Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation as a Cause of Cardiac Hypertrophy in Adults. Masatoshi FUJISHIMA, M.D., Kenjiro TANAKA, M.D., and Teruo OMAE, M.D.
|
|
|
- Marcia Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation as a Cause of Cardiac Hypertrophy in Adults Masatoshi FUJISHIMA, M.D., Kenjiro TANAKA, M.D., and Teruo OMAE, M.D. SUMMARY Seventeen adult patients with cerebral arteriovenous malformation were studied on cardiac effects of this disease. Of all 17 patients tested, the electrocardiogram revealed left ventricular hypertrophy in 5, sinus bradycardia in 4, WPW syndrome in one, and no abnormality in 7 others. There were 3 patients having a slight increase in the cardiothoracic ratio over 51%, and 14 having normal heart size determined from the chest X-ray taken. Of all 11 patients, in whom brain circulation was measured by the intravenous RISA technique, cranial blood flow (CBF) increased significantly in 5, remained within normal value in 4, and slightly decreased in 2 patients. Left ventricular hypertrophy on ECG was observed in 3 of 5 patients with a high CBF, but in none from the patients with normal or subnormal CBF, suggesting that the occurrence of ventricular hypertrophy was highly related with an increased CBF. The relationship between cerebral arteriovenous malformation and cardiac changes is discussed. Additional Indexing Words: Cranial blood flow Brain transit time Left ventricular hypertrophy Cardiothoracic ratio ERIPHERAL arteriovenous fistulas such as the femoral, the brachial and the carotid have been reported to cause elevation of cardiac output, changes in systemic hemodynamics, and increase in cardiac size.1)-3) Furthermore, it is not uncommon to be cause of heart failure in femoral arteriovenous fistulas.4) Intracranial arteriovenous malformation (AVM), however, has been observed to cause congestive heart failure in newborn infants,5)-8) but it has not been reported in adults. In the present study, cardiac enlargement or left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) was demonstrated in adult patients with intracranial AVM. METHODS The patients were 14 males and 3 females with an average age of 35 years and From the Second Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Kyushu University, 1276 Katakasu, Fukuoka 812, Japan. Received for publication August 18,
2 472 FUJISHIMA, TANAKA, AND OMAE Jap. Heart J. N ovember, years respectively. Twelve of all 17 patients were diagnosed as subarachnoid hemorrhage, and 5 others as Jacksonian epilepsy. No patient had a history of heart diseases, hypertension, or renal diseases. Cranial blood flow (CBF), brain transit time (TT), and arm-to-brain circulation time (ABCT) were measured in 11 patients by the external counting method of the intravenously injected RISA.9) All patients underwent complete neurological examinations and had routine laboratory tests, electrocardiograms (ECG), chest X-rays and bilateral carotid angiograms. None of patients having cerebral "Moyamoya" disease, or fistula between the extracranial artery and the intracranial vein was included in this series. RESULTS Clinical Findings: Either systolic or diastolic blood pressure was normal in all but one having a mild hypotension (Table I). The average blood pressure of all patients was 119mm. Hg systolic, and 65mm. Hg diastolic. Seven had normal ocular fundi, 8 had a mild retinopathy of group 1 by Keith-Wagener's classification, and 2 others had a papilledema. No patient had heart murmur or proteinuria, and 2 had a positive test for syphilis, which had been treated previously. Table I. Clinical Findings in 17 Patients K-W: Keith-Wagener classification, CTR: cardiothoracic ratio, SAH: subarachnoid hemorartery, AVM: arteriovenous malformation
3 Vol.13 No.6 CEREBRAL A-V MALFORMATION 473 The mean hemoglobin value was 14.2Gm./100ml., ranging Gm./100ml. A spinal tap was performed in all but one; 11 having normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure below 200mm. H2O, and 5 having a higher pressure than 200mm. H2O, among which the highest value was 350mm. H2O. There were 3 patients of cardiothoracic ratio (CTR) greater than 51% as determined from the chest X-ray taken, 5 between 46-50%, and the remaining 9 less than 45%. On the cerebral angiograms, there were 12 patients having AVM located in the territories of the middle cerebral artery; in 6 the middle cerebral artery only as a feeding vessel to AVM, in 3 both the middle and the anterior cerebral arteries. Two of all 17 had AVM in the areas of the anterior cerebral artery, and 3 others had of the posterior cerebral artery. The ECG as shown in Table II, revealed normal in 7 patients, sinus bradycardia in 4, LVH in 5, and WPW syndrome in one. A non-specific depression of ST segment was recorded in 2 patients. Electrocardiographic diagnosis of LVH was made on the basis of the voltage criteria described by Mori and his collaborators10),11) SV1+RV5 40mm. (50mm. for adolescent males under age 30), and SV2+RV5+SaVF 45mm. (55mm.). In the latter criteria, a false positivity for LVH was much less frequent and a coincidence with Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation rhage, MCA: middle cerebral artery, ACA: anterior cerebral artery, PCA: posterior cerebral
4 474 FUJISHIMA, TANAKA, AND OMAE Jap. Heart J. N ovember, 1972 Table II. Electrocardiographic Findings in 17 Patients with Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation *,** Voltage criteria of Mori, et al., see text, RSR: regular sinus rhythm, LVH: left ventricular hypertrophy, WNL: within normal limits, SB: sinus bradycardia, n: normal, dep, C-L: ST depression in chest and limb leads, J-dep, L: junction typed depression of ST segment in limb leads, neg, C: negative T wave in chest leads, WPW: WPW syndrome with LVH proved at autopsy was higher than that in the former. Eight of the 17 patients took the surgical treatments such as complete extirpation of AVM, or clipping the feeding arteries. Brain Circulation Study: Five of all 11 patients studied had a significant increase in CBF, being greater than 2,000ml./min., 4 had normal CBF, and 2 others a slight decrease in CBF (Table III). The highest CBF was 2,910ml./min., which was double as great as that of normal subjects. The mean CBF was 1,977ml./min. in patients with AVM comparable to that of 1,569ml./min. in the normal subjects aged under, and 1,504ml./min. in those aged over 40 years. In 8 patients, TT was normal but tended to be shorter in the affected * 1) Mori and Kawamata's correction for the Japanese adults of Sokolow -Lyon' criteria for diagnosis of LVH is as follsws: RV5(6)+SV1 40mm. (50mm.), RI+SIII 20mm., RV5 30mm., RV6 23mm., RaVL 11mm., or RaVF 22mm. 2) Mori and Nakagawa's criteria on the basis of total left ventricular potentials is as follows; SV2+RV5+SaVF 45mm. (55mm.), SV2+RV6+ SaVF 40mm. (50mm.), or SV1+RV6+SaVF 35mm. (45mm.). When any one of these items is satisfied, the presence of LVH is sufficiently presumed.
