The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page
|
|
|
- Dwain Davis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page The Role of Susceptibility Weighted Imaging (SWI) in Evaluation of Acute Stroke Maha Abdelhamed El Nouby*, Eman Ahmed Fouad Darwish, Eman Ahmed Shawky Geneidi Radiology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt *Corresponding author: Maha Abdelhamed El Nouby, Mobile: , ABSTRACT Background and Objectives: SWI provides information about blood oxygenation levels in intracranial vessels. Prior reports have shown that SWI focusing on venous drainage can provide noninvasive information about the degree of brain perfusion in arterialischemic stroke. We aimed to evaluate the influence of the SWI venous signal pattern in predicting stroke evolution. Materials and Methods: a semiquantitative analysis of venous signal intensity on SWI and diffusion characteristics on DTI was performed in 2o adult patients with acute stroke of MCA vascular territories. The mismatch between areas with SWI-hypointense venous signal and restricted diffusion was correlated with stroke progression on follow-up. Results: we included 2O patients with a confirmed diagnosis of arterial ischemic stroke. Follow-up images were available for. MCA stroke progression on follow-up was observed in 11/12 patient with DWI -SWI mismatch. Initial SWI hypointense venous signal and areas of restricted diffusion on DTI. This mismatch showed a statistically significant association (P _ ) for infarct progression. Conclusion: SWI-DWI mismatch predicts stroke progression in arterial ischemic stroke. Keywords: stroke, MRI, Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI), (PWI), DWI. INTRODUCTION A stroke is caused by the interruption of the blood supply to the brain, usually because a blood vessel bursts or is blocked by a clot. This cuts off the supply of oxygen and nutrients, causing damage to the brain tissue (1). The effects of a stroke depend on which part of the brain is injured and how severely it is affected. A very severe stroke can cause sudden death, so predicting the risk of further infarct growth in stroke patients is critical to therapeutic decision making (2). Contemporary therapy for acute ischemic stroke is based on the concept of penumbra, which is an area with reduced blood flow but not to such a level that causes irreversible cell membrane failure. Although challenged by several limitations, mismatch between larger abnormal areas on MR perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI) and smaller restricted areas on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a widely accepted approach to detecting penumbra, predicting stroke evolution and determining patients with the greatest potential to benefit from thrombolytic therapy. However, PWI requires administration of a contrast agent, which is contraindicated in a variety of clinical conditions, such as renal insufficiency and previous reactions to contrast agents (3). Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) which is a high-resolution, three-dimensional, gradient-echo T2* MR technique with enhanced sensitivity for paramagnetic substances is a potential alternative for detecting ischemic penumbra and thus predicting infarct growth. In the ischemic brain, the increased oxygen extraction fraction and slow flow contribute to a higher level of deoxyhemoglobin and vein dilatation, which increases the conspicuity of vessels on SWI. As a result, SWI can show asymmetric prominent hypointense vessels potentially from different concentrations of deoxyhemoglobin between ischemic and normal brain areas. This potential metabolic information on SWI may help to delineate penumbra without contrast agent administration (4). Recently, a study on pediatric arterial ischemic stroke has reported that SWI/DWI mismatch is useful in detecting penumbra in middle cerebral artery (MCA) infarct, thus predicting progression of infarction on follow-up images (5). AIM OF THE WORK This study aims to assess the diagnostic value of SWI-DWI mismatch in detecting ischemic penumbra, and predicting early infarct growth in patients with acute MCA territory ischemic stroke. PATIENTS AND METHODS Patients: During a period of 8 months duration from October 2017, twenty patients were enrolled in the study. All patients presented clinically with acute stroke. The study was approved by the Ethics Board of Ain Shams University and an informed written consent was taken from each participant in the study. Inclusion criteria: Patients with radiological evidence of acute non-lacunar ischemic infarct in the territory of the middle cerebral artery presenting within not less than 6 hours and not Received:21/6/2018 Accepted:30/6/
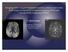
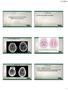
2 The Role of Susceptibility Weighted Imaging (SWI). more than 24 hours of symptom onset, both sexes were included, adults only (From 18 to 75 year old). Exclusion criteria: patients known to have contraindications for MRI, e.g. an implanted magnetic device, pacemakers or claustrophobia, patients potentially eligible for receiving RTP or thrombectomy (those presenting within 6 hours of symptom onset), patients with bad general condition needing life support, patients with hemorrhagic transformation of the infarction, Histopathological Analysis: the histology was reviewed by an experienced pathologist. MRI imaging: Selected patients were imaged by MRI stroke protocol which includes the following sequences: T1WI (Tr =120, Te = 21), T2WI (Tr = 5288, Te = 120), FLAIR (Tr = 1100/2800, Te = 130). DWI and ADC maps (Tr = 3580, Te = 112), MRA( Tr = 17, Te = 6.9). High resolution SWI sequence will be then be added with the following parameters: TR/TE 24/34, flip angle 10, Postprocessing will be performed and MIP images will be generated during the exam. Follow-up MR fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) and T2 weighted images will be obtained at least 7 days later if the patient s condition is stable or earlier if the clinical condition worsens for assessment of final infarct (FI) size. MRI data analysis: A 10- point semi-quantitative CT scoring system, Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) will be used to assess the extent of abnormal signal intensities on individual DWI, SWI, and follow up FLAIR images, for calculating ASPECTS values, 1 point is subtracted from 10 for each area of abnormal signal as follows, on DWI, 1 point will be subtracted from 10 for each area of infarction (which is defined as an area of high signal intensity on DWI with dark signal intensity on ADC), on SWI, 1 point will be subtracted from 10 for each area displaying asymmetric prominent vessels on SWI, defined as a local prominence of hypo intense vessels with either increased vessel number or diameter in the target area (MCA territory), when compared with the contralateral normal side. On follow up FLAIR images, 1 point will be subtracted from 10 for each area of hyperintensity. Statistical analysis: According to the relationship between ASPECTS values on initial DWI and FI studies, patients will be classified as infarct growth (IG) group (DWI > FI), non-infarct growth (NIG) group (DWI = FI), or DWI reversal group (DWI < FI). SWI-DWI Mismatches will be determined if DWI ASPECTS values is greater than SWI ASPECTS values, aspects values of different sequences will be compared to one another in each group and across different groups, aspect scores of different sequences will be compared to aspects scores of final infarct on follow up images as well as infarct growth, SWI-DWI mismatches will be compared to infarct growth, Statistical tests were used to determine statistically significant correlations and differences, results were displayed in form of tables and graphs. RESULTS Twenty-adult patients (11 females) were included in our study. The median age of patients was 57 years (range, 45 t0 74years), The average PSI (prediagnostic symptomatic interval) was 10 hours (range, 3 to 24 hour). None of the patients had acute thrombolytic therapy. Figure (1): The results of the semiquantitative evaluation of acute DTI, SWI, and T2 data are shown. Follow-up neuroimaging studies WITH T2 and FLAIR were available and were performed, on average 7 days after acute neuroimaging (range, 5 day to 14 days). In the acute neuroimaging studies, a mismatch between SWI and DWI was found in 12 patients (60%). The number of vascular territories with SWI-hypointense venous signal was greater than the number of vascular territories with restricted diffusion in 12 patients (60%) and equal in 8 patients (40%). In 8 patient (40%), the vascular territories with SWI-hypointense venous signal and restricted diffusion matched. A mismatch between SWI and ASL was found in 11patients (55%). In 1 patient, the vascular territories with SWI-hypointense venous signal and reduced perfusion matched perfectly. The results of the semiquantitative evaluation of acute DTI, SWI, and T2 /FLAIR data of 20 patients with a stroke 5399
