Intracranial hypotension
|
|
|
- Coleen Gilbert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
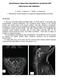
1 Romanian Neurosurgery (2011) XVIII 3: Intracranial hypotension Şt.M. Iencean Neurosurgery, Emergency Clinical Hospital Prof. Dr. N. Oblu Iaşi, Romania Abstract The intracranial hypotension is the decrease in the intracranial pressure caused by the decrease in the volume of the cerebrospinal fluid secondary to the CSF loss. The intracranial hypotension is characterized by an orthostatic cephalea, not calmed by antalgics accompanied by nausea, vomiting, vertigos, diplopia, etc. The diagnosis is confirmed by a lumbar manometry and by the performed paraclinical explorations (cerebral CT, cerebral MRI). The intracranial hypotension treatment is - etiologic, and it consists in closing the CSF fistula; pathogenic, which consists in recreating the normal CSF volume, and symptomatic, which refers to the treatment of the symptoms related to intracranial hypotension. Keywords: cerebrospinal fluid, CSF fistula, intracranial hypotension, intracranial pressure Introduction The intracranial hypotension represents the intracranial pressure decrease; it may be generated by the decrease in the volume of any of the intracranial components: the cerebral parenchyma, the cerebrospinal fluid, and the sanguine content and/or by the rapid removal of a pathologic volume under the circumstances of a pressure equilibrium achieved by the efficient compensating mechanisms (especially in the case of chronic subdural hematomas). The decrease in the volume of the cerebral parenchyma, by various mechanisms senile cerebral atrophy, surgical resection, etc., does not generate first of all an intracranial hypotension syndrome, but there may be focal neurological symptoms depending on the suffering cerebral areas. The volume of the diminished cerebral parenchyma is progressively diminished by gliosis and/or by CSF; therefore, the intracranial pressure is maintained at normal values. The decrease in the intracranial sanguine volume by arterial hypotension leads to the decrease in the cerebral perfusion pressure with ischemic phenomena; this may also lead to a decreased CSF secretion, but the intracranial pressure decrease seems to be less important than ischemia. The surgical removal of a pathologic volume produces a sudden decrease in the endocranial volume and in the intracranial pressure, also known as the surgical cerebral-ventricular collapse, and which is rapidly compensated from a therapeutic point of view. Once the neurosurgical intervention has been performed, the endocranial cavity is no longer a close environment, and there is no correspondence between the intracranial hypotension and the surgical cerebral collapse. Therefore, of the three intracranial components, only the diminished volume of the cerebrospinal fluid intervenes in the generation of the intracranial hypotension. (Figure 1).
2 280 Şt.M. Iencean Intracranial hypotension Figure 1 Scheme of the meningeal layers Figure 2 The ventricular system schematic drawing The intracranial hypotension is, therefore, the decrease in the intracranial pressure caused by the decrease in the volume of the cerebrospinal fluid secondary to the CSF loss (Figure 2). The intracranial hypotension is characterized by an orthostatic cephalea, exacerbated by coughing, laughing, the Valsalva maneuver, which is not calmed by antalgics and is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, vertigos, diplopia, etc. The diagnosis is confirmed by a lumbar manometry and by the performed paraclinical explorations (cisternography, cerebral CT, cranial-cerebral RMN).
3 Romanian Neurosurgery (2011) XVIII 3: From a clinical perspective, the intracranial hypotension may be represented as: - an acute form, with a violent symptomatology present in clinostatism, and which may evolve towards psychic disorders and the modification of the conscience state, - a sub-acute form with absent symptoms or of a reduced intensity in clinostatism; they occur or they are exacerbated in orthostatism, - a chronic, frequent form, with a symptomatology occurred in orthostatism, of smaller, bearable intensity and a tiresome feeling that may allow the development of an activity, but with a reduced efficiency though. Etiology and pathogeny The decrease in the normal CSF quantity in the cranial-spinal space may be generated by: the persistence of a dural continuity solution and the most frequent causes are the following ones: - operations involving the lumbar puncture: the exploratory lumbar puncture, myelography, myelo-ct, rachianesthesia, - cranial-spinal traumatisms with the generation of a CSF fistula, - cranial-cerebral neurosurgical or spinal interventions, - extremely rarely, by a spinal anteriorlateral CSF fistula in thoracic surgery, decrease in the CSF secretion by various mechanisms (after radiotherapy, senile, etc.) reduced CSF quantity by a ventricular-peritoneal drainage, the so-called spontaneous intracranial hypotension, when none of the above-mentioned causes is underlined, but the explorations prove the existence of several arachnoid fissures at the level of the spinal radicular sheath, or the case of the occult nasal CSF fistula. There have been cases of intracranial hypotension without the identification of a dural lesion in situations of dehydration, diabetic coma, uremia, or severe systemic illnesses. There are two theories concerning the mechanism leading to the intracranial hypotension symptomatology: - the decrease in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid leads to movements of the endocranial structures with the traction of the formations that contain pain receptors: meninx, draining veins to sinuses, trigeminus, glossopharyngeal and vague nerves, as well as the first cervical spinal nerves. Orthostatism increases the traction of these structures, emphasizing the symptomatology. - the decrease in the CSF volume leads to the intracranial pressure decrease and, therefore, according to the Monro Kellie theory, a dilatation of the intracranial vascular structures is produced, which generated the accentuated cephalea in orthostatism. Moreover, there is a dilatation of the spinal epidural veins, explaining the spinal radicular pains. It is currently considered that these two mechanisms are concomitant, they act together and they justify the symptomatology. Clinical presentation The main symptom of the intracranial hypotension is the orthostatic cephalea: a cephalea that occurs or is emphasized in orthostatism. The characteristics of the cephalea vary from one patient to another, but the common element is the fact that it