5 Vol.13 No.6 CEREBRAL A-V MALFORMATION 475 Table III. Brain Circulation in 11 Patients with Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation Measured by Intravenous RISA Technique CBF: cranial blood flow, TT: brain transit time, ABCT: arm-to-brain circulation time, L or R: left or right hemisphere hemisphere than in the contralateral one. In other 3, TT was significantly shorter in both the affected and non-affected hemispheres than that in the control subjects. ABCT, as the sum of the part of systemic and the pulmonary circulation times, was significantly shorter in 2, and normal in 8 of all 10 patients tested. DISCUSSION Five out of the 11 patients tested showed a significant increase in CBF by 33 to 93% from control value. Of these 5 patients, 3 had LVH in their ECGs, one had WPW syndrome, and the remaining one normal ECG. There were no associated conditions such as those of hypertension, arteriosclerosis, severe anemia or renal disease to cause cardiac hypertrophy. In the remaining 6 patients of normal or subnormal CBF, their ECGs showed either normal or sinus bradycardia, but no LVH. These results strongly suggest that LVH found in their ECGs is related to an increase in CBF. On the basis of Mori and his collaborators' criteria for electrocardiographic diagnosis of LVH, a value for SV2+RV5+SaVF 45mm. (55mm. for males under age 30), defined as the summation of left ventricular potential has a almost negligible false positivity and a much higher coincidence with
6 476 FUJISHIMA, TANAKA, AND OMAE Jap. Heart J. N ovember, 1972 the autopsy proved LVH being 70%, than that on the basis of Sokolow-Lyon's original criteria. Besides LVH observed in 5 patients in present series, no other abnormality was found such as a strain pattern of ST segment, or inversion of T waves, which may result from a relative hypoxia of the myocardium. The data may indicate that ECG change in patients with cerebral AVM is much less severe than that frequently observed in cases with hypertensive cardiovascular or cardiac valvular diseases, and might explain why cerebral AVM hardly causes congestive heart failure in the adult. Meanwhile, Cabrera and Monroy12) described that diastolic overloading of left ventricle produces an elevation of R wave and high positive T wave in V5 as well as V6 where the left ventricular potentials are transmitted, whereas in systolic overloading, T wave tends to be flattening or negative with a simultaneous depression of ST segment. Cerebral AVM is the case of diastolic overloading, despite no satisfactory explanation for high T waves. Concerning the brain hemodynamics in cerebral AVM, many investigators observed that CBF increases double as great,13) triple,14) or rarely fourfold15) as that in normal subjects, implying that the estimated cardiac output might simultaneously increase by 750 to 2,250ml./min., or 12 to 35% from normal cardiac output of approximately 6.4L./min. Wallace and his coworkers16) have measured the mean cardiac output in 8 patients with cerebral AVM and in other 8 control patients, being 4.40 and 2.82L./min./M.2 respectively. The average AVM shunt flow in their study was estimated to be 2,804ml./min. on the basis of cardiac output data obtained by a dye-dilution technique, or to be 2,780ml./min. from the systemic arteriovenous difference of oxygen content. It seems unlikely that their estimation of cerebral shunt flow such as these is correct, since the present results show brain transit time being shortened in both the affected and non-affected hemispheres, indicating that CBF increases even in the contralateral hemisphere of cerebral AVM. A similar observation to ours was reported by Lassen and Munck,17) that cerebral blood flow measured by Krypton-85 method was 222ml./100Gm./ min. on the side of AVM, and 108 on the contralateral one before, and 92 and 59ml./100Gm./min. respectively, after a surgical removal of the shunt. Although other studies showed normal appearance times in vessels not feeding the fistula in patients with peripheral arteriovenous anomalies, arm-to-brain circulation time was significantly shortened in some patients of the present study. It is well recognized that arteriovenous fistula of sufficient size such as the femoral may have produced effects on the cardiovascular system. There are increases in blood volume as well as cardiac output primarily due to increase in stroke volume, and may develop congestive heart failure. Although