3 Maha Abdelhamed El Nouby et al. within at least 1 of the 10 regions of the right MCA territory was found in17 patient (85%). Figure (2): Follow-up images were available for all patients included in the statistical analysis. A mismatch between SWI hypointense veins with vascular territories greater than those on DTI was found in12 patient, of which 11 patient showed infarct progression. A match between SWI hypointense veins with vascular territories was found in 8 patients. Figure (3): This mismatch between SWI and DTI was significantly associated with stroke progression on follow-up imaging (P _ ). Figure (4): Progression. Table (1): Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test Z Value P Value Significance DWI VS SWI S DWI VS T S SWI VS T2 * NS SWI VS T NS DISCUSSION SWI has been increasingly shown to be a useful non-contrast enhanced imaging sequence in the evaluation of acute stroke (5). SWI may do the following: Detect hemorrhagic components within infarcted tissue with higher sensitivity than other MR imaging sequences or imaging modalities (6). 1) Demonstrate hypointense signals in the veins draining hypoperfused areas and evaluate the ischemic penumbra by focusing on the venous drainage (7). 2) Show hyperintense signal in the veins draining regions of hyperperfusion or luxury perfusion indicating an increased risk of developing postischemic malignant edema (8). 3) Detect acute occlusive arterial thromboemboli (9). 4) Quantify microhemorrhages and predict hemorrhagic transformation before thrombolytic (10). Ischemic penumbra is characterized by hypoperfused brain tissue with the potential for functional recovery without morphologic damage (11). This is possible if local blood flow can be reestablished at a sufficient level within a certain time interval. The identification of the ischemic penumbra is important because it represents tissue that could potentially be salvaged with the use of thrombolytic therapy. Although the benefit of thrombolytic therapy in acute stroke has yet to be demonstrated in prospective clinical trials, retrospective studies show that at least a subset of patients with AIS may potentially benefit from it (12). Thrombolysis in Stroke trial. Ischemic penumbra can be depicted as a mismatch between reduced perfusion and normal diffusion by combining PWI and DWI/DTI.23. However, the routine application of PWI outside research protocols and tertiary care centers is still limited. DSC-PWI requires a rapid bolus injection of intravenous paramagnetic contrast agents that may delay acute antithrombotic therapy. ASL is a noncontrast-enhanced PWI method capable of measuring tissue perfusion by using blood as an endogenous contrast agent. ASL is not routinely performed in the acute setting because of the low SNR and limited spatial resolution. In addition, changes in signal intensity on ASL may be determined by factors other than reduced flow or ischemia, and knowledge of ASL-related artifacts is crucial for accurate interpretation (12). The relationship between CBF and the oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) has been shown in both animal stroke models and humans by using PET, 5400
4 The Role of Susceptibility Weighted Imaging (SWI). and 4 patterns have been observed in focal brain ischemia. In the first pattern, an increase in CBV was observed to maintain CBF in response to physiologic conditions or demands (autoregulation). The second pattern is an increase of OEF to maintain a stable cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) in response to a reduction of CBF. The third pattern is characterized by an increase of OEF in brain regions with reduction of both CBF andcmro2 and represents ischemic penumbra (13). The fourth pattern represents the infarct core and is characterized by very low CBF andcmro2 with poor OEF. SWI accentuates the magnetic susceptibility differences between deoxygenated hemoglobin in the vessels and adjacent oxygenated tissues and is an ideal MR imaging sequence to depict changes in OEF noninvasively. In a retrospective study including 15 adult patients with Non lacunar ischemic stroke, Kao et al. (14) showed that both SWIDWI and PWI (MTT)-DWI mismatches were significantly associated with a higher incidence of infarct progression and had a similar ability to predict stroke evolution. In addition, they showed that semiquantitative evaluation of SWI patterns and MTT values correlated best in the MCA territories. The authors concluded that SWI is an alternative to PWI to assess ischemic penumbra and predict stroke evolution. In children, the role of SWI in depicting the ischemic penumbra was previously shown only in a small case series and a few case reports (15). Also in aretro spective study including 24 children with acute non lacunar infarcts, Polan et al. (16) showed that SWI/DWI mismatch was significantly assosciated with higher incidence of infarcts progression. In our present study, we found a mismatch between vascular territories with SWIhypointense venous signal and restricted diffusion in 12 patients. In 11 of them, stroke progression was observed at follow up. By contrast, no stroke progression on follow-up was found in Patients without SWI-DTI mismatch. Our results show that a mismatch between vascular territories with SWIhypointense venous signal and restricted diffusion is significantly associated with infarct progression in acute stroke. Our present study had several limitations; The number of patients was still small, also, the study was retrospective; images were evaluated using a semi-quantitative approach (approximate measurements may be difficult to reproduce), the difference in slice thickness between DWI and minip SWI images may have caused partial misregistration, some patients with a serious acute ischemic stroke were uncooperative during the examination, and this led to some mobile false images and deviations in judgment, the scan time of SWI was long (5to 8 min), that some patients with serious clinical symptoms cannot remain stationary in the whole examination, it may produce some motion artifacts and then affected the image interpretation. CONCLUSION Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) which is a high-resolution, three-dimensional, gradient-echo T2* MR technique with enhanced sensitivity for paramagnetic substances is a potential alternative for detecting ischemic penumbra and thus predicting infarct growth. In the ischemic brain, the increased oxygen extraction fraction and slow flow contribute to a higher level of deoxyhemoglobin and vein dilatation, which increases the conspicuity of vessels on SWI. As a result, SWI can show asymmetric prominent hypointense vessels potentially from different concentrations of deoxyhemoglobin between ischemic and normal brain areas. This potential metabolic information on SWI may help to delineate penumbra without contrast agent administration. CONFLICTS OF INTEREST There are no conflicts of interest. REFERENCES 1. Cho KH, Kwon SU et al. (2012): An Early infarct growth predicts long-term clinical outcome after thrombolysis. J Neurol Sci., 316: Davis SM, Donnan GA and Butcher KS (2005): Selection of thrombolytic therapy beyond 3h using magnetic resonance imaging. Curr Opin Neurol., 18: Haacke EM, Xu Y and Cheng YC (2004): Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Magn Reson Med., 52: Tsui YK, Tsai FY and Hasso AN (2009): Susceptibility-weighted imaging for differential diagnosis of cerebral vascular pathology: a pictorial review. J Neurol Sci., 287:
