Clinical Symptoms in the Lateral Type of Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage
|
|
|
- Daisy Chapman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 676 Correlation Between the Location of Hematoma and its Clinical Symptoms in the Lateral Type of Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage Observations on Pantopaque Radiography of the Hematoma Cavity in Cases of Early Surgical Treatment TOMOMI KOBA, M.D., TETSUO YOKOYAMA, M.D., AND MITSUO KANEKO, M.D. SUMMARY The authors studied the Pantopaque radiograms of a hematoma cavity' in 46 patients following early surgical treatment for the lateral type of hypertensive intracerebral hematoma. All patients were operated on within 7 hours after the apoplectic attack 4 and most of them had a localized hematoma. It was concluded that they could be classified in three subtypes from the location of hematoma in the antero-posterior direction. Each subtype had particular clinical symptoms and prognosis. LATERAL HYPERTENSIVE intracerebral hematomas show different clinical symptoms and signs depending upon their location and extension. It has been difficult to assess the actual site of a hematoma and the extent of cerebral tissue destruction by ordinary carotid angiography or pneumoencephalography. In 1973 we developed Pantopaque radiography of the hematoma cavity. 6 In this technique a few drops of Pantopaque are put into the hematoma cavity at the time of operation and the extent of the hematoma is then determined on the postoperative carotid angiogram. By using a stereotaxic atlas to localize the hematoma, we reviewed 46 patients with a lateral hematoma, all operated on within 7 hours after the apoplectic attack. The accuracy of this method was recently proved by computerized axial tomography. This method was valuable to show the exact location of destroyed brain tissue after surgery and to relate this to the prognosis of an individual case. Methods Pantopaque Radiography of the Hematoma Cavity Tagging of the cavity was done at the time of operation as follows: After the intracerebral hematoma was evacuated, small pieces of cottonoid oxycel soaked in Pantopaque were put into the cavity and fixed on the wall at each end. Cottonoid oxycel is an absorbable fibrin fiber and can be left in the tissue for its original purpose as a hemostatic agent. The distribution of the droplets of Pantopaque can be observed on the plain skull film after operation. They are evaluated on the postoperative carotid angiogram usually two weeks after the operation when brain edema subsides and an accurate diagnosis of the extent of destroyed brain tissue can be made. Peterson's method 7 was used to distinguish the anterior and posterior commissures from the deep veins in the venous phase of the carotid angiogram. Both commissures can be identified from the average distances on the VA-VG line shown in figure 1. The location of each droplet of Pantopaque appears as a spot on the AC-PC line and is then transcribed using the stereotaxic atlas of Andrews & Watkins 1 or of Schaltenbrand. 8 This method has been applied to more than 80 patients with several varieties of intracerebral hematoma. From the Department of Neurosurgery, Hamamatsu Medical Center Hospital, 326 Tomitsuka-cho, Hamamatsu, Japan. To localize the hematoma and correlate its clinical symptoms, 46 patients were studied all operated upon within 7 hours after the apoplectic attack. During the early period after the onset the hematoma is almost always localized. The cavity becomes shrunken to one-half or twothirds of its previous size by removing the clot. Results The Pantopaque radiograms of 46 patients showed variable location and extent of the hematoma in each patient. When classified into three groups related to the anterior two-thirds of the posterior limb of the internal capsule each group had particular clinical symptoms. These 3 groups were the anterior subtype, the middle subtype and posterior subtype of lateral intracerebral hematoma. The characteristic symptoms and the frequency of each are as follows: /. The Anterior Subtype The hematoma is located anterior to the level of the pyramidal tract or the anterior two-thirds of the posterior limb. Six of 46 patients were in this group. The clinical characteristics were mild disturbances of consciousness from onset with hemiplegia. Postoperative recovery of gross muscle power was satisfactory but fine movement of the hands were clumsy. Before operation all patients had occular conjugate deviation and extensor plantar responses which continued for a few days after operation. No visual field defect or sensory disturbance were noted. These patients showed fairly good functional recovery and they were often able to return to work. The angiographic findings, included elevation of the Sylvian point and the loop of early M-2 was pushed latero-inferiorly. The lateral lenticulo-striate arteries were shifted medially at their origin (fig. 1). In the postoperative Pantopaque radiogram of the hematoma cavity, drops of Pantopaque were located anteriorly to the venous angle of the internal cerebral vein. If mapped on the stereotaxic atlas the hematoma was located in the region of the anterior limb of the internal capsule (fig. 2). 2. The Middle Subtype This was the most frequent type of hematoma and was located in the region of the anterior two-thirds of the
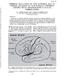
2 HEMATOMA LOCATION AND CLINICAL SYMPTOMS/Koba et al. 677 FIGURE 1. Carotid angiogram of the Anterior subtype. The elevation of the Sylvian point is not marked and the beginning of the M2 is compressed latero-inferiorly. The proximal portion of the lenticulo-striate artery is swept medially and the distal portion is back to the normal position. posterior limb of the internal capsule near the posterior half of the putamen. Twenty-eight patients were in this group. The clinical symptoms were motor weakness, the severity of which depended on the distance between the hematoma and the internal capsule. If the hematoma was located more laterally around the external capsule, recovery from hemiplegia was rapid after surgery. Complete transection of the internal capsule was rarely observed. Recovery from weakness was generally less likely in the arm than the leg in most of the patients. With hemorrhage in the dominant hemisphere, variable degrees of aphasia were observed. Sensory disturbances were minimal. No visual field defect was observed. Conjugate deviation of the eyes and Babinski's sign were often observed. Characteristics of the carotid angiogram were that the Sylvian point was moderately elevated, the M-2 portion was swept laterally and the middle portion of the lenticulo-striated artery was pressed medially (fig. 3). On Pantopaque radiography of the hematoma FIGURE 3. Carotid angiogram of the Middle subtype. The Sylvian point is elevated moderately, the portion of M-2 is swept laterally and the lenticulo-striate artery is shifted medially (arrow). FIGURE 2. Two examples of the Anterior subtype. The hematoma is located in the level of the anterior limb of the internal capsule.
