CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ
|
|
|
- Kristian Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ 1. Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What is his right atrial pressure? Why might he be short of breath? 2. Which point on the jugular venous pulse occurs near the beginning of diastole? a. The A wave b. The C wave c. The x descent d. The V wave e. The y descent 3. Systole starts: a. At S1 b. At S2 c. At the highest point of the jugular venous pulse d. At the lowest point of the jugular venous pulse 4. S1 is loudest at the: a. Right upper sternal border b. Left upper sternal border c. Left lower sternal border d. Apex 5. S2: 6. S4: a. Is loudest at the apex b. May be normally split in both inspiration and expiration c. Splits audibly at the left lower sternal border d. Consists of aortic followed in inspiration by pulmonic closure a. Usually comes shortly after S3 b. Is not unusual in healthy young athletes c. Often is caused by reduced ventricular elasticity d. Is intermittent in atrial fibrillation, when the atria don t contract 7. Your patient has a loud murmur at the left lower sternal border. Your hand on her parasternal area feels no vibration. This murmur is: a. I/VI b. II/VI c. III/VI d. IV/VI 8. Innocent murmurs: a. Often occur at the right sternal border b. Occasionally occur in diastole c. Are accompanied by inspiratory splitting of S2 d. May be accompanied by a palpable thrill 9. Which finding makes aortic stenosis least likely? a. Delayed rise of upstroke of carotid pulse b. Late peaking intensity of murmur c. Quiet S2 d. Failure of murmur to radiate to the right carotid
2 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE HEART Objectives: By the end of this session, you will be able to: 1. Recognize the elements and significance of the jugular venous pulse. 2. Understand and hear S1 and S2. 3. Know the physiology and sound of S3 and S4. 4. Identify systole and diastole by palpation and listening 5. Be able to describe heart murmurs. 5. Hear and understand the mechanism of three common systolic murmurs. 1. JUGULAR VENOUS PULSE (JVP): What: Visible pressure changes in the right atrium. ACxVy A: Atria contract; blood flows back briefly into the vena cava C: Closure of tricuspid valve stops forward flow of blood x: Downslope as atria begin to fill V: Volume of atria increases with filling, increasing pressure in vena cava y: Downslope as tricuspid valve opens and ventricles begin to fill Where: near (superficial JV) and under (deep JV) the sternocleidomastoid muscle How: patient at 30 to 45 degrees; measure cm. above sternal angle (angle of Louis). Sternal angle is 5 cm above right atrium; height of JVP above sternal angle plus 5 equals right atrial pressure. Normal RA pressure: 5-10 cm H20. Why: 1. Diagnose heart failure or fluid overload. Either will elevate RA pressure and thus raise JVP. Abdominojugular reflux (also called hepatojugular reflux - HJR): pressure on epigastrium briefly increases JVP. Accentuated in right heart failure. 2. Diagnose complete heart block or AV dissociation: atria and ventricles beat independently, RA often contracts against closed tricuspid valve, causing cannon A waves. 2. PALPATION 1. Location of heart: Right ventricle: anterior Left ventricle: left heart border/apex/posterior Right atrium: right heart border Left atrium: posterior
3 2. PMI - Point of Maximum Impulse What: palpable contraction of left ventricle (LV) during systole Location: around 5 th intercostal space in midclavicular line; lower and more medial in slender patients or patients with emphysema Size: one interspace; approximately dime-size Duration: brief (longer is sustained ) Intensity: not strong (if intense, a lift or heave ) Not always palpable: about 75% of people have palpable PMI 3.Palpation of parasternal area and base: Lifts: in parasternal area (left sternal border) may mean right ventricular hypertrophy (thickening) Thrills: palpable heart murmur (murmurs are graded I/VI to VI/VI; thrill = IV/VI) 3. AUSCULTATION: (listening) How: Use both bell (low pitched sounds such as S3 and S4 gallops) and diaphragm (high pitched sounds, including S1, S2 and most murmurs). LIGHT touch with bell. Where: at least four locations (valve areas): Aortic or RSB: right 2nd intercostal space (just under and right of angle of Louis) Pulmonic or LUSB: left second intercostal space, just left of sternum Tricuspid or LLSB: left fourth intercostal space Mitral or Apex: 5 th intercostal space in midclavicular line Optional: left 3 rd intercostal space Location notes: 1. Valves are not always noisiest in their assigned areas 2. Loud murmurs may be in several areas and difficult to localize 3. Named area is direction of flow, not location of valve What: What makes noises in the heart? Valves closing: Atrioventricular (S1) and semilunar (S2) valves Blood striking left ventricle: S3 and S4 (these are audible thus only at apex=lv) Increased flow across normal valves Turbulence through abnormal valve
