THE NORMAL MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY AXIS* By JOHN P. JIMENEZ, M.D., and JOHN A. GOREE, M.D. DURHAM, NORTH CAROLINA
|
|
|
- Mabel Baker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SEPTEMBER, 197 THE NORMAL MDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY AXS* By JOHN P. JMENEZ, M.D., and JOHN A. GOREE, M.D. DURHAM, NORTH CAROLNA Downloaded from by on 12/02/17 from P address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved T HE significance ofdisplacement of the major middle cerebral artery trunks in the angiographic localization of expanding intracranial lesions has been appreciated since the initial studies of Moniz,3 who considered the groupe sylvien to represent the arterial axis of the brain. Gross elevation of these vessels by both intnacerebral and extracerebral masses in the middle fossa is easily recognized. However, a minor upward displacement of this arterial complex may be more difficult to assess, particularly in infants and children. Methods for measuring the normal and pathologic locations of the middle cerebral artery trunks from the lateral carotid anteniogram have been described by Tavenas and Poser,5 and Woninger and Gernez. The purpose of this paper is to present a simple method for determining the normal middle cerebral artery axis as visualized on the lateral projection of the carotid arteniognam. The accuracy of this method is to be evaluated in both the normal child and adult, and also in a series of verified mass lesions in the middle fossa. MATERALS AND METHODS From the cerebral angiographic material in the teaching file of the Department of Radiology at Duke University Medical Center, 500 normal lateral carotid arteniograms in adult patients were selected as representing technically satisfactory examinations. Particular attention was paid to rotation of the skull. Any case with rotation of the mid-sagittal plane amounting to more than several millimeters, defined by measuring the degree of incomplete superimposition of both the orbital plates and the petrous pyramids (Fig. i, A and B) was discarded, since this limitation will obviously alter the position of the middle cerebral artery trunks. A second group of 75 normal carotid arteniograms was similarly selected from the pediatric material for FG.. Normal adult carotid arteriogram. (A) Exact superimposition of orbital plates and petrous pyramids. ( B) Pseudo-elevation of middle cerebral artery axis from rotation of skull. Same case as in A. B From the Department of Radiology, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina.
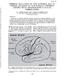
2 VOL. 101, No. The Normal Middle Cerebral Artery Axis 9 Downloaded from by on 12/02/17 from P address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved P 0 FG. 2. (A) Diagram of the method of determining the middle cerebral artery axis. (B) Normal middle cerebral artery axis in a year old child. (C) Normal middle cerebral artery axis in an adult. study, the patients ranging in age from months to i years. A third group was selected, consisting of ioo cases of verified expanding lesions in the middle fossa. As in the normal cases, only anteniograms with very little or no rotation were included. All of the patients in the pathologic group were adults. Two points on the inner table of the skull were utilized, namely, the inner table margin of the bregma (A) and the internal occipital protuberance (B) (Fig. 2, 4, B and C). A line was drawn to connect these two points of reference and the mid-point (C) was considered to be the posterior limit of the middle cerebral artery axis. The limbus sphenoidalis (D) was selected as an additional landmark. This structure is reasonably well seen on the lateral carotid arteniogram, and as Holman points out, the pituitary fossa is in a relatively lower position with respect to the level of the planum sphenoidale in the newborn than it is in older people (Fig. 3, z and B). Therefore, bone landmarks more closely related to the sella turcica proper, such as the tubenculum sellae and the anterior clinoid processes, will tend to give a lower estimate of the middle cerebral artery axis than if the limbus sphenoidalis is utilized, particularly in infants and children. Occasionally, the exact point of the limbus was difficult to
