Effects of Amiodarone in a Swine Model of Nortryptiline Toxicity
|
|
|
- Wendy Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Toxicology Investigations Effects of Amiodarone in a Swine Model of Nortryptiline Toxicity Fermin Barrueto, Jr., MD a, Indira Murr, MD b, Andrew Meltzer, MD a, Kori Brewer, PhD b, and William Meggs, MD, PhD b a University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD b Brody School of Medicine at East Carolina University, Greenville, NC ABSTRACT Objectives: Antiarrhythmics can have devastating effects in cardiotoxic poisonings. Amiodarone is recommended for treatment of wide complex tachycardia, but its hemodynamic effects in wide complex tachycardia induced by tricyclic antidepressant poisoning are unknown. The objective of this study was to compare the effects of sodium bicarbonate, amiodarone, and normal saline in treating wide complex tachycardia secondary to nortriptyline poisoning. Methods: This unblended randomized controlled animal study involved 18 anesthetized, intubated pigs with arterial and venous lines. Nortriptyline (2 mg/ml) was infused at 20 mg/min until the onset of toxicity, defined as a systolic blood pressure 50 mmhg or QRS 120 ms. At that point, the pigs were randomized into three groups of six. Group I received 0.9% normal saline, 10 ml/kg. Group II received hypertonic sodium bicarbonate, 1 meq/kg. Group III received amiodarone, 15 mg/kg. The pigs were observed until death or survival at 60 minutes. Results: After treatment, the changes in QRS were as follows: Group I, 2.0 ms; Group II, 33.0 ms; Group III, 21.7 ms. ANOVA demonstrated no significant difference between the groups (p = 0.28). Mean arterial pressures 10 minutes after treatment were as follows: Group I, 19.4 mmhg; Group II, 23.7 mmhg; Group III, 12.5 mmhg. Based on ANOVA, there was no significant difference between any of the groups (p = 0.50). Conclusions: In this model of nortriptyline poisoning, the administration of amiodarone to correct wide complex tachycardia did not have a harmful effect. INTRODUCTION Some medications have the potential to cause devastating effects when administered in the setting of drug overdoses. Examples include treatment of digoxin toxicity and resultant hyperkalemia with calcium, treatment of cocaine toxicity with beta blockers, and treatment of tricyclic antidepressant overdoses with physostigmine [1 3]. The hemodynamic effects of amiodarone in the treatment of wide complex tachycardias are unknown when the cause is a tricyclic antidepressant overdose. Keywords: amiodarone, nortryptiline, tachycardia, poisoning, tricyclic antidepressants Acknowledgements: The authors thank Linda J. Kesselring, MS, ELS, technical editor/writer in the Department of Emergency Medicine at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, for her invaluable assistance with the preparation of this manuscript. Notes: Presented at the Residents Research Forum, Division of Emergency Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, June 1, 2005, and at the Scientific Assembly of the American College of Emergency Physicians, Washington, DC, September This study was supported by the East Carolina University Resident Research Fund. Corresponding Author: Fermin Barrueto, Jr., MD, Division of Emergency Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, 110 South Paca Street 6th floor, Suite 200, Baltimore, MD fbarr001@umaryland.edu JOURNAL OF MEDICAL TOXICOLOGY VOLUME 2, NUMBER 4 DECEMBER
2 The Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) protocol for the treatment of wide-complex tachycardia of unknown etiology calls for the administration of amiodarone [4 5]. Although this approach is appropriate for patients with ischemic heart disease, ACLS might exacerbate cardiac dysfunction in a toxin-induced wide-complex tachycardia such as that caused by an overdose of a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA), a sodium channel blocker. Sodium bicarbonate is known to effectively reverse TCA cardiotoxicity. In some TCA poisonings, the etiology may be unknown, and amiodarone may be inadvertently administered. Hence, it is important to know if amiodarone causes an adverse effect in TCA overdoses. An initial mouse survival study showed that there was no statistical difference in the amitriptyline LD 50 of mice pretreated with amiodarone when compared to a normal saline control [6]. Since hemodynamic monitoring and electrocardiographic (ECG) analysis were not possible in that small-animal model, a swine model was devised to evaluate these critical measures. Using a swine model of severe nortriptyline poisoning developed by McCabe et al, the purpose of this study was to determine if amiodarone, a class III antidysrrhythmic, had harmful hemodynamic effects on a wide-complex tachycardia [7]. The null hypothesis is that there would be no difference in the QRS complex or mean arterial pressure between TCA-poisoned subjects treated with amiodarone and those treated with hypertonic sodium bicarbonate, the standard of care for known TCA poisoning. MATERIALS AND METHODS The Animal Care and Use Committees of the participating universities approved this experiment. This was a non-blinded, randomized controlled animal study evaluating the effects of amiodarone in a swine model of severe nortriptyline toxicity. A change of 50% in QRS duration was considered significant in sample size calculations made with ANOVA. Ten pigs were found to have a 90% chance of finding a 50% difference for a single endpoint of a QRS duration at a fixed time. This is comparing one treatment modality to control; for example, amiodarone versus control (normal saline) or hypertonic sodium bicarbonate versus control (normal saline). Subjects were 18 male domestic swine weighing 10 to 13 kilograms. All animals were prepared and instrumented in the same fashion and randomly assigned to three treatment arms. This model was adapted from that described by McCabe et al [7]. The dosing of each arm was determined by information from previous literature; the only exception was the normal saline dose because it was the negative control arm. We wanted to administer a volume that was similar to the amiodarone and sodium bicarbonate arms to determine the toxic effects of this nortriptyline infusion. Amiodarone has been found to increase the ventricular fibrillatory threshold