3 678 STROKE VOL 8, No 6, NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 1977 cavity, the hematoma was located near the posterior half of the putamen (fig. 4). 3. The Posterior Subtype Ten of 46 patients were in this group. The hematoma was located more posteriorly than the middle type and extended from the posterior one-third of the posterior limb of the internal capsule to the occipital white matter. The clinical symptoms were more sensory disturbances than motor weakness. They often were associated with autotopagnosia, astereognosia or slight disturbance of superficial sensation in the opposite half of the body. Some patients had inferior homonymous quadrantopsia (fig. 8). Generally motor weakness improved and the patient often could walk. Conjugate deviation of the eyes was usually eliminated and Babinski's sign disappeared, even if present at onset. The angiographic characteristics included elevation of the Sylvian point, slight lateral sweep of M-l and M-2, and medial shift of the distal portion of the lenticulo-striate artery (fig. 5). Pantopaque radiography of the hematoma cavity is shown in the figures (figs. 6, 7). FIGURE 4. An example of the Middle subtype. The hematoma is located in the level of the anterior two-third of the posterior limb of the internal capsule. FIGURE 6. Two cases of the Posterior subtype. The hematoma is located more posteriorly than the Middle subtype. FIGURE 5. Carotid angiogram of the Posterior subtype. The Sylvian point is markedly elevated and the distal portion of the tenliculostriate artery is shifted medially.
4 FIGURE 7. Pantopaque radiogram of the hematoma cavity in the Posterior type. The Pantopaque droplets are scattered around the Galen's vein on the lateral view. FIGURE 8. Visual field defect in the Posterior subtype. Homonymous inferior quadrantopsia was often identified in this subtype.
5 680 STROKE VOL 8, No 6, NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 1977 Discussion The pathogenesis of the hypertensive intracerebral hematoma supposes rupture of a microaneurysm of a cerebral arteriole due to angionecrosis. Oneda 11 found that microaneurysms develop after fibrinoid degeneration of the arterial wall. As to the frequency and distribution of microaneurysms Oneda showed they were more frequent in the putamen, thalamus and caudate nucleus and rarely found in the globus pallidus. Matsuoka 6 found 120 microaneurysms on histological examination of serial sections of the brain. They were distributed as follows: 51.7% in the putamen, 21.7% in the thalamus, 12.5% in the pons and 4.2% in the pallidum. According to Cole 2 they are found more frequently in the putamen, globus pallidus and thalamus and less frequently in the caudate nucleus, internal capsule and subcortical white matter. Those reports help explain why intracerebral hemorrhages are found more frequently outside the internal capsule. The variation in the location of the hematoma in the anteroposterior direction was previously thought to be due to the difference in the hematoma extension. Now it is believed that this variation is due to the differences in the site of a microaneurysm which ruptures. There are 4 to 7 lenticulo-striate arteries 10 on the proximal middle cerebral artery. If a microaneurysm ruptures on the medial lenticulostriate artery it then develops into the Anterior sub-type. If it ruptures on the middle lenticulo-striate artery it develops into the Middle sub-type of hematoma. The Posterior subtype is due to the rupture of a microaneurysm on the lateral lenticulo-striate artery. From our experience in early surgery 4 arid autopsy examination, we believe that a hematoma is usually caused by rupture of a single microaneurysm on a branch of a lenticulo-striate artery. These three subtypes of intracerebral hematoma can be attributed to the location of the microaneurysm which ruptures originally. References 1. Andrew J, Watkins ES: A stereotaxic atlas of the human thalamus and adjacent structures. Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins, Cole FM, Yates PO: The occurrence and significance of intracerebral microaneurysms. J Pathol Bact 93: , Gawler J et al: Computerized axial tomography, the normal EMI scan. J Neur Neurosurg Psychiatry 38: , Kaneko M: Trial of the surgical treatment for hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage in peracute stage. J Neurosurg (Tokyo) 2: , Kaneko M, Koba T, Yokoyama T: The Pantopaque radiography of the hematoma cavity in intracerebral hemorrhage and its stereotaxic evaluation. Brain & Nerve (Tokyo) 28: , Matsuoka S: Pathology of the cerebral apoplexy. Jap J Pathol 39: 1-10, Peterson DI, Austin GM: Identification of the anterior and posterior commissure by angiography. J Neurosurg 40: , Schaltenbrand G, Bailey P: Introduction to stereotaxis with an atlas of the human