Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension pathogenesis?: Diffusion weighted MR imaging study
|
|
|
- Alaina Ward
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at ORIGINAL RESEARCH Medicine Science International Medical Journal Medicine Science 2019; ( ): Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension pathogenesis?: Diffusion weighted MR imaging study Kerim Aslan Ondokuz Mayis University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Radiology, Samsun, Turkey Received 13 June 2018; Accepted 29 July2018 Available online with doi: /medscience Copyright 2018 by authors and Medicine Science Publishing Inc. Abstract The aim of this study is to research whether cerebral edema is effective in the pathogenesis of patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) by using diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) measurements. Thirty-six IHH patients who received DWI and 36 age- and sex-matched healthy control group were assessed retrospectively. ADCmin, ADCmean, and ADCmax values were measured from different regions of the brain for both IHH patients and the control group. The Student s t-test was used to compare the ADCmin, ADCmax, ADCmean values acquired from distinct parts of the brain parenchyma of IIH patients with the values of control group. No significant difference was found between ADCmin, ADCmax, and ADCmean values of IIH and control group in bilateral frontal, parietal temporal and occipital lobe cortical and subcortical white matter, caudate nucleus head, putamen, thalamus, corpus callosum splenium and genu (P>0.05). This study showed that cerebral edema cannot be a significant mechanism in the pathogenesis of IIH. Keywords: Diffusion-weighted imaging, apparent diffusion coefficient, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, cerebral edema Introduction Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is a neurological disease characterized by increased intracranial pressure (ICP) in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) component is normal and the etiology of which is not known [1-3]. The most common symptom in IHH is headache, permanent or temporary sight disturbance, back and neck pain, and pulsatile tinnitus. Comorbid findings are papilledema and increased CSF pressure [4-6]. Although the definitive pathophysiology of IIH is still unknown, cerebral edema, increased cerebral blood flow, increase in CSF production, CSF outflow obstruction and increase in venous sinus pressure are among potential pathogenic mechanisms [6,7]. Although Sahs et al. [8] found histological proof about cerebral edema in post-mortem in patients with IIH, Wall et al. [9] could not find histological proof of cerebral edema. In patients with IIH, the presence of cerebral edema and its role in increased intracranial *Coresponding Author: Kerim Aslan, Department of Radiology, Ondokuz Mayis University Faculty of Medicine, Samsun, Turkey mdkerim@hotmail.com pressure can be evaluated non-invasively with diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) techniques which characterize the diffusion features of water molecules in the brain. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), which is obtained from DWI, measures the isotropic total size of water diffusion in tissue and gives quantitative information about free water fraction which includes extracellular and intracellular water in the tissue [10]. A few previous DWI studies showed that IIH patients have a convective transepandimal water flow which causes cerebral edema [11-13]. However, some diffusion studies reported that cerebral edema is not a factor in IIH pathogenesis [14-16]. It is not yet clear whether cerebral edema is effective in IIH pathogenesis due to the inconsistency of studies conducted on the subject so far. Recent studies conducted with DWI reported that minimum ADC (ADCmin) values are superior to mean ADC (ADCmean) and maximum ADC (ADCmax) values in differentiating high-grade glioma from solitary metastases [17,18] and low-grade meningioma from high-grade meningioma [19,20]. To the best of our knowledge, there are no studies in literature which have reported the use of MR diffusion metrics including ADCmin, ADCmax, and ADCmean parameters to research whether cerebral edema is effective in the pathogenesis of IIH. 1
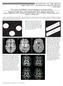
2 doi: /medscience The aim of this study is to research whether cerebral edema has a role in the pathogenesis of IIH patients by using DWI and ADCmin, ADCmean, and ADCmax measurements. Materials and Methods Patients This study was approved by the local ethics committee of our institution. Electronic medical records (March February 2018) were used for this retrospective study. Patients were first identified in the electronic medical records database by searching for the keywords idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Seventyfour patients were determined retrospectively. Only the patients who had a definitive diagnosis of IIH fulfilling the revised Dandy criteria [21] and those with minimum age of 18 were included in the study (n=55). Of these, 13 patients were excluded due to the following exclusion criteria: cerebral vascular disease (n=2), pregnancy (n=1), history of head trauma (n=1), neurological or psychiatric disease (n=2), other severe medical disease (n=3), alcohol or drug dependency (n=1), incidentally found arachnoid cyst (n=1) and cerebral atrophy (n=2). In addition, 4 patients were excluded since they did not have DWI and 2 patients were excluded since their DWI had obvious artefacts. Finally, 36 patients (5 men, 31 women; mean age [±SD], 35.1±5.3 years) were included in the study. All of these patients had one or more MR findings [optic nerve sheath distension (21/36), intraocular protrusion of prelaminar optic nerve (7/36), tortuosity of optic nerve (12/36), and partially empty sella (15/36)] supporting IIH diagnosis (Figure 1). In all IIH patients, CSF opening pressures were measured by LP. The mean CSF opening pressure was 34.9±5.7 cm H2O. matter, caudate nucleus head, putamen, thalamus, corpus callosum splenium and genu) similar to Giedon et al. [13] and Bastin et al. s [14] studied (Figure 2). ROI area was between 17 and 86 mm2 (mean 37 ± 4 mm2). Figure 1. Qualitative