in a dose-dependent fashion [8]. Utilizing a maximal and safe dose found in a previous swine model, 15 mg/kg of amiodarone would clinically parallel an administered 300 mg bolus [8]. The clinical dose of sodium bicarbonate is 1 2 meq/kg, and thus we administered the first bolus, 1 meq/kg, to our swine model. This would also assist with keeping the volume infused equivalent in all arms. The animals were intramuscularly sedated with a mixture of 1 mg/kg of xylazine and tiletamine hydrochloride (Telazol) (5 mg/ml). An ear vein was cannulated, and each animal was intubated with a 5.0 endotracheal tube and maintained on 1 mg/ml of inhaled isofluorane. ECG leads were placed, and lead II was continuously monitored. A femoral arterial line was placed either percutaneously or via femoral cutdown for continuous monitoring of blood pressure and blood sampling. The pig was allowed 5 minutes after instrumentation and anesthesia to acquire baseline parameters. Nortriptyline (Sigma-Aldridge Chemical, St. Louis) was added to normal saline to a final concentration of 2 mg/ml and intravenously infused at a rate of 20 mg/min until toxicity was reached. Toxicity was defined as a systolic blood pressure 50 mmhg or a QRS duration 120 ms. After toxicity was achieved, a continuous infusion of the nortriptyline solution was maintained at a rate of 5 mg/min. At this point, group I, serving as a negative control, received 10 ml/kg of 0.9% normal saline solution; group II, serving as a positive control, received 10 ml/kg of an 8.4% sodium bicarbonate solution; and group III received 15 mg/kg of amiodarone solution followed by normal saline to equal a total volume of 10 ml/kg. In one case, one of the pigs from group I was removed from the study because of a failure of the infusion pump; therefore, although 18 animals were used for the study, only data from 17 pigs could be statistically analyzed. All animals were observed for 60 minutes after the onset of toxicity or until death. Death was defined as asystole or zero blood pressure for at least 60 seconds. Surviving animals were intravenously euthanized with sodium pentobarbital (100 mg/kg). Blood pressure, pulse, and QRS duration were measured at 5- minute intervals. Arterial ph, PCO 2, and PO 2 were measured at baseline and every 15 minutes thereafter. Serum nortriptyline levels were measured at toxicity. The outcome measures, posttreatment change in QRS duration, and mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) 10 minutes after treatment were compared between groups using ANOVA. RESULTS Prior to the administration of intravenous nortriptyline, baseline parameters of weight (kg), ph, QRS duration, mean arterial pressure, all pulse and nortriptyline serum concentration were similar across groups (Table 1). Wide complex tachycardia, defined as a QRS duration 120 ms, occurred in 16 of the 17 pigs. All 5 animals in the negative control group I (NS) developed wide complex tachycardia and deteriorated to asystole. All 6 animals in the positive control group II (NaHCO 3 ) experienced wide complex tachycardia; 3 of the animals deteriorated to asystole. Five of the 6 animals in group III (amiodarone) experienced wide complex tachycardia; 4 of them deteriorated to asystole. (See Figure 1 for time of 148 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL TOXICOLOGY VOLUME 2, NUMBER 4 DECEMBER 2006
3 TABLE 1. Baseline Parameters Mean Parameters Normal Saline NaHCO 3 Amiodarone (Baseline) (N = 5) (N = 6) (N = 6) Weight (kg) ± ± ± 0.87 ph 7.48 ± ± ± 0.06 QRS (msec) 76.0 ± ± ± 10.3 MAP 71.2 ± ± ± 7.1 Pulse (beats/min) 129 ± ± ± 21 [TCA] level (ng/l) ± ± ± 2860 death). The mean changes in QRS at 10 minutes after treatment were as follows: saline, narrowed by 2.0 ms; bicarbonate, narrowed by 33.0 ms; amiodarone, narrowed by 21.7 ms. There was no statistically significant difference between the groups after treatment (p = 0.28), though the trend favored sodium bicarbonate (Figure 2). MAP at 10 minutes after treatment was measured in negative control group I (NS), positive control group II (NaHCO 3 ), and in test group III (amiodarone). In the negative control group I (NS), the MAP was 19.4 mmhg; in the positive control group II (NaHCO 3 ), MAP was 23.7 mmhg; and in test group III (amiodarone), MAP was 12.5 mmhg. There was no statistically significant difference between the groups (p = 0.50). Again, the trend indicated that sodium bicarbonate was superior (Figure 3). Survival rates at 60 minutes were as follows: Group I: 0/5(0%), Group II: 3/6 (50%), and Group III 2/6(33%) (Figure 1). After analysis of our primary outcome measure, change in QRS, our power was <50%; 169 animals per group would be required to demonstrate 95% power. Analysis of the secondary outcome measure of MAP demonstrated a power of 50% to 80%. To obtain 95% power, 17 animals per group would be needed. DISCUSSION In this model of nortriptyline poisoning, administering amiodarone to treat wide complex tachycardias was not harmful. Hypertonic sodium bicarbonate actually showed the most favorable trend with regard to MAP and QRS duration and was superior to amiodarone. Interestingly, it has been assumed that the narrowing of the QRS indicates improvement of inotropy; however, in the amiodarone group, the three swine that had a narrowing of the QRS complex died. The sodium channel blockade with resultant negative inotropy in combination with the α-blocking effects of TCAs places a patient in a precarious hemodynamic state; theoretically, amiodarone could exacerbate that state. Although this swine study did not demonstrate this additive effect to the point of statistical significance, the possibility may be likened to the theoretic concern about administering calcium to a digoxin-poisoned patient and causing stone heart. [9] Since amiodarone is known to cause hypotension and QT prolongation, a potential physiologic mechanism exists. Figure 1. Time to death for each animal. JOURNAL OF MEDICAL TOXICOLOGY VOLUME 2, NUMBER 4 DECEMBER
