Salt-sensitivity of blood pressure: a paradigm of gene-environment interaction
|
|
|
- Blaze Small
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Salt-sensitivity of blood pressure: a paradigm of gene-environment interaction Pasquale Strazzullo, Alfonso Siani*, Paola Russo* Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Federico II University of Naples Medical School, Naples, *Institute of Food Science and Technology, National Research Council, Avellino, Italy Key words: Hypertension; Age; Cardiovascular disease; Sex; Elderly. (Ital Heart J 2000; 1 (Suppl 3): S15-S19) Address: Prof. Pasquale Strazzullo Dipartimento di Medicina Clinica e Sperimentale Università degli Studi Federico II Via S. Pansini, Napoli strazzul@unina.it The multifactorial origins of hypertension Arterial hypertension is not a disease in itself but rather a powerful risk factor for cardiovascular and renal disease. The risk associated with hypertension is graded and continuous, starting with blood pressure levels well below the clinically useful but arbitrary definition of hypertension given by the guidelines for the physician 1,2. While it is true that the higher the blood pressure the greater the individual relative risk of cardiovascular and renal complications, on epidemiological grounds and with regard to public health, the population attributable risk is of even greater interest. In fact, by multiplying the relative risk associated with a certain blood pressure level by the number of people exposed to that level, it may be found that the large number of people affected by the mildest forms of hypertension or just having high-normal blood pressure levels contribute to a large proportion of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. This is, for instance, the lesson coming from the analysis carried out by the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial Investigators 3. Accordingly, the study of the genetic causes of hypertension should not focus solely on patients and families with severe forms of hypertension but should aim to unveil the genetic contribution to population blood pressure variability all over the blood pressure range 4. The growing interest in a number of genes coding for proteins involved at various levels in the metabolic handling of dietary sodium chloride has to be seen within this intellectual framework. Dietary salt intake as a risk factor for hypertension The relationship between dietary salt and blood pressure is supported by overwhelming evidence from epidemiological, clinical and experimental studies 5. The earliest observations on this subject are found in the history of Chinese medicine and date back to about one thousand years BC 6. A dramatic switch from a low-salt to a progressively salt-enriched diet is believed to have taken place when mankind made the transition from hunting and collecting food to food producing. The agricultural man learned to use salt to preserve food, particularly meat, for long periods of time, with sodium chloride acting as a dehydrator and a preservative against bacterial growth 7,8. These anthropological considerations led to the concept of maladaptation of blood pressure homeostasis in the face of a major environmental modification which occurred over a relatively short span of human evolution 7. It is conceivable that a genetic array that had been biologically appropriate for what used to be a low-salt environment became unfavorable once the dietary intake of salt started to rise, in as much as the prevailing physiological challenge for the kidney was no longer conservation but rather quantitative elimination of excess salt. Although the clinician s interest in dietary salt intake focuses on its role as a determinant of arterial hypertension, the issue of excess salt intake contribution to population variability of blood pressure is scientifically more sound and far more attractive for the clinical geneticist. S15
2 Ital Heart J Vol 1 Suppl Definition and determinants of salt-sensitivity Salt-sensitivity can be defined as the measurable effect of a sodium chloride load on individual blood pressure levels. The interest in salt-sensitivity stems from the observation that the effect of sodium chloride on blood pressure is heterogeneous within the hypertensive population 9,10 and also among normotensive individuals 11. Similarly to what has been said for blood pressure, it is quite arbitrary to classify an individual as salt-sensitive or salt-resistant for the very reason that the blood pressure response to a sodium load (or to salt restriction) follows a typical Gaussian curve. Thus, the classifications adopted in most published clinical studies, based on a pre-defined cut-off, fail to provide the correct perception of a truly quantitative phenomenon 9,10. Several studies have been conducted in an attempt to identify predictors of blood pressure salt-sensitivity, for the assessment of which these studies have relied on either short-term dietary trials or acute sodium loads and volume expansion maneuvers 11. Although several organs are presumably involved in the blood pressure response to salt, the kidney is both the final track and the fine modulator of the response. According to the well known theory proposed by De Wardener et al. 12, sodium-dependent hypertension is the consequence of an inherited and/or acquired inability of the kidney to excrete a sodium load. In a high sodium environment, the renal defect would determine an increase in extracellular fluid and intrathoracic blood volume that in time may induce an increase in blood pressure. A number of factors are able to impair the natriuretic ability of the kidney and shift the pressure-natriuresis curve to the right. Hyperactivity of the sympathetic nervous system or of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone axis, insulin resistance, reduced production of atrial natriuretic peptides and other natriuretic substances, functional alterations of renal tubular ion transport systems, are among the factors involved in renal sodium handling acknowledged as potential acquired contributors to saltsensitivity of blood pressure. The excess sympathetic activity associated with stressful lifestyles and the reduced sensitivity to insulin associated with overweight or obesity are good examples of these mechanistic pathways. Excess noradrenaline released at the sympathetic end-terminals within the kidney as well as the hyperinsulinemia associated with insulin resistance have the power to enhance tubular sodium reabsorption and shift the pressure-natriuresis curve to the right. Genetic versus acquired causes of salt-sensitivity and their interaction An intriguing question one has to ask is to what extent these factors are