brain. New York, Grune and Stratton, Scott WR et al: Computerized axial tomography of intracerebral and intraventricular hemorrhage. Radiology 112: 73-80, Stephens RB, Stilwell DL: Arteries and Veins of the Human Brain, CC Thomas, Yoshida Y, Oneda G: Pathology of the intracerebral hemorrhage. Saishin-igaku 25: , 1970 Long-Term Prognosis for Cerebral Infarction in Relation to Brain Circulation - A 7-Year Follow Up Study MASATOSHI FUJISHIMA, M.D., KATSUYA NISHIMARU, M.D., AND TERUO OMAE, SUMMARY Seventy-seven patients with cerebral infarction have been re-examined every year and followed for 7 years. Thirty-one patients had normal cranial blood flow (BF) and the remaining 46 had subnormal cranial BF, determined by the intravenous RISA method at the time of the original attack. During a 7-year follow up, 7 patients (22.6%) of the normal cranial BF group died; 3 of stroke and the remaining 4 from other causes, M.D. while 24 patients (52.2%) of the subnormal cranial BF group died; 13 of stroke and the remaining 11 of various diseases. The cumulative survival rate was consistently lower in the subnormal cranial BF group than the normal one. This difference reached statistical significance at 5 and 7 years of follow up. However, stroke recurrence did not differ significantly between the 2 groups. This suggests that a decreased cranial BF is an indicator of a poor long-term prognosis. THERE HAS BEEN no report of a prospective study on the long-term prognosis of patients with cerebral infarction related to cerebral hemodynamics, although cerebral blood flow is frequently determined in these patients. It seems reasonable to expect that the prognosis of patients with From Second Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Kyushu University, and Third Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka University, Fukuoka City, Japan. Reprint requests to Dr. Fujishima, 2nd Dept. Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Kyushu University, Maidashi 3-1-1, Higashi-Ku, Fukuoka City 812, Japan. stroke who have a decreased cerebral or cranial blood flow might be worse than for those who have a normal blood flow. It is not known whether recurrence, and long-term mortality are different in these two groups of patients. Methods Of 260 patients admitted to our clinic for evaluation of cerebrovascular diseases between 1962 and 1967, 153 had had cerebral infarction. Of these 153 patients, 77 were selected for study. They had had a stroke within the
Stroke School for Internists Part 1
 Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Blood Supply. Allen Chung, class of 2013
 Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
I T IS well known that aneurysms occur at
 The Lateral Perforating Branches of the Anterior and Middle Cerebral Arteries* HARRY A. KAPLAN, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Seton Hall College of Medicine, and Jersey City Medical Center, Jersey City,
The Lateral Perforating Branches of the Anterior and Middle Cerebral Arteries* HARRY A. KAPLAN, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Seton Hall College of Medicine, and Jersey City Medical Center, Jersey City,
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
OBJECTIVES. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries.
 DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas
 External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
EMBOLIC OCCLUSION OF THE SUPERIOR AND IN- FERIOR DIVISIONS OF THE MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY WITH ANGIOGRAPHIC-CLINICAL CORRELATION*
 MARCH, 1976 Pre EMBOLIC OCCLUSION OF THE SUPERIOR AND IN- FERIOR DIVISIONS OF THE MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY WITH ANGIOGRAPHIC-CLINICAL CORRELATION* ABSTRACT: Superior Rolandlc rolandic By L. REED ALTEMUS,
MARCH, 1976 Pre EMBOLIC OCCLUSION OF THE SUPERIOR AND IN- FERIOR DIVISIONS OF THE MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY WITH ANGIOGRAPHIC-CLINICAL CORRELATION* ABSTRACT: Superior Rolandlc rolandic By L. REED ALTEMUS,
Fig.1: A, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a
 Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Blood Supply of the CNS
 Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Spasm of the extracranial internal carotid artery resulting from blunt trauma demonstrated by angiography
 Spasm of the extracranial internal carotid artery resulting from blunt trauma demonstrated by angiography Case report ELISHA S. GURDJIAN, M.D., BLAISE AUDET, M.D., RENATO W. SIBAYAN, M.D., AND LLYWELLYN
Spasm of the extracranial internal carotid artery resulting from blunt trauma demonstrated by angiography Case report ELISHA S. GURDJIAN, M.D., BLAISE AUDET, M.D., RENATO W. SIBAYAN, M.D., AND LLYWELLYN
The NIHSS score is 4 (considering 2 pts for the ataxia involving upper and lower limbs.
 Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology
 Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Pathological Studies on the Intracerebral and Retinal Arteries in Cerebrovascular and Noncerebrovascular Diseases
 Pathological Studies on the Intracerebral and Retinal Arteries in Cerebrovascular and Noncerebrovascular Diseases BY IKUO GOTO, M.D.,* KATSUHARU KIMOTO, M.D.,t SHIBANOSUKE KATSUKI, M.D.,t TAKAAKI MIMATSU,
Pathological Studies on the Intracerebral and Retinal Arteries in Cerebrovascular and Noncerebrovascular Diseases BY IKUO GOTO, M.D.,* KATSUHARU KIMOTO, M.D.,t SHIBANOSUKE KATSUKI, M.D.,t TAKAAKI MIMATSU,
Lecturer. Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014
 Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Assessing the Stroke Patient. Arlene Boudreaux, MSN, RN, CCRN, CNRN
 Assessing the Stroke Patient Arlene Boudreaux, MSN, RN, CCRN, CNRN Cincinnati Pre-Hospital Stroke Scale May be done by EMS o One of many o F facial droop on one side o A arm drift (hold a pizza box, close
Assessing the Stroke Patient Arlene Boudreaux, MSN, RN, CCRN, CNRN Cincinnati Pre-Hospital Stroke Scale May be done by EMS o One of many o F facial droop on one side o A arm drift (hold a pizza box, close
Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis
 Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas. Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template
 Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Moyamoya disease is an unusual form of chronic, occlusive
 Angiographic Dilatation and Branch Extension of the Anterior Choroidal and Posterior Communicating Arteries Are Predictors of Hemorrhage in Adult Moyamoya Patients Motohiro Morioka, MD; Jun-Ichiro Hamada,
Angiographic Dilatation and Branch Extension of the Anterior Choroidal and Posterior Communicating Arteries Are Predictors of Hemorrhage in Adult Moyamoya Patients Motohiro Morioka, MD; Jun-Ichiro Hamada,
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
In cerebral embolism, recanaiization occurs very
 680 Case Reports Recanaiization of Intracranial Carotid Occlusion Detected by Duplex Carotid Sonography Haruhiko Hoshino, MD, Makoto Takagi, MD, Ikuo Takeuchi, MD, Tsugio Akutsu, MD, Yasuyuki Takagi, MD,
680 Case Reports Recanaiization of Intracranial Carotid Occlusion Detected by Duplex Carotid Sonography Haruhiko Hoshino, MD, Makoto Takagi, MD, Ikuo Takeuchi, MD, Tsugio Akutsu, MD, Yasuyuki Takagi, MD,
Leah Militello, class of 2018
 Leah Militello, class of 2018 Objectives 1. Describe the general organization of cerebral hemispheres. 2. Describe the locations and features of the different functional areas of cortex. 3. Understand
Leah Militello, class of 2018 Objectives 1. Describe the general organization of cerebral hemispheres. 2. Describe the locations and features of the different functional areas of cortex. 3. Understand
INSTITUTE OF NEUROSURGERY & DEPARTMENT OF PICU
 CEREBRAL BYPASS An Innovative Treatment for Arteritis INSTITUTE OF NEUROSURGERY & DEPARTMENT OF PICU CASE 1 q 1 year old girl -recurrent seizure, right side limb weakness, excessive cry and irritability.
CEREBRAL BYPASS An Innovative Treatment for Arteritis INSTITUTE OF NEUROSURGERY & DEPARTMENT OF PICU CASE 1 q 1 year old girl -recurrent seizure, right side limb weakness, excessive cry and irritability.
Stereotaxic evacuation of spontaneous intracerebral hematomas EDWARD I. KANDEI~ M.D., D.SC., AND VJACHESLAW V. PERESEDOV, M.D.
