3. A plane is an imaginary line dividing the body into.
|
|
|
- Jeremy Norris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 2 Multiple Choice Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Knowing the exact body region where pain is located can help a physician determine the. a. proper diagnosis b. patient s size c. extent of injury d. proper medication 2. A body in the prone position is facing. a. upward b. left c. right d. downward 3. A plane is an imaginary line dividing the body into. a. squares b. sections c. organs
2 d. tissues 4. Directional terms are used with within the body. a. vertical points b. horizontal points c. lateral points d. reference points 5. The midsagittal plane divides the body into which parts? a. Superior and inferior b. Internal and external c. Right and left d. Front and back 6. Which test gives the greatest detail of tissue structures? a. MRI b. EKG c. Blood test d. X-ray 7. What directional term would you use to indicate the wrist if the shoulder is your point of reference? a. External
3 b. Distal c. Internal d. Proximal 8. Cyanosis is a condition that is usually a result of low levels of within the body. a. blood b. oxygen c. saline d. calcium 9. The heart and lungs are located in the cavity. a. posterior b. abdominal c. pelvic d. thoracic 10. The dorsal cavity contains which cavities? a. Thoracic and abdominal cavities b. Cranial and spinal cavities c. Pelvic and pericardial cavities d. Pleural and pelvic cavities
4 11. The cervical spine contains how many vertebrae? a. 12 b. 7 c. 5 d The thoracic spine contains how many vertebrae? a. 3 b. 5 c. 7 d The space within the mouth is known as the cavity. a. nasal b. orbital c. cranial d. oral
5 14. The belly button is located in which region? a. Epigastric b. Umbilical c. Iliac d. Hypogastric 15. Tenderness in the quadrant can be a symptom of appendicitis. a. RUQ b. LUQ c. RLQ d. LLQ 16. Patients experiencing orthopnea,. a. need to sleep without pillows b. breathe easier in an elevated position c. have a lower blood pressure when sitting down d. complain of dizziness when breathing
6 17. The type of scan that provides a series of cross-sectional slices of the body is. a. MRI b. ultrasound c. CT scan d. sonography 18. Blood is MOST commonly drawn from. a. deep veins b. central veins c. superficial veins d. deep arteries 19. Jugular venous distention is visible in the area. a. neck b. chest c. brain d. lungs
7 20. The Fowler s position facilitates. a. sleeping b. sll treatments c. dizziness d. breathing 21. A sudden obstruction of a blood vessel by debris can include. a. hormones b. nutrients c. thrombi d. glucose 22. An injury to the abdominopelvic cavity could include injury to the. a. brain b. heart c. spleen d. sternum
8 23.A patient with peripheral cyanosis needs. a. oxygen b. white blood cells c. insulin d. potassium 24. The danger of a hernia is. a. pnternal bleeding b. blood flow is restricted to the portion of the organ protruding c. when an umbilical hernia becomes an inguinal hernia d. when the muscle protrudes through an organ 25. Deep leg veins are a common site for thrombi to form that can break away and travel to the. a. lungs b. liver c. ears d. intestines
9 26. The supine position. a. describes the body lying face upward b. is also called the anatomical position c. describes the body lying face downward d. Both a and b 27. The term dorsal can be used in place of the term. a. inferior b. posterior c. anterior d. distal 28. A section would divide the eyes from the back of the head. a. sagittal b. frontal c. transverse d. midsagittal
10 29. devices use a narrowly focused x-ray beam that circles rapidly around the body. a. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) b. X-ray c. Ultrasound d. Computed tomography (CT) scanning 30. The prone position. a. describes the body lying face upward b. is also called the anatomical position c. describes the body lying face downward d. Both b and c 31. The cavity contains the heart, lungs, and large blood vessels. a. thoracic cavity b. abdominopelvic cavity c. cranial cavity d. spinal cavity
11 32. The directional term means toward or at the body surface. a. superficial b. medial c. inferior d. deep 33. The opposite of superficial is. a. deep b. inferior c. posterior d. medial 34. What plane would divide the body into right and left halves? a. frontal plane b. cross section plane c. midsagittal plane d. transverse plane