4 282 Şt.M. Iencean Intracranial hypotension is exacerbated in the orthostatic position, at a coughing effort, when laughing, etc., and it is not influenced by antalgics. Vertigo is the nest symptom from the frequency point of view, vertigos that occur or are accentuated in orthostatism too. There may also be feelings of nausea, vomiting, tingles, facial paresthesias, and radicular pains at the level of the superior limbs, all of them being emphasized in orthostatism. The establishment of how severe the symptomatology is and of the etiology makes the distinction between the clinical forms: acute, sub-acute and chronic. In the chronic form of intracranial hypotension, symptoms are accentuated in orthostatism, and they diminish or disappear in clinostatism. Sometimes, symptoms have a reduced intensity with the presence of an accentuated feeling of asthenia. Based on the dominating symptom, there are forms which are mainly cephalalgic, vertiginous, paresthesic, with vegetative disorders, etc. In the sub-acute form, symptoms are manifested in the horizontal position, and they are exacerbated in orthostatism with an invalidating effect. The acute form is characterized by an accentuated symptomatology, which is present in clinostatism, with vomiting, to dehydration, photophobia, sometimes even convulsive crises. Moreover, there may be psychic disorders or even modifications of the conscience state. The acute form is very rarely registered nowadays. Explorations The intracranial hypotension diagnosis implies the corroboration of the clinical data with the anamnesis, as well as the performance of certain explorations that may exclude other pathology and confirm the intracranial pressure decrease. In the context of certain maneuvers that include the lumbar puncture (myelography, myelo- CT, rachianesthesia), the occurrence of a clinical syndrome that announces the intracranial hypotension does not require the performance of other investigations in the case of a patient who has already undergone a cranial-cerebral exploration. In the case of cranial-cerebral or spinal traumatisms, the investigations performed in order to establish the traumatic lesions underline the dural lesion. The occurrence of the symptomatology at temporal distance from a particular situation, which suggests the existence of a persistent dural fistula, requires the performance of certain explorations that may establish the diagnosis. It is considered that the testing of a patient with chronic cephalea by arranging him or her in a Trendelenburg position, followed by the improvement of the cephalea, suggests a possible occult CSF fistula and it requires supplementary explorations. The intracranial pressure measurement establishes the diagnosis, but it must be performed after the cranial-cerebral explorations that exclude another pathology. The cerebrospinal fluid has a quasi-normal composition; sometimes, there may be an increase in the cerebrospinal fluid proteins, lymphocytosis; erythrocytes may be present, with a xanthochromic aspect. The cranial-cerebral computer tomography may prove the erasure of the basal cisterns without the existence of a cerebral lesion. The cerebral nuclear magnetic resonance with a contrast substance may reveal: - dura mater thickening,
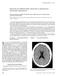
5 Romanian Neurosurgery (2011) XVIII 3: venous sinus dilatation, - presence of certain subdural fluid collections, - increase in the volume of the hypophysis gland, - the movement of the brain downwards: the basal cisterns become smaller, there is an inferior motion of the optic chiasm, and sometimes the cerebellar amygdales descend. (Figure 3) The presence and the intensity of these signs are in direct relation to the clinical gravity, and the improvement of the symptomatology is accompanied by the attenuation and erasure of the MNR modifications. The radioactive isotope cisternography allows the outlining of the CSF fistulas: - directly, by noticing the radio-isotopic accumulation outside the sub-arachnoid space, or - indirectly, by the lack of outlining regarding the radio-isotope at the level of the cerebral convexity and the notification of the latter in urine or in the adipose tissue. The computer myelography (myelo- CT) allows the outlining of the CSF spinal fistulas right at the level of the cranium base. Treatment The intracranial hypotension treatment is: - etiologic, and it consists in closing the CSF fistula, - pathogenic, which consists in recreating the normal CSF volume, and - symptomatic, which refers to the treatment of the symptoms related to intracranial hypotension. Figure 3 A T1-weighted sagittal MRI with general descent of the brain and sagging of the cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum and expansion of the sellar contents
6 284 Şt.M. Iencean Intracranial hypotension As the intracranial hypotension syndrome frequently occurs after the lumber puncture, the pathogenic and symptomatic treatment is often in the foreground, waiting for the dural orifice produced by the lumbar puncture to become obstruent. The symptomatic treatment of cephalea consists in avoiding the orthostatism, having the patient resting in bed, and by the oral or intravenous administration of caffeine or theophyline. Xanthins (theophyline) also increase the vascular resistance in the cerebral territory, reducing the circulation and diminishing the venous dilatation. Bed rest decreases the CSF pressure in the spinal dural sac and at the level of the remaining lumbar puncture orifice. The CSF volume is recovered by oral and intravenous hydration, as well as by the administration of mineral corticoids. Based on the registered evolution, one may appreciate whether the dural orifice of the lumbar puncture is maintained and if the CSF loss persists. In this case, a patch applying operation is performed at the level of the dural puncture