7 Vol.13 No.6 CEREBRAL A-V MALFORMATION 477 a precise mechanism responsible for the compensatory increases in blood volume and cardiac output has not been fully understood, these cardiac changes are reversible, and the heart size returns to normal after operative removal of the fistula.1) Congestive heart failure has not been uncommon in the newborn or the infant with cerebral AVM. According to the 51 published cases,2) 18 had neonatal congestive heart failure, and 17 of them died within 5 months of age. In the adult cases, however, neither abnormalities of ECG nor changes in cardiac size has been reported. The reason why the cardiovascular effects of cerebral AVM in the adult would be less pronounced than those of the extracranial arteriovenous shunts might be considered as follows; at first, the middle cerebral artery, most frequently implicated as a feeding artery to AVM, is several times smaller in diameter than the peripheral arteries such as the femoral or the brachial.18) Secondly, the intracranial location of AVM higher than heart level might favor a lower shunt flow in the upright posture, and finally, cerebral AVM being enclosed by the skull might retard enlargement of the growth of AVM as well as collateral channels.16) It might be possible, but not fully proved, that in some of the patients with cerebral AVM, congestive heart failure could occur late in life, since a long-lasting hyperkinetic circulatory states19) cause reduction of cardiac reserve,4) and changes in myocardial function resulting in circulatory congestion to develop. REFERENCES 1. Warren, J.V., Nickerson, J.L., and Elkin, D.C.: J. Clin. Invest. 30: 210, Nickerson, J.L., Elkin, D.C., and Warren, J.V.: J. Clin. Invest. 30: 215, Frank, C.W., Wang, H-H., Lammerlant, J., Miller, R., and Weria, R.: J. Clin. Invest. 34: 722, Spurny, O.M. and Pierce, J.A.: Am. Heart J. 61: 21, Hamby, R.I. and Desposito, F.: J. Pediat. 61: 590, Hernandez, A., Jr., Schwasz, H.G., and Goldring, D.: J. Pediat. 66: 722, Levine, O.R., Jameson, A.G., Nellhaus, G., and Gold, A.P.: Pediatrics 30: 563, Montoya, G., Dohn, D.F., and Mercer, R.D.: Neurology 21: 1054, Fujishima, M.: Fukuoka Acta Med. 58: 194, Mori, H., Murakami, T., and Kawamata, K.: Jap. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 38: 570, Mori, H.: Jap. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 45: 371, Cabrera, E. and Monroy, J.R.: Am. Heart J. 43: 669, Atarashi, J., Yoshimura, M., Wada, Y., et al.: Clin. Neurol. 3: 252, Shenkin, H.A., Spitz, E.B., Grant, F.C., and Kety, S.S.: J. Neurosurg. 5: 165, Tonnis, W., Schiefer, W., and Walter, W.: J. Neurosurg. 15: 471, Wallace, J.M., Nashold, B.S., and Slewka, A.P.: Circulation. 31: 696, Lassen, N.A. and Munck, O.: Acta Psychiat. Neurol. Scand. 31: 71, Ray, B.S.: Surg. Gyne. Obst. 73: 615, Eichna, L.W.: Circulation. 22: 864, 1960.
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
QRS Waves of the Spatial Velocity Electrocardiogram
 QRS Waves of the Spatial Velocity Electrocardiogram in Atrial Septal Defect Hiroyoshi MORI, M.D., Kouichi MIKAWA, M.D., Toshiharu NIKI, M.D., Takashi NAGAO, M.D., Satoru MATSUMO, M.D., Tomoo NII, M.D.,
QRS Waves of the Spatial Velocity Electrocardiogram in Atrial Septal Defect Hiroyoshi MORI, M.D., Kouichi MIKAWA, M.D., Toshiharu NIKI, M.D., Takashi NAGAO, M.D., Satoru MATSUMO, M.D., Tomoo NII, M.D.,
(D) (E) (F) 6. The extrasystolic beat would produce (A) increased pulse pressure because contractility. is increased. increased
 Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis
 Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Transcatheter closure of right coronary artery fistula to the right ventricle
 Case Report Transcatheter closure of right coronary artery fistula to the right ventricle Abstract Coronary artery fistula (CAF) is an uncommon anomaly usually congenital but can be acquired. Although,
Case Report Transcatheter closure of right coronary artery fistula to the right ventricle Abstract Coronary artery fistula (CAF) is an uncommon anomaly usually congenital but can be acquired. Although,
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH. General. Heart Rate. Starship Children s Health Clinical Guideline
 General Heart Rate QRS Axis T Wave Axis PR Interval according to Heart Rate & Age P Wave Duration and Amplitude QRS Duration according to Age QT Interval R & S voltages according to Lead & Age R/S ratio
General Heart Rate QRS Axis T Wave Axis PR Interval according to Heart Rate & Age P Wave Duration and Amplitude QRS Duration according to Age QT Interval R & S voltages according to Lead & Age R/S ratio
TRANSCRANIAL DOPPLER ULTRASOUND INTRODUCTION TO TCD INTERPRETATION
 TRANSCRANIAL DOPPLER ULTRASOUND INTRODUCTION TO TCD INTERPRETATION ---Rune Aaslid First TCD Publication 1982 WHAT IS TCD? Uses 2 MHz pulsed Doppler ultrasound Passes through cranial windows Provides information
TRANSCRANIAL DOPPLER ULTRASOUND INTRODUCTION TO TCD INTERPRETATION ---Rune Aaslid First TCD Publication 1982 WHAT IS TCD? Uses 2 MHz pulsed Doppler ultrasound Passes through cranial windows Provides information
ECGs of structural heart disease: Part I
 Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 2011; 52(12) 855 CME Article ECGs of structural heart disease: Part I Poh K K, Teo S G, Tay E L W, Yip J WL Cardiac Department, National University Heart Centre,
Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 2011; 52(12) 855 CME Article ECGs of structural heart disease: Part I Poh K K, Teo S G, Tay E L W, Yip J WL Cardiac Department, National University Heart Centre,
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Paediatric ECG Interpretation
 Paediatric ECG Interpretation Dr Sanj Fernando (thanks to http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/paediatric-ecginterpretation/) 3 yo boy complaining of abdominal pain and chest pain Child ECG vs Adult
Paediatric ECG Interpretation Dr Sanj Fernando (thanks to http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/paediatric-ecginterpretation/) 3 yo boy complaining of abdominal pain and chest pain Child ECG vs Adult
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
Cerebral arteriovenous aneurysm presenting
 British Heart Journal, 1974, 36, 9I9-923. Cerebral arteriovenous aneurysm presenting with heart failure Report of three cases Philip N. Cunliffe From the Department of Cardiology, The Children's Hospital,
British Heart Journal, 1974, 36, 9I9-923. Cerebral arteriovenous aneurysm presenting with heart failure Report of three cases Philip N. Cunliffe From the Department of Cardiology, The Children's Hospital,
Cardiac Output MCQ. Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology. Cairo University 2007
 Cardiac Output MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 90- Guided by Ohm's law when : a- Cardiac output = 5.6 L/min. b- Systolic and diastolic BP
Cardiac Output MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 90- Guided by Ohm's law when : a- Cardiac output = 5.6 L/min. b- Systolic and diastolic BP
HIGH voltage of R waves in left precordial leads of the electrocardiogram
 R-WAVE VOLTAGE CHANGES IN RELATION TO ARTERIAL PRESSURE IN HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS ATHAN J. GEORGOPOULOS, M.D.,* PHILIP A. VLASTARIS, M.D.,f and WILLIAM L. PROUDFIT, M.D. Department of Cardiovascular Disease
R-WAVE VOLTAGE CHANGES IN RELATION TO ARTERIAL PRESSURE IN HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS ATHAN J. GEORGOPOULOS, M.D.,* PHILIP A. VLASTARIS, M.D.,f and WILLIAM L. PROUDFIT, M.D. Department of Cardiovascular Disease
Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Chapter 9, Part 2. Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise
 Chapter 9, Part 2 Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise Electrical Activity of the Heart Contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium Impulse is initiated in the right
Chapter 9, Part 2 Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise Electrical Activity of the Heart Contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium Impulse is initiated in the right
DEPARTMENT NAME PRE-PARTICIPATION SCREENING THE SPORTS PHYSICAL
 PRE-PARTICIPATION SCREENING THE SPORTS PHYSICAL Michele Krenek, MSN, RN, FNP-C TCHAPP Conference, Houston, TX April 4, 2019 PRE-PARTICIPATION SPORTS SCREENING According to the AHA the definition of the
PRE-PARTICIPATION SCREENING THE SPORTS PHYSICAL Michele Krenek, MSN, RN, FNP-C TCHAPP Conference, Houston, TX April 4, 2019 PRE-PARTICIPATION SPORTS SCREENING According to the AHA the definition of the
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]
![[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD] [(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]](/thumbs/89/98619893.jpg) 2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
Hemodynamic Monitoring
 Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
GUIDELINES FOR THE EARLY MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 2018 UPDATE QUICK SHEET 2018 American Heart Association GUIDELINES FOR THE EARLY MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE A Summary for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American
2018 UPDATE QUICK SHEET 2018 American Heart Association GUIDELINES FOR THE EARLY MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE A Summary for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery
 Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
Transorbital blood flow sound recordings have the
 397 Noninvasive Detection of Intracranial Vascular Lesions by Recording Blood Flow Sounds Yasushi Kurokawa, MD; Seisho Abiko, MD; Kohsaku Watanabe, MD Background and Purpose Transorbital blood flow sound
397 Noninvasive Detection of Intracranial Vascular Lesions by Recording Blood Flow Sounds Yasushi Kurokawa, MD; Seisho Abiko, MD; Kohsaku Watanabe, MD Background and Purpose Transorbital blood flow sound
Other 12-Lead ECG Findings
 Other 12-Lead ECG Findings Left Atrial Enlargement Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom
Other 12-Lead ECG Findings Left Atrial Enlargement Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System
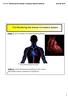 12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
M Tipple. Interpretation of electrocardiograms in infants and children. Images Paediatr Cardiol Jan-Mar; 1(1): 3 13.