 J Neurosurg 62:206-213, 1985 Stereotaxic evacuation of spontaneous intracerebral hematomas EDWARD I. KANDEI~ M.D., D.SC., AND VJACHESLAW V. PERESEDOV, M.D. Neurosurgical Clinic, Institute of Neurology,
J Neurosurg 62:206-213, 1985 Stereotaxic evacuation of spontaneous intracerebral hematomas EDWARD I. KANDEI~ M.D., D.SC., AND VJACHESLAW V. PERESEDOV, M.D. Neurosurgical Clinic, Institute of Neurology,
Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences
 Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ٢ Level of consciousness is depressed Stuporous patients respond only to repeated
Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ٢ Level of consciousness is depressed Stuporous patients respond only to repeated
TIA AND STROKE. Topics/Order of the day 1. Topics/Order of the day 2 01/08/2012
 Charles Ashton Medical Director TIA AND STROKE Topics/Order of the day 1 What Works? Clinical features of TIA inc the difference between Carotid and Vertebral territories When is a TIA not a TIA TIA management
Charles Ashton Medical Director TIA AND STROKE Topics/Order of the day 1 What Works? Clinical features of TIA inc the difference between Carotid and Vertebral territories When is a TIA not a TIA TIA management
Longitudinal anterior-to-posterior shift of collateral channels in patients with moyamoya disease: an implication for its hemorrhagic onset
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Longitudinal anterior-to-posterior shift of collateral channels in patients with moyamoya disease: an implication for its hemorrhagic onset Shusuke Yamamoto, MD, Satoshi Hori, MD, PhD,
CLINICAL ARTICLE Longitudinal anterior-to-posterior shift of collateral channels in patients with moyamoya disease: an implication for its hemorrhagic onset Shusuke Yamamoto, MD, Satoshi Hori, MD, PhD,
Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Arterial Blood Supply
 Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations is often extensive
 NOVEMBER, 1974 ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE OCCIPITAL LOBE* By B. TODD TROOST, M.D.,t and THOMAS H. NEWTON, M.D4 T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
NOVEMBER, 1974 ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE OCCIPITAL LOBE* By B. TODD TROOST, M.D.,t and THOMAS H. NEWTON, M.D4 T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
Stroke: clinical presentations, symptoms and signs
 Stroke: clinical presentations, symptoms and signs Professor Peter Sandercock University of Edinburgh EAN teaching course Burkina Faso 8 th November 2017 Clinical diagnosis is important to Ensure stroke
Stroke: clinical presentations, symptoms and signs Professor Peter Sandercock University of Edinburgh EAN teaching course Burkina Faso 8 th November 2017 Clinical diagnosis is important to Ensure stroke
Lab 2. we will look into several angled horizontal sections ( orbitomeatal plane ) i.e passing from the orbit into the ear
 we will look into several angled horizontal sections ( orbitomeatal plane ) i.e passing from the orbit into the ear Figure I page 76 : looking at the key on the left side this section passed through the
we will look into several angled horizontal sections ( orbitomeatal plane ) i.e passing from the orbit into the ear Figure I page 76 : looking at the key on the left side this section passed through the
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Marc Norman, Ph.D. - Do Not Use without Permission 1. Cerebrovascular Accidents. Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry
 Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations and Fistulae (DAVM S DAVF S)
 Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Stroke/TIA. Tom Bedwell
 Stroke/TIA Tom Bedwell tab1g11@soton.ac.uk The Plan Definitions Anatomy Recap Aetiology Pathology Syndromes Brocas / Wernickes Investigations Management Prevention & Prognosis TIAs Key Definitions Transient
Stroke/TIA Tom Bedwell tab1g11@soton.ac.uk The Plan Definitions Anatomy Recap Aetiology Pathology Syndromes Brocas / Wernickes Investigations Management Prevention & Prognosis TIAs Key Definitions Transient
Effect of clot removal on cerebral vasospasm TETSUJI INAGAWA, M.D., MITSUO YAMAMOTO, M.D., AND KAZUKO KAMIYA, M.D.