MRI signs in a 35-year-old female patient with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. A, Axial T2-weighted image shows bilateral distension of the perioptic subarachnoid space (thin green arrows), bilateral intraocular protrusion of prelaminar optic nerve (arrowheads), and bilateral tortuosity of optic nerve (thin green arrows). B, Coronal fat-suppressed T2-weighted image shows bilateral distension of the perioptic subarachnoid space (thin green arrows). C, Sagittal T2-weighted image shows partially empty sella (thin green arrow). D, Sagittal T2-weighted image shows bilateral tortuosity of optic nerve (green arrow). The control group consisted of 36 age- and sex-matched patients without brain metastases who were being investigated for staging of primary malignancies of other systems in a similar database (May 2015 June 2017) (5 men, 31 women; mean age [±SD], 38.4±6.1 years). There were no significant differences in age or sex distribution between patients with IHH and controls (p=0.34; p=1.000, respectively). These patients not suffered from neurological disorders. Brain MRIs of these patients were reported to be normal in neuroradiology department. In addition, electronic medical records of all control patients were reviewed and the patients who had the specified IIH diagnosis were excluded from the control group. MR Imaging DWI was performed with a single-shot spin-echo EPI (repetition time/ echo time: 3376/74 ms, section thickness: 5 mm, field of view: 230, matrix: 128x128, number of excitations: 2, intersection gap: 1 mm, b values: 0 and 1000 s/mm2, scanning time: 1 min 02 s). ADC maps were automatically generated. Image Analysis DWI datasets were transferred to the workstation. A neuroradiologist who was unaware to the clinical symptoms of the IIH patients and control groups reviewed the DWI independently and randomly. Since cortex and white matter distinction was not made clearly over ADC maps for both IIH patients and the control group, T2 weighted sequence was used as reference imaging. Quantitative ADCmin, ADCmean, and ADCmax values were measured with regions of interest (ROIs) from brain regions (bilateral frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobe cortical and subcortical white Figure 2. ROI measurement areas of a 21-year-old female IIH patient hand-drawn circular regions of interest (ROIs) through T2 weighted sequence were placed automatically on same localization and same size ADC maps. In T2-weighted (A) and ADC maps (B), there are hand-drawn circular ROIs in bilateral putamen, caudate nucleus head, thalamus, corpus callosum splenium and genu, frontal cortical and subcortical white matter. In T2-weighted (C) and ADC maps (D), there are ROIs in bilateral temporal and occipital cortical and subcortical white matter. In T2-weighted (E) and ADC maps (F), there are ROIs in bilateral parietal cortical and subcortical white matter. Statistical Analysis Statistical analyses were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (IBM SPSS Statistics version 21; IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). The Student s t-test was used to compare 2
3 doi: /medscience the ADCmin, ADCmax, ADCmean values acquired from distinct parts of the brain parenchyma of IIH patients with the values of control group. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Results Table 1 shows the demographic and clinical characteristics of IIH patients and the control group. There were no significant differences in age or sex distribution between patients with IHH and controls (p=0.34; p=1.000, respectively). The mean CSF opening pressure was 34.9±5.7 cm H2O. Parenchymal abnormality was not found in conventional MRI and DWI sequences off all IIH patients and the control group. Table 2 summarizes the quantitative values containing mean and related statistical analysis of ADCmin, ADCmax and ADC mean values, in different brain regions for IIH and control group. There was no statistically significant difference between ADCmin, ADCmax, and ADCmean values of IHH and control group in bilateral frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobe cortical and subcortical white matter, caudate nucleus head, putamen, thalamus, corpus callosum splenium and genu (P>0.05). Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the participants IHH Control group p value (Mean±SD) (Mean±SD) Age (years) 35.1 ± ± Gender, Females/Males 31/5 (86%/14%) 31/5 (86%/14%) 1.00 CSF pressure (cmh2o) 34.9 ± 5.7 NA Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH). NA not applicable Table 2. Mean ADCmin, ADCmax, and ADCmean values for IIH patients and control group* ADCmin ADCmax ADCmean Region IHH Control p IHH Control p IHH Control p Frontal CX R Frontal CX L Frontal SWM R Frontal SWM L Parietal CX R Parietal CX L Parietal SWM R Parietal SWM L Temporal CX R Temporal CX L Temporal SWM R Temporal SWM L Occipital CX R Occipital CX L Occipital SWM R Occipital SWM L CC splenium CC genu Thalamus R Thalamus L Head of caudate R Head of caudate L Putamen R Putamen L *Except for the p-values, minimum, maximum, and mean apparent diffusion coefficient (ADCmin, ADCmax, and ADCmean) (s/mm²), idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), right cortex (CX R), left cortex (CX L), right subcortical white matter (SWM R), left subcortical white matter (SWM L), corpus callosum (CC). 3