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 1999 PMCID: PMC3232475 Interpretation of electrocardiograms in infants and children M Tipple * * Paediatric Cardiologist, British Columbia Children's
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 1999 PMCID: PMC3232475 Interpretation of electrocardiograms in infants and children M Tipple * * Paediatric Cardiologist, British Columbia Children's
ECG SIGNS OF HYPERTROPHY OF HEART ATRIUMS AND VENTRICLES
 Ministry of Health of Ukraine Kharkiv National Medical University ECG SIGNS OF HYPERTROPHY OF HEART ATRIUMS AND VENTRICLES Methodical instructions for students Рекомендовано Ученым советом ХНМУ Протокол
Ministry of Health of Ukraine Kharkiv National Medical University ECG SIGNS OF HYPERTROPHY OF HEART ATRIUMS AND VENTRICLES Methodical instructions for students Рекомендовано Ученым советом ХНМУ Протокол
Vascular Malformations of the Brain. William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist. September 8, 2014
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
b) List the steps that may occur in hemostasis with a brief explanation of what happens in those steps.
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood (use anatomy vocabulary)? b) List
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood (use anatomy vocabulary)? b) List
General Introduction to ECG. Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline )
 General Introduction to ECG Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline ) Objectives 1. Practice the 5-step Method 2. Differential Diagnosis: R & L axis deviation 3. Differential Diagnosis: Poor R-wave progression
General Introduction to ECG Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline ) Objectives 1. Practice the 5-step Method 2. Differential Diagnosis: R & L axis deviation 3. Differential Diagnosis: Poor R-wave progression
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
ECG Interpretation. Best to have a system to methodically evaluate ECG (from Dubin) * Rate * Rhythm * Axis * Intervals * Hypertrophy * Infarction
 ECG to save Babies ECG Interpretation Best to have a system to methodically evaluate ECG (from Dubin) * Rate * Rhythm * Axis * Intervals * Hypertrophy * Infarction Electrical Activity in the heart 5 events
ECG to save Babies ECG Interpretation Best to have a system to methodically evaluate ECG (from Dubin) * Rate * Rhythm * Axis * Intervals * Hypertrophy * Infarction Electrical Activity in the heart 5 events
REtrive. REpeat. RElearn Design by. Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book
 Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book REtrive REpeat RElearn Design by S I T T I N U N T H A N G J U I P E E R I Y A W A
Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book REtrive REpeat RElearn Design by S I T T I N U N T H A N G J U I P E E R I Y A W A
Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk
 1. Periodical Evaluations: each 2 years. Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk 2. Personal history: Personal history of murmur in childhood; dizziness, syncope, palpitations, intolerance
1. Periodical Evaluations: each 2 years. Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk 2. Personal history: Personal history of murmur in childhood; dizziness, syncope, palpitations, intolerance
Cardiac output and Venous Return. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Cardiac output and Venous Return Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives Define cardiac output and venous return Describe the methods of measurement of CO Outline the factors that regulate cardiac output
Cardiac output and Venous Return Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives Define cardiac output and venous return Describe the methods of measurement of CO Outline the factors that regulate cardiac output
Neurosurg Focus 5 (5):Article 4, 1998
 Neurosurg Focus 5 (5):Article 4, 1998 Multiple combined indirect procedure for the surgical treatment of children with moyamoya disease. A comparison with single indirect anastomosis with direct anastomosis
Neurosurg Focus 5 (5):Article 4, 1998 Multiple combined indirect procedure for the surgical treatment of children with moyamoya disease. A comparison with single indirect anastomosis with direct anastomosis
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
EFFECTS OF SUDDEN AND PROLONGED STANDING FROM SUPINE POSTURE ON HEART RATE, ECG-PATTERN AND BLOOD PRESSURE
 J. Human Ergol.,17: 3-12,1988 Center for Academic Publications Japan. Printed in Japan. EFFECTS OF SUDDEN AND PROLONGED STANDING FROM SUPINE POSTURE ON HEART RATE, ECG-PATTERN AND BLOOD PRESSURE Satipati
J. Human Ergol.,17: 3-12,1988 Center for Academic Publications Japan. Printed in Japan. EFFECTS OF SUDDEN AND PROLONGED STANDING FROM SUPINE POSTURE ON HEART RATE, ECG-PATTERN AND BLOOD PRESSURE Satipati
Cardiovascular System: Blood and Blood Vessels. Formed Elements of Blood
 Cardiovascular System: Blood and Blood Vessels Formed Elements of Blood 1 Whole Blood and the Hematocrit What is the likely cause of a WBC count of 34K, in which most of the WBCs are lymphocytes? How much
Cardiovascular System: Blood and Blood Vessels Formed Elements of Blood 1 Whole Blood and the Hematocrit What is the likely cause of a WBC count of 34K, in which most of the WBCs are lymphocytes? How much
Topics to be Covered. Cardiac Measurements. Distribution of Blood Volume. Distribution of Pulmonary Ventilation & Blood Flow
 Topics to be Covered MODULE F HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING Cardiac Output Determinants of Stroke Volume Hemodynamic Measurements Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Control of Blood Pressure Heart Failure Cardiac
Topics to be Covered MODULE F HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING Cardiac Output Determinants of Stroke Volume Hemodynamic Measurements Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Control of Blood Pressure Heart Failure Cardiac
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016
 Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016 Disclosures: EKG Workshop Louis Mancano, MD Speaker has no disclosures
Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016 Disclosures: EKG Workshop Louis Mancano, MD Speaker has no disclosures
Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right ventricular sinusoids
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
 CLINICAL FEATURES THAT SUPPORT ATHEROSCLEROTIC STROKE 1. cerebral cortical impairment (aphasia, neglect, restricted motor involvement, etc.) or brain stem or cerebellar dysfunction 2. lacunar clinical
CLINICAL FEATURES THAT SUPPORT ATHEROSCLEROTIC STROKE 1. cerebral cortical impairment (aphasia, neglect, restricted motor involvement, etc.) or brain stem or cerebellar dysfunction 2. lacunar clinical
PAEDIATRIC ECG Dimosthenis Avramidis, MD.
