
 ab133078 Lysosome/Cytotoxicity Dual Staining Kit Instructions for Use For studying lysosome function at the cellular level. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
ab133078 Lysosome/Cytotoxicity Dual Staining Kit Instructions for Use For studying lysosome function at the cellular level. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
Recombinant Trypsin, Animal Origin Free
 Recombinant Trypsin, Animal Origin Free PRODUCT INFORMATION: BioGenomics r-trypsin powder is ready to use, animal origin free optimized for cell culture applications. It is derived by r-dna technology.
Recombinant Trypsin, Animal Origin Free PRODUCT INFORMATION: BioGenomics r-trypsin powder is ready to use, animal origin free optimized for cell culture applications. It is derived by r-dna technology.
Product Information Sheet (M ) MarkerGene TM LysoLive TM Lysosomal Sulfatase Assay Kit (Product M1377)
 1 Product Information Sheet (M1377-004) MarkerGene TM LysoLive TM Lysosomal Sulfatase Assay Kit (Product M1377) Marker Gene Technologies, Inc. University of Oregon Riverfront Research Park 1850 Millrace
1 Product Information Sheet (M1377-004) MarkerGene TM LysoLive TM Lysosomal Sulfatase Assay Kit (Product M1377) Marker Gene Technologies, Inc. University of Oregon Riverfront Research Park 1850 Millrace
DC were seeded into tissue culture dishes in IMDM 2% FCS, and added with PMN. (1:1; PMN: DC) for 16h also in the presence of DNAse (100 U/ml); DC were
 Supplementary methods Flow cytometric analysis of DCs. DC were seeded into tissue culture dishes in IMDM 2% FCS, and added with PMN (1:1; PMN: DC) for 16h also in the presence of DNAse (100 U/ml); DC were
Supplementary methods Flow cytometric analysis of DCs. DC were seeded into tissue culture dishes in IMDM 2% FCS, and added with PMN (1:1; PMN: DC) for 16h also in the presence of DNAse (100 U/ml); DC were
High throughput screening of nanotoxicity based on oxidative stress paradigm
 December 11 28 High throughput screening of nanotoxicity based on oxidative stress paradigm Saji George Dr Andre Nel s lab Dept. of Medicine (Division of Nanomedicine) UCLA December 11 28 Growing nanotech
December 11 28 High throughput screening of nanotoxicity based on oxidative stress paradigm Saji George Dr Andre Nel s lab Dept. of Medicine (Division of Nanomedicine) UCLA December 11 28 Growing nanotech
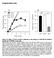
Supplemental Data Figure S1 Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells.
 Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). View kit datasheet: www.abcam.com/ab14085
ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). View kit datasheet: www.abcam.com/ab14085
Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit
 RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 Mar 20, 2014 (Cat#: 68C5-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 Mar 20, 2014 (Cat#: 68C5-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
ImmunoTools special Award 2014
 ImmunoTools special Award 2014 Davide Ferrari, PhD University of Ferrara, Department of Morphology, Surgery and Experimental Medicine. Section of Pathology, Oncology and Exper. Biology via L. Borsari 46,
ImmunoTools special Award 2014 Davide Ferrari, PhD University of Ferrara, Department of Morphology, Surgery and Experimental Medicine. Section of Pathology, Oncology and Exper. Biology via L. Borsari 46,
LDL Uptake Flow Cytometry Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Flow Cytometry Assay Kit Item No. 601470 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
LDL Uptake Flow Cytometry Assay Kit Item No. 601470 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Effect of Transplantation Site on the Results of Pancreatic Islet Isografts in Diabetic Rats
 Diabetologia 9, 486--491 (1973) 9 by Springer-Verlag 1973 Effect of Transplantation Site on the Results of Pancreatic Islet Isografts in Diabetic Rats C.B. Kemp, M.J. Knight, D.W. Seharp, W.F: Ballinger
Diabetologia 9, 486--491 (1973) 9 by Springer-Verlag 1973 Effect of Transplantation Site on the Results of Pancreatic Islet Isografts in Diabetic Rats C.B. Kemp, M.J. Knight, D.W. Seharp, W.F: Ballinger
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Spherical Nucleic Acids For Advanced Wound Healing Applications Chad A. Mirkin
 Spherical Nucleic Acids For Advanced Wound Healing Applications Chad A. Mirkin Departments of Chemistry, Infectious Disease, Materials Science & Engineering, Chemical & Biological Engineering, and Biomedical