acquired causes of impairment in renal natriuretic capacity, as it appears, and to what degree they are under the influence of genetic variation. The Trp64Arg polymorphism in the beta 3 -adrenergic receptor, for instance, is associated with predisposition to abdominal adiposity, hypertension and possibly insulin resistance 13,14. In turn, the reduction in renal sodium excretory ability consequent to insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia and sympathetic activation may be seen, at least to some extent, as genetically determined. Hypertension due to single gene abnormalities is a rare condition; nevertheless, a number of monogenic forms following a Mendelian type of inheritance have been described. Classic linkage analysis has located the genes implicated in glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism 15, in Liddle s syndrome 16 and in the apparent mineralocorticoid excess syndrome 17. It is noteworthy that all these forms of monogenic hypertension, due to well characterized genetic abnormalities, are related to an altered renal sodium handling. Much more frequently arterial hypertension is caused by the synergistic action of multiple environmental and genetic factors. Thus, its phenotypic expression derives from the interaction between a large number of susceptibility genes (polygenes) of variable penetrance (Table I) and various other influences partly related to lifestyle (e.g. nutritional factors, physical activity, etc.). Considerable and growing efforts are being made in order to identify candidate genes ; as a consequence, the number of polymorphic variants of genes possibly implicated in high blood pressure is continuously in- Table I. Candidate genes for arterial hypertension. Angiotensin-converting enzyme* 18,19 Angiotensinogen* 20,21 Angiotensin II type 1 receptor 22 Atrial natriuretic peptide* 23 Natriuretic peptide clearance receptor* 24 Aldosterone synthase* 25,26 Na + /K + ATPase* 27 β subunit epithelial sodium channel* 28 α-adducin* 29,30 α 1B -adrenergic receptor 31 α 2 -adrenergic receptor* 32 β 2 -adrenergic receptor* 33 β 3 -adrenergic receptor* 13,34 Glucocorticoid receptor 35 Insulin receptor 36 Glucagon receptor* 37 Lipoprotein lipase 38 Pancreatic phospholipase 39 Growth hormone 40 Complement C3F 41 Type 1A dopamine receptor 31 Endothelial nitric oxide synthase* 42 SA gene 43 G-protein β 3 subunit* 44 Prostacyclin synthase 45 Hp1-haptoglobin* 46 * genes more likely to be involved in the salt-sensitivity of blood pressure. S16
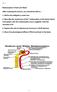
3 P Strazzullo et al - Salt and gene-environment interaction creasing. Many of these variants are associated with a functional alteration. The interaction between functional mutations associated with altered renal sodium handling and changes in dietary sodium intake represents a paradigm for the study of gene-environment interaction. Figure 1 shows a schematic frame of the complex multifactorial interactions between genes, environment, demographic and metabolic factors implicated in salt-sensitivity of blood pressure. A reasonable working hypothesis is that each one of a number of less severe mutations in genes directly or indirectly related to renal sodium handling gives a contribution to the individual blood pressure sensitivity to changes in sodium intake. Candidate genes possibly contributing to salt-sensitivity are listed in table I Attention has been focused on genes involved in the regulation of the reninangiotensin axis, in transmembrane ion exchange, in the modulation of sympathetic activity and in other metabolic pathways relevant to sodium handling. In a study of over 1500 subjects participating in the phase II of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention, Hunt et al. 21 showed that individuals homozygous for a mutation in the angiotensinogen gene had a significantly better response to sodium restriction as compared to individuals with the wild-type genotype. The frequence of the insertion allele of the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene was higher in salt-sensitive than in saltresistant Japanese hypertensive patients 19. An increased frequence of polymorphic variants of the atrial natriuretic peptide gene has been identified among hypertensive African-Americans, supporting the hypothesis that a deficient atrial natriuretic peptide secretion contributes to elevated salt-sensitivity in people of African descent 23. Recently, Sarzani et al. 24 detected, in a population of obese hypertensive Caucasian patients, a biallelic (A/C) polymorphism at position 55 of the promoter of the natriuretic peptide clearance receptor: the C(-55) variant was associated with lower atrial natriuretic peptide levels and higher blood pressure levels. The association between polymorphic variants of α- and β-adrenergic receptors and salt-sensitivity has been the object of investigation. A linkage between the β 2 -adrenergic receptor locus and the blood pressure response to sodium load was suggested by Svetkey et al. 33 in a study on Afro-American families; moreover, Lockette et al. 32 showed a significant difference in a restriction fragment length polymorphism for the α 2 -adrenoceptor between black and white hypertensive patients. In a large population sample of middle aged men (The Olivetti Prospective Heart Study), we have recently observed that the carriers of the Trp64Arg polymorphism of the β 3 -adrenergic receptor had significantly higher levels of plasma aldosterone in comparison with the carriers of the wild type Arg64Arg allele 13. In the same population sample, we have also found that the Gly40Ser mutation of the glucagon receptor gene was associated with significantly increased sodium reabsorption at the proximal tubule and high blood pressure (Strazzullo P. et al., unpublished data). Bianchi and coworkers 29,30 have reported convincing evidence for a role of genetic variants of the α-adducin gene associated with functional alterations of the Na + - K + pump, higher blood pressure and enhanced sensitivity to diuretics. Evidence is also accumulating in favor of a significant contribution by variants of the epithelial sodium channel gene at least in some populations 28, leading to the conclusion that the renal tubule might be the site of multiple dysfunction potentially relevant to saltsensitivity of blood pressure. This very brief and inevitably incomplete review of the multifaceted background of blood pressure salt-sensitivity supports the contention of a complex interaction between a number of genes influencing renal sodium handling and several metabolic, nutritional and neurohormonal factors converging on the same final pathway 47 : the final result of these multiple interactions is an impairment in the natriuretic ability of the kidney with a resultant shift in the pressure-natriuresis curve to the right 48. The elucidation of the precise role of the gene products involved in this process is a promising approach to the comprehension of the molecular bases of blood pressure regulation. Figure 1. Interaction between genetic and acquired factors associated with salt-sensitivity of blood pressure. S17