12 35. The liver can be found in the. a. right upper quadrant (RUQ) and left upper quadrant (LUQ) b. left upper quadrant (LUQ) and left lower quadrant (LLQ) c. left lower quadrant (LLQ) and right lower quadrant (RLQ) d. right lower quadrant (RLQ) and right upper quadrant (RUQ) 36. Using the ankle as a reference point, the knee is to the ankle a. inferior b. superior c. posterior d. anterior 37. If you like to sleep on your stomach, you prefer sleeping in the position. a. supine b. prone c. orthoptic d. abdominal
13 38. The vertebrae are located in the neck. a. sacral b. thoracic c. cervical d. cranial 39. The lungs are to the heart. a. medial b. lateral c. superficial d. infraorbital 40. The region is where the thigh meets the trunk and is also called the groin region. a. umbilical b. abdominal c. lumbar d. inguinal
14 41.When a person quickly arises from a seated position, he or she becomes weak and dizzy. This may be a sign of. a. hypertension b. hypotension c. orthostatic hypotension d. normal blood pressure 42. Trendelenburg position may be contraindicated in patients with. a. cerebral injury b. hypertension c. skin disease d. None of the above 43. A condition where it is easier to breathe in a more upright position than lying flat is called. a. orthopnea b. eupnea c. dyspnea d. tachypnea
15 44.Which of the following can cause an embolism? a. Blood clots b. Plaques c. cancer cells d. All of the above 45. Cyanosis causes what coloration of the skin? a. Red b. Blue c. Black d. White 46. Cyanosis is usually the result of low levels of in the blood. a. carbon dioxide b. nitrogen c. oxygen d. carbon monoxide
16 47. Of the following, which is the most serious? a. Cyanosis b. Central cyanosis c. Peripheral cyanosis d. All three are equally serious 48. The MOST common type of radiologic diagnostic modality is the. a. x-ray b. CT scan c. MRI d. ultrasound 49. The thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities are separated by the. a. ribs b. spinal cord c. diaphragm d. sternum
17 50. The large, dome-shaped muscle called the diaphragm is used for. a. circulation b. digestion c. reproduction d. breathing 51. To standardize the orientation for the study of anatomy, scientists developed the position a. prone b. anatomical c. trendelenburg d. supine 52. The directional term refers to body parts toward or in front of the body. a. dorsal b. anterior c. ventral d. posterior
18 53.The doctor has ordered a study to look at the action of heart valves. Which procedure has he or she ordered? a. X-ray b. CT Scan c. MRI d. Ultrasound 54. A patient is scheduled to undergo a test and has stated that he or she has had surgery for a valve replacement. Which procedure could be contraindicated in this situation? a. X-ray b. CT Scan c. MRI d. Ultrasound
19 Short Answer Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1. The position is laying face upward. 2. The position is with the bed or examination table elevated degrees. 3. The transverse (horizontal) plane divides the body into superior and areas. 4. refers to body parts located away from the midline. 5. The or coronal plane divides the body into front and back sections. 6. and posterior mean towards the back of the body. 7. refers to body parts close to a point of reference on the body. 8. means on the outside. 9. The word meaning at or towards or at the body surface is. 10. The opposite of dorsal is (anterior). 11. The wrist is proximal to the hand and to the elbow. 12. While central refers to the center of the body, refers to the extremities (arms and legs) or surrounding or outer regions. 13. Death of tissue is called. 14. The anterior surface of the elbow is called. 15. The armpit is located in the region. 16. When the head is lower than the heart, gravity increases the blood flow and
20 therefore increases the pressure. 17. Left and right always refers to the left and right. 18. Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition of the. 19. The region, more commonly known as the buttocks, is a region used for injections. 20. Patients are more prone to aspirate vomitus into their lungs in the Trendelenburg position and therefore should NOT within two to four hours of being placed in that position. 21. Open MRI machines have been developed to decrease the feelings of experienced by some individuals in a closed MRI, which takes place inside a very small tunnel. 22. The sternal area, also known as the, is used for CPR. 23. Pain in the general area of the can indicate a variety of problems, including an ulcer, heart attack, appendicitis, or liver problems. 24. One of the problems with an x-ray film is that it is a one view of a specific area. 25. A is a tear in the muscle wall that can allow a structure (usually an organ) to protrude through it. 26. The regions are located on either side of the epigastric region and contain the lower ribs.