4 Sounds: lub-dub = S1-S2 S1: Mitral and tricuspid (atrioventricular or AV) valves closing Loudest at apex Usually single S2: Aortic and pulmonic valves (semilunar) closing Loudest at base (top of heart is base) Usually splits with inspiration; this is audible only in pulmonic area Combines sounds of closing Aortic (A2) and Pulmonic (P2) valves Aortic is louder; can distinguish Pulmonic (P2) at LUSB - its area Pulmonic closes later than aortic in inspiration - thus split then Abnormal conduction can cause fixed split (never closes) or paradoxic split (expiratory split, closes with inspiration) Rhythm: should be regular, but often normal sinus arrhythmia: slower in expiration A few sounds that are often abnormal (but may be heard in healthy people): S3 and S4: sounds of blood striking the left ventricle (thus heard at the apex). Both occur in diastole. S3: Rapid ventricular filling just after aortic valve closes and mitral valve opens, i.e. just after S2 ; low pitched (hear with bell) May be a sign of a flaccid ventricle, e.g. congestive heart failure May be heard in healthy athletic young people Sound: Sloshing-in or It s-floppy S4: Atrial contraction fills ventricle rapidly just before mitral valve closes, i.e. just before S1 ; low pitched (hear with bell) Heard if left ventricle is stiff: from high blood pressure, heart attack, etc. Sound: a-stiff-wall
5 HEART MURMURS Murmurs: What they are: Turbulence caused by -- increased flow across normal valves: pregnancy, innocent murmur -- turbulent flow through abnormal valves: tight valve (stenosis) or leaky valve (regurgitation or insufficiency) Murmurs: How to describe them Timing: Systolic: Between S1 and S2 If unsure: check carotid pulse and/or palpate PMI. Both of these occur during systole. Most common murmurs occur in systole Can be early systolic, late systolic or holosystolic (all of systole) Diastolic: After S2 Intensity (Loudness): I/VI: Need quiet room and trained ear to hear II/VI: Audible to anyone who listens attentively III/VI: Loud, but not palpable IV/VI: Like III, but with a palpable thrill V/VI: Audible with stethoscope placed perpendicular to chest wall VI/VI: Audible without a stethoscope 3. Quality: Shape of murmur: Diamond-shaped (can hear S1 and S2) typical of stenosis (narrowing) or flow murmurs; Constant intensity (may blur S1 and S2) typical of valvular regurgitation (leak) Can be musical (often innocent), blowing (regurgitant or innocent), harsh (stenosis) 4. Location (see above)
6 A FEW COMMON MURMURS: SYSTOLIC: Innocent (flow) murmur: II/VI or softer, blowing, diamond-shaped, at pulmonic area Listen for S2: if fixed split, think atrial septal defect Mitral insufficiency/ regurgitation (leaky valve) Holosystolic, blowing, constant intensity Loudest at apex; often radiates to axilla Aortic stenosis: Diamond-shaped; somewhat harsher quality Usually loudest at aortic area (though sometimes in tricuspid area) If worse, may have S4, too Evidence-based lesson: Does this patient have aortic stenosis? Best to rule in aortic stenosis: Delayed rate of rise of carotid pulse Mid to late peak in intensity of murmur Quieter S2 Best to rule in aortic stenosis: Failure of murmur to radiate to right carotid artery JAMA 1997; 277: RUB: Mitral valve prolapse: Classically preceded by one or more clicks in midsystole Murmur (if present) follows is late systolic Heard at apex Common in slender young women usually benign DIASTOLIC Aortic insufficiency/regurgitation: Blowing Loudest in aortic or tricuspid areas Louder if patient squats or clenches hands (this increases systemic vascular resistance, increasing regurgitation) Leathery, squeaky sound made by pericardial friction Often has 3 components heard in systole and diastole Sometimes louder with position change (e.g. sitting up)
Heart sounds and murmurs. Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct
 Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
SMALL GROUP SESSION 19 January 30 th or February 1st. Groups 1-12: Cardiac Case and Cardiac Exam Workshop
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 19 January 30 th or February 1st Groups 1-12: Cardiac Case and Cardiac Exam Workshop Readings: Complete the cardiac examination tutorial on the POM1 web site. Optional: http://medicine.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/heart.htm
SMALL GROUP SESSION 19 January 30 th or February 1st Groups 1-12: Cardiac Case and Cardiac Exam Workshop Readings: Complete the cardiac examination tutorial on the POM1 web site. Optional: http://medicine.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/heart.htm
2. The heart sounds are produced by a summed series of mechanical events, as follows:
 Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly
 Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Chapter 8 1 Cardiovascular System Functions: pump saturated oxygenated blood into arterial system cells pump desaturated deoxygenated blood to lungs via veins for reoxygenation Heart