4 Figure 2. QRS at initial toxicity and at 10 minutes after treatment; change in QRS. Amiodarone did not appear to have a harmful effect in this limited animal model of severe nortriptiline toxicity. Further research is required to determine if amiodarone is beneficial in other toxin-induced wide complex tachycardias. Another arm that combines amiodarone and sodium bicarbonate would have been interesting and may be a future direction for this work. LIMITATIONS The animal model does not reproduce human toxicity though the swine model does provide a close approximation of the human cardiovascular system. The route of exposure that is typically seen in a clinical setting is oral and not intravenous as was Figure 3. Mean MAPs for each arm. 150 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL TOXICOLOGY VOLUME 2, NUMBER 4 DECEMBER 2006
5 performed in this study. In this study, a single dose of sodium bicarbonate was given; but in clinical practice, an initial bolus is followed by an infusion. The efficacy of sodium bicarbonate relative to amiodarone could have been enhanced if larger doses and infusions of sodium bicarbonate had been instituted. In this study, more swine would have improved our statistical power. Analysis showed that 17 more animals per group would be needed, but that number is not practical to manage in a laboratory setting. The investigators were not blinded to treatment and would have added scientific validity. Also, another amiodarone arm administered without TCAs would allow us to compare its typical effect on MAP and QRS duration with the effect we have seen in a model of severe nortryptiline poisoning. The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to report. REFERENCES 1. Van Deusen SK, Birkhahn RH, Gaeta TJ. Treatment of hyperkalemia in a patient with unrecognized digitalis toxicity. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 2003;41(4): Lange RA, Cigarroa RG, Flores ED, McBride W, Kim AS, Wells PJ, et al. Potentiation of cocaine-induced coronary vasoconstriction by beta-adrenergic blockade. Ann Intern Med 1990;112(12): Pentel P, Peterson CD. Asystole complicating physostigmine treatment of tricyclic antidepressant overdose. Ann Emerg Med 1980;9(11): Caron MF, Kluger J; White CM. Amiodarone in the new AHA guidelines for ventricular tachyarrhythmias. Ann Pharmacother 2001;35: Kudenchuk PJ, Cobb LA, Copass MK, Cummins RO, Doherty AM, Fahrenbruch CE, et al. Amiodarone for resuscitation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest due to ventricular fibrillation. N Engl J Med 1999;341: Barrueto F Jr, Chuang A, Cotter BW, Hoffman RS, Nelson LS. Amiodarone fails to improve survival in amitriptylinepoisoned mice. Clin Toxicol 2005;43(3): McCabe JL, Cobaugh DJ, Menegazzi JJ, Fata J. Experimental tricyclic antidepressant toxicity: a randomized, controlled comparison of hypertonic saline solution, sodium bicarbonate and hyperventilation. Ann Emerg Med 1998;32: Zhou L, White CM, Chen BP, Chow MS, Fan C, Kluger J. A comparison of the antifibrillatory effects of desethylamiodarone to amiodarone in a swine model. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1999;34(3): Hutchins GM, Silverman KJ. Pathology of the stone heart syndrome: massive myocardial contraction band necrosis and widely patent coronary arteries. Am J Pathol 1979;95(3): JOURNAL OF MEDICAL TOXICOLOGY VOLUME 2, NUMBER 4 DECEMBER
The Hypotensive Poisoned Patient. Robert S. Hoffman, MD Director, NYC PCC
 The Hypotensive Poisoned Patient Robert S. Hoffman, MD Director, NYC PCC Some Definitions Hypotension = Low blood pressure Failure of macrocirculation Shock = Poor tissue perfusion Failure of microcirculation
The Hypotensive Poisoned Patient Robert S. Hoffman, MD Director, NYC PCC Some Definitions Hypotension = Low blood pressure Failure of macrocirculation Shock = Poor tissue perfusion Failure of microcirculation
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
Adenosine. poison/drug induced. flushing, chest pain, transient asystole. Precautions: tachycardia. fibrillation, atrial flutter. Indications: or VT
 Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Limited Efficacy of Calcium and Magnesium in a Porcine Model of Hydrofluoric Acid Ingestion
 Toxicology Investigations Limited Efficacy of Calcium and Magnesium in a Porcine Model of Hydrofluoric Acid Ingestion Jason A. Coffey, MD a, Kori L. Brewer, PhD a, Robert Carroll, PhD b, John Bradfield,
Toxicology Investigations Limited Efficacy of Calcium and Magnesium in a Porcine Model of Hydrofluoric Acid Ingestion Jason A. Coffey, MD a, Kori L. Brewer, PhD a, Robert Carroll, PhD b, John Bradfield,
WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA
 CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
EM Cases Course 2017 Toxicology Module
 EM Cases Course 2017 Toxicology Module quick IV access and diazepam is administered. The seizure stops. The first set of vitals show: HR 30bpm, BP 70/40. His ECG is shown below. Margaret Thompson & JP
EM Cases Course 2017 Toxicology Module quick IV access and diazepam is administered. The seizure stops. The first set of vitals show: HR 30bpm, BP 70/40. His ECG is shown below. Margaret Thompson & JP
Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent
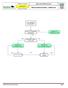 C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Levosimendan Does Not Improve Survival Time in a Rat Model of Verapamil Toxicity
 Levosimendan Does Not Improve Survival Time in a Rat Model of Verapamil Toxicity Toxicology Investigations Michael K. Abraham, MD a, Sara B. Scott, MD a, Andrew Meltzer, MD b, Fermin Barrueto Jr, MD a,b
Levosimendan Does Not Improve Survival Time in a Rat Model of Verapamil Toxicity Toxicology Investigations Michael K. Abraham, MD a, Sara B. Scott, MD a, Andrew Meltzer, MD b, Fermin Barrueto Jr, MD a,b
Cardiotoxic Medications
 Cardiotoxic Medications Dean Olsen, DO Faculty, New York City Poison Control Center Director Emergency Medicine Residency Nassau University Medical Center Assistant Professor Pharmacology, Toxicology New
Cardiotoxic Medications Dean Olsen, DO Faculty, New York City Poison Control Center Director Emergency Medicine Residency Nassau University Medical Center Assistant Professor Pharmacology, Toxicology New
Objectives: This presentation will help you to:
 emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
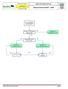 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation
 The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation Introduction The ARREST (Amiodarone in out-of-hospital Resuscitation of REfractory Sustained
The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation Introduction The ARREST (Amiodarone in out-of-hospital Resuscitation of REfractory Sustained
