Physical Exam Of The Cardio- Vascular System. James G. Laws D.O. MACOI
|
|
|
- Harry Skinner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physical Exam Of The Cardio- Vascular System James G. Laws D.O. MACOI
2 An Important Part Of The Physical Exam Of The Cardio-Vascular System That Is Commonly Overlooked Is? 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 1. Palpation Of The PMI Which Can Bring Out Findings Causing You To Suspect Mitral Stenosis. 2. Auscultation Of Left Sternal Border Which Can Help In The Diagnosis Of Tricuspid Regurgitation. 3. Auscultation Of The Neck Which Can Suggest Either Aortic Stenosis Or Carotid Stenosis. 4. Comparison Of Both Radial Pulses Which Can Suggest Ascending Aortic Aneurysm. 5. Checking For The Hepato-jugular Reflux Which Can Bring Out Signs Of Mitral Regurgitation. 10 Countdown
3 Always Begin Exam On Right Side Of The Patient This Allows You To Reach Across The Patient To The PMI Always Expose The Chest For The Best Results This Allows The Stethoscope Tubing To Be Straight And Does Not Loop Down Making Contact With Patient Or Bed Covering Remember The Shorter The Tubing The Less Distance The Sound Has To Travel Best Exam Done With The Patient At Degree Head Up Position
4 Always Begin Exam With Palpation Then Go To Auscultation First Check The PMI Second Palpate Both The Carotids And The Femorals Third Palpate The Aorta Fourth Compare Both Radials
5 Note How Close Carotids Are to Both The Skin of Neck And The Aorta Apex Beat = PMI
6 Note Relationship Between Nipple Line And PMI
7 GUESS WHERE You Should Place Your Hand To Begin Palpation Of The Chest? If The LV Is Enlarged What Happens To The PMI??? Duhhh Down And To The Left CORRECT!!!!
8 Guess What This Will Do To The PMI And If The Heart Is Also Dilated It Will Be Moved Down As Well You Guessed Right If You Said It Moved It To The LEFT
9 Where Will The PMI Be On A Patient With This Thick Dilated Heart!!! Yep Down And To The Left
10 Why Does This Happen??? Leak 3 Liters/Min. 5 Liters/Min. The LV Will Pump The Normal Cardiac Output Plus The Leak The LV Will Dilate And Again A Large Heart Same Thing Can Happen To Ao. Valve The LV Will Now Have To Pump 8 liters/min. How Does The LV Respond To This Volume Once Overload Again A Volume What Will Happen Overload To The PMI
11 A Vol. Over Load LV AI Or MR Normal Size LV BP120/80 LV With A Pressure Overload Such As HBP Or AS 210/?
12 Severe Pulmonic Stenosis What Will This Do To The PMI? Note The Marked Thickening Of Right Ventricular Myocardium STERNUM Correct!!!! If You Said It Will Move MEDIALLY
13 And RV Enlargement Is Up And Medial Near The Sternum Acute MI Would Be In Normal Position. (Not Enough Time For Change To Take Place) Sooooo LV Enlargement Is Down And Left
14 Caused By The Large Volume Of Blood Being Ejected Through The AV i.e. The Normal Forward Flow Plus The Regurgitant Volume Palpation Of Carotid Pulse Is Often Overlooked During Physical Exam Bounding Pulse Waterhammer Pulse Wide Pulse Pressure Corrigan s Pulse Aortic Stenosis Slow Upstroke Prolonged Pulse
15 Eliciting The Hepatojugular Reflux (A Sign Of Right Heart Failure Usually Following Left Heart Failure) Patient Must Be Relaxed Breathing Normally If Face Turns Red Patient Is Holding Their Breath Or Doing A Valsalva Either Of Which Results In Error Trunk Elevated 30 Degrees Firm Sustained Pressure On Abdomen While Observing Jugular Pulse This Causes Venous Pressure To Rise And Gives A False Positive With Right Heart Failure Or Constrictive Pericarditis The Jugular Pulse Level Rises
16 Start Your Exam From The Patient s Right So Your Stethoscope Tubing Will Be In A Straight Line To The Area You Are Use Reverse Listening Z To i.e.. Less Noise To Auscultate Banging All On The Patient Valve Areas And Less Resistance To Air Flow Auscultation Of The Neck In My Experience Is Commonly Overlooked Right Aortic Left Pulmonic Tricuspid Neath The Sternum The Mitral Gets The Apex Beat Here s How And I Was Taught Auscultation That s The When Way I We Was Learn A Student Em After Palpation Comes Auscultation
17 Right Carotid Arises From The Brachio- Cephalic Trunk Must Re- Emphasize Relationship Between Carotids And Aorta QUESTION? Which Carotid Might Transmit An Aortic Murmur The LOUDEST? AV Left Carotid Arises Directly From The Aorta Duhhhhhh
18 One Of The Most Commonly Missed Note They Have Parts Of The Physical Auscultated From Base Exam Is Auscultation To Angle Of Jaw Of The Neck Carotid Bruits Are High Pitched And I Feel Best Heard With The Diaphragm But As Long As You Auscultate The Carotids I Don t Care What Side Of The Stethoscope You Use So This Aortic One Stenosis Part Of Is The Transmitted To The Physical Exam Allows Evaluation Carotids As Both Well For Usually AS And Harsh Carotid And Stenosis Rumbling
19 Anterior Surface Pulmonic Valve Aortic Valve With This Anatomy In Mind Why Is It Logical To Listen To The Areas Just Described
20
21 Right 2 nd Intercostal Space Equals Aortic Listening Post Left 2 nd Intercostal Space Equals Pulmonic Listening Post AI Heard Along Left Sternal Border Remember The Aorta And The Pulmonary Artery Cross Each Other