5 Maha Abdelhamed El Nouby et al. 5. Meoded A, Poretti A, Benson JE et al. (2014): Evaluation of the ischemic penumbra focusing on the venous drainage: the role of susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) in pediatric ischemic cerebral stroke. Journal of Neuroradiology, 41(2): Wycliffe ND, Choe J, Holshouser B et al. (2004): Reliability in detection of hemorrhage in acute stroke by a new three-dimensional gradient recalled echo susceptibility weighted imaging technique compared to computed tomography: a retrospective study. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 20(3): Kesavadas C, Thomas B, Pendharakar H et al. (2011): Susceptibility weighted imaging: does it give information similar to perfusion weighted imaging in acute stroke?. Journal of Neurology, 258(5): Bosemani T, Poretti A, Orman G et al. (2013): Pediatric cerebral stroke: susceptibility-weighted imaging may predict post-ischemic malignant edema. The Neuroradiology Journal, 26(5): Mittal S, Wu Z, Neelavalli J et al. (2009): Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 2. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 30(2): Verschuuren S, Poretti A and Buerki S (2012): Susceptibility-weighted imaging of the pediatric brain. AJR Am J Roentgenol,198: W Bernard TJ, Rivkin MJ, Scholz K et al. (2014): Emergence of the primary pediatric stroke center: impact of the thrombolysis in pediatric stroke trial. Stroke, 45(7): Marecos C, Gunny R, Robinson R et al. (2015): Are children with acute arterial ischaemic stroke eligible for hyperacute thrombolysis? A retrospective audit from a tertiary UK centre. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, 57(2): Baron JC (1999): Mapping the ischaemic penumbra with PET: implications for acute stroke treatment. Cerebrovascular Diseases, 9(4): Kao HW, Tsai FY and Hasso AN (2012): Predicting stroke evolution: comparison of susceptibility-weighted MR imaging with MR perfusion. European Radiology, 22(7): Chalian M, Tekes A, Meoded A et al. (2011): Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI): a potential non-invasive imaging tool for characterizing ischemic brain injury?. Journal of Neuroradiology, 38(3): Polan RM, Poretti A, Huisman TA et al. (2015): Susceptibility-weighted imaging in pediatric arterial ischemic stroke: a valuable alternative for the noninvasive evaluation of altered cerebral hemodynamics. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 36:
Clinical applications of susceptibility weighted imaging in patients with major stroke
 J Neurol (2012) 259:1426 1432 DOI 10.1007/s00415-011-6369-2 ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Clinical applications of susceptibility weighted imaging in patients with major stroke Poyin Huang Chun-Hung Chen Wei-Chen
J Neurol (2012) 259:1426 1432 DOI 10.1007/s00415-011-6369-2 ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Clinical applications of susceptibility weighted imaging in patients with major stroke Poyin Huang Chun-Hung Chen Wei-Chen
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
Advanced Neuroimaging for Acute Stroke
 Advanced Neuroimaging for Acute Stroke E. Bradshaw Bunney, MD, FACEP Professor Department Of Emergency Medicine University of Illinois at Chicago Swedish American Belvidere Hospital Disclosures FERNE Board
Advanced Neuroimaging for Acute Stroke E. Bradshaw Bunney, MD, FACEP Professor Department Of Emergency Medicine University of Illinois at Chicago Swedish American Belvidere Hospital Disclosures FERNE Board
Heejin Shim, Hyun Seok Choi, So-Lyung Jung, Kook-Jin Ahn, Bum-soo Kim
 Susceptibility Weighted MR Imaging at 3T in Patients with Occlusion of Middle Cerebral Artery : Comparison with Diffusion Weighted Imaging Score (ASPECTS) Heejin Shim, Hyun Seok Choi, So-Lyung Jung, Kook-Jin
Susceptibility Weighted MR Imaging at 3T in Patients with Occlusion of Middle Cerebral Artery : Comparison with Diffusion Weighted Imaging Score (ASPECTS) Heejin Shim, Hyun Seok Choi, So-Lyung Jung, Kook-Jin
occlusions. Cerebral perfusion is driven fundamentally by regional cerebral
 Appendix Figures Figure A1. Hemodynamic changes that may occur in major anterior circulation occlusions. Cerebral perfusion is driven fundamentally by regional cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP). In response
Appendix Figures Figure A1. Hemodynamic changes that may occur in major anterior circulation occlusions. Cerebral perfusion is driven fundamentally by regional cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP). In response
Predicting stroke evolution: comparison of susceptibility-weighted MR imaging with MR perfusion
 Eur Radiol (2012) 22:1397 1403 DOI 10.1007/s00330-012-2387-4 NEURO Predicting stroke evolution: comparison of susceptibility-weighted MR imaging with MR perfusion Hung-Wen Kao & Fong Y. Tsai & Anton N.
Eur Radiol (2012) 22:1397 1403 DOI 10.1007/s00330-012-2387-4 NEURO Predicting stroke evolution: comparison of susceptibility-weighted MR imaging with MR perfusion Hung-Wen Kao & Fong Y. Tsai & Anton N.
Background. Recommendations for Imaging of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association
 for Imaging of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association An Scientific Statement from the Stroke Council, American Heart Association and American Stroke Association
for Imaging of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association An Scientific Statement from the Stroke Council, American Heart Association and American Stroke Association
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive
 Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke
 Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke Dr Lakmalie Paranahewa MBBS, MD(Radiology), FRCR Consultant Interventional Radiologist Asiri Group of Hospitals Objectives Imaging in Stroke Neurovascular
Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke Dr Lakmalie Paranahewa MBBS, MD(Radiology), FRCR Consultant Interventional Radiologist Asiri Group of Hospitals Objectives Imaging in Stroke Neurovascular
PHYSICS OF MRI ACQUISITION. Alternatives to BOLD for fmri
 PHYSICS OF MRI ACQUISITION Quick Review for fmri HST-583, Fall 2002 HST.583: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology
PHYSICS OF MRI ACQUISITION Quick Review for fmri HST-583, Fall 2002 HST.583: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology
Functional aspects of anatomical imaging techniques
 Functional aspects of anatomical imaging techniques Nilendu Purandare Associate Professor & Consultant Radiologist Tata Memorial Centre Functional/metabolic/molecular imaging (radioisotope scanning) PET
Functional aspects of anatomical imaging techniques Nilendu Purandare Associate Professor & Consultant Radiologist Tata Memorial Centre Functional/metabolic/molecular imaging (radioisotope scanning) PET
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence
 A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging F. A. Fellner 1, M. R. Vosko 2, C. M. Fellner 1, D. Flöry 1 1. AKH Linz, Institute of Radiology, Austria. 2.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging F. A. Fellner 1, M. R. Vosko 2, C. M. Fellner 1, D. Flöry 1 1. AKH Linz, Institute of Radiology, Austria. 2.
Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences
 Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences Nils Daniel Forkert 1, Dennis Säring 1, Andrea Eisenbeis 2, Frank Leypoldt 3, Jens Fiehler 2, Heinz Handels
Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences Nils Daniel Forkert 1, Dennis Säring 1, Andrea Eisenbeis 2, Frank Leypoldt 3, Jens Fiehler 2, Heinz Handels
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
Imaging Acute Stroke and Cerebral Ischemia
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging Acute Stroke and Cerebral Ischemia John R. Hesselink, M.D. Causes of Stroke Arterial stenosis Thrombosis Embolism Dissection Hypotension
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging Acute Stroke and Cerebral Ischemia John R. Hesselink, M.D. Causes of Stroke Arterial stenosis Thrombosis Embolism Dissection Hypotension
Diagnostic improvement from average image in acute ischemic stroke
 Diagnostic improvement from average image in acute ischemic stroke N. Magne (1), E.Tollard (1), O. Ozkul- Wermester (2), V. Macaigne (1), J.-N. Dacher (1), E. Gerardin (1) (1) Department of Radiology,
Diagnostic improvement from average image in acute ischemic stroke N. Magne (1), E.Tollard (1), O. Ozkul- Wermester (2), V. Macaigne (1), J.-N. Dacher (1), E. Gerardin (1) (1) Department of Radiology,
Imaging Stroke: Is There a Stroke Equivalent of the ECG? Albert J. Yoo, MD Director of Acute Stroke Intervention Massachusetts General Hospital
 Imaging Stroke: Is There a Stroke Equivalent of the ECG? Albert J. Yoo, MD Director of Acute Stroke Intervention Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Penumbra, Inc. research grant (significant) for
Imaging Stroke: Is There a Stroke Equivalent of the ECG? Albert J. Yoo, MD Director of Acute Stroke Intervention Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Penumbra, Inc. research grant (significant) for
LATEST IMAGING FOR ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE AND INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE
 LATEST IMAGING FOR ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE AND INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE Brian A. Stettler, MD Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, OH OBJECTIVES: 1) To describe the role
LATEST IMAGING FOR ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE AND INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE Brian A. Stettler, MD Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, OH OBJECTIVES: 1) To describe the role
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
MEDICAL POLICY EFFECTIVE DATE: 12/18/08 REVISED DATE: 12/17/09, 03/17/11, 05/19/11, 05/24/12, 05/23/13, 05/22/14
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CT (COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY) PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CT (COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY) PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
Recent studies have demonstrated that multiparametric
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D. Kaya A. Dinçer M.E. Yıldız M.O. Çizmeli C. Erzen Acute Ischemic Infarction Defined by a Region of Multiple Hypointense Vessels on Gradient-Echo T2* MR Imaging at 3T BACKGROUND AND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH D. Kaya A. Dinçer M.E. Yıldız M.O. Çizmeli C. Erzen Acute Ischemic Infarction Defined by a Region of Multiple Hypointense Vessels on Gradient-Echo T2* MR Imaging at 3T BACKGROUND AND
Imaging in Stroke. D Nagaraja, N Karthik
 Imaging in Stroke D Nagaraja, N Karthik Cerebro-vascular disease (stroke) is the second leading cause of death. Prior to CT era, diagnosis was essentially clinical supported by angio and lumbar puncture.
Imaging in Stroke D Nagaraja, N Karthik Cerebro-vascular disease (stroke) is the second leading cause of death. Prior to CT era, diagnosis was essentially clinical supported by angio and lumbar puncture.
STATE OF THE ART IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE
 STATE OF THE ART IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE Marin Penkov UH St Ivan Rilski Sofia RadiologyTogether 2-3 June 2017 GOALS The concept and significance of penumbra CT and MRI Basic Principles Clinical application
STATE OF THE ART IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE Marin Penkov UH St Ivan Rilski Sofia RadiologyTogether 2-3 June 2017 GOALS The concept and significance of penumbra CT and MRI Basic Principles Clinical application
While MR imaging is superior in the diagnosis of acute
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH X.-C. Wang P.-Y. Gao J. Xue G.-R. Liu L. Ma Identification of Infarct Core and Penumbra in Acute Stroke Using CT Perfusion Source Images BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: CT perfusion (CTP) mapping
ORIGINAL RESEARCH X.-C. Wang P.-Y. Gao J. Xue G.-R. Liu L. Ma Identification of Infarct Core and Penumbra in Acute Stroke Using CT Perfusion Source Images BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: CT perfusion (CTP) mapping
On Call Guide to CT Perfusion. Updated: March 2011
 On Call Guide to CT Perfusion Updated: March 2011 CT Stroke Protocol 1. Non contrast CT brain 2. CT perfusion: contrast 40cc bolus dynamic imaging at 8 slice levels ~ 60 sec creates perfusion color maps
On Call Guide to CT Perfusion Updated: March 2011 CT Stroke Protocol 1. Non contrast CT brain 2. CT perfusion: contrast 40cc bolus dynamic imaging at 8 slice levels ~ 60 sec creates perfusion color maps
Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging. Ronald L. Wolf, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Radiology
 Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging Ronald L. Wolf, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Radiology Title of First Slide of Substance An Illustrative Case 2 Disclosures No financial disclosures Off-label uses of some
Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging Ronald L. Wolf, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Radiology Title of First Slide of Substance An Illustrative Case 2 Disclosures No financial disclosures Off-label uses of some
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Gradient-echo (GRE) imaging is a robust MR imaging. Improved T2* Imaging without Increase in Scan Time: SWI Processing of 2D Gradient Echo
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Improved T2* Imaging without Increase in Scan Time: SWI Processing of 2D Gradient Echo S. Soman, S.J. Holdsworth, P.D. Barnes, J. Rosenberg, J.B. Andre, R. Bammer, and K.W. Yeom
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Improved T2* Imaging without Increase in Scan Time: SWI Processing of 2D Gradient Echo S. Soman, S.J. Holdsworth, P.D. Barnes, J. Rosenberg, J.B. Andre, R. Bammer, and K.W. Yeom
Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials
 Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials Sample size 500 # sites 70 (100 planned) 316 (500 planned) 196 (833 estimated) 206 (690 planned) 16 10 22 39 4 Treatment contrasts Baseline
Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials Sample size 500 # sites 70 (100 planned) 316 (500 planned) 196 (833 estimated) 206 (690 planned) 16 10 22 39 4 Treatment contrasts Baseline
Noncontrast CT scan is currently the imaging modality
 Original Contributions MRI Features of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Within 2 Hours From Symptom Onset Italo Linfante, MD; Rafael H. Llinas, MD; Louis R. Caplan, MD; Steven Warach, MD, PhD Background and Purpose
Original Contributions MRI Features of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Within 2 Hours From Symptom Onset Italo Linfante, MD; Rafael H. Llinas, MD; Louis R. Caplan, MD; Steven Warach, MD, PhD Background and Purpose
Imaging veins, oxygen extraction fraction, arteries and vessel wall using susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) and susceptibility mapping (SWIM)
 Imaging veins, oxygen extraction fraction, arteries and vessel wall using susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) and susceptibility mapping (SWIM) SWI E. Mark Haacke Department of Radiology, Wayne State
Imaging veins, oxygen extraction fraction, arteries and vessel wall using susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) and susceptibility mapping (SWIM) SWI E. Mark Haacke Department of Radiology, Wayne State
11/1/2018. Disclosure. Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke 2018 Neuro Symposium. Is NCCT good enough? Keystone Heart Consultant, Stock Options
 Disclosure Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke 2018 Neuro Symposium Keystone Heart Consultant, Stock Options Kevin Abrams, M.D. Chief of Radiology Medical Director of Neuroradiology Baptist Hospital, Miami,
Disclosure Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke 2018 Neuro Symposium Keystone Heart Consultant, Stock Options Kevin Abrams, M.D. Chief of Radiology Medical Director of Neuroradiology Baptist Hospital, Miami,
Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke
 Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Assessing Tissue Oxygenation and Predicting Tissue Outcome in Acute Stroke
 The Danish National Research Foundation s Center of Functionally Integrative Neuroscience Aarhus University / Aarhus University Hospital - DENMARK Assessing Tissue Oxygenation and Predicting Tissue Outcome
The Danish National Research Foundation s Center of Functionally Integrative Neuroscience Aarhus University / Aarhus University Hospital - DENMARK Assessing Tissue Oxygenation and Predicting Tissue Outcome
AMSER Case of the Month: March 2019
 AMSER Case of the Month: March 2019 62 year-old male with left-sided weakness Ashley Graziano OMS IV, Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine Erik Yannone MD, Charles Q. Li MD, Warren Chang MD, Matthew
AMSER Case of the Month: March 2019 62 year-old male with left-sided weakness Ashley Graziano OMS IV, Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine Erik Yannone MD, Charles Q. Li MD, Warren Chang MD, Matthew
Stroke imaging. Why image stroke patients? Stroke. Treatment of infarct. Methods for infarct diagnosis. Treatment of infarct.