4 Ital Heart J Vol 1 Suppl References 01. International Task Force for Prevention of Coronary Heart Disease. Coronary heart disease: reducing the risk. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 1998; 8: WHO-ISH Guidelines Subcommittee World Health Organization-International Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the management of hypertension. J Hypertens 1999; 17: Stamler J, Stamler R, Neaton JD. Blood pressure, systolic and diastolic, and cardiovascular risks: US population data. Arch Intern Med 1993; 153: Harrap SB. Genetics. In: Oparil S, Weber MA, eds. Hypertension: a companion to Brenner and Rector s The Kidney. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders, 2000: Siani A, Guglielmucci F, Farinaro E, Strazzullo P. Increasing evidence for the role of salt and salt-sensitivity in hypertension. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2000; 10: Huang Ti Nei Ching Su Wen (1000 BC) from the translation by Wang Ping (AD 762). 07. Eaton SB, Konner M. Paleolithic nutrition. A consideration of its nature and current implications. N Engl J Med 1985; 312: Blyth WB. Salt and water in culture and medicine. N Engl J Med 1994; 330: Luft FC, Weinberger MH. Heterogeneous responses to changes in dietary salt intake: the salt-sensitivity paradigm. Am J Clin Nutr 1997; 65 (Suppl): 612S-617S. 10. Galletti F, Ferrara I, Stinga F, Iacone R, Noviello F, Strazzullo P. Evaluation of a rapid protocol for the assessment of salt sensitivity against the blood pressure response to dietary sodium chloride restriction. Am J Hypertens 1997; 10: Miller JZ, Weinberger MH, Dougherty SA, Fineberg NS, Christian GC, Grim CE. Heterogeneity of blood pressure response to dietary sodium restriction in normotensive adults. J Chron Dis 1987; 40: De Wardener HE, Clarkson EM, Bitensky L, MacGregor GA, Alaghband- Zadeh J, Chayen J. Effect of sodium intake on ability of human plasma to inhibit renal Na + -K + -adenosine triphosphatase in vitro. Lancet 1981; 1: Strazzullo P, Siani A, Barba G, et al. Relationship between plasma aldosterone, insulin resistance and beta 3 -AR Trp64Arg gene polymorphism in a 20-year follow-up study. (abstr) In: Proceedings of the 10th European Meeting on Hypertension. Goteborg, 2000: S Arner P, Hoffstedt J. Adrenoceptor genes in human obesity. J Intern Med 1999; 245: Lifton RP, Dluhy RG, Powers M, et al. A chimeric 11 betahydroxylase/aldosterone synthase gene causes glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism and human hypertension. Nature 1992; 355: Shimkets RA, Warnock DG, Bositis CM, et al. Liddle s syndrome: heritable human hypertension caused by mutations in the beta sub-unit of the epithelial sodium channel. Cell 1994; 79: Mune T, Rogerson FM, Nikkila H, Agarwal AK, White PC. Human hypertension caused by mutations in the kidney isozyme of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Nat Genet 1995; 10: Fornage M, Amos CI, Kardia S, Sing CF, Turner ST, Boerwinkle E. Variation in the region of the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene influences inter-individual differences in blood pressure levels in young white males. Circulation 1991; 97: Hiraga H, Oshima T, Watanabe M, et al. Angiotensin I converting enzyme gene polymorphism and salt sensitivity in essential hypertension. Hypertension 1999; 27: Jeunemaitre X, Soubrier F, Kotelevtsev YV, et al. Molecular basis of human hypertension: role of angiotensinogen. Cell 1992; 71: Hunt SC, Cook NR, Oberman A, et al. Angiotensinogen genotype, sodium reduction, weight loss, and prevention of hypertension. Trials of Hypertension Prevention, phase II. Hypertension 1998; 32: Bonnardeaux A, Davies E, Jeunemaitre X, et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene polymorphisms in human essential hypertension. Hypertension 1994; 24: Rutledge DR, Sun Y, Ross EA. Polymorphism within the atrial natriuretic peptide gene in essential hypertension. J Hypertens 1995; 13: Sarzani R, Dess -Fulgheri P, Salvi F, et al. A novel promoter variant of the natriuretic peptide clearance receptor gene is associated with lower atrial natriuretic peptide and higher blood pressure in obese hypertensives. J Hypertens 1999; 17: Holland OB, Carr B. Modulation of aldosterone synthase messenger ribonucleic acid levels by dietary sodium and potassium and by adrenocorticotropin. Endocrinology 1993; 132: Brand E, Schorr U, Ringel J, Beige J, Distler A, Sharma AM. Aldosterone synthase gene (CYP11B2) C-344T polymorphism in Caucasians from the Berlin Salt-Sensitivity Trial (BeSST). J Hypertens 1999; 17: Perusse L, Deriaz O, Dionne FT, et al. Association and linkage analyses of the alpha and beta genes of the sodium-potassium ATPase with age-related changes in blood pressure. (abstr) Am J Hum Genet 1994; 55: 199A. 28. Baker EH, Dong YB, Sagnella GA, et al. Association of hypertension with T594M mutation in beta subunit of epithelial sodium channels in black people resident in London. Lancet 1998; 351: Casari G, Barlassina C, Cusi D, et al. Association of the alpha-adducin locus with essential hypertension. Hypertension 1995; 25: Glorioso N, Manunta P, Filigheddu F, et al. The role of α-adducin polymorphism in blood pressure and sodium handling regulation may not be excluded by a negative association study. Hypertension 1999; 34: Krushkal J, Xiong M, Ferrel R, et al. Linkage and association of adrenergic and dopamine receptor genes in the distal portion of the long arm of chromosome 5 with systolic blood pressure variation. Hum Mol Genet 1991; 7: Lockette W, Ghosh S, Farrow S, et al. Alpha 2 adrenergic receptor gene polymorphism and hypertension in blacks. Am J Hypertens 1995; 4: Svetkey LP, Chen YT, McKeown SP, Preis L, Wilson AF. Preliminary evidence of linkage of salt sensitivity in black Americans at the β 2 -adrenergic receptor locus. Hypertension 1997; 29: Fujisawa T, Ikegami H, Yamato E, et al. Trp64Arg mutation of β 3 -adrenergic receptor in essential hypertension. Insulin resistance and the adrenergic system. Am J Hypertens 1997; 10: Watt GC, Harrap SB, Foy CJ, et al. Abnormalities of glucocorticoid metabolism and the renin-angiotensin system: a four corners approach to the identification of genetic determinants of blood pressure. J Hypertens 1992; 10: Ying LH, Zee RY, Griffiths LR, Morris BJ. Association of a RFLP for the insulin receptor gene, but not insulin, with essential hypertension. Biophys Biochem Res Commun 1991; 181: Brand E, Bankir L, Plouin PF, Soubrier F. Glucagon receptor gene mutation (Gly40Ser) in human essential hypertension: the PEGASE study. Hypertension 1999; 34: Wu DA, Ku X, Warden CH, et al. Quantitative trait locus mapping of human blood pressure to a genetic region at or near the lipoprotein lipase gene locus on chromosome 8p22. J Clin Invest 1996; 97: S18