22 Most Common Differentiation Between Murmurs Physicians Will Need To Make Is Between AS And MR Commonly These Patients Will Have PVC s And These Can Be Used To Differentiate Between These Two Murmurs
23 Beat Before PVC Beat After PVC Sinus Beat Sinus Beat PVC Sinus Beat Beat Before PVC Beat After PVC
24 PULSUS ALTERNANS (A Sign Of Heart Failure) When Taking B.P. Very Common In Cath Lab To Have Lower The Cuff You Pressure Can Take To High Low Alternation Of LV Systolic Level Where Advantage Korotkoff Of Sounds This Pressure In A Heart Failure Case First In A Heard Office Setting Less Forceful Alternate Beat Does Not Pass This Systolic Pressure Take Pulse At Wrist HR Will Be Half That Detected By Aulscultation Of Heart
25 How To Auscultate For Gallop Sounds You Do Need To Listen To The Heart However Raising The Legs Will Increase Return To Heart And Can Bring Out Both Gallops Or Murmurs You Can Also Exercise The Patient By Having Them Hop Up And On One Leg Or Do Sit ups
26 Aortic Insufficiency Is Difficult To Hear Best Heard With Patient Sitting Up Leaning Forward In Full Exhalation All This Brings Heart Closer To Chest Wall Use The Diaphragm In The 3 rd Or 4 th Left Intercostal Space
27 Another Position That Brings Heart Closer To Chest Wall Also Have Patient Exhale Then Examine During Exhalation Remember For AI Listen In 3 rd Or 4 th Intercostal Space Just Left Of Sternum Use The Diaphragm
28 The Murmur Of Mitral Stenosis Is Also Very Difficult To Hear Listen For This Murmur With The Bell Have Patient In Left Lateral Decubitus Position. Place Yourself On Their Right Side As Shown Start Auscultation Halfway Between The PMI And The Xiphoid Process Exercise Such As Sit-ups In Bed Can Bring Out This Murmur
29 IHSS Or Obstructive Cardiomyopathy Outflow Tract Obstruction Note The Obstruction Is Much Worse Soooo What Happens To The Murmur During Valsalva? Thickness Of Septum Is Fixed During Valsalva The LV Gets Smaller i.e. Less Volume
30 A Very Soft Systolic Murmur Could Be Heard At 4LSB No Pressure Gradient Aortic Pressure LV Pressure
31 Same Patient Pressures Measured During Valsalva Sooooo What Would Have Happened To The Loudness Of The Murmur??? Gradient During Valsalva Aortic Pressure LV Pressure
32 An Important Part Of The Physical Exam Of The Cardio-Vascular System That Is Commonly Overlooked Is? 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 1. Palpation Of The PMI Which Can Bring Out Findings Causing You To Suspect Mitral Stenosis. 2. Auscultation Of Left Sternal Border Which Can Help In The Diagnosis Of Tricuspid Regurgitation. 3. Auscultation Of The Neck Which Can Suggest Either Aortic Stenosis Or Carotid Stenosis. 4. Comparison Of Both Radial Pulses Which Can Suggest Ascending Aortic Aneurysm. 5. Checking For The Hepato-jugular Reflux Which Can Bring Out Signs Of Mitral Regurgitation. 10 Countdown
33 An Important Part Of The Physical ExamOf The Cardio- Vascular System That IsCommonly Overlooked Is? Palpation Of The PMI Which Can Bring Out Findings Causing You To Suspect Mitral Stenosis. 20% 20% Auscultation Of Left Sternal Border Which Can Help In The Diagnosis Of Tricuspid Regurgitation. 20% 20% Auscultation Of The Neck Which Can Suggest Either Aortic Stenosis Or Carotid Stenosis. 20% 20% Comparison Of Both Radial Pulses Which Can Suggest Ascending Aortic Aneurysm. 20% 20% Checking For The Hepato-jugular Reflux Which Can Bring Out Signs Of Mitral Regurgitation. 20% 20% First Slide Second Slide
34 The End Any Questions?
35 Post PVC Beat Greater Contractility Causes Increased Gradient Valsalva Results In Smaller LV Cavity But Septal Thickness Remains The Same Therefore More Obstructive And Murmur Increases
36 Important Bedside Tool To Differentiate AORTIC STENOSIS From MITRAL REGURGITATION
37
38
39
40 Remember!!! Aortic Insufficiency Causes Bounding Carotids And Wide Pulse Pressure One Of The Most Frequently Overlooked Portions Of The Physical Exam Of The HEART Is Palpation And Auscultation Of The Carotids
41
42
43
44 Remember Larger The LV Less Obstructive The Septum Smaller The LV More Obstructive
45 Had Holter While Driving A Motorcycle Down A Ohio Highway At Over 100 Miles Per Hour Showed Him To Be Going In And Out Of VT Note Thickening And Redundantancy Of The Mitral Valve Including Leaflets Cordae And Papillary Muscle
46 Decreased Blood Volume Allows The Mitral Valve Apparatus To Reach The Point Where It Suddenly Stops At An Earlier Time During Systole Therefore The Mid Systolic Click Occurs Earlier In Systole Increased Blood Volume Causes The Mitral Leaflets And Cordal Structures To Reach The Point Where They Suddenly Stop Later In Systole Therefore The Mid Systolic Click Occurs Later During Systole
47 Control Click Is Mid Systolic Standing Reduces Volume Return To Heart Mitral Structures Reach Their End Sooner Click Earlier Squat Increases Volume Return Mitral Structures Reach Their End Later Click Later
48 Hypokinetic Pulse ( Small, Weak) 1.Related To Decreased Rate Of Rise Of L.V. Press. 2.Related To Decreased Stroke Volume Of L.V. 3.Related To Obstruction To Outflow Of L.V.