3 90 J ohn P. Jimenez and John A. Goree SEPTEMBER, ,. 5 S 5_S Downloaded from by on 12/02/17 from P address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved FG. 3. (A) Sella turcica in a normal infant. (B) Sella turcica in a normal adult. The upper arrow points to the limbus sphenoidalis and the lower arrow is at the tuberculum sellae. define. n such a case, the most posterior point visible along the planum sphenoidale was considered to be point D. The estimated middle cerebral artery axis, considered here as merely the trend of direction and location of the major arterial trunks of the middle cerebral artery, was then drawn directly on each roentgenogram. The main trunks of the middle cerebral artery have been arbitrarily defined by Ring4 as those major vessels passing without interruption through the middle third of the sylvian fissure. A line (CD) was then constructed (Fig. 2, ii, B and C) and the distance in millimeters between the line CD and the estimated axis, measured at the mid-point E, was recorded in each case. When the middle cerebral artery trunks were found to be clearly bowed upward by an expanding lesion, it was obviously impossible to define a rectilinear axis. n such cases, the measurement to the major middle cerebral artery trunks opposite point E was made without a middle cerebral artery axis estim ation. RESULTS The measurements in the normal adult material are listed in Table i. The figures for normal infants and children are shown in Table and the data for the group of verified expanding lesions in the middle fossa are listed in Table. Table V compares the average mean and the range between these 3 groups. The range of elevation of the middle THE MDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY AXS N 500 NORMAL ADULT CAROTD ARTEROGRAMS mm. Above Line CD No. of Cases Per Cent LineCD i ! mm. Below Line CD
4 VOL. 101, No. The Normal Middle Cerebral Artery Axis 9 THE MDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY AXS N 75 NORMAL CAROTD ARTEROGRAMS N CHLDREN THE MDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY AXS in 100 EXPANDNG LESONS N THE MDDLE FOSSA Downloaded from by on 12/02/17 from P address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved mm. Above Line CD No. of Cases Per Cent o.o cerebral artery axis in the ioo pathologic cases was to 41 mm. above line CD, with a single case having as little as mm. elevation and 95 cases measuring 10 mm. or more above this line. On the contrary, only a single case in the normal adult series was found to have a middle cerebral artery axis of more than mm. above line CD. Since there is no surgical or autopsy evidence for the presence of a disease process in the middle fossa of this patient, her clinical findings are briefly reviewed. J.B.M., DUMC No. F A 22 year old white female was involved in an automobile accident 2 days before admission to this hospital. She was thrown from the car and rendered unconscious. Upon admission to her local hospital, she was found to have lacerations of the right scalp, an alternating state of consciousness and right occipital and temporal linear skull fractures. She became less responsive over the following week and examination Children Adults Pathologic mm. Above Line CD No. of Cases Per Cent V 4 mm.-5 mm upon admission to this hospital revealed a moderately obtunded state of consciousness, hyperactive reflexes and a left extensor plantar response. A right carotid arteriogram was performed 2 days later (Fig. 4) and was interpreted as normal. The patient subsequently improved, her neurologic status reverted to normal and she was discharged with the diagnosis of cerebral contusion. Comment. The measurements made in this case are shown in Figure 4. There is an elevation of the middle cerebral artery axis of 12 mm. above line CD. t is assumed that this finding represents some swelling of the right temporal lobe, probably from contusion, although it would be impossible to exclude hemorrhage. n the Too verified pathologic cases, minor elevations of the middle cerebral anteny axis (io mm. or less), were found to be due to hemorrhage in 3 cases. The other small elevations were seen in 2 cases of temporal lobe astrocytoma, one case of THE RELATONSHP BETWEEN LNE CD AND THE MDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY AXS Average Distance Above Line CD (mm.) No. of Cases Range Above and Below Line CD (mm.) o-io above below- above* -4! above 2 * Excluding one case 12 mm. above (see Fig. 4).
