팔로사징을가진소아에서좌경부대동맥궁과 연관이상소견. Left cervical aortic arch and Associated Abnormalities in a child with Tetralogy of Fallot. Abstract *
|
|
|
- Mervin Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 부산대병원학술지통권제 31 호, 2012 팔로사징을가진소아에서좌경부대동맥궁과 연관이상소견 양산부산대학교병원영상의학과 김용우 Left cervical aortic arch and Associated Abnormalities in a child with Tetralogy of Fallot Yong-Woo Kim Department of Radiology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital Abstract * 경부대동맥궁은대동맥궁이쇄골상부에위치하는드문선천성기형이다. 경부대동맥궁은보통증상없는독립된기형으로발생하나, 다른심혈관계이상들과동반해서발생하기도한다. 대동맥류와협착이흔히같이발생하지만, 본증례처럼대동맥궁변이가동반되는경우는매우드물다. 저자는팔로사징의심도자술중에진단된환아에서, 전산화단층촬영혈관조영술로확인된, 좌측쇄골하동맥기시부동맥류와이중기시부를가진추골동맥을동반한좌경부대동맥궁 1례를경험하였기에보고한다. * 본연구는 2010 년도양산부산대학교병원임상연구비지원으로이루어졌음
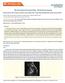
2 김용우 중심단어 : 대동맥궁, 팔로사징, 대동맥류, 추골동맥중복, 기형중복기원, 전산화단층촬영대동맥기형 Key words: Barin metastases, Lung cancer, Radiation therapy Introduction Cervical aortic arch (CAA) is a rare congenital anomaly in which the aortic arch is situated on cranial position above the clavicle. 1,2. The position of the arch varies from slightly superior to normal to very high in the neck, lying on either side of the trachea. 1,3 CAA usually occurs as an isolated anomaly without symptom, but in some cases it may be associated with other cardiac and aortic abnormalities. 1-4 Whereas aortic aneurysm and coarctation are well-documented associations, CAA accompanied by aortic arch variation is very rare. 1-4 Presenting features vary from a pulsatile mass in the supraclavicular fossa to symptoms simulating a respiratory tract infection. 5 Hence its diagnosis by non-invasive means is desirable. We report a case of left CAA with left subclavian artery aneurysm and aortic arch variation that was accompanied by duplicate origin of left vertebral artery in a patient with tetralogy of Fallot (TOF). To our best knowledge, this is the first report of CAA complicated by aortic arch variation and duplicate origin of left vertebral artery. Case Report A 2-year-old girl was admitted to our hospital for further evaluation of cardiac murmur known at birth. On physical examination, she had a cyanosis of lip and systolic murmur best heard on the left midsternal border (grade lll or lv). The plain chest radiography showed normal shaped heart but the aortic shadow was not well demarcated and the widening of superior mediastinum was noted (Fig 1a). Echocardiography demonstrated a large perimenbranous VSD (about 14mm), pulmonary stenosis, and the overriding of aorta. Patient was diagnosed as TOF. Cardiac catheterization was done for the evaluation of TOF and associated cardiac abnormalities. The angiogram following contrast injection in the left ventricle through VSD showed that the aortic arch was left sided and tortuously elongated to the level of the 7 th cervical spine. It also showed the descending
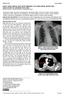
3 팔로사징을가진환아에서좌경부대동맥궁과연관이상소견 thoracic aorta to be lef tsided (Fig1b). For further evaluation of aortic arch and its branching pattern, the CT angiography of chest (Volumezoom,Erlangen,Siemens) was performed. The CT angiography confirmed anomalous course of the aortic arch above left clavicle, normal vessel dimensions, and absence of concomitant coarctation or aneurysm. CT angiography provided additional information about aortic branch vessels. The left branch arteries of aortic arch were hypoplastic and left subclavian and vertebral artery anomalously originated from the upper portion of the descending thoracic aorta. Left subclavian artery was accompanied by small aneurysm at the origin (Fig2). Left vertebral artery had duplicated origin from the left subclavian artery and the aortic arch distal to the left subclavian artery. The two segments joined each other at the level of C6 vertebra and ascend into the C5 transverse foramen (Fig 3). For the evaluation of associated chromosome 22q11 deletion syndrome, a chromosome examination was conducted by the fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) method. Cytogenetic analysis revealed no evidence of the chromosome 22q11 deletion. She underwent surgery for repair of TOF but anomalous aortic arch was remained without surgical treatment. Discussion Cervical aortic arch is a rare congenital anomaly in which the ascending aorta extends in such a way that the aortic arch is situated cranial to its usual position. 5 The position of the arch varies from slightly superior to normal to very high in the neck, lying on either side of the trachea. 1,3 Nonetheless the diagnosis of this anomaly should be made when the aortic arch is supraclavicular. 5,6 The prevalence of CAA is less than a case every 10,000 live births. 7 Many patients with CAA are asymptomatic, while others present with respiratory problems, dysphagia, pain around the neck and chest, and ischemic cerebrovascular attack. 6 Left CAA is often asymptomatic as opposed to right CAA, which is usually associated with dysphagia and respiratory distress due to the compression by the vascular rings. The mechanism of development of an aortic arch anomaly is explained by the hypothetical double aortic arch system. 8 The persistence of the left fourth branchial arch and the regression of the right fourth branchial arch produce a normal left aortic arch between the fifth and seventh embryonic weeks. Various theories have been proposed to
4 김용우 explain the CAA. 4,9,10 There are three major theories explaining the development of the CAA. Persistence of the second or third branchial arch combined with the resorption of the fourth branchial arch is one theory. Lack of caudal migration of an otherwise normal fourth arch is the second theory. The third theory explains the high position as the result of fusion between the third and fourth arch combined with failure to descend into the thorax. Recent work suggests that the CAA is often associated with chromosomal abnormality (deletions in chromosome 22q11 region) Hence these lesions could be included in the spectrum of defects known as catch 22. This syndrome is characterized by cardiac defects, abnormal facies, thymic hypoplasia, cleft palate, hypocalcemia, and a deletion in choromosome 22. But in our case, there is no evidence of chromosome 22q11 deletion in the cytogenetic analysis. Many patients with CAA are asymptomatic, but others present with respiratory problems due to compression of the trachea or esophagus by a vascular ring. In about 30 % of the cases of CAA, cardiac anomalies are also present, such as TOF, VSD, or double-outlet right ventricle. 