49 And RV Enlargement Is Up And Medial Near The Sternum Acute MI Normal No Time For Change To Take Place Sooooo LV Enlargement Is Down And Left
50 Hyperkinetic ( Large, Strong; Waterhammer;Collapsing;Corrigan) 1.Related To Increased Rate Of L.V.Press.Development 2.Related To Large L.V. Stroke Volume With Decreased SVR 3.Pulse Press. May Be Increased (AI Or PDA) Or Normal (IHSS,MR)
51 Anacrotic Pulse( Twice Beating Type) 1. Produced By An Anacrotic (Upslope) Shoulder Or Halt On Ascending Limb Of Arterial Pulse 2. Only Rarely Appreciated On Physical Exam When Present Best Felt In Carotid 3.Very Frequently Recorded Especially In Aortic Stenosis
52 Pulsus Parvus et Tardus 1. Pulse With Slow Rate Of Press. Increase 2. A Small Pulse Pressure 3.A Late Systolic Peak 4.A Slow Collapse 5. Frequently Associated With AS ( Discrete Obstruction To L.V.)
53
54
55 Physical Exam Of The Heart And Special Maneuvers James G. Laws D.O. MACOI
56 Bisferiens Pulse 1. Twice Beating Pulse Produced By Two Palpable Pulse Waves In Systole 2. Two Waves That Are Exaggerations Of Waves That Can Be Recorded 3. These Two Waves Are Referred To As Percussion Wave And Tidal Wave Best Felt In Carotid Two Systolic Pulses Dicrotic Notch Pulse Of IHSS
57 Dicrotic Pulse 1. A Type Of Twice Beating Pulse Or Double Pulse 2. Combination Of Systolic Pulse Wave Followed By A Palpable Dicrotic Wave 3. This Is Distinct From Two Systolic Peaks i.e. Bisferiends Pulse 4. Classically Found In Sever Cardiac Failure, Hypovolemic Shock, or Cardiac Tamponade Systolic Pulse Dicrotic Notch Diastolic Pulse
58
59
60 This Will Bring Heart Closer To Wall
61 Increased Intrathoracic Pressure Decreases Return Of Blood To Heart Less Blood In LV Decreases Murmurs Of MR And AS But!!!!! Decreased Blood In LV Causes Thick Septum To Be More Obstructive
62 Pulsus Paradoxus 1. Abnormal Exaggeration Of Normal Decrease Of Systolic BP During Inspiration 2. Frequently Associated With Abnormal Decrease In Filling Of L.V. During Inspiration 3. Causes Include Compression Of Myocardium ( Pericardial Tamponade ) Or Decrease Lung Compliance
63 Bigeminal Pulse ( Bigeminy ) 1. Regular Coupling Of Two Beats With Interval Between Pair Greater Than Interval Between Coupled Beats 2. Second Beat Usually A Premature Beat 3. Other Mechanisms Occur i.e. 3:2 Wenckebach And Non Conducted Premature Atrial Beat
64
65 Less Blood Click Earlier More Blood Click Later Less Blood lick Earlier More Blood Click Later Control Midsystole
66
67
68 Second: Palpate Both Carotid and Femoral Pulses First: Check PMI Third: Auscultate Both The Carotid And Femoral Areas Compare Both Radial Pulses
69 Increase Return To Heart Can Increase Gallop Sounds You Do need To have Your Stethoscope On The Patients Chest However
70 This Allows Stethoscope Tubing To Be Straight And Does Not Make Contact With Patient Or Bedding Always Begin Exam On Right Side Of The Patient Remember The Shorter The Tubing Of The Stethoscope The Less Distance The Sound Waves Have To Travel
71 Patients In Bed can roll onto Abdomen And Prop Up On Elbows Place Stethoscope Under Them Against Their Chest 4LSB
72 Note: Very Common In Cath Lab To Have Alternating High Low Systolic BP Of LV Pressure Curve In Patients With Heart Failure
73
74 Thickness Of Septum Is Fixed Therefore When LV IS Smaller Then Relative Obstruction Is Greater
75 If Face Turns Red Probably Holding Breath
76 Increased Return To Right Heart Prolongs RV Systole Delaying Closure Of Pulmonic Valve Increased Capacitance Of Pulmonary Vasculature Causes Slower Rate Of Flow Into The Pulmonary Artery System Also Delaying Closure Of Pulmonary Valve
77
78 Redundant Tissue Of Mitral Valve Apparatus Leads To Prolapse
79 Murmur Unchanged Murmur Increased In The Post PVC Beat
80
81
82 Anacrotic: Displaying Anacrotisim- Anacrotic Limb =The Up- Stroke Of The Pressure Pulse. Anacrotism = An Irregularity Of The Ascending Curve Of The Pressure Pulse
83 In December I Laid A common Field Gate On The Ground, On Which A White Mare Was Cast On Her Side, And In That Position Bound fast To The Gate. Then Laying Bare The Left Carotid Artery, I Fixed To It Towards The Heart The Brass Pipe And To That The Wind Pipe Of A Goose; To The Other End Of Which A Glass Tube Was Fixed Which Was Twelve Feet Nine Inches Long. The Blood Rose In The Tube In The same manner As In The Case Of The Two Former Horses, Till It Reached To Nine Feet Six Inches Height Experiment III From STATICAL ESSAYS 1733 By The Rev. Stephen Hales
CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ
 CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ 1. Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What
CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ 1. Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly
 Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Physical Exam Part II
 Physical Exam Part II University of Michigan Cardiovascular Center Kim A. Eagle, MD Albion Walter Hewlett Professor Director Physical Exam: Part II Heart Sounds Heart Murmurs HEART SOUNDS S1 MITRAL + TRICUSPID
Physical Exam Part II University of Michigan Cardiovascular Center Kim A. Eagle, MD Albion Walter Hewlett Professor Director Physical Exam: Part II Heart Sounds Heart Murmurs HEART SOUNDS S1 MITRAL + TRICUSPID
2. The heart sounds are produced by a summed series of mechanical events, as follows:
 Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Heart sounds and murmurs. Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct
 Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
Leicester Medical School