5 92 J ohn P. Jimenez and John A. Gonee SEPTEMBER, 97 Downloaded from by on 12/02/17 from P address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved FG. 4. Elevation of the middle cerebral artery axis in a case of probable contusion of the temporal lobe. glioblastoma multiforme of the temporal lobe, and a single instance of (ptenional) meningioma. Elevation of the middle cerebral artery axis was found to be as little as mm. in a single case of intracerebral hematoma and 7 mm. in one instance of glioblastoma multiforme. The 75 pediatric measurements produced a maximum normal distance of the middle cerebral artery axis above line CD of io mm. in 3 cases, with no particular differences noted in the various age groups. DSCUSSON One of the fufidamental considerations in attempting to establish a linear measurement for the normal middle cerebral artery axis is that most measurements in diagnostic roentgenology are sharply limited in value and the absolute demarcation between normal and pathologic is difficult to define. Any measurement must be utilized in context with the total roentgenognaphic picture and an individual measurement that just exceeds the upper limits of normal in the face of an otherwise negative examination must be viewed with strong reservations. A widely utilized measurement of the middle cerebral artery axis is the clino- parietal line described by Taveras and Poser.5 This measurement requires the antenor clinoid process and the lambda (or internal occipital protuberance) for reference points. These authors have stated that occasionally the line is just above the lowest major branch in the adult. n children, the major middle cerebral branches are always above the clino-panietal line. t is v noted that in i of the 75 children listed in Table,, the middle cerebral artery axis coincided exactly with line CD. Taveras and Poser5 also mentioned that it may be noted that in younger children the distance from the clino-panietal line to the lowest major branch of the middle cerebral antery... is greater than in older children. We have found no such change in the middle cerebral artery axis with advancing age (Fig. ) other than the gross comparison between the pediatric and adult series. Woninger and Gennez attempted to establish a normal middle cerebral artery axis by measuring the angle between the middle cerebral artery trunks on the lateral arteniogram and a line drawn from the internal occipital protuberance to the center of the sella turcica. Since it is often the case that an expanding process elevates the middle cerebral artery trunks in a fashion parallel to the original course of these vessels, this measurement has limited value. The general appearance of the middle cerebral artery trunks, the status of the antenor choroidal, posterior communicating 0 U , l4B Ag. n Yars FG. 5. Relation of the middle cerebral artery axis to line CD in 75 normal infants and children.
6 VOL. O, No. The Normal Middle Cerebral Artery Axis 93 Downloaded from by on 12/02/17 from P address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved and posterior cerebral arteries and the basilan vein, midline dislocations, the appearance of the middle cerebral artery in the frontal plane of anteniography, and the presence and type of tumor neovasculanity are all important in the angiognaphic diagnosis of middle fossa expanding lesions. n addition, there is a certain degree of observer variation in estimating the middle cerebral artery axis from the lateral noentgenogram. Nevertheless, it is believed that the combination of this simple linear measurement, together with the insistence upon an accurately positioned patient during the examination, will improve the evaluation of the middle cerebral artery axis in the problem case. SUMMARY A simple method for the evaluation of the normal and pathologic middle cerebral artery axis as determined from the lateral carotid arteniogram is presented. These measurements have been applied to both adults and children and have been found to be of assistance in cerebral angiographic interpretation. John P. Jimenez, M.D. Department of Radiology Duke University Medical Center Durham, North Carolina 2770 RE FERENCES. HOLMAN, C. B. Roentgenologic manifestations of glioma of optic nerve and chiasm. Ars. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1959, 2, LUSTED, L. B., and KEATS, T. E. Atlas of Roentgenographic Measurement. Year Book Publishers, nc., Chicago, 1959, pp MoNz, E. L Angiographic C#{233}r#{233}brale. Masson et Cie, Paris, RNG, B. A. Middle cerebral artery: anatomical and radiographic study. Acta radio!., 192, 57, TAvERAS, J. M., and POSER, C. M. Roentgenologic aspects of cerebral angiography in children. AM. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1959, 2, WORNGER, E., and GERNEZ, A. L art#{233}riogramme c#{233}r#{233}bral; essai de definition des frontiers de l art#{233}riogramme carotidien normal et de ses variations: analyse de 100 cas. Presse med., 194,5, 1-2.