orifice. The epidural blood patch is achieved by an autologous blood injection in the epidural space at the level of the previously performed lumbar puncture, with very good results; this operation needs to be repeated only very rarely. The surgical solution of the CSF fistula is applied from the very beginning in traumatic dural lesions (cranial-cerebral wound, vertebral-medullar wound, cranium base fracture with CSF fistula, etc.), or the surgery may be temporized based on the intensity of the CSF loss and on the fistula location, with therapeutic protection, supervising its spontaneous closure (in the CSF fistula from the cranium base fracture). Therefore postoperative CSF leaks after brain surgery are initially managed conservatively with bed rest, stool softeners and a lumbar drain and persistence of the leak beyond 1 week indicates need for surgical repair. Patients with postoperative CSF leaks after endoscopic approaches are taken back to surgical repair immediately. There may also be surgical solutions for the spinal dural lesions remaining after the lumbar puncture only if none of the previously presented procedures has proven to be efficient. Conclusions 1. The intracranial hypotension diagnosis implies the corroboration of the clinical data with the anamnesis, as well as the performance of certain explorations that may exclude other pathology and confirm the intracranial pressure decrease. 2. The intracranial pressure measurement establishes the diagnosis, but it must be performed after the cranialcerebral explorations that exclude another pathology. 3. The treatment of intracranial hypotension is etiologic, and consists in closing the CSF fistula; pathogenic, which consists in recreating the normal CSF volume and symptomatic, which refers to the treatment of the symptoms related to intracranial hypotension. The surgery for CSF fistula is applied from the very beginning in traumatic dural lesions or the surgery may be temporized with therapeutic protection, supervising its spontaneous closure.
7 Romanian Neurosurgery (2011) XVIII 3: References 1. Albayram S, Wasserman BA, Yousem DM, et al: Intracranial hypotension as a cause of radiculopathy from cervical epidural venous engorgement: case report. AJNR 23: , Alvarez-Linera J, Escribano J, Benito-Leon J, et al: Pituitary enlargement in patients with intracranial hypotension syndrome. Neurology 55: , Benamor M, Tainturier C, Graveleau P, et al: Radionuclide cisternography in spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Clin. Nucl. Med 23: , Binder DK, Sarkissian V, Dillon WP, Weinstein PR. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension associated with transdural thoracic osteophyte reversed by primary dural repair. Case report. J. Neurosurg Spine. 2005;2(5): Brightbill TC, Goodwin RS, Ford RG: Magnetic resonance imaging of intracranial hypotension syndrome with pathophysiological correlation. Headache, 2000, 40: Bruera O, Bonamico L, Giglio JA, et al: Intracranial hypotension: the nonspecific nature of MRI findings. Headache, 2000, 40: Chen CC, Luo CL, Wang SJ, et al: Colour Doppler imaging for diagnosis of intracranial hypotension. Lancet,1999, 354: Davenport RJ, Chataway SJ, Warlow CP: Spontaneous intracranial hypotension from a CSF leak in a patient with Marfan s syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg Psychiatry,1995, 59: Dickerman RD, Morgan J. Pathogenesis of subdural hematoma in healthy athletes: postexertional intracranial hypotension? Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005;147(3): Evan RW, Mokri B: Spontaneous intracranial hypotension resulting in coma. Headache,2002, 42: Ferrante E, Savino A. Thunderclap headache caused by spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurol.Sci ;26 Suppl 2 12.Fishman RA, Dillon WP: Dural enhancement and cerebral displacement secondary to intracranial hypotension. Neurology,1993, 43: Good DC, Ghobrial M: Pathologic changes associated with intracranial hypotension and meningeal enhancement on MRI. Neurology,1993, 43: Hannerz J, Dahlgren G, Irestedt L, Meyerson B, Ericson K. Treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypotension: cervicothoracic and lumbar blood patch and peroral steroid treatment. Headache Mar;46(3): Hong M, Shah GV, Adams KM, et al: Spontaneous intracranial hypotension causing reversible frontotemporal dementia. Neurology,2002,58: Iencean St M A new classification and a synergetical pattern in intracranial hypertension. Medical Hypotheses, 2002 ;58(2): Inenaga C, Tanaka T, Sakai N, et al: Diagnostic and surgical strategies for intractable spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Case report. J. Neurosurg,2001, 94: Kong DS, Park K, Nam do H, Lee JI, Kim JS, Eoh W, Kim JH. Clinical features and long-term results of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurosurgery (1): Koss SA, Ulmer JL, Hacein-Bey L: Angiographic features of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. AJNR,2003, 24: Kremer S, Taillandier L, Schmitt E, Bologna S, Moret C, Picard L, Bracard S. Atypical clinical presentation of intracranial hypotension: coma. J.Neurol 2005; 252 (11): Moriyama E, Nishida A. Intracranial hypotension.j. Neurosurg. 2005;102(5): Schievink WI, Akopov SE. Filum ependymoma mimicking spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Headache ;45(5): Schievink WI, Maya MM, Tourje J, Moser FG. Pseudo-subarachnoid hemorrhage: a CT-finding in spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurology. 2005,12;65(1): Takahashi M, Momose T, Kameyama M, Mizuno S, Kumakura Y, Ohtomo K. Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2005;19(4):
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment
 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:34 38, January 2005 Case Report Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension M. Todd Burtis, John L. Ulmer, Glenn A. Miller, Alexandru C. Barboli, Scott A. Koss,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:34 38, January 2005 Case Report Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension M. Todd Burtis, John L. Ulmer, Glenn A. Miller, Alexandru C. Barboli, Scott A. Koss,
Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities
 DOI 10.1007/s10072-013-1364-2 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities Angelo Franzini G. Messina L. Chiapparini G.
DOI 10.1007/s10072-013-1364-2 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities Angelo Franzini G. Messina L. Chiapparini G.
Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3775-z CASE STUDY Open Access Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage Yake Zheng 1, Yajun Lian 1*, Chuanjie Wu 1, Chen
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3775-z CASE STUDY Open Access Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage Yake Zheng 1, Yajun Lian 1*, Chuanjie Wu 1, Chen
Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
 SHORT COMMUNICATION Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 4, 339 343, 2005 Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
SHORT COMMUNICATION Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 4, 339 343, 2005 Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
Low PRESSURE Headaches. What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah
 Low PRESSURE Headaches aka Low CSF volume headache: What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah Disclosure: I have a part ownership on a patent for thin filmed technology
Low PRESSURE Headaches aka Low CSF volume headache: What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah Disclosure: I have a part ownership on a patent for thin filmed technology
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis
 Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report
 NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-0890 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Endo, Y. Kubo, M. Ida; Tokyo/JP Hemorrhage, Embolism / Thrombosis,
Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-0890 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Endo, Y. Kubo, M. Ida; Tokyo/JP Hemorrhage, Embolism / Thrombosis,
Intracranial hypotension (IH) is a syndrome characterized
 Case Report 293 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension in a Patient with Reversible Pachymeningeal Enhancement and Brain Descent Yu-Lung Tseng, MD; Yung-Yee Chang, MD; Min-Yu Lan, MD; Hsiu-Shan Wu, MD; Jia-Shou
Case Report 293 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension in a Patient with Reversible Pachymeningeal Enhancement and Brain Descent Yu-Lung Tseng, MD; Yung-Yee Chang, MD; Min-Yu Lan, MD; Hsiu-Shan Wu, MD; Jia-Shou
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
While some patients with SIH recover without intervention
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P.H. Luetmer K.M. Schwartz L.J. Eckel C.H. Hunt R.E. Carter F.E. Diehn When Should I Do Dynamic CT Myelography? Predicting Fast Spinal CSF Leaks in Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P.H. Luetmer K.M. Schwartz L.J. Eckel C.H. Hunt R.E. Carter F.E. Diehn When Should I Do Dynamic CT Myelography? Predicting Fast Spinal CSF Leaks in Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial
Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman
 Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman A. Soupart, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine BSIM, December 12, 2014 48 years old woman with Sudden Headache 7/2014 * Admitted for Headache
Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman A. Soupart, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine BSIM, December 12, 2014 48 years old woman with Sudden Headache 7/2014 * Admitted for Headache
Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension
 Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension Stephen D Silberstein, MD Jefferson Headache Center Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA Stephen D. Silberstein, MD, FACP Director, Jefferson
Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension Stephen D Silberstein, MD Jefferson Headache Center Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA Stephen D. Silberstein, MD, FACP Director, Jefferson
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach
 Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery Department of Neurosurgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery Department of Neurosurgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles,
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Following a Yoga Class: A Case Report
 American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 10, 314-318 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/3/10/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-3-10-3 Spontaneous Intracranial
American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 10, 314-318 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/3/10/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-3-10-3 Spontaneous Intracranial
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Intracranial hypotension after trauma
 Sarrafzadeh et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:153 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Intracranial hypotension after trauma Asita S Sarrafzadeh 1*, Stephanie A Hopf 1, Oliver P Gautschi 1, Ana-Paula
Sarrafzadeh et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:153 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Intracranial hypotension after trauma Asita S Sarrafzadeh 1*, Stephanie A Hopf 1, Oliver P Gautschi 1, Ana-Paula
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive cases
 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.76380 Received: 15.05.2017 Accepted: 27.07.2017 Published: 22.05.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Case report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.76380 Received: 15.05.2017 Accepted: 27.07.2017 Published: 22.05.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Case report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive
Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal
 Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Technical Note Michael Carstensen 1*, Navjot
Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Technical Note Michael Carstensen 1*, Navjot
Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch
 J Neurosurg Spine 9:000 000, 9:483 487, 2008 Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch Case report As o k u m a r