 Leicester Medical School THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Overview The cardiovascular examination should include the following: - General inspection from the end of the bed. - General examination
Leicester Medical School THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Overview The cardiovascular examination should include the following: - General inspection from the end of the bed. - General examination
SMALL GROUP SESSION 19 January 30 th or February 1st. Groups 1-12: Cardiac Case and Cardiac Exam Workshop
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 19 January 30 th or February 1st Groups 1-12: Cardiac Case and Cardiac Exam Workshop Readings: Complete the cardiac examination tutorial on the POM1 web site. Optional: http://medicine.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/heart.htm
SMALL GROUP SESSION 19 January 30 th or February 1st Groups 1-12: Cardiac Case and Cardiac Exam Workshop Readings: Complete the cardiac examination tutorial on the POM1 web site. Optional: http://medicine.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/heart.htm
Murmur Sounds made by turbulence in the heart or blood stream. 1. Timing. 5. Intensity 2. Shape. 6. Pitch 3. Location of maximum intensity
 Definition Items in description of Timing Shape Location of maximum intensity Murmur Sounds made by turbulence in the heart or blood stream. 1. Timing 5. Intensity 2. Shape 6. Pitch 3. Location of maximum
Definition Items in description of Timing Shape Location of maximum intensity Murmur Sounds made by turbulence in the heart or blood stream. 1. Timing 5. Intensity 2. Shape 6. Pitch 3. Location of maximum
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY LECTURE 4 Cardiac cycle Polygram - analysis of cardiac activity Ana-Maria Zagrean MD, PhD The Cardiac Cycle - definitions: the sequence of electrical and mechanical events that
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY LECTURE 4 Cardiac cycle Polygram - analysis of cardiac activity Ana-Maria Zagrean MD, PhD The Cardiac Cycle - definitions: the sequence of electrical and mechanical events that
Cardiac Examination. Pediatrics Clinical Examination
 Pediatrics Clinical Examination Symptoms of Cardiovascular Affection: Cardiac Examination 1. Perinatal history: Maternal DM, cyanosis, respiratory distress 2. Symptoms of lung congestion: Poor interrupted
Pediatrics Clinical Examination Symptoms of Cardiovascular Affection: Cardiac Examination 1. Perinatal history: Maternal DM, cyanosis, respiratory distress 2. Symptoms of lung congestion: Poor interrupted
How to Examine the Cardiovascular System The Essentials
 How to Examine the Cardiovascular System The Essentials Joel Niznick MD FRCPC Learning Objectives Explain a basic approach Demonstrate how to take to the physical an office blood pressure as examination
How to Examine the Cardiovascular System The Essentials Joel Niznick MD FRCPC Learning Objectives Explain a basic approach Demonstrate how to take to the physical an office blood pressure as examination
Cardiac Cycle MCQ. Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology. Cairo University 2007
 Cardiac Cycle MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Regarding the length of systole and diastole: a- At heart rate 75 b/min, the duration of
Cardiac Cycle MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Regarding the length of systole and diastole: a- At heart rate 75 b/min, the duration of
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Chapter 8 1 Cardiovascular System Functions: pump saturated oxygenated blood into arterial system cells pump desaturated deoxygenated blood to lungs via veins for reoxygenation Heart
Cardiovascular System Chapter 8 1 Cardiovascular System Functions: pump saturated oxygenated blood into arterial system cells pump desaturated deoxygenated blood to lungs via veins for reoxygenation Heart
See below for descriptions of the waveform
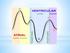 The internal jugular vein (IJV) connects to the right atrium without any intervening valves. The pulsation of the right atrium therefore causes the column of blood in the IJV to rise and fall this is called
The internal jugular vein (IJV) connects to the right atrium without any intervening valves. The pulsation of the right atrium therefore causes the column of blood in the IJV to rise and fall this is called
1. how a careful cardiovascular evaluation can accurately assess pathology and physiology at the bedside, and
 This program will demonstrate: 1. how a careful cardiovascular evaluation can accurately assess pathology and physiology at the bedside, and 2. the importance of integrating this information with selected
This program will demonstrate: 1. how a careful cardiovascular evaluation can accurately assess pathology and physiology at the bedside, and 2. the importance of integrating this information with selected
Abdominal Examination Benchmarks
 Abdominal Examination Benchmarks Preparation and Positioning: Stand on the right side of the patient. The patient should be supine and double draped so only the abdomen is exposed o To relax the abdominal
Abdominal Examination Benchmarks Preparation and Positioning: Stand on the right side of the patient. The patient should be supine and double draped so only the abdomen is exposed o To relax the abdominal
Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations
 ighapmlre33apg269_274 5/12/04 3:10 PM Page 269 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise
ighapmlre33apg269_274 5/12/04 3:10 PM Page 269 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise
Hemodynamic Monitoring
 Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D.