14 Our patient had TOF with the cervical aortic arch. CAA usually presents between the ages of 20 and 40 and has an equal sex distribution except when associated with aneurysm formation, which occurs in approximately 20% of patients, only female patients with CAA have developed aneurysm. The aneurysm formation may occur secondary to left CAA in 20% of cases and particularly in female patient. Most aneurysms are in the transverse aortic arch, which is the location least affected by other types of aortic aneurysm. So female patients with CAA, such as our case, should take follow-up imaging annually to identify the possible formation of aneurysm. CAA commonly occurs as an isolated anomaly andis usually silent. Presenting features vary from a pulsatile swelling in the supraclavicular fossa to symptoms simulating a respiratory tract infection. Infant and children may present with features caused by associated congenital heart condition. The predominant congenital heart anomaly associated with right CAA is ventricular septal defect.other cardiac abnormalities include double outlet right ventricle, tricuspid atresia and atrial septal defect. Left CAA has been associated with patent ductus arteriosus, TOF, and pseudotruncus. 1-3 The present case is left CAA with TOF
5 팔로사징을가진환아에서좌경부대동맥궁과연관이상소견 as associated cardiac abnormality. It also has been known that TOF is associated with aortic arch anomalies such as a right aortic arch, an aberrant subclavian artery, an elongated ascending aorta or a high aortic arch. 15. But in that report, patients with high aortic arch almost had a right aortic arch and there was no case in which the apex of the arch was in the cervical position. 15 In our survey, the only one case has been reported about cervical aortic arch associated with TOF. 16 The patient was an adult (38-year-old) with right cervical aortic arch and he had a chromosome 22 abnormality. 16. But in this case, the patient was very young (2-year-old) and she was not associated with chromosome 22 abnormality. CAAs were classified into five morphologic types based on the side of the descending aorta and the branching pattern by Haughton et al. 17, although some cases were unclassifiable. Type D in the Haughton classification is the most frequent type of CAA. Type D CAA manifests ipsilateral descending aorta with normal sequence of the major three arteries. 10 Our case has left cervical aortic arch with left sided descending aorta, close to Haughton type D. But the branching pattern is different with type D. In our case, left subclavian artery was origin from descending aorta and left vertebral artery had anomalous origin distal to left subclavian artery on 3D-volume rendering images. In our case, the review of the acquired axial data of CTA showed duplicate origin of left vertebral artery from the aortic arch and left subclavian artery. The term duplication is applied to a vertebral artery that has two origins with a variable level of fusion in the neck. Duplication is very rare, with few reports in the literature. Vertebral artery duplication is reported to be more common on the left. 18 The duplicated segments usually fuse at C4-6. The vertebral artery develops from net-like and longitudinal anastomoses between the cervical intersegmental arteries at the early embryonic stage. Normally the cervical intersegmental arteries regress, except for the sixth vessel. The sixth cervical intersegmental artery becomes the proximal portion of the subclavian artery and the point of origin of the vertebral artery. Duplication of the vertebral arteries arises as a result of failure of involution of intersegmental arteries. This persists as an additional origin to the vertebral artery, along with the sixth artery (schema)
6 김용우 To our knowledge, only several cases demonstrating a duplicate origin of the left vertebral artery from the aortic arch and left subclavian artery have been reported But all cases had anomalous aortic arch origin between the left common carotid and the left subclavian arteries. In our case, the anomalous origin of left vertebral artery arises directly from the aorta distal to the left subclavian artery. Our case would be explained as follows: the branch arising from the left subclavian artery would represent the normal persistence of the sixth intersegmental artery, with the anomalous origin from the aortic arch representing a persistence of the seventh intersegmental artery. 18,20 With the advent of multislice helical CT scanner, CTA can provide anatomic and pathologic information of aortic arch and its branches. While three-dimensional reconstructions enable visualization of the entire course of the aortic arch and its branch arteries, review of the acquired axial data is important to fully understand the vertebral artery configuration and identify abnormalities in the adjacent tissues. In our case, there was focal aneurysm in the origin of the left subclavian artery. Although various congenital anomalies and/or cardiovascular abnormalities are occasionally complicated in CAA, there has been only one case report of CAA with branch artery aneurysm. The hemodynamic alteration, such as tortuous kinking, and abnormal structural integrity of branch artery may contribute to this rare branch aneurysm. In conclusion, the CAA associated with TOF, branch artery aneurysm, and duplicate origin of left vertebral artery is the first case. We could successfully demonstrate the location of the arch, its branching pattern, and associated complication using CT angiography. We considered that CT angiography was suitable for evaluating congenital anomaly of the aortic arch and related vessels without invasive procedure and for accurate follow-up monitoring the aneurysm formation which may occur secondary to left CAA (20% of cases) or abrupt aortic rupture, particularly in female patient. We recommend the patient with CAA and associated anomalies under a program of annual surveillance to identify the possible formation of aneurysm. References 1. Kumar S, Mandalam KR, Unni M, Roy S, Gupta AK, Rao VR. Left cervical arch and associated abnormalities. Cardiovasc Intervent