 Stroke imaging Stroke Infarct: -Arterial thrombosis/embolus -Hypoxic/ischemic -Venous thrombosis Non-traumatic hemorrhage: -Intracerebral -Subarachnoid Johan Wikström MD PhD Associate Professor of Radiology
Stroke imaging Stroke Infarct: -Arterial thrombosis/embolus -Hypoxic/ischemic -Venous thrombosis Non-traumatic hemorrhage: -Intracerebral -Subarachnoid Johan Wikström MD PhD Associate Professor of Radiology
STROKE - IMAGING. Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli.
 STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
MRI qbold Based Evaluation. Renal Oxidative Metabolism. Department of Radiology and Hernando Gomez, MD Critical Care Medicine
 MRI qbold Based Evaluation of Renal Oxidative Metabolism Xiang He, PhD Department of Radiology and Hernando Gomez, MD Critical Care Medicine Background High oxygen-demand and lower medullary blood flow
MRI qbold Based Evaluation of Renal Oxidative Metabolism Xiang He, PhD Department of Radiology and Hernando Gomez, MD Critical Care Medicine Background High oxygen-demand and lower medullary blood flow
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA
 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
Distal hyperintense vessels on FLAIR An MRI marker for collateral circulation in acute stroke?
 Distal hyperintense vessels on FLAIR An MRI marker for collateral circulation in acute stroke? K.Y. Lee, MD, PhD L.L. Latour, PhD M. Luby, PhD A.W. Hsia, MD J.G. Merino, MD, MPhil S. Warach, MD, PhD Address
Distal hyperintense vessels on FLAIR An MRI marker for collateral circulation in acute stroke? K.Y. Lee, MD, PhD L.L. Latour, PhD M. Luby, PhD A.W. Hsia, MD J.G. Merino, MD, MPhil S. Warach, MD, PhD Address
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Susceptibility-Diffusion Mismatch Predicts Thrombolytic Outcomes: A Retrospective Cohort Study M. Lou, Z. Chen, J. Wan, H. Hu, X. Cai, Z. Shi, and J. Sun ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Susceptibility-Diffusion Mismatch Predicts Thrombolytic Outcomes: A Retrospective Cohort Study M. Lou, Z. Chen, J. Wan, H. Hu, X. Cai, Z. Shi, and J. Sun ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND
Course objectives. Head Ultrasound. Introduction
 Disclosure Information AACPDM 68 th Annual Meeting September 10-13, 2014 Imaging of the pediatric brain, spinal cord and muscle: Tools and clinical applications Andrea Poretti, MD Research Associate Section
Disclosure Information AACPDM 68 th Annual Meeting September 10-13, 2014 Imaging of the pediatric brain, spinal cord and muscle: Tools and clinical applications Andrea Poretti, MD Research Associate Section
UPDATES IN INTRACRANIAL INTERVENTION Jordan Taylor DO Metro Health Neurology 2015
 UPDATES IN INTRACRANIAL INTERVENTION Jordan Taylor DO Metro Health Neurology 2015 NEW STUDIES FOR 2015 MR CLEAN ESCAPE EXTEND-IA REVASCAT SWIFT PRIME RECOGNIZED LIMITATIONS IV Alteplase proven benefit
UPDATES IN INTRACRANIAL INTERVENTION Jordan Taylor DO Metro Health Neurology 2015 NEW STUDIES FOR 2015 MR CLEAN ESCAPE EXTEND-IA REVASCAT SWIFT PRIME RECOGNIZED LIMITATIONS IV Alteplase proven benefit
CT Perfusion Parameter Values in Regions of Diffusion Abnormalities
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1205 1210, August 2004 CT Perfusion Parameter Values in Regions of Diffusion Abnormalities Marcello Galvez, Gerald E. York, II, and James D. Eastwood BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Dynamic
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1205 1210, August 2004 CT Perfusion Parameter Values in Regions of Diffusion Abnormalities Marcello Galvez, Gerald E. York, II, and James D. Eastwood BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Dynamic
Acute stroke imaging
 Acute stroke imaging Aims Imaging modalities and differences Why image acute stroke Clinical correlation to imaging appearance What is stroke Classic definition: acute focal injury to the central nervous
Acute stroke imaging Aims Imaging modalities and differences Why image acute stroke Clinical correlation to imaging appearance What is stroke Classic definition: acute focal injury to the central nervous
ACUTE STROKE IMAGING
 ACUTE STROKE IMAGING Mahesh V. Jayaraman M.D. Director, Inter ventional Neuroradiology Associate Professor Depar tments of Diagnostic Imaging and Neurosurger y Alper t Medical School at Brown University
ACUTE STROKE IMAGING Mahesh V. Jayaraman M.D. Director, Inter ventional Neuroradiology Associate Professor Depar tments of Diagnostic Imaging and Neurosurger y Alper t Medical School at Brown University
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke. Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV
 The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
Original Article Susceptibility-diffusion mismatch: an effective method by which to detect perfusion-diffusion mismatch in acute ischemic stroke
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(10):19691-19699 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0030856 Original Article Susceptibility-diffusion mismatch: an effective method by which to detect perfusion-diffusion mismatch
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(10):19691-19699 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0030856 Original Article Susceptibility-diffusion mismatch: an effective method by which to detect perfusion-diffusion mismatch
Prediction of Hemorrhage in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Permeability MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2213 2217, October 2005 Technical Note Prediction of Hemorrhage in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Permeability MR Imaging Andrea Kassner, Timothy Roberts, Keri Taylor, Frank Silver,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2213 2217, October 2005 Technical Note Prediction of Hemorrhage in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Permeability MR Imaging Andrea Kassner, Timothy Roberts, Keri Taylor, Frank Silver,
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Perfusion Physics. ICMRI2018 March 29-31, 2018 Grand Hilton Hotel, Seoul, Korea. Asian Forum Ⅱ: Perfusion MRI SY24-1.