 The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm!
 Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
#6 - Cardiovascular III Heart Sounds, Pulse Rate, Hemoglobin Saturation, and Blood Pressure
 #6 - Cardiovascular III Heart Sounds, Pulse Rate, Hemoglobin Saturation, and Blood Pressure Objectives: Observe slide of artery and vein cross-section Auscultate heart sounds using a stethoscope Measure
#6 - Cardiovascular III Heart Sounds, Pulse Rate, Hemoglobin Saturation, and Blood Pressure Objectives: Observe slide of artery and vein cross-section Auscultate heart sounds using a stethoscope Measure
HEALTH ASSESSMENT. Afnan Tunsi BSN, RN, MSc.
 HEALTH ASSESSMENT Afnan Tunsi BSN, RN, MSc. Learning Outcomes 2 After completion of this lecture, the student will be able to: Describe suggested sequencing to conduct a thorax and lungs physical health
HEALTH ASSESSMENT Afnan Tunsi BSN, RN, MSc. Learning Outcomes 2 After completion of this lecture, the student will be able to: Describe suggested sequencing to conduct a thorax and lungs physical health
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
What s That Sound? Pediatric Murmur Evaluation
 What s That Sound? Pediatric Murmur Evaluation Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director, Pediatric
What s That Sound? Pediatric Murmur Evaluation Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director, Pediatric
SMALL GROUP SESSION 18A January 17th or January 19th. Groups 1-12: VS and Chest Exam and Harvey Stethophone Session
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 18A January 17th or January 19th Groups 1-12: VS and Chest Exam and Harvey Stethophone Session Readings: Complete the cardiac examination web module. Mosby s Physical Examination, 4
SMALL GROUP SESSION 18A January 17th or January 19th Groups 1-12: VS and Chest Exam and Harvey Stethophone Session Readings: Complete the cardiac examination web module. Mosby s Physical Examination, 4
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
PART I: HEART ANATOMY
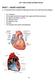 Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
PPE Findings That Require Further Cardiac Evaluation
 PPE Findings That Require Further Cardiac Evaluation Jaron Santelli, MD University of Maryland Assistant Professor, Team Physician Primary Care Sports Medicine and Emergency Medicine Department of Orthopaedics
PPE Findings That Require Further Cardiac Evaluation Jaron Santelli, MD University of Maryland Assistant Professor, Team Physician Primary Care Sports Medicine and Emergency Medicine Department of Orthopaedics
Physiology of the Heart Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
 Physiology of the Heart 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Physiology of the Heart State Standards 35) Outline the structure and functions of the anatomy of the cardiovascular system,
Physiology of the Heart 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Physiology of the Heart State Standards 35) Outline the structure and functions of the anatomy of the cardiovascular system,
HISTORY. Question: What type of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance.
 HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
Chapter 14. Circulatory System Images. VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II
 Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Congenital heart disease. By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics
 Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
8/31/2016. Mitraclip in Matthew Johnson, MD
 Mitraclip in 2016 Matthew Johnson, MD 1 Abnormal Valve Function Valve Stenosis Obstruction to valve flow during that phase of the cardiac cycle when the valve is normally open. Hemodynamic hallmark - pressure
Mitraclip in 2016 Matthew Johnson, MD 1 Abnormal Valve Function Valve Stenosis Obstruction to valve flow during that phase of the cardiac cycle when the valve is normally open. Hemodynamic hallmark - pressure
M-Mode Echocardiography Is it still Alive? Itzhak Kronzon, MD,FASE. Sampling Rate M-Mode: 1800 / sec 2D: 30 / sec
 M-Mode Echocardiography Is it still Alive? Itzhak Kronzon, MD,FASE Honoraria: Philips Classical M-mode Echocardiography M-Mode offers better time and image resolution. Sampling Rate M-Mode: 1800 / sec
M-Mode Echocardiography Is it still Alive? Itzhak Kronzon, MD,FASE Honoraria: Philips Classical M-mode Echocardiography M-Mode offers better time and image resolution. Sampling Rate M-Mode: 1800 / sec
cardiac vascular mediastinal Causes airway chest pain wall determine Character Dyspnoea palpitation
 Written by: Mohammad Al Marhoon Dr.Marhoon@gmail.com Reference: Clinical Examination (Talley) Major Symptoms chest pain Causes determine Character cardiac vascular mediastinal ischemia MI Pleuropericardial
Written by: Mohammad Al Marhoon Dr.Marhoon@gmail.com Reference: Clinical Examination (Talley) Major Symptoms chest pain Causes determine Character cardiac vascular mediastinal ischemia MI Pleuropericardial
PEDIATRIC HEART MURMURS. Manish Bansal, MD Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Cardiology University of Iowa
 PEDIATRIC HEART MURMURS Manish Bansal, MD Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Cardiology University of Iowa Murmur murmur. (n.d.). Dictionary.com Unabridged. Retrieved March 9, 2018 from