5 P Strazzullo et al - Salt and gene-environment interaction 39. Frossard PM, Lestringant GG. Association between a dimorphic site on chromosome 12 and clinical diagnosis of hypertension in three independent populations. Clin Genet 1995; 48: Julier C, Delepine M, Keavney B, et al. Genetic susceptibility for human familial essential hypertension in a region of homology with blood pressure linkage on rat chromosome 10. Hum Mol Genet 1997; 6: Schaadt O, Sorensen H, Krogsgaard AR. Association between the C3F-gene and essential hypertension. Clin Sci 1981; 61: 363S-365S. 42. Miyamoto Y, Saito Y, Kajiyama N, et al. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene is positively associated with essential hypertension. Hypertension 1998; 32: Iwai N, Ohmichi N, Hanai K, Nakamura Y, Kinoshita M. Human SA gene locus as a candidate locus for essential hypertension. Hypertension 1994; 23: Siffert W, Rosskopf D, Siffert G, et al. Association of a human G-protein beta 3 subunit variant with hypertension. Nat Genet 1998; 18: Nakayama T, Soma M, Kanmatsuse K. Organization of the human prostacyclin synthase gene and association analysis of a novel CA repeat in essential hypertension. Adv Exp Med Biol 1997; 433: Weinberger MH, Miller JZ, Fineberg NS, Luft FC, Grim CE, Christian JC. Association of haptoglobin with sodium sensitivity and resistance of blood pressure. Hypertension 1987; 10: Cowley AWJ. Genetic and non-genetic determinants of salt sensitivity and blood pressure. Am J Clin Nutr 1997; 65: 587S-593S. 48. Guyton AC. The surprising kidney-fluid mechanism for pressure control: its infinite gain! Hypertension 1990; 16: S19
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance
 Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Slide notes: This presentation highlights the issues involved in preventing hypertension. Slide notes are included for the majority of slides,
 3/23/2016 1 This presentation highlights the issues involved in preventing hypertension. Slide notes are included for the majority of slides, containing source materials and references. 2 The Framingham,
3/23/2016 1 This presentation highlights the issues involved in preventing hypertension. Slide notes are included for the majority of slides, containing source materials and references. 2 The Framingham,
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Interaction of six candidate genes in essential hypertension
 Interaction of six candidate genes in essential hypertension D.C. Hu, X.L. Zhao, J.C. Shao, W. Wang, J. Qian, A.H. Chen, H.Q. Zhang, H. Guo, J. Jiang and H.Y. Li Department of Clinical Laboratory, The
Interaction of six candidate genes in essential hypertension D.C. Hu, X.L. Zhao, J.C. Shao, W. Wang, J. Qian, A.H. Chen, H.Q. Zhang, H. Guo, J. Jiang and H.Y. Li Department of Clinical Laboratory, The
2015/03/11. Dr Patience Sigwadi Paediatric Nephrologist UNITAS NETCARE. Case
 Dr Patience Sigwadi Paediatric Nephrologist UNITAS NETCARE Case 1 Case Report 17-month-old female toddler Presented with hypertensive encephalopathy manifesting with convulsions right hemiparesis and blindness.
Dr Patience Sigwadi Paediatric Nephrologist UNITAS NETCARE Case 1 Case Report 17-month-old female toddler Presented with hypertensive encephalopathy manifesting with convulsions right hemiparesis and blindness.
Keywords: CYP11B2, aldosterone synthase, polymorphism, blood pressure, ageing, aldosterone
 Original article 1785 Interaction between the C( 344)T polymorphism of CYP11B2 and age in the regulation of blood pressure and plasma aldosterone levels: cross-sectional and longitudinal findings of the
Original article 1785 Interaction between the C( 344)T polymorphism of CYP11B2 and age in the regulation of blood pressure and plasma aldosterone levels: cross-sectional and longitudinal findings of the
Role of Minerals in Hypertension
 Role of Minerals in Hypertension Lecture objectives By the end of the lecture students will be able to Define primary and secondary hypertention and their risk factors. Relate role of minerals with hypertention.
Role of Minerals in Hypertension Lecture objectives By the end of the lecture students will be able to Define primary and secondary hypertention and their risk factors. Relate role of minerals with hypertention.
BODY FLUID. Outline. Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid. Regulation of fluid homeostasis
 BODY FLUID Nutritional Biochemistry Yue-Hwa Chen Dec 13, 2007 Chen 1 Outline Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid Intake vs output Regulation of body fluid Fluid
BODY FLUID Nutritional Biochemistry Yue-Hwa Chen Dec 13, 2007 Chen 1 Outline Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid Intake vs output Regulation of body fluid Fluid
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume. Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM
 Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Genetic and physiological markers of salt sensitivity and its effects on salt taste perception and intake
 Genetic and physiological markers of salt sensitivity and its effects on salt taste perception and intake NuGO week 2017, Varna 31/08/2017 LETA PILIC AND YIANNIS MAVROMMATIS SCHOOL OF SPORT, HEALTH AND
Genetic and physiological markers of salt sensitivity and its effects on salt taste perception and intake NuGO week 2017, Varna 31/08/2017 LETA PILIC AND YIANNIS MAVROMMATIS SCHOOL OF SPORT, HEALTH AND
Relation between the angiotensinogen (AGT) M235T gene polymorphism and blood pressure in a large, homogeneous study population
 (2003) 17, 555 559 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between the angiotensinogen (AGT) M235T gene polymorphism and blood
(2003) 17, 555 559 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between the angiotensinogen (AGT) M235T gene polymorphism and blood
Endocrine hypertensionmolecules. Marie Freel Caledonian Endocrine Society Meeting 29 th November 2015
 Endocrine hypertensionmolecules and genes Marie Freel Caledonian Endocrine Society Meeting 29 th November 2015 Plan Mineralocorticoid hypertension Myths surrounding Primary Aldosteronism (PA) New developments
Endocrine hypertensionmolecules and genes Marie Freel Caledonian Endocrine Society Meeting 29 th November 2015 Plan Mineralocorticoid hypertension Myths surrounding Primary Aldosteronism (PA) New developments