 J Neurosurg 72:224-230, 1990 Effect of clot removal on cerebral vasospasm TETSUJI INAGAWA, M.D., MITSUO YAMAMOTO, M.D., AND KAZUKO KAMIYA, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Shimane Prefectural Central Hospital,
J Neurosurg 72:224-230, 1990 Effect of clot removal on cerebral vasospasm TETSUJI INAGAWA, M.D., MITSUO YAMAMOTO, M.D., AND KAZUKO KAMIYA, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Shimane Prefectural Central Hospital,
POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY
 Nagoya postoperative Med. J., chronic subdural hematoma after aneurysmal clipping 13 POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY TAKAYUKI OHNO, M.D., YUSUKE NISHIKAWA, M.D., KIMINORI
Nagoya postoperative Med. J., chronic subdural hematoma after aneurysmal clipping 13 POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY TAKAYUKI OHNO, M.D., YUSUKE NISHIKAWA, M.D., KIMINORI
[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]
![[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD] [(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]](/thumbs/89/98619893.jpg) 2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
 INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE Sheba Medical Center, Acute Medicine Department Irene Frantzis P-Year student SGUL 2013 Normal Values Normal intracranial volume: 1700 ml Volume of brain: 1200-1400 ml CSF:
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE Sheba Medical Center, Acute Medicine Department Irene Frantzis P-Year student SGUL 2013 Normal Values Normal intracranial volume: 1700 ml Volume of brain: 1200-1400 ml CSF:
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Perforating Branches of the Middle Cerebral Artery
 1022 Perforating Branches of the Middle Cerebral Artery Microanatomy and Clinical Significance of Their Intracerebral Segments SLOBODAN V. MARINKOVIC, M.D.* MILAN M. MILISAVLJEVIC, M.D.,* MIROSLAV S. KOVACEVIC,
1022 Perforating Branches of the Middle Cerebral Artery Microanatomy and Clinical Significance of Their Intracerebral Segments SLOBODAN V. MARINKOVIC, M.D.* MILAN M. MILISAVLJEVIC, M.D.,* MIROSLAV S. KOVACEVIC,
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Computerised axial tomography in patients with severe migraine: a preliminary report
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 990-994 Computerised axial tomography in patients with severe migraine: a preliminary report G. D. HUNGERFORD', G. H. du BOULAY2, AND K. J.
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 990-994 Computerised axial tomography in patients with severe migraine: a preliminary report G. D. HUNGERFORD', G. H. du BOULAY2, AND K. J.
Michael Horowitz, MD Pittsburgh, PA
 Michael Horowitz, MD Pittsburgh, PA Introduction Cervical Artery Dissection occurs by a rupture within the arterial wall leading to an intra-mural Hematoma. A possible consequence is an acute occlusion
Michael Horowitz, MD Pittsburgh, PA Introduction Cervical Artery Dissection occurs by a rupture within the arterial wall leading to an intra-mural Hematoma. A possible consequence is an acute occlusion
Blow-in fracture of both orbital roofs caused by shear strain to the skull. Department of Neurosurgery, Kanto Teishin Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
 J Neurosurg 49:734-738, 1978 Blow-in fracture of both orbital roofs caused by shear strain to the skull Case report OSAMU SATO, M.D., HIROSHI KAMITANI, M.D., AND TAKASHI KOKUNAI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery,
J Neurosurg 49:734-738, 1978 Blow-in fracture of both orbital roofs caused by shear strain to the skull Case report OSAMU SATO, M.D., HIROSHI KAMITANI, M.D., AND TAKASHI KOKUNAI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery,
Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke
 Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma
 Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma Poster No.: C-0123 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: X. Han, J. Chen, K. Shi; Haikou/CN Keywords: Neuroradiology
Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma Poster No.: C-0123 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: X. Han, J. Chen, K. Shi; Haikou/CN Keywords: Neuroradiology
Distal anterior cerebral artery (DACA) aneurysms are. Case Report
 248 Formos J Surg 2010;43:248-252 Distal Anterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysm: an Infrequent Cause of Transient Ischemic Attack Followed by Diffuse Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Report of a Case Che-Chuan Wang
248 Formos J Surg 2010;43:248-252 Distal Anterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysm: an Infrequent Cause of Transient Ischemic Attack Followed by Diffuse Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Report of a Case Che-Chuan Wang
Brain Atrophy. Brain Atrophy
 Aging Central Nervous System Processes Age related brain atrophy Non-age related brain atrophy Cerebrovascular disease Cerebral infarction Hypertensive hemorrhage Carotid artery stenosis and occlusion
Aging Central Nervous System Processes Age related brain atrophy Non-age related brain atrophy Cerebrovascular disease Cerebral infarction Hypertensive hemorrhage Carotid artery stenosis and occlusion
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata
 Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
External guide for safe orthogonal approach