21 27. The position is sitting in bed with the head of the bed elevated 45 to 60 degrees. 28. Placing patients with secretions in the bases of their lungs in the position helps drain those segments of the lungs. 29. imagers use magnetic energy to produce cross sectional images of body structures. 30. A patient is placed in a supine position and instructed to raise his or her right leg while the practitioner places a hand on the patient s right thigh and gives a slight opposing downward force. This procedure is known as the test. 31. is a condition of bluish-colored skin that is usually the result of low levels of oxygen in the blood. 32. The region is where the thigh meets the trunk and is also called the groin region. 33. devices use sound waves to distinguish structures and allow body activities to be viewed in real time. 34. In the position, the patient s posterior is against the x-ray film. The x-ray beam travels through the patient s anterior region, out the posterior, and onto the film. 35. A blood clot that breaks away and travels to the lungs is called a. 36. A blood clot that breaks away and travels to the brain is called a. 37. The region of the abdomen, lies inferior to the umbilical region and is
22 flanked by the right and left iliac regions.
23 38. Heart failure can cause the back up of fluid into the venous system thus causing the veins to become filled with extra blood. 39. In an x-ray, is the least dense and therefore the MOST radiolucent showing up as black on the film. 40. In an x-ray, /fat densities depend on the thickness. The thicker the layer, the more radiation is absorbed, and the lighter the film. 41. In an x-ray, density can be represented by blood or edema, and is a midrange density. 42. In an x-ray, and metal are the highest density and will show up on the film lighter than other densities. 43. An x-ray is a dimensional view of a specific area. (Use the numeral in your answer) 44. A CT scan creates a dimensional view of structures in the body. (Use the numeral in your answer) 45. A patient recovering from brain surgery is in the Intensive Care Unit and is suffering from an increased intracranial pressure. The position is contraindicated in this situation. 46. You are assisting a patient into a chair who has spent the last two weeks in bed. The patient starts to complain of dizziness and you suspect that he or she is suffering from 47. Ultrasound uses waves to distinguish structures in the body.
24 48. The doctor suspects that there is a lesion in the left lung behind the heart and has ordered a lateral x-ray. True/False Write T if the statement is true and F if the statement is false. 1. In the anatomical position, a person stands erect, faces forward with both feet parallel and the arms hanging at the side with palms facing backward. 2. The Fowler s position is the BEST position for patients having trouble breathing. 3. The prone position is BEST position to perform an abdominal exam. 4. Cranial means superior. 5. Medial means to the side. 6. Computed tomography (CT) scanning uses a narrowly focused x-ray beam that circles rapidly around the body. 7. A CT scan can show the TRUE depth of a quarter-sized tumor shown on a regular x-ray. 8. Peripheral refers to the torso and head. 9. The opposite of superficial is lateral. 10. The cranial cavity houses the brain. 11. An orbital injury can cause damage to sight.
25 12. The pubic area is used for cardiopulmonary resuscitation. 13. A doctor referring to a person's digits, is referring to their fingers. 14. Cervical means relating to the knee. 15. Brachial means lower arm. 16. When a person quickly stands from a seated position and becomes weak and dizzy, they may have orthostatic hypertension. 17. An ultrasound study would NOT be useful to observe the actions of heart valves. 18. An embolism is a sudden obstruction of a blood vessel. 19. When a patient has blood drawn, the clinician normally draws from the deep veins. 20. There are seven lumbar (L) vertebrae in a normal human being. 21. Anatomical position is the standardized position for the directional terms of the body. 22. The elbow is distal to the shoulder. 23. Proximal and medial are opposite terms. 24. Frontal and coronal sections are the same thing. 25. Sagittal and midsagittal sections are the same thing. 26. A plane dividing the body into front and back portions is a sagittal plane. 27. A transverse plane would divide the eyes from the back of the head.