7 팔로사징을가진환아에서좌경부대동맥궁과연관이상소견 Radiol. 1989;12: Tsukamoto O, Seto S, Moriya M, Yano K. Left cervical aortic arch associated with aortic aneurysm, aortic coarctation, and branch artery aneurysm--a case report and review. Angiology. 2003;54: Moncada R, Shannon M, Miller R, White H, Friedman J, Shuford WH. The cervical aortic arch. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975;125: DuBrow IW, Burman SO, Elias DO, Hastreiter AR, Pietras RJ. Aortic arch in the neck. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1974;68: Kumar S, Bajaj R, Gujral R. Case report: MR angiography of cervical aortic arch. Clin Radiol. 1997;52: Doorenbos BM, Mooyaart EL, Hoorntje JC. MR diagnosis of a right cervical aortic arch. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1991;15: Samánek M, Slavík Z, Zborilová B, Hrobonová V, Vorísková M, Skovránek J. Prevalence, treatment, and outcome of heart disease in live-born children: a prospective analysis of 91,823 live-born children. Pediatr Cardiol. 1989;10: Stewart JR, Kincaid OW, Edwards JE. An atlas of vascular rings and related malformations of the aortic arch system. Charles C Thomas, Springfield, IL, 1964, 8-13, Hirao K, Miyazaki A, Noguchi M, Shibata R, Hayashi K. The cervical aortic arch with aneurysm formation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999;23: Ogawa S, Ozaki Y, Sumi Y, Kyogoku S, Maehara T. MR angiography of left-sided cervical aortic arch with aneurysm formation. Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;20: Ikonomidis JS, Robbins RC. Cervical aortic arch with pseudocoarctation: presentation with spontaneous rupture. Ann Thorac Surg 1999;67: McElhinney DB, Clark BJ 3rd, Weinberg PM, Kenton ML, McDonald-McGinn D, Driscoll DA, et al. Association of chromosome 22q11 deletion with isolated anomalies of aortic arch laterality and branching. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37: Pearson GD, Kan JS, Neill CA, Midgley FM, Gardner TJ, Hougen TJ. Cervical aortic arch with aneurysm formation. Am J Cardiol. 1997;79: Kazuma N, Murakami M, Suzuki Y, Umezu R, Murata M. Cervical aortic arch associated with 22q11.2 deletion. Pediatr Cardiol. 1997;18:
8 김용우 15. Nakajima Y, Nishibatake M, Ikeda K, Momma K, Takao A, Terai M. Abnormal development of fourth aortic arch derivatives in the pathogenesis of tetralogy of Fallot. Pediatr Cardiol. 1990;11: Emmel M, Schmidt B, Schickendantz S. Double aortic arch in a patient with Fallot's tetralogy. Cardiol Young. 2005;15: Haughton VM, Fellows KE, Rosenbaum AE. The cervical aortic arches. Radiology 1975;114: Goddard AJ, Annesley-Williams D, Guthrie JA, Weston M. Duplication of the vertebral artery: report of two cases and review of the literature. Neuroradiology 2001;43: Padget DH. The development of cranial arteries in the human embryo. Contrib Embryol 1948;32: Suzuki S, Kuwabara Y, Hatano R, Iwai T. Duplicate origin of left vertebral artery. Neuroradiology 1978;15: Eisenberg RA, Vines FS, Taylor SB. Bifid origin of the left vertebral artery. Radiology 1986;159: Hashimoto H, Ohnishi H, Yuasa T, Kawaguchi S. Duplicate origin of the vertebral artery: report of two cases. Neuroradiology 29:
9 팔로사징을가진환아에서좌경부대동맥궁과연관이상소견 Figure legands Fig. 1. On chest radiography (1a), heart seemed normal. But the aortic shadow was not well demarcated and mild superior mediastinal widening was noted (arrows). Cardiac angiography (1b) in the left ventricle through VSD, showed that the aortic arch was elongated to the level of the seventh cervical spine and was tortuous with kinking (arrows)
10 김용우 Fig. 2. The MIP and 3D images of chest CT angiography (A-C) showed a left side cervical aortic arch with ipsilateral descending aorta. The right brachiocephalic artery and its branches had normal size (thin arrows in 2A-B), but the left side branching arteries were hypoplastic. And left common carotid artery (thick arrows in 2A-B) directly originated from the top of aortic arch. The left subclavian artery is arising from descending aorta and associated with small aneurysm at the origin (thin arrow in 2C ). The left vertebral artery originated from descending aorta, just below left subclavian artery (thick arrow in 2C)
11 팔로사징을가진환아에서좌경부대동맥궁과연관이상소견 Fig. 3. The sequential axial images of chest CT angiography (a-d) showed a left sided aortic arch with ipsilateral descending aorta. Left common carotid artery (long arrow in 3A) directly originated from the ascending aorta. Left subclavian artery (thin double arrow in 3B & 3C) is arising from descending aorta and it is associated with small aneurysm (thin arrow, 3C). Left verterbral artery has duplicated origin with one segment arising from the aortic arch (arrowhead in 3A-3D) and the other off the left subclavian artery (short arrow, 3A & 3B). Two duplicated segments join into a single vessel at the level of C-6 and enter into the foramen transversarium of the fifth cervical vertebra
12
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Cervical aortic arch with aortic obstruction:
 Thorax, 1980, 35, 26-30 Cervical aortic arch with aortic obstruction: report of two cases ROBERTO TIRABOSCHI, GIANCARLO CRUPI, GIUSEPPE LOCATELLI, SIEW YEN HO, AND LUCIO PARENZAN From the Department of
Thorax, 1980, 35, 26-30 Cervical aortic arch with aortic obstruction: report of two cases ROBERTO TIRABOSCHI, GIANCARLO CRUPI, GIUSEPPE LOCATELLI, SIEW YEN HO, AND LUCIO PARENZAN From the Department of
The Uncommon Vascular Ring - Not that Uncommon
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report The Uncommon Vascular Ring - Not that Uncommon Roshan D Souza MD 1, Deepa Prasad MD 1, James Strainic MD 1, Anoop Mohamed Iqbal MD 2 and Ravi Ashwath MD
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report The Uncommon Vascular Ring - Not that Uncommon Roshan D Souza MD 1, Deepa Prasad MD 1, James Strainic MD 1, Anoop Mohamed Iqbal MD 2 and Ravi Ashwath MD
Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience
 Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience Ximing Wang, M.D., Zhaoping Cheng, M.D., Dawei Wu, M.D., Lebin
Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience Ximing Wang, M.D., Zhaoping Cheng, M.D., Dawei Wu, M.D., Lebin
9/8/2009 < 1 1,2 3,4 5,6 7,8 9,10 11,12 13,14 15,16 17,18 > 18. Tetralogy of Fallot. Complex Congenital Heart Disease.