Life Threatening EKG s In the Toxicology Patient
 Life Threatening EKG s In the Toxicology Patient Dean Olsen, DO Faculty, New York City Poison Control Center Director Emergency Medicine Residency Nassau University Medical Center Assistant Professor Pharmacology,
Life Threatening EKG s In the Toxicology Patient Dean Olsen, DO Faculty, New York City Poison Control Center Director Emergency Medicine Residency Nassau University Medical Center Assistant Professor Pharmacology,
Contra Costa County Emergency Medical Services Drug Reference. Indication Dosing Cautions Comments
 Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies)
 SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
 Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology
 ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
Atrial fibrillation in the ICU
 Atrial fibrillation in the ICU Atrial fibrillation Preexisting or incident (new onset) among nearly one in three critically ill patients Formation of arrhythogenic substrate usually fibrosis (CHF, hypertension,
Atrial fibrillation in the ICU Atrial fibrillation Preexisting or incident (new onset) among nearly one in three critically ill patients Formation of arrhythogenic substrate usually fibrosis (CHF, hypertension,
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case. VF/Asystole
 Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency
 Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Icu-cpr PICTURE QUIZ march 2014
 Department of surgery Icu-cpr PICTURE QUIZ march 2014 Prepared by Dr. Karam Kamal Younis Assistant professor and consultant surgeon Convener of the Department of Surgery College of Medicine University
Department of surgery Icu-cpr PICTURE QUIZ march 2014 Prepared by Dr. Karam Kamal Younis Assistant professor and consultant surgeon Convener of the Department of Surgery College of Medicine University
PEDIATRIC SVT MANAGEMENT
 PEDIATRIC SVT MANAGEMENT 1 INTRODUCTION Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) can be defined as an abnormally rapid heart rhythm originating above the ventricles, often (but not always) with a narrow QRS
PEDIATRIC SVT MANAGEMENT 1 INTRODUCTION Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) can be defined as an abnormally rapid heart rhythm originating above the ventricles, often (but not always) with a narrow QRS
Samphant Ponvilawan Bumrungrad International
 Samphant Ponvilawan Bumrungrad International Definitions Artificial circulation using VA ECMO as an alternative to ventilation and external cardiac massage Indications Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest (OHCA)
Samphant Ponvilawan Bumrungrad International Definitions Artificial circulation using VA ECMO as an alternative to ventilation and external cardiac massage Indications Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest (OHCA)
POISON ANTIDOTE DOSE* COMMENTS
 Antidotes Acetaminophen N-acetylcysteine 140 mg/kg initial oral dose, followed Most effective within 16 24 hr; may by 70 mg/kg every 4 hr 17 doses be useful after chronic intoxication or intravenously
Antidotes Acetaminophen N-acetylcysteine 140 mg/kg initial oral dose, followed Most effective within 16 24 hr; may by 70 mg/kg every 4 hr 17 doses be useful after chronic intoxication or intravenously
Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose
 Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose Intravenous access Oxygen Pulse oximetry n-invasive blood pressure monitoring Accu-Check ECG monitoring and ECG Chest x-ray Respiratory depression?
Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose Intravenous access Oxygen Pulse oximetry n-invasive blood pressure monitoring Accu-Check ECG monitoring and ECG Chest x-ray Respiratory depression?
2/1/2013. Poisoning pitfalls. The original pitfall
 The original pitfall Poisoning pitfalls Craig Smollin MD Associate Medical Director, California Poison Control System - SF Division Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine, UCSF What will we talk about?
The original pitfall Poisoning pitfalls Craig Smollin MD Associate Medical Director, California Poison Control System - SF Division Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine, UCSF What will we talk about?
Krittin Bunditanukul Pharm.D, BCPS Department of Pharmacy Practice, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chulalongkorn University
 Krittin Bunditanukul Pharm.D, BCPS Department of Pharmacy Practice, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chulalongkorn University Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest can be caused by 4 rhythms: Ventricular fibrillation
Krittin Bunditanukul Pharm.D, BCPS Department of Pharmacy Practice, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chulalongkorn University Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest can be caused by 4 rhythms: Ventricular fibrillation
JUST SAY NO TO DRUGS?
 JUST SAY NO TO DRUGS? THE EVIDENCE BEHIND MEDICATIONS USED IN CARDIAC RESUSCITATION NTI 2014 CLASS CODE 148 Nicole Kupchik RN, MN, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN Objectives 1. Discuss the historical evidence supporting
JUST SAY NO TO DRUGS? THE EVIDENCE BEHIND MEDICATIONS USED IN CARDIAC RESUSCITATION NTI 2014 CLASS CODE 148 Nicole Kupchik RN, MN, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN Objectives 1. Discuss the historical evidence supporting
European Resuscitation Council
 European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
MICHIGAN. State Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
CSI Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment
 CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
DYSRHYTHMIAS. D. Assess whether or not it is the arrhythmia that is making the patient unstable or symptomatic
 DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
RESEARCH IN BASIC SCIENCE
 RESEARCH IN BASIC SCIENCE Effect of High-Dose Sodium Bicarbonate on the Vasopressor Effects of Epinephrine During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Barry E. Bleske, Pharm.D., Eric W Warren, Pharm.D., Ted L.
RESEARCH IN BASIC SCIENCE Effect of High-Dose Sodium Bicarbonate on the Vasopressor Effects of Epinephrine During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Barry E. Bleske, Pharm.D., Eric W Warren, Pharm.D., Ted L.
