Published July 31, 2014 as /ajnr.A4050
|
|
|
- Abraham Wilcox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Published July 31, 2014 as /ajnr.A4050 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Neuromyelitis Optica: A Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Study T.M. Doring, F.C.R. Lopes, T.T.A. Kubo, G. Tukamoto, M.C. Kimura, R.M. Strecker, R.C. Domingues, and E.L. Gasparetto ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Conventional MR imaging typically yields normal images of the brain or indicates lesions in areas of high aquaporin expression in patients with neuromyelitis optica. Diffusional kurtosis imaging was applied in patients with neuromyelitis optica to determine whether this technique could detect alterations in diffusion and diffusional kurtosis parameters in normal-appearing white matter and to explore the relationship between diffusional kurtosis imaging and DTI parameters. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Thirteen patients with neuromyelitis optica and 13 healthy controls underwent MR imaging of the brain with conventional and diffusional kurtosis imaging sequences. Tract-based spatial statistics and region-of-interest-based analyses were conducted to identify differences between patients with neuromyelitis optica and controls through conventional DTI and diffusional kurtosis imaging parameters. The parameters were correlated to determine the potential relationship between them. RESULTS: Compared with healthy controls, several diffusional kurtosis imaging and DTI parameters were altered in various fiber tracts of patients with neuromyelitis optica (P.05). A significant decrease (P.05) in radial kurtosis was observed in the corpus callosum and anterior corona radiata and left optic radiation. Differences (P.1) in mean kurtosis were found in patients with neuromyelitis optica. We found a negative correlation between diffusional kurtosis imaging (radial kurtosis, axial kurtosis, mean kurtosis) and the corresponding DTI parameters (radial diffusivity, axial diffusivity, mean diffusivity). Positive correlations were found for radial kurtosis and mean kurtosis with fractional anisotropy. CONCLUSIONS: This study demonstrated differences in conventional diffusion and diffusional kurtosis parameters, especially radial kurtosis, in the normal-appearing white matter of patients with neuromyelitis optica compared with healthy controls. Larger studies of patients with neuromyelitis optica should be performed to assess the potential clinical impact of these findings. ABBREVIATIONS: AD axial diffusivity; AK axial kurtosis; CC corpus callosum; DKI diffusional kurtosis imaging; FA, fractional anisotropy; MD mean diffusivity; MK mean kurtosis; NMO neuromyelitis optica; OR optic radiation; RD radial diffusivity; RK radial kurtosis; TBSS tract-based spatial statistics Received March 13, 2014; accepted after revision June 2. From the Universidade Federal Rio de Janeiro (T.M.D., F.C.R.L., G.T., E.L.G.), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; Clínica de Diagnóstico Por Imagem and Multi-imagem (T.M.D., F.C.R.L., T.T.A.K., G.T., M.C.K., R.C.D., E.L.G.), Diagnósticos da América, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; and Siemens Healthcare (R.M.S.), São Paulo, Brazil. This work was supported by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES). Please address correspondence to Thomas Doring, MS, Avenue Das Américas 4666, Sala 323, CEP Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; thomas.doring@gmail.com Indicates open access to non-subscribers at Indicates article with supplemental on-line table. Neuromyelitis optica (NMO) is a severe, recurrent demyelinating disease that typically affects the optic nerve and spinal cord. 1,2 In patients with NMO, conventional MR imaging typically yields images with normal findings of the brain or indicates lesions in areas of high aquaporin expression. 3 Studies by using diffusion-tensor MR imaging, which depicts several diffusion parameters, have identified extensive damage in the normal-appearing white matter in patients with NMO, affecting the pyramidal tract, optic radiation (OR), and corpus callosum (CC). 4,5 Diffusional kurtosis imaging (DKI) is an extension of the DTI technique that allows the simultaneous estimation of diffusion and kurtosis parameters. 6 The DTI model assumes that diffusion occurs in a random unrestricted way, following a Gaussian diffusion probability distribution function. However, the complexity of tissue is the reason that water diffusion deviates from that strict Gaussian behavior and occurs in a restricted way. DKI considers this in its model by quantifying this deviation, the diffusional kurtosis; thus, it is a more accurate description of restricted diffusion than DTI and may provide additional biomarkers in various disease states. 7,8 In combined DTI and DKI acquisitions, at least 15 distinct nonlinear diffusion directions (gradients), with at least 3 distinct b-values, 9 are obtained. Typical b-values for DKI in the brain are 0, 1000, and 2000 s/mm 2. An advantage of DKI is that it apparently accounts for fiber-crossing, whereas DTI fails in Copyright 2014 by American Society of Neuroradiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :
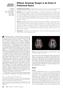
2 this respect. 10 Q-ball imaging, a previously described technique that also accounts for fiber crossing, requires numerous encoding directions and even greater b-values, resulting in high acquisition times. 11,12 Therefore, DKI might be useful when shorter acquisition times are needed because it requires only 15 independent directions and lower b-values. Mean kurtosis (MK), which provides a measure of the overall kurtosis, is the main DKI parameter of interest in an isotropic medium. When diffusion becomes anisotropic (eg, within nerve fibers), directional kurtosis metrics, such as axial kurtosis (AK) and radial kurtosis (RK), can be derived. As in conventional DTI, AK is defined as the kurtosis along the principal eigenvector, whereas RK is the kurtosis perpendicular to the principal eigenvector. Kurtosis parameters have been shown to correlate negatively with DTI parameters. 13 In a previous study, 14 the DKI parameters, especially RK, showed high sensitivity to the degree of myelination of the brain in rats. RK was increased due to a more restricted diffusion perpendicular to the axon during myelination. Conversely, it is expected that RK will decrease when diffusion becomes less restricted during demyelination. Lättetal 15 recently estimated and compared the regional DKI values of healthy brain tissues with DKI values obtained from previous studies of different pathologies. In another study in which DKI was applied after stroke onset, 16 higher MK values were observed in ischemic WM, which eventually progressed to gliosis, compared with ischemic WM that maintained a normal appearance. These findings suggest the usefulness of DKI for predicting the outcome of ischemic tissue. Finally, DKI parameters were found to be more effective than conventional DTI parameters for differentiating high- and low-grade gliomas. 17 To date, few studies have assessed the clinical application of DKI. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the brains of patients with NMO by DKI, to determine whether DKI can detect differences in DKI parameters compared with healthy controls and to explore the relationship between DKI and conventional DTI parameters. MATERIALS AND METHODS Subjects Thirteen patients diagnosed with NMO (mean age, years; age range, years; 6 females and 7 males) were selected from the Clinical Demyelinating Disease data base of our university hospital. All patients fulfilled the revised Criteria of 2006 of Wingerchuk et al. 1 Thirteen demographically matched healthy controls (mean age, years; age range, years), free of neurologic or psychiatric disorders, were also enrolled. All subjects gave written informed consent, and the study was approved by the institutional review board. MR Imaging Acquisition All subjects underwent MR imaging at 3T (Tim Trio; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). In addition to standard sagittal T1WI and axial T2WI (FLAIR) sequences, a work-in-progress DKI sequence was acquired with 30 gradient directions and the following parameters: b- values of 1 b 0 s/mm 2,30b 1000 s/mm 2, and 30 b 2000 s/mm 2 ; TR/TE 5300/90 ms; FOV 220 mm; 45 sections; matrix 82 82; section thickness 2.7 mm; voxel size 2.7 mm 3 isotropic; bipolar gradient scheme; bandwidth 3048 Hz/Px; parallel imaging factor 2; echo spacing 0.59 ms; no gap. 2 Doring DTI and DKI Parametric Map Calculations DKI raw datasets were processed off-line on a workstation. To calculate the diffusion and kurtosis parametric maps, a customwritten software in Matlab (MathWorks, Natick, Massachusetts) 6 was used. The kurtosis model, as described previously, 5,6 was fitted to the diffusion-weighted signal intensities in each voxel by nonlinear least-squares minimization. The fitted kurtosis tensor was used to calculate AK, RK, and MK, as described by Tabesh et al. 6 Fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusion (MD), axial diffusion (AD), and radial diffusion (RD) were calculated from the diffusion tensor in the kurtosis model by using conventional equations. 6 After this, parametric maps were constructed for each parameter (Fig 1). Data Analysis Tract-Based Spatial Statistics for Group Analysis. First, all subject data were analyzed statistically by using tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS), a software tool within the fmri of the Brain Software Library (FSL; 18 All of the FA maps of subjects were aligned by using nonlinear registration. Then, a mean FA image was created and thinned to generate a mean FA skeleton, which represents the center of all tracts common to the group. We registered each subject s parametric diffusion (MD, RD, and AD) and kurtosis images (MK, RK, and AK) into the same space as the FA, applying the same nonlinear registration used for the previously processed FA images, and projected them onto the skeleton. To perform group comparisons (patients with NMO versus healthy controls), we determined voxelwise cross-subject statistics for each parameter, by using permutation-based inference with 5000 permutations and thresholdfree cluster enhancement with a threshold of P.05, corrected for multiple comparisons, by using family-wise error correction. Areas with significantly altered parameters in patients with NMO compared with healthy controls were identified by the Johns Hopkins University White Matter Tractography Atlas ( cmrm.med.jhmi.edu/) (Fig 2). Region-of-Interest-Based Group Analysis. Second, a region-ofinterest-driven analysis was performed by 2 experienced neuroscientists (F.C.R.L. and T.M.D., each with 7 years of experience) by placing hand-drawn ROIs on the splenium and genu of the CC, corticospinal tract in the cerebral peduncles, and ORs on the B0 maps of each subject by using OsiriX (Version 4.1.2; The purpose of this second a priori analysis was to corroborate the TBSS analysis, by choosing specific regions where alterations were expected according to a previous report. 4 The ROIs positioned in the CC, corticospinal tract, and OR had areas of 0.25, 0.15, and 0.29 cm 2, respectively. Then the ROIs were automatically propagated within OsiriX software to all DKI and DTI maps. Statistical analysis was performed with the R statistical computing software ( Normality was tested by applying the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The Cronbach was used to evaluate the interrater reliability. Group analysis (Student t test) was performed to test for differences between the control and NMO groups. P.05 was considered statistically significant.
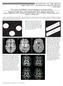
3 FIG 1. Parametric DKI maps of 1 subject. Common diffusion parameters FA, AD, RD, and MD (upper row). Diffusional kurtosis parameters AK, RK, and MK (lower row). Correlation between DTI and DKI Parameters. To compare conventional diffusion and DKI parameters, we calculated the Pearson correlation coefficient for all ROIs defined in the second analysis of each subject that were drawn by 1 rater (T.M.D.). A correlation coefficient of r 0.7 was considered a strong correlation, and a coefficient of 0.5 r 0.7 was considered a moderate correlation. RESULTS Tract-Based Spatial Statistics DTI. All results are listed in the On-line Table and illustrated in Fig 2. Reductions in FA were found in the CC (splenium and body), bilateral ORs, inferior fronto-occipital and superior longitudinal fascicules, and left internal capsule (all P.05). MD and RD were increased in the CC (splenium, body, and genu); bilateral ORs; anterior, posterior, and superior corona radiata; inferior fronto-occipital and superior longitudinal fascicules; and bilateral corticospinal tracts in the frontal lobe (all P.05). AD was increased in the CC (splenium, body, and genu), left anterior corona radiata, bilateral superior longitudinal fascicules, and bilateral ORs (all P.05). DKI. RK was decreased in the splenium, body, and genu of the CC (P.05) and the right anterior corona radiata (Fig 2). A tendency (P.1) for RK reduction was observed in both ORs. Tendencies for MK reduction (P.1) were found in the body and genu of the CC and in the superior corona radiata. AK showed no significant alteration. Region-of-Interest Analysis The results of Cronbach to evaluate the interrater reliability are listed in the Table. All values showed acceptable, good, or excellent interrater reliability ( 0.7), expect for 2 values. One value was questionable (.6432, right corticospinal tract, MD), and one was poor (.5438, left corticospinal tract, MD). The On-line Table lists the results of group comparisons. Only regions in which the parameters showed a significant increase or decrease or altered tendency are shown, and only significant P values with an underlying normal distribution are reported. DTI. Rater 2 found that FA was reduced in the left OR of patients with NMO compared with controls (P.05). Both raters found that MD was increased (P.05) in the genu of the CC in patients with NMO. RD and AD were increased in the same regions (P.05). DKI. In patients with NMO, both raters found that MK was decreased in the left OR (P.05). Rater 1 found that MK was increased (P.05) in the corticospinal tract of the right peduncle, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :
4 whereas rater 2 observed only a tendency of increase (P.056) compared with controls. Both raters found that RK was decreased in the left OR (P.05). Rater 1 found that RK was decreased in the CC splenium (P.05), whereas rater 2 found the same result in the genu of the CC (P.05). No significant alterations in AK were observed. Correlation between DTI and DKI Parameters Based on Region-of-Interest Analysis Strong negative correlations were found in the genu and splenium of the CC between RK and MK (r 0.709, P.0001 and r 0.881, P.0001, respectively) and between MD and RD (r 0.752, P.0001 and r 0.821, P.0001, respectively). There was a moderate negative correlation between AK and AD in the bilateral ORs (r 0.523, P.006 and r 0.584, P.002, respectively). A moderate positive correlation was found between FA and MK in the genu and splenium of the CC (r 0.549, P.003 and r 0.677, P.0001, respectively). A strong positive correlation was found between FA and RK in the splenium of the CC (r 0.763, P.0001), and a moderate positive correlation was found in the genu of the CC and the left OR (r 0.673, P.0001 and r P.001, respectively). FA and AK were not correlated significantly. FIG 2. TBSS analysis. Significance P maps, corrected for multiple comparison, for DTI and DKI parameters are overlaid color-coded on the skeleton and mean FA image. In green, the mean FA skeleton, where statistical analysis was performed. The following areas are significantly reduced in patients with NMO compared with controls: FA (red-yellow) and RK (blue), or significantly higher, MD (yellow), AD (red), RD (blue). DISCUSSION In this study, we analyzed the WM in patients with NMO compared with healthy controls by applying the novel DKI technique, by using both TBSS (which requires no a priori hypothesis) and a region-of-interest-driven approach (which uses an a priori hypothesis). Within TBSS, several DTI and DKI parameters were altered significantly in extensive WM tracts, but the only kurtosis parameter that was altered significantly was RK. Within the region-of-interest analysis, the DTI parameters FA, MD, RD, and AD showed significant alterations in some ROIs. The kurtosis parameters RK and MK were altered significantly. Negative correlations were found between several kurtosis and diffusion parameters. A decrease of RK corroborates the presence of demyelination. 14 Lopes et al 4 previously found significant changes of DTI parameters by a Interrater reliability test for ROI-based analysis a CC Genu CC Splenium OR R OR L CST R CST L Interpretation FA Excellent MD Good AD Acceptable RD Questionable MK Poor AK Unacceptable RK Note: CST indicates corticospinal tract; R, right; L, left. a The Cronbach for each ROI, DTI, and DKI parameter is listed. 4 Doring