 PAEDIATRIC ECG Dimosthenis Avramidis, MD. Consultant Mitera Children s Hospital Athens Greece S. Associate 1st Cardiology Dpt Evangelismos Hospital Athens Greece 5 y/o with sinus tach Background ECG changes
PAEDIATRIC ECG Dimosthenis Avramidis, MD. Consultant Mitera Children s Hospital Athens Greece S. Associate 1st Cardiology Dpt Evangelismos Hospital Athens Greece 5 y/o with sinus tach Background ECG changes
Clinical Symptoms in the Lateral Type of Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 676 Correlation Between the Location of Hematoma and its Clinical Symptoms in the Lateral Type of Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage Observations on Pantopaque Radiography of the Hematoma Cavity in
676 Correlation Between the Location of Hematoma and its Clinical Symptoms in the Lateral Type of Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage Observations on Pantopaque Radiography of the Hematoma Cavity in
Right ECG. Contents. RAE vs. P Pulmonale: Are they the same? 12 Lead ECGs of Patient with COPD Exacerbation Before and After Treatment
 Contents Right ECG Wang, Tzong-Luen MD, PhD, JM, FESC, FACC, FCAPSC Professor, Medical College, Fu-Jen Catholic University Chief, ED, Shin-Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital CEO, National Resuscitation Council,
Contents Right ECG Wang, Tzong-Luen MD, PhD, JM, FESC, FACC, FCAPSC Professor, Medical College, Fu-Jen Catholic University Chief, ED, Shin-Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital CEO, National Resuscitation Council,
Please check your answers with correct statements in answer pages after the ECG cases.
 ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
Supplement Table 1. Definitions for Causes of Death
 Supplement Table 1. Definitions for Causes of Death 3. Cause of Death: To record the primary cause of death. Record only one answer. Classify cause of death as one of the following: 3.1 Cardiac: Death
Supplement Table 1. Definitions for Causes of Death 3. Cause of Death: To record the primary cause of death. Record only one answer. Classify cause of death as one of the following: 3.1 Cardiac: Death
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA)
 PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA) It is a channel that connect the pulmonary artery with the descending aorta (isthumus part). It results from the persistence of patency of the fetal ductus arteriosus after
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA) It is a channel that connect the pulmonary artery with the descending aorta (isthumus part). It results from the persistence of patency of the fetal ductus arteriosus after
Coronary Arteriovenous Malformation presenting as Acute Myocardial Infarction. Choon Ta NG, Aaron WONG, Foong-Koon CHEAH, Chi Keong CHING
 Coronary Arteriovenous Malformation presenting as Acute Myocardial Infarction Choon Ta NG, Aaron WONG, Foong-Koon CHEAH, Chi Keong CHING The patient 49 year old Male presented with Chest tightness x 1
Coronary Arteriovenous Malformation presenting as Acute Myocardial Infarction Choon Ta NG, Aaron WONG, Foong-Koon CHEAH, Chi Keong CHING The patient 49 year old Male presented with Chest tightness x 1
CORONARY arteriovenous fistulas are uncommon, but their detection has. Rupture of a Giant Saccular Aneurysm of Coronary Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Rupture of a Giant Saccular Aneurysm of Coronary Arteriovenous Fistulas Masahiro ITO, MD, Makoto KODAMA, MD, Makihiko SAEKI, 1 MD, Hiroshi FUKUNAGA, MD, Tomoji GOTO, 2 MD, Hidenori INOUE, 2 MD, Shigetaka
Rupture of a Giant Saccular Aneurysm of Coronary Arteriovenous Fistulas Masahiro ITO, MD, Makoto KODAMA, MD, Makihiko SAEKI, 1 MD, Hiroshi FUKUNAGA, MD, Tomoji GOTO, 2 MD, Hidenori INOUE, 2 MD, Shigetaka
Skin supplied by T1-4 (medial upper arm and neck) T5-9- epigastrium Visceral afferents from skin and heart are the same dorsal root ganglio
 Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Product Catalog. Pediatric Learning Solutions. Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association.