 SY24-1 Perfusion Physics Hiroyuki Kabasawa MR Collaborations and Development, GE Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan Perfusion is referred as the blood supply to micro capillary in tissue. Perfusion parameter such
SY24-1 Perfusion Physics Hiroyuki Kabasawa MR Collaborations and Development, GE Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan Perfusion is referred as the blood supply to micro capillary in tissue. Perfusion parameter such
Associated Brain Parenchymal Abnormalities in Developmental Venous Anomalies: Evaluation with Susceptibility-weighted MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:146-152 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.146 Associated Brain Parenchymal Abnormalities in Developmental Venous Anomalies: Evaluation with Susceptibility-weighted
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:146-152 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.146 Associated Brain Parenchymal Abnormalities in Developmental Venous Anomalies: Evaluation with Susceptibility-weighted
framework for flow Objectives Acute Stroke Treatment Collaterals in Acute Ischemic Stroke framework & basis for flow
 Acute Stroke Treatment Collaterals in Acute Ischemic Stroke Objectives role of collaterals in acute ischemic stroke collateral therapeutic strategies David S Liebeskind, MD Professor of Neurology & Director
Acute Stroke Treatment Collaterals in Acute Ischemic Stroke Objectives role of collaterals in acute ischemic stroke collateral therapeutic strategies David S Liebeskind, MD Professor of Neurology & Director
Title: Stability of Large Diffusion/Perfusion Mismatch in Anterior Circulation Strokes for 4 or More Hours
 Author's response to reviews Title: Stability of Large Diffusion/Perfusion Mismatch in Anterior Circulation Strokes for 4 or More Hours Authors: Ramon G. Gonzalez (rggonzalez@partners.org) Reza Hakimelahi
Author's response to reviews Title: Stability of Large Diffusion/Perfusion Mismatch in Anterior Circulation Strokes for 4 or More Hours Authors: Ramon G. Gonzalez (rggonzalez@partners.org) Reza Hakimelahi
Imaging for Acute Stroke
 Imaging for Acute Stroke Nine case studies detailing the impact of imaging on stroke therapy. BY ANSAAR T. RAI, MD Ischemic stroke is a dynamic process, and the term stroke in evolution precisely underscores
Imaging for Acute Stroke Nine case studies detailing the impact of imaging on stroke therapy. BY ANSAAR T. RAI, MD Ischemic stroke is a dynamic process, and the term stroke in evolution precisely underscores
Endovascular Treatment Updates in Stroke Care
 Endovascular Treatment Updates in Stroke Care Autumn Graham, MD April 6-10, 2017 Phoenix, AZ Endovascular Treatment Updates in Stroke Care Autumn Graham, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Emergency Medicine
Endovascular Treatment Updates in Stroke Care Autumn Graham, MD April 6-10, 2017 Phoenix, AZ Endovascular Treatment Updates in Stroke Care Autumn Graham, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Emergency Medicine
Research Status of Three-Dimensional Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling in Ischemic Cerebrovascular Diseases
 Radiation Science and Technology 2018; 4(1): 1-5 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/rst doi: 10.11648/j.rst.20180401.11 ISSN: 2575-5935 (Print); ISSN: 2575-5943 (Online) Review Article Research Status
Radiation Science and Technology 2018; 4(1): 1-5 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/rst doi: 10.11648/j.rst.20180401.11 ISSN: 2575-5935 (Print); ISSN: 2575-5943 (Online) Review Article Research Status
Analysis of DWI ASPECTS and Recanalization Outcomes of Patients with Acute-phase Cerebral Infarction
 J Med Dent Sci 2012; 59: 57-63 Original Article Analysis of DWI ASPECTS and Recanalization Outcomes of Patients with Acute-phase Cerebral Infarction Keigo Shigeta 1,2), Kikuo Ohno 1), Yoshio Takasato 2),
J Med Dent Sci 2012; 59: 57-63 Original Article Analysis of DWI ASPECTS and Recanalization Outcomes of Patients with Acute-phase Cerebral Infarction Keigo Shigeta 1,2), Kikuo Ohno 1), Yoshio Takasato 2),
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/44385 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Ayata, C. Title: Spreading depolarizations : the missing link between mirgraine
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/44385 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Ayata, C. Title: Spreading depolarizations : the missing link between mirgraine
Medical Policy. MP Computed Tomography Perfusion Imaging of the Brain
 Medical Policy MP 6.01.49 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.49 Last Review: 09/28/2017 Effective Date: 09/28/2017 Section: Radiology Related Policies 2.01.54 Endovascular Procedures for Intracranial Arterial Disease
Medical Policy MP 6.01.49 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.49 Last Review: 09/28/2017 Effective Date: 09/28/2017 Section: Radiology Related Policies 2.01.54 Endovascular Procedures for Intracranial Arterial Disease
The diagnostic value of susceptibilityweighted imaging for ischemic penumbra in patients with acute ischemic stroke
 Technology and Health Care 25 (2017) S449 S457 DOI 10.3233/THC-171348 IOS Press S449 The diagnostic value of susceptibilityweighted imaging for ischemic penumbra in patients with acute ischemic stroke
Technology and Health Care 25 (2017) S449 S457 DOI 10.3233/THC-171348 IOS Press S449 The diagnostic value of susceptibilityweighted imaging for ischemic penumbra in patients with acute ischemic stroke
Susceptibility-weighted MRI ups contrast, offers minute detail 9/15/04 By: Shalmali Pal
 Susceptibility-weighted MRI ups contrast, offers minute detail 9/15/04 By: Shalmali Pal With its flashy sequences and high-speed protocols, there's no shortage of razzle-dazzle in MRI. But learning to
Susceptibility-weighted MRI ups contrast, offers minute detail 9/15/04 By: Shalmali Pal With its flashy sequences and high-speed protocols, there's no shortage of razzle-dazzle in MRI. But learning to
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI)
 Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
PERFUSION MRI CONTRAST BASED TECHNIQUES
 PERFUSION MRI CONTRAST BASED TECHNIQUES by Kenny K Israni Mar 28, 2006 PERFUSION - MRI Dynamic Susceptibility contrast Dynamic Relaxivity contrast STEADY-STATE STATE TECHNIQUES Steady-state Susceptibility
PERFUSION MRI CONTRAST BASED TECHNIQUES by Kenny K Israni Mar 28, 2006 PERFUSION - MRI Dynamic Susceptibility contrast Dynamic Relaxivity contrast STEADY-STATE STATE TECHNIQUES Steady-state Susceptibility
Cardiac Imaging Tests
 Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
Perfusion MRI. Youngkyoo Jung, PhD Associate Professor Radiology, Biomedical Engineering, and Clinical & Translational Science Institute
 Perfusion MRI Youngkyoo Jung, PhD Associate Professor Radiology, Biomedical Engineering, and Clinical & Translational Science Institute Perfusion The delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue Perfusion