5 TBSS analysis in patients with NMO. They observed significant reductions in FA in the CC, ORs, internal and external capsules, corona radiata, and cerebral peduncles and significant increases in RD in the CC, corona radiata, and centrum semiovale. They also found a highly significant negative correlation between FA and RD (r 0.976, P.0001). In the present study, we found a significant FA reduction in those regions, except for the corticospinal tract in the cerebral peduncles. We detected a significant increase in RD in the CC, corona radiata, and centrum semiovale. We found a strong negative correlation between FA and RD in all ROIs, except in the left OR, in which the correlation was moderate and negative. We found a strong positive correlation between FA and RK in the splenium of the CC and moderate positive correlations in the genu of the CC and the left OR. These findings support the hypothesis that the WM damage in patients with NMO is more related to demyelination (RK) than axonal degeneration (AK). This hypothesis was previously stressed in histologic studies, 19,20 which showed that the demyelination process could take place even before axonal death. 20 Cheung et al 14 demonstrated that RK is highly sensitive to brain maturation due to myelination and, therefore, to its inverse effect, demyelination. Myelin sheath reduction increases the possibility of water diffusion in a direction perpendicular to the nerve fibers, thereby increasing RD and decreasing RK. We observed a significant decrease in RK in the CC and ORs (P.028 and P.011 for raters 1 and 2, respectively, by region-of-interest analysis; P.1 by TBSS). The observed strong negative correlation between RK and RD in the genu and splenium of the CC supports the hypothesis that demyelination is related to a decreased RK and increased RD. Furthermore, MK was increased in the corticospinal tract at the peduncle (P.047 and P.56 by raters 1 and 2, respectively; there was no TBSS result in this area) (without representation on MD maps). This finding might be related to an initial inflammatory process in which high cellularity could restrict overall diffusion, with the diffusion distribution becoming more non-gaussian and the MK increasing. Recently, Lättetal 15 provided estimates of DKI for various cerebral regions in healthy brains and compared them with DTI parameters. They found a strong positive correlation between MK and FA in WM (r 0.81, P 10 5 ) and a strong negative correlation between RK and RD (r 0.95, P 10 5 ). In the present study, we found a moderate positive correlation between MK and FA and a strong negative correlation between RK and RD in the splenium and genu of the CC. Our study had some limitations. During the skull-stripping process by the DKI software, regions in the cerebral peduncle were misclassified as skull in some subjects. In TBSS, after averaging the subject s images to generate a mean FA image, black regions appeared in some cases, and cross-subject statistical analysis was compromised. Unfortunately, the sensibility threshold that determines the degree of skull-stripping was not adjustable within the software version used to reconstruct the DT and DK parametric maps. This aspect of the TBSS analysis might explain why TBSS was unable to detect the significant increase of MK in the right corticospinal tract in the cerebral peduncle. Another limitation may be the incorrect placements of ROIs during region-of-interest-driven analysis. However, we included this analysis because it is based on a priori data and allowed the comparison with results of previous studies because a TBSS analysis of DKI had not been performed to date, to our knowledge. Moreover, the results of the region-of-interest analysis could verify the TBSS results. The limitation of the region-of-interest analysis (lack of multiple-comparison correction) was overcome by the TBSS analysis by doing a family-wise error multiple comparison correction. Another limitation was the suboptimal acquisition resulting from the sequence applied, which consisted of b-values of only 1 b 0, 30 b 1000, and 30 b Noise is a general problem in diffusion MR imaging acquisitions, and its effects have been investigated extensively. 21 Using higher b-values in DKI acquisitions increases the sensitivity of the measurement to noise and, therefore, the possibility that the diffusion and kurtosis parameter estimates will vary from their true values, causing erroneous inferences. A better understanding of the effects of noise on DKI would be helpful in interpreting DKI results. Finally, because NMO is an uncommon disease, the patient population is quite heterogeneous when considering clinical data and treatment options; this heterogeneity is another limitation to our study, and these findings should be replicated in a different group to validate our results. CONCLUSIONS This study demonstrated significant differences in diffusion and kurtosis parameters in patients with NMO compared with healthy controls. Conventional diffusion parameters such as FA, MD, RD, and AD were more sensitive to the disease than kurtosis parameters. Only RK was significantly reduced, while MK presented a reduction tendency. AK did not show alterations. Kurtosis parameters were inversely correlated with the corresponding diffusion parameters. RK and MK correlated positively with FA. Further studies are necessary to prove the benefit of DKI parameters as biomarkers for patients with NMO. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors would like to thank Dr Ali Tabesh for his technical assistance. REFERENCES 1. Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Pittock SJ, et al. Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2006;66: Aboul-Enein F, Krssák M, Höftberger R, et al. Diffuse white matter damage is absent in neuromyelitis optica. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010;31: Pires CE, da Silva CMC, Lopes CRF, et al. Brain MRI abnormalities in Brazilian patients with neuromyelitis optica. J Clin Neurosci 2012; 19: Lopes CRF, Doring TM, Martins C, et al. The role of demyelination in neuromyelitis optica damage: diffusion tensor MR imaging study. Radiology 2012;263: Rueda-Lopes CR, da Cruz LC, Doring TM, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging and demyelinating diseases: new aspects of an old advanced sequence. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2014;202:W Tabesh A, Jensen JH, Ardekani BA, et al. Estimation of tensors and tensor-derived measures in diffusional kurtosis imaging. Magn Reson Med 2011;65: AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :
6 7. Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, et al. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 2005; 53: Lu H, Jensen JH, Ramani A, et al. Three-dimensional characterization of non-gaussian water diffusion in humans using diffusion kurtosis imaging. NMR Biomed 2006;19: Jensen JH, Helpern JA. MRI quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis. NMR Biomed 2010;23: Lazar M, Jensen JH, Xuan L, et al. Estimation of the orientation distribution function from diffusional kurtosis imaging. Magn Reson Med 2008;60: Tuch DS, Reese TG, Wiegell MR, et al. Diffusion MRI of complex neural architecture. Neuron 2003;40: Tuch DS. Q-ball imaging. Magn Reson Med 2004;52: Hui ES, Cheung MM, Qi L, et al. Towards better MR characterization of neural tissues using directional diffusion kurtosis analysis. Neuroimage 2008;42: Cheung MM, Hui ES, Chan KC, et al. Does diffusion kurtosis imaging lead to better neural tissue characterization? A rodent brain maturation study. Neuroimage 2009;45: Lätt J, Nilsson M, Wirestam R, et al. Regional values of diffusional kurtosis estimates in the healthy brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 2013;37: Fung SH, Roccatagliata L, Gonzalez RG, et al. MR diffusion imaging in ischemic stroke. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2011;21:345 77, xi 17. Van Cauter S, Veraart J, Sijbers J, et al. Gliomas: diffusion kurtosis MR imaging in grading. Radiology 2012;263: Smith SM, Johansen-Berg H, Jenkinson M, et al. Acquisition and voxelwise analysis of multi subject diffusion data with tract-based spatial statistics. Nat Protoc 2007;2: Lucchinetti CF, Mandler RN, McGavern D, et al. A role for humoral mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Devic s neuromyelitis optica. Brain 2002;125(pt 7): Marignier R, Nicolle A, Watrin C, et al. Oligodendrocytes are damaged by neuromyelitis optica immunoglobulin G via astrocyte injury. Brain 2010;133: Farrell JA, Landman BA, Jones CK, et al. Effects of signal-to noise ratio on the accuracy and reproducibility of diffusion tensor imaging-derived fractional anisotropy, mean diffusivity, and principal eigenvector measurements at 1.5T. J Magn Reson Imaging 2007;26: Doring
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging: An Emerging Technique for Evaluating the Microstructural Environment of the Brain
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Review Steven et al. Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging of the Brain Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Review FOCUS ON: Andrew J. Steven 1 Jiachen Zhuo Elias R. Melhem Steven
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Review Steven et al. Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging of the Brain Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Review FOCUS ON: Andrew J. Steven 1 Jiachen Zhuo Elias R. Melhem Steven
Summary of findings from the previous meta-analyses of DTI studies in MDD patients. SDM (39) 221 Left superior longitudinal
 Supplemental Data Table S1 Summary of findings from the previous meta-analyses of DTI studies in MDD patients Study Analysis Method Included studies, n MDD (medicated) HC Results (MDDHC)
Supplemental Data Table S1 Summary of findings from the previous meta-analyses of DTI studies in MDD patients Study Analysis Method Included studies, n MDD (medicated) HC Results (MDDHC)
Overview. Fundamentals of functional MRI. Task related versus resting state functional imaging for sensorimotor mapping
 Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Kurtosis is a descriptor of the peakedness of a variable relative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016)
 International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography
 Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
Fibre orientation dispersion in the corpus callosum relates to interhemispheric functional connectivity
 Fibre orientation dispersion in the corpus callosum relates to interhemispheric functional connectivity ISMRM 2017: http://submissions.mirasmart.com/ismrm2017/viewsubmissionpublic.aspx?sei=8t1bikppq Jeroen
Fibre orientation dispersion in the corpus callosum relates to interhemispheric functional connectivity ISMRM 2017: http://submissions.mirasmart.com/ismrm2017/viewsubmissionpublic.aspx?sei=8t1bikppq Jeroen
Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic?
 Current Literature In Clinical Science Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic? Spatial Patterns of Water Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
Current Literature In Clinical Science Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic? Spatial Patterns of Water Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
Research Article Corticospinal Tract Change during Motor Recovery in Patients with Medulla Infarct: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 524096, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/524096 Research Article Corticospinal Tract Change during Motor Recovery in Patients with Medulla Infarct: A Diffusion
BioMed Research International, Article ID 524096, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/524096 Research Article Corticospinal Tract Change during Motor Recovery in Patients with Medulla Infarct: A Diffusion
The potential role of novel diffusion imaging techniques in the understanding and treatment of epilepsy
 Review Article The potential role of novel diffusion imaging techniques in the understanding and treatment of epilepsy Gavin P. Winston 1,2 1 Epilepsy Society MRI Unit, Chesham Lane, Chalfont St Peter,
Review Article The potential role of novel diffusion imaging techniques in the understanding and treatment of epilepsy Gavin P. Winston 1,2 1 Epilepsy Society MRI Unit, Chesham Lane, Chalfont St Peter,
Post Stroke Brain Plasticity
 Post Stroke Brain Plasticity François CHOLLET MD, PhD Neurology Department: Stroke Unit Toulouse University Hospital (CHU) Neurosciences Institute of Toulouse CNRS, INSERM, University, CHU Versailles le
Post Stroke Brain Plasticity François CHOLLET MD, PhD Neurology Department: Stroke Unit Toulouse University Hospital (CHU) Neurosciences Institute of Toulouse CNRS, INSERM, University, CHU Versailles le
SCA is a hereditary red blood cell disorder that is characterized
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH B. Sun R.C. Brown L. Hayes T.G. Burns J. Huamani D.J. Bearden R.A. Jones EBM2 White Matter Damage in Asymptomatic Patients with Sickle Cell Anemia: Screening with Diffusion Tensor Imaging
ORIGINAL RESEARCH B. Sun R.C. Brown L. Hayes T.G. Burns J. Huamani D.J. Bearden R.A. Jones EBM2 White Matter Damage in Asymptomatic Patients with Sickle Cell Anemia: Screening with Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury
 Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury Stéphane Sizonenko, MD-PhD Division of Development and Growth Department of Child and Adolescent Medicine Geneva University
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury Stéphane Sizonenko, MD-PhD Division of Development and Growth Department of Child and Adolescent Medicine Geneva University
Heidi M. Feldman, MD, PhD,* Jason D. Yeatman, BA, Eliana S. Lee, BS,* Laura H. F. Barde, PhD,* Shayna Gaman-Bean, MD*
 Review Article Diffusion Tensor Imaging: A Review for Pediatric Researchers and Clinicians Heidi M. Feldman, MD, PhD,* Jason D. Yeatman, BA, Eliana S. Lee, BS,* Laura H. F. Barde, PhD,* Shayna Gaman-Bean,
Review Article Diffusion Tensor Imaging: A Review for Pediatric Researchers and Clinicians Heidi M. Feldman, MD, PhD,* Jason D. Yeatman, BA, Eliana S. Lee, BS,* Laura H. F. Barde, PhD,* Shayna Gaman-Bean,
During human aging, the brain exhibits both macro- and
 Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Sjögren syndrome is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease. White Matter Water Diffusion Changes in Primary Sjögren Syndrome ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN White Matter Water Diffusion Changes in Primary Sjögren Syndrome L.C. Tzarouchi, A.K. Zikou, N. Tsifetaki, L.G. Astrakas, S. Konitsiotis, P. Voulgari, A. Drosos, and M.I. Argyropoulou
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN White Matter Water Diffusion Changes in Primary Sjögren Syndrome L.C. Tzarouchi, A.K. Zikou, N. Tsifetaki, L.G. Astrakas, S. Konitsiotis, P. Voulgari, A. Drosos, and M.I. Argyropoulou