4 doi: /medscience Discussion IIH is a cerebral intracranial pressure increase with normal CSF compound which is not dependent on a secondary reason (the reason of which is not found). In IIH, neuroimaging findings are optic nerve sheath distension, intraocular protrusion of prelaminar optic nerve, tortuosity of optic nerve, and partially empty sella [22,23]. Despite the increasing number of researches, the pathophysiology underlying IIH has not been completely clarified. Among these, cerebral edema is remarkable. In the current study, I researched whether cerebral edema can play a role in the pathogenesis of patients with IIH with quantitative ADC measurements by using DWI. No statistically significant difference was found in ADCmin, ADCmax, and ADCmean values of different regions of the brain between healthy control group and IIH (P > 0.05). These results can bring to mind that cerebral edema does not play a role in IIH pathogenesis. DWI measures the random translational motion of water molecules in biological tissues of ADC isotropic quantitatively and reflects some pathological states in the brain [24, 25]. This way, ADC gives clues about the cellularity of the tissue, interstitial distance, myelinization degree and the microstructural organization of white matter tracts. Increase in water diffusion in interstitial distance in white matter tracts results in ADC increase [26]. Water diffusion is anisotropic in cerebral white matter. For this reason, water diffusion is restricted perpendicularly, while it is not restricted in parallel direction in white matter tracts. Water diffusion in gray matter is not restricted [27]. Some of the DWI studies in IIH patients reported ADC increase in some regions of the brain, which indicates cerebral edema [11-13]. In their two studies, Sorensen et al. [11,12] compared IIH patients with the control group and reported periventricular increased water diffusion in some patients while they reported increased water diffusion in the whole brain in other patients. Thus, they reported that IIH patients have a convective transependimal water flow and intracellular brain water accumulation which causes cerebral edema. Partly supporting this hypothesis, Gideon et al. [13] showed increase in ACD values associated with increased water diffusion in subcortical white matter in IIH patients when they were compared with the control group. However, they did not find significant ADC increase in other regions of the brain in IIH patients. As a result, unlike my study, these studies reported significant increase in some regions of the brain in IIH patients when compared with the control group. Some of the DWI studies which examined whether cerebral edema was a factor in the pathogenesis of IIH patients could not find diffusion abnormalities signaling brain edema in the patients [14-16]. Bastin et al. [14] demonstrated that no significant difference between IIH patients and the control group in the average diffusivity of water in any region of the brain and they reported that diffuse brain edema was not a feature of IIH. Similarly, Bicakci et al. [16] did not find any diffusion anomaly in IIH patients with DWI. However, they did not conduct quantitative assessment in their study. Similarly, in the current study no significant difference was found between ADC values of IHH patients and control group in different regions of the brain including bilateral frontal, parietal temporal and occipital lobe cortical and subcortical white matter, caudate nucleus head, putamen, thalamus, corpus callosum splenium and genu (P > 0.05). Owler et al. [15] showed that when compared with the control group, diffusion parameters in putamen and head of the caudate nucleus increased in IIH patients; however, no significant differences were found in thalamus, cerebral white matter or cortical regions. They reported that cerebral edema was not a factor in the pathogenesis of IIH. Schmidt et al. [28] did not find significant differences in fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) values between IIH patients and the control group by using diffusion tensor imaging. Although FA and MD have very high sensitivity in microstructural changes, they are not very specific. Recently directional diffusivity metrics radial and axial diffusivity (RD and AD) have been used to better characterize WM microstructure and to maximize specificity [29]. Tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) is the voxel wise statistical analytical method developed to assess DTI metrics (FA, MD, RD, AD). TBSS can assess automatic, operator-independent whole-brain WM integrity [30]. Future studies can assess with TBSS whether cerebral edema is effective in the pathogenesis of IIH patients. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study reporting ADCmin values in researching cerebral edema in IIH pathogenesis. In my study, no difference was found between ADCmin, ADCmax and ADCmean values in different regions of the brain in IIH patients (P > 0.05). Although there were no statistically significant differences in ADCmin, ADCmean and ADCmax values between IIH patients and the control group, ADCmin values were found to be superior to ADCmean and ADCmax values. In the current study, the results brought to mind that cerebral edema cannot have a role in IIH pathogenesis. There were some limitations in the study. First of all, since it was a retrospective study, BMI index was not known for the patient and the control group. In order to confirm the results of our study, prospective studies which measure BMI index for the patient and the control group are needed. Secondly, lumbar puncture was not performed on the healthy control group. In addition, the whole healthy control group did not show any signs of intracranial pressure increase (headache, impaired sight) and since they did not have OCT screening, papilledema symptom is not probable. Lastly, some of the IIH patients did not have (n=15) MR venography. However, despite being highly unlikely, I may therefore have missed small venous pathologies. Conclusion In this study, no significant difference was found between the ADCmin, ADCmax and ADCmean values obtained from the certain diverse regions of the brains of IHH patients compared to the normal healthy control group. The results of this study suggested that cerebral edema cannot be an important mechanism in IIH pathogenesis. In the next step, whole brain DTI studies are required which are conducted with diffusion parameters including axial and radial diffusivity which are more specific when compared with microstructural tissue changes. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interest Financial Disclosure The financial support for this study was provided by the investigators themselves. Ethical approval This work has been approved by the Institutional Review Board. 4