 Current Indications for Pediatric CTA S Bruce Greenberg Professor of Radiology Arkansas Children s Hospital University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences greenbergsbruce@uams.edu 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
Current Indications for Pediatric CTA S Bruce Greenberg Professor of Radiology Arkansas Children s Hospital University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences greenbergsbruce@uams.edu 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
Devendra V. Kulkarni, Rahul G. Hegde, Ankit Balani, and Anagha R. Joshi. 2. Case Report. 1. Introduction
 Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 614647, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/614647 Case Report A Rare Case of Pulmonary Atresia with Ventricular Septal Defect with a Right Sided Aortic Arch and
Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 614647, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/614647 Case Report A Rare Case of Pulmonary Atresia with Ventricular Septal Defect with a Right Sided Aortic Arch and
Postgraduate Student, Department of Radiodiagnosis, MVJ Medical College and Research Hospital, Hoskote, Bangalore. 2
 RIGHT-SIDED AORTIC ARCH WITH ABERRANT LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY AND DUPLICATION OF SUPERIOR VENA CAVA Parikhita Hazarika 1, Tejaswani Penmetsa 2, Narendranath Kudva 3 1 Postgraduate Student, Department of
RIGHT-SIDED AORTIC ARCH WITH ABERRANT LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY AND DUPLICATION OF SUPERIOR VENA CAVA Parikhita Hazarika 1, Tejaswani Penmetsa 2, Narendranath Kudva 3 1 Postgraduate Student, Department of
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We. ACHD Patients
 Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Anomalous origin of the right subclavian artery from main pulmonary artery
 Anomalous origin of the right subclavian artery from main pulmonary artery Award: AOSR Best Exhibit Prize - Bronze Poster No.: R-0178 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: U. Chaumrattanakul,
Anomalous origin of the right subclavian artery from main pulmonary artery Award: AOSR Best Exhibit Prize - Bronze Poster No.: R-0178 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: U. Chaumrattanakul,
Chapter 3.14 Aortic arch interruption
 Chapter 3.14 Aortic arch interruption z Definition The aortic arch is described as three segments: proximal, distal and isthmus. The proximal component extends from the takeoff of the innominate artery
Chapter 3.14 Aortic arch interruption z Definition The aortic arch is described as three segments: proximal, distal and isthmus. The proximal component extends from the takeoff of the innominate artery
JMSCR Vol. 03 Issue 06 Page June 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Anatomical Variation in Arch of Aorta: A Case Report Authors Bandopadhyay Debasis Lt Col Dr 1, Krishnan Mythili Dr 2, Kumar Sushil 3 1
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Anatomical Variation in Arch of Aorta: A Case Report Authors Bandopadhyay Debasis Lt Col Dr 1, Krishnan Mythili Dr 2, Kumar Sushil 3 1
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016
 1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
Surgical implications of right aortic arch with isolation of left subclavian artery'
 British Heart journal, I975, 37, 93I-936. Surgical implications of right aortic arch with isolation of left subclavian artery' L. Rodriguez,2 T. Izukawa, C. A. F. MoEs, G. A. Trusler, and W. G. Williams
British Heart journal, I975, 37, 93I-936. Surgical implications of right aortic arch with isolation of left subclavian artery' L. Rodriguez,2 T. Izukawa, C. A. F. MoEs, G. A. Trusler, and W. G. Williams
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
Congenital Anomalies of the Aortic Arch: Evaluation with the Use of Multidetector Computed Tomography
 Congenital nomalies of the ortic rch: Evaluation with the Use of Multidetector Computed Tomography ysel Türkvatan, MD Fatma Gül üyükbayraktar, MD Tülay Ölçer, MD Turhan Cumhur, MD Index terms: ortic arch
Congenital nomalies of the ortic rch: Evaluation with the Use of Multidetector Computed Tomography ysel Türkvatan, MD Fatma Gül üyükbayraktar, MD Tülay Ölçer, MD Turhan Cumhur, MD Index terms: ortic arch
Two Cases of Incidentally Picked Up Adult Unilateral Pulmonary Artery Atresia with Variable Imaging Features
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. III (Dec. 2017), PP 45-49 www.iosrjournals.org Two Cases of Incidentally Picked Up
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. III (Dec. 2017), PP 45-49 www.iosrjournals.org Two Cases of Incidentally Picked Up
Index. cardiology.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES. PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU
 CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, June: 63-70, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients MOHAMED ZAKI, M.D.
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, June: 63-70, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients MOHAMED ZAKI, M.D.