Perfusion MRI Youngkyoo Jung, PhD Associate Professor Radiology, Biomedical Engineering, and Clinical & Translational Science Institute Perfusion The delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue Perfusion
Carotid Embolectomy and Endarterectomy for Symptomatic Complete Occlusion of the Carotid Artery as a Rescue Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke
 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the article
This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the article
CT perfusion scans are widely applied to assess ischemia (low
 Published April 17, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3935 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Early Basal Ganglia Hyperperfusion on CT Perfusion in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Marker of Irreversible Damage? V. Shahi, J.E. Fugate,
Published April 17, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3935 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Early Basal Ganglia Hyperperfusion on CT Perfusion in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Marker of Irreversible Damage? V. Shahi, J.E. Fugate,
Dong Gyu Na, Vincent N. Thijs, Gregory W. Albers, Michael E. Moseley, and Michael P. Marks. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25: , September 2004
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1331 1336, September 2004 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Acute Ischemia: Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Signal Intensity Thresholds in Predicting Tissue at Risk
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1331 1336, September 2004 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Acute Ischemia: Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Signal Intensity Thresholds in Predicting Tissue at Risk
Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging Innovations
 Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging Innovations Guilherme Dabus, MD, FAHA Director, Fellowship NeuroInterventional Surgery Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute Baptist Neuroscience Center Baptist Neuroscience
Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging Innovations Guilherme Dabus, MD, FAHA Director, Fellowship NeuroInterventional Surgery Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute Baptist Neuroscience Center Baptist Neuroscience
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
New Frontiers in Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 New Frontiers in Intracerebral Hemorrhage Ryan Hakimi, DO, MS Director, Neuro ICU Director, Inpatient Neurology Services Greenville Health System Clinical Associate Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology)
New Frontiers in Intracerebral Hemorrhage Ryan Hakimi, DO, MS Director, Neuro ICU Director, Inpatient Neurology Services Greenville Health System Clinical Associate Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology)
Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care. (Updated 2008) Section # 3 Section # 3 Hyperacute Stroke Management
 Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care (Updated 2008) Section # 3 Section # 3 Hyperacute Stroke Management Reorganization of Recommendations 2008 2006 RECOMMENDATIONS: 2008 RECOMMENDATIONS:
Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care (Updated 2008) Section # 3 Section # 3 Hyperacute Stroke Management Reorganization of Recommendations 2008 2006 RECOMMENDATIONS: 2008 RECOMMENDATIONS:
MRI Assessment of the Right Ventricle and Pulmonary Blood Flow, Perfusion and Ventilation
 MRI Assessment of the Right Ventricle and Pulmonary Blood Flow, Perfusion and Ventilation Dr. Richard Thompson Department of Biomedical Engineering University of Alberta Heart and Lung Imaging Many Constantly
MRI Assessment of the Right Ventricle and Pulmonary Blood Flow, Perfusion and Ventilation Dr. Richard Thompson Department of Biomedical Engineering University of Alberta Heart and Lung Imaging Many Constantly
ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE. Current Treatment Approaches for Acute Ischemic Stroke
 ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Current Treatment Approaches for Acute Ischemic Stroke EARLY MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Rapid identification of a stroke Immediate EMS transport to nearest stroke center
ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Current Treatment Approaches for Acute Ischemic Stroke EARLY MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Rapid identification of a stroke Immediate EMS transport to nearest stroke center
11/6/2013. Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science (VUIIS) 7 Tesla Vascular Imaging. Evaluating stroke risk
 Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science (VUIIS) New MI Techniques for Imaging Cerebrovascular Disease Manus J. Donahue Depts. of adiology, Physics, Neurology and Physics Vanderbilt University
Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science (VUIIS) New MI Techniques for Imaging Cerebrovascular Disease Manus J. Donahue Depts. of adiology, Physics, Neurology and Physics Vanderbilt University
Disclosure. + Outline. What is a stroke? Role of imaging in stroke Ischemic stroke Venous infarct Current topics
 + Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 + Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Thank you
+ Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 + Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Thank you
Neuroradiology: Imaging and Stroke
 Neuroradiology: Imaging and Stroke Stroke 2017 William Gallmann January 28, 2017 Stroke Arterial ischemia/infarct accounts for ~85% Cerebral venous occlusions - 0.5-1% Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage
Neuroradiology: Imaging and Stroke Stroke 2017 William Gallmann January 28, 2017 Stroke Arterial ischemia/infarct accounts for ~85% Cerebral venous occlusions - 0.5-1% Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage
Introduction. Abstract. Michael Yannes 1, Jennifer V. Frabizzio, MD 1, and Qaisar A. Shah, MD 1 1
 Reversal of CT hypodensity after acute ischemic stroke Michael Yannes 1, Jennifer V. Frabizzio, MD 1, and Qaisar A. Shah, MD 1 1 Abington Memorial Hospital in Abington, Pennsylvania Abstract We report
Reversal of CT hypodensity after acute ischemic stroke Michael Yannes 1, Jennifer V. Frabizzio, MD 1, and Qaisar A. Shah, MD 1 1 Abington Memorial Hospital in Abington, Pennsylvania Abstract We report
Benign Oligemia Despite a Malignant MRI Profile in Acute Ischemic Stroke
 CASE REPORT J Clin Neurol 2010;6:41-45 Print ISSN 1738-6586 / On-line ISSN 2005-5013 10.3988/jcn.2010.6.1.41 Benign Oligemia Despite a Malignant MRI Profile in Acute Ischemic Stroke Oh Young Bang, MD a
CASE REPORT J Clin Neurol 2010;6:41-45 Print ISSN 1738-6586 / On-line ISSN 2005-5013 10.3988/jcn.2010.6.1.41 Benign Oligemia Despite a Malignant MRI Profile in Acute Ischemic Stroke Oh Young Bang, MD a
A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging
 Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
CT/MRI 第 42 回日本脳卒中学会講演シンポジウム 総説 はじめに. MRI magnetic resonance imaging DWI diffusion-weighted. DWI/CBF malignant profile