Association between the CYP11B2 gene 344T>C polymorphism and coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis
 Association between the CYP11B2 gene 344T>C polymorphism and coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis Y. Liu, H.L. Liu, W. Han, S.J. Yu and J. Zhang Department of Cardiology, The General Hospital of the
Association between the CYP11B2 gene 344T>C polymorphism and coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis Y. Liu, H.L. Liu, W. Han, S.J. Yu and J. Zhang Department of Cardiology, The General Hospital of the
Blood pressure control Contin. Reflex Mechanisms. Dr. Hiwa Shafiq
 Blood pressure control Contin. Reflex Mechanisms Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 17-12-2018 A. Baroreceptor reflexes Baroreceptors (stretch receptors) located in the walls of several large systemic arteries( specially
Blood pressure control Contin. Reflex Mechanisms Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 17-12-2018 A. Baroreceptor reflexes Baroreceptors (stretch receptors) located in the walls of several large systemic arteries( specially
The genetics of essential hypertension
 Genes for common diseases edited by Prof. M. J. Caulfield The genetics of essential hypertension Kevin M. O'Shaughnessy Clinical Pharmacology Unit, Addenbrooke's Centre for Clinical Investigation, Addenbrooke's
Genes for common diseases edited by Prof. M. J. Caulfield The genetics of essential hypertension Kevin M. O'Shaughnessy Clinical Pharmacology Unit, Addenbrooke's Centre for Clinical Investigation, Addenbrooke's
Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the Central Nervous System Ischemic Response. 2. Describe chemical sensitivities of arterial and cardiopulmonary chemoreceptors,
Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the Central Nervous System Ischemic Response. 2. Describe chemical sensitivities of arterial and cardiopulmonary chemoreceptors,
Journal of Hypertension 2006, 24: a Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Federico II Medical School,
 Original article 1633 Abnormalities of renal sodium handling in the metabolic syndrome. Results of the Olivetti Heart Study Pasquale Strazzullo a, Antonio Barbato a, Ferruccio Galletti a, Gianvincenzo
Original article 1633 Abnormalities of renal sodium handling in the metabolic syndrome. Results of the Olivetti Heart Study Pasquale Strazzullo a, Antonio Barbato a, Ferruccio Galletti a, Gianvincenzo
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
AJH 1998;11: by the American Journal of Hypertension, Ltd /98/$19.00
 AJH 1998;11:8 13 Acute Effects of Intravenous Sodium Chloride Load on Calcium Metabolism and on Parathyroid Function in Patients With Primary Aldosteronism Compared With Subjects With Essential Hypertension
AJH 1998;11:8 13 Acute Effects of Intravenous Sodium Chloride Load on Calcium Metabolism and on Parathyroid Function in Patients With Primary Aldosteronism Compared With Subjects With Essential Hypertension
GENETIC EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HYPERTENSION: AN UPDATE ON THE AFRICAN DIASPORA
 GENETIC EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HYPERTENSION: AN UPDATE ON THE AFRICAN DIASPORA Hypertension is a serious global public health problem, affecting approximately 600 million people worldwide. The lifetime risk of
GENETIC EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HYPERTENSION: AN UPDATE ON THE AFRICAN DIASPORA Hypertension is a serious global public health problem, affecting approximately 600 million people worldwide. The lifetime risk of
raised (> 750) aldosterone-to-renin ratio (ARR). Journal of Hypertension 2004, 22:
 Original article 1895 Aldosterone synthase gene (CYP11B2) C-344T polymorphism, plasma aldosterone, renin activity and blood pressure in a multi-ethnic population Antonio Barbato a *, Paola Russo b *, Alfonso
Original article 1895 Aldosterone synthase gene (CYP11B2) C-344T polymorphism, plasma aldosterone, renin activity and blood pressure in a multi-ethnic population Antonio Barbato a *, Paola Russo b *, Alfonso
Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR
 Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Central Role for ENaC in Development of Hypertension
 Central Role for ENaC in Development of Hypertension J. Howard Pratt Department of Medicine, Indiana University School of Medicine, and the Richard L. Roudebush Veterans Administration Medical Center,
Central Role for ENaC in Development of Hypertension J. Howard Pratt Department of Medicine, Indiana University School of Medicine, and the Richard L. Roudebush Veterans Administration Medical Center,
Renal Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Positive association of CYP11B2 gene polymorphism with genetic predisposition
 (2002) 16, 789 793 & 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Positive association of CYP11B2 gene polymorphism with genetic predisposition
(2002) 16, 789 793 & 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Positive association of CYP11B2 gene polymorphism with genetic predisposition
The ability of the kidneys to regulate extracellular fluid volume by altering sodium
 REGULATION OF EXTRACELLULAR FLUID VOLUME BY INTEGRATED CONTROL OF SODIUM EXCRETION Joey P. Granger Department of Physiology and Biophysics, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, Mississippi
REGULATION OF EXTRACELLULAR FLUID VOLUME BY INTEGRATED CONTROL OF SODIUM EXCRETION Joey P. Granger Department of Physiology and Biophysics, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, Mississippi
High blood pressure is common in black people living in
 Transepithelial Sodium Absorption Is Increased in People of African Origin Emma H. Baker, Nicola J. Ireson, Christine Carney, Nirmala D. Markandu, Graham A. MacGregor Abstract Salt-sensitive hypertension
Transepithelial Sodium Absorption Is Increased in People of African Origin Emma H. Baker, Nicola J. Ireson, Christine Carney, Nirmala D. Markandu, Graham A. MacGregor Abstract Salt-sensitive hypertension
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
What is New in the Pathogenesis of Salt-sensitive Hypertension?
 What is New in the Pathogenesis of Salt-sensitive Hypertension? Prof. Andrzej Wiecek Department of Nephrology, Transplantation and Internal Medicine Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland e-mail:
What is New in the Pathogenesis of Salt-sensitive Hypertension? Prof. Andrzej Wiecek Department of Nephrology, Transplantation and Internal Medicine Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland e-mail:
Patterns of Sodium Excretion During Sympathetic Nervous System Arousal. Gregory A. Harshfield, Derrick A. Pulliam, and Bruce S.