5 doi: /medscience References 1. 1Wall M. Update on Idiopathic Intracranial hypertension. Neurol Clin. 2017;35: Dhungana S, Sharrack B, Woodroofe N. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Acta Neurol Scand. 2010;121: Bicakci K, Bicakci S, Aksungur E. Perfusion and diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Acta Neurol Scand. 2006;114: Han C, Huang S, Guo J, et al. Use of a high b-value for diffusion weighted imaging of peritumoral regions to differentiate high-grade gliomas and solitary metastases. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;42: McCluskey G, Mulholland DA, McCarron P, et al. Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in the Northwest of Northern Ireland: Epidemiology and Clinical Management. Neuroepidemiology. 2015;45: Ball AK, Clarke CE. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5: Wall M, George D. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a prospective study of 50 patients. Brain. 1991;114: Markey KA, Mollan SP, Jensen RH, et al. Understanding idiopathic intracranial hypertension: mechanisms, management, and future directions. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15: Skau M, Brennum J, Gjerris F, et al. What is new about idiopathic intracranial hypertension? An updated review of mechanism and treatment. Cephalalgia. 2006;26: Joynt RJ, Sahs AL. Brain swelling of unknown cause. Neurology. 1956;6: Wall M, Dollar JD, Sadun AA, et al. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Lack of histologic evidence for cerebral edema. Arch Neurol. 1995;52: Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, et al. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology. 1988;168: Sorensen PS, Thomsen C, Gjerris F, et al. Increased brain water content in pseudotumour cerebri measured by magnetic resonance imaging of brain water self-diffusion. Neurol Res. 1989;11: Sorensen PS, Thomsen C, Gjerris F, et al. Brain water accumulation in pseudotumour cerebri demonstrated by MR-imaging of brain water selfdiffusion. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien). 1990;51: Gideon P, Sorensen PS, Thomsen C, et al. Increased brain water self-diffusion in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Am J Neuroradiol. 1995;16: Bastin ME, Sinha S, Farrall AJ, et al. Diffuse brain edema in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003;74: Lee EJ, terbrugge K, Mikulis D, et al. Diagnostic value of peritumoral minimum apparent diffusion coefficient for differentiation of glioblastoma multiforme from solitary metastatic lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011;196: Watanabe Y, Yamasaki F, Kajiwara Y, et al. Preoperative histological grading of meningioma s using apparent diffusion coefficient at 3T MRI. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82: Aslan K, Gunbey HP, Tomak L, et al. The diagnostic value of using combined MR diffusion tensor imaging parameters to differentiate between low- and high-grade meningioma. Br J Radiol. Published Online: Wall M, Corbett JJ. Revised diagnostic criteria for the pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in adults and children. Neurology 2014;83; Raoof N, Sharrack B, Pepper IM, et al. The incidence and prevalence of idiopathic intracranial hypertension in Sheffield, UK. Eur J Neurol. 2011;18: Friedmann DI, Liu GT, Digre KB. Revised criteria for the pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in adults and children. Neurology. 2013;81: Kanaan RA, Shergill SS, Barker GJ, et al. Tract-specific anisotropy measurements in diffusion tensor imaging. Psychiatr Res. 2006;146: Mukherjee P. Diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tractography in acute stroke. Neuroimaging Clin North Am. 2005;15: Salvay DM, Padhye LV, Huecker JB, et al. Correlation Between Papilledema Grade and Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. J Neuroophthalmol. 2014;34: Hajnal JV, Doran M, Hall AS, et al. MR imaging of anisotropically restricted diffusion of water in the nervous system: technical, anatomic and pathologic considerations. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1991;15: Schmidt C, Wiener E, Lüdemann L, et al. Does IIH Alter Brain Microstructures? - A DTI-Based Approach. Headache. 2017;57: Alexander AL1, Lee JE, Lazar M, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics. 2007;4: Owler BK, Higgins JN, Péna A, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of benign intracranial hypertension: absence of cerebral oedema. Br J Neurosurg. 2006;20: Smith SM, JenkinsonM, Johansen-Berg H, et al. Tract based spatial statistics: voxel wise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 2006;31:
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
 Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain
 DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography
 Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings. Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 24 year old African American woman is referred for bilateral optic
Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 24 year old African American woman is referred for bilateral optic
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Khalil Zahra, M.D Neuro-interventional radiology
 Khalil Zahra, M.D Neuro-interventional radiology 1 Disclosure None 2 Outline Etiology and pathogensis Imaging techniques and Features Literature review Treatment modalities Endovascular techniques Long
Khalil Zahra, M.D Neuro-interventional radiology 1 Disclosure None 2 Outline Etiology and pathogensis Imaging techniques and Features Literature review Treatment modalities Endovascular techniques Long
Magnetic resonance imaging in pseudotumor cerebri
 Magnetic resonance imaging in pseudotumor cerebri Poster No.: C-1004 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Saad 1, F. Marrakchi 2, F. Harbi 1 ; 1 Nejran/SA, 2 Ksour Essaf/TN
Magnetic resonance imaging in pseudotumor cerebri Poster No.: C-1004 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Saad 1, F. Marrakchi 2, F. Harbi 1 ; 1 Nejran/SA, 2 Ksour Essaf/TN
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection. Page inserted by evaluation version
 PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury
 Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury Stéphane Sizonenko, MD-PhD Division of Development and Growth Department of Child and Adolescent Medicine Geneva University
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury Stéphane Sizonenko, MD-PhD Division of Development and Growth Department of Child and Adolescent Medicine Geneva University
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic?