ANZCOR Guideline 12.4 Medications and Fluids in Paediatric Advanced Life Support
 ANZCOR Guideline 12. Medications and Fluids in Paediatric Advanced Life Support Who does this guideline apply to? This guideline applies to infants and children. Summary Who is the audience for this guideline?
ANZCOR Guideline 12. Medications and Fluids in Paediatric Advanced Life Support Who does this guideline apply to? This guideline applies to infants and children. Summary Who is the audience for this guideline?
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Evidence for Lidocaine and Amiodarone in Cardiac Arrest Due to VF/Pulseless VT
 Evidence for Lidocaine and Amiodarone in Cardiac Arrest Due to VF/Pulseless VT Introduction Evidence supporting the use of lidocaine and amiodarone for advanced cardiac life support was considered by international
Evidence for Lidocaine and Amiodarone in Cardiac Arrest Due to VF/Pulseless VT Introduction Evidence supporting the use of lidocaine and amiodarone for advanced cardiac life support was considered by international
Norepinephrine (Levophed )
 Norepinephrine (Levophed ) Scope C3IFT CCT Generic Name: Norepinephrine Trade Name: Levophed Chemical Class: Therapeutic Class: Actions: Pharmacokinetics: Vasopressor Vasopressor Mechanism of Action: Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (Levophed ) Scope C3IFT CCT Generic Name: Norepinephrine Trade Name: Levophed Chemical Class: Therapeutic Class: Actions: Pharmacokinetics: Vasopressor Vasopressor Mechanism of Action: Norepinephrine
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms. Introduction to the Algorithms
 Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Introduction to the Algorithms Cardiac Arrest Algorithms Prehospital Medication Profiles Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Introduction to the Algorithms Cardiac Arrest Algorithms Prehospital Medication Profiles Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate
Cardiac Arrhythmias & Drugs used in Advanced Life Support and Cardiac Emergencies
 Cardiac Arrhythmias & Drugs used in Advanced Life Support and Cardiac Emergencies CNHE Ballarat Health Services Valid from 1 st March 2016 to 31 st June 2018 1 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) An atrial
Cardiac Arrhythmias & Drugs used in Advanced Life Support and Cardiac Emergencies CNHE Ballarat Health Services Valid from 1 st March 2016 to 31 st June 2018 1 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) An atrial
ECMO for treatment of cardiotoxic intoxications
 ECMO for treatment of cardiotoxic intoxications Bruno Mégarbane, MD, PhD Medical and Toxicological Critical Care Department Lariboisiere Hospital, INSERM UMRS-1144, Paris-Diderot University Paris France
ECMO for treatment of cardiotoxic intoxications Bruno Mégarbane, MD, PhD Medical and Toxicological Critical Care Department Lariboisiere Hospital, INSERM UMRS-1144, Paris-Diderot University Paris France
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Prevention and Treatment Patrick Levelle, MD
 Prevention and Treatment Patrick Levelle, MD LOCAL ANESTHETIC TOXICITY 1. PERIPHERAL NERVE BLOCKS 2. ROLE OF THE PERIANESTHESIA RN 3. LOCAL ANESTHETIC TOXICITY Use of Lipid Emulsion Regional and Peripheral
Prevention and Treatment Patrick Levelle, MD LOCAL ANESTHETIC TOXICITY 1. PERIPHERAL NERVE BLOCKS 2. ROLE OF THE PERIANESTHESIA RN 3. LOCAL ANESTHETIC TOXICITY Use of Lipid Emulsion Regional and Peripheral
Requirements to successfully complete PALS:
 The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. The new AHA Handbook of Emergency Cardiac Care (ECC) contains these 2010 Guidelines.The 2010
The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. The new AHA Handbook of Emergency Cardiac Care (ECC) contains these 2010 Guidelines.The 2010
ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS) RECERTIFICATION EXAMINATION
 ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS) RECERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. Ten minutes after an 85 year old woman collapses, paramedics arrive and start CPR for the first time. The monitor shows fine (low amplitude)
ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS) RECERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. Ten minutes after an 85 year old woman collapses, paramedics arrive and start CPR for the first time. The monitor shows fine (low amplitude)
The most common. hospitalized patients. hypotension due to. filling time Rate control in ICU patients may be difficult as many drugs cause hypotension
 Arrhythmias in the critically ill ICU patients: Approach for rapid recognition & management Objectives Be able to identify and manage: Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response Atrial flutter
Arrhythmias in the critically ill ICU patients: Approach for rapid recognition & management Objectives Be able to identify and manage: Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response Atrial flutter
HealthCare Training Service
 HealthCare Training Service Advanced Life Support Exam Time: Perusal Time: 20 minutes 5 minutes Total Marks: 25 Instructions: Read each question carefully. Using a pencil, record your response to each
HealthCare Training Service Advanced Life Support Exam Time: Perusal Time: 20 minutes 5 minutes Total Marks: 25 Instructions: Read each question carefully. Using a pencil, record your response to each
Arrhythmic Complications of MI. Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine
 Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Advanced Cardiac Life Support ACLS
 Essential Medical Training, LLC Providing Quality, Professional Training Advanced Cardiac Life Support ACLS Course Study Guide and Agenda 772-781-9249 office 772-382-0607 fax Email: treasurecoastcpr@gmail.com
Essential Medical Training, LLC Providing Quality, Professional Training Advanced Cardiac Life Support ACLS Course Study Guide and Agenda 772-781-9249 office 772-382-0607 fax Email: treasurecoastcpr@gmail.com
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION. 1. Safe scene, standard precautions. 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness. 3. Quick look (monitor)
 LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
1/29/2014. Objectives. The unstable overdose patient. Unstable overdose case #1. Outline
 Objectives The unstable overdose patient Craig Smollin MD Associate Medical Director California Poison Control Center, SF Division Discuss clinical scenarios unique to the acutely poisoned patient and