PEDIATRIC HEART MURMURS Manish Bansal, MD Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Cardiology University of Iowa Murmur murmur. (n.d.). Dictionary.com Unabridged. Retrieved March 9, 2018 from
Miscellaneous Cardiology Topics pregnancy - congenital - myocarditis - pericardial disease. Pregnancy and Cardiovascular Disease MCQ
 Miscellaneous Cardiology Topics pregnancy - congenital - myocarditis - pericardial disease Maan Jokhadar, MD, FACC Emory Center for Advanced Heart Failure Therapy Emory Adult Congenital Heart Center Pregnancy
Miscellaneous Cardiology Topics pregnancy - congenital - myocarditis - pericardial disease Maan Jokhadar, MD, FACC Emory Center for Advanced Heart Failure Therapy Emory Adult Congenital Heart Center Pregnancy
PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG)
 PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG) The technique of listening to sounds produced by the organs and vessels of the body is called auscultation. The areas at which the heart sounds are heard better are called auscultation
PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG) The technique of listening to sounds produced by the organs and vessels of the body is called auscultation. The areas at which the heart sounds are heard better are called auscultation
Heart and Neck Vessels
 CHAPTER 12 Heart and Neck Vessels ANATOMY The precordium is the area on the anterior chest overlying the heart and great vessels. The heart extends from the second to the fifth intercostal space, and from
CHAPTER 12 Heart and Neck Vessels ANATOMY The precordium is the area on the anterior chest overlying the heart and great vessels. The heart extends from the second to the fifth intercostal space, and from
Pathological Arrhythmias/ Tachyarrhythmias
 Pathological Arrhythmias/ Tachyarrhythmias caused by: 1.Ectopic focus: Extrasystole or premature beat. If discharge is occasional. Can be: Atrial Extrasystole Vevtricular Extrasystole 2.Cardiac Arrhythmia
Pathological Arrhythmias/ Tachyarrhythmias caused by: 1.Ectopic focus: Extrasystole or premature beat. If discharge is occasional. Can be: Atrial Extrasystole Vevtricular Extrasystole 2.Cardiac Arrhythmia
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
Cardiology. the Sounds: #7 HCM. LV Outflow Obstruction: Aortic Stenosis. (Coming Soon - HCM)
 A Cardiology HCM LV Outflow Obstruction: Aortic Stenosis (Coming Soon - HCM) the Sounds: #7 Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com E-mail: Howard@12daysinmarch.com Aortic Valve Disorders Stenosis Regurgitation
A Cardiology HCM LV Outflow Obstruction: Aortic Stenosis (Coming Soon - HCM) the Sounds: #7 Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com E-mail: Howard@12daysinmarch.com Aortic Valve Disorders Stenosis Regurgitation
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Notes by Sandra Dankwa 2009 HF- Heart Failure DS- Down Syndrome IE- Infective Endocarditis ET- Exercise Tolerance. Small VSD Symptoms -asymptomatic
 Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection
 AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection Project 1 - BLOOD Supply to the Myocardium (Figs. 18.5 &18.10) The myocardium is not nourished by the blood while it is being pumped through the
AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection Project 1 - BLOOD Supply to the Myocardium (Figs. 18.5 &18.10) The myocardium is not nourished by the blood while it is being pumped through the
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
DOWNLOAD PDF HURSTS THE HEART, UPDATE I
 Chapter 1 : Hurstâ s the Heart, 14th Edition (PDF) â ebooks Library [PDF]Free Hursts The Heart Update 1 download Book Hursts The Heart Update blog.quintoapp.com FREE DOWNLOAD** HURSTS THE HEART UPDATE
Chapter 1 : Hurstâ s the Heart, 14th Edition (PDF) â ebooks Library [PDF]Free Hursts The Heart Update 1 download Book Hursts The Heart Update blog.quintoapp.com FREE DOWNLOAD** HURSTS THE HEART UPDATE
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Heart 2
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso
 2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
SAMPLE HLTEN610A. TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank. Practise in the cardiovascular nursing environment
 TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank HLTEN610A Practise in the cardiovascular nursing environment Version 1.0 Flexible Learner Resource Product Code: ISO 9001 HLTEN610A
TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank HLTEN610A Practise in the cardiovascular nursing environment Version 1.0 Flexible Learner Resource Product Code: ISO 9001 HLTEN610A
Tracheal normal sound heard over trachea loud tubular quality high-pitched expiration equal to or slightly longer than inspiration
 = listening for sounds produced in the body over chest to ID normal & abnormal lung sounds all BS made by turbulent flow in the airways useful in making initial D & evaluating effects of R 4 characteristics
= listening for sounds produced in the body over chest to ID normal & abnormal lung sounds all BS made by turbulent flow in the airways useful in making initial D & evaluating effects of R 4 characteristics
The Heart and Cardiovascular System
 The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
Are you too quick to refer?