 1156 Patterns of Sodium Excretion During Sympathetic Nervous System Arousal Gregory A. Harshfield, Derrick A. Pulliam, and Bruce S. Alpert The purpose of this study was to examine Na + handling and regulation
1156 Patterns of Sodium Excretion During Sympathetic Nervous System Arousal Gregory A. Harshfield, Derrick A. Pulliam, and Bruce S. Alpert The purpose of this study was to examine Na + handling and regulation
Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140
 هللامسب Na regulation: Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140 meq\l. Na is important because: -It determines the volume of extracellular fluid : the more Na intake will expand extracellular
هللامسب Na regulation: Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140 meq\l. Na is important because: -It determines the volume of extracellular fluid : the more Na intake will expand extracellular
Hypokalemia in Acute Coronary Syndromes and Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
 Hypokalemia in Acute Coronary Syndromes and Acute Decompensated Heart Failure Joseph S. Van Tuyl, Pharm.D. PGY1 Pharmacy Resident The University of Oklahoma College of Pharmacy April 4, 2014 Disclosures
Hypokalemia in Acute Coronary Syndromes and Acute Decompensated Heart Failure Joseph S. Van Tuyl, Pharm.D. PGY1 Pharmacy Resident The University of Oklahoma College of Pharmacy April 4, 2014 Disclosures
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Dysglycaemia and Hypertension. Dr E M Manuthu Physician Kitale
 Dysglycaemia and Hypertension Dr E M Manuthu Physician Kitale None Disclosures DM is MI equivalent MR FIT Objective was to assess predictors of CVD mortality among men with and without diabetes and
Dysglycaemia and Hypertension Dr E M Manuthu Physician Kitale None Disclosures DM is MI equivalent MR FIT Objective was to assess predictors of CVD mortality among men with and without diabetes and
Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note
![Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note](/thumbs/77/75431210.jpg) Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Cardiovascular diseases identification of genomic markers Potential interest, limitations
 Cardiovascular diseases identification of genomic markers Potential interest, limitations Degenerative cardiovascular diseases Complexity of anatomical and clinical phenotypes (arterial remodeling, obstruction,
Cardiovascular diseases identification of genomic markers Potential interest, limitations Degenerative cardiovascular diseases Complexity of anatomical and clinical phenotypes (arterial remodeling, obstruction,
M.I. Ebomoyi * and V.I. Iyawe Department of Physiology, College of Medical Sciences, University of Benin, Benin City, Nigeria.
 African Journal of Biomedical Research, Vol. 10 (2007); 1-8 ISSN 1119 5096 Ibadan Biomedical Communications Group Review Article Essential Hypertension: Another Look at Possible Aetiology and Treatment
African Journal of Biomedical Research, Vol. 10 (2007); 1-8 ISSN 1119 5096 Ibadan Biomedical Communications Group Review Article Essential Hypertension: Another Look at Possible Aetiology and Treatment
Renal-Related Questions
 Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
Adrenal gland And Pancreas
 Adrenal gland And Pancreas Structure Cortex Glucocorticoids Effects Control of secretion Mineralocorticoids Effects Control of secretion Sex steroids Medulla Catecholamines Adrenal cortex 80% of an adrenal
Adrenal gland And Pancreas Structure Cortex Glucocorticoids Effects Control of secretion Mineralocorticoids Effects Control of secretion Sex steroids Medulla Catecholamines Adrenal cortex 80% of an adrenal
Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance
 Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance Body fluid The fluids are distributed throughout the body in various compartments. Body fluid is composed primarily of water Water is the solvent in which all solutes
Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance Body fluid The fluids are distributed throughout the body in various compartments. Body fluid is composed primarily of water Water is the solvent in which all solutes
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions Linkage Analysis Question Question 8.1 Affected members of the pedigree above have an autosomal dominant disorder, and cytogenetic analyses using conventional
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions Linkage Analysis Question Question 8.1 Affected members of the pedigree above have an autosomal dominant disorder, and cytogenetic analyses using conventional
THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES
 THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES K + BALANCE Cells (3400 meq) ECF (60 meq) External K Pump insulin catechols Na intake Leak K ph; osmolality membrane integrity distal Na + renal { delivery output aldosterone
THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES K + BALANCE Cells (3400 meq) ECF (60 meq) External K Pump insulin catechols Na intake Leak K ph; osmolality membrane integrity distal Na + renal { delivery output aldosterone
Kidneys in regulation of homeostasis
 Kidneys in regulation of homeostasis Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important terms
Kidneys in regulation of homeostasis Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important terms
Hormonal Control of Osmoregulatory Functions *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44828 1 Hormonal Control of Osmoregulatory Functions * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of
OpenStax-CNX module: m44828 1 Hormonal Control of Osmoregulatory Functions * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), body composition assessment 62
 Subject Index 3 -Adrenergic receptor, gene polymorphisms and obesity 10 Aging, body composition effects 64, 65 Air-displacement plethysmography, body composition assessment 62 Bioelectrical impedance analysis
Subject Index 3 -Adrenergic receptor, gene polymorphisms and obesity 10 Aging, body composition effects 64, 65 Air-displacement plethysmography, body composition assessment 62 Bioelectrical impedance analysis
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Hypertension Update Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital
 Hypertension Update 2008 Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital Definition of Hypertension Continuous variable At some point the risk becomes high enough to justify treatment Treatment
Hypertension Update 2008 Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital Definition of Hypertension Continuous variable At some point the risk becomes high enough to justify treatment Treatment
The organs of the human body were created to perform ten functions among which is the function of the kidney to furnish the human being with thought.