Cardiovascular System Chapter 8 1 Cardiovascular System Functions: pump saturated oxygenated blood into arterial system cells pump desaturated deoxygenated blood to lungs via veins for reoxygenation Heart
Heart and Neck Vessels
 CHAPTER 12 Heart and Neck Vessels ANATOMY The precordium is the area on the anterior chest overlying the heart and great vessels. The heart extends from the second to the fifth intercostal space, and from
CHAPTER 12 Heart and Neck Vessels ANATOMY The precordium is the area on the anterior chest overlying the heart and great vessels. The heart extends from the second to the fifth intercostal space, and from
HEALTH ASSESSMENT. Afnan Tunsi BSN, RN, MSc.
 HEALTH ASSESSMENT Afnan Tunsi BSN, RN, MSc. Learning Outcomes 2 After completion of this lecture, the student will be able to: Describe suggested sequencing to conduct a thorax and lungs physical health
HEALTH ASSESSMENT Afnan Tunsi BSN, RN, MSc. Learning Outcomes 2 After completion of this lecture, the student will be able to: Describe suggested sequencing to conduct a thorax and lungs physical health
1. how a careful cardiovascular evaluation can accurately assess pathology and physiology at the bedside, and
 This program will demonstrate: 1. how a careful cardiovascular evaluation can accurately assess pathology and physiology at the bedside, and 2. the importance of integrating this information with selected
This program will demonstrate: 1. how a careful cardiovascular evaluation can accurately assess pathology and physiology at the bedside, and 2. the importance of integrating this information with selected
Murmur Sounds made by turbulence in the heart or blood stream. 1. Timing. 5. Intensity 2. Shape. 6. Pitch 3. Location of maximum intensity
 Definition Items in description of Timing Shape Location of maximum intensity Murmur Sounds made by turbulence in the heart or blood stream. 1. Timing 5. Intensity 2. Shape 6. Pitch 3. Location of maximum
Definition Items in description of Timing Shape Location of maximum intensity Murmur Sounds made by turbulence in the heart or blood stream. 1. Timing 5. Intensity 2. Shape 6. Pitch 3. Location of maximum
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY LECTURE 4 Cardiac cycle Polygram - analysis of cardiac activity Ana-Maria Zagrean MD, PhD The Cardiac Cycle - definitions: the sequence of electrical and mechanical events that
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY LECTURE 4 Cardiac cycle Polygram - analysis of cardiac activity Ana-Maria Zagrean MD, PhD The Cardiac Cycle - definitions: the sequence of electrical and mechanical events that
Cardiac Examination. Pediatrics Clinical Examination
 Pediatrics Clinical Examination Symptoms of Cardiovascular Affection: Cardiac Examination 1. Perinatal history: Maternal DM, cyanosis, respiratory distress 2. Symptoms of lung congestion: Poor interrupted
Pediatrics Clinical Examination Symptoms of Cardiovascular Affection: Cardiac Examination 1. Perinatal history: Maternal DM, cyanosis, respiratory distress 2. Symptoms of lung congestion: Poor interrupted
Leicester Medical School
 Leicester Medical School THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Overview The cardiovascular examination should include the following: - General inspection from the end of the bed. - General examination
Leicester Medical School THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Overview The cardiovascular examination should include the following: - General inspection from the end of the bed. - General examination
Tracheal normal sound heard over trachea loud tubular quality high-pitched expiration equal to or slightly longer than inspiration
 = listening for sounds produced in the body over chest to ID normal & abnormal lung sounds all BS made by turbulent flow in the airways useful in making initial D & evaluating effects of R 4 characteristics
= listening for sounds produced in the body over chest to ID normal & abnormal lung sounds all BS made by turbulent flow in the airways useful in making initial D & evaluating effects of R 4 characteristics
What s That Sound? Pediatric Murmur Evaluation
 What s That Sound? Pediatric Murmur Evaluation Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director, Pediatric
What s That Sound? Pediatric Murmur Evaluation Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director, Pediatric
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
COLIC AND MURMURS: AN OVERVIEW
 COLIC AND MURMURS: AN OVERVIEW Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Department of Large Animal Internal Medicine, Ghent University, Merelbeke, Belgium Introduction Many horses with colic present with a cardiac
COLIC AND MURMURS: AN OVERVIEW Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Department of Large Animal Internal Medicine, Ghent University, Merelbeke, Belgium Introduction Many horses with colic present with a cardiac
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm!
 Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Clarke Atkins, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Internal Medicine and Cardiology) Jane Lewis Seaks Distinguished Professor Emeritus North Carolina State University, College of
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Clarke Atkins, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Internal Medicine and Cardiology) Jane Lewis Seaks Distinguished Professor Emeritus North Carolina State University, College of
CARDIOLOGY FOR DUMMIES
 CARDIOLOGY FOR DUMMIES Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Dipl ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine, Fac. of Veterinary Medicine, Ghent University, Salisburylaan 133, B-9820 Merelbeke, Belgium
CARDIOLOGY FOR DUMMIES Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Dipl ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine, Fac. of Veterinary Medicine, Ghent University, Salisburylaan 133, B-9820 Merelbeke, Belgium
Pocket Companion. Australian Adapting Editors. Clare Cole Olivia Hill Rosemary Saunders
 Pocket Companion Australian and New Zealand edition Australian Adapting Editors Clare Cole Olivia Hill Rosemary Saunders Contents About the author/s (TBC) 0 Preface 0 Acknowledgments 0 Chapter 1 The health
Pocket Companion Australian and New Zealand edition Australian Adapting Editors Clare Cole Olivia Hill Rosemary Saunders Contents About the author/s (TBC) 0 Preface 0 Acknowledgments 0 Chapter 1 The health
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
See below for descriptions of the waveform
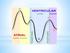 The internal jugular vein (IJV) connects to the right atrium without any intervening valves. The pulsation of the right atrium therefore causes the column of blood in the IJV to rise and fall this is called
The internal jugular vein (IJV) connects to the right atrium without any intervening valves. The pulsation of the right atrium therefore causes the column of blood in the IJV to rise and fall this is called
Physical Exam Of The Cardio- Vascular System. James G. Laws D.O. MACOI
 Physical Exam Of The Cardio- Vascular System James G. Laws D.O. MACOI An Important Part Of The Physical Exam Of The Cardio-Vascular System That Is Commonly Overlooked Is? 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 1. Palpation
Physical Exam Of The Cardio- Vascular System James G. Laws D.O. MACOI An Important Part Of The Physical Exam Of The Cardio-Vascular System That Is Commonly Overlooked Is? 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 1. Palpation
Physiology of the Heart Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
 Physiology of the Heart 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Physiology of the Heart State Standards 35) Outline the structure and functions of the anatomy of the cardiovascular system,
Physiology of the Heart 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Physiology of the Heart State Standards 35) Outline the structure and functions of the anatomy of the cardiovascular system,
PART I: HEART ANATOMY
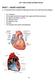 Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Physical Exam Part II
 Physical Exam Part II University of Michigan Cardiovascular Center Kim A. Eagle, MD Albion Walter Hewlett Professor Director Physical Exam: Part II Heart Sounds Heart Murmurs HEART SOUNDS S1 MITRAL + TRICUSPID
Physical Exam Part II University of Michigan Cardiovascular Center Kim A. Eagle, MD Albion Walter Hewlett Professor Director Physical Exam: Part II Heart Sounds Heart Murmurs HEART SOUNDS S1 MITRAL + TRICUSPID
Are you too quick to refer?