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas
 External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
I N individuals who have sustained antenor polar brain injury, the differentiation
 VOL. 122, No. 3 FRONTAL EPIDURAL HEMATOMA* THE ANGIOGRAPHIC DIAGNOSIS WITH A NEW FINDING By DAVID DEE, JR., M.D.,f MERLIN E. WOESNER, M.D., and ISAAC SANDERS, M.D. LOS ANGELES, CALIFORNIA I N individuals
VOL. 122, No. 3 FRONTAL EPIDURAL HEMATOMA* THE ANGIOGRAPHIC DIAGNOSIS WITH A NEW FINDING By DAVID DEE, JR., M.D.,f MERLIN E. WOESNER, M.D., and ISAAC SANDERS, M.D. LOS ANGELES, CALIFORNIA I N individuals
Vascular Pattern in Tumours
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Vascular Pattern in Tumours To cite this article: (1957) Vascular Pattern in Tumours, Acta Radiologica,
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Vascular Pattern in Tumours To cite this article: (1957) Vascular Pattern in Tumours, Acta Radiologica,
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
EMBOLIC OCCLUSION OF THE SUPERIOR AND IN- FERIOR DIVISIONS OF THE MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY WITH ANGIOGRAPHIC-CLINICAL CORRELATION*
 MARCH, 1976 Pre EMBOLIC OCCLUSION OF THE SUPERIOR AND IN- FERIOR DIVISIONS OF THE MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY WITH ANGIOGRAPHIC-CLINICAL CORRELATION* ABSTRACT: Superior Rolandlc rolandic By L. REED ALTEMUS,
MARCH, 1976 Pre EMBOLIC OCCLUSION OF THE SUPERIOR AND IN- FERIOR DIVISIONS OF THE MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY WITH ANGIOGRAPHIC-CLINICAL CORRELATION* ABSTRACT: Superior Rolandlc rolandic By L. REED ALTEMUS,
Chapter XII: Temporal Expanding Processes, Including Those in the Sylvian Fissure and the Insula
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Chapter XII: Temporal Expanding Processes, Including Those in the Sylvian Fissure and the Insula
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Chapter XII: Temporal Expanding Processes, Including Those in the Sylvian Fissure and the Insula
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
T THE level of the anterior clinoid
 VOL. 104, No. i KINKING OF THE SUPRACLINOID SEGMENT OF THE INTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY OVER NEIGHBORING ANATOMIC STRUCTURES IN ACUTE AND SUB- ACUTE INTRACRANIAL MASS LESIONS* ANATOMY By JORGEN STOVRING, M.D.t
VOL. 104, No. i KINKING OF THE SUPRACLINOID SEGMENT OF THE INTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY OVER NEIGHBORING ANATOMIC STRUCTURES IN ACUTE AND SUB- ACUTE INTRACRANIAL MASS LESIONS* ANATOMY By JORGEN STOVRING, M.D.t
ANATOMIC VARIATION OF THE HEIGHT OF THE FALX CEREBRI*
 VOL. zo6, No. 2 ANATOMIC VARIATION OF THE HEIGHT OF THE FALX CEREBRI* ITS RELATIONSHIP TO DISPLACEMENT OF THE ANTERIOR CEREBRAL ARTERY IN FRONTAL SPACE-OCCUPYING LESIONS By F. GALLIGIONI,t R. BERNARDI,
VOL. zo6, No. 2 ANATOMIC VARIATION OF THE HEIGHT OF THE FALX CEREBRI* ITS RELATIONSHIP TO DISPLACEMENT OF THE ANTERIOR CEREBRAL ARTERY IN FRONTAL SPACE-OCCUPYING LESIONS By F. GALLIGIONI,t R. BERNARDI,
Neuroradiology. & Contrast Agents in Neuroradiology. & CAT Scan
 Neuroradiology & Contrast Agents in Neuroradiology 1. Complete the following for an iodinated contrast allergy prep. With regard to a prednisone i. pretest timing in hours ii. dose in mg iii. route b Benadryl
Neuroradiology & Contrast Agents in Neuroradiology 1. Complete the following for an iodinated contrast allergy prep. With regard to a prednisone i. pretest timing in hours ii. dose in mg iii. route b Benadryl
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations is often extensive
 NOVEMBER, 1974 ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE OCCIPITAL LOBE* By B. TODD TROOST, M.D.,t and THOMAS H. NEWTON, M.D4 T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