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection. Page inserted by evaluation version
 PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive
 Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 August 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 August ; 143(2): 304 306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.012. Application of diffusion tensor imaging
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 August ; 143(2): 304 306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.012. Application of diffusion tensor imaging
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS
 Anvita Bieza FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS Summary of Doctoral Thesis to obtain PhD degree in medicine Specialty Diagnostic Radiology Riga, 2013 Doctoral thesis
Anvita Bieza FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS Summary of Doctoral Thesis to obtain PhD degree in medicine Specialty Diagnostic Radiology Riga, 2013 Doctoral thesis
Stroke Assessment With Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging
 Stroke Assessment With Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Edward S. Hui, PhD; Els Fieremans, PhD; Jens H. Jensen, PhD; Ali Tabesh, PhD; Wuwei Feng, MD, MS; Leonardo Bonilha, MD, PhD; Maria V. Spampinato, MD;
Stroke Assessment With Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Edward S. Hui, PhD; Els Fieremans, PhD; Jens H. Jensen, PhD; Ali Tabesh, PhD; Wuwei Feng, MD, MS; Leonardo Bonilha, MD, PhD; Maria V. Spampinato, MD;
Stereotactic Diffusion Tensor Tractography For Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Diffusion Tensor Imaging 12/06/2013
 12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
Disclosure Information AACPDM 68 th Annual Meeting September 10-13, 2014 Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Analysis options in pediatric neuroimaging research
 Disclosure Information AACPDM 68 th Annual Meeting September 10-13, 2014 Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Analysis options in pediatric neuroimaging research Andrea Poretti, MD Research Associate Section of Pediatric
Disclosure Information AACPDM 68 th Annual Meeting September 10-13, 2014 Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Analysis options in pediatric neuroimaging research Andrea Poretti, MD Research Associate Section of Pediatric
Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
C ognitive and vocational sequelae are common complications
 850 PAPER Evidence for white matter disruption in traumatic brain injury without macroscopic lesions N Nakayama, A Okumura, J Shinoda, Y-T Yasokawa, K Miwa, S-I Yoshimura, T Iwama... J Neurol Neurosurg
850 PAPER Evidence for white matter disruption in traumatic brain injury without macroscopic lesions N Nakayama, A Okumura, J Shinoda, Y-T Yasokawa, K Miwa, S-I Yoshimura, T Iwama... J Neurol Neurosurg
doi: /brain/awq347 Brain 2011: 134; White matter damage and cognitive impairment after traumatic brain injury
 doi:10.1093/brain/awq347 Brain 2011: 134; 449 463 449 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY White matter damage and cognitive impairment after traumatic brain injury Kirsi Maria Kinnunen, 1 Richard Greenwood, 2
doi:10.1093/brain/awq347 Brain 2011: 134; 449 463 449 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY White matter damage and cognitive impairment after traumatic brain injury Kirsi Maria Kinnunen, 1 Richard Greenwood, 2
HIV infections around the world are increasing constantly. 1
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PEDIATRICS White Matter Development is Potentially Influenced in Adolescents with Vertically Transmitted HIV Infections: A Tract-Based Spatial Statistics Study X J. Li, G. Wu, Z. Wen,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PEDIATRICS White Matter Development is Potentially Influenced in Adolescents with Vertically Transmitted HIV Infections: A Tract-Based Spatial Statistics Study X J. Li, G. Wu, Z. Wen,
DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy
 DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy Poster No.: C-2328 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors:
DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy Poster No.: C-2328 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors:
Parameters of diffusional kurtosis imaging for the diagnosis of acute cerebral infarction in different brain regions
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 12: 933-938, 2016 Parameters of diffusional kurtosis imaging for the diagnosis of acute cerebral infarction in different brain regions YUE LIN GUO 1, SU JUAN LI 1,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 12: 933-938, 2016 Parameters of diffusional kurtosis imaging for the diagnosis of acute cerebral infarction in different brain regions YUE LIN GUO 1, SU JUAN LI 1,
Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension pathogenesis?: Diffusion weighted MR imaging study
 Available online at www.medicinescience.org ORIGINAL RESEARCH Medicine Science International Medical Journal Medicine Science 2019; ( ): Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Available online at www.medicinescience.org ORIGINAL RESEARCH Medicine Science International Medical Journal Medicine Science 2019; ( ): Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry
 2003 KHBM DTI in Psychiatry Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry KHBM 2003. 11. 21. 서울대학교 의과대학 정신과학교실 권준수 Neuropsychiatric conditions DTI has been studied in Alzheimer s disease Schizophrenia Alcoholism
2003 KHBM DTI in Psychiatry Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry KHBM 2003. 11. 21. 서울대학교 의과대학 정신과학교실 권준수 Neuropsychiatric conditions DTI has been studied in Alzheimer s disease Schizophrenia Alcoholism
ajnr am j. neuroradiol apr; 28(4):
 ajnr am j. neuroradiol. 2007 apr; 28(4): 724-30 7 Diffusion tensor imaging-based fractional anisotropy quantification in the corticospinal tract of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using a probabilistic
ajnr am j. neuroradiol. 2007 apr; 28(4): 724-30 7 Diffusion tensor imaging-based fractional anisotropy quantification in the corticospinal tract of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using a probabilistic
Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) comprise
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.M. de Souza R.C. Domingues L.C.H. Cruz, Jr. F.S. Domingues T. Iasbeck E.L. Gasparetto Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for the Evaluation of Patients with Familial Cerebral Cavernous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.M. de Souza R.C. Domingues L.C.H. Cruz, Jr. F.S. Domingues T. Iasbeck E.L. Gasparetto Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for the Evaluation of Patients with Familial Cerebral Cavernous
The Optimal Trackability Threshold of Fractional Anisotropy for DiŠusion Tensor Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract
 Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 1, p. 11 17, 2004 MAJOR PAPER The Optimal Trackability Threshold of Fractional Anisotropy for DiŠusion Tensor Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract
Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 1, p. 11 17, 2004 MAJOR PAPER The Optimal Trackability Threshold of Fractional Anisotropy for DiŠusion Tensor Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract
Mild traumatic brain injury is one of the most significant
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Cognitive Impairment in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Longitudinal Diffusional Kurtosis and Perfusion Imaging Study E.J. Grossman, J.H. Jensen, J.S. Babb, Q. Chen, A. Tabesh, E.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Cognitive Impairment in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Longitudinal Diffusional Kurtosis and Perfusion Imaging Study E.J. Grossman, J.H. Jensen, J.S. Babb, Q. Chen, A. Tabesh, E.