26 28. The abdominopelvic cavity is inferior to the thoracic cavity. 29. A muscle called the diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity. 30. In the anatomical position, the arms hang at the side with the palms facing medially. 31. A symptom of heart failure is jugular venous distention. 32. An embolism is a sudden obstruction of a blood vessel by debris. 33. Cyanosis is a reddish coloring of the skin. 34. Peripheral cyanosis presents as bluish fingers and toes. 35. Central cyanosis presents as bluish fingers and toes. 36. Peripheral cyanosis is sometimes difficult to detect in people of dark skin. 37. Necrosis is the growth of new tissue. 38. Pain in the RUQ may be a symptom of appendicitis. 39. The Psoas test helps to determine carpal tunnel syndrome. 40. Generally, the distance between the x-ray machine and the film is six feet. 41. A CT Scan looks at cross-sections of the body. 42. A MRI uses magnetic energy to produce high resolution images of body structures. 43. Ultrasound is less sensitive than a regular x-ray.
27 44. There are six sets of vertebrae labeled for the body regions. Essay Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 1. List two organs found in each of the RUQ, LUQ, RLQ, and LLQ. 2. Discuss the significance of central vs. peripheral cyanosis. 3. If a patient complains of pain, what questions should you ask?
28 4.Give the opposite of caudal, distal, external, superficial, and posterior. 5. Explain why sectioning is done and how this helps determine pathology. 6. Describe in your own words what occurs in orthostatic hypotension.
29 7. List the three main views of x-rays that are normally seen in the clinical setting and briefly describe how the x-ray would travel through the body for each one. 8. Describe what a hernia is and why a hernia can be very dangerous.
30 Matching Match the following. 1. Peripheral cyanosis 2. Thoracic 3. CT scan 4. MRI 5. Posteroanterior (PA) 6. Pubic area 7. Ultrasound 8. Orbital injury 9. Quadrants 10. Necrosis a. The x-ray is taken from the back to the front of the patient b. Uses magnetic energy to produce even greater detail of structures c. Bluish fingers and toes d. Death of tissue e. Chest cavity f. Uses sound waves to distinguish structures in the body g. Uses a narrowly focused x-ray beam that circles rapidly around the body and the computer constructs thin sliced images h. Can cause damage to eyesight i. Genital region j. Compartments of the abdominal region
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
https://testbanksolution.net/
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine
 Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
9. Which term refers to the back? A. Inferior B. Lateral C. Posterior D. Peripheral 10. The heart is to the lungs. A. dorsal B. superior C.
 1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology Introduction Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism and the relationship to its parts Anatomy is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up which is still how we learn
Anatomy & Physiology Introduction Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism and the relationship to its parts Anatomy is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up which is still how we learn
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
The Language of Anatomy
 The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
Anatomy & Physiology. Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout
 Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
**Confirm accuracy of above with your instructor.** Revised 8/22/2017 1
 AP1 Lab 1 Cavities, Organs, Serous Membranes, Quadrants, Regions, and Directional Terms, Planes & Sections Project 1 Directional Terminology Step 1: Define/Describe what is known as the "ANATOMICAL POSITION."
AP1 Lab 1 Cavities, Organs, Serous Membranes, Quadrants, Regions, and Directional Terms, Planes & Sections Project 1 Directional Terminology Step 1: Define/Describe what is known as the "ANATOMICAL POSITION."
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation
 1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
Introduction to Anatomical Terms. Packet #3
 Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Lab #2 Scientific Method, Metric System, Directional Terms and Body Cavities
 Page1 Lab #2 Scientific Method, Metric System, Directional Terms and Body Cavities Objectives Understand the purpose of the scientific method and describe the six steps involved List and describe the sections
Page1 Lab #2 Scientific Method, Metric System, Directional Terms and Body Cavities Objectives Understand the purpose of the scientific method and describe the six steps involved List and describe the sections
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation. Short Answer. Figure 1.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study. Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School
 A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy. General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position
 #1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
If time is limited, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment.
 EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
2) The level of organization when different multiple types of tissues join together is called the
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Bio 5/6
 Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy 25 KEY ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Guthrie
 THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy
 Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy Definition of Terms Anatomy- term applied to the science of the structure of the body Physiology- study of the function
Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy Definition of Terms Anatomy- term applied to the science of the structure of the body Physiology- study of the function
Chapter Overview. Chapter 1. Anatomy. Physiology
 Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology are of either Greek or Latin origin. (In fact, the term anatomy is derived from
Chapter 1 Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology are of either Greek or Latin origin. (In fact, the term anatomy is derived from
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Introduction Anatomy Deals with the structures (morphology) of body parts Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts. What they do and how they do it. Structure
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Introduction Anatomy Deals with the structures (morphology) of body parts Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts. What they do and how they do it. Structure
Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body
 1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
Body Regions Review. Anatomical Position. Anatomical Planes. Supine versus Prone 9/9/2009
 Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units
 hapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units TRUE/FLSE 1. The pelvic cavity contains the organs of the reproductive and excretory system. NS: T 2. The thoracic cavity protects the heart and lungs. NS:
hapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units TRUE/FLSE 1. The pelvic cavity contains the organs of the reproductive and excretory system. NS: T 2. The thoracic cavity protects the heart and lungs. NS:
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Anatomical Language. Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors Ms. Chase
 Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY. Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER. The Human Body in Health and Disease Content Review Slides
 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 4 The Human Body in Health and Disease Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the word parts used to create terms for the human
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 4 The Human Body in Health and Disease Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the word parts used to create terms for the human
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide
 Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Body Organizations Flashcards
 1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
Body Structure. Directional Terms
 Body Structure 6 Directional Terms In describing the location or direction of a given point in the body, it is always assumed that the subject is in the anatomical position, that is, upright, with face
Body Structure 6 Directional Terms In describing the location or direction of a given point in the body, it is always assumed that the subject is in the anatomical position, that is, upright, with face
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
The Human Body An Overview
 The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
Organization of the Body Chapter 1. Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden
 Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body
 Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Anatomy & Physiology. An Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
Introduction. Chapter 1. Structure and Function. Introduction. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated Anatomy
 Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Then think about these: Check your Packet- three pills and tells you to take one pill every half hour, how long will they last?
 Chapter 1 Check your Packet- Then think about these: 1. If a doctor gives your three pills and tells you to take one pill every half hour, how long will they last? 2. Mrs. Smith has 5 children. Half of
Chapter 1 Check your Packet- Then think about these: 1. If a doctor gives your three pills and tells you to take one pill every half hour, how long will they last? 2. Mrs. Smith has 5 children. Half of
Definition of Anatomy. Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts.
 Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics
 Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele
 OpenStax-CNX module: m47807 1 Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m47807 1 Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract By the end of this section,
Body Planes & Positions
 Learning Objectives Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how it is used to reference the body. Distinguish
Learning Objectives Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how it is used to reference the body. Distinguish
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Medical Terminology. Unit 2
 Medical Terminology Unit 2 Students will apply medical terminology. Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how
Medical Terminology Unit 2 Students will apply medical terminology. Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how
Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body
 Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
First stage Lec.1 : Introduction. Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY
 First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms
 1 Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Use the terms listed below to fill in the sentence blanks. abdominal cavity cavity nasal cavity posterior (dorsal) body abdominopelvic cavity cranial cavity
1 Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Use the terms listed below to fill in the sentence blanks. abdominal cavity cavity nasal cavity posterior (dorsal) body abdominopelvic cavity cranial cavity
EHS Benchmark #1-2016
 EHS Benchmark #1-2016 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The study of the processes of living organisms, or why and how they work, is. a.
EHS Benchmark #1-2016 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The study of the processes of living organisms, or why and how they work, is. a.