 External guide for safe orthogonal approach Poster No.: C-0768 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. SEOL, J. CHOI, H. KIM ; Jeonju, Jeonrabukdo/KR, Jeonju/ KR Keywords: Ischaemia / Infarction,
External guide for safe orthogonal approach Poster No.: C-0768 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. SEOL, J. CHOI, H. KIM ; Jeonju, Jeonrabukdo/KR, Jeonju/ KR Keywords: Ischaemia / Infarction,
T HIS paper is based upon experience
 DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOMAS OF THE BRAIN CLINICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL CORRELATION* B. RAMAMURTHI, M.D., AND M. G. VARADARAJAN, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Madras Medical College, Madras, India (Received
DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOMAS OF THE BRAIN CLINICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL CORRELATION* B. RAMAMURTHI, M.D., AND M. G. VARADARAJAN, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Madras Medical College, Madras, India (Received
Unit I Problem 5 Anatomy: Types of Movements and Joints
 Unit I Problem 5 Anatomy: Types of Movements and Joints - Anatomical position: The person is standing erect, with the upper limbs by the sides and the face and palms of the hands directed forward. - Imaginary
Unit I Problem 5 Anatomy: Types of Movements and Joints - Anatomical position: The person is standing erect, with the upper limbs by the sides and the face and palms of the hands directed forward. - Imaginary
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Pontine haemorrhage: a clinical analysis of 26 cases
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1985;48:658-662 Pontine haemorrhage: a clinical analysis of 26 cases SHOJI MASIYAMA, HIROSHI NIIZUMA, JIRO SUZUKI From the Division ofneurosurgery, Institute
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1985;48:658-662 Pontine haemorrhage: a clinical analysis of 26 cases SHOJI MASIYAMA, HIROSHI NIIZUMA, JIRO SUZUKI From the Division ofneurosurgery, Institute
Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine
 Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine Etiology and pathogenesis ICH accounts for ~10% of all strokes 30 day mortality - 35 45% Incidence rates
Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine Etiology and pathogenesis ICH accounts for ~10% of all strokes 30 day mortality - 35 45% Incidence rates
Anton-Babinski syndrome as a rare complication of chronic bilateral subdural hematomas
 DOI: 10.2478/romneu-2018-0050 Article Anton-Babinski syndrome as a rare complication of chronic bilateral subdural hematomas D. Adam, D. Iftimie, Cristiana Moisescu, Gina Burduşa ROMANIA Romanian Neurosurgery
DOI: 10.2478/romneu-2018-0050 Article Anton-Babinski syndrome as a rare complication of chronic bilateral subdural hematomas D. Adam, D. Iftimie, Cristiana Moisescu, Gina Burduşa ROMANIA Romanian Neurosurgery
ANASTAMOSIS FOR BRAIN STEM ISCHEMIA/Khodadad et al.
 ANASTAMOSIS FOR BRAIN STEM ISCHEMIA/Khodadad et al. visualization of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. The patient, now 11 months post-operative, has shown further neurological improvement since
ANASTAMOSIS FOR BRAIN STEM ISCHEMIA/Khodadad et al. visualization of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. The patient, now 11 months post-operative, has shown further neurological improvement since
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Chapter XII: Temporal Expanding Processes, Including Those in the Sylvian Fissure and the Insula
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Chapter XII: Temporal Expanding Processes, Including Those in the Sylvian Fissure and the Insula
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Chapter XII: Temporal Expanding Processes, Including Those in the Sylvian Fissure and the Insula
Done By: manar aljebreen Abdulrahman alsharidah
 Female Side Male side Done By: manar aljebreen Abdulrahman alsharidah Revised By: Nour Al-Khawajah Mohammed Asiri 2 Slide No.( 1 ) Slide No.( 2 ) 3 Slide No.( 3 ) Slide No.( 4 ) Upper motor neurons are
Female Side Male side Done By: manar aljebreen Abdulrahman alsharidah Revised By: Nour Al-Khawajah Mohammed Asiri 2 Slide No.( 1 ) Slide No.( 2 ) 3 Slide No.( 3 ) Slide No.( 4 ) Upper motor neurons are
Incidence of Strokes and Its Prognosis in Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis
 Incidence of Strokes and Its Prognosis in Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis Kaoru ONOYAMA, M.D., Harumitsu KUMAGAI, M.D., Tiaki MIISHIMA, M.D., Hiroshi TSURUDA, M.D., Suguru TOMOOKA, M.D., Kenichi MOTOMURA,
Incidence of Strokes and Its Prognosis in Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis Kaoru ONOYAMA, M.D., Harumitsu KUMAGAI, M.D., Tiaki MIISHIMA, M.D., Hiroshi TSURUDA, M.D., Suguru TOMOOKA, M.D., Kenichi MOTOMURA,
Module 3. The Blood Supply of the Brain
 Module 3. The Blood Supply of the Brain Relating Vascular and Functional Anatomy Objectives for Module 3 Knowledge! Describe or sketch the course of the major arteries and their branches that comprise
Module 3. The Blood Supply of the Brain Relating Vascular and Functional Anatomy Objectives for Module 3 Knowledge! Describe or sketch the course of the major arteries and their branches that comprise
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Neck Ultrasound. Faculty Info: Amy Kule, MD
 Neck Ultrasound Date: Friday, October 19, 2018 Time: 11:00 AM Location: SMALL GROUP LABORATORY SSOM L71 Watch: Ø Neck Ultrasound Scanning Protocol (4:00): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zozd2x2ll4q Faculty