 The organs of the human body were created to perform ten functions among which is the function of the kidney to furnish the human being with thought. Leviticus Rabba 3 Talmud Berochoth 6 1 b Nephrology
The organs of the human body were created to perform ten functions among which is the function of the kidney to furnish the human being with thought. Leviticus Rabba 3 Talmud Berochoth 6 1 b Nephrology
IN this issue of Hypertension is an article by Kimura and his colleagues
 Hypertension Editorials Renal Function Curve A Key to Understanding the Pathogenesis of Hypertension IN this issue of Hypertension is an article by Kimura and his colleagues 1 entitled "Renal Function
Hypertension Editorials Renal Function Curve A Key to Understanding the Pathogenesis of Hypertension IN this issue of Hypertension is an article by Kimura and his colleagues 1 entitled "Renal Function
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Title: Oct 12 3:37 PM (1 of 39) Ch 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Title: Oct 12 3:37 PM (1 of 39) Ch 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Water Balance and Waste Disposal osmoregulation managing water content and solute composition based on movements of solutes excretion
Title: Oct 12 3:37 PM (1 of 39) Ch 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Water Balance and Waste Disposal osmoregulation managing water content and solute composition based on movements of solutes excretion
THE GENETICS AND DEFINITION OF SALT SENSITIVITY IN BLACKS
 THE GENETICS AND DEFINITION OF SALT SENSITIVITY IN BLACKS by KAINE CHAMBERLAIN ONWUZULIKE, M.D. Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements For the degree Doctor of Philosophy Dissertation Advisor:
THE GENETICS AND DEFINITION OF SALT SENSITIVITY IN BLACKS by KAINE CHAMBERLAIN ONWUZULIKE, M.D. Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements For the degree Doctor of Philosophy Dissertation Advisor:
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Fal Fal P h y s i o l o g y 6 1 1, S a n F r a n c i s c o S t a t e U n i v e r s i t y
 Fall 12 OSMOTIC REGULATION OF THE RENAL SYSTEM: Effects of fasting and ingestion of water, coke, or Gatorade on urine flow rate and specific gravity Dorette Franks The purpose of the physiology experiment
Fall 12 OSMOTIC REGULATION OF THE RENAL SYSTEM: Effects of fasting and ingestion of water, coke, or Gatorade on urine flow rate and specific gravity Dorette Franks The purpose of the physiology experiment
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2
 Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2 Blood Pressure Main factors influencing blood pressure: Cardiac output (CO) Peripheral resistance (PR) Blood volume Peripheral resistance is a major factor
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2 Blood Pressure Main factors influencing blood pressure: Cardiac output (CO) Peripheral resistance (PR) Blood volume Peripheral resistance is a major factor
Knowledge that a large fraction of interindividual variation in blood pressure is
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 92, pp. 8545-8551, September 1995 Review Genetic determinants of human hypertension Richard P. Lifton Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Boyer Center for Molecular Medicine,
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 92, pp. 8545-8551, September 1995 Review Genetic determinants of human hypertension Richard P. Lifton Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Boyer Center for Molecular Medicine,
Introduction to linkage and family based designs to study the genetic epidemiology of complex traits. Harold Snieder
 Introduction to linkage and family based designs to study the genetic epidemiology of complex traits Harold Snieder Overview of presentation Designs: population vs. family based Mendelian vs. complex diseases/traits
Introduction to linkage and family based designs to study the genetic epidemiology of complex traits Harold Snieder Overview of presentation Designs: population vs. family based Mendelian vs. complex diseases/traits
ARGININE VASOPRESSIN (AVP)
 ARGININE VASOPRESSIN (AVP) AFFECTS BLOOD PRESSURE AND RENAL WATER REABSORPTION WHAT ELSE DOES IT DO? Michael F. Michelis, M.D., F.A.C.P., F.A.S.N. Director, Division of Nephrology Lenox Hill Hospital,
ARGININE VASOPRESSIN (AVP) AFFECTS BLOOD PRESSURE AND RENAL WATER REABSORPTION WHAT ELSE DOES IT DO? Michael F. Michelis, M.D., F.A.C.P., F.A.S.N. Director, Division of Nephrology Lenox Hill Hospital,
Combination Therapy for Hypertension
 Combination Therapy for Hypertension Se-Joong Rim, MD Cardiology Division, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Goals of Therapy Reduce CVD and renal morbidity and mortality. Treat to BP
Combination Therapy for Hypertension Se-Joong Rim, MD Cardiology Division, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Goals of Therapy Reduce CVD and renal morbidity and mortality. Treat to BP
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
Systemic Hypertension Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor Internal medicine dept
 Systemic Hypertension Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor Internal medicine dept Continents 1- introduction 2- classification/definition 3- classification/etiology 4-etiology in both categories 5- complications
Systemic Hypertension Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor Internal medicine dept Continents 1- introduction 2- classification/definition 3- classification/etiology 4-etiology in both categories 5- complications
The kidneys are excretory and regulatory organs. By
 exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
After studying this lecture, you should be able to...
 Reabsorption of Salt and Water After studying this lecture, you should be able to... 1. Define the obligatory water loss. 2. Describe the mechanism of Na ++ reabsorption in the distal tubule and explain
Reabsorption of Salt and Water After studying this lecture, you should be able to... 1. Define the obligatory water loss. 2. Describe the mechanism of Na ++ reabsorption in the distal tubule and explain
Hypertension and obesity. Dr Wilson Sugut Moi teaching and referral hospital
 Hypertension and obesity Dr Wilson Sugut Moi teaching and referral hospital No conflict of interests to declare Obesity Definition: excessive weight that may impair health BMI Categories Underweight BMI
Hypertension and obesity Dr Wilson Sugut Moi teaching and referral hospital No conflict of interests to declare Obesity Definition: excessive weight that may impair health BMI Categories Underweight BMI
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB
 COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB CG Musso ¹, J Reynaldi¹, N Imperiali ¹, L Algranati ¹, DG Oreopoulos ² Nephrology Department Hospital Italiano
COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB CG Musso ¹, J Reynaldi¹, N Imperiali ¹, L Algranati ¹, DG Oreopoulos ² Nephrology Department Hospital Italiano
Vol. 43, No. 1, September 1997 BIOCHEMISTRY ond MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Pages
 Vol. 43, No. 1, September 1997 BIOCHEMISTRY ond MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Pages 227-231 ANGIOTENSIN II TYPE I RECEPTOR POLYMORPHISM IN AFRICAN AMERICANS LOWER FREQUENCY OF THE C n66 VARIANT Short
Vol. 43, No. 1, September 1997 BIOCHEMISTRY ond MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Pages 227-231 ANGIOTENSIN II TYPE I RECEPTOR POLYMORPHISM IN AFRICAN AMERICANS LOWER FREQUENCY OF THE C n66 VARIANT Short
RENAL FUNCTION An Overview
 RENAL FUNCTION An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ. Temple 1 Kidneys
RENAL FUNCTION An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ. Temple 1 Kidneys
Na + /K + interaction in the kidney, blood vessels, brain, and beyond
 Na + /K + interaction in the kidney, blood vessels, brain, and beyond Horacio J. Adrogué, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine Chief, Clinical Nephrology and Hypertension. Houston Methodist
Na + /K + interaction in the kidney, blood vessels, brain, and beyond Horacio J. Adrogué, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine Chief, Clinical Nephrology and Hypertension. Houston Methodist
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
What is the inheritance pattern (e.g., autosomal, sex-linked, dominant, recessive, etc.)?
 Module I: Introduction to the disease Give a brief introduction to the disease, considering the following: the symptoms that define the syndrome, the range of phenotypes exhibited by individuals with the
Module I: Introduction to the disease Give a brief introduction to the disease, considering the following: the symptoms that define the syndrome, the range of phenotypes exhibited by individuals with the
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 November 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2013 May ; 83(5): 779 782. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.468. Need to quickly excrete K +? Turn off NCC Alicia A. McDonough 1 and
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2013 May ; 83(5): 779 782. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.468. Need to quickly excrete K +? Turn off NCC Alicia A. McDonough 1 and
Relation Between Sodium Intake, Renal Function, and the Regulation of Arterial Pressure. Jeffrey L. Osborn
 1-91 Relation Between Sodium Intake, Renal Function, and the Regulation of Arterial Pressure Jeffrey L. Osborn The long-term regulation of arterial pressure requires the maintenance of a balance between
1-91 Relation Between Sodium Intake, Renal Function, and the Regulation of Arterial Pressure Jeffrey L. Osborn The long-term regulation of arterial pressure requires the maintenance of a balance between
Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido Boerrigter, Horng C Chen, Fernando L Martin, and John C Burnett Jr
 Cardiorenal Enhancing and Aldosterone Suppressing Actions of a Novel Designer Natriuretic Peptide in Experimental Hypertension with Ventricular Pressure Overload Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido
Cardiorenal Enhancing and Aldosterone Suppressing Actions of a Novel Designer Natriuretic Peptide in Experimental Hypertension with Ventricular Pressure Overload Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido
Objectives. Systolic Heart Failure: Definitions. Heart Failure: Historical Perspective 2/7/2009
 Objectives Diastolic Heart Failure and Indications for Echocardiography in the Asian Population Damon M. Kwan, MD UCSF Asian Heart & Vascular Symposium 02.07.09 Define diastolic heart failure and differentiate
Objectives Diastolic Heart Failure and Indications for Echocardiography in the Asian Population Damon M. Kwan, MD UCSF Asian Heart & Vascular Symposium 02.07.09 Define diastolic heart failure and differentiate
Prof. Andrzej Wiecek Department of Nephrology, Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases Medical University of Silesia Katowice, Poland.
 What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
Present status of genetic mechanisms in hypertension
 Med Clin N Am 88 (2004) 1 18 Present status of genetic mechanisms in hypertension Friedrich C. Luft, MD* Franz Volhard Clinic and Max Delbru ck Center for Molecular Medicine, Wiltberg Strasse 50, 13125
Med Clin N Am 88 (2004) 1 18 Present status of genetic mechanisms in hypertension Friedrich C. Luft, MD* Franz Volhard Clinic and Max Delbru ck Center for Molecular Medicine, Wiltberg Strasse 50, 13125
The Na-Li CT is an ion transport system that exchanges
 Red Blood Cell Sodium-Lithium Countertransport and Risk of Future Hypertension The Olivetti Prospective Heart Study Pasquale Strazzullo, Alfonso Siani, Francesco P. Cappuccio, Maurizio Trevisan, Eliana
Red Blood Cell Sodium-Lithium Countertransport and Risk of Future Hypertension The Olivetti Prospective Heart Study Pasquale Strazzullo, Alfonso Siani, Francesco P. Cappuccio, Maurizio Trevisan, Eliana
Beta 1 Beta blockers A - Propranolol,
 Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Chapter 1 RENAL HAEMODYNAMICS AND GLOMERULAR FILTRATION
 3 Chapter 1 RENAL HAEMODYNAMICS AND GLOMERULAR FILTRATION David Shirley, Giovambattista Capasso and Robert Unwin The kidney has three homeostatic functions that can broadly be described as excretory, regulatory
3 Chapter 1 RENAL HAEMODYNAMICS AND GLOMERULAR FILTRATION David Shirley, Giovambattista Capasso and Robert Unwin The kidney has three homeostatic functions that can broadly be described as excretory, regulatory
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis.
 Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX
 One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance
 Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
Comparison of nasal ph values in black and white individuals with normal and high blood pressure
 Clinical Science (2001) 100, 327 333 (Printed in Great Britain) 327 Comparison of nasal ph values in black and white individuals with normal and high blood pressure N. J. IRESON, J. S. TAIT, G. A. MACGREGOR
Clinical Science (2001) 100, 327 333 (Printed in Great Britain) 327 Comparison of nasal ph values in black and white individuals with normal and high blood pressure N. J. IRESON, J. S. TAIT, G. A. MACGREGOR
CASE 13. What neural and humoral pathways regulate arterial pressure? What are two effects of angiotensin II?
 CASE 13 A 57-year-old man with long-standing diabetes mellitus and newly diagnosed hypertension presents to his primary care physician for follow-up. The patient has been trying to alter his dietary habits
CASE 13 A 57-year-old man with long-standing diabetes mellitus and newly diagnosed hypertension presents to his primary care physician for follow-up. The patient has been trying to alter his dietary habits
BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation
 Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
8. URINE CONCENTRATION
 8. URINE CONCENTRATION The final concentration of the urine is very dependent on the amount of liquid ingested, the losses through respiration, faeces and skin, including sweating. When the intake far
8. URINE CONCENTRATION The final concentration of the urine is very dependent on the amount of liquid ingested, the losses through respiration, faeces and skin, including sweating. When the intake far