NOVEMBER, 1974 ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE OCCIPITAL LOBE* By B. TODD TROOST, M.D.,t and THOMAS H. NEWTON, M.D4 T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report
 Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
The Value of Angiography in Diagnosis of Extradural Hematoma of the Anterior Fossa
 The Value of Angiography in Diagnosis of Extradural Hematoma of the Anterior Fossa Report of Two Cases IBRAHIM HIGAZI, M.D., AND AHMED EL-BANHAWY, M.D. Department of Neurological Surgery, Ein-Shams University
The Value of Angiography in Diagnosis of Extradural Hematoma of the Anterior Fossa Report of Two Cases IBRAHIM HIGAZI, M.D., AND AHMED EL-BANHAWY, M.D. Department of Neurological Surgery, Ein-Shams University
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
T HIS paper is based upon experience
 DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOMAS OF THE BRAIN CLINICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL CORRELATION* B. RAMAMURTHI, M.D., AND M. G. VARADARAJAN, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Madras Medical College, Madras, India (Received
DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOMAS OF THE BRAIN CLINICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL CORRELATION* B. RAMAMURTHI, M.D., AND M. G. VARADARAJAN, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Madras Medical College, Madras, India (Received
Neurosurgical Techniques
 Neurosurgical Techniques EBEN ALEXANDER, JR., M.D., EDITOR Supratentorial Skull Flaps GuY L. ODOM, M.D., AND BARNES WOODHALL,!V[.D. Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical
Neurosurgical Techniques EBEN ALEXANDER, JR., M.D., EDITOR Supratentorial Skull Flaps GuY L. ODOM, M.D., AND BARNES WOODHALL,!V[.D. Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Surgical management of diastatic linear skull fractures in infants
 Surgical management of diastatic linear skull fractures in infants JOHN B. THOMPSON, M.D., THOMAS H. MASON, M.D., GERALD L. HAINES, M.D., AND ROBERT J. CASSIDY, M.D. Divisions of Neurosurgery and Neurology,
Surgical management of diastatic linear skull fractures in infants JOHN B. THOMPSON, M.D., THOMAS H. MASON, M.D., GERALD L. HAINES, M.D., AND ROBERT J. CASSIDY, M.D. Divisions of Neurosurgery and Neurology,
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Neuropathology Of Head Trauma. Mary E. Case, M.D. Professor of Pathology St. Louis University Health Sciences Center
 Neuropathology Of Head Trauma Mary E. Case, M.D. Professor of Pathology St. Louis University Health Sciences Center Nothing to disclose Disclosure Introduction 500,000 cases/year of serious head injury
Neuropathology Of Head Trauma Mary E. Case, M.D. Professor of Pathology St. Louis University Health Sciences Center Nothing to disclose Disclosure Introduction 500,000 cases/year of serious head injury
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
External guide for safe orthogonal approach
 External guide for safe orthogonal approach Poster No.: C-0768 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. SEOL, J. CHOI, H. KIM ; Jeonju, Jeonrabukdo/KR, Jeonju/ KR Keywords: Ischaemia / Infarction,
External guide for safe orthogonal approach Poster No.: C-0768 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. SEOL, J. CHOI, H. KIM ; Jeonju, Jeonrabukdo/KR, Jeonju/ KR Keywords: Ischaemia / Infarction,
The University Hospital/ 90! Twenty-Third.Street, N.IV./ Washington, D.C Representatives Select Committee on Assassinations Staff Member
 222 ADDENDUM D REPORT OF DAVID O. DAVIS, M.D., CONCERNING THE EXAMINATION OF THE AUTOPSY X-RAYS OF PRESIDENT JOHN F. KENNEDY, DATED AUGUST 23, 1975 REPORT OF DAVID 0. DAVIS, M.D., CONCERNING THE EXAMINATION
222 ADDENDUM D REPORT OF DAVID O. DAVIS, M.D., CONCERNING THE EXAMINATION OF THE AUTOPSY X-RAYS OF PRESIDENT JOHN F. KENNEDY, DATED AUGUST 23, 1975 REPORT OF DAVID 0. DAVIS, M.D., CONCERNING THE EXAMINATION
ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 473. ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC ARTERY AND CHOROIDAL PLEXUS OF THE EYE* BY P. H. SCHURR From the Department of Neurosurgery, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford THE ophthalmic
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 473. ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC ARTERY AND CHOROIDAL PLEXUS OF THE EYE* BY P. H. SCHURR From the Department of Neurosurgery, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford THE ophthalmic
Brain Injuries. Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama
 Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
N EOPLASMS of the optic nerves occur
 Tumors of the optic nerve and optic chiasm COLLINS. MAcCARTY~ M.D., ALLEN S. BOYD, JR., M.D., AND DONALD S. CHILDS, JR,, M.D. Departments of Neurologic Surgery and Therapeutic Radiology, Mayo Clinic and
Tumors of the optic nerve and optic chiasm COLLINS. MAcCARTY~ M.D., ALLEN S. BOYD, JR., M.D., AND DONALD S. CHILDS, JR,, M.D. Departments of Neurologic Surgery and Therapeutic Radiology, Mayo Clinic and
Atlas Of Skull Base Surgery And Neurotology
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with atlas of skull base
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with atlas of skull base
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019
 Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Sectional Anatomy Quiz - III
 Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
The orbit-1. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound
 SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 + Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
+ Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
WADE H. RENN, M.D., AND ALBERT L. RHOTON, JR., M.D.
 Microsurgical anatomy of the sellar region WADE H. RENN, M.D., AND ALBERT L. RHOTON, JR., M.D. Division of Neurological Surgery, University of Florida Health Center, Gainesville, Florida v' Fifty adult
Microsurgical anatomy of the sellar region WADE H. RENN, M.D., AND ALBERT L. RHOTON, JR., M.D. Division of Neurological Surgery, University of Florida Health Center, Gainesville, Florida v' Fifty adult
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Radiological Analysis of Sella Turcica
 Radiological Analysis of Sella Turcica S. R. Chavan 1, M. A. Kathole 1, A. S. Katti 2, N. G. Herekar 3 { 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor and Head}Dept. of Anatomy, Govt. Medical
Radiological Analysis of Sella Turcica S. R. Chavan 1, M. A. Kathole 1, A. S. Katti 2, N. G. Herekar 3 { 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor and Head}Dept. of Anatomy, Govt. Medical
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
ANTERIOR MENINGEAL BRANCH OF THE VERTEBRAL ARTERY IN EXTRA-AXIAL POSTERIOR FOSSA LESIONS*
 VOL. 122, No. 3 ANTERIOR MENINGEAL BRANCH OF THE VERTEBRAL ARTERY IN EXTRA-AXIAL POSTERIOR FOSSA LESIONS* By HAROLD PACHTMAN, M.D.,f and ROBERT WALDRON, II, M.D4 T HE anterior meningeal branch of the vertebral
VOL. 122, No. 3 ANTERIOR MENINGEAL BRANCH OF THE VERTEBRAL ARTERY IN EXTRA-AXIAL POSTERIOR FOSSA LESIONS* By HAROLD PACHTMAN, M.D.,f and ROBERT WALDRON, II, M.D4 T HE anterior meningeal branch of the vertebral
Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma
 Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma Poster No.: C-0123 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: X. Han, J. Chen, K. Shi; Haikou/CN Keywords: Neuroradiology
Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma Poster No.: C-0123 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: X. Han, J. Chen, K. Shi; Haikou/CN Keywords: Neuroradiology
I N ONE year we have observed 3 cases of
 Angiographic Images of False Aneurysmal Sac Caused by Rupture of Median Meningeal Artery in the Course of Traumatic Extradural Hematomata Report of 3 Cases J. E. ]:DAILLAS, M.D., J. BONNAL, M.D., AND J.