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Original Article. Double Aortic Arch in Infants and Children CH XIE, FQ GONG, GP JIANG, SL FU. Key words. Background
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2018;23:233-238 Original Article Double Aortic Arch in Infants and Children CH XIE, FQ GONG, GP JIANG, SL FU Abstract Key words Background: This study aimed to report the diagnosis,
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2018;23:233-238 Original Article Double Aortic Arch in Infants and Children CH XIE, FQ GONG, GP JIANG, SL FU Abstract Key words Background: This study aimed to report the diagnosis,
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography
 485 JACC Vol. 5, No. I Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography DOUGLAS S., MD, FACC Cleveland, Ohio The use of intravenous digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of patients
485 JACC Vol. 5, No. I Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography DOUGLAS S., MD, FACC Cleveland, Ohio The use of intravenous digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of patients
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery
 A Doubtful Cause of Symptoms Thomas P. Comer, M.D., Malvin Weinberger, M.D., and Howard D. Sirak, M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with surgically treated aberrant right subclavian artery are reviewed. In half,
A Doubtful Cause of Symptoms Thomas P. Comer, M.D., Malvin Weinberger, M.D., and Howard D. Sirak, M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with surgically treated aberrant right subclavian artery are reviewed. In half,
DR Turner, JA Vincent, and ML Epstein. Isolated right pulmonary artery discontinuity. Images Paediatr Cardiol Jul-Sep; 2(3):
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images PMCID: PMC3232486 Isolated right pulmonary artery discontinuity DR Turner, MD, * JA Vincent, ** and ML Epstein *** * Senior Fellow, Division of Cardiology, Children's
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images PMCID: PMC3232486 Isolated right pulmonary artery discontinuity DR Turner, MD, * JA Vincent, ** and ML Epstein *** * Senior Fellow, Division of Cardiology, Children's
CongHeartDis.doc. Андрій Миколайович Лобода
 CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
List of Videos. Video 1.1
 Video 1.1 Video 1.2 Video 1.3 Video 1.4 Video 1.5 Video 1.6 Video 1.7 Video 1.8 The parasternal long-axis view of the left ventricle shows the left ventricular inflow and outflow tract. The left atrium
Video 1.1 Video 1.2 Video 1.3 Video 1.4 Video 1.5 Video 1.6 Video 1.7 Video 1.8 The parasternal long-axis view of the left ventricle shows the left ventricular inflow and outflow tract. The left atrium
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome: Echocardiographic Assessment
 Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome: Echocardiographic Assessment Craig E Fleishman, MD, FACC, FASE Director, Non-invasive Cardiac Imaging The Hear Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome: Echocardiographic Assessment Craig E Fleishman, MD, FACC, FASE Director, Non-invasive Cardiac Imaging The Hear Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI
VASCULAR RINGS A CASE - BASED REVIEW
 VASCULAR RINGS A CASE - BASED REVIEW Beverley Newman, BSc. MB.Bch. FACR Professor of Radiology Stanford University and Lucile Packard Children s Hospital Q1,2,3 Frontal chest radiographs on three different
VASCULAR RINGS A CASE - BASED REVIEW Beverley Newman, BSc. MB.Bch. FACR Professor of Radiology Stanford University and Lucile Packard Children s Hospital Q1,2,3 Frontal chest radiographs on three different
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Right Sided Aortic Arch and its rare Associations- A Case Series
 DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2018/35392:2410 Radiology Section Case Series Right Sided Aortic Arch and its rare Associations- A Case Series Nidhi Aggarwal, Narender kumar kardam, Kushal Babu Gehlot ABSTRACT Right
DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2018/35392:2410 Radiology Section Case Series Right Sided Aortic Arch and its rare Associations- A Case Series Nidhi Aggarwal, Narender kumar kardam, Kushal Babu Gehlot ABSTRACT Right
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery
 Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION
 ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION By Adel El Badrawy, Ahmed Abdel Razek, Nermin Soliman, Hala El Marsafawy *, Sameh Amer** From Radiodiagnosis, Pediatric Cardiology* & Cardiothoracic
ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION By Adel El Badrawy, Ahmed Abdel Razek, Nermin Soliman, Hala El Marsafawy *, Sameh Amer** From Radiodiagnosis, Pediatric Cardiology* & Cardiothoracic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Cardiac Catheterization Cases Primary Cardiac Diagnoses Facility 12 month period from to PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient)
 PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT WITH CAVEATS 1. In one study of 50 CHARGE patients with CHD, 75% required surgery. 2. Children with CHARGE may be resistant to chlo
 CARDIOLOGY IN CHARGE SYNDROME: FOR THE PHYSICIAN Angela E. Lin, M.D. Teratology Program/Active Malformation Surveillance, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Old PBBH-B501, 75 Francis St., Boston, MA 02115 alin@partners.org
CARDIOLOGY IN CHARGE SYNDROME: FOR THE PHYSICIAN Angela E. Lin, M.D. Teratology Program/Active Malformation Surveillance, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Old PBBH-B501, 75 Francis St., Boston, MA 02115 alin@partners.org
MEDICAL SCIENCES Vol.I -Adult Congenital Heart Disease: A Challenging Population - Khalid Aly Sorour
 ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: A CHALLENGING POPULATION Khalid Aly Sorour Cairo University, Kasr elaini Hospital, Egypt Keywords: Congenital heart disease, adult survival, specialized care centers. Contents
ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: A CHALLENGING POPULATION Khalid Aly Sorour Cairo University, Kasr elaini Hospital, Egypt Keywords: Congenital heart disease, adult survival, specialized care centers. Contents
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery Aneurysm
 Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery William S. Stoney, M.D., William C. Alford, Jr., M.D., George R. Burrus, M.D., and Clarence S. Thomas, Jr., M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with aneurysm of an aberrant right
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery William S. Stoney, M.D., William C. Alford, Jr., M.D., George R. Burrus, M.D., and Clarence S. Thomas, Jr., M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with aneurysm of an aberrant right
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.1, March 2000 Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant F Hakim, MD* A Madani, MD* A Abu Haweleh, MD,MRCP*
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.1, March 2000 Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant F Hakim, MD* A Madani, MD* A Abu Haweleh, MD,MRCP*
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome
 Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart
 Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
IMAGING the AORTA. Mirvat Alasnag FACP, FSCAI, FSCCT, FASE June 1 st, 2011
 IMAGING the AORTA Mirvat Alasnag FACP, FSCAI, FSCCT, FASE June 1 st, 2011 September 11, 2003 Family is asking $67 million in damages from two doctors Is it an aneurysm? Is it a dissection? What type of
IMAGING the AORTA Mirvat Alasnag FACP, FSCAI, FSCCT, FASE June 1 st, 2011 September 11, 2003 Family is asking $67 million in damages from two doctors Is it an aneurysm? Is it a dissection? What type of
PAEDIATRIC EMQs. Andrew A Mallick Paediatrics.info.
