Accurate placement of a ventricular catheter is crucial
|
|
|
- Corey Parker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 clinical article J Neurosurg 124: , 2016 Calvarial slope affecting accuracy of Ghajar Guide technique for ventricular catheter placement Jaechan Park, MD, PhD, 1,2 Wonsoo Son, MD, 1,2 Ki-Su Park, MD, 1,2 Min Young Kim, PhD, 2 and Joomi Lee, PhD 3 1 Department of Neurosurgery, 2 Research Center for Neurosurgical Robotic Systems, and 3 Cell & Matrix Research Institute, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea Objective The Ghajar Guide technique is used to direct a ventricular catheter at a 90 angle to the skull surface at Kocher s point. However, the human calvaria is not completely spherical. Lateral to the sagittal midline, the calvaria slopes downward with individual variation and thereby affects the accuracy of ventricular catheter placement. Accordingly, the authors investigated the accuracy of the orthogonal catheter trajectory using radiographic simulation and examined the effect of the calvarial slope on this accuracy. Methods A catheter trajectory orthogonal to the skull surface at Kocher s point and the ideal catheter trajectory to the foramen of Monro were drawn bilaterally on coronal head images of 52 patients with hydrocephalus. The correction angle, the difference between the 2 catheter trajectories, was then measured. Meanwhile, the calvarial slope was measured around Kocher s point by using a coronal head image. The correlation between the correction angle and factors such as the calvarial slope and bicaudate index was then assessed using a Pearson correlation analysis. Results The ventricular catheter trajectory orthogonal to the skull at Kocher s point in the patients with hydrocephalus led to a catheter trajectory into the ipsilateral (70.2%) or contralateral (29.8%) lateral ventricles. The correction angles ranged from -3.3 to 16.4 (mean ± SD 5.7 ± 3.7 ). In 87 (83.7%) head sides, lateral deviation from the orthogonal trajectory was required to approximate the ideal trajectory, and the correction angle ranged from 2.0 to 16.4 (mean 6.7 ± 2.9 ). The calvarial slope in the 104 head sides ranged from 15.6 to 32.5 (mean 24.2 ± 3.1 ). Pearson correlation analysis revealed a strong positive correlation (r = 0.733) between the calvarial slope and the correction angle. Conclusions The accuracy of ventricular catheter placement using the Ghajar Guide technique is affected primarily by the calvarial slope around Kocher s point. A radiographic analysis of a preoperative coronal head image can be used to estimate the accuracy of ventricular catheter placement and enable adjustment to approximate the ideal catheter trajectory. Key Words catheterization; cerebral ventricles; hydrocephalus; skull; ventriculoperitoneal shunt; surgical technique Accurate placement of a ventricular catheter is crucial for ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement and external ventricular drainage. Although frameless stereotaxis can be used in patients with smaller ventricles, 1,2,7,14,15 the ventricular catheter is still commonly placed based on the surface anatomy of the head or just orthogonal to the skull for ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement in patients with larger ventricles or for external ventricular drainage. 3,4,6 8,10,16 The Ghajar Guide technique, using a catheter guide with a rigid tripod, was introduced for ventricular catheter placement in This guide was designed to direct the ventricular catheter at a 90 angle to the skull surface at Kocher s point based on the facts that the body of the lateral ventricle is located in the midpupillary line and the curve of the superior aspect of the frontal horn roughly parallels the curve of the overlying skull. However, the human skull is not exactly spherical. Lateral to the sagittal midline, the calvaria slopes downward and exhibits individual variations. Thus, catheter placement orthogonal to the skull at Kocher s point does not guarantee ideal catheter placement in the ipsilateral submitted January 30, accepted May 14, include when citing Published online November 6, 2015; DOI: / JNS AANS, 2016 J Neurosurg Volume 124 May
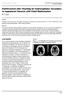
2 J. Park et al. frontal horn of the lateral ventricle near the foramen of Monro. 9,11,17 Accordingly, we investigated the accuracy of ventricular catheter placement orthogonal to the skull using radiographic simulation and examined the effect of the calvarial slope on this accuracy. Methods Patient Population Between January 2013 and December 2014, a total of 89 patients underwent ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement for hydrocephalus at our institution. The inclusion criteria for this study included the following: 1) age > 20 years, 2) a diagnosis of hydrocephalus, 3) treatment with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt, and 4) available preoperative coronal CT or MR images. The exclusion criteria included the following: 1) midline brain shift and 2) compressed, distorted, or enlarged frontal horn of the lateral ventricle caused by an adjacent parenchymal lesion. As a result, 52 of the 89 patients were finally included in this study. The study was reviewed and approved by the Kyungpook National University institutional ethics committee. Informed consent was obtained from each patient. Radiographic Simulation of Catheter Trajectories Various CT scanners (LightSpeed, General Electric; Aquilion 64, Toshiba Medical Systems) were used to perform axial head imaging based on a collimated slice width of 2.5 mm from the skull base to the vertex (120 kvp [kilovolt potential], 180 ma, 0.8 seconds). The coronal images were then reconstructed by using a slice thickness of mm and 0.5-mm increments based on a soft-tissue algorithm. Meanwhile, the coronal T2-weighted MR images were obtained at 3.0 T for the whole brain using the following parameters: TR 3400 msec, TE 102 msec, slice thickness 6 mm, gap 2 mm, matrix , and FOV 200 mm. The technique of catheter placement orthogonal to the skull surface was simulated on the preoperative coronal images by using PiViewSTAR (INFINITT Co., Ltd.), an electronic picture-archiving and communication system that integrates simple measurement tools (e.g., distance and angle measurements). On a coronal image at or around the foramen of Monro, a bur-hole site was marked at a point 3 cm lateral to the midline on the skull. On the circular line outlining the skull surface, a 3-cm-long chord was drawn with both ends equidistant from the bur-hole site. A perpendicular line starting at the middle of the chord was then drawn to the ventricular system, corresponding to a catheter trajectory orthogonal to the skull surface. Thereafter, the ideal catheter trajectory toward the foramen of Monro was drawn from the middle of the chord (Fig. 1). The correction angle, the difference between the ideal trajectory and the orthogonal trajectory, was then measured, which resulted in a positive or negative number according to whether the orthogonal catheter trajectory lay medial or lateral, respectively, to the ideal trajectory. This procedure was performed bilaterally with each coronal head image. Fig. 1. Coronal CT image showing radiographic analysis of the catheter trajectories. The correction angle is the difference between the catheter trajectory (90 ) orthogonal to the skull surface and the ideal catheter trajectory (100 ) to the foramen of Monro. Here, the correction angle is 10. Associated Factors That Affect Accuracy of the Ghajar Guide Technique The calvarial slope and bicaudate index of each patient were measured by using a picture-archiving and communication system. To measure the calvarial slope using the coronal head image, a 3-cm-long chord was drawn with both ends equidistant from the bur hole site (Kocher s point, 3 cm lateral to the midline) on the circular line outlining the skull surface. The angle between the chord below Kocher s point and the horizontal line (i.e., the calvarial slope) was then measured (Fig. 2). In addition, the bicaudate index, the ratio of the width of both lateral ventricles at the level of the heads of the caudate nuclei to the distance between the inner tables of the skull at the same level, was measured by using the preoperative axial CT or MR images. Intraobserver and Interobserver Variabilities Two experienced neurosurgeons (W.S. and K.S.P.) independently evaluated the preoperative coronal CT and MR images to determine the correction angle and calvarial slope. The 2 observers evaluated each image twice at an interval of > 1 week. The mean value of the measurements recorded by both observers was then used as the measurement result. Also, the interobserver variability was calculated by comparing the results from both observers, and the intraobserver variability was assessed by comparing the results recorded by each observer. Statistical Analysis The statistical analyses were performed by using SPSS version 18.0 for Windows (SPSS, Inc.) to calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient for evaluating the intraobserver and interobserver variabilities of the correction an J Neurosurg Volume 124 May 2016
3 Accuracy of the Ghajar Guide technique Fig. 2. Coronal CT image showing measurement of the calvarial slope. The calvarial slope is defined as the angle between a 3-cm-long chord with both ends equidistant from Kocher s point and the horizontal line. An angle of 25 means a high calvarial slope. gle and calvarial slope measurements. The intraobserver and interobserver agreement was considered good if the Pearson coefficient was between 0.6 and 0.8 and excellent if the coefficient was greater than 0.8. The correlation between the correction angle and the associated factors, such as the calvarial slope and bicaudate index, was assessed by using Pearson correlation analysis. The results were considered significant for probability values less than Mean values are presented ± SD. Results Patients The patient population (n = 52) consisted of 31 men and 21 women with a mean age of 63.6 ± 12.1 years (range years). Preoperative coronal CT images that were reconstructed by using preoperative axial CT scans were available for 44 patients, whereas preoperative coronal MR images were available for 8 patients. The ventricles in each patient were dilated and located in the midline. The bicaudate index values ranged from 0.15 to 0.49 (mean 0.28 ± 0.06). Radiographic Simulation of Catheter Trajectories In 22 of the 52 patients, radiographic simulation of catheter placement orthogonal to the skull showed a catheter trajectory into the contralateral lateral ventricle unilaterally (n = 13) or bilaterally (n = 9). Notwithstanding, there was no failure of ventricular catheterization. Of the 104 head sides of the 52 patients, radiographic simulation in 31 (29.8%) sides revealed a catheter trajectory into the contralateral lateral ventricle; simulation in 12 (11.5%) of these sides revealed a contralateral trajectory without traversing the ipsilateral lateral ventricle and in the other 19 sides (18.3%) revealed a catheter trajectory into the contralateral lateral ventricle after traversing the superomedial corner of the ipsilateral lateral ventricle and upper half of the septum pellucidum. Radiographic simulation in the remaining 73 (70.2%) head sides revealed a satisfactory catheter trajectory into the ipsilateral frontal horn of the lateral ventricle. The Pearson coefficient that indicates interobserver agreement on the correction angle was 0.96, whereas the coefficients that indicate intraobserver agreement on the correction angle were 0.99 and 0.95 for the 2 observers. The correction angles ranged from -3.3 to 16.4 (mean 5.7 ± 3.7 ). The orthogonal catheter trajectory approximated the ideal trajectory (correction angle less than ± 2 ) in 15 sides (14.4%). However, in 87 sides (83.7%), lateral tilting of the orthogonal trajectory was required to approximate the ideal trajectory (correction angle range [mean 6.7 ± 2.9 ]), whereas medial tilting was required in only 2 sides (correction angles -2.3 and -3.3 ). Associated Factors That Affect Accuracy of the Ghajar Guide Technique The Pearson coefficient that indicates interobserver agreement on the calvarial slope was 0.86, whereas the coefficients that indicate intraobserver agreement on the calvarial slope were 0.99 and 0.85 for the 2 observers. The calvarial slopes of the 104 head sides ranged from 15.6 to 32.3 (mean 24.2 ± 3.1 ). Pearson correlation analysis revealed a strong positive correlation between the calvarial slope and the correction angle (p < 0.001; r = 0.733), as shown in Fig. 3. A simple linear regression analysis was used to develop an equation for predicting the dependent variable (y, correction angle) given a value (x, calvarial slope) for the independent variable. This equation was y = x The value of R 2 was Meanwhile, Pearson correlation analysis of the bicaudate index and the correction angle revealed a significant (p < 0.01) yet weak positive correlation (r = 0.310), as shown in Fig. 4. Discussion The Ghajar Guide technique using a catheter guide with a rigid tripod is often applied for external ventricular drainage and ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement, 5,9,17 and it has been reported to provide better accuracy than freehand catheter placement. However, application of the technique is not always accurate, 9,11 and the difference from the ideal catheter trajectory had not been reported previously for patients with hydrocephalus. A radiographic analysis of the ventricular catheter trajectory orthogonal to the skull was performed by Rehman et al. 11 However, their study focused only on patients with a normal ventricular size and revealed a catheter trajectory in a nonventricular space in 10% of the patients. In our radiographic study, we analyzed patients with hydrocephalus with a bicaudate index of 0.15, and although the catheter trajectory passed through a ventricular space in every case, it passed into the contralateral lateral ventricle in 30% of the head sides. J Neurosurg Volume 124 May
4 J. Park et al. Fig. 3. Graph of Pearson correlation analysis results for the calvarial slope and correction angle, showing a strong positive correlation (r = 0.733). Fig. 4. Graph of Pearson correlation analysis results for the bicaudate index and correction angle, showing a weak positive correlation (r = 0.310). To our knowledge, our study of how the calvarial slope affects the accuracy of catheter placement orthogonal to the skull is novel, and the results are crucial for understanding and successfully applying the Ghajar Guide technique. As such, a patient with a high-slope calvaria can suffer catheterization into the contralateral lateral ventricle when the neurosurgeon uses the Ghajar Guide technique, whereas a patient with a low-slope calvaria and smaller ventricle can suffer nonventricular catheterization lateral to the ipsilateral lateral ventricle. The correction angle varied predictably as a function of the calvarial slope according to the following equation: correction angle = ( calvarial slope) When the calvarial slope is > 18, the catheter trajectory directs medially toward the contralateral lateral ventricle. Thus, if the calvarial slope is 30, the catheter trajectory directs medial to the ipsilateral foramen of Monro with a correction angle of Meanwhile, when the slope is below 18, the catheter trajectory directs lateral to the foramen of Monro and then to the brain parenchyma lateral to the ventricular wall. Also, if the slope is < 12, the lateral deviation of the orthogonal catheter trajectory from the trajectory toward the foramen of Monro is greater than 5, which thereby increases the risk of catheterization into the brain parenchyma and necessitates the use of a more accurate stereotactic technique. Among our cases with large ventricular size and a high bicaudate index, the success rate of ventricular catheterization including the ipsilateral and contralateral lateral ventricles was high. However, the incidence of a catheter trajectory close to the ideal trajectory was low and the correction angle was high, showing a weak positive correlation between the bicaudate index and the correction angle. Thus, to overcome the limitations of the Ghajar Guide technique, an adjustable catheter guide is needed to realign the orthogonal trajectory according to a preoperative radiographic assessment using a coronal head image. 13 If a more accurate catheter placement is needed, a frameless or frame-based stereotactic technique can be used. 1,2,7,14,15 In a recent US survey of the surgical techniques used for ventriculostomy placement in patients with slit ventricles, the Ghajar Guide technique was used by only 6.7% of the respondents, whereas the remaining respondents used image guidance or a freehand technique. 12 When the survey asked about improvements that would increase usage of the Ghajar Guide, 22.1% of the respondents suggested an adjustable guide for a midline shift or abnormal ventricular anatomy, and 19.0% suggested the availability of more data on the use of the Ghajar Guide technique. Thus, the results of our study may encourage greater use of a Ghajar Guide based technique with coronal adjustment. Our study has several important limitations. First, it was based on only a small series of patients from a single institution. Second, the series included only Asian patients, which raises the possibility of racial differences in calvarial morphology. Third, the sagittal calvarial slope was not evaluated; it was considered less important because the ventricular system is oriented sagittally. Notwithstanding, the results of our study shed light on the coronal calvarial slope and accuracy of the Ghajar Guide technique and warrant future studies to improve the Ghajar Guide technique. Conclusions A radiographic analysis of the ventricular catheter trajectory orthogonal to the skull surface at Kocher s point in patients with hydrocephalus showed a catheter trajectory into the ipsilateral (70%) or contralateral (30%) lateral ventricles. The accuracy of the ventricular catheterization using the Ghajar Guide technique was affected primarily by the calvarial slope. Radiographic analysis of a preoperative coronal head image can be used to estimate the accuracy of ventricular catheter placement and enable adjustment to achieve the ideal catheter trajectory. Acknowledgments This research was supported by the Korea Health Technology 1432 J Neurosurg Volume 124 May 2016
5 Accuracy of the Ghajar Guide technique R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (Grant HI15C0001). References 1. Abu-Serieh B, Ghassempour K, Duprez T, Raftopoulos C: Stereotactic ventriculoperitoneal shunting for refractory idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurosurgery 60: , Azeem SS, Origitano TC: Ventricular catheter placement with a frameless neuronavigational system: a 1-year experience. Neurosurgery 60 (4 Suppl 2): , Bergsneider M, Stiner E: Management of adult hydrocephalus: shunting, in Winn HR (ed): Youmans Neurological Surgery, ed 6. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2011, pp Epstein MH, Duncan JA: Surgical management of hydrocephalus in adults, in Schmidek HH (ed): Schmidek & Sweet Operative Neurosurgical Techniques: Indications, Methods, and Results, ed 4. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2000, pp Ghajar JB: A guide for ventricular catheter placement. Technical note. J Neurosurg 63: , Huyette DR, Turnbow BJ, Kaufman C, Vaslow DF, Whiting BB, Oh MY: Accuracy of the freehand pass technique for ventriculostomy catheter placement: retrospective assessment using computed tomography scans. J Neurosurg 108:88 91, Kandasamy J, Hayhurst C, Clark S, Jenkinson MD, Byrne P, Karabatsou K, et al: Electromagnetic stereotactic ventriculoperitoneal csf shunting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a successful step forward? World Neurosurg 75: , 32 33, Lind CR, Correia JA, Law AJ, Kejriwal R: A survey of surgical techniques for catheterising the cerebral lateral ventricles. J Clin Neurosci 15: , O Leary ST, Kole MK, Hoover DA, Hysell SE, Thomas A, Shaffrey CI: Efficacy of the Ghajar Guide revisited: a prospective study. J Neurosurg 92: , Piatt JH Jr: Hydrocephalus: treatment, in Wilkins RH, Rengachary SS (eds): Neurosurgery, ed 2. New York: McGraw- Hill, 1996, pp Rehman T, Rehman Au, Ali R, Rehman A, Bashir H, Ahmed Bhimani S, et al: A radiographic analysis of ventricular trajectories. World Neurosurg 80: , Rehman T, Rehman AU, Rehman A, Bashir HH, Ali R, Bhimani SA, et al: A US-based survey on ventriculostomy practices. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 114: , Thomale UW, Knitter T, Schaumann A, Ahmadi SA, Ziegler P, Schulz M, et al: Smartphone-assisted guide for the placement of ventricular catheters. Childs Nerv Syst 29: , Wilson TJ, Stetler WR Jr, Al-Holou WN, Sullivan SE: Comparison of the accuracy of ventricular catheter placement using freehand placement, ultrasonic guidance, and stereotactic neuronavigation. J Neurosurg 119:66 70, Woerdeman PA, Willems PW, Han KS, Hanlo PW, Berkelbach van der Sprenkel JW: Frameless stereotactic placement of ventriculoperitoneal shunts in undersized ventricles: a simple modification to free-hand procedures. Br J Neurosurg 19: , Woo H, Kang DH, Park J: Preoperative determination of ventriculostomy trajectory in ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery using a simple modification of the standard coronal MRI. J Clin Neurosci 20: , Yamada SM, Yamada S, Goto Y, Nakaguchi H, Murakami M, Hoya K, et al: A simple and consistent technique for ventricular catheter insertion using a tripod. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 114: , 2012 Disclosure The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper. Author Contributions Conception and design: J Park. Acquisition of data: Son, KS Park. Analysis and interpretation of data: J Park, KS Park, Lee. Drafting the article: J Park. Approved the final version of the manuscript on behalf of all authors: J Park. Statistical analysis: Lee. Administrative/technical/material support: Kim. Study supervision: J Park. Correspondence Jaechan Park, Department of Neurosurgery, Kyungpook National University Hospital, 50 Samduk 2-ga, Jung-gu, Daegu , Republic of Korea. jparkmd@hotmail.com. J Neurosurg Volume 124 May
Accuracy and Safety of Bedside External Ventricular Drain Placement at Two Different Cranial Sites : Kocher s Point versus Forehead
 online ML Comm www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2011.50.4.317 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 50 : 317-321, 2011 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2011 The Korean Neurosurgical
online ML Comm www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2011.50.4.317 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 50 : 317-321, 2011 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2011 The Korean Neurosurgical
Accuracy of the Free Hand Placement of an External Ventricular Drain (EVD)
 KOR J CEREBROVASCULAR SURGERY June 2O10 Vol. 12 No 2, page 82-6 Accuracy of the Free Hand Placement of an External Ventricular Drain (EVD) Department of Neurosurgery, Gachon University of Medicine & Science,
KOR J CEREBROVASCULAR SURGERY June 2O10 Vol. 12 No 2, page 82-6 Accuracy of the Free Hand Placement of an External Ventricular Drain (EVD) Department of Neurosurgery, Gachon University of Medicine & Science,
The misplacement of external ventricular drain by freehand method in emergent neurosurgery
 Acta Neurol. Belg., 2011, 111, 22-28 Original articles The misplacement of external ventricular drain by freehand method in emergent neurosurgery Cheng-Ta HsieH 1,2, Guann-Juh CHen 1, Hsin-i Ma 1, Cheng-Fu
Acta Neurol. Belg., 2011, 111, 22-28 Original articles The misplacement of external ventricular drain by freehand method in emergent neurosurgery Cheng-Ta HsieH 1,2, Guann-Juh CHen 1, Hsin-i Ma 1, Cheng-Fu
Freehand insertion of external ventricular drains
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Utilizing preprocedural CT scans to identify patients at risk for suboptimal external ventricular drain placement with the freehand insertion technique Mitchell P. Wilson, MD, 1 Cian O
CLINICAL ARTICLE Utilizing preprocedural CT scans to identify patients at risk for suboptimal external ventricular drain placement with the freehand insertion technique Mitchell P. Wilson, MD, 1 Cian O
Effect of Electromagnetic Navigated Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Placement on Failure Rates
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.53.3.150 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 53 : 150-154, 2013 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2013 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.53.3.150 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 53 : 150-154, 2013 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2013 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
External ventricular drain (EVD) placement for cerebrospinal. FOCUS Neurosurg Focus 43 (5):E5, 2017
 NEUROSURGICAL FOCUS Neurosurg Focus 43 (5):E5, 2017 Real-time ultrasound-guided external ventricular drain placement: technical note James H. Manfield, MBBS, MSc, MRCS, 1 and Kenny K. H. Yu, MBBS, MRCS,
NEUROSURGICAL FOCUS Neurosurg Focus 43 (5):E5, 2017 Real-time ultrasound-guided external ventricular drain placement: technical note James H. Manfield, MBBS, MSc, MRCS, 1 and Kenny K. H. Yu, MBBS, MRCS,
An approach using the occipital parietal point for placement of ventriculoperitoneal catheters in adults. Abstract Introduction Methods Results
 An approach using the occipital parietal point for placement of ventriculoperitoneal catheters in adults. Jason Duong, DO 1, Dan Miulli DO 1, Fanglong Dong, PhD 2, Andrew Sumida MSIV 3, 1 Neurosurgery
An approach using the occipital parietal point for placement of ventriculoperitoneal catheters in adults. Jason Duong, DO 1, Dan Miulli DO 1, Fanglong Dong, PhD 2, Andrew Sumida MSIV 3, 1 Neurosurgery
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
The Hydrocephalus Clinical Research Network
 J Neurosurg Pediatrics 14:173 178, 2014 AA, 2014 Factors associated with ventricular catheter movement and inaccurate catheter location: post hoc analysis of the Hydrocephalus Clinical Research Network
J Neurosurg Pediatrics 14:173 178, 2014 AA, 2014 Factors associated with ventricular catheter movement and inaccurate catheter location: post hoc analysis of the Hydrocephalus Clinical Research Network
Placement and revision of ventricular shunts for hydrocephalus
 J Neurosurg 120:684 696, 2014 AANS, 2014 Improvement in clinical outcomes following optimal targeting of brain ventricular catheters with intraoperative imaging Clinical article Christopher G. Janson,
J Neurosurg 120:684 696, 2014 AANS, 2014 Improvement in clinical outcomes following optimal targeting of brain ventricular catheters with intraoperative imaging Clinical article Christopher G. Janson,
Ann Marie Flannery, M.D., 1 Ann-Christine Duhaime, M.D., 2 1
 J Neurosurg Pediatrics (Suppl) 14:24 29, 2014 AANS, 2014 Pediatric hydrocephalus: systematic literature review and evidence-based guidelines. Part 3: Endoscopic computer-assisted electromagnetic navigation
J Neurosurg Pediatrics (Suppl) 14:24 29, 2014 AANS, 2014 Pediatric hydrocephalus: systematic literature review and evidence-based guidelines. Part 3: Endoscopic computer-assisted electromagnetic navigation
Placement of an external ventricular drain (EVD) is. Ultrasound stylet for non image-guided ventricular catheterization PEDIATRICS
 PEDIATRICS laboratory investigation J Neurosurg Pediatr 16:393 401, 2015 Ultrasound stylet for non image-guided ventricular catheterization *Nathaniel K. Coulson, MS, 1 Peter A. Chiarelli, MD, PhD, 2 David
PEDIATRICS laboratory investigation J Neurosurg Pediatr 16:393 401, 2015 Ultrasound stylet for non image-guided ventricular catheterization *Nathaniel K. Coulson, MS, 1 Peter A. Chiarelli, MD, PhD, 2 David
Ventriculostomy is one of the most common procedures. Revisiting the rules for freehand ventriculostomy: a virtual reality analysis
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 128:1250 1257, 2018 Revisiting the rules for freehand ventriculostomy: a virtual reality analysis Clemens Raabe, 1,2 Jens Fichtner, MD, 2 Jürgen Beck, MD, 2 Jan Gralla, MD,
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 128:1250 1257, 2018 Revisiting the rules for freehand ventriculostomy: a virtual reality analysis Clemens Raabe, 1,2 Jens Fichtner, MD, 2 Jürgen Beck, MD, 2 Jan Gralla, MD,
CT Based Study of Frontal Horn Ratio And Ventricular Index in South Indian Population
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. VI (July. 2017), PP 55-59 www.iosrjournals.org CT Based Study of Frontal Horn Ratio
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. VI (July. 2017), PP 55-59 www.iosrjournals.org CT Based Study of Frontal Horn Ratio
Reformatted Imaging to Define the Intercommissural Line for CT -Guided Stereotaxic Functional Neurosurgery
 Reformatted Imaging to Define the Intercommissural Line for CT -Guided Stereotaxic Functional Neurosurgery 429 Richard E. Latchaw1.2 L. Dade Lunsford 1. 2 William H. Kennedi Functional stereotaxic neurosurgery
Reformatted Imaging to Define the Intercommissural Line for CT -Guided Stereotaxic Functional Neurosurgery 429 Richard E. Latchaw1.2 L. Dade Lunsford 1. 2 William H. Kennedi Functional stereotaxic neurosurgery
Moron General Hospital Ciego de Avila Cuba. Department of Neurological Surgery
 Moron General Hospital Ciego de Avila Cuba Department of Neurological Surgery Early decompressive craniectomy in severe head injury with intracranial hypertension Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD,
Moron General Hospital Ciego de Avila Cuba Department of Neurological Surgery Early decompressive craniectomy in severe head injury with intracranial hypertension Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD,
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HIROSHI NAKAGUCHI, M.D., PH.D., TAKEO TANISHIMA, M.D., PH.D., Clinical Material and Methods
 J Neurosurg 93:791 795, 2000 Relationship between drainage catheter location and postoperative recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole irrigation and closed-system drainage HIROSHI NAKAGUCHI,
J Neurosurg 93:791 795, 2000 Relationship between drainage catheter location and postoperative recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole irrigation and closed-system drainage HIROSHI NAKAGUCHI,
Error analysis in neuronavigation
 Fakultät für Informatik - Humanoids and Intelligence Systems Lab Institut für Anthropomatik Mittwochs von 12:15-13:45 Error analysis in neuronavigation Uwe Spetzger Neurochirurgische Klinik, Klinikum Karlsruhe
Fakultät für Informatik - Humanoids and Intelligence Systems Lab Institut für Anthropomatik Mittwochs von 12:15-13:45 Error analysis in neuronavigation Uwe Spetzger Neurochirurgische Klinik, Klinikum Karlsruhe
The incidence of CT scan use is drastically on the
 J Neurosurg Pediatrics 12:406 410, 2013 AANS, 2013 Low-dose head computed tomography in children: a single institutional experience in pediatric radiation risk reduction Clinical article Ryan P. Morton,
J Neurosurg Pediatrics 12:406 410, 2013 AANS, 2013 Low-dose head computed tomography in children: a single institutional experience in pediatric radiation risk reduction Clinical article Ryan P. Morton,
Multiple Intracranial High Density Foci after Brain Parenchymal Catheterization
 CLINICL RTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2016;12(2):118-122 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 https://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2016.12.2.118 Multiple Intracranial High Density Foci after rain Parenchymal Catheterization
CLINICL RTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2016;12(2):118-122 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 https://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2016.12.2.118 Multiple Intracranial High Density Foci after rain Parenchymal Catheterization
Neurosurgical Techniques
 Neurosurgical Techniques EBEN ALEXANDER, JR., M.D., EDITOR Supratentorial Skull Flaps GuY L. ODOM, M.D., AND BARNES WOODHALL,!V[.D. Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical
Neurosurgical Techniques EBEN ALEXANDER, JR., M.D., EDITOR Supratentorial Skull Flaps GuY L. ODOM, M.D., AND BARNES WOODHALL,!V[.D. Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical
Over the last few decades, endoscopic third ventriculostomy
 clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 17:734 738, 2016 Long-term follow-up of endoscopic third ventriculostomy performed in the pediatric population Matthew G. Stovell, MBBS, 1 Rasheed Zakaria, MA, BMBCh,
clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 17:734 738, 2016 Long-term follow-up of endoscopic third ventriculostomy performed in the pediatric population Matthew G. Stovell, MBBS, 1 Rasheed Zakaria, MA, BMBCh,
Original Article. Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction. Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH
 Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
The use of intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring in the
 Training Protocol for Intracranial Pressure Monitor Placement by Nonneurosurgeons: 5-Year Experience Kathryn Ko, MD, and Alicia Conforti, RN Background: This report evaluates a protocol for training nonneurosurgeon
Training Protocol for Intracranial Pressure Monitor Placement by Nonneurosurgeons: 5-Year Experience Kathryn Ko, MD, and Alicia Conforti, RN Background: This report evaluates a protocol for training nonneurosurgeon
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35771 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Palm, Walter Miguel Title: Ventricular dilatation in aging and dementia Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35771 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Palm, Walter Miguel Title: Ventricular dilatation in aging and dementia Issue
Relation between brain displacement and local cerebral blood flow in patients with chronic subdural haematoma
 J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 01;71:741 746 741 Department of Neurosurgery, Nagoya University School of Medicine, 65 Tsarumai Showa, Nagoya 466 8550, Japan S Inao TKawai R Kabeya T Sugimoto M Yamamoto
J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 01;71:741 746 741 Department of Neurosurgery, Nagoya University School of Medicine, 65 Tsarumai Showa, Nagoya 466 8550, Japan S Inao TKawai R Kabeya T Sugimoto M Yamamoto
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Parkinsonism after Shunting for Hydrocephalus Secondary to Aqueductal Stenosis with Chiari Malformation
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 6 Number 2 Parkinsonism after Shunting for Hydrocephalus Secondary to Aqueductal Stenosis with Chiari M Turgut Citation M Turgut. Parkinsonism after
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 6 Number 2 Parkinsonism after Shunting for Hydrocephalus Secondary to Aqueductal Stenosis with Chiari M Turgut Citation M Turgut. Parkinsonism after
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Risk Factors for Hinge Fracture Associated with Surgery Following Cervical Open-Door Laminoplasty
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 18;14(2):118-122 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 https://doi.org/1.134/kjnt.18.14.2.118 Risk Factors for Hinge Fracture Associated with Surgery Following Cervical
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 18;14(2):118-122 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 https://doi.org/1.134/kjnt.18.14.2.118 Risk Factors for Hinge Fracture Associated with Surgery Following Cervical
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma
 Neurology Asia 2013; 18(1) : 117 121 Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma 1 Dharmendra Ganesan MS FRCS(SN), 1 Sheau Fung Sia MS MRCS, 1 Vairavan Narayanan MS, 2 Gnana Kumar FRCR,
Neurology Asia 2013; 18(1) : 117 121 Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma 1 Dharmendra Ganesan MS FRCS(SN), 1 Sheau Fung Sia MS MRCS, 1 Vairavan Narayanan MS, 2 Gnana Kumar FRCR,
Manual Occipital Ventricular Puncture for Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunt Surgery: Can Aiming Be Standardized?
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 44, 353 358, 2004 Manual Occipital Ventricular Puncture for Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunt Surgery: Can Aiming Be Standardized? Satoru SHIMIZU*, **, RyusuiTANAKA*, HideoIIDA**, and Kiyotaka
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 44, 353 358, 2004 Manual Occipital Ventricular Puncture for Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunt Surgery: Can Aiming Be Standardized? Satoru SHIMIZU*, **, RyusuiTANAKA*, HideoIIDA**, and Kiyotaka
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts
 Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
Pedicle screw placement accuracy in thoracic and lumbar spinal surgery with a patient-matched targeting guide: A cadaveric study
 Pedicle screw placement accuracy in thoracic and lumbar spinal surgery with a patient-matched targeting guide: A cadaveric study [ based on the homonymous paper from Prof.Lamartina et al. Anticipated publication
Pedicle screw placement accuracy in thoracic and lumbar spinal surgery with a patient-matched targeting guide: A cadaveric study [ based on the homonymous paper from Prof.Lamartina et al. Anticipated publication
CT Dosimetry in the Clinical Environment: Methods and Analysis
 CT Dosimetry in the Clinical Environment: Methods and Analysis Manuel Arreola, Ph.D. DABR Associate Chair of Radiology Director, Medical Physics Graduate Program Department of Radiology University of Florida
CT Dosimetry in the Clinical Environment: Methods and Analysis Manuel Arreola, Ph.D. DABR Associate Chair of Radiology Director, Medical Physics Graduate Program Department of Radiology University of Florida
KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol
 KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol Sample referral sticker Referral Sticker Insert here Corin 17 Bridge Street Pymble NSW Australia 2073 P: +61 (0)2 9497 7400 F: +61 (0)2 9497 7498 E: KAS.customerservice@coringroup.com
KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol Sample referral sticker Referral Sticker Insert here Corin 17 Bridge Street Pymble NSW Australia 2073 P: +61 (0)2 9497 7400 F: +61 (0)2 9497 7498 E: KAS.customerservice@coringroup.com
Infraclavicular brachial plexus blocks have been designed
 The Supraclavicular Lateral Paravascular Approach for Brachial Plexus Regional Anesthesia: A Simulation Study Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Øivind Klaastad, MD* and Örjan Smedby, Dr Med Sci *Department
The Supraclavicular Lateral Paravascular Approach for Brachial Plexus Regional Anesthesia: A Simulation Study Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Øivind Klaastad, MD* and Örjan Smedby, Dr Med Sci *Department
CT SCAN PROTOCOL. Shoulder
 CT SCAN PROTOCOL Shoulder Purpose and Summary CT images made with this protocol are used to provide the orthopedic surgeon with a detailed 3D anatomical reconstruction of the patient s scapula and proximal
CT SCAN PROTOCOL Shoulder Purpose and Summary CT images made with this protocol are used to provide the orthopedic surgeon with a detailed 3D anatomical reconstruction of the patient s scapula and proximal
Chapter 6. Hester Gietema Cornelia Schaefer-Prokop Willem Mali Gerard Groenewegen Mathias Prokop. Accepted for publication in Radiology
 Chapter 6 Interscan variability of semiautomated volume measurements in intraparenchymal pulmonary nodules using multidetector-row computed tomography: Influence of inspirational level, nodule size and
Chapter 6 Interscan variability of semiautomated volume measurements in intraparenchymal pulmonary nodules using multidetector-row computed tomography: Influence of inspirational level, nodule size and
Focused ultrasound (FUS) thalamotomy was recently. FOCUS Neurosurg Focus 44 (2):E5, 2018
 NEUROSURGICAL FOCUS Neurosurg Focus 44 (2):E5, 2018 Predicting lesion size during focused ultrasound thalamotomy: a review of 63 lesions over 3 clinical trials Aaron E. Bond, MD, PhD, and W. Jeffrey Elias,
NEUROSURGICAL FOCUS Neurosurg Focus 44 (2):E5, 2018 Predicting lesion size during focused ultrasound thalamotomy: a review of 63 lesions over 3 clinical trials Aaron E. Bond, MD, PhD, and W. Jeffrey Elias,
Radiological Analysis of Ponticulus Posticus in Koreans
 Yonsei Med J 50(1):45-49, 2009 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.1.45 Radiological Analysis of Ponticulus Posticus in Koreans Department of Neurosurgery, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Yonsei Med J 50(1):45-49, 2009 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.1.45 Radiological Analysis of Ponticulus Posticus in Koreans Department of Neurosurgery, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Combined endoscopic third ventriculostomy and tumor biopsy in the management of pineal region tumors, safety considerations
 Amer and Elatrozy Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery (2018) 33:23 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41984-018-0022-7 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery RESEARCH Open Access Combined endoscopic third ventriculostomy
Amer and Elatrozy Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery (2018) 33:23 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41984-018-0022-7 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery RESEARCH Open Access Combined endoscopic third ventriculostomy
A Simple, Fast and Fully Automated Approach for Midline Shift Measurement on Brain Computed Tomography
 A Simple, Fast and Fully Automated Approach for Midline Shift Measurement on Brain Computed Tomography Huan-Chih Wang, Shih-Hao Ho, Furen Xiao, Jen-Hai Chou 2 Mar 2017 Abstract: Brain CT has become a standard
A Simple, Fast and Fully Automated Approach for Midline Shift Measurement on Brain Computed Tomography Huan-Chih Wang, Shih-Hao Ho, Furen Xiao, Jen-Hai Chou 2 Mar 2017 Abstract: Brain CT has become a standard
X-Ray Guided Robotic Radiosurgery for Solid Tumors
 X-Ray Guided Robotic Radiosurgery for Solid Tumors Mohan Bodduluri Accuray Incorporated 570 Del Rey Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94085 USA and J. M. McCarthy Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
X-Ray Guided Robotic Radiosurgery for Solid Tumors Mohan Bodduluri Accuray Incorporated 570 Del Rey Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94085 USA and J. M. McCarthy Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
CASE REPORT. Jackson Hayes, Marie Roguski and Ron I Riesenburger *
 Hayes et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:393 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Rapid resolution of an acute subdural hematoma by increasing the shunt valve pressure in
Hayes et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:393 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Rapid resolution of an acute subdural hematoma by increasing the shunt valve pressure in
Novel adaptation of the AxiEM electromagnetic neuronavigation system for intraoperative tracking of neuroendoscope during intraventricular surgery
 www.edoriumjournals.com CASE SERIES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Novel adaptation of the AxiEM electromagnetic neuronavigation system for intraoperative tracking of neuroendoscope during intraventricular
www.edoriumjournals.com CASE SERIES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Novel adaptation of the AxiEM electromagnetic neuronavigation system for intraoperative tracking of neuroendoscope during intraventricular
354 Korean J Radiol 9(4), August 2008
 Review of Failed CT Phantom Image Evaluations in 2005 and 2006 by the CT Accreditation Program of the Korean Institute for Accreditation of Medical Image Hye Jung Park, MD 1 Seung Eun Jung, MD 1, 2 Young
Review of Failed CT Phantom Image Evaluations in 2005 and 2006 by the CT Accreditation Program of the Korean Institute for Accreditation of Medical Image Hye Jung Park, MD 1 Seung Eun Jung, MD 1, 2 Young
The View through the Nose: ENT considerations for Pituitary/Skull Base Surgery
 The View through the Nose: ENT considerations for Pituitary/Skull Base Surgery Edsel Kim, M.D. Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery The Oregon Clinic Providence Brain and Spine Institute Pituitary, Thyroid
The View through the Nose: ENT considerations for Pituitary/Skull Base Surgery Edsel Kim, M.D. Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery The Oregon Clinic Providence Brain and Spine Institute Pituitary, Thyroid
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
ventriculography compared, those with mass lesions involving the cerebral hemispheres were excluded.
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 203-211 Computerized tomography (the EMAI Scanner): a comparison with pneumoencephalography and ventriculography J. GAWLER, G. H. DU BOULAY,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 203-211 Computerized tomography (the EMAI Scanner): a comparison with pneumoencephalography and ventriculography J. GAWLER, G. H. DU BOULAY,
Correlation of Computed Tomography findings with Glassgow Coma Scale in patients with acute traumatic brain injury
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2014, Vol-10, No-2 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE To correlate Computed Tomography (CT) findings with Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) in patients with acute traumatic brain injury
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2014, Vol-10, No-2 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE To correlate Computed Tomography (CT) findings with Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) in patients with acute traumatic brain injury
Original Research THE USE OF REFORMATTED CONE BEAM CT IMAGES IN ASSESSING MID-FACE TRAUMA, WITH A FOCUS ON THE ORBITAL FLOOR FRACTURES
 DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-601 Original Research THE USE OF REFORMATTED CONE BEAM CT IMAGES IN ASSESSING MID-FACE TRAUMA, WITH A FOCUS ON THE ORBITAL FLOOR FRACTURES RALUCA ROMAN 1, MIHAELA HEDEȘIU 1, FLOAREA
DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-601 Original Research THE USE OF REFORMATTED CONE BEAM CT IMAGES IN ASSESSING MID-FACE TRAUMA, WITH A FOCUS ON THE ORBITAL FLOOR FRACTURES RALUCA ROMAN 1, MIHAELA HEDEȘIU 1, FLOAREA
Quality Assurance of Ultrasound Imaging in Radiation Therapy. Zuofeng Li, D.Sc. Murty S. Goddu, Ph.D. Washington University St.
 Quality Assurance of Ultrasound Imaging in Radiation Therapy Zuofeng Li, D.Sc. Murty S. Goddu, Ph.D. Washington University St. Louis, Missouri Typical Applications of Ultrasound Imaging in Radiation Therapy
Quality Assurance of Ultrasound Imaging in Radiation Therapy Zuofeng Li, D.Sc. Murty S. Goddu, Ph.D. Washington University St. Louis, Missouri Typical Applications of Ultrasound Imaging in Radiation Therapy
Laminar Thickness: Correlation Against Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis and Changes with Age
 Laminar Thickness: Correlation Against Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis and Changes with Age Hamed Shalikar, MD 1, Sean L. Borkowski, MS 2, Juan Pablo Villablanca, MD 1, Sophia N. Sangiorgio, PhD 2, Edward
Laminar Thickness: Correlation Against Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis and Changes with Age Hamed Shalikar, MD 1, Sean L. Borkowski, MS 2, Juan Pablo Villablanca, MD 1, Sophia N. Sangiorgio, PhD 2, Edward
PROPHECY. Preoperative Navigation Guides ANKLE CT SCAN PROTOCOL
 PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Guides ANKLE CT SCAN PROTOCOL 90 FIGURE 1 Examples FIGURE 1 Examples of neutral ankle positioning. PROPHECY Ankle CT Scan Protocol PROPHECY INBONE and PROPHECY INFINITY
PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Guides ANKLE CT SCAN PROTOCOL 90 FIGURE 1 Examples FIGURE 1 Examples of neutral ankle positioning. PROPHECY Ankle CT Scan Protocol PROPHECY INBONE and PROPHECY INFINITY
S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA
 AN INSIGHT TO THE DILEMMA- CO-EXISTENCE OF OSSIFICAION OF POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT AND CERVICAL DISC PROLAPSE A SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA BACKGROUND
AN INSIGHT TO THE DILEMMA- CO-EXISTENCE OF OSSIFICAION OF POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT AND CERVICAL DISC PROLAPSE A SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA BACKGROUND
Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD)
 Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD) Dr. Vijay Tarnal MBBS, FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Neuroanesthesiology Division of Head & Neck Anesthesiology Michigan Medicine
Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD) Dr. Vijay Tarnal MBBS, FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Neuroanesthesiology Division of Head & Neck Anesthesiology Michigan Medicine
HEAD & NECK IMAGING. Iranian Journal of Radiology September; 10(3): Published Online 2013 August 30.
 Iranian Journal of Radiology. 2013 September; 10(3): 140-7. Published Online 2013 August 30. HEAD & NECK IMAGING 10.5812/iranjradiol.6353 Research Article Identification of Nasal Bone Fractures on Conventional
Iranian Journal of Radiology. 2013 September; 10(3): 140-7. Published Online 2013 August 30. HEAD & NECK IMAGING 10.5812/iranjradiol.6353 Research Article Identification of Nasal Bone Fractures on Conventional
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip
 197 Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip Ching-Yi Lee 1, Chieh-Tsai Wu 1, Kuang-Lin Lin 2, Hsun-Hui Hsu 3 Abstract-
197 Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip Ching-Yi Lee 1, Chieh-Tsai Wu 1, Kuang-Lin Lin 2, Hsun-Hui Hsu 3 Abstract-
W. CHRISTOPHER FOX, M.D., 1 SCOTT WAWRZYNIAK, 2 AND WILLIAM F. CHANDLER, M.D. 1. be very useful during transsphenoidal pituitary surgery as well.
 J Neurosurg 108:746 750, 2008 Intraoperative acquisition of three-dimensional imaging for frameless stereotactic guidance during transsphenoidal pituitary surgery using the Arcadis Orbic System W. CHRISTOPHER
J Neurosurg 108:746 750, 2008 Intraoperative acquisition of three-dimensional imaging for frameless stereotactic guidance during transsphenoidal pituitary surgery using the Arcadis Orbic System W. CHRISTOPHER
The arrest of treated hydrocephalus in children
 J Neurosurg 61:752-756, 1984 The arrest of treated hydrocephalus in children A radionuclide study IAN H. JOHNSTON, F.R.C.S., ROBERT HOWMAN-GILES, F.R.A.C.P., AND IAN R. WHITTLE, M.B., B.S. T. Y. Nelson
J Neurosurg 61:752-756, 1984 The arrest of treated hydrocephalus in children A radionuclide study IAN H. JOHNSTON, F.R.C.S., ROBERT HOWMAN-GILES, F.R.A.C.P., AND IAN R. WHITTLE, M.B., B.S. T. Y. Nelson
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy. Dr Kanwaljeet Garg
 Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy Dr Kanwaljeet Garg Introduction Endoscopic third ventriculostomyis a technique to treat non communicating hydrocephalus. Involves making a hole in the floor of the third
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy Dr Kanwaljeet Garg Introduction Endoscopic third ventriculostomyis a technique to treat non communicating hydrocephalus. Involves making a hole in the floor of the third
Comparison of CT findings of between MDR-TB and XDR-TB: A propensity score matching study
 Comparison of CT findings of between MDR-TB and XDR-TB: A propensity score matching study Purpose: The purpose of this study was to compare the CT findings between MDR-TB and XDR-TB groups using by propensity
Comparison of CT findings of between MDR-TB and XDR-TB: A propensity score matching study Purpose: The purpose of this study was to compare the CT findings between MDR-TB and XDR-TB groups using by propensity
The management of ICH when to operate when not to?
 The management of ICH when to operate when not to? Intracranial Hemorrhage High Incidence o Accounts for 10-15% of all strokes 1,2,5 o 80,000 cases in US; 2 million WW 2,5 o Incidence doubles for African-
The management of ICH when to operate when not to? Intracranial Hemorrhage High Incidence o Accounts for 10-15% of all strokes 1,2,5 o 80,000 cases in US; 2 million WW 2,5 o Incidence doubles for African-
Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study
 Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study Mark C. DeLano, F. Y. Fun, and S. James Zinreich PURPOSE: To delineate the relationship between the optic nerves
Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study Mark C. DeLano, F. Y. Fun, and S. James Zinreich PURPOSE: To delineate the relationship between the optic nerves
Three-Dimensional Cephalometry Using Helical Computer Tomography: Measurement Error Caused by Head Inclination
 Original Article Three-Dimensional Cephalometry Using Helical Computer Tomography: Measurement Error Caused by Head Inclination Kumiko Togashi, DDS a ; Hideki Kitaura, DDS, PhD b ; Koichi Yonetsu, DDS,
Original Article Three-Dimensional Cephalometry Using Helical Computer Tomography: Measurement Error Caused by Head Inclination Kumiko Togashi, DDS a ; Hideki Kitaura, DDS, PhD b ; Koichi Yonetsu, DDS,
Dr. Park s SDR Publication
 Dr. Park s SDR Publication Journal Papers 1. Phillips LH, Park TS: Electrophysiological mapping of the segmental anatomy of the muscles of the lower extremity. Muscle and Nerve 1991; 14:1213-121 2. Harris
Dr. Park s SDR Publication Journal Papers 1. Phillips LH, Park TS: Electrophysiological mapping of the segmental anatomy of the muscles of the lower extremity. Muscle and Nerve 1991; 14:1213-121 2. Harris
Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonate
 Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonate Angela Forbes, RN, MN, ARNP Seattle Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery Seattle, Washington, U.S.A. Intraventricular Hemorrhage Who Premature
Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonate Angela Forbes, RN, MN, ARNP Seattle Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery Seattle, Washington, U.S.A. Intraventricular Hemorrhage Who Premature
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Gregg NM, Kim AE, Gurol ME, et al. Incidental cerebral microbleeds and cerebral blood flow in elderly individuals. JAMA Neurol. Published online July 13, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1359.
Supplementary Online Content Gregg NM, Kim AE, Gurol ME, et al. Incidental cerebral microbleeds and cerebral blood flow in elderly individuals. JAMA Neurol. Published online July 13, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1359.
EVALUATION OF MODIFIED EXTRAORAL TECHNIQUE IN ZYGOMATIC ARCH EXAMINATION
 EVALUATION OF MODIFIED EXTRAORAL TECHNIQUE IN ZYGOMATIC ARCH EXAMINATION Aditya Dupare 1 *, Apeksha Dhole (Balpande) 2, Mukta Motwani 3, Anuraag Choudhary 4 1. Post graduate student, Department of oral
EVALUATION OF MODIFIED EXTRAORAL TECHNIQUE IN ZYGOMATIC ARCH EXAMINATION Aditya Dupare 1 *, Apeksha Dhole (Balpande) 2, Mukta Motwani 3, Anuraag Choudhary 4 1. Post graduate student, Department of oral
Stereotactic Biopsy of Brain Tumours
 Stereotactic Biopsy of Brain Tumours Pages with reference to book, From 176 To 178 Shahzad Shams, Rizwan Masood Butt, Afaq Sarwar ( Department of Neurosurgery Unit 1, Lahore General Hospital, Lahore. )
Stereotactic Biopsy of Brain Tumours Pages with reference to book, From 176 To 178 Shahzad Shams, Rizwan Masood Butt, Afaq Sarwar ( Department of Neurosurgery Unit 1, Lahore General Hospital, Lahore. )
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound
 SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
The "Keyhole": A Sign of
 473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain
 Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Hooshmand B, Magialasche F, Kalpouzos G, et al. Association of vitamin B, folate, and sulfur amino acids with brain magnetic resonance imaging measures in older adults: a longitudinal
Supplementary Online Content Hooshmand B, Magialasche F, Kalpouzos G, et al. Association of vitamin B, folate, and sulfur amino acids with brain magnetic resonance imaging measures in older adults: a longitudinal
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Long segment composite split cord malformation with double bony spur
 Long segment composite split cord malformation with double bony spur Anand Sharma, Achal Sharma, R.S. Mittal SMS Medical College, Jaipur, India Abstract: A composite type of SCM is very rare and only a
Long segment composite split cord malformation with double bony spur Anand Sharma, Achal Sharma, R.S. Mittal SMS Medical College, Jaipur, India Abstract: A composite type of SCM is very rare and only a
Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure. Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point
 Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point BJORN MAGNAES, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Rikshospitalet, Oslo
Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point BJORN MAGNAES, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Rikshospitalet, Oslo
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children
 Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 584567, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/584567 Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children Eva Brichtova, 1
Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 584567, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/584567 Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children Eva Brichtova, 1
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process
 ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
Although neuroendoscopy was originally devised. Small-ventricle neuroendoscopy for pediatric brain tumor management.
 J Neurosurg Pediatrics 7:000 000, 7:104 110, 2011 Small-ventricle neuroendoscopy for pediatric brain tumor management Clinical article Robert P. Naftel, M.D., 1 Chevis N. Shannon, M.B.A., M.P.H., Dr.P.H.,
J Neurosurg Pediatrics 7:000 000, 7:104 110, 2011 Small-ventricle neuroendoscopy for pediatric brain tumor management Clinical article Robert P. Naftel, M.D., 1 Chevis N. Shannon, M.B.A., M.P.H., Dr.P.H.,
QMJ VOL. 4 No.5 JUNE 2008
 Comparative study between trans-fontanelle us& spiral CT scan in the diagnosis of the congenital hydrocephalus. -Najat A. AL-Hassnaw (M.B. CH.B. F.I.C.M.S.)Dept. College of Medicine University of al-qadisiah,iraq.
Comparative study between trans-fontanelle us& spiral CT scan in the diagnosis of the congenital hydrocephalus. -Najat A. AL-Hassnaw (M.B. CH.B. F.I.C.M.S.)Dept. College of Medicine University of al-qadisiah,iraq.
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Metal Artefact Reduction in CT
 Metal Artefact Reduction in CT DANIEL MARRINER Metal Artefact Reduction in CT Metal Artefact Clinical Indications for MAR SEMAR and How It Works Technical Considerations Case Studies utilising SEMAR Metal
Metal Artefact Reduction in CT DANIEL MARRINER Metal Artefact Reduction in CT Metal Artefact Clinical Indications for MAR SEMAR and How It Works Technical Considerations Case Studies utilising SEMAR Metal
Researcher 2018;10(3)
 Comparative study between frontal and posterior parietal ventriculo-peritoneal shunts in management of hydrocephalus Prof. Dr. Abdelhalim Moasa, Dr. Mohamed Hasan and Mohamed Abdelrazek Department of Neurosurgery,
Comparative study between frontal and posterior parietal ventriculo-peritoneal shunts in management of hydrocephalus Prof. Dr. Abdelhalim Moasa, Dr. Mohamed Hasan and Mohamed Abdelrazek Department of Neurosurgery,
Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections in Patients with Hydrocephalus
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
Clinical Article Anatomy of the cerebral ventricular system for endoscopic neurosurgery: a magnetic resonance study
 Acta Neurochir (2003) 145: 359 368 DOI 10.1007/s00701-003-0021-6 Clinical Article Anatomy of the cerebral ventricular system for endoscopic neurosurgery: a magnetic resonance study F. Duffner 1, H. Schiffbauer
Acta Neurochir (2003) 145: 359 368 DOI 10.1007/s00701-003-0021-6 Clinical Article Anatomy of the cerebral ventricular system for endoscopic neurosurgery: a magnetic resonance study F. Duffner 1, H. Schiffbauer
Instrumentation and fixation of the C2 spinal segment. Evaluation of C2 pedicle screw placement via the freehand technique by neurosurgical trainees
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Spine 29:235 240, 2018 Evaluation of C2 pedicle screw placement via the freehand technique by neurosurgical trainees Martin H. Pham, MD, Joshua Bakhsheshian, MD, Patrick C.
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Spine 29:235 240, 2018 Evaluation of C2 pedicle screw placement via the freehand technique by neurosurgical trainees Martin H. Pham, MD, Joshua Bakhsheshian, MD, Patrick C.
Nature and Science 2017;15(7) Surgical Options for Treatment of Posterior Fossa Tumors with Hydrocephalus
 Surgical Options for Treatment of Posterior Fossa Tumors with Hydrocephalus Mohamed Mahmoud Abohashima; Ahmed Mohamed Hasan Salem; Magdy Asaad El-Hawary Neurosurgery department, Faculty of Medicine, Al-azhar
Surgical Options for Treatment of Posterior Fossa Tumors with Hydrocephalus Mohamed Mahmoud Abohashima; Ahmed Mohamed Hasan Salem; Magdy Asaad El-Hawary Neurosurgery department, Faculty of Medicine, Al-azhar
Two-Stage Management of Mega Occipito Encephalocele
 Two-Stage Management of Mega Occipito Encephalocele CASE REPORT A I Mardzuki*, J Abdullah**, G Ghazaime*, A R Ariff!'*, M Ghazali* *Department of Neurosciences, **Department of Radiology, Hospital Universiti
Two-Stage Management of Mega Occipito Encephalocele CASE REPORT A I Mardzuki*, J Abdullah**, G Ghazaime*, A R Ariff!'*, M Ghazali* *Department of Neurosciences, **Department of Radiology, Hospital Universiti
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Morita 3D Accuitomo Scanning Protocol
 Morita 3D Accuitomo Scanning Protocol Page 1 Scanning Protocol for the Morita 3D Accuitomo General For Use with ident This protocol is written specifically for users of Morita 3D CBCT scanner. Patient
Morita 3D Accuitomo Scanning Protocol Page 1 Scanning Protocol for the Morita 3D Accuitomo General For Use with ident This protocol is written specifically for users of Morita 3D CBCT scanner. Patient
In patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension
 Neurosurg Focus 37 (5):E4, 2014 AANS, 2014 A comparison of lumboperitoneal and ventriculoperitoneal shunting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: an analysis of economic impact and complications using
Neurosurg Focus 37 (5):E4, 2014 AANS, 2014 A comparison of lumboperitoneal and ventriculoperitoneal shunting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: an analysis of economic impact and complications using
Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Linear accelerators. Basic technique. Indications of SRS
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery Annette Quinn, MSN, RN Program Manager, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Using stereotactic techniques, give a lethal dose of ionizing
Stereotactic Radiosurgery Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery Annette Quinn, MSN, RN Program Manager, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Using stereotactic techniques, give a lethal dose of ionizing