Angiographic Images of False Aneurysmal Sac Caused by Rupture of Median Meningeal Artery in the Course of Traumatic Extradural Hematomata Report of 3 Cases J. E. ]:DAILLAS, M.D., J. BONNAL, M.D., AND J.
CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS PRESENTING WITH VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 251 CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS PRESENTING WITH VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS* BY University Department of Ophthalmology and Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh ANEURYSMS occur more frequently within
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 251 CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS PRESENTING WITH VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS* BY University Department of Ophthalmology and Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh ANEURYSMS occur more frequently within
Bones of the Skull Lateral View
 Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
EEG IN FOCAL ENCEPHALOPATHIES: CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASE, NEOPLASMS, AND INFECTIONS
 246 Figure 8.7: FIRDA. The patient has a history of nonspecific cognitive decline and multiple small WM changes on imaging. oligodendrocytic tumors of the cerebral hemispheres (11,12). Electroencephalogram
246 Figure 8.7: FIRDA. The patient has a history of nonspecific cognitive decline and multiple small WM changes on imaging. oligodendrocytic tumors of the cerebral hemispheres (11,12). Electroencephalogram
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives
 Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
ADDENDUM C DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY. THE HOSPITAk..O,Is THR ;GOIDD SAMARITAN T.- --T dnjfopnaa sooty
 217 ADDENDUM C REPORT OF G, M. MCDONNEL, M.D., CONCERNING THE OBSERVATIONS, ANALYSIS, AND CONCLUSIONS IN CONNECTION WITH THE RADIOGRAPHIC IMAGES AND EN- HANCED IMAGES OF X-RAYS ATTRIBUTED TO PRESIDENT
217 ADDENDUM C REPORT OF G, M. MCDONNEL, M.D., CONCERNING THE OBSERVATIONS, ANALYSIS, AND CONCLUSIONS IN CONNECTION WITH THE RADIOGRAPHIC IMAGES AND EN- HANCED IMAGES OF X-RAYS ATTRIBUTED TO PRESIDENT
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: OBJECTIVES OSTEOLOGY. Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD
 Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
 SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-THE DURA
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-THE DURA
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
We describe some of the conceptual nuances and
 Suprasellar Meningiomas Ivan Ciric, M.D., Sami Rosenblatt, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Evanston Northwestern Healthcare, Evanston Hospital, Northwestern University Medical School, Evanston, Illinois
Suprasellar Meningiomas Ivan Ciric, M.D., Sami Rosenblatt, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Evanston Northwestern Healthcare, Evanston Hospital, Northwestern University Medical School, Evanston, Illinois
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP:
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 3, pp. 194 198 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries Mansoor
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 3, pp. 194 198 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries Mansoor
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci. Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D Tuesday
 View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
Pathologies of postchiasmatic visual pathways and visual cortex
 Pathologies of postchiasmatic visual pathways and visual cortex Optic radiation: anatomy Pathologies of the postchiamsatic visual pathways and visual cortex Characterized by homonymous hemianopsia. This
Pathologies of postchiasmatic visual pathways and visual cortex Optic radiation: anatomy Pathologies of the postchiamsatic visual pathways and visual cortex Characterized by homonymous hemianopsia. This
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
SKULL / CRANIUM BONES OF THE NEUROCRANIUM (7) Occipital bone (1) Sphenoid bone (1) Temporal bone (2) Frontal bone (1) Parietal bone (2)
 Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Skeletal System: Skull.
 Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22,
 JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22, 1990 16 SECTIONAL ANATOMY: STANDARDIZED METHODOLOGY Alexander Lane, Coordinator of Anatomy and Physiology, Triton College, Visiting Associate Professor, University of Illinois
JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22, 1990 16 SECTIONAL ANATOMY: STANDARDIZED METHODOLOGY Alexander Lane, Coordinator of Anatomy and Physiology, Triton College, Visiting Associate Professor, University of Illinois
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
Muscles of the Eyeball (Extra Ocular Muscles) Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi
 Muscles of the Eyeball (Extra Ocular Muscles) Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi There are six extrinsic muscles of the eyeball, namely the (S), Medial (M), (I), & Lateral (L) recti, and (SO) and (IO) Obliques. In
Muscles of the Eyeball (Extra Ocular Muscles) Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi There are six extrinsic muscles of the eyeball, namely the (S), Medial (M), (I), & Lateral (L) recti, and (SO) and (IO) Obliques. In
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
Visual pathways in the chiasm
 Visual pathways in the chiasm Intracranial relationships of the optic nerve Fixation of the chiasm Chiasmatic pathologies The function of the optic chiasm may be altered by the presence of : 4) Artero
Visual pathways in the chiasm Intracranial relationships of the optic nerve Fixation of the chiasm Chiasmatic pathologies The function of the optic chiasm may be altered by the presence of : 4) Artero
Tutorials. By Dr Sharon Truter
 Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter To the Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter What to expect from the Tutorials What to expect from these tutorials Outlines, structure, guided reading, explanations, mnemonics Begin
Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter To the Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter What to expect from the Tutorials What to expect from these tutorials Outlines, structure, guided reading, explanations, mnemonics Begin
Blow-in fracture of both orbital roofs caused by shear strain to the skull. Department of Neurosurgery, Kanto Teishin Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
 J Neurosurg 49:734-738, 1978 Blow-in fracture of both orbital roofs caused by shear strain to the skull Case report OSAMU SATO, M.D., HIROSHI KAMITANI, M.D., AND TAKASHI KOKUNAI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery,
J Neurosurg 49:734-738, 1978 Blow-in fracture of both orbital roofs caused by shear strain to the skull Case report OSAMU SATO, M.D., HIROSHI KAMITANI, M.D., AND TAKASHI KOKUNAI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery,
NEURO PROTOCOLS MRI NEURO PROTOCOLS (SIEMENS SCANNERS)
 Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics. Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6. Typical Cervical Vertebra Anterior 10/5/2017
 Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
The anatomy of the subarachnoid cisterns
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 The anatomy of the subarachnoid cisterns B. Liliequist To cite this article: B. Liliequist (1956)
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 The anatomy of the subarachnoid cisterns B. Liliequist To cite this article: B. Liliequist (1956)
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Traumatic brain injuries are caused by external mechanical forces such as: - Falls - Transport-related accidents - Assault
 PP2231 Brain injury Cerebrum consists of frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes Diencephalon consists of thalamus, hypothalamus Cerbellum Brain stem consists of midbrain, pons, medulla Central
PP2231 Brain injury Cerebrum consists of frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes Diencephalon consists of thalamus, hypothalamus Cerbellum Brain stem consists of midbrain, pons, medulla Central
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 71
 71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
Picture of patient with apparent lid retraction and poor elevation. Shows you Orbital CT-Scan with muscle involvement including IR and asks is this
 NEUROLOGY Q: MENINGIOMAS AND SKULL (*2) Real skull is given, and you are asked to point to tuberculum sella What kind of meningioma occurs at this location? Where is the anterior clinoid process? Where
NEUROLOGY Q: MENINGIOMAS AND SKULL (*2) Real skull is given, and you are asked to point to tuberculum sella What kind of meningioma occurs at this location? Where is the anterior clinoid process? Where
T HE visual field changes that accompany
 J. Neurosurg. / Volume 31 / September, 1969 The Arterial Supply of the Human Optic Chiasm RICHARD BERGLAND, M.D.,* AND BRONSON S. RAY, M.D. Department of Surgery (Neurosurgery), New York Hospital-Cornell
J. Neurosurg. / Volume 31 / September, 1969 The Arterial Supply of the Human Optic Chiasm RICHARD BERGLAND, M.D.,* AND BRONSON S. RAY, M.D. Department of Surgery (Neurosurgery), New York Hospital-Cornell