Spherical Nucleic Acids For Advanced Wound Healing Applications Chad A. Mirkin Departments of Chemistry, Infectious Disease, Materials Science & Engineering, Chemical & Biological Engineering, and Biomedical
Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis
 icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis Introduction The skeletal muscle is one of the
icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis Introduction The skeletal muscle is one of the
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells
 The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
Quantitative Assay of Paravaccinia Virus Based
 APPrU MICROBIOLOGY, JUly 1972, p. 138-142 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Quantitative Assay of Paravaccinia Virus Based on Enumeration of Inclusion-Containing
APPrU MICROBIOLOGY, JUly 1972, p. 138-142 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Quantitative Assay of Paravaccinia Virus Based on Enumeration of Inclusion-Containing
Gladstone Institutes, University of California (UCSF), San Francisco, USA
 Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Getting Beyond the Flags: Quantitative assessment of immature granulocyte (IG) populations may improve the assessment of sepsis and inflammation.
 Getting Beyond the Flags: Quantitative assessment of immature granulocyte (IG) populations may improve the assessment of sepsis and inflammation. Sysmex America White Paper One Nelson C. White Parkway,
Getting Beyond the Flags: Quantitative assessment of immature granulocyte (IG) populations may improve the assessment of sepsis and inflammation. Sysmex America White Paper One Nelson C. White Parkway,
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Assessment of leukocyte adhesion in flow chambers
 Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Monocyte subsets in health and disease. Marion Frankenberger
 Monocyte subsets in health and disease Marion Frankenberger main cellular components: Leukocytes Erythrocytes Composition of whole blood Monocytes belong to the cellular components of peripheral blood
Monocyte subsets in health and disease Marion Frankenberger main cellular components: Leukocytes Erythrocytes Composition of whole blood Monocytes belong to the cellular components of peripheral blood
Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum...1. Trademarks: HiLyte Fluor (AnaSpec, Inc.)
 Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
Best Practices for PBMC Processing
 Immunology Quality Assessment Cryopreservation Proficiency Testing Program Best Practices for PBMC Processing 2015 ACTG Network Annual Meeting Presented by: Sarah Keinonen June 23, 2015 1 IQA Cryopreservation
Immunology Quality Assessment Cryopreservation Proficiency Testing Program Best Practices for PBMC Processing 2015 ACTG Network Annual Meeting Presented by: Sarah Keinonen June 23, 2015 1 IQA Cryopreservation
Cell Migration and Invasion Assays INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM. Real-time automated measurements of cell motility inside your incubator
 Cell Migration and Invasion Assays INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM Real-time automated measurements of cell motility inside your incubator See the whole story Real-time cell motility visualization and
Cell Migration and Invasion Assays INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM Real-time automated measurements of cell motility inside your incubator See the whole story Real-time cell motility visualization and
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Tube 1 : FLAER/CD24/CD16/CD15/CD45
 Gating procedure for white blood cells (WBC) on FC500 The French PNH diagnosis working group has developed an optimized gating strategy adapted to a two-tubes diagnostic test (PMN, MO), evaluated in a
Gating procedure for white blood cells (WBC) on FC500 The French PNH diagnosis working group has developed an optimized gating strategy adapted to a two-tubes diagnostic test (PMN, MO), evaluated in a
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2*
 Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Idoyaga et al. 10.1073/pnas.0812247106 SSC a) Single cell suspension 99 Aqua b) Live cells 96 -W c) Singlets 92 -A CD19+ER119 d) CD19 ER119 cells 97 CD3 e) CD3 cells 27 f) DX5 cells
Supporting Information Idoyaga et al. 10.1073/pnas.0812247106 SSC a) Single cell suspension 99 Aqua b) Live cells 96 -W c) Singlets 92 -A CD19+ER119 d) CD19 ER119 cells 97 CD3 e) CD3 cells 27 f) DX5 cells