Neck Ultrasound Date: Friday, October 19, 2018 Time: 11:00 AM Location: SMALL GROUP LABORATORY SSOM L71 Watch: Ø Neck Ultrasound Scanning Protocol (4:00): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zozd2x2ll4q Faculty
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Effect of early operation for ruptured aneurysms on prevention of delayed ischemic symptoms
 J Neurosurg 57:622-628, 1982 Effect of early operation for ruptured aneurysms on prevention of delayed ischemic symptoms MAMORU TANEDA, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Hanwa Memorial Hospital, Osaka,
J Neurosurg 57:622-628, 1982 Effect of early operation for ruptured aneurysms on prevention of delayed ischemic symptoms MAMORU TANEDA, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Hanwa Memorial Hospital, Osaka,
Vascular Disorders. Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14. Cerebrovascular disease S/S 1/9/2013
 Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
In some patients with pituitary macroadenoma, visual acuity
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.M. Tokumaru I. Sakata H. Terada S. Kosuda H. Nawashiro M. Yoshii Optic Nerve Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images among Patients with Pituitary Macroadenoma: Correlation with Visual
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.M. Tokumaru I. Sakata H. Terada S. Kosuda H. Nawashiro M. Yoshii Optic Nerve Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images among Patients with Pituitary Macroadenoma: Correlation with Visual
CVA. Alison Atwater PA-C
 CVA Alison Atwater PA-C Types of CVAs Ischemic strokes 80% of strokes 2/3 are thrombotic 1/3 are embolic emboli from the heart or arteries feeding the brain such as carotids, vertebral and basilar etc
CVA Alison Atwater PA-C Types of CVAs Ischemic strokes 80% of strokes 2/3 are thrombotic 1/3 are embolic emboli from the heart or arteries feeding the brain such as carotids, vertebral and basilar etc
The Nervous system is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System (CNS): found within bones & consists of:
 The Nervous system is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System (CNS): found within bones & consists of: - The Brain: within the skull, composed of cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem.
The Nervous system is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System (CNS): found within bones & consists of: - The Brain: within the skull, composed of cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem.
Cerebrovascular diseases-2
 Cerebrovascular diseases-2 Primary angiitis of CNS - Other causes of infarction i. Hypercoagulable states ii. Drug-abuse such as amphetamine, heroin and cocain Note - The venous side of the circulation
Cerebrovascular diseases-2 Primary angiitis of CNS - Other causes of infarction i. Hypercoagulable states ii. Drug-abuse such as amphetamine, heroin and cocain Note - The venous side of the circulation
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Voluntary Movement. Ch. 14: Supplemental Images
 Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
MUSCLES. Anconeus Muscle
 LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
Acute cerebral MCA ischemia with secondary severe head injury and acute intracerebral and subdural haematoma. Case report
 214 Balasa et al - Acute cerebral MCA ischemia Acute cerebral MCA ischemia with secondary severe head injury and acute intracerebral and subdural haematoma. Case report D. Balasa 1, A. Tunas 1, I. Rusu
214 Balasa et al - Acute cerebral MCA ischemia Acute cerebral MCA ischemia with secondary severe head injury and acute intracerebral and subdural haematoma. Case report D. Balasa 1, A. Tunas 1, I. Rusu
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
I N individuals who have sustained antenor polar brain injury, the differentiation
 VOL. 122, No. 3 FRONTAL EPIDURAL HEMATOMA* THE ANGIOGRAPHIC DIAGNOSIS WITH A NEW FINDING By DAVID DEE, JR., M.D.,f MERLIN E. WOESNER, M.D., and ISAAC SANDERS, M.D. LOS ANGELES, CALIFORNIA I N individuals
VOL. 122, No. 3 FRONTAL EPIDURAL HEMATOMA* THE ANGIOGRAPHIC DIAGNOSIS WITH A NEW FINDING By DAVID DEE, JR., M.D.,f MERLIN E. WOESNER, M.D., and ISAAC SANDERS, M.D. LOS ANGELES, CALIFORNIA I N individuals
Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after Surgery for Maxillary Cancer
 Case Report J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (1) : 89-93, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.1206.001 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after
Case Report J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (1) : 89-93, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.1206.001 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Brain Arteriovenous Malformations Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos
 Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Ruptured aberrant internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with spontaneous massive ear bleeding following a single sneeze: a case report
 Case eport JNET 7:312-316, 2013 uptured aberrant internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with spontaneous massive ear bleeding following a single sneeze: a case report Seiichiro HIONO 1) Eiichi
Case eport JNET 7:312-316, 2013 uptured aberrant internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with spontaneous massive ear bleeding following a single sneeze: a case report Seiichiro HIONO 1) Eiichi