 HEART MURMURS IN CHILDREN Are you too quick to refer? Many children with murmurs are unnecessarily referred, say the authors, who describe a thorough cardiovascular exam you can perform in three to five
HEART MURMURS IN CHILDREN Are you too quick to refer? Many children with murmurs are unnecessarily referred, say the authors, who describe a thorough cardiovascular exam you can perform in three to five
Congenital heart disease. By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics
 Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
CARDIAC CYCLE CONTENTS. Divisions of cardiac cycle 11/13/13. Definition. Badri Paudel GMC
 CARDIAC CYCLE Badri Paudel GMC CONTENTS Ø DEFINATION Ø DIVISION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUB DIVISION AND DURATION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SYSTOLE Ø DIASTOLE Ø DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUMMARY Ø ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
CARDIAC CYCLE Badri Paudel GMC CONTENTS Ø DEFINATION Ø DIVISION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUB DIVISION AND DURATION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SYSTOLE Ø DIASTOLE Ø DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUMMARY Ø ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
Cardiac Cycle MCQ. Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology. Cairo University 2007
 Cardiac Cycle MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Regarding the length of systole and diastole: a- At heart rate 75 b/min, the duration of
Cardiac Cycle MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Regarding the length of systole and diastole: a- At heart rate 75 b/min, the duration of
The Jugular Venous Pressure and Pulse Contour
 19 The Jugular Venous Pressure and Pulse Contour MARK M. APPLEFELD Definition Information that can be derived from an assessment of the jugular venous pulse includes determination of the mean venous pressure,
19 The Jugular Venous Pressure and Pulse Contour MARK M. APPLEFELD Definition Information that can be derived from an assessment of the jugular venous pulse includes determination of the mean venous pressure,
PEDIATRIC HEART MURMURS. Manish Bansal, MD Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Cardiology University of Iowa
 PEDIATRIC HEART MURMURS Manish Bansal, MD Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Cardiology University of Iowa Murmur murmur. (n.d.). Dictionary.com Unabridged. Retrieved March 9, 2018 from
PEDIATRIC HEART MURMURS Manish Bansal, MD Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Cardiology University of Iowa Murmur murmur. (n.d.). Dictionary.com Unabridged. Retrieved March 9, 2018 from
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
cardiac vascular mediastinal Causes airway chest pain wall determine Character Dyspnoea palpitation
 Written by: Mohammad Al Marhoon Dr.Marhoon@gmail.com Reference: Clinical Examination (Talley) Major Symptoms chest pain Causes determine Character cardiac vascular mediastinal ischemia MI Pleuropericardial
Written by: Mohammad Al Marhoon Dr.Marhoon@gmail.com Reference: Clinical Examination (Talley) Major Symptoms chest pain Causes determine Character cardiac vascular mediastinal ischemia MI Pleuropericardial
HEART MURMURS: DECIPHERING THEIR CAUSE AND SIGNIFICANCE
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk HEART MURMURS: DECIPHERING THEIR CAUSE AND SIGNIFICANCE Author : Pedro Oliveira Categories : Vets Date : May 27, 2013 PEDRO
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk HEART MURMURS: DECIPHERING THEIR CAUSE AND SIGNIFICANCE Author : Pedro Oliveira Categories : Vets Date : May 27, 2013 PEDRO
PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG)
 PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG) The technique of listening to sounds produced by the organs and vessels of the body is called auscultation. The areas at which the heart sounds are heard better are called auscultation
PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG) The technique of listening to sounds produced by the organs and vessels of the body is called auscultation. The areas at which the heart sounds are heard better are called auscultation
UNIT 08: ASSESSMENT OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) UNIT 08: ASSESSMENT OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN Instructor New Life College of Nursing December 01, 2015
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) UNIT 08: ASSESSMENT OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN Instructor New Life College of Nursing December 01, 2015
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D.
 The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
CAMOSUN COLLEGE BIOLOGY 144 (2010) LABS
 LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
Murmurs and the Cardiac Physical Exam. Carolyn A. Altman Texas Children s Hospital Advanced Practice Provider Conference Houston, TX April 6, 2018
 Murmurs and the Cardiac Physical Exam Carolyn A. Altman Texas Children s Hospital Advanced Practice Provider Conference Houston, TX April 6, 2018 The Cardiac Physical Exam Before applying a stethoscope..