J Neurosurg Spine 9:000 000, 9:483 487, 2008 Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch Case report As o k u m a r
Time-Dependent Changes in Dural Enhancement Associated With Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Peter G. Kranz 1 Timothy J. mrhein Kingshuk Roy Choudhury Teerath Peter Tanpitukpongse Linda
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Peter G. Kranz 1 Timothy J. mrhein Kingshuk Roy Choudhury Teerath Peter Tanpitukpongse Linda
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report
 Case Report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report Murali Krishna Menon 1, Thara Prathap 2, Muhammed Jasim Abdul Jalal 3 1
Case Report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report Murali Krishna Menon 1, Thara Prathap 2, Muhammed Jasim Abdul Jalal 3 1
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation
 Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation C. Heine 1, H. Altinova 1, T. Pietilä 1, LC Stavrinou 1 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld, Germany
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation C. Heine 1, H. Altinova 1, T. Pietilä 1, LC Stavrinou 1 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld, Germany
LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch
 LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch Michael D. Staudt Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine, Western University London Health Sciences Centre, London,
LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch Michael D. Staudt Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine, Western University London Health Sciences Centre, London,
Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report and review of literature
 Available online at Available online at: www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 1:153-157 Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report
Available online at Available online at: www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 1:153-157 Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report
 Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report Poster No.: P-0105 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: M. Tzalonikou, D. KECHAGIAS, A. Plomaritoglou, A. 1 1 2
Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report Poster No.: P-0105 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: M. Tzalonikou, D. KECHAGIAS, A. Plomaritoglou, A. 1 1 2
Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension
 online ML Comm CASE REPORT J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc 2011;7:103-107 ISSN 1738-8708 Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension Yong-Sang Kim, MD, Byung Moon Cho, MD, Sung-Min Cho, MD, Se-Hyuck Park,
online ML Comm CASE REPORT J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc 2011;7:103-107 ISSN 1738-8708 Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension Yong-Sang Kim, MD, Byung Moon Cho, MD, Sung-Min Cho, MD, Se-Hyuck Park,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
CSF Leaks. Abnormal communication between the subarachnoid space and the tympanomastoid space or nasal cavity. Presenting symptoms:
 CSF Leaks Steven Wright, M.D. Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, M.D. The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation January 5, 2005 CSF Leaks Abnormal communication
CSF Leaks Steven Wright, M.D. Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, M.D. The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation January 5, 2005 CSF Leaks Abnormal communication
Spinal Imaging Findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Medina et al. MRI and CT of Intracranial Hypotension Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Jocelyn H. Medina 1 Kevin brams 2 Steven
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Medina et al. MRI and CT of Intracranial Hypotension Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Jocelyn H. Medina 1 Kevin brams 2 Steven
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION
 PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION HAI NGUYEN, DO, MPH Anesthesiology Resident (University of Kansas Wichita) JOEL CAVAZOS, MD Pain
PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION HAI NGUYEN, DO, MPH Anesthesiology Resident (University of Kansas Wichita) JOEL CAVAZOS, MD Pain
Radiological Findings on MRI in Intracranial Hypotension
 Radiological Findings on MRI in Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-1678 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. VELASCO, P. Redondo Buil, N. Sanchez Rubio, N. A. Abbas 1 2 2 2 2 3
Radiological Findings on MRI in Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-1678 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. VELASCO, P. Redondo Buil, N. Sanchez Rubio, N. A. Abbas 1 2 2 2 2 3
Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache
 Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache MORRIS LEVIN, MD PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY CHIEF, DIVISION OF HEADACHE MEDICINE, UCSF Disclosures Consulting for Amgen, Lilly, Allergan, Supernus, Pernix No
Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache MORRIS LEVIN, MD PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY CHIEF, DIVISION OF HEADACHE MEDICINE, UCSF Disclosures Consulting for Amgen, Lilly, Allergan, Supernus, Pernix No
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53, 207 212, 2013 Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage Takaaki HOSOYA, 1 Jun HATAZAWA,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53, 207 212, 2013 Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage Takaaki HOSOYA, 1 Jun HATAZAWA,
Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote Spontaneous Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak
 Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 4798465, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4798465 Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote
Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 4798465, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4798465 Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote
Remembering Donald J. Dalessio, MD The Headache Clinic Featuring the Baylor Scott & White Headache Clinic in Temple, Texas.
 Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak An Under-recognized Cause of Headache More common than expected, why is this type of headache so often misdiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed? Challenging the One Size
Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak An Under-recognized Cause of Headache More common than expected, why is this type of headache so often misdiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed? Challenging the One Size
PA SYLLABUS. Syllabus for students of the FACULTY OF MEDICINE No.2
 Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension
 J Neurosurg 103:608 613, 2005 Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D., M. MARCEL MAYA, M.D., FRANKLIN G. MOSER, M.D., AND JAMES TOURJE,
J Neurosurg 103:608 613, 2005 Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D., M. MARCEL MAYA, M.D., FRANKLIN G. MOSER, M.D., AND JAMES TOURJE,
Definition by ICHD: 7.2 Headache attributed to low cerebrospinal fluid pressure (see ICHD 3 rd edition beta version Cephalalgia 2013; 33(9): )
 Low pressure Headache syndromes 2016: Kathleen Digre MD, University of Utah Objectives 1) List the clinical manifestations of CSF hypovolemic headaches 2) list 4 predisposing factors to low pressure headaches
Low pressure Headache syndromes 2016: Kathleen Digre MD, University of Utah Objectives 1) List the clinical manifestations of CSF hypovolemic headaches 2) list 4 predisposing factors to low pressure headaches
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is caused by
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M. Adachi S. Mugikura A. Shibata E. Kawaguchi T. Sato S. Takahashi Relative Decrease in Signal Intensity of Subcortical White Matter in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension on Fluid-Attenuated
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M. Adachi S. Mugikura A. Shibata E. Kawaguchi T. Sato S. Takahashi Relative Decrease in Signal Intensity of Subcortical White Matter in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension on Fluid-Attenuated
2017 BASIC RECOGNIZING AND EVALUATING LOW PRESSURE HEADACHE SYNDROMES
 2017 BASIC RECOGNIZING AND EVALUATING LOW PRESSURE HEADACHE SYNDROMES Kathleen Digre, MD University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT Headache is the most common symptom associated with changes of intracranial
2017 BASIC RECOGNIZING AND EVALUATING LOW PRESSURE HEADACHE SYNDROMES Kathleen Digre, MD University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT Headache is the most common symptom associated with changes of intracranial
Review Article. Abstract. Introduction. Pathophysiology:
 Pathophysiology and management of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension A Review Nadir Ali Syed, 1 Farhan Arshad Mirza, 2 Aqueel Hussain Pabaney, 3 Rameez-ul-Hassan 4 Review Article Department of Neurology,
Pathophysiology and management of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension A Review Nadir Ali Syed, 1 Farhan Arshad Mirza, 2 Aqueel Hussain Pabaney, 3 Rameez-ul-Hassan 4 Review Article Department of Neurology,
Post-Dural Puncture Headache. Dr. Jacobs Aurélie Krans Anesthesie 18/03/2016 Kliniek St.-Jan, Brussel
 Post-Dural Puncture Headache Dr. Jacobs Aurélie Krans Anesthesie 18/03/2016 Kliniek St.-Jan, Brussel I - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY August Bier (intrathecal cocaïn1898)! first 2 cases PDPH CSF leak trough dura mater
Post-Dural Puncture Headache Dr. Jacobs Aurélie Krans Anesthesie 18/03/2016 Kliniek St.-Jan, Brussel I - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY August Bier (intrathecal cocaïn1898)! first 2 cases PDPH CSF leak trough dura mater
Pseudotumour cerebri Idiopathic intracranial hypertension and vascular intracranial hypertension
 Romanian Neurosurgery (2015) XXIX 4: 397-409 397 Pseudotumour cerebri Idiopathic intracranial hypertension and vascular intracranial hypertension St.M. Iencean 1, A.St. Iencean 2, A. Tascu 3 1 Grigore
Romanian Neurosurgery (2015) XXIX 4: 397-409 397 Pseudotumour cerebri Idiopathic intracranial hypertension and vascular intracranial hypertension St.M. Iencean 1, A.St. Iencean 2, A. Tascu 3 1 Grigore
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) classically
 clinical article J Neurosurg 123:732 736, 2015 Intrathecal preservative-free normal saline challenge magnetic resonance myelography for the identification of cerebrospinal fluid leaks in spontaneous intracranial
clinical article J Neurosurg 123:732 736, 2015 Intrathecal preservative-free normal saline challenge magnetic resonance myelography for the identification of cerebrospinal fluid leaks in spontaneous intracranial
Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache
 Pain Physician 2016; 19:E1115-E1122 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Evaluation Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache Yun So, MD, Jung Min Park, MD, Pil-moo
Pain Physician 2016; 19:E1115-E1122 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Evaluation Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache Yun So, MD, Jung Min Park, MD, Pil-moo
Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation
 206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
 Ian Carroll MD, MS https://med.stanford.edu/profiles/ian-carroll CarrollCSFleak@gmail.com SIH and/or POTS? Disclosures No Conflicts of Interest This work is supported by the Considine CSF Leaks Fund Thank
Ian Carroll MD, MS https://med.stanford.edu/profiles/ian-carroll CarrollCSFleak@gmail.com SIH and/or POTS? Disclosures No Conflicts of Interest This work is supported by the Considine CSF Leaks Fund Thank
Intracranial Hypotension: Improved MRI Detection With Diagnostic Intracranial Angles
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Shah et al. MRI Diagnosis of Intracranial Hypotension Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Lubdha M. Shah 1 Logan. McLean Marta
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Shah et al. MRI Diagnosis of Intracranial Hypotension Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Lubdha M. Shah 1 Logan. McLean Marta