 Current Literature In Clinical Science Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic? Spatial Patterns of Water Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
Current Literature In Clinical Science Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic? Spatial Patterns of Water Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
During human aging, the brain exhibits both macro- and
 Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Stereotactic Diffusion Tensor Tractography For Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Keep Imaging Simple: An Introduction To Neuroimaging
 Keep Imaging Simple: An Introduction To Neuroimaging Meghan Elkins, OD, FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others can sit. Unauthorized recording of this session is
Keep Imaging Simple: An Introduction To Neuroimaging Meghan Elkins, OD, FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others can sit. Unauthorized recording of this session is
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging
 Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging Yoshiyuki Nomura, Hajime Sakuma, Kan Takeda, Tomoyasu Tagami, Yasuyuki Okuda,
Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging Yoshiyuki Nomura, Hajime Sakuma, Kan Takeda, Tomoyasu Tagami, Yasuyuki Okuda,
Diffusion Tensor Imaging 12/06/2013
 12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive
 Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Published July 31, 2014 as /ajnr.A4050
 Published July 31, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4050 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Neuromyelitis Optica: A Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Study T.M. Doring, F.C.R. Lopes, T.T.A. Kubo, G. Tukamoto, M.C. Kimura, R.M. Strecker,
Published July 31, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4050 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Neuromyelitis Optica: A Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Study T.M. Doring, F.C.R. Lopes, T.T.A. Kubo, G. Tukamoto, M.C. Kimura, R.M. Strecker,
Brain Imaging in Pediatric Pseudotumor Cerebri Syndrome
 Review Article 49 Brain Imaging in Pediatric Pseudotumor Cerebri Syndrome Emanuele David 1,2 Kshitij Mankad 3 1 Department of Radiology, Anatomopathology and Oncology, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome,
Review Article 49 Brain Imaging in Pediatric Pseudotumor Cerebri Syndrome Emanuele David 1,2 Kshitij Mankad 3 1 Department of Radiology, Anatomopathology and Oncology, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome,
Intracranial hypertension and headache. Daniel Tibussek, MD
 Intracranial hypertension and headache. Daniel Tibussek, MD none Disclosures Overview Case Clinical presentation of pediatric PTC Nomenclature, Definition What is intracranial hypertension? Diagnostic
Intracranial hypertension and headache. Daniel Tibussek, MD none Disclosures Overview Case Clinical presentation of pediatric PTC Nomenclature, Definition What is intracranial hypertension? Diagnostic
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation
 MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
Diffusion MRI explores new indications
 DECEMBER 2001 Diffusion MRI finds new indications Neuroimaging expands with functional MRI 3-tesla MRI bests 1.5-tesla in body and brain Diffusion MRI explores new indications Diffusion tensor imaging
DECEMBER 2001 Diffusion MRI finds new indications Neuroimaging expands with functional MRI 3-tesla MRI bests 1.5-tesla in body and brain Diffusion MRI explores new indications Diffusion tensor imaging
Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 20:555 562 (2004) Original Research Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 20:555 562 (2004) Original Research Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries
 1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries such as ligaments, membranes and macro molecules. Diffusion
1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries such as ligaments, membranes and macro molecules. Diffusion
THE SWOLLEN DISC. Valerie Biousse, MD Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA
 THE SWOLLEN DISC Valerie Biousse, MD Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA Updated from: Neuro-Ophthalmology Illustrated. Biousse V, Newman NJ. Thieme, New-York,NY. 2 nd Ed, 2016. Edema of the
THE SWOLLEN DISC Valerie Biousse, MD Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA Updated from: Neuro-Ophthalmology Illustrated. Biousse V, Newman NJ. Thieme, New-York,NY. 2 nd Ed, 2016. Edema of the
Study of the CNS. Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David Norman Thomas H. Newton
 271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD
 Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan ethans@med.umich.edu Disclosures Royalties from Elsevier
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan ethans@med.umich.edu Disclosures Royalties from Elsevier
Meningiomas account for between 16% and 20% of primary
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.-H. Toh M. Castillo A.M.-C. Wong K.-C. Wei H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng Y.-L. Wan Differentiation Between and s with Use of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The differentiation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.-H. Toh M. Castillo A.M.-C. Wong K.-C. Wei H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng Y.-L. Wan Differentiation Between and s with Use of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The differentiation
Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients
 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
Diagnostic Value of Peritumoral Minimum Apparent Diffusion Coefficient for Differentiation of Glioblastoma Multiforme From Solitary Metastatic Lesions