 HEART MURMURS IN CHILDREN Are you too quick to refer? Many children with murmurs are unnecessarily referred, say the authors, who describe a thorough cardiovascular exam you can perform in three to five
HEART MURMURS IN CHILDREN Are you too quick to refer? Many children with murmurs are unnecessarily referred, say the authors, who describe a thorough cardiovascular exam you can perform in three to five
Case 2 Dwayne A. Williams CASE 2
 CASE 2 A 40- year- old male with no past medical history presents with bilateral flank pain and dark colored urine for 5 days. During family history taking, he states his father died from kidney failure
CASE 2 A 40- year- old male with no past medical history presents with bilateral flank pain and dark colored urine for 5 days. During family history taking, he states his father died from kidney failure
Skin supplied by T1-4 (medial upper arm and neck) T5-9- epigastrium Visceral afferents from skin and heart are the same dorsal root ganglio
 Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Do Now. Get out work from last class to be checked
 Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Congestive Heart Failure Patient Profile. Patient Identity - Mr. Douglas - 72 year old man - No drugs, smokes, moderate social alcohol consumption
 Congestive Heart Failure Patient Profile Patient Identity - Mr. Douglas - 72 year old man - No drugs, smokes, moderate social alcohol consumption Chief Complaint - SOB - When asked: Increasing difficulty
Congestive Heart Failure Patient Profile Patient Identity - Mr. Douglas - 72 year old man - No drugs, smokes, moderate social alcohol consumption Chief Complaint - SOB - When asked: Increasing difficulty
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery. George L. Hicks, Jr., MD
 TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
The Jugular Venous Pressure and Pulse Contour
 19 The Jugular Venous Pressure and Pulse Contour MARK M. APPLEFELD Definition Information that can be derived from an assessment of the jugular venous pulse includes determination of the mean venous pressure,
19 The Jugular Venous Pressure and Pulse Contour MARK M. APPLEFELD Definition Information that can be derived from an assessment of the jugular venous pulse includes determination of the mean venous pressure,
Pocket Companion. Australian Adapting Editors. Clare Cole Olivia Hill Rosemary Saunders
 Pocket Companion Australian and New Zealand edition Australian Adapting Editors Clare Cole Olivia Hill Rosemary Saunders Contents About the author/s (TBC) 0 Preface 0 Acknowledgments 0 Chapter 1 The health
Pocket Companion Australian and New Zealand edition Australian Adapting Editors Clare Cole Olivia Hill Rosemary Saunders Contents About the author/s (TBC) 0 Preface 0 Acknowledgments 0 Chapter 1 The health
Heart Valve disease: MR. AS tough patient When to echo, When to refer, What s new
 Heart Valve disease: MR. AS tough patient When to echo, When to refer, What s new B. Sonnenberg UAH Cardiology CME Day 5 May 2015 Disclosures Speaker s or Advisory Boards: none Research grants: none (co-investigator
Heart Valve disease: MR. AS tough patient When to echo, When to refer, What s new B. Sonnenberg UAH Cardiology CME Day 5 May 2015 Disclosures Speaker s or Advisory Boards: none Research grants: none (co-investigator
Coronary Anomalies & Hemodynamic Identification
 Coronary Anomalies & Hemodynamic Identification David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 May 2, 2006 Anomaly #1 Anomaly #2 Anomaly #3 Figure 18-27 Anomalous origin of the left circumflex artery.
Coronary Anomalies & Hemodynamic Identification David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 May 2, 2006 Anomaly #1 Anomaly #2 Anomaly #3 Figure 18-27 Anomalous origin of the left circumflex artery.
Heart Anatomy. 7/5/02 Stephen G Davenport 1
 Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009
 Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
Valvular Heart Disease. Dr. HANAN ALBACKR
 Valvular Heart Disease Dr. HANAN ALBACKR Valvular Heart Disease Format for this lecture IMPORTANT CLINICAL INFO know for boards, tests and clinical practice Spectrum of VHD Aortic Valve Mitral Valve Tricuspid
Valvular Heart Disease Dr. HANAN ALBACKR Valvular Heart Disease Format for this lecture IMPORTANT CLINICAL INFO know for boards, tests and clinical practice Spectrum of VHD Aortic Valve Mitral Valve Tricuspid
Chest Pain in Children and Adolescents What an EMS Needs to Know. Frank C. Smith, M.D. Pediatric Cardiology Associates
 Chest Pain in Children and Adolescents What an EMS Needs to Know Frank C. Smith, M.D. Pediatric Cardiology Associates Chest Pain in Children and Adolescents Common in children (10-15%) Non-cardiac causes
Chest Pain in Children and Adolescents What an EMS Needs to Know Frank C. Smith, M.D. Pediatric Cardiology Associates Chest Pain in Children and Adolescents Common in children (10-15%) Non-cardiac causes
Atrial Fibrillaton. Key: RA: right atrium RV: right ventricle PA: pulmonic artery LA: left atrium LV: left ventricle AO: aorta
 Atrial Fibrillaton How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Atrial Fibrillaton How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
LAB: Blood Pressure Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System!