Objectives The unstable overdose patient Craig Smollin MD Associate Medical Director California Poison Control Center, SF Division Discuss clinical scenarios unique to the acutely poisoned patient and
DRUG DOSAGES & CONTINUOUS RATE INFUSION PROTOCOLS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR RESEARCH IN SWINE
 DRUG DOSAGES & CONTINUOUS RATE INFUSION PROTOCOLS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR RESEARCH IN SWINE M. Michael Swindle, DVM, Diplomate ACLAM & ECLAM, swinetech@hotmail.com INTRODUCTION Swine are prone to arrhythmias
DRUG DOSAGES & CONTINUOUS RATE INFUSION PROTOCOLS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR RESEARCH IN SWINE M. Michael Swindle, DVM, Diplomate ACLAM & ECLAM, swinetech@hotmail.com INTRODUCTION Swine are prone to arrhythmias
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1984, 29
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Efficacy of Coenzyme Q10 Administra Aortic Stenosis and Pacemaker Induc Igarashi, Katsuro Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1984, 29 Issue Date 1984-10-25
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Efficacy of Coenzyme Q10 Administra Aortic Stenosis and Pacemaker Induc Igarashi, Katsuro Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1984, 29 Issue Date 1984-10-25
Indian Diploma in Critical Care Nursing
 Indian Diploma in Critical Care Nursing MCQ Section A - Only one answer is correct 1. Four emergency interventions used in resuscitating a patient in cardiac arrest. a. Adrenaline/Atropine/ Amiodarone/Defibrillation
Indian Diploma in Critical Care Nursing MCQ Section A - Only one answer is correct 1. Four emergency interventions used in resuscitating a patient in cardiac arrest. a. Adrenaline/Atropine/ Amiodarone/Defibrillation
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
Bryan D. Hayes, PharmD, FAACT University of
 Session Title: Pearls for the Critically Ill Poisoned Patient Bryan D. Hayes, PharmD, FAACT Session overview Managing the critically ill poisoned patient is challenging, particularly toxin-induced shock.
Session Title: Pearls for the Critically Ill Poisoned Patient Bryan D. Hayes, PharmD, FAACT Session overview Managing the critically ill poisoned patient is challenging, particularly toxin-induced shock.
Antiarrhythmic Drugs
 Antiarrhythmic Drugs DR ATIF ALQUBBANY A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R O F M E D I C I N E / C A R D I O L O G Y C O N S U L T A N T C A R D I O L O G Y & I N T E R V E N T I O N A L E P A C H D /
Antiarrhythmic Drugs DR ATIF ALQUBBANY A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R O F M E D I C I N E / C A R D I O L O G Y C O N S U L T A N T C A R D I O L O G Y & I N T E R V E N T I O N A L E P A C H D /
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes
 Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
Update of CPR AHA Guidelines
 Update of CPR AHA Guidelines Donald Hal Shaffner Course objective is to have an updated understanding of the American Heart Association s treatment algorithms for the management of cardiac decompensation
Update of CPR AHA Guidelines Donald Hal Shaffner Course objective is to have an updated understanding of the American Heart Association s treatment algorithms for the management of cardiac decompensation
Review Packet EKG Competency This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test.
 Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test. Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 60-100 bpm
Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test. Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 60-100 bpm
Chapter 13. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications
 Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
P V Praveen Kumar 1*, P. Archana 2. Original Research Article. Abstract
 Original Research Article Comparative clinical study of attenuation of cardiovascular responses to laryngoscopy intubation diltiazem, lignocaine and combination of diltiazem and lignocaine P V Praveen
Original Research Article Comparative clinical study of attenuation of cardiovascular responses to laryngoscopy intubation diltiazem, lignocaine and combination of diltiazem and lignocaine P V Praveen
JUST SAY NO? THE LATEST LOOK AT ACLS MEDICATIONS BRIDGETTE SVANCAREK, MD
 JUST SAY NO? THE LATEST LOOK AT ACLS MEDICATIONS BRIDGETTE SVANCAREK, MD OBJECTIVES Review the progression of the American Heart Association s ACLS cardiac arrest medication guidelines Identify the latest
JUST SAY NO? THE LATEST LOOK AT ACLS MEDICATIONS BRIDGETTE SVANCAREK, MD OBJECTIVES Review the progression of the American Heart Association s ACLS cardiac arrest medication guidelines Identify the latest
Final Written Exam ASHI ACLS
 Final Written Exam ASHI ACLS Instructions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Questions 1 and 2 pertain to the following scenario: A 54-year-old man has experienced
Final Written Exam ASHI ACLS Instructions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Questions 1 and 2 pertain to the following scenario: A 54-year-old man has experienced
STANDARDIZED PROCEDURE CARDIAC STRESS TESTING-EXERCISE TESTING (Adult, Peds)
 I. Definition: During the exercise test, the patient exercises on a bike or treadmill while being monitored with a 12 lead ECG, blood pressure device, pulse oximetry and, if requested, oxygen consumption,
I. Definition: During the exercise test, the patient exercises on a bike or treadmill while being monitored with a 12 lead ECG, blood pressure device, pulse oximetry and, if requested, oxygen consumption,
DETERMINATION OF THE EFFICACY OF A NEW HEMOSTATIC DRESSING IN A MODEL OF EXTREMITY ARTERIAL HEMORRHAGE IN SWINE
 NATIONAL DEFENSE MEDICAL CENTER TRI-SERVICE GENERAL HOSPITAL DETERMINATION OF THE EFFICACY OF A NEW HEMOSTATIC DRESSING IN A MODEL OF EXTREMITY ARTERIAL HEMORRHAGE IN SWINE Niann-Tzyy Dai, MD, PhD; JingYu
NATIONAL DEFENSE MEDICAL CENTER TRI-SERVICE GENERAL HOSPITAL DETERMINATION OF THE EFFICACY OF A NEW HEMOSTATIC DRESSING IN A MODEL OF EXTREMITY ARTERIAL HEMORRHAGE IN SWINE Niann-Tzyy Dai, MD, PhD; JingYu
HigHligHts of the 2018 Focused In 2015 Updates to the American Heart Association Guidelines for CPR and ECC: Advanced Cardiovascular Life
 Highlights of the 2018 Focused Updates to the American Heart Association Guidelines for CPR and ECC: Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support and Pediatric Advanced Life Support - Heart and Stroke Foundation
Highlights of the 2018 Focused Updates to the American Heart Association Guidelines for CPR and ECC: Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support and Pediatric Advanced Life Support - Heart and Stroke Foundation