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension associated with transdural thoracic osteophyte reversed by primary. dural repair. Case report
 J Neurosurg: Spine 2:614 618, 2005 Spontaneous intracranial hypotension associated with transdural thoracic osteophyte reversed by primary dural repair Case report DEVIN K. BINDER, M.D., PH.D., VAHÉ SARKISSIAN,
J Neurosurg: Spine 2:614 618, 2005 Spontaneous intracranial hypotension associated with transdural thoracic osteophyte reversed by primary dural repair Case report DEVIN K. BINDER, M.D., PH.D., VAHÉ SARKISSIAN,
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Marc Norman, Ph.D. - Do Not Use without Permission 1. Cerebrovascular Accidents. Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry
 Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
CSF. Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System
 Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS
 HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH), also
 CASE REPORT J Neurosurg 129:205 210, 2018 Multilevel, ultra-large-volume epidural blood patch for the treatment of neurocognitive decline associated with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: case report
CASE REPORT J Neurosurg 129:205 210, 2018 Multilevel, ultra-large-volume epidural blood patch for the treatment of neurocognitive decline associated with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: case report
Cerebral Vascular Diseases. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure. Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point
 Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point BJORN MAGNAES, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Rikshospitalet, Oslo
Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point BJORN MAGNAES, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Rikshospitalet, Oslo
Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea as the Presenting Symptom of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Series
 CASE REPORT Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea as the Presenting Symptom of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Series Hossein Ghalaenovi 1, Maziar Azar 1, Morteza Taheri 1, Mahdi Safdarian
CASE REPORT Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea as the Presenting Symptom of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Series Hossein Ghalaenovi 1, Maziar Azar 1, Morteza Taheri 1, Mahdi Safdarian
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgety, and Psychiatry 1995;59:511-515 51 SHORT REPORT Neuroradiology S A Renowden Neurology, Radcliffe Infirmary NHS Trust, Woodstock Road, Oxford OX2 6HE, UK R Gregory N Hyman
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgety, and Psychiatry 1995;59:511-515 51 SHORT REPORT Neuroradiology S A Renowden Neurology, Radcliffe Infirmary NHS Trust, Woodstock Road, Oxford OX2 6HE, UK R Gregory N Hyman
Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report
 Fujiwara et al. JA Clinical Reports (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-016-0073-2 CASE REPORT Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report Open Access
Fujiwara et al. JA Clinical Reports (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-016-0073-2 CASE REPORT Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report Open Access
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves. Chapter 14 Part A
 Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Part A Central Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for: Receiving impulses from receptors Integrating information Sending
Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Part A Central Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for: Receiving impulses from receptors Integrating information Sending
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
Overview. Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord. Anatomy of the dura. Anatomy of the arachnoid. Anatomy of the spinal meninges
 European Course in Neuroradiology Module 1 - Anatomy and Embryology Dubrovnik, October 2018 Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord Johan Van Goethem Overview spinal meninges & spaces spinal cord
European Course in Neuroradiology Module 1 - Anatomy and Embryology Dubrovnik, October 2018 Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord Johan Van Goethem Overview spinal meninges & spaces spinal cord
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY
 Nagoya postoperative Med. J., chronic subdural hematoma after aneurysmal clipping 13 POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY TAKAYUKI OHNO, M.D., YUSUKE NISHIKAWA, M.D., KIMINORI
Nagoya postoperative Med. J., chronic subdural hematoma after aneurysmal clipping 13 POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY TAKAYUKI OHNO, M.D., YUSUKE NISHIKAWA, M.D., KIMINORI
Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings. Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 24 year old African American woman is referred for bilateral optic
Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 24 year old African American woman is referred for bilateral optic
Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory headache due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report
 DOI 0.86/s40064-06-975- RESEARCH Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report Justin Elwood *, Misha Dewan 2, Jolene Smith
DOI 0.86/s40064-06-975- RESEARCH Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report Justin Elwood *, Misha Dewan 2, Jolene Smith
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
Current & Evolving Percutaneous Treatment Approaches: Cedars-Sinai. Interventional Options
 10/20/2017 Current & Evolving Percutaneous Treatment Approaches: Cedars-Sinai Charles Luoy and Marcel Maya Cedars Sinai Blood Patch Single level Bilevel Targeted Fibrin Glue Interventional Options 1 10/20/2017
10/20/2017 Current & Evolving Percutaneous Treatment Approaches: Cedars-Sinai Charles Luoy and Marcel Maya Cedars Sinai Blood Patch Single level Bilevel Targeted Fibrin Glue Interventional Options 1 10/20/2017