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MRI to Diagnose Glioblastoma Multiforme Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Eun Ja Lee 1,2 Karel terbrugge
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MRI to Diagnose Glioblastoma Multiforme Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Eun Ja Lee 1,2 Karel terbrugge
Management of Pseudo Tumor Cerebri by Frequent Tapping VS lumboperitoneal Shunt
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (5), Page 4556-4560 Management of Pseudo Tumor Cerebri by Frequent Tapping VS lumboperitoneal Shunt Ali K. Ali, Maamoun M. Abo Shousha, Mohammed
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (5), Page 4556-4560 Management of Pseudo Tumor Cerebri by Frequent Tapping VS lumboperitoneal Shunt Ali K. Ali, Maamoun M. Abo Shousha, Mohammed
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry
 WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
Diffusion Tensor Imaging Assessment of Brain White Matter Maturation During the First Postnatal Year
 DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016)
 International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
CSM is the most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction
 Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry
 2003 KHBM DTI in Psychiatry Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry KHBM 2003. 11. 21. 서울대학교 의과대학 정신과학교실 권준수 Neuropsychiatric conditions DTI has been studied in Alzheimer s disease Schizophrenia Alcoholism
2003 KHBM DTI in Psychiatry Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry KHBM 2003. 11. 21. 서울대학교 의과대학 정신과학교실 권준수 Neuropsychiatric conditions DTI has been studied in Alzheimer s disease Schizophrenia Alcoholism
Imaging in Pediatric `neurohiv Dr Jackie Hoare Head of Liaison Psychiatry Groote Schuur Hospital, UCT
 Imaging in Pediatric `neurohiv Dr Jackie Hoare Head of Liaison Psychiatry Groote Schuur Hospital, UCT ? Spectrum of Neurocognitive disorders The adult literature on HIV related CNS damage supports a spectrum
Imaging in Pediatric `neurohiv Dr Jackie Hoare Head of Liaison Psychiatry Groote Schuur Hospital, UCT ? Spectrum of Neurocognitive disorders The adult literature on HIV related CNS damage supports a spectrum
Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology
 Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology Nancy J. Newman, MD Emory University Atlanta, GA Consultant for Gensight Biologics, Santhera Data Safety Monitoring Board for Quark AION Study Medical-legal
Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology Nancy J. Newman, MD Emory University Atlanta, GA Consultant for Gensight Biologics, Santhera Data Safety Monitoring Board for Quark AION Study Medical-legal
Characterization of Soft Tissue Tumors by Diffusion-Weighted Imaging
 Iran J Radiol. 2015 July; 12(3): e15478. Published online 2015 July 22. MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.15478v2 Research Article Characterization of Soft Tissue Tumors by Diffusion-Weighted
Iran J Radiol. 2015 July; 12(3): e15478. Published online 2015 July 22. MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.15478v2 Research Article Characterization of Soft Tissue Tumors by Diffusion-Weighted
Disclosures. Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck. Learning objectives ???
 Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Summary of findings from the previous meta-analyses of DTI studies in MDD patients. SDM (39) 221 Left superior longitudinal
 Supplemental Data Table S1 Summary of findings from the previous meta-analyses of DTI studies in MDD patients Study Analysis Method Included studies, n MDD (medicated) HC Results (MDDHC)
Supplemental Data Table S1 Summary of findings from the previous meta-analyses of DTI studies in MDD patients Study Analysis Method Included studies, n MDD (medicated) HC Results (MDDHC)
Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience
 African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
MRI and CT of the CNS
 MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
Magnetic resonance (MR) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is
 Diagn Interv Radiol DOI 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability
Diagn Interv Radiol DOI 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability
A Case of Stent Placement for Intracranial Hypertension Associated with Venous Sinus Stenosis
 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0080 A Case of Stent Placement for Intracranial Hypertension Associated with Venous Sinus Stenosis Rei Yamaguchi, Koji Sato, Hiroya Fujimaki, and Ken Asakura Objective: We encountered
DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0080 A Case of Stent Placement for Intracranial Hypertension Associated with Venous Sinus Stenosis Rei Yamaguchi, Koji Sato, Hiroya Fujimaki, and Ken Asakura Objective: We encountered
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging features of intracranial lesions
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2
 Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme
 Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme Adil Bata 1, Jai Shankar 2 1 Faculty of Medicine, Class of 2017 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Division of Neuroradiology,
Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme Adil Bata 1, Jai Shankar 2 1 Faculty of Medicine, Class of 2017 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Division of Neuroradiology,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Gregg NM, Kim AE, Gurol ME, et al. Incidental cerebral microbleeds and cerebral blood flow in elderly individuals. JAMA Neurol. Published online July 13, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1359.