 Product Catalog Pediatric Learning Solutions Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association. Acquired Heart Disease in Children WBT Acute Respiratory Distress
Product Catalog Pediatric Learning Solutions Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association. Acquired Heart Disease in Children WBT Acute Respiratory Distress
Assessment of fetal heart function and rhythm
 Assessment of fetal heart function and rhythm The fetal myocardium Early Gestation Myofibrils 30% of myocytes Less sarcoplasmic reticula Late Gestation Myofibrils 60% of myocytes Increased force per unit
Assessment of fetal heart function and rhythm The fetal myocardium Early Gestation Myofibrils 30% of myocytes Less sarcoplasmic reticula Late Gestation Myofibrils 60% of myocytes Increased force per unit
Preface: Wang s Viewpoints
 AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram: Part IV, Ischemia and Infarction Presented by: WANG, TZONG LUEN, MD, PhD, JM, FACC, FESC, FCAPSC Professor,
AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram: Part IV, Ischemia and Infarction Presented by: WANG, TZONG LUEN, MD, PhD, JM, FACC, FESC, FCAPSC Professor,
Lab 16. The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
Central haemodynamics during spontaneous angina pectoris
 British Heart Journal, I974, 36, I0-I09I Central haemodynamics during spontaneous angina pectoris From the Department of Clinical Physiology, Malmo General Hospital, S-214 OI Malmo, Sweden. Central pressures
British Heart Journal, I974, 36, I0-I09I Central haemodynamics during spontaneous angina pectoris From the Department of Clinical Physiology, Malmo General Hospital, S-214 OI Malmo, Sweden. Central pressures
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Case Report Inverted (Reverse) Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy following Cerebellar Hemorrhage
 Case Reports in Cardiology, Article ID 781926, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/781926 Case Report Inverted (Reverse) Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy following Cerebellar Hemorrhage Sophie Piérard, 1 Marco
Case Reports in Cardiology, Article ID 781926, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/781926 Case Report Inverted (Reverse) Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy following Cerebellar Hemorrhage Sophie Piérard, 1 Marco
How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate https://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate https://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/
A NEW SIGN OF LEFT VENTRICULAR FAILURE
 A NEW SIGN OF LEFT VENTRICULAR FAILURE BY PAUL WOOD AND A. SELZER t (From the National Hospital.for Diseases of the Heart and the British Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith, London) The prominent
A NEW SIGN OF LEFT VENTRICULAR FAILURE BY PAUL WOOD AND A. SELZER t (From the National Hospital.for Diseases of the Heart and the British Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith, London) The prominent
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography
 Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
12-Lead ECG Interpretation. Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP
 12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
BOTH ATEOPINE and isoproterenol
 Effects of tropine and Isoproterenol on Cardiac Output, Central Venous Pressure, and Transit Time of Indicators Placed at Three Different Sites in the Venous System y KLPH RTEX, M.D., J. CULIE GUNXELLS,
Effects of tropine and Isoproterenol on Cardiac Output, Central Venous Pressure, and Transit Time of Indicators Placed at Three Different Sites in the Venous System y KLPH RTEX, M.D., J. CULIE GUNXELLS,
(3.5 cc. per 100 Gm. per min.) is extracted from
 CEREBRAL HEMODYNAMICS DURING CEREBRAL ISCHEMIA INDUCED BY ACUTE HYPOTENSION 1 BY FRANK A. FINNERTY, JR., LLOYD WITKIN, AND JOSEPH F. FAZEKAS WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE OF MARIE LANGBART AND WILLIAM
CEREBRAL HEMODYNAMICS DURING CEREBRAL ISCHEMIA INDUCED BY ACUTE HYPOTENSION 1 BY FRANK A. FINNERTY, JR., LLOYD WITKIN, AND JOSEPH F. FAZEKAS WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE OF MARIE LANGBART AND WILLIAM
Electrical System Overview Electrocardiograms Action Potentials 12-Lead Positioning Values To Memorize Calculating Rates
 Electrocardiograms Electrical System Overview James Lamberg 2/ 74 Action Potentials 12-Lead Positioning 3/ 74 4/ 74 Values To Memorize Inherent Rates SA: 60 to 100 AV: 40 to 60 Ventricles: 20 to 40 Normal
Electrocardiograms Electrical System Overview James Lamberg 2/ 74 Action Potentials 12-Lead Positioning 3/ 74 4/ 74 Values To Memorize Inherent Rates SA: 60 to 100 AV: 40 to 60 Ventricles: 20 to 40 Normal
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG)
 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) The heart is a muscular organ, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assists in
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) The heart is a muscular organ, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assists in
TCD IN THE NICU, PICU AND OTHER APPLICATIONS. Dorothy Bulas M.D. Professor of Pediatrics & Radiology Children s National Washington D.C.