Murmurs and the Cardiac Physical Exam Carolyn A. Altman Texas Children s Hospital Advanced Practice Provider Conference Houston, TX April 6, 2018 The Cardiac Physical Exam Before applying a stethoscope..
Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations
 ighapmlre33apg269_274 5/12/04 3:10 PM Page 269 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise
ighapmlre33apg269_274 5/12/04 3:10 PM Page 269 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso
 2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Objectives of the Heart
 Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Auscultation of the Heart I
 Res Medica, Summer 1960, Volume II, Number 2 Page 1 of 8 Auscultation of the Heart I R. W. D. Turner O.B.E., M.A.(Cantab.). M.D., F.R.C.P. Ed., F.R.C.P. Lond. Abstract "And the babe leaps up on his mother's
Res Medica, Summer 1960, Volume II, Number 2 Page 1 of 8 Auscultation of the Heart I R. W. D. Turner O.B.E., M.A.(Cantab.). M.D., F.R.C.P. Ed., F.R.C.P. Lond. Abstract "And the babe leaps up on his mother's
Cardiovascular Patient Assessment. Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
 Cardiovascular Patient Assessment Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Objectives Outline a systematic approach to cardiovascular assessment. Differentiate normal from abnormal findings when assessing
Cardiovascular Patient Assessment Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Objectives Outline a systematic approach to cardiovascular assessment. Differentiate normal from abnormal findings when assessing
Pathological Arrhythmias/ Tachyarrhythmias
 Pathological Arrhythmias/ Tachyarrhythmias caused by: 1.Ectopic focus: Extrasystole or premature beat. If discharge is occasional. Can be: Atrial Extrasystole Vevtricular Extrasystole 2.Cardiac Arrhythmia
Pathological Arrhythmias/ Tachyarrhythmias caused by: 1.Ectopic focus: Extrasystole or premature beat. If discharge is occasional. Can be: Atrial Extrasystole Vevtricular Extrasystole 2.Cardiac Arrhythmia
SAMPLE HLTEN610A. TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank. Practise in the cardiovascular nursing environment
 TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank HLTEN610A Practise in the cardiovascular nursing environment Version 1.0 Flexible Learner Resource Product Code: ISO 9001 HLTEN610A
TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank HLTEN610A Practise in the cardiovascular nursing environment Version 1.0 Flexible Learner Resource Product Code: ISO 9001 HLTEN610A
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
NTI 2010 Boot Camp. Paradigm Shift. Hemodynamics: Cardiac Output. Basic Hemodynamic Formula
 Cardiovascular Assessment and Hemodynamic Principles NTI 2010 Boot Camp Hemodynamics does not equal invasive monitoring Paradigm Shift Karen Marzlin MSN, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC Cardiovascular Nursing Education
Cardiovascular Assessment and Hemodynamic Principles NTI 2010 Boot Camp Hemodynamics does not equal invasive monitoring Paradigm Shift Karen Marzlin MSN, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC Cardiovascular Nursing Education
(YDOXDWLRQ&RS\ Surface Projections of the Heart and Great Vessels
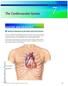 C H A P T E R 7 The Cardiovascular System ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Surface Projections of the Heart and Great Vessels Learn to visualize the underlying structures of the heart as you examine the anterior
C H A P T E R 7 The Cardiovascular System ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Surface Projections of the Heart and Great Vessels Learn to visualize the underlying structures of the heart as you examine the anterior
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
NASCO LF01199 AUSCULTATION POSTERIOR BOARD INSTRUCTION SHEET
 NASCO LF01199 AUSCULTATION POSTERIOR BOARD INSTRUCTION SHEET Attaching to a Case Without Side Rails If you have a case without rails on the inside of the cover, with the metal Serial Tag riveted in the
NASCO LF01199 AUSCULTATION POSTERIOR BOARD INSTRUCTION SHEET Attaching to a Case Without Side Rails If you have a case without rails on the inside of the cover, with the metal Serial Tag riveted in the
What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should.
 What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should. How Do Heart Valves Work? MAINTAIN ONE-WAY BLOOD FLOW THROUGH YOUR HEART The four heart
What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should. How Do Heