Acute cor pulmonale due to pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy in two patients with breast cancer
|
|
|
- Cori Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Korean J Intern Med 2017;32: Acute cor pulmonale due to pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy in two patients with breast cancer Sung Young Moon, Kang Hoon Lee, Jong Sik Lee, Hyun Suk Yang, Hong Ghi Lee, Yo Han Cho, and So Young Yoon Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Received : April 27, 2015 Revised : July 3, 2015 Accepted : July 6, 2015 Correspondence to So Young Yoon, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Neungdong-ro, Gwangjin-gu, Seoul 05030, Korea Tel: Fax: greenteamd@gmail.com To the Editor, Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy (PTTM), a rare manifestation of cancer, was first reported by von Herbay et al. [1] in 1990; it is a fatal clinical syndrome characterized by rapid progression of dyspnea because of acute pulmonary hypertension, causing right heart failure and death within a few days of onset. The pathogenesis involves microscopic tumor-cell infiltration into small pulmonary vessels, inducing local paraneoplastic thromboses and fibrocellular intimal hyperplasia, resulting in stenosis and occlusion. Antemortem PTTM diagnosis is difficult because of rapid progression from onset of dyspnea to death; therefore, antemortem PTTM diagnosis in breast cancer is rare. We report two cases of PTTM in patients with breast cancer and discuss the pathogenesis and clinical course of PTTM. A 45-year-old woman was diagnosed with triple negative, invasive ductal carcinoma within her left breast. She underwent left modified radical mastectomy, six cycles of adjuvant chemotherapy (docetaxel 75 mg/m 2, doxorubicin 50 mg/m 2, and cyclophosphamide 500 mg/m 2 ), and postoperative radiation therapy (50.4 Gy). This patient s initial disease was stage IIIc with T3N3M0. After 7 months, she had breast cancer relapse with left anterior chest wall, left supraclavicular, mediastinal, subcarinal lymph node, and multiple bone metastases. She received palliative chemotherapy consisting of gemcitabine 100 mg/m 2 on days 1 and 8, and cisplatin 60 mg/m 2 on day 1, repeated every 3 weeks. However, she was lost to follow-up after completing one cycle, and 6 months later she presented to the emergency department with a 3-week history of progressive dyspnea on exertion (New York Heart Association function class II). She had used complimentary medicine before admission and since the loss to follow-up. A chest radiograph showed clear lung field. There was no crackle or wheezing on chest auscultation. Arterial blood gas analysis results in room air indicated hypoxemia: PaO2, 47.4 mmhg; SaO2, 82.1%. Blood analysis showed D-dimer elevated to 4.46 µg/ml (normal, 0 to 0.4), with troponin I elevated to 0.2 ng/ml (normal, 0 to 0.02), brain natriuretic peptide elevated to 578 pg/ml (normal, 0 to 100), and lactate dehydrogenase elevated to 1,326 IU/L (normal, 263 to 450). Prothrombin time (PT) was elevated slightly above normal, with normal partial thromboplastin time (PTT). A peripheral blood smear showed mild anisopoikilocytosis consisting of elliptocytes, suggesting hemolytic anemia. On chest computed Copyright 2017 The Korean Association of Internal Medicine This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. pissn eissn
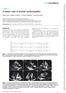
2 Moon SY, et al. Acute cor pulmonale due to PTTM A B C D Figure 1. Computed tomography showed multiple centrilobular nodules with tree-in-bud appearances in cases 1, 2. A mediastinal setting showed a dilated right ventricle and a compressed D-shaped left ventricle in cases 1 and 2, respectively (A, C). A lung setting showed multiple ill-defined centrilobular nodules with tree-in-bud appearances in cases 1 and 2, respectively (B, D). tomography (CT), there was new appearance of multiple, ill-defined centrilobular nodules in both lungs, but neither lymphangitic lung metastases nor pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) were detected (Fig. 1A and 1B). A transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) showed a D-shaped left ventricle with normal left ventricular systolic function with right ventricular enlargement, moderate tricuspid regurgitation, and moderate resting pulmonary hypertension with an estimated right ventricular systolic pressure of 63 mmhg, indicating right heart failure. PTTM was diagnosed based on right heart failure with pulmonary hypertension; the presence of underlying malignancy; no other significant causes of pulmonary hypertension; and PTE, primary lung disease, and valvular heart disease. Three days after admission, treatment was initiated with oxygen therapy and chemotherapy with vinorelbine (25 mg/m 2 on days 1 and 8, and carboplatin, area under the curve 5, on day 1, repeated every 3 weeks). Worsening dyspnea and hypoxia lead to admission to the intensive care unit, 2 hours after chemotherapy injection. Despite chemotherapy administration, the patient died of right heart failure 4 days after admission. The second case was a 58-year-old woman who presented to the Emergency Department with altered mental status. She had a history of breast cancer with right breast conserving surgery performed at another hospital 9 years earlier. One year before admission, she was diagnosed with recurrent cancer in the remaining breast tissue; ultrasonography revealed multiple right axillary lymph node metastases. However, the patient refused further work-up and treatment. On this admission, she presented with stage IV metastatic breast cancer, including bilateral supraclavicular, cervical, and paraaortic lymph node and multiple bone metastases. Blood examination confirmed hyperglycemia, ketonuria, and metabolic acidosis. Therefore, the initial diagnosis was metabolic encephalopathy caused by infection, dehydration, and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). Brain magnet
3 The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine Vol. 32, No. 1, January 2017 A B C Figure 2. Echocardiography in case 2. (A) Parasternal short axis view, mid-ventricular plane on transthoracic echocardiography reveals a D-shaped LV throughout the systolic and diastolic period. (B) The 2-dimensional and color Doppler comparative focused image of the apical 4-chamber view showed mild-to-moderate tricuspid regurgitation. (C) The peak tricuspid regurgitation velocity was 3.7 m/sec, pressure gradient 55 mmhg, indicating pulmonary hypertension. (D) The dilated inferior vena cava (IVC) diameter in case 1 was 21 mm without inspiratory collapse. RV, right ventricle; LV, left ventricle. D ic resonance imaging revealed a cerebral venous sinus thrombus, possibly related to the hypercoagulable status of her systemic circulation. Although DKA was corrected, mental status deterioration continued. Furthermore, she rapidly developed progressive dyspnea and hypoxia. Pulmonary embolism chest CT showed no PTE, deep vein thrombosis, or other significant cause for dyspnea; however, nonspecific multiple centrilobular nodules were evident (Fig. 1C and 1D). TTE showed D-shaped left ventricle with normal left ventricular systolic function with right ventricular enlargement, moderate tricuspid regurgitation, and severe resting pulmonary hypertension with estimated right ventricular systolic pressure of 80 mmhg, indicating acute cor pulmonale (Fig. 2). Blood examination showed D dimer elevation to > 20 µg/ml, with elevated brain natriuretic peptide level of 452 pg/ ml. Fibrin degradation product was elevated to 120 µg/ ml (normal, 0 to 5), and the fibrinogen level was elevated to 623 mg/dl with a slightly increased PT of 16 seconds (international normalized ratio, 1.33) and normal PTT. These measures suggested disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). A peripheral blood smear revealed burr cells and schistocytes, suggesting microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA). Seven days after admission, the patient had desaturation and PTTM was considered. Despite anticoagulation and oxygen therapy, her respiration worsened and she died of right heart failure 8 days after admission. Despite a timely antemortem diagnosis 192
4 Moon SY, et al. Acute cor pulmonale due to PTTM and chemotherapy or anticoagulation treatment, the two patients died from acute cor pulmonale 4 and 8 days after admission, respectively. PTTM is a rare disease. From evaluation of an autopsy series, PTTM incidence varies from 2.4% to 26% in solid malignancies [2,3]. PTTM was caused by tumor cell infiltration into small pulmonary arterioles and by paraneoplastic thrombosis and fibrocellular intimal hyperplasia. The time of occurrence is variable, but it rarely presents as the initial manifestation of disease. The first clinical symptom is usually progressive dyspnea. The median patient survival time following oxygen treatment was 9 days [3]. With a proper antemortem diagnosis and chemotherapy, one patient with gastric cancer survived for 7 months after PTTM diagnosis; however, long-term survival is extremely rare [4]. PTTM can simultaneously present with DIC and MAHA. Paraneoplastic thrombosis, DIC, and MAHA can be induced by undefined procoagulant factors released from cancer cells. Both patients showed features of DIC and MAHA. The second PTTM case developed dural venous sinus thrombosis. Dural venous sinus thrombosis is associated with multiple risk factors, including systemic hypercoagulability. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of the co-occurrence of dural venous thrombosis and PTTM. Cerebral venous thrombosis and PTTM could develop because of paraneoplastic hypercoagulability. Most of the chest CT findings in patients with PTTM are nonspecific. There could be consolidation, ground-glass opacity, small nodules, and a tree-in-bud appearance [4]. The tree-in-bud centrilobular nodules were observed in both of our cases. Differential PTTM diagnosis with lymphangitic lung metastases and PTE are crucial. Furthermore, 85.7% of PTTM cases occur coincidently with lymphangitic lung metastases [1]. However, isolated lymphangitic lung metastases without PTTM typically have an insidious and longer evolution; therefore, they rarely cause acute cor pulmonale. PTE differs from PTTM in terms of pulmonary vasculature location, involving larger pulmonary arteries and the absence of intimal hyperplasia. Although PTE may cause pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure, the clinical course of PTE is reversible and can be resolved with anticancer and heparin therapies. The clinical PTTM diagnosis may be possible with a high index of suspicion and exclusive diagnosis in patients who develop acute or subacute cor pulmonale. Definitive pathologic diagnosis through an invasive surgical procedure is not necessary for PTTM diagnosis because it is time consuming and the severity of the patient s condition typically excludes performing invasive diagnostic procedures. Although PTTM diagnosis is not difficult, treatment and reversal of right heart failure, the main cause of death, is challenging. Intimal hyperplasia and fibromuscular proliferation of small arterioles are nearly irreversible pathologies regardless of treatment [5]. Irreversible pulmonary vascular changes causing acute cor pulmonale result in very rapid clinical deterioration in these patients with no time for anticancer treatment. Therefore, very early diagnosis before the occurrence of irreversible pulmonary vascular changes is crucial. In a recent autopsy series, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), tissue factor and platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) were overexpressed in 97%, 100%, and 62% of cases, respectively [3]. PDGF blockade with STI571, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, reversed pulmonary vascular changes and cor pulmonale in an experimental animal model [5]. Blocking the activity of cytokines such as VEGF and PDGF in addition to standard chemotherapy may help in effective PTTM treatment. In summary, PTTM with acute cor pulmonale can be diagnosed with a high index of suspicion and exclusive diagnosis, including the presence of pulmonary hypertension, underlying malignancy, and the absence of other causes of pulmonary hypertension, such as chronic obstructive lung disease and valvular heart disease. Presence of MAHA and DIC were helpful for diagnosis, although a work-up for underlying malignancy should be warranted for acute or subacute cor pulmonale without specific lung or heart disease. However, very early diagnosis, before the development of irreversible pulmonary hypertension and vascular changes, and timely treatment are challenging [5]. Keywords: Breast neoplasms; Thrombi; Pulmonary heart disease Conflict of interest No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported
5 The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine Vol. 32, No. 1, January 2017 REFERENCES 1. von Herbay A, Illes A, Waldherr R, Otto HF. Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy with pulmonary hypertension. Cancer 1990;66: Montero A, Vidaller A, Mitjavila F, Chivite D, Pujol R. Microscopic pulmonary tumoral embolism and subacute cor pulmonale as the first clinical signs of cancer. Acta Oncol 1999;38: Uruga H, Fujii T, Kurosaki A, et al. Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy: a clinical analysis of 30 autopsy cases. Intern Med 2013;52: Miyano S, Izumi S, Takeda Y, et al. Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy. J Clin Oncol 2007;25: Schermuly RT, Dony E, Ghofrani HA, et al. Reversal of experimental pulmonary hypertension by PDGF inhibition. J Clin Invest 2005;115:
THE MANY FACES OF PULMONARY TUMOR EMBOLISM
 THE MANY FACES OF PULMONARY TUMOR EMBOLISM D Preciado, MD; E Castañer, MD; M Andreu, MD; X Gallardo, MD; I Costa, MD; V P Beltran, MD; B Consola, MD, J M Mata, MD,PhD. Department of Radiology, Section
THE MANY FACES OF PULMONARY TUMOR EMBOLISM D Preciado, MD; E Castañer, MD; M Andreu, MD; X Gallardo, MD; I Costa, MD; V P Beltran, MD; B Consola, MD, J M Mata, MD,PhD. Department of Radiology, Section
Successful Antemortem Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy
 CASE REPORT Successful Antemortem Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy Kenjuro Higo 1, Kayoko Kubota 1, Ayano Takeda 1, Michiyo Higashi 2 andmitsuruohishi 1 Abstract Pulmonary
CASE REPORT Successful Antemortem Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy Kenjuro Higo 1, Kayoko Kubota 1, Ayano Takeda 1, Michiyo Higashi 2 andmitsuruohishi 1 Abstract Pulmonary
Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy by Lung Adenocarcinoma. Key words: Adenocarcinoma, Pulmonary Hypertension, Lung Neoplasms, Liver, Dypnea.
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2013;3(2):232-236 Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy by Lung Adenocarcinoma Ikutarou Furuno 1,2, Seiya Tanaka 1, Hiromichi Ueno 2, Hisaharu Ooe 2, Yugo Yoshida 3, Takashi
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2013;3(2):232-236 Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy by Lung Adenocarcinoma Ikutarou Furuno 1,2, Seiya Tanaka 1, Hiromichi Ueno 2, Hisaharu Ooe 2, Yugo Yoshida 3, Takashi
The many faces of pulmonary tumor embolism
 The many faces of pulmonary tumor embolism Poster No.: C-1790 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Preciado Borreguero, E. Castañer, M. Andreu, X. Gallardo, 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 I. Costa
The many faces of pulmonary tumor embolism Poster No.: C-1790 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Preciado Borreguero, E. Castañer, M. Andreu, X. Gallardo, 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 I. Costa
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY
 CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
Antemortem diagnosis of pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy in a patient with recurrent breast cancer: a case report
 Takahashi et al. BMC Cancer (2016) 16:666 DOI 10.1186/s12885-016-2721-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Antemortem diagnosis of pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy in a patient with recurrent breast cancer:
Takahashi et al. BMC Cancer (2016) 16:666 DOI 10.1186/s12885-016-2721-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Antemortem diagnosis of pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy in a patient with recurrent breast cancer:
PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT-
 University Goce Delcev, Faculty of Medical sciences, Stip University Clinic of Cardiology, Skopje R. Of Macedonia PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT- Gordana Kamceva MD mr.sci Acknowledgment Marija Vavlukis
University Goce Delcev, Faculty of Medical sciences, Stip University Clinic of Cardiology, Skopje R. Of Macedonia PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT- Gordana Kamceva MD mr.sci Acknowledgment Marija Vavlukis
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Cardiovascular Images
 Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Cor pulmonale. Dr hamid reza javadi
 1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
2/4/2011. Nathan Kerner, M.D.
 Nathan Kerner, M.D. Definition Elevated pressures - cut off usually >40 mmhg pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP) Usually associated with elevated pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) measured in dynessec/cm
Nathan Kerner, M.D. Definition Elevated pressures - cut off usually >40 mmhg pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP) Usually associated with elevated pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) measured in dynessec/cm
Dyspnea with a Slow-Growing Mass in. Mukae, Hiroshi; Kohno, Shigeru
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Dyspnea with a Slow-Growing Mass in Amenomori, Misato; Sakamoto, Noriho Tomayoshi; Kohno, Ryouta; Yamamoto, Mukae, Hiroshi; Kohno, Shigeru Citation Respiration,
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Dyspnea with a Slow-Growing Mass in Amenomori, Misato; Sakamoto, Noriho Tomayoshi; Kohno, Ryouta; Yamamoto, Mukae, Hiroshi; Kohno, Shigeru Citation Respiration,
Case Report Respirophasic Variations in the QRS Complex and Echocardiographic Equivalent in Pulmonary Embolism
 www.ipej.org 313 Case Report Respirophasic Variations in the QRS Complex and Echocardiographic Equivalent in Pulmonary Embolism Eftychios Siniorakis, MD, Spyridon Arvanitakis, BM, Dimitris Barlagiannis,
www.ipej.org 313 Case Report Respirophasic Variations in the QRS Complex and Echocardiographic Equivalent in Pulmonary Embolism Eftychios Siniorakis, MD, Spyridon Arvanitakis, BM, Dimitris Barlagiannis,
Pulmonary hypertension
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2012 Pulmonary hypertension Glaus, T M Posted at the Zurich Open Repository
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2012 Pulmonary hypertension Glaus, T M Posted at the Zurich Open Repository
Case Report Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect as a Cause of Palpitations and Dyspnea in an Adult: A Diagnostic Imaging Challenge
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 128462, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/128462 Case Report Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect as a Cause of Palpitations and Dyspnea in an Adult:
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 128462, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/128462 Case Report Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect as a Cause of Palpitations and Dyspnea in an Adult:
Case Report Free Floating Right Heart Thrombus Associated with Acute Pulmonary Embolism: An Unsettled Therapeutic Difficulty
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2015, Article ID 364780, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/364780 Case Report Free Floating Right Heart Thrombus Associated with Acute Pulmonary Embolism: An Unsettled
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2015, Article ID 364780, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/364780 Case Report Free Floating Right Heart Thrombus Associated with Acute Pulmonary Embolism: An Unsettled
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine
 Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Imatinib could be a new strategy for pulmonary hypertension caused by pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy in metastatic breast cancer
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3280-4 CASE STUDY Open Access Imatinib could be a new strategy for pulmonary hypertension caused by pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy in metastatic breast cancer Ippei Fukada
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3280-4 CASE STUDY Open Access Imatinib could be a new strategy for pulmonary hypertension caused by pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy in metastatic breast cancer Ippei Fukada
Fat Embolism in Differential Diagnosis of Acute Cor Pulmonale: Case Report
 Fat Embolism in Differential Diagnosis of Acute Cor Pulmonale: José Luis de Castro e Silva Pretto, Andriéli Cristina de Oliveira, Daniel Spilmann, Eduardo Dal Magro Marcon, Elias Sato de Almeida, Lucas
Fat Embolism in Differential Diagnosis of Acute Cor Pulmonale: José Luis de Castro e Silva Pretto, Andriéli Cristina de Oliveira, Daniel Spilmann, Eduardo Dal Magro Marcon, Elias Sato de Almeida, Lucas
A 50-year-old woman with syncope
 Hira Shahzad 1, Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi 2 1 Medical College, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi 2 Department of Medicine, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi Associate
Hira Shahzad 1, Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi 2 1 Medical College, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi 2 Department of Medicine, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi Associate
Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach
 Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach Hae Giu Lee, MD Professor, Dept of Radiology Seoul St. Mary s Hospital The Catholic University of Korea Introduction Incidence High incidence: 250,000-1,000,000/year
Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach Hae Giu Lee, MD Professor, Dept of Radiology Seoul St. Mary s Hospital The Catholic University of Korea Introduction Incidence High incidence: 250,000-1,000,000/year
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) Seminar. Ron Kopilov 4 th year Medical Student, Tel Aviv University Internal Medicine A 8.3.
 Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) Seminar Ron Kopilov 4 th year Medical Student, Tel Aviv University Internal Medicine A 8.3.2012 1 Our plan: Understand the pathophysiology Identify risk factors
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) Seminar Ron Kopilov 4 th year Medical Student, Tel Aviv University Internal Medicine A 8.3.2012 1 Our plan: Understand the pathophysiology Identify risk factors
Heart Failure. Cardiac Anatomy. Functions of the Heart. Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics. Determinants of Cardiac Output. Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
ECHO HAWAII. My home. Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Embolism: Role of Echo U.S.A. Japan. Hawaii Island 1/9/2018
 Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Embolism: Role of Echo ECHO HAWAII January 15 19, 2018 Kenya Kusunose, MD, PhD, FASE Tokushima University Hospital Japan My home Japan U.S.A Hawaii Island 1 Economy
Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Embolism: Role of Echo ECHO HAWAII January 15 19, 2018 Kenya Kusunose, MD, PhD, FASE Tokushima University Hospital Japan My home Japan U.S.A Hawaii Island 1 Economy
Successfully Treated Massive Pulmonary Thromboembolism and Thrombus in the Right Atrium Due to Diffuse Malignant Lymphoma: A Case Report
 Successfully Treated Massive Pulmonary Thromboembolism and Thrombus in the Right Atrium Due to Diffuse Malignant Lymphoma: A Case Report Hiromu Takanori Koji Norifumi Junji Masanobu Muneyasu INOUE, MD
Successfully Treated Massive Pulmonary Thromboembolism and Thrombus in the Right Atrium Due to Diffuse Malignant Lymphoma: A Case Report Hiromu Takanori Koji Norifumi Junji Masanobu Muneyasu INOUE, MD
Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia
 Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue
 59 Breast cancer 1 It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue including both early stages which are potentially curable, and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) which is usually incurable. Most breast
59 Breast cancer 1 It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue including both early stages which are potentially curable, and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) which is usually incurable. Most breast
Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy: A Clinical Analysis of 30 Autopsy Cases
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy: A Clinical Analysis of 30 Autopsy Cases Hironori Uruga 1,4,5, Takeshi Fujii 2,4, Atsuko Kurosaki 3, Shigeo Hanada 1, Hisashi Takaya 1, Atsushi
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy: A Clinical Analysis of 30 Autopsy Cases Hironori Uruga 1,4,5, Takeshi Fujii 2,4, Atsuko Kurosaki 3, Shigeo Hanada 1, Hisashi Takaya 1, Atsushi
Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy
 Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Case Report Thoracic Imaging INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 Case Report Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.4.936 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(4):936-941 A Case Report: Cavitary Infarction Caused by Pulmonary Tumor
Case Report Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.4.936 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(4):936-941 A Case Report: Cavitary Infarction Caused by Pulmonary Tumor
Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy
 Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy Jeong-Am Ryu 1, Oh Young Bang 2, Daesang Lee 1, Jinkyeong Park 1, Jeong Hoon Yang 1, Gee Young Suh 1, Joongbum Cho 1, Chi Ryang Chung 1, Chi-Min
Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy Jeong-Am Ryu 1, Oh Young Bang 2, Daesang Lee 1, Jinkyeong Park 1, Jeong Hoon Yang 1, Gee Young Suh 1, Joongbum Cho 1, Chi Ryang Chung 1, Chi-Min
Multimodality imaging for PAH: Is CT better than MRI?
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI TORINO Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia Dipartimento di Scienze Chirurgiche Istituto di Radiologia Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Città della Salute e della scienza di Torino
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI TORINO Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia Dipartimento di Scienze Chirurgiche Istituto di Radiologia Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Città della Salute e della scienza di Torino
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Pulmonary Embolism. Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri
 Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest
 Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest Michelle S. Ginsberg, MD Objectives Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest To understand the mechanisms of action of different classes of
Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest Michelle S. Ginsberg, MD Objectives Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest To understand the mechanisms of action of different classes of
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Pulmonary Embolism Is it the Greatest Danger in Deep Vein Thrombosis?
 Difficult issues in Deep Vein Thrombosis: Pulmonary Embolism Is it the Greatest Danger in Deep Vein Thrombosis? Raluca Dulgheru; C Gherghinescu; B Dorobat; H Muresan; R Darabont; M Cinteza; D Vinereanu
Difficult issues in Deep Vein Thrombosis: Pulmonary Embolism Is it the Greatest Danger in Deep Vein Thrombosis? Raluca Dulgheru; C Gherghinescu; B Dorobat; H Muresan; R Darabont; M Cinteza; D Vinereanu
Shock, Hemorrhage and Thrombosis
 Shock, Hemorrhage and Thrombosis 1 Shock Systemic hypoperfusion due to: Reduction in cardiac output Reduction in effective circulating blood volume Hypotension Impaired tissue perfusion Cellular hypoxia
Shock, Hemorrhage and Thrombosis 1 Shock Systemic hypoperfusion due to: Reduction in cardiac output Reduction in effective circulating blood volume Hypotension Impaired tissue perfusion Cellular hypoxia
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
 Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Whal Lee, M.D. Seoul National University Hospital Department of Radiology 2 nd EFORT Asia Symposium, 3 rd November 2010, Taipei DVT - Risk Factors Previous
Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Whal Lee, M.D. Seoul National University Hospital Department of Radiology 2 nd EFORT Asia Symposium, 3 rd November 2010, Taipei DVT - Risk Factors Previous
Pathology of pulmonary vascular disease. Dr.Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab. Assistant Professor of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Almajma ah University
 Pathology of pulmonary vascular disease Dr.Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab Assistant Professor of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Almajma ah University Pulmonary vascular disease Type of pulmonary circulation: Types
Pathology of pulmonary vascular disease Dr.Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab Assistant Professor of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Almajma ah University Pulmonary vascular disease Type of pulmonary circulation: Types
Emergency department bedside echocardiography diagnosis of massive pulmonary embolism with direct visualization of thrombus in the pulmonary artery
 Crit Ultrasound J (2011) 3:155 160 DOI 10.1007/s13089-011-0081-4 CASE REPORT Emergency department bedside echocardiography diagnosis of massive pulmonary embolism with direct visualization of thrombus
Crit Ultrasound J (2011) 3:155 160 DOI 10.1007/s13089-011-0081-4 CASE REPORT Emergency department bedside echocardiography diagnosis of massive pulmonary embolism with direct visualization of thrombus
Occult Gastric Cancer Presenting as Hypoxia from Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy
 J Gastric Cancer 2014;14(2):142-146 http://dx.doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2014.14.2.142 Case Report Occult Gastric Cancer Presenting as Hypoxia from Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy Rohan Mandaliya,
J Gastric Cancer 2014;14(2):142-146 http://dx.doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2014.14.2.142 Case Report Occult Gastric Cancer Presenting as Hypoxia from Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy Rohan Mandaliya,
Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis?
 Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? December 19, 2017 Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? Indications for Thrombolytic Therapy in Patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism Case Scenario A 28 year old woman
Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? December 19, 2017 Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? Indications for Thrombolytic Therapy in Patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism Case Scenario A 28 year old woman
Coexistence of parathyroid adenoma and papillary thyroid carcinoma. Yong Sang Lee, Kee-Hyun Nam, Woong Youn Chung, Hang-Seok Chang, Cheong Soo Park
 J Korean Surg Soc 2011;81:316-320 http://dx.doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.81.5.316 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JKSS Journal of the Korean Surgical Society pissn 2233-7903 ㆍ eissn 2093-0488 Coexistence of parathyroid
J Korean Surg Soc 2011;81:316-320 http://dx.doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.81.5.316 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JKSS Journal of the Korean Surgical Society pissn 2233-7903 ㆍ eissn 2093-0488 Coexistence of parathyroid
Pulmonary Hypertension in Patient with Neurofibromatosis Type 1
 https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2017.32.2.227 KMJ Case Report Pulmonary Hypertension in Patient with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Yeong min Lee, Tae Hyun Yang, HeeSoo Jung, Tae-Seon Oh, Jeong-Hoon Song, Seung-Jung
https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2017.32.2.227 KMJ Case Report Pulmonary Hypertension in Patient with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Yeong min Lee, Tae Hyun Yang, HeeSoo Jung, Tae-Seon Oh, Jeong-Hoon Song, Seung-Jung
Interesting Cases. Pulmonary
 Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy
 Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy Report of 3 Cases and Review of the Literature Eukene Gainza, MD, Sara Fernández, MD, Daniel Martínez, MD, Pedro Castro, MD, PhD, Xavier Bosch, MD, PhD, José
Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy Report of 3 Cases and Review of the Literature Eukene Gainza, MD, Sara Fernández, MD, Daniel Martínez, MD, Pedro Castro, MD, PhD, Xavier Bosch, MD, PhD, José
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction
 Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy associated
 CASE REPORT Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy associated with urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder: antemortem diagnosis by pulmonary microvascular cytology Hideaki Yamakawa 1, Masahiro
CASE REPORT Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy associated with urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder: antemortem diagnosis by pulmonary microvascular cytology Hideaki Yamakawa 1, Masahiro
2019 Qualified Clinical Data Registry (QCDR) Performance Measures
 2019 Qualified Clinical Data Registry (QCDR) Performance Measures Description: This document contains the 18 performance measures approved by CMS for inclusion in the 2019 Qualified Clinical Data Registry
2019 Qualified Clinical Data Registry (QCDR) Performance Measures Description: This document contains the 18 performance measures approved by CMS for inclusion in the 2019 Qualified Clinical Data Registry
Recurrent Pulmonary Embolism From Left Subclavian Thrombosis: A Case Report
 J Cardiol 2000 ; 36: 191 196 Recurrent Pulmonary Embolism From Left Subclavian Thrombosis: A Case Report Junji Makoto Tetsunori Hideo Junko Toshihide Kunihide Toshio KAWAGOE, MD TAKENAGA, MD ISHIKAWA,
J Cardiol 2000 ; 36: 191 196 Recurrent Pulmonary Embolism From Left Subclavian Thrombosis: A Case Report Junji Makoto Tetsunori Hideo Junko Toshihide Kunihide Toshio KAWAGOE, MD TAKENAGA, MD ISHIKAWA,
Echocardiography Conference
 Echocardiography Conference David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY-6 September 20, 2005 Atrial Septal Aneurysm Bulging of Fossa Ovalis Associated commonly with Atrial septal defect or small perforations
Echocardiography Conference David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY-6 September 20, 2005 Atrial Septal Aneurysm Bulging of Fossa Ovalis Associated commonly with Atrial septal defect or small perforations
Point-of-Care Ultrasound Closer look at the Inferior Vena Cavae &
 Point-of-Care Ultrasound Closer look at the Inferior Vena Cavae & Brief Introduction to Gross Systolic Function Omar S. Darwish, MS, DO Certified in Point-of-Care Ultrasound Hospitalist University of California,
Point-of-Care Ultrasound Closer look at the Inferior Vena Cavae & Brief Introduction to Gross Systolic Function Omar S. Darwish, MS, DO Certified in Point-of-Care Ultrasound Hospitalist University of California,
2/14/2018 CASE STUDIES: COMPLICATIONS OF MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION. Judy Hung, MD Cardiology Division Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA CASE 1
 CASE STUDIES: COMPLICATIONS OF MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION Judy Hung, MD Cardiology Division Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA CASE 1 1 PRESENTATION 57 yo male with a past medical history of hypertension
CASE STUDIES: COMPLICATIONS OF MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION Judy Hung, MD Cardiology Division Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA CASE 1 1 PRESENTATION 57 yo male with a past medical history of hypertension
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy
 Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
A fatal case of acute pulmonary embolism caused by right ventricular masses of acute lymphoblastic lymphoma-leukemia in a 13 year old girl
 Case report http://dx.doi.org/10.3345/kjp.2012.55.7.249 Korean J Pediatr 2012;55(7):249-253 eissn 1738-1061 pissn 2092-7258 A fatal case of acute pulmonary embolism caused by right ventricular masses of
Case report http://dx.doi.org/10.3345/kjp.2012.55.7.249 Korean J Pediatr 2012;55(7):249-253 eissn 1738-1061 pissn 2092-7258 A fatal case of acute pulmonary embolism caused by right ventricular masses of
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Synephrine-containing dietary supplement precipitating apical ballooning syndrome in a young female
 CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:356-360 Synephrine-containing dietary supplement precipitating apical ballooning syndrome in a young female Hyemoon Chung 1, Sung Woo Kwon 2, Tae Hoon Kim 3, Ji
CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:356-360 Synephrine-containing dietary supplement precipitating apical ballooning syndrome in a young female Hyemoon Chung 1, Sung Woo Kwon 2, Tae Hoon Kim 3, Ji
Pulmonary-Vascular Disease. Howard J. Sachs, MD.
 Pulmonary-Vascular Disease Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Disorders COPD/ILD Chronic Hypoxia Vasoconstrictive Obliterative PPH Obstructive Hyperkinetic LEFT right Shunt Passive 2 nd to LV
Pulmonary-Vascular Disease Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Disorders COPD/ILD Chronic Hypoxia Vasoconstrictive Obliterative PPH Obstructive Hyperkinetic LEFT right Shunt Passive 2 nd to LV
Dr. Md. Rajibul Alam Prof. of Medicine Dinajpur Medical college
 Dr. Md. Rajibul Alam Prof. of Medicine Dinajpur Medical college PULMONARY HYPERTENSION Difficult to diagnose early Because Not detected during routine physical examination and Even in advanced cases symptoms
Dr. Md. Rajibul Alam Prof. of Medicine Dinajpur Medical college PULMONARY HYPERTENSION Difficult to diagnose early Because Not detected during routine physical examination and Even in advanced cases symptoms
Angiostrongylus vasorum
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2012 Angiostrongylus vasorum Glaus, T M Posted at the Zurich Open Repository
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2012 Angiostrongylus vasorum Glaus, T M Posted at the Zurich Open Repository
ASCeXAM / ReASCE. Practice Board Exam Questions Monday Morning
 ASCeXAM / ReASCE Practice Board Exam Questions Monday Morning Ultrasound Physics Artifacts Doppler Physics Imaging, Knobology, and Artifacts Echocardiographic Evaluation of the RV Tricuspid and Pulmonary
ASCeXAM / ReASCE Practice Board Exam Questions Monday Morning Ultrasound Physics Artifacts Doppler Physics Imaging, Knobology, and Artifacts Echocardiographic Evaluation of the RV Tricuspid and Pulmonary
EXTENSIVE PULMONARY THROMBOEMBOLISM AS FIRST SIGN OF A LUNG CANCER - CASE REPORT
 EXTENSIVE PULMONARY THROMBOEMBOLISM AS FIRST SIGN OF A LUNG CANCER - CASE REPORT A. Bondaryev 1, D. Makris 2, E. Zakynthinos 2, Luminiţa Lucaci 1, Oana Florea 1 1. Centre Hospitalier Dr. Schaffner Lens,
EXTENSIVE PULMONARY THROMBOEMBOLISM AS FIRST SIGN OF A LUNG CANCER - CASE REPORT A. Bondaryev 1, D. Makris 2, E. Zakynthinos 2, Luminiţa Lucaci 1, Oana Florea 1 1. Centre Hospitalier Dr. Schaffner Lens,
CHAPTER X - SECONDARY PULMONARY HYPERTENSION CHRONIC PULMONARY THROMBOEMBOLISM (HTP). PULMONARY THROMBENDARTERECTOMY
 CHAPTER X - SECONDARY PULMONARY HYPERTENSION CHRONIC PULMONARY THROMBOEMBOLISM (HTP). PULMONARY THROMBENDARTERECTOMY Walter KLEPETKO, PhD, VIENNA - AUSTRIA Marian GASPAR, PhD, TIMISOARA 10. 1. Definition.
CHAPTER X - SECONDARY PULMONARY HYPERTENSION CHRONIC PULMONARY THROMBOEMBOLISM (HTP). PULMONARY THROMBENDARTERECTOMY Walter KLEPETKO, PhD, VIENNA - AUSTRIA Marian GASPAR, PhD, TIMISOARA 10. 1. Definition.
Hemodynamic Assessment. Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics
 Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Non-Invasive Bed-Side Assessment of Pulmonary Vascular Resistance in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
 Aim of the Work This study aimed to evaluate the degree of pulmonary hypertension as well as alterations in the pulmonary vascular resistance in critically ill children with ARDS using bed- side echocardiography.
Aim of the Work This study aimed to evaluate the degree of pulmonary hypertension as well as alterations in the pulmonary vascular resistance in critically ill children with ARDS using bed- side echocardiography.
Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary
 1 IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND 2 3 4 Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary Artery 5 6 7 Byung Gyu Kim, MD 1, Sung Woo Cho, MD 1, Dae Hyun Hwang, MD 2 and Jong
1 IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND 2 3 4 Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary Artery 5 6 7 Byung Gyu Kim, MD 1, Sung Woo Cho, MD 1, Dae Hyun Hwang, MD 2 and Jong
Das recht Ventrikel ist auch noch da! RV function The RV operates as. Physiology Not very sensitive to preload Good compliance of the free wall
 Das recht Ventrikel ist auch noch da! I.Michaux Intensive Care Medicine University Hospital CHU UCL Namur Mont-Godinne Belgium RV function The RV operates as a low pressure, volume pump, moving the blood
Das recht Ventrikel ist auch noch da! I.Michaux Intensive Care Medicine University Hospital CHU UCL Namur Mont-Godinne Belgium RV function The RV operates as a low pressure, volume pump, moving the blood
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
TGA atrial vs arterial switch what do we need to look for and how to react
 TGA atrial vs arterial switch what do we need to look for and how to react Folkert Meijboom, MD, PhD, FES Dept ardiology University Medical entre Utrecht The Netherlands TGA + atrial switch: Follow-up
TGA atrial vs arterial switch what do we need to look for and how to react Folkert Meijboom, MD, PhD, FES Dept ardiology University Medical entre Utrecht The Netherlands TGA + atrial switch: Follow-up
Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV
 Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV Prabhakar Rajiah, MBBS, MD, FRCR Associate Professor of Radiology Associate Director, Cardiac CT and MRI University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, USA
Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV Prabhakar Rajiah, MBBS, MD, FRCR Associate Professor of Radiology Associate Director, Cardiac CT and MRI University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, USA
PULMONARY HYPERTENSION
 PULMONARY HYPERTENSION REVIEW & UPDATE Olga M. Fortenko, M.D. Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine Pulmonary Vascular Diseases Sequoia Hospital 650-216-9000 Olga.Fortenko@dignityhealth.org Disclosures None
PULMONARY HYPERTENSION REVIEW & UPDATE Olga M. Fortenko, M.D. Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine Pulmonary Vascular Diseases Sequoia Hospital 650-216-9000 Olga.Fortenko@dignityhealth.org Disclosures None
Hematologic Disorders. Assistant professor of anesthesia
 Preoperative Evaluation Hematologic Disorders Dr M.Razavi Assistant professor of anesthesia Anemia Evaluation needs to consider the extent and type of surgery, the anticipated blood loss, and the patient's
Preoperative Evaluation Hematologic Disorders Dr M.Razavi Assistant professor of anesthesia Anemia Evaluation needs to consider the extent and type of surgery, the anticipated blood loss, and the patient's
Right Ventricle Steven J. Lester MD, FACC, FRCP(C), FASE Mayo Clinic, Arizona
 Right Ventricle Steven J. Lester MD, FACC, FRCP(C), FASE Mayo Clinic, Arizona 1. In which scenario will applying the simplified Bernoulli equation to the peak tricuspid regurgitation velocity and adding
Right Ventricle Steven J. Lester MD, FACC, FRCP(C), FASE Mayo Clinic, Arizona 1. In which scenario will applying the simplified Bernoulli equation to the peak tricuspid regurgitation velocity and adding
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly
 Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal radiotherapy, toxic effects of, 636 637 Acute promyelocytic leukemia, associated with acquired bleeding problems, 614 615 Acute renal
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal radiotherapy, toxic effects of, 636 637 Acute promyelocytic leukemia, associated with acquired bleeding problems, 614 615 Acute renal
Molly Boyd, MD Glenn Mills, MD Syed Jafri, MD 1/1/2010
 LSU HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER NSCLC Guidelines Feist-Weiller Cancer Center Molly Boyd, MD Glenn Mills, MD Syed Jafri, MD 1/1/2010 Initial Evaluation/Intervention: 1. Pathology Review 2. History and Physical
LSU HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER NSCLC Guidelines Feist-Weiller Cancer Center Molly Boyd, MD Glenn Mills, MD Syed Jafri, MD 1/1/2010 Initial Evaluation/Intervention: 1. Pathology Review 2. History and Physical
Asymptomatic Primary Isolated Pulmonary Vein Stenosis in an Adult: A Case Report 1
 Asymptomatic Primary Isolated Pulmonary Vein Stenosis in an Adult: A Case Report 1 Ji Hyun Kim, M.D., Ho Sung Lee, M.D., Jae Sung Choi, M.D., Ju Ock Na, M.D., Yong Hoon Kim, M.D., Sung Shick Jou, M.D.
Asymptomatic Primary Isolated Pulmonary Vein Stenosis in an Adult: A Case Report 1 Ji Hyun Kim, M.D., Ho Sung Lee, M.D., Jae Sung Choi, M.D., Ju Ock Na, M.D., Yong Hoon Kim, M.D., Sung Shick Jou, M.D.
Left ventricle pseudoaneurysm as late postoperative complication of a large apical aneurysm
 CASE REPORT Left ventricle pseudoaneurysm as late postoperative complication of a large apical aneurysm Mariana M. Floria 1, 4, Carmen Elena Pleșoianu 2, 4, Michel Buche 3, Baudouin Marchandise 4, Erwin
CASE REPORT Left ventricle pseudoaneurysm as late postoperative complication of a large apical aneurysm Mariana M. Floria 1, 4, Carmen Elena Pleșoianu 2, 4, Michel Buche 3, Baudouin Marchandise 4, Erwin
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Valve Prosthesis
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Valve Prosthesis Amr E Abbas, MD, FACC, FASE, FSCAI, FSVM, RPVI Co-Director, Echocardiography, Director, Interventional Cardiology Research, Beaumont Health System
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Valve Prosthesis Amr E Abbas, MD, FACC, FASE, FSCAI, FSVM, RPVI Co-Director, Echocardiography, Director, Interventional Cardiology Research, Beaumont Health System
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Pericardial Diseases. Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD. Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University
 Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
MITRAL STENOSIS. Joanne Cusack
 MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
ECG Workshop. Nezar Amir
 ECG Workshop Nezar Amir Myocardial Ischemia ECG Infarct ECG in STEMI is dynamic & evolving Common causes of ST shift Infarct Localisation Left main artery occlusion: o diffuse ST-depression with ST elevation
ECG Workshop Nezar Amir Myocardial Ischemia ECG Infarct ECG in STEMI is dynamic & evolving Common causes of ST shift Infarct Localisation Left main artery occlusion: o diffuse ST-depression with ST elevation
Pseudothrombosis of the Subclavian Vein
 416507JDMXXX10.1177/8756479311416507Wash ko et al.journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Pseudothrombosis of the Subclavian Vein Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography 27(5) 231 235 The Author(s) 2011
416507JDMXXX10.1177/8756479311416507Wash ko et al.journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Pseudothrombosis of the Subclavian Vein Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography 27(5) 231 235 The Author(s) 2011
Cerebral infarctions as manifestation of ovarian clear cell carcinoma: report of two cases and review of the literature
 Int Canc Conf J (2013) 2:206 210 DOI 10.1007/s13691-013-0092-z CASE REPORT Cerebral infarctions as manifestation of ovarian clear cell carcinoma: report of two cases and review of the literature Hirokazu
Int Canc Conf J (2013) 2:206 210 DOI 10.1007/s13691-013-0092-z CASE REPORT Cerebral infarctions as manifestation of ovarian clear cell carcinoma: report of two cases and review of the literature Hirokazu
Rare tumors of the heart - angiosarcoma, pericardial lipoma, leiomyosarcoma Three case reports
 , pp.178 182 Rare tumors of the heart - angiosarcoma, pericardial lipoma, leiomyosarcoma Three case reports Ioana Stoian, Ileana Tepes Piser, Iulia Kulcsar, O Chioncel, A Carp, C Macarie Prof Dr CC Iliescu
, pp.178 182 Rare tumors of the heart - angiosarcoma, pericardial lipoma, leiomyosarcoma Three case reports Ioana Stoian, Ileana Tepes Piser, Iulia Kulcsar, O Chioncel, A Carp, C Macarie Prof Dr CC Iliescu
Case Report Section Subacute Cor Pulmonale Due to Metastatic Carcinomatosis of the Lung: Report of a Case with Autopsy Findings
 Case Report Section Subacute Cor Pulmonale Due to Metastatic Carcinomatosis of the Lung: Report of a Case with Autopsy Findings JOSEPH T. GIAMMALVO, M.D. and STEWART H. JONES, M.D. Boston, Massachusetts
Case Report Section Subacute Cor Pulmonale Due to Metastatic Carcinomatosis of the Lung: Report of a Case with Autopsy Findings JOSEPH T. GIAMMALVO, M.D. and STEWART H. JONES, M.D. Boston, Massachusetts
Radiological staging of lung cancer. Shukri Loutfi,MD,FRCR Consultant Thoracic Radiologist KAMC-Riyadh
 Radiological staging of lung cancer Shukri Loutfi,MD,FRCR Consultant Thoracic Radiologist KAMC-Riyadh Bronchogenic Carcinoma Accounts for 14% of new cancer diagnoses in 2012. Estimated to kill ~150,000
Radiological staging of lung cancer Shukri Loutfi,MD,FRCR Consultant Thoracic Radiologist KAMC-Riyadh Bronchogenic Carcinoma Accounts for 14% of new cancer diagnoses in 2012. Estimated to kill ~150,000
The Fontan circulation. Folkert Meijboom
 The Fontan circulation Folkert Meijboom What to expect? Why a Fontan-circulation Indications How does it work Types of Fontan circulation Historical overview Role of echocardiography What to expect? Why
The Fontan circulation Folkert Meijboom What to expect? Why a Fontan-circulation Indications How does it work Types of Fontan circulation Historical overview Role of echocardiography What to expect? Why
Endovascular treatment of acquired arteriovenous fistula with severe hemodynamic effects: a case report
 Endovascular treatment of acquired arteriovenous fistula with severe hemodynamic effects: a case report The Leipzig Interventional Course, January 24 27, 2017 El Samman K., Šedivý P., Šnajdrová A., Přindišová
Endovascular treatment of acquired arteriovenous fistula with severe hemodynamic effects: a case report The Leipzig Interventional Course, January 24 27, 2017 El Samman K., Šedivý P., Šnajdrová A., Přindišová
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Doppler ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis, and color Doppler
 - - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
- - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
Pathophysiology. Tutorial 3 Hemodynamic Disorders
 Pathophysiology Tutorial 3 Hemodynamic Disorders ILOs Recall different causes of thrombosis. Explain different types of embolism and their predisposing factors. Differentiate between hemorrhage types.
Pathophysiology Tutorial 3 Hemodynamic Disorders ILOs Recall different causes of thrombosis. Explain different types of embolism and their predisposing factors. Differentiate between hemorrhage types.
CMR for Congenital Heart Disease
 CMR for Congenital Heart Disease * Second-line tool after TTE * Strengths of CMR : tissue characterisation, comprehensive access and coverage, relatively accurate measurements of biventricular function/
CMR for Congenital Heart Disease * Second-line tool after TTE * Strengths of CMR : tissue characterisation, comprehensive access and coverage, relatively accurate measurements of biventricular function/
Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases
 Case Report DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.395 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):395-399 Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases Hyoung Nam Lee, MD, Young
Case Report DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.395 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):395-399 Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases Hyoung Nam Lee, MD, Young