Supplementary Online Content Gregg NM, Kim AE, Gurol ME, et al. Incidental cerebral microbleeds and cerebral blood flow in elderly individuals. JAMA Neurol. Published online July 13, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1359.
Differentiation between cerebral solitary MET and GBM is
 Published July 5, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3106 ORIGINAL RESEARCH X.Z. Chen X.M. Yin L. Ai Q. Chen S.W. Li J.P. Dai Differentiation between Brain Glioblastoma Multiforme and Solitary Metastasis: Qualitative
Published July 5, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3106 ORIGINAL RESEARCH X.Z. Chen X.M. Yin L. Ai Q. Chen S.W. Li J.P. Dai Differentiation between Brain Glioblastoma Multiforme and Solitary Metastasis: Qualitative
Post Stroke Brain Plasticity
 Post Stroke Brain Plasticity François CHOLLET MD, PhD Neurology Department: Stroke Unit Toulouse University Hospital (CHU) Neurosciences Institute of Toulouse CNRS, INSERM, University, CHU Versailles le
Post Stroke Brain Plasticity François CHOLLET MD, PhD Neurology Department: Stroke Unit Toulouse University Hospital (CHU) Neurosciences Institute of Toulouse CNRS, INSERM, University, CHU Versailles le
POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES
 Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
Findings of DTI-p maps in comparison with T 2 /T 2 -FLAIR to assess postoperative hyper-signal abnormal regions in patients with glioblastoma
 Beigi et al. Cancer Imaging (2018) 18:33 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40644-018-0166-4 REGULAR ARTICLE Open Access Findings of DTI-p maps in comparison with T 2 /T 2 -FLAIR to assess postoperative hyper-signal
Beigi et al. Cancer Imaging (2018) 18:33 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40644-018-0166-4 REGULAR ARTICLE Open Access Findings of DTI-p maps in comparison with T 2 /T 2 -FLAIR to assess postoperative hyper-signal
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
An analysis of MRI findings in patients referred with fits
 An analysis of MRI findings in patients referred with fits Pallewatte AS 1, Alahakoon S 1, Senanayake G 1, Bulathsinghela BC 1 1 National Hospital of Sri Lanka, Colombo, Sri Lanka Abstract Introduction:
An analysis of MRI findings in patients referred with fits Pallewatte AS 1, Alahakoon S 1, Senanayake G 1, Bulathsinghela BC 1 1 National Hospital of Sri Lanka, Colombo, Sri Lanka Abstract Introduction:
What is IIH? Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH)
 What is IIH? Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) What is Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension? Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also known as benign intracranial hypertension or pseudotumour
What is IIH? Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) What is Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension? Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also known as benign intracranial hypertension or pseudotumour
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology
 Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
Overview. Fundamentals of functional MRI. Task related versus resting state functional imaging for sensorimotor mapping
 Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Naoaki Yamada, Satoshi Imakita, and Toshiharu Sakuma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
Professional boxing is a controversial sport, and research
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
Axial Diffusivity of the Corona Radiata Correlated With Ventricular Size in Adult Hydrocephalus
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Cauley and Cataltepe Imaging Adult Hydrocephalus Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Keith A Cauley Oguz Cataltepe 2 Cauley KA,
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Cauley and Cataltepe Imaging Adult Hydrocephalus Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Keith A Cauley Oguz Cataltepe 2 Cauley KA,
Kurtosis is a descriptor of the peakedness of a variable relative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Pseudotumor cerebri comorbid with meningioma: A review and case series
 SNI: Unique Case Observations OPEN ACCESS For entire Editorial Board visit : http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com Editor: Ather Enam, M.D., Aga Khan University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan Case Report Pseudotumor
SNI: Unique Case Observations OPEN ACCESS For entire Editorial Board visit : http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com Editor: Ather Enam, M.D., Aga Khan University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan Case Report Pseudotumor
Use of Multimodal Neuroimaging Techniques to Examine Age, Sex, and Alcohol-Related Changes in Brain Structure Through Adolescence and Young Adulthood
 American Psychiatric Association San Diego, CA 24 May 2017 Use of Multimodal Neuroimaging Techniques to Examine Age, Sex, and Alcohol-Related Changes in Brain Structure Through Adolescence and Young Adulthood
American Psychiatric Association San Diego, CA 24 May 2017 Use of Multimodal Neuroimaging Techniques to Examine Age, Sex, and Alcohol-Related Changes in Brain Structure Through Adolescence and Young Adulthood
Tracking the language pathways in edema patients: Preliminary results.