Diffusion-Tensor Imaging Assessment of White Matter Maturation in Childhood and Adolescence
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Moon et al. White Matter Diffusion-Tensor Imaging Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Won-Jin Moon 1 James M. Provenzale 2,3 Basar
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Moon et al. White Matter Diffusion-Tensor Imaging Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Won-Jin Moon 1 James M. Provenzale 2,3 Basar
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis
 Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
The clinical pathology underlying TBI-related impairment is
 Published January 10, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3395 REVIEW ARTICLE A Decade of DTI in Traumatic Brain Injury: 10 Years and 100 Articles Later M.B. Hulkower, D.B. Poliak, S.B. Rosenbaum, M.E. Zimmerman, and
Published January 10, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3395 REVIEW ARTICLE A Decade of DTI in Traumatic Brain Injury: 10 Years and 100 Articles Later M.B. Hulkower, D.B. Poliak, S.B. Rosenbaum, M.E. Zimmerman, and
Professional boxing is a controversial sport, and research
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis. Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis by Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis by Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT
The Effect of Local Fiber Model On Population Studies
 The Effect of Local Fiber Model On Population Studies James G. Malcolm Marek Kubicki Martha E. Shenton Yogesh Rathi Psychiatry Neuroimaging Laboratory, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA VA Boston Healthcare
The Effect of Local Fiber Model On Population Studies James G. Malcolm Marek Kubicki Martha E. Shenton Yogesh Rathi Psychiatry Neuroimaging Laboratory, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA VA Boston Healthcare
Diffusion Tensor Imaging Assessment of Brain White Matter Maturation During the First Postnatal Year
 DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
White matter integrity of the cerebellar peduncles as a mediator of effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on eyeblink conditioning
 White matter integrity of the cerebellar peduncles as a mediator of effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on eyeblink conditioning Jia Fan 1,2, Sandra W. Jacobson 2-3,5, Christopher D. Molteno 3, Bruce
White matter integrity of the cerebellar peduncles as a mediator of effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on eyeblink conditioning Jia Fan 1,2, Sandra W. Jacobson 2-3,5, Christopher D. Molteno 3, Bruce
Published May 14, 2015 as /ajnr.A4311
 Published May 14, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4311 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ADULT BRAIN Mean Diffusional Kurtosis in Patients with Glioma: Initial Results with a Fast Imaging Method in a Clinical Setting A. Tietze,
Published May 14, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4311 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ADULT BRAIN Mean Diffusional Kurtosis in Patients with Glioma: Initial Results with a Fast Imaging Method in a Clinical Setting A. Tietze,
Brain diffusion tensor imaging changes in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis reversed with
 Brain diffusion tensor imaging changes in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis reversed with treatment Claudia B. Catarino, MD, PhD, 1*, Christian Vollmar, MD, PhD, 2,3* Clemens Küpper, MD, 1,4 Klaus Seelos,
Brain diffusion tensor imaging changes in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis reversed with treatment Claudia B. Catarino, MD, PhD, 1*, Christian Vollmar, MD, PhD, 2,3* Clemens Küpper, MD, 1,4 Klaus Seelos,
Group-Wise FMRI Activation Detection on Corresponding Cortical Landmarks
 Group-Wise FMRI Activation Detection on Corresponding Cortical Landmarks Jinglei Lv 1,2, Dajiang Zhu 2, Xintao Hu 1, Xin Zhang 1,2, Tuo Zhang 1,2, Junwei Han 1, Lei Guo 1,2, and Tianming Liu 2 1 School
Group-Wise FMRI Activation Detection on Corresponding Cortical Landmarks Jinglei Lv 1,2, Dajiang Zhu 2, Xintao Hu 1, Xin Zhang 1,2, Tuo Zhang 1,2, Junwei Han 1, Lei Guo 1,2, and Tianming Liu 2 1 School
Master of Science Thesis in Medical Radiation Physics. Improved analysis of MRI tractography data: Group comparisons of parameters along fibre tracks
 Master of Science Thesis in Medical Radiation Physics Improved analysis of MRI tractography data: Group comparisons of parameters along fibre tracks Supervisors: Jimmy Lätt and Markus Nilsson Medical Radiation
Master of Science Thesis in Medical Radiation Physics Improved analysis of MRI tractography data: Group comparisons of parameters along fibre tracks Supervisors: Jimmy Lätt and Markus Nilsson Medical Radiation
The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry
 WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
Diffusion tensor imaging of the infant brain: From technical problems to neuroscientific breakthroughs Jessica Dubois
 Diffusion tensor imaging of the infant brain: From technical problems to neuroscientific breakthroughs Jessica Dubois L. Hertz-Pannier, G. Dehaene-Lambertz, J.F. Mangin, D. Le Bihan Inserm U56, U663; NeuroSpin
Diffusion tensor imaging of the infant brain: From technical problems to neuroscientific breakthroughs Jessica Dubois L. Hertz-Pannier, G. Dehaene-Lambertz, J.F. Mangin, D. Le Bihan Inserm U56, U663; NeuroSpin
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology
 Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) WCPCG 2014
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
Research Article Cognitive Intraindividual Variability and White Matter Integrity in Aging
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 350623, 16 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/350623 Research Article Cognitive Intraindividual Variability and White
Hindawi Publishing Corporation The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 350623, 16 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/350623 Research Article Cognitive Intraindividual Variability and White
Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Yu Zhang, Katherine Wu, Shannon Buckley, Norbert Schuff On behalf of the Parkinson
Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Yu Zhang, Katherine Wu, Shannon Buckley, Norbert Schuff On behalf of the Parkinson
Fig.1: A, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a
 Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Diffusion tensor imaging detects Wallerian degeneration of the corticospinal tract early after cerebral infarction**
 NEUAL EGENEATION ESEACH Volume 7, Issue 12, April 2012 www.nrronline.org Cite this article as: Neural egen es. 2012;7(12):900-905. Diffusion tensor imaging detects Wallerian degeneration of the corticospinal
NEUAL EGENEATION ESEACH Volume 7, Issue 12, April 2012 www.nrronline.org Cite this article as: Neural egen es. 2012;7(12):900-905. Diffusion tensor imaging detects Wallerian degeneration of the corticospinal
Multiple sclerosis (MS) generally begins in the second-tothird
 Published October 22, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1776 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.S. Vishwas T. Chitnis R. Pienaar B.C. Healy P.E. Grant Tract-Based Analysis of Callosal, Projection, and Association Pathways in Pediatric
Published October 22, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1776 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.S. Vishwas T. Chitnis R. Pienaar B.C. Healy P.E. Grant Tract-Based Analysis of Callosal, Projection, and Association Pathways in Pediatric
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Brain MRI findings in patients at our institution and literature review.
 Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Brain MRI findings in patients at our institution and literature review. Poster No.: C-0817 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. I. MICHELIN,
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Brain MRI findings in patients at our institution and literature review. Poster No.: C-0817 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. I. MICHELIN,
Modeling of early-infant brain growth using longitudinal data from diffusion tensor imaging.