Titrating Critical Care Medications
 Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Nitroglycerin and Heparin Drip Interfacility Protocols
 Nitroglycerin and Heparin Drip Interfacility Protocols EMS Protocol This protocol applies to nitroglycerin and Heparin drips that are initiated at the transferring facility prior to transport and are not
Nitroglycerin and Heparin Drip Interfacility Protocols EMS Protocol This protocol applies to nitroglycerin and Heparin drips that are initiated at the transferring facility prior to transport and are not
Blood Pressure Management in Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Blood Pressure Management in Acute Ischemic Stroke Kimberly Clark, PharmD, BCCCP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Critical Care, Greenville Health System Adjunct Assistant Professor, South Carolina College
Blood Pressure Management in Acute Ischemic Stroke Kimberly Clark, PharmD, BCCCP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Critical Care, Greenville Health System Adjunct Assistant Professor, South Carolina College
Pediatric Code Blue FOCUS on Medications. Objectives
 Pediatric Code Blue FOCUS on Medications Objectives The learner will be able to: 1. List commonly used pediatric code drugs based on PALS 2015 guidelines 2. Discuss mechanism of action, clinical indications,
Pediatric Code Blue FOCUS on Medications Objectives The learner will be able to: 1. List commonly used pediatric code drugs based on PALS 2015 guidelines 2. Discuss mechanism of action, clinical indications,
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes
 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters. Dilution not necessary (Available in prefilled syringe)
 Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters Acetazolamide 500 mg Reconstitute with at least 5ml sterile water (max concentration should not exceed 100mg/ml) 100-500 mg/min Hypotension
Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters Acetazolamide 500 mg Reconstitute with at least 5ml sterile water (max concentration should not exceed 100mg/ml) 100-500 mg/min Hypotension
MEDICATIONS CARDIOVASCULAR URGENCIES & EMERGENCIES 12/29/14. Cardiovascular Emergency Medications. Cardiovascular Emergency Medications
 CARDIOVASCULAR URGENCIES & EMERGENCIES Steven Ganzberg, DMD, MS Director of Anesthesiology, Century City Outpatient Surgery Center Clinical Professor of Anesthesiology, UCLA School of Dentistry sganzberg@ucla.edu
CARDIOVASCULAR URGENCIES & EMERGENCIES Steven Ganzberg, DMD, MS Director of Anesthesiology, Century City Outpatient Surgery Center Clinical Professor of Anesthesiology, UCLA School of Dentistry sganzberg@ucla.edu
ACLS Prep. Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep.
 November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
Dysrhythmias. Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics. EKG Parameters. Dysrhythmias. Components of an ECG Wave. Dysrhythmias
 Dysrhythmias Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics Rhythm bad in the heart: Whitewater rafting Electrical impulses coordinate heart Reduction in Cardiac Output PEA Asystole Components of an ECG Wave EKG Parameters
Dysrhythmias Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics Rhythm bad in the heart: Whitewater rafting Electrical impulses coordinate heart Reduction in Cardiac Output PEA Asystole Components of an ECG Wave EKG Parameters
Arrhythmias. Sarah B. Murthi Department of Surgery University of Maryland Medical School R. Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
 Arrhythmias Sarah B. Murthi Department of Surgery University of Maryland Medical School R. Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center 2012 Clinical Congress Presenter Disclosure Slide American College of Surgeons
Arrhythmias Sarah B. Murthi Department of Surgery University of Maryland Medical School R. Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center 2012 Clinical Congress Presenter Disclosure Slide American College of Surgeons
Cardiac arrhythmias. Janusz Witowski. Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences. J. Witowski
 Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
THE EVIDENCED BASED 2015 CPR GUIDELINES
 SAUDI HEART ASSOCIATION NATIONAL CPR COMMITTEE THE EVIDENCED BASED 2015 CPR GUIDELINES Page 1 Chapter 3 ACLS AND SPECIAL SITUATIONS CHAPTER The International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR)
SAUDI HEART ASSOCIATION NATIONAL CPR COMMITTEE THE EVIDENCED BASED 2015 CPR GUIDELINES Page 1 Chapter 3 ACLS AND SPECIAL SITUATIONS CHAPTER The International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR)
national CPR committee Saudi Heart Association (SHA). International Liason Commission Of Resuscitation (ILCOR)
 2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
Michigan Adult Cardiac Protocols TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Asystole Section 2-1 Bradycardia Section 2-2 Cardiac Arrest General Section 2-3 Cardiac Arrest ROSC Section 2-4 Chest Pain Acute Coronary Syndrome
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Asystole Section 2-1 Bradycardia Section 2-2 Cardiac Arrest General Section 2-3 Cardiac Arrest ROSC Section 2-4 Chest Pain Acute Coronary Syndrome
Potassium Efflux from Myocardial Cells Induced by Defibrillator Shock
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering Faculty Publications Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering 1986 Potassium Efflux from Myocardial Cells Induced by Defibrillator
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering Faculty Publications Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering 1986 Potassium Efflux from Myocardial Cells Induced by Defibrillator
ADULT CARDIAC EMERGENCIES
 ADULT CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Last Revised: September 2018 Cardiac Emergencies Section A 1 CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST NOTE: High quality CPR includes: 1. Chest Compressions at a depth of at least 2 inches 2. Rate
ADULT CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Last Revised: September 2018 Cardiac Emergencies Section A 1 CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST NOTE: High quality CPR includes: 1. Chest Compressions at a depth of at least 2 inches 2. Rate
PUZZLE. EARLY IMPACT ALS Jamie Syrett, MD Director of Prehospital Care Rochester General Health System PUZZLE THINKING OUTSIDE THE BOX! EARLY IMPACT?