 LAB: Blood Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System! Lab Objectives. At the completion of the lab, you should be able to: measure pulse or heart rate (HR) and respiratory rate (RR);
LAB: Blood Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System! Lab Objectives. At the completion of the lab, you should be able to: measure pulse or heart rate (HR) and respiratory rate (RR);
Mitral Valve Disease. Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna
 Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
Heart Failure with Johnny Crash: LEFT VENTRICULAR EJECTION FRACTION (LVEF) SYMPTOMATOLOGY: Assess VENTRICULAR DYSFUNCTION HEART FAILURE:
 Heart Failure with Johnny Crash: Joan E. King, PhD, ACNP-BC, ANP-BC Melissa Smith, DNP, ANP-BC Vanderbilt University School of Nursing HEART FAILURE: Heart Failure (HF): a complex clinical syndrome resulting
Heart Failure with Johnny Crash: Joan E. King, PhD, ACNP-BC, ANP-BC Melissa Smith, DNP, ANP-BC Vanderbilt University School of Nursing HEART FAILURE: Heart Failure (HF): a complex clinical syndrome resulting
12 Lead ECG Interpretation
 12 Lead ECG Interpretation Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CNS, CCRN Significant increase in mortality for every 15 minutes of delay! N Engl J Med 2007;357:1631-1638 Who should get a 12-lead ECG? Also include
12 Lead ECG Interpretation Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CNS, CCRN Significant increase in mortality for every 15 minutes of delay! N Engl J Med 2007;357:1631-1638 Who should get a 12-lead ECG? Also include
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
OUTPUT IN CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE
 TRICUSPID INCOMPETENCE AND RIGHT VENTRICULAR OUTPUT IN CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE BY PAUL KORNER* AND JOHN SHILLINGFORDt From the Department of Medicine, Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Received
TRICUSPID INCOMPETENCE AND RIGHT VENTRICULAR OUTPUT IN CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE BY PAUL KORNER* AND JOHN SHILLINGFORDt From the Department of Medicine, Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Received
CARDIAC CYCLE CONTENTS. Divisions of cardiac cycle 11/13/13. Definition. Badri Paudel GMC
 CARDIAC CYCLE Badri Paudel GMC CONTENTS Ø DEFINATION Ø DIVISION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUB DIVISION AND DURATION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SYSTOLE Ø DIASTOLE Ø DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUMMARY Ø ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
CARDIAC CYCLE Badri Paudel GMC CONTENTS Ø DEFINATION Ø DIVISION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUB DIVISION AND DURATION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SYSTOLE Ø DIASTOLE Ø DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUMMARY Ø ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Case # 1. Page: 8. DUKE: Adams
 Case # 1 Page: 8 1. The cardiac output in this patient is reduced because of: O a) tamponade physiology O b) restrictive physiology O c) coronary artery disease O d) left bundle branch block Page: 8 1.
Case # 1 Page: 8 1. The cardiac output in this patient is reduced because of: O a) tamponade physiology O b) restrictive physiology O c) coronary artery disease O d) left bundle branch block Page: 8 1.
Valvular Heart Disease
 Valvular Heart Disease MITRAL STENOSIS Pathophysiology rheumatic fever. calcific degeneration, malignant carcinoid disease, congenital mitral stenosis. SLE. The increased pressure gradient across the mitral
Valvular Heart Disease MITRAL STENOSIS Pathophysiology rheumatic fever. calcific degeneration, malignant carcinoid disease, congenital mitral stenosis. SLE. The increased pressure gradient across the mitral
Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects
 Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director,
Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director,
What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should.
 What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should. How Do Heart Valves Work? MAINTAIN ONE-WAY BLOOD FLOW THROUGH YOUR HEART The four heart
What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should. How Do Heart Valves Work? MAINTAIN ONE-WAY BLOOD FLOW THROUGH YOUR HEART The four heart
CATCH A WAVE.. INTRODUCTION NONINVASIVE HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING 4/12/2018
 WAVES CATCH A WAVE.. W I S C O N S I N P A R A M E D I C S E M I N A R A P R I L 2 0 1 8 K E R I W Y D N E R K R A U S E R N, C C R N, E M T - P Have you considered that if you don't make waves, nobody
WAVES CATCH A WAVE.. W I S C O N S I N P A R A M E D I C S E M I N A R A P R I L 2 0 1 8 K E R I W Y D N E R K R A U S E R N, C C R N, E M T - P Have you considered that if you don't make waves, nobody
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
NTI 2010 Boot Camp. Paradigm Shift. Hemodynamics: Cardiac Output. Basic Hemodynamic Formula
 Cardiovascular Assessment and Hemodynamic Principles NTI 2010 Boot Camp Hemodynamics does not equal invasive monitoring Paradigm Shift Karen Marzlin MSN, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC Cardiovascular Nursing Education
Cardiovascular Assessment and Hemodynamic Principles NTI 2010 Boot Camp Hemodynamics does not equal invasive monitoring Paradigm Shift Karen Marzlin MSN, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC Cardiovascular Nursing Education
CongHeartDis.doc. Андрій Миколайович Лобода
 CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Disclosures. Cardiac Ultrasound. Introductory Case. 80 y/o male Syncope at home Emesis x 3 in ambulance Looks sick. No pain.
 Disclosures Cardiac Ultrasound Justin A Davis, MD MPH RDMS Subchief for Emergency Ultrasound Kaiser Permanente East Bay Medical Center I have nothing to disclose. Introductory Case HR 118 BP 65/43 RR 27
Disclosures Cardiac Ultrasound Justin A Davis, MD MPH RDMS Subchief for Emergency Ultrasound Kaiser Permanente East Bay Medical Center I have nothing to disclose. Introductory Case HR 118 BP 65/43 RR 27
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Heart Failure Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor internal medicin dept
 Heart Failure Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor internal medicin dept (MBBS)(SBMD) Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology diastolic/systolic Risk factors Signs and symptoms Classification of HF
Heart Failure Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor internal medicin dept (MBBS)(SBMD) Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology diastolic/systolic Risk factors Signs and symptoms Classification of HF
Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO)
 Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) Dr. Siân Jaggar Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Brompton Hospital London UK Congenital Cardiac Services
Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) Dr. Siân Jaggar Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Brompton Hospital London UK Congenital Cardiac Services
Cardiovascular Patient Assessment. Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
 Cardiovascular Patient Assessment Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Objectives Outline a systematic approach to cardiovascular assessment. Differentiate normal from abnormal findings when assessing
Cardiovascular Patient Assessment Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Objectives Outline a systematic approach to cardiovascular assessment. Differentiate normal from abnormal findings when assessing