 TCD IN THE NICU, PICU AND OTHER APPLICATIONS Dorothy Bulas M.D. Professor of Pediatrics & Radiology Children s National Washington D.C. Objectives Recognize normal and abnormal cranial blood flow patterns
TCD IN THE NICU, PICU AND OTHER APPLICATIONS Dorothy Bulas M.D. Professor of Pediatrics & Radiology Children s National Washington D.C. Objectives Recognize normal and abnormal cranial blood flow patterns
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
ECG Workshop. Nezar Amir
 ECG Workshop Nezar Amir Myocardial Ischemia ECG Infarct ECG in STEMI is dynamic & evolving Common causes of ST shift Infarct Localisation Left main artery occlusion: o diffuse ST-depression with ST elevation
ECG Workshop Nezar Amir Myocardial Ischemia ECG Infarct ECG in STEMI is dynamic & evolving Common causes of ST shift Infarct Localisation Left main artery occlusion: o diffuse ST-depression with ST elevation
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Lnformation Coverage Guidance
 Lnformation Coverage Guidance Coverage Indications, Limitations, and/or Medical Necessity Abstract: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a cardiac neurohormone produced mainly in the left ventricle. It
Lnformation Coverage Guidance Coverage Indications, Limitations, and/or Medical Necessity Abstract: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a cardiac neurohormone produced mainly in the left ventricle. It
Section V. Objectives
 Section V Landscape of an MI Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to Outline a systematic approach to 12 lead ECG interpretation Demonstrate the process for determining
Section V Landscape of an MI Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to Outline a systematic approach to 12 lead ECG interpretation Demonstrate the process for determining
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF AMI/ACS
 DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF AMI/ACS Diagnostic criteria are used to validate clinical diagnoses. Those used in epidemiological studies are here below reported. 1. MONICA - Monitoring trends and determinants
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF AMI/ACS Diagnostic criteria are used to validate clinical diagnoses. Those used in epidemiological studies are here below reported. 1. MONICA - Monitoring trends and determinants
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM. General Instructions: ID NUMBER: FORM NAME: H F A DATE: 10/13/2017 VERSION: CONTACT YEAR NUMBER:
 ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE. There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood
 CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood THE CARDIAC PUMP 1) The forward pull(vis a fronte) This
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood THE CARDIAC PUMP 1) The forward pull(vis a fronte) This
THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS. 1. Cardiovascular Disease
 THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS 1. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is considered to have developed if there was a definite manifestation
THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS 1. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is considered to have developed if there was a definite manifestation
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
Determination of Stroke Volume from Left Ventricular Isovolumetric Contraction and Ejection Times
 Determination of Stroke Volume from Left Ventricular Isovolumetric Contraction and Ejection Times Clarence M. AGRESS, M.D. and Stanley WEGNER SUMMARY Examination was made of the relationship of left ventricular
Determination of Stroke Volume from Left Ventricular Isovolumetric Contraction and Ejection Times Clarence M. AGRESS, M.D. and Stanley WEGNER SUMMARY Examination was made of the relationship of left ventricular
7/5/2016. Neonatal high-output cardiac failure. Case 1 POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 John Deveikis, M.D. POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS JULY, 2016 Neonatal high-output cardiac failure Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, failure to thrive When congenital heart
John Deveikis, M.D. POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS JULY, 2016 Neonatal high-output cardiac failure Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, failure to thrive When congenital heart
Cardiac Pathophysiology
 Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
HISTORY. Question: What type of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance.
 HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations
 Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Arterial Peaks in Regional Cerebral Blood Flow 133 Xenon Clearance Curves
 Arterial Peaks in Regional Cerebral Blood Flow 133 Xenon Clearance Curves BY STEPHEN G. ROSENBAUM, B.A., LINNETTE D. ILIFF, B.SC, M. PHIL., PH.D., J. W. D. BULL, M.D., F.R.C.P., F.F.R., G. H. DU BOULAY,
Arterial Peaks in Regional Cerebral Blood Flow 133 Xenon Clearance Curves BY STEPHEN G. ROSENBAUM, B.A., LINNETTE D. ILIFF, B.SC, M. PHIL., PH.D., J. W. D. BULL, M.D., F.R.C.P., F.F.R., G. H. DU BOULAY,
c) What is the name of RBC (erythrocyte) formation? Where do blood cells form?
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 69 Case 13 Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise Cassandra Farias is a 34-year-old dietician at an academic medical center. She believes in the importance of a healthy lifestyle
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 69 Case 13 Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise Cassandra Farias is a 34-year-old dietician at an academic medical center. She believes in the importance of a healthy lifestyle
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Revised: 11/2013
 DEFINITIONS: Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Revised: 11/2013 Chain of survival (adult) - early activation, early
DEFINITIONS: Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Revised: 11/2013 Chain of survival (adult) - early activation, early
Blood Supply. Allen Chung, class of 2013
 Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system
 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
Cardiovascular Disorders. Heart Disorders. Diagnostic Tests for CV Function. Bio 375. Pathophysiology
 Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER
 CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER CLEAR Surgical Center Team July 2011 Trial Enrollment Status Updates Insert latest enrollment update chart from most recent CLEAR newsletter Imaging
CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER CLEAR Surgical Center Team July 2011 Trial Enrollment Status Updates Insert latest enrollment update chart from most recent CLEAR newsletter Imaging
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND RESPONSES TO EXERCISE Mr. S. Kelly PSK 4U North Grenville DHS THE HEART: A REVIEW Cardiac muscle = myocardium Heart divided into two sides, 4 chambers (L & R) RS: pulmonary
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND RESPONSES TO EXERCISE Mr. S. Kelly PSK 4U North Grenville DHS THE HEART: A REVIEW Cardiac muscle = myocardium Heart divided into two sides, 4 chambers (L & R) RS: pulmonary
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Bhakta N, Liu Q, Yeo F, et al. Cumulative burden
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Bhakta N, Liu Q, Yeo F, et al. Cumulative burden
Physiology #14. Heart Failure & Circulatory Shock. Mohammad Ja far Tuesday 5/4/2016. Turquoise Team. Page 0 of 13
 45 Physiology #14 Heart Failure & Circulatory Shock Mohammad Ja far Tuesday 5/4/2016 Turquoise Team Page 0 of 13 Heart Failure: It s a condition in which the heart can t perform its function properly;
45 Physiology #14 Heart Failure & Circulatory Shock Mohammad Ja far Tuesday 5/4/2016 Turquoise Team Page 0 of 13 Heart Failure: It s a condition in which the heart can t perform its function properly;