A&P 1. Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist
 A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
Review. Labeling Exercise. 80 Part I Introduction to Medical Terminology
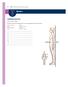 80 Part I Introduction to Medical Terminology Chapter Review Labeling Exercise Directional Terms Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer sheet. Anterior (ventral) Distal
80 Part I Introduction to Medical Terminology Chapter Review Labeling Exercise Directional Terms Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer sheet. Anterior (ventral) Distal
The HUMAN BODY. Concepts of ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY
 The HUMAN BODY Concepts of ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY 1 1 ANATOMY The scientific study of structures and the relationship of structures to each other. FORM Other terms include shape, structure, and appearance.
The HUMAN BODY Concepts of ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY 1 1 ANATOMY The scientific study of structures and the relationship of structures to each other. FORM Other terms include shape, structure, and appearance.
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders
 Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body
 1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body Midclavicular line: Imaginary line at center of clavicle (collar
1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body Midclavicular line: Imaginary line at center of clavicle (collar
Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1)
 Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Dr.Susan Maskel. BIO 105 Western Connecticut State University A&P I BIO 211 Naugatuck Valley Community College A&P I.
 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click to advance. Arrow keys etc.also work. Dr.Susan Maskel BIO 105 Western Connecticut State University A&P I BIO 211 Naugatuck Valley Community
1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click to advance. Arrow keys etc.also work. Dr.Susan Maskel BIO 105 Western Connecticut State University A&P I BIO 211 Naugatuck Valley Community
Levels of Organization. Anatomical Position
 Levels of Organization Anatomical Position A stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor, arms at the sides, and the palms, face, and eyes facing forward. The body standing erect,
Levels of Organization Anatomical Position A stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor, arms at the sides, and the palms, face, and eyes facing forward. The body standing erect,
2. Draw or define ANTERIOR/VENTRAL and POSTERIOR/DORSAL. Give an example.
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Anatomical Terminology: Relative Position Go to the following site: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=ap15305 1. Draw or define
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Anatomical Terminology: Relative Position Go to the following site: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=ap15305 1. Draw or define
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition
 Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition Chapter 01-A: Organization of the Body Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1 A scientific theory is a fact ANS: F DIF: Application TOP: Science and Society REF: Page 4 2 A
Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition Chapter 01-A: Organization of the Body Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1 A scientific theory is a fact ANS: F DIF: Application TOP: Science and Society REF: Page 4 2 A
Chapter 1: The Human Organism
 Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
1. Define Anatomy and Physiology-
 Name Date Anatomy and Physiology Midterm Study Guide Directions: This packet contains an extensive study guide that will help you prepare for the upcoming Midterm Exam. Pace yourself and be prepared to
Name Date Anatomy and Physiology Midterm Study Guide Directions: This packet contains an extensive study guide that will help you prepare for the upcoming Midterm Exam. Pace yourself and be prepared to
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS What is anatomy and physiology? Anatomy Describes the structures of the body: what they are made of, where they are located associated
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS What is anatomy and physiology? Anatomy Describes the structures of the body: what they are made of, where they are located associated
"Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Name(s): Period: Date: "Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates http://www.skyscanner.net/news/x_ray_full.jpg
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Name(s): Period: Date: "Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates http://www.skyscanner.net/news/x_ray_full.jpg
Unit 1: Intro to Physiology
 Unit 1: Intro to Physiology Anatomy The branch of science that studies body parts. Physiology! The branch of science that describes HOW the body works, or functions.! Example - how the heart pumps blood
Unit 1: Intro to Physiology Anatomy The branch of science that studies body parts. Physiology! The branch of science that describes HOW the body works, or functions.! Example - how the heart pumps blood
7a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Body Compass
 7a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Body Compass 7a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Body Compass! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Grade
7a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Body Compass 7a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Body Compass! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Grade
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1
 1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
Tonight s handouts: Syllabus These slides (you will usually print these yourself) Worksheet (later)
 Welcome to BIOL 241! Tonight s handouts: Syllabus These slides (you will usually print these yourself) Worksheet (later) Tonight s agenda: Go over syllabus Peek at course website Chapter 1 of textbook
Welcome to BIOL 241! Tonight s handouts: Syllabus These slides (you will usually print these yourself) Worksheet (later) Tonight s agenda: Go over syllabus Peek at course website Chapter 1 of textbook
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology
 Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