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
No Financial Interest
 Pituitary Apoplexy Michael Vaphiades, D.O. Professor Department of Ophthalmology, Neurology, Neurosurgery University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL No Financial Interest N E U R O L O G I C
Pituitary Apoplexy Michael Vaphiades, D.O. Professor Department of Ophthalmology, Neurology, Neurosurgery University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL No Financial Interest N E U R O L O G I C
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019. Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 2: Disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019 Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 2: Disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019 Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 2: Disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
Spontaneous Low Pressure, Low CSF Volume Headaches: Spontaneous CSF Leaks. Bahram Mokri, MD
 Headache 2013 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/head.12149 Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Article Spontaneous Low Pressure, Low CSF Volume Headaches: Spontaneous CSF Leaks
Headache 2013 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/head.12149 Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Article Spontaneous Low Pressure, Low CSF Volume Headaches: Spontaneous CSF Leaks
Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Brain Injuries. Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama
 Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
An Unusual Presentation of Large Pneumoencephaly after Frequent Falls in an Elderly Patient
 104 An Unusual Presentation of Large Pneumoencephaly after Frequent Falls in an Elderly Patient Ching-Hua Chu 1, Wei-Chiu Huang, Yi-Lan Lin 2, and Chao-Ran Wang 3 Abstract- Pneumoencephaly is usually a
104 An Unusual Presentation of Large Pneumoencephaly after Frequent Falls in an Elderly Patient Ching-Hua Chu 1, Wei-Chiu Huang, Yi-Lan Lin 2, and Chao-Ran Wang 3 Abstract- Pneumoencephaly is usually a
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes
 Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Chapter 14. The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid
 Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
Case Report Pneumocephalus Associated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula as a Complication of Spinal Surgery: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2010, Article ID 328103, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/328103 Case Report Pneumocephalus Associated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula as a Complication of Spinal Surgery: A Case
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2010, Article ID 328103, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/328103 Case Report Pneumocephalus Associated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula as a Complication of Spinal Surgery: A Case
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives
 Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Cranio-cervical decompression. Information for patients Neurosurgery
 Cranio-cervical decompression Information for patients Neurosurgery page 2 of 12 What is a cranio-cervical decompression? A cranio-cervical decompression is an operation involving the back of the head
Cranio-cervical decompression Information for patients Neurosurgery page 2 of 12 What is a cranio-cervical decompression? A cranio-cervical decompression is an operation involving the back of the head
Thoracic spine stab injury with pneumocephalus and pneumorrhachiasis: a unique case report and review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXX Number 4 2016 October - December Article Thoracic spine stab injury with pneumocephalus and pneumorrhachiasis: a unique case report and review of literature Rakesh Kumar,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXX Number 4 2016 October - December Article Thoracic spine stab injury with pneumocephalus and pneumorrhachiasis: a unique case report and review of literature Rakesh Kumar,
Sample page. Radiology. Cross Coder. Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS
 Cross Coder 2018 Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com. Contents Introduction...
Cross Coder 2018 Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com. Contents Introduction...
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
 Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Concussions This presentation is for information purposes only, not for any commercial purpose, and may not be sold or redistributed. David Wesley, M.D. Outline Epidemiology
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Concussions This presentation is for information purposes only, not for any commercial purpose, and may not be sold or redistributed. David Wesley, M.D. Outline Epidemiology
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
Acute subdural hematoma as a complication of diagnostic lumbar puncture: case report
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXX Number 4 2016 October - December Article Acute subdural hematoma as a complication of diagnostic lumbar puncture: case report Luis Rafael Moscote-Salazar 1, Andres M. Rubiano
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXX Number 4 2016 October - December Article Acute subdural hematoma as a complication of diagnostic lumbar puncture: case report Luis Rafael Moscote-Salazar 1, Andres M. Rubiano
Unit #3: Dry Lab A. David A. Morton, Ph.D.
 Unit #3: Dry Lab A David A. Morton, Ph.D. Skull Intracranial Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Epidural Hematoma Pg. 26 Skull Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Subarachnoid
Unit #3: Dry Lab A David A. Morton, Ph.D. Skull Intracranial Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Epidural Hematoma Pg. 26 Skull Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Subarachnoid
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
 Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