 第 42 回日本脳卒中学会講演シンポジウム 総説 CT/MRI 1 要旨 rt-pa MRI magnetic resonance imaging DWI diffusion-weighted image Tmax time-to-maximum DWI/PWI perfusion image mismatch CT computed tomography CBF cerebral blood flow
第 42 回日本脳卒中学会講演シンポジウム 総説 CT/MRI 1 要旨 rt-pa MRI magnetic resonance imaging DWI diffusion-weighted image Tmax time-to-maximum DWI/PWI perfusion image mismatch CT computed tomography CBF cerebral blood flow
Disclosures. CREST Trial: Summary. Lecture Outline 4/16/2015. Cervical Atherosclerotic Disease
 Disclosures Your Patient Has Carotid Bulb Stenosis and a Tandem Intracranial Stenosis: How Do SAMMPRIS and Other Evidence Inform Your Treatment? UCSF Vascular Symposium 2015 Steven W. Hetts, MD Associate
Disclosures Your Patient Has Carotid Bulb Stenosis and a Tandem Intracranial Stenosis: How Do SAMMPRIS and Other Evidence Inform Your Treatment? UCSF Vascular Symposium 2015 Steven W. Hetts, MD Associate
Broadening the Stroke Window in Light of the DAWN Trial
 Broadening the Stroke Window in Light of the DAWN Trial South Jersey Neurovascular and Stroke Symposium April 26, 2018 Rohan Chitale, MD Assistant Professor of Neurological Surgery Vanderbilt University
Broadening the Stroke Window in Light of the DAWN Trial South Jersey Neurovascular and Stroke Symposium April 26, 2018 Rohan Chitale, MD Assistant Professor of Neurological Surgery Vanderbilt University
The Value of Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke Comparison With Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast-Enhanced MRI
 The Value of Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke Comparison With Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast-Enhanced MRI Danny J.J. Wang, PhD, MSCE; Jeffry R. Alger, PhD; Joe X. Qiao,
The Value of Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke Comparison With Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast-Enhanced MRI Danny J.J. Wang, PhD, MSCE; Jeffry R. Alger, PhD; Joe X. Qiao,
Importance of susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) in management of cerebro-vascular strokes (CVS)
 Alexandria Journal of Medicine (2014) 50, 83 91 Alexandria University Faculty of Medicine Alexandria Journal of Medicine www.sciencedirect.com Importance of susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) in management
Alexandria Journal of Medicine (2014) 50, 83 91 Alexandria University Faculty of Medicine Alexandria Journal of Medicine www.sciencedirect.com Importance of susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) in management
Newborn Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury. Hisham Dahmoush, MBBCh FRCR Lucile Packard Children s Hospital at Stanford
 Newborn Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury Hisham Dahmoush, MBBCh FRCR Lucile Packard Children s Hospital at Stanford NO DISCLOSURES INTRODUCTION Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a major cause
Newborn Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury Hisham Dahmoush, MBBCh FRCR Lucile Packard Children s Hospital at Stanford NO DISCLOSURES INTRODUCTION Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a major cause
5/31/2018. Interventional Therapies that Expand Time Windows for Acute Ischemic Stroke Treatment. Disclosures. Impact of clot burden
 Good Outcome (%) Rankin 0-2 at 90 days 5/31/2018 Interventional Therapies that Expand Time Windows for Acute Ischemic Stroke Treatment Disclosures Cerenovus: I am on Executive Committee for ARISE2 Trial
Good Outcome (%) Rankin 0-2 at 90 days 5/31/2018 Interventional Therapies that Expand Time Windows for Acute Ischemic Stroke Treatment Disclosures Cerenovus: I am on Executive Committee for ARISE2 Trial
Neuroimaging plays a central role in the evaluation of patients. Role of EPI-FLAIR in Patients with Acute Stroke: A Comparative Analysis with FLAIR
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Role of EPI-FLAIR in Patients with Acute Stroke: A Comparative Analysis with FLAIR A. Meshksar, J.P. Villablanca, R. Khan, R. Carmody, B. Coull, and K. Nael ABSTRACT BACKGROUND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Role of EPI-FLAIR in Patients with Acute Stroke: A Comparative Analysis with FLAIR A. Meshksar, J.P. Villablanca, R. Khan, R. Carmody, B. Coull, and K. Nael ABSTRACT BACKGROUND
Endovascular Therapy: Beyond the Guidelines
 Endovascular Therapy: Beyond the Guidelines Ashutosh P. Jadhav, MD PhD Assistant Professor, Neurology and Neurological Surgery Center for Neuro-endovascular Therapy UPMC Stroke Institute Pittsburgh, PA
Endovascular Therapy: Beyond the Guidelines Ashutosh P. Jadhav, MD PhD Assistant Professor, Neurology and Neurological Surgery Center for Neuro-endovascular Therapy UPMC Stroke Institute Pittsburgh, PA
Index of Changes. Examiner 1
 Index of Changes Examiner 1 Previous Page: 84 Current Page: 76 Suggested changes: 1. There are different methods to assess the penumbra or mismatch in acute ischemic stroke: some are pure imaging-based
Index of Changes Examiner 1 Previous Page: 84 Current Page: 76 Suggested changes: 1. There are different methods to assess the penumbra or mismatch in acute ischemic stroke: some are pure imaging-based
CT INTERPRETATION COURSE
 CT INTERPRETATION COURSE Refresher Course ASTRACAT October 2012 Stroke is a Clinical Diagnosis A clinical syndrome characterised by rapidly developing clinical symptoms and/or signs of focal loss of cerebral
CT INTERPRETATION COURSE Refresher Course ASTRACAT October 2012 Stroke is a Clinical Diagnosis A clinical syndrome characterised by rapidly developing clinical symptoms and/or signs of focal loss of cerebral
9/18/16. Setting: Community ED, 30k admissions per year Time: Friday night, 11pm. CC: Syncope
 William A. Knight IV MD, FACEP Associate Professor Emergency Medicine & Neurosurgery University of Cincinnati September 21, 2016 (William.knight@uc.edu) ED as the Front Door Spectrum of care with Endovascular
William A. Knight IV MD, FACEP Associate Professor Emergency Medicine & Neurosurgery University of Cincinnati September 21, 2016 (William.knight@uc.edu) ED as the Front Door Spectrum of care with Endovascular
Cerebral Misery Perfusion on Susceptibility Weighted Imaging in Acute Carotid Dissection
 Cerebral Misery Perfusion on Susceptibility Weighted Imaging in Acute Carotid Dissection Arian Mashhood 1, Paggie Kim 1, Frankis Almaguel 1, Geoffery McWilliams 2, J Paul Jacobson 1* 1. Department of Radiology,
Cerebral Misery Perfusion on Susceptibility Weighted Imaging in Acute Carotid Dissection Arian Mashhood 1, Paggie Kim 1, Frankis Almaguel 1, Geoffery McWilliams 2, J Paul Jacobson 1* 1. Department of Radiology,
EFFECTIVENESS OF CTA AND CTP IN GUIDING MANAGEMENT DECISIONS FOR ACUTE STROKE
 EFFECTIVENESS OF CTA AND CTP IN GUIDING MANAGEMENT DECISIONS FOR ACUTE STROKE Jon Benton MS-4, Chirag Dani MD, Vincent Persaud MD, Bilal A. Manzer, Macksood Aftab DO, MHA OBJECTIVES 1. Utility of advanced
EFFECTIVENESS OF CTA AND CTP IN GUIDING MANAGEMENT DECISIONS FOR ACUTE STROKE Jon Benton MS-4, Chirag Dani MD, Vincent Persaud MD, Bilal A. Manzer, Macksood Aftab DO, MHA OBJECTIVES 1. Utility of advanced