 PUZZLE EARLY IMPACT ALS Jamie Syrett, MD Director of Prehospital Care Rochester General Health System PUZZLE THINKING OUTSIDE THE BOX! EARLY IMPACT? IV ACCESS? What things do we do that make a difference?
PUZZLE EARLY IMPACT ALS Jamie Syrett, MD Director of Prehospital Care Rochester General Health System PUZZLE THINKING OUTSIDE THE BOX! EARLY IMPACT? IV ACCESS? What things do we do that make a difference?
CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL CONSIDERATION
 CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL CONSIDERATION A. Age delineation: Infant CPR guidelines apply to victims less than one year of age; Child CPR guidelines apply to victims one year of age to the onset of adolescence
CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL CONSIDERATION A. Age delineation: Infant CPR guidelines apply to victims less than one year of age; Child CPR guidelines apply to victims one year of age to the onset of adolescence
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Verma A, Champagne J, Sapp J, et al. Asymptomatic episodes of atrial fibrillation before and after catheter ablation: a prospective, multicenter study. JAMA Intern Med. Published
Supplementary Online Content Verma A, Champagne J, Sapp J, et al. Asymptomatic episodes of atrial fibrillation before and after catheter ablation: a prospective, multicenter study. JAMA Intern Med. Published
ADULT CARDIAC EMERGENCIES
 ADULT CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Last Revised: July 2017 Cardiac Emergencies Section A 1 CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST NOTE: High quality CPR includes: 1. Chest Compressions at a depth of at least 2 inches 2. Rate of
ADULT CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Last Revised: July 2017 Cardiac Emergencies Section A 1 CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST NOTE: High quality CPR includes: 1. Chest Compressions at a depth of at least 2 inches 2. Rate of
Management Of Medical Emergencies. Zakaria S. Messieha, DDS
 Management Of Medical Emergencies Zakaria S. Messieha, DDS Z.S. Messieha Associate Professor, Anesthesiology University Of Illinois At Chicago Necessity Of Emergency Protocol Aging patient population.
Management Of Medical Emergencies Zakaria S. Messieha, DDS Z.S. Messieha Associate Professor, Anesthesiology University Of Illinois At Chicago Necessity Of Emergency Protocol Aging patient population.
Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
Heart Failure. Dr. William Vosik. January, 2012
 Heart Failure Dr. William Vosik January, 2012 Questions for clinicians to ask Is this heart failure? What is the underlying cause? What are the associated disease processes? Which evidence-based treatment
Heart Failure Dr. William Vosik January, 2012 Questions for clinicians to ask Is this heart failure? What is the underlying cause? What are the associated disease processes? Which evidence-based treatment
The pill-in-the-pocket strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
 The pill-in-the-pocket strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation KONSTANTINOS P. LETSAS, MD, FEHRA LABORATORY OF CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY EVANGELISMOS GENERAL HOSPITAL OF ATHENS ARRHYTHMIAS UPDATE,
The pill-in-the-pocket strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation KONSTANTINOS P. LETSAS, MD, FEHRA LABORATORY OF CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY EVANGELISMOS GENERAL HOSPITAL OF ATHENS ARRHYTHMIAS UPDATE,
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services. Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual
 Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Optional CE for EMT-B, Paramedics and PHRN s Bradycardia and Treatments Optional #7 2018
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Optional CE for EMT-B, Paramedics and PHRN s Bradycardia and Treatments Optional #7 2018 This month we will be looking at a specific ECG Rhythm and its treatments
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Optional CE for EMT-B, Paramedics and PHRN s Bradycardia and Treatments Optional #7 2018 This month we will be looking at a specific ECG Rhythm and its treatments
ACLS. Advanced Cardiac Life Support Practice Test Questions. 1. The following is included in the ACLS Survey?
 1. The following is included in the ACLS Survey? a. Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Differential Diagnosis b. Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Defibrillation c. Assessment, Breathing, Circulation, Defibrillation
1. The following is included in the ACLS Survey? a. Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Differential Diagnosis b. Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Defibrillation c. Assessment, Breathing, Circulation, Defibrillation
Hyperkalemia Protect, Shift, and Eliminate
 Disclosure Michael C. Thomas reports no relevant financial relationships. Lytes Off in Vegas! The Acute Management of Potassium and Calcium Disorders Program Objectives Design a plan to replace and monitor
Disclosure Michael C. Thomas reports no relevant financial relationships. Lytes Off in Vegas! The Acute Management of Potassium and Calcium Disorders Program Objectives Design a plan to replace and monitor
Neosynephrine. Name of the Medicine
 Name of the Medicine Neosynephrine Phenylephrine hydrochloride 1% injection Neosynephrine Presentation Neosynephrine is a clear, colourless, aqueous solution, free from visible particulates, in sterile
Name of the Medicine Neosynephrine Phenylephrine hydrochloride 1% injection Neosynephrine Presentation Neosynephrine is a clear, colourless, aqueous solution, free from visible particulates, in sterile
Ventricular tachycardia Ventricular fibrillation and ICD
 EKG Conference Ventricular tachycardia Ventricular fibrillation and ICD Samsung Medical Center CCU D.I. Hur Ji Won 2006.05.20 Ventricular tachyarrhythmia ventricular tachycardia ventricular fibrillation
EKG Conference Ventricular tachycardia Ventricular fibrillation and ICD Samsung Medical Center CCU D.I. Hur Ji Won 2006.05.20 Ventricular tachyarrhythmia ventricular tachycardia ventricular fibrillation
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac
 Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