 Modeling of early-infant brain growth using longitudinal data from diffusion tensor imaging. Guido Gerig, Neda Sadeghi, PhD, Marcel Prastawa, Tom Fletcher, Clement Vachet Scientific Computing and Imaging
Modeling of early-infant brain growth using longitudinal data from diffusion tensor imaging. Guido Gerig, Neda Sadeghi, PhD, Marcel Prastawa, Tom Fletcher, Clement Vachet Scientific Computing and Imaging
Diffusion tensor imaging: serial quantitation of white matter tract maturity in premature newborns $
 Diffusion tensor imaging: serial quantitation of white matter tract maturity in premature newborns $ Savannah C. Partridge, a Pratik Mukherjee, a Roland G. Henry, a Steven P. Miller, b,c Jeffrey I. Berman,
Diffusion tensor imaging: serial quantitation of white matter tract maturity in premature newborns $ Savannah C. Partridge, a Pratik Mukherjee, a Roland G. Henry, a Steven P. Miller, b,c Jeffrey I. Berman,
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
ALS is a chronic neurodegenerative disease that selectively
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Carrara C. Carapelli F. Venturi M.M. Ferraris L. Lequio A. Chiò A. Calvo S. Sirgiovanni A. Cistaro M.C. Valentini A Distinct MR Imaging Phenotype in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Carrara C. Carapelli F. Venturi M.M. Ferraris L. Lequio A. Chiò A. Calvo S. Sirgiovanni A. Cistaro M.C. Valentini A Distinct MR Imaging Phenotype in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis:
NeuroImage. A study of diffusion tensor imaging by tissue-specific, smoothing-compensated voxel-based analysis
 NeuroImage 44 (2009) 870 883 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect NeuroImage journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ynimg A study of diffusion tensor imaging by tissue-specific, smoothing-compensated
NeuroImage 44 (2009) 870 883 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect NeuroImage journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ynimg A study of diffusion tensor imaging by tissue-specific, smoothing-compensated
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is a major consequence
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Assaf L. Ben-Sira S. Constantini L.C. Chang L. Beni-Adani Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Hydrocephalus: Initial Experience PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is an
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Assaf L. Ben-Sira S. Constantini L.C. Chang L. Beni-Adani Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Hydrocephalus: Initial Experience PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is an
Diffusion Tensor Metrics as Biomarkers in Alzheimer s Disease
 Diffusion Tensor Metrics as Biomarkers in Alzheimer s Disease Julio Acosta-Cabronero 1 *, Stephanie Alley 2, Guy B. Williams 3, George Pengas 1, Peter J. Nestor 1,4 1 Cognition, Memory and Language Group,
Diffusion Tensor Metrics as Biomarkers in Alzheimer s Disease Julio Acosta-Cabronero 1 *, Stephanie Alley 2, Guy B. Williams 3, George Pengas 1, Peter J. Nestor 1,4 1 Cognition, Memory and Language Group,
Traumatic axonal injury is a frequent cause of impaired clinical
 Published July 10, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1213 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.R. Rutgers P. Fillard G. Paradot M. Tadié P. Lasjaunias D. Ducreux Diffusion Tensor Imaging Characteristics of the Corpus Callosum in Mild,
Published July 10, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1213 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.R. Rutgers P. Fillard G. Paradot M. Tadié P. Lasjaunias D. Ducreux Diffusion Tensor Imaging Characteristics of the Corpus Callosum in Mild,
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a motor neuron disease
 ORIGINL RESERCH S. Ngai Y.M. Tang L. Du S. Stuckey Hyperintensity of the Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter and Hypointensity of the Precentral Gyrus on Fluid-ttenuated Inversion Recovery: Variation
ORIGINL RESERCH S. Ngai Y.M. Tang L. Du S. Stuckey Hyperintensity of the Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter and Hypointensity of the Precentral Gyrus on Fluid-ttenuated Inversion Recovery: Variation
An Atlas of Brainstem Connectomes from HCP Data
 An Atlas of Brainstem Connectomes from HCP Data Presented During: Poster Session Tuesday, June 27, 2017: 12:45 PM - 02:45 PM Stand-By Time Tuesday, June 27, 2017: 12:45 PM - 2:45 PM Submission No: 1653
An Atlas of Brainstem Connectomes from HCP Data Presented During: Poster Session Tuesday, June 27, 2017: 12:45 PM - 02:45 PM Stand-By Time Tuesday, June 27, 2017: 12:45 PM - 2:45 PM Submission No: 1653
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari
 Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study of Treatment-Naïve Adults with Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder
 Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study of Treatment-Naïve Adults with Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder Tiffany M. Chaim 1,2,3 *, Tianhao Zhang 4, Marcus V. Zanetti 1,2, Maria Aparecida da
Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study of Treatment-Naïve Adults with Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder Tiffany M. Chaim 1,2,3 *, Tianhao Zhang 4, Marcus V. Zanetti 1,2, Maria Aparecida da
WHAT DOES THE BRAIN TELL US ABOUT TRUST AND DISTRUST? EVIDENCE FROM A FUNCTIONAL NEUROIMAGING STUDY 1
 SPECIAL ISSUE WHAT DOES THE BRAIN TE US ABOUT AND DIS? EVIDENCE FROM A FUNCTIONAL NEUROIMAGING STUDY 1 By: Angelika Dimoka Fox School of Business Temple University 1801 Liacouras Walk Philadelphia, PA
SPECIAL ISSUE WHAT DOES THE BRAIN TE US ABOUT AND DIS? EVIDENCE FROM A FUNCTIONAL NEUROIMAGING STUDY 1 By: Angelika Dimoka Fox School of Business Temple University 1801 Liacouras Walk Philadelphia, PA
HAL author manuscript
 HAL author manuscript 1 Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry / Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery an Diffusion tensor imaging and voxel-based morphometry study in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis:
HAL author manuscript 1 Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry / Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery an Diffusion tensor imaging and voxel-based morphometry study in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis:
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cases with Visual Field Defect after Anterior Temporal Lobectomy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:797 803, April 2005 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cases with Visual Field Defect after Anterior Temporal Lobectomy Toshiaki Taoka, Masahiko Sakamoto, Satoru Iwasaki, Hiroyuki Nakagawa,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:797 803, April 2005 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cases with Visual Field Defect after Anterior Temporal Lobectomy Toshiaki Taoka, Masahiko Sakamoto, Satoru Iwasaki, Hiroyuki Nakagawa,
doi: /brain/awq175 Brain 2010: 133;
 doi:10.1093/brain/awq175 Brain 2010: 133; 2348 2364 2348 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY The structural plasticity of white matter networks following anterior temporal lobe resection Mahinda Yogarajah, 1
doi:10.1093/brain/awq175 Brain 2010: 133; 2348 2364 2348 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY The structural plasticity of white matter networks following anterior temporal lobe resection Mahinda Yogarajah, 1
DIFFUSION TENSOR IMAGING OF THE BRAIN IN TYPE 1 DIABETES
 DIFFUSION TENSOR IMAGING OF THE BRAIN IN TYPE 1 DIABETES Jo Ann V. Antenor-Dorsey, a Joshua S. Shimony, b *Tamara Hershey a-c Psychiatry, a Radiology, b and Neurology c Departments, Washington University
DIFFUSION TENSOR IMAGING OF THE BRAIN IN TYPE 1 DIABETES Jo Ann V. Antenor-Dorsey, a Joshua S. Shimony, b *Tamara Hershey a-c Psychiatry, a Radiology, b and Neurology c Departments, Washington University
Web Training Modules Module 13: MR Imaging for Brain Injuries
 Web Training Modules Module 13: MR Imaging for Brain Injuries 1 Introduction... 4 Mild Traumatic Brain Injuries... 5 Structural MRI... 5 Diffusion Tensor Imaging... 6 Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging... 11 Functional
Web Training Modules Module 13: MR Imaging for Brain Injuries 1 Introduction... 4 Mild Traumatic Brain Injuries... 5 Structural MRI... 5 Diffusion Tensor Imaging... 6 Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging... 11 Functional
What is DTI, its use in research and clinical practice, and its future potential
 NA-MIC What is DTI, its use in research and clinical practice, and its future potential Martin Styner with thanks to many, many people Departments of Computer Science and Psychiatry UNC Neurodevelopmental
NA-MIC What is DTI, its use in research and clinical practice, and its future potential Martin Styner with thanks to many, many people Departments of Computer Science and Psychiatry UNC Neurodevelopmental
Online supplement data :
 Online supplement data : ROI ROI name MNI coord (mm) HC>SZ HC>S ZR HC>P BP HC>P BPR Heritabil ity h^2 Heritability p-value MCP Middle cerebellar peduncle 0-41 -44 2.05 2.12 1.63 0.69 0.38 0.004473 PCT
Online supplement data : ROI ROI name MNI coord (mm) HC>SZ HC>S ZR HC>P BP HC>P BPR Heritabil ity h^2 Heritability p-value MCP Middle cerebellar peduncle 0-41 -44 2.05 2.12 1.63 0.69 0.38 0.004473 PCT
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis
 In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
A Comparative Evaluation of Voxel-based Spatial Mapping in Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 A Comparative Evaluation of Voel-based Spatial Mapping in Diffusion Tensor Imaging Ryan P. Cabeen 1, Mark E. Bastin 2, David H. Laidlaw 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Brown University, Providence,
A Comparative Evaluation of Voel-based Spatial Mapping in Diffusion Tensor Imaging Ryan P. Cabeen 1, Mark E. Bastin 2, David H. Laidlaw 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Brown University, Providence,
Stuttering Research. Vincent Gracco, PhD Haskins Laboratories
 Stuttering Research Vincent Gracco, PhD Haskins Laboratories Stuttering Developmental disorder occurs in 5% of children Spontaneous remission in approximately 70% of cases Approximately 1% of adults with
Stuttering Research Vincent Gracco, PhD Haskins Laboratories Stuttering Developmental disorder occurs in 5% of children Spontaneous remission in approximately 70% of cases Approximately 1% of adults with
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Original Article Artigo Original
 Original Article Artigo Original Itagiba VGA et al. Use of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of patterns of white matter involvement in patients with brain tumors: is it useful
Original Article Artigo Original Itagiba VGA et al. Use of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of patterns of white matter involvement in patients with brain tumors: is it useful
Activated Fibers: Fiber-centered Activation Detection in Task-based FMRI
 Activated Fibers: Fiber-centered Activation Detection in Task-based FMRI Jinglei Lv 1, Lei Guo 1, Kaiming Li 1,2, Xintao Hu 1, Dajiang Zhu 2, Junwei Han 1, Tianming Liu 2 1 School of Automation, Northwestern
Activated Fibers: Fiber-centered Activation Detection in Task-based FMRI Jinglei Lv 1, Lei Guo 1, Kaiming Li 1,2, Xintao Hu 1, Dajiang Zhu 2, Junwei Han 1, Tianming Liu 2 1 School of Automation, Northwestern
Water Diffusion Changes in Wallerian Degeneration and Their Dependence on White Matter Architecture
 NeuroImage 13, 1174 1185 (2001) doi:10.1006/nimg.2001.0765, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Water Diffusion Changes in Wallerian Degeneration and Their Dependence on White Matter Architecture
NeuroImage 13, 1174 1185 (2001) doi:10.1006/nimg.2001.0765, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Water Diffusion Changes in Wallerian Degeneration and Their Dependence on White Matter Architecture
Advanced multimodal imaging in malformations of cortical development
 Advanced multimodal imaging in malformations of cortical development Seok Jun Hong (sjhong@bic.mni.mcgill.ca) NOEL Neuroimaging of Epilepsy Lab MICA Multimodal Imaging and Connectome Analysis Lab w4 w5
Advanced multimodal imaging in malformations of cortical development Seok Jun Hong (sjhong@bic.mni.mcgill.ca) NOEL Neuroimaging of Epilepsy Lab MICA Multimodal Imaging and Connectome Analysis Lab w4 w5
The corticospinal tract is a major neural tract for motor function
 Published January 31, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3389 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Different Characteristics of the Corticospinal Tract According to the Cerebral Origin: DTI Study J.P. Seo and S.H. Jang ABSTRACT
Published January 31, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3389 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Different Characteristics of the Corticospinal Tract According to the Cerebral Origin: DTI Study J.P. Seo and S.H. Jang ABSTRACT
Research Article Tract-Based Bayesian Multivariate Analysis of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
 Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 120182, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/120182 Research Article Tract-Based Bayesian Multivariate Analysis of Mild Traumatic Brain
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 120182, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/120182 Research Article Tract-Based Bayesian Multivariate Analysis of Mild Traumatic Brain
PRETERM BIRTH RESULTS IN ALTERATIONS IN NEURAL CONNECTIVITY AT AGE 16 YEARS
 Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Yale Medicine Thesis Digital Library School of Medicine 8-17-2010 PRETERM BIRTH RESULTS IN ALTERATIONS IN NEURAL CONNECTIVITY
Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Yale Medicine Thesis Digital Library School of Medicine 8-17-2010 PRETERM BIRTH RESULTS IN ALTERATIONS IN NEURAL CONNECTIVITY
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using Linear Discriminative Analysis and Quadratic Discriminative Analysis
 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST) ISSN: 2347-5552, Volume-2, Issue-6, November-2014 Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using
International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST) ISSN: 2347-5552, Volume-2, Issue-6, November-2014 Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation
 MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain
 DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
Leah Militello, class of 2018
 Leah Militello, class of 2018 Objectives 1. Describe the general organization of cerebral hemispheres. 2. Describe the locations and features of the different functional areas of cortex. 3. Understand
Leah Militello, class of 2018 Objectives 1. Describe the general organization of cerebral hemispheres. 2. Describe the locations and features of the different functional areas of cortex. 3. Understand
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