 PAEDIATRIC EMQs Andrew A Mallick Paediatrics.info www.paediatrics.info Paediatric EMQs Paediatrics.info First published in the United Kingdom in 2012. While the advice and information in this book is believed
PAEDIATRIC EMQs Andrew A Mallick Paediatrics.info www.paediatrics.info Paediatric EMQs Paediatrics.info First published in the United Kingdom in 2012. While the advice and information in this book is believed
Cardiopulmonary Syndromes: Conditions With Concomitant Cardiac and Pulmonary Abnormalities
 Cardiopulmonary Syndromes: Conditions With Concomitant Cardiac and Pulmonary Abnormalities Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Professor of Radiology The University of Texas HSC at San Antonio Cardiopulmonary Syndromes
Cardiopulmonary Syndromes: Conditions With Concomitant Cardiac and Pulmonary Abnormalities Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Professor of Radiology The University of Texas HSC at San Antonio Cardiopulmonary Syndromes
Journal of Radiology Case Reports
 Pseudocoarctation with saccular aneurysms, left sided SVC and aberrant right subclavian artery - Balaji Rao 1,2, Rajesh Botchu 1*, Aman Khan 1, Mansoor Aslam 2 1. Department of Radiology, University Hospitals
Pseudocoarctation with saccular aneurysms, left sided SVC and aberrant right subclavian artery - Balaji Rao 1,2, Rajesh Botchu 1*, Aman Khan 1, Mansoor Aslam 2 1. Department of Radiology, University Hospitals
The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists
 Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
J Somerville and V Grech. The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2. Images Paediatr Cardiol Jan-Mar; 12(1): 1 8.
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2010 PMCID: PMC3228330 The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2 J Somerville and V Grech Paediatric Department, Mater Dei Hospital, Malta Corresponding
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2010 PMCID: PMC3228330 The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2 J Somerville and V Grech Paediatric Department, Mater Dei Hospital, Malta Corresponding
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA
 Patent ductus arteriosus PDA Is connecting between the aortic end just distal to the origin of the LT sub clavian artery& the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation. Female/male ratio is 2:1 and it is more
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA Is connecting between the aortic end just distal to the origin of the LT sub clavian artery& the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation. Female/male ratio is 2:1 and it is more
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
Aortography in Fallot's Tetralogy and Variants
 Brit. Heart J., 1969, 31, 146. Aortography in Fallot's Tetralogy and Variants SIMON REES AND JANE SOMERVILLE From The Institute of Cardiology and National Heart Hospital, London W.J In patients with Fallot's
Brit. Heart J., 1969, 31, 146. Aortography in Fallot's Tetralogy and Variants SIMON REES AND JANE SOMERVILLE From The Institute of Cardiology and National Heart Hospital, London W.J In patients with Fallot's
S. Bruce Greenberg, MD FNASCI and President, NASCI Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
 S. Bruce Greenberg, MD FNASCI and President, NASCI Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences No financial disclosures Aorta Congenital aortic stenosis/insufficiency
S. Bruce Greenberg, MD FNASCI and President, NASCI Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences No financial disclosures Aorta Congenital aortic stenosis/insufficiency
Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot
 36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan
 PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR
 cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR Dianna M. E. Bardo, M. D. Assistant Professor of Radiology & Cardiovascular Medicine Director of Cardiac Imaging cardiac imaging planes
cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR Dianna M. E. Bardo, M. D. Assistant Professor of Radiology & Cardiovascular Medicine Director of Cardiac Imaging cardiac imaging planes
Transient malformations like PDA and PDA of prematurity were not considered. We have divided cardiac malformations in 2 groups:
 CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS DETECTED AT BIRTH Anwar Dudin-MD, Annie Rambaud-Cousson-MD, Mahmoud Nashashibi-MD Pediatric Department Makassed Hospital Jerusalem Diagnosis of congenital heart disease in the neonatal
CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS DETECTED AT BIRTH Anwar Dudin-MD, Annie Rambaud-Cousson-MD, Mahmoud Nashashibi-MD Pediatric Department Makassed Hospital Jerusalem Diagnosis of congenital heart disease in the neonatal
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
3/14/2011 MANAGEMENT OF NEWBORNS CARDIAC INTENSIVE CARE CONFERENCE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IRVINE, CA. MARCH 7, 2011 WITH HEART DEFECTS
 CONFERENCE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IRVINE, CA. MARCH 7, 2011 MANAGEMENT OF NEWBORNS WITH HEART DEFECTS A NTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH M E D I C AL D I RE C T OR, HEART I N S T I T U T E C H I LDRE N
CONFERENCE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IRVINE, CA. MARCH 7, 2011 MANAGEMENT OF NEWBORNS WITH HEART DEFECTS A NTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH M E D I C AL D I RE C T OR, HEART I N S T I T U T E C H I LDRE N
HISTORY. Question: What type of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance.
 HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease A Hospital-Based Study *Sadiq Mohammed Al-Hamash MBChB, FICMS
 Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease A Hospital-Based Study *Sadiq Mohammed Al-Hamash MBChB, FICMS ABSTRACT Background: The congenital heart disease occurs in 0,8% of live births and they have a wide spectrum
Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease A Hospital-Based Study *Sadiq Mohammed Al-Hamash MBChB, FICMS ABSTRACT Background: The congenital heart disease occurs in 0,8% of live births and they have a wide spectrum
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE
 By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
Hybrid Procedure of Bilateral Pulmonary Artery Banding and Bilateral Ductal Stenting in an Infant With Aortic Atresia and Interrupted Aortic Arch
 Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 84:1157 1162 (2014) Hybrid Procedure of Bilateral Pulmonary Artery Banding and Bilateral Ductal Stenting in an Infant With Aortic Atresia and Interrupted
Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 84:1157 1162 (2014) Hybrid Procedure of Bilateral Pulmonary Artery Banding and Bilateral Ductal Stenting in an Infant With Aortic Atresia and Interrupted
24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by
 24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by diagnosis? ndings, what is the most likely A. Pulmonary sequestration B. Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by diagnosis? ndings, what is the most likely A. Pulmonary sequestration B. Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Morrison ML, 1 Sands AJ, 1 Paterson A. 2 Primitive hepatic venous plexus in a child with scimitar syndrome and pulmonary 1 Department of Paediatric Cardiology, Royal Belfast
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Morrison ML, 1 Sands AJ, 1 Paterson A. 2 Primitive hepatic venous plexus in a child with scimitar syndrome and pulmonary 1 Department of Paediatric Cardiology, Royal Belfast
Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries
 Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries Slide 1: In this presentation I am going to describe for you the development of what are known as the great arteries. The great arteries
Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries Slide 1: In this presentation I am going to describe for you the development of what are known as the great arteries. The great arteries
3 Aortopulmonary Window
 0 0 0 0 0 Aortopulmonary Window Introduction Communications between the ascending aorta and pulmonary artery constitute a spectrum of malformations which is collectively designated aortopulmonary window,
0 0 0 0 0 Aortopulmonary Window Introduction Communications between the ascending aorta and pulmonary artery constitute a spectrum of malformations which is collectively designated aortopulmonary window,
Notes: 1)Membranous part contribute in the formation of small portion in the septal cusp.
 Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects
 Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director,
Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director,
PULMONARY VENOLOBAR SYNDROME. Dr.C.Anandhi DNB Resident, Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital.
 PULMONARY VENOLOBAR SYNDROME Dr.C.Anandhi DNB Resident, Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital. Presenting complaint: 10 yrs old girl with recurrent episodes of lower respiratory tract infection from infancy.
PULMONARY VENOLOBAR SYNDROME Dr.C.Anandhi DNB Resident, Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital. Presenting complaint: 10 yrs old girl with recurrent episodes of lower respiratory tract infection from infancy.
Case Report Anomalous Origin of the Left Common Carotid Artery from the Main Pulmonary Artery: A Rare Association in an Infant with CHARGE Syndrome
 Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2016, Article ID 2064937, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2064937 Case Report Anomalous Origin of the Left Common Carotid Artery from the Main Pulmonary Artery:
Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2016, Article ID 2064937, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2064937 Case Report Anomalous Origin of the Left Common Carotid Artery from the Main Pulmonary Artery:
Oesophageal atresia and associated anomalies
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 364-368 Oesophageal atresia and associated anomalies S CHIrTMITRAPAP, L SPITZ, E M KIELY, AND R J BRERETON The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 364-368 Oesophageal atresia and associated anomalies S CHIrTMITRAPAP, L SPITZ, E M KIELY, AND R J BRERETON The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street,
Index. radiologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALCAPA. See Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery. Angiosarcoma computed tomographic assessment of, 809 811 Anomalous
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALCAPA. See Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery. Angiosarcoma computed tomographic assessment of, 809 811 Anomalous
Echocardiography in Congenital Heart Disease
 Chapter 44 Echocardiography in Congenital Heart Disease John L. Cotton and G. William Henry Multiple-plane cardiac imaging by echocardiography can noninvasively define the anatomy of the heart and the
Chapter 44 Echocardiography in Congenital Heart Disease John L. Cotton and G. William Henry Multiple-plane cardiac imaging by echocardiography can noninvasively define the anatomy of the heart and the
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Surgical Treatment of Aortic Arch Hypoplasia
 Surgical Treatment of Aortic Arch Hypoplasia In the early 1990s, 25% of patients could face mortality related to complica-tions of hypertensive disease Early operations and better surgical techniques should
Surgical Treatment of Aortic Arch Hypoplasia In the early 1990s, 25% of patients could face mortality related to complica-tions of hypertensive disease Early operations and better surgical techniques should
Research article. Primary detection of congenital heart diseases in the Kyrgyz Republic
 Research article Primary detection of congenital heart diseases in the Kyrgyz Republic Irina A. Akhmedova, Gulzada A. Imanalieva, Damir A.Abibillaev, Taalaibek Z. Kudaiberdiev Scientific Research Institute
Research article Primary detection of congenital heart diseases in the Kyrgyz Republic Irina A. Akhmedova, Gulzada A. Imanalieva, Damir A.Abibillaev, Taalaibek Z. Kudaiberdiev Scientific Research Institute
SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
 SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Mr. W. Brawn Birmingham Children s Hospital. Aims of surgery The aim of surgery in congenital heart disease is to correct or palliate the heart
SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Mr. W. Brawn Birmingham Children s Hospital. Aims of surgery The aim of surgery in congenital heart disease is to correct or palliate the heart
Aortic arch pathology. Cerebral ischemia following carotid artery stenosis.