 Tracking the language pathways in edema patients: Preliminary results. Sarah M. E. Gierhan 1,2, Peter Rhone 3,4, Alfred Anwander 1, Isabel Jost 3, Clara Frydrychowicz 3, Karl-Titus Hoffmann 4, Jürgen Meixensberger
Tracking the language pathways in edema patients: Preliminary results. Sarah M. E. Gierhan 1,2, Peter Rhone 3,4, Alfred Anwander 1, Isabel Jost 3, Clara Frydrychowicz 3, Karl-Titus Hoffmann 4, Jürgen Meixensberger
A Multimodal Imaging Analysis of Subcortical Gray Matter in Fragile X Premutation
 A Multimodal Imaging Analysis of Subcortical Gray Matter in Fragile X Premutation Jun Y. Wang, Randi J. Hagerman, Susan M. Rivera 2012 International Fragile X Conference Center for Mind and Brain Subcortical
A Multimodal Imaging Analysis of Subcortical Gray Matter in Fragile X Premutation Jun Y. Wang, Randi J. Hagerman, Susan M. Rivera 2012 International Fragile X Conference Center for Mind and Brain Subcortical
MRI in MS. MRI in multiple sclerosis. MS T2 Lesions: Pathology. Brain lesions Morphology Matters. Sagittal FLAIR Morphology Matters
 MRI in multiple sclerosis MRI in MS Rohit Bakshi, MD, MA Breakstone Professor of Neurology & Radiology Director, Laboratory for Neuroimaging Research Senior Neurologist, MS Center Brigham & Women s Hospital
MRI in multiple sclerosis MRI in MS Rohit Bakshi, MD, MA Breakstone Professor of Neurology & Radiology Director, Laboratory for Neuroimaging Research Senior Neurologist, MS Center Brigham & Women s Hospital
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!!
 Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Neurological Conditions. Lawrance Yip Department of Radiology Queen Mary Hospital
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Neurological Conditions Lawrance Yip Department of Radiology Queen Mary Hospital Outline Strength and limitations of MRI for neurological conditions MR Imaging techniques
Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Neurological Conditions Lawrance Yip Department of Radiology Queen Mary Hospital Outline Strength and limitations of MRI for neurological conditions MR Imaging techniques
DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy
 DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy Poster No.: C-2328 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors:
DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy Poster No.: C-2328 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors:
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
Meningoceles in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Bialer et al. Meningoceles in IIH Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Omer Y. Bialer 1 Mario Perez Rueda 1 Beau B. Bruce 1,2 Nancy
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Bialer et al. Meningoceles in IIH Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Omer Y. Bialer 1 Mario Perez Rueda 1 Beau B. Bruce 1,2 Nancy
BMB Disclosures. Papilledema can be a. Neurological Emergency, Causing Preventable Blindness
 Reasonable Doubt: Can High Intracranial Pressure Occur Without Papilledema? 15 February 2013 Jonathan C. Horton hortonj@vision.ucsf.edu http://www.ucsf.edu/hortonlab BMB Disclosures Financial Disclosures
Reasonable Doubt: Can High Intracranial Pressure Occur Without Papilledema? 15 February 2013 Jonathan C. Horton hortonj@vision.ucsf.edu http://www.ucsf.edu/hortonlab BMB Disclosures Financial Disclosures
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
The estimated annual incidence of central nervous system
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
3D diffuse tensor imaging important acquisition in diagnostic and preoperative planning of intracranial lesions
 110 Rizea et al 3D diffuse tensor imaging for preoperative planning 3D diffuse tensor imaging important acquisition in diagnostic and preoperative planning of intracranial lesions R.E. Rizea, A.V. Ciurea,
110 Rizea et al 3D diffuse tensor imaging for preoperative planning 3D diffuse tensor imaging important acquisition in diagnostic and preoperative planning of intracranial lesions R.E. Rizea, A.V. Ciurea,
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Biopsy-Proven Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in iopsy-proven reutzfeldt-jakob Disease Hyo-heol Kim, MD 1 Kee-Hyun hang, MD 1 In han Song, PhD 1 Sang Hyun Lee, MD 1 ae Ju Kwon, MD 1 Moon Hee Han, MD 1 Sang-Yun Kim, MD
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in iopsy-proven reutzfeldt-jakob Disease Hyo-heol Kim, MD 1 Kee-Hyun hang, MD 1 In han Song, PhD 1 Sang Hyun Lee, MD 1 ae Ju Kwon, MD 1 Moon Hee Han, MD 1 Sang-Yun Kim, MD
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is a major consequence
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Assaf L. Ben-Sira S. Constantini L.C. Chang L. Beni-Adani Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Hydrocephalus: Initial Experience PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is an
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Assaf L. Ben-Sira S. Constantini L.C. Chang L. Beni-Adani Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Hydrocephalus: Initial Experience PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is an
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note
 High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a motor neuron disease
 ORIGINL RESERCH S. Ngai Y.M. Tang L. Du S. Stuckey Hyperintensity of the Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter and Hypointensity of the Precentral Gyrus on Fluid-ttenuated Inversion Recovery: Variation
ORIGINL RESERCH S. Ngai Y.M. Tang L. Du S. Stuckey Hyperintensity of the Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter and Hypointensity of the Precentral Gyrus on Fluid-ttenuated Inversion Recovery: Variation