 Important: -Subclavian Steal Syndrome -Cerebral ischemia Aortic arch pathology. Cerebral ischemia following carotid artery stenosis. Mina Aubeed & Alba Hernández Pinilla Aortic arch pathology Common arch
Important: -Subclavian Steal Syndrome -Cerebral ischemia Aortic arch pathology. Cerebral ischemia following carotid artery stenosis. Mina Aubeed & Alba Hernández Pinilla Aortic arch pathology Common arch
Congenital Heart Disease
 Congenital Heart Disease Mohammed Alghamdi, MD, FRCPC, FAAP, FACC Associate Professor and Consultant Pediatric Cardiology, Cardiac Science King Fahad Cardiac Centre King Saud University INTRODUCTION CHD
Congenital Heart Disease Mohammed Alghamdi, MD, FRCPC, FAAP, FACC Associate Professor and Consultant Pediatric Cardiology, Cardiac Science King Fahad Cardiac Centre King Saud University INTRODUCTION CHD
Making Sense of Cardiac Views and Imaging Characteristics for 13 Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs)
 Making Sense of Cardiac Views and Imaging Characteristics for 13 Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs) Manny Gaziano, MD, FACOG obimages.net obimages.net@gmail.com Acknowledgements: Krista Wald, RDMS, sonographer,
Making Sense of Cardiac Views and Imaging Characteristics for 13 Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs) Manny Gaziano, MD, FACOG obimages.net obimages.net@gmail.com Acknowledgements: Krista Wald, RDMS, sonographer,
Imaging by multislice CT of a large aortico-left ventricular tunnel mimicking as ventricular septal defect
 Case Report Page 1 of 5 Imaging by multislice CT of a large aortico-left ventricular tunnel mimicking as ventricular septal defect Sarv Priya 1, Gurpreet S. Gulati 1, Anita Saxena 2, Balram Airan 3 1 Department
Case Report Page 1 of 5 Imaging by multislice CT of a large aortico-left ventricular tunnel mimicking as ventricular septal defect Sarv Priya 1, Gurpreet S. Gulati 1, Anita Saxena 2, Balram Airan 3 1 Department
Research Presentation June 23, Nimish Muni Resident Internal Medicine
 Research Presentation June 23, 2009 Nimish Muni Resident Internal Medicine Research Question In adult patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot, how does Echocardiography compare to MRI in evaluating
Research Presentation June 23, 2009 Nimish Muni Resident Internal Medicine Research Question In adult patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot, how does Echocardiography compare to MRI in evaluating
"Lecture Index. 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development.
 "Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
"Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival:
 Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
Right subclavian steal syndrome in a patient with aberrant right subclavian artery, common carotid trunk and hypoplastic left vertebral artery
 CASE REPORT 406 OPEN ACCESS Right subclavian steal syndrome in a patient with aberrant right subclavian artery, common carotid trunk and hypoplastic left vertebral artery Boochi Babu Mannuva, Rajasekhar
CASE REPORT 406 OPEN ACCESS Right subclavian steal syndrome in a patient with aberrant right subclavian artery, common carotid trunk and hypoplastic left vertebral artery Boochi Babu Mannuva, Rajasekhar
Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic venous anomaly
 World Database for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery Appendix B: Diagnosis (International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Codes (IPCCC) and definitions) Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic
World Database for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery Appendix B: Diagnosis (International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Codes (IPCCC) and definitions) Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic
CARDIAC AND CORONARY ARTERY ANATOMY NO DISCLOSURES. Axial Anatomy of Heart. Axial Anatomy of Heart. Axial Anatomy of Heart
 CARDIAC AND CORONARY ARTERY ANATOMY NO DISCLOSURES NASCI MEETING, ORLANDO FLORIDA 2009 KOSTAKI G. BIS, MD, FACR DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL Royal Oak, Michigan OBJECTIVES CARDIAC
CARDIAC AND CORONARY ARTERY ANATOMY NO DISCLOSURES NASCI MEETING, ORLANDO FLORIDA 2009 KOSTAKI G. BIS, MD, FACR DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL Royal Oak, Michigan OBJECTIVES CARDIAC
Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine. The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine
 The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2011) 42, 297 303 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2011) 42, 297 303 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
5/22/2013. Alan Zuckerman 1, Swapna Abhyankar 1, Tiffany Colarusso 2, Richard Olney 2, Kristin Burns 3, Marci Sontag 4
 Alan Zuckerman 1, Swapna Abhyankar 1, Tiffany Colarusso 2, Richard Olney 2, Kristin Burns 3, Marci Sontag 4 1 National Library of Medicine, NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA, 2 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,
Alan Zuckerman 1, Swapna Abhyankar 1, Tiffany Colarusso 2, Richard Olney 2, Kristin Burns 3, Marci Sontag 4 1 National Library of Medicine, NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA, 2 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,
Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases
 Case Report DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.395 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):395-399 Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases Hyoung Nam Lee, MD, Young
Case Report DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.395 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):395-399 Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases Hyoung Nam Lee, MD, Young
Original Report. Imaging Findings in Pediatric Patients with Persistent Airway Symptoms After Surgery for Double Aortic Arch
 Robert J. Fleck 1,2 Preeyacha Pacharn 1,3 Bradley L. Fricke 1 Matthew A. Ziegler 1 Robin T. Cotton 4 Lane F. Donnelly 1 Received August 30, 2001; accepted after revision October 22, 2001. 1 Department
Robert J. Fleck 1,2 Preeyacha Pacharn 1,3 Bradley L. Fricke 1 Matthew A. Ziegler 1 Robin T. Cotton 4 Lane F. Donnelly 1 Received August 30, 2001; accepted after revision October 22, 2001. 1 Department
Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions
 Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions Tier 1 surgeries AV Canal Atrioventricular Septal Repair, Complete Repair of complete AV canal (AVSD) using one- or two-patch or other technique,
Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions Tier 1 surgeries AV Canal Atrioventricular Septal Repair, Complete Repair of complete AV canal (AVSD) using one- or two-patch or other technique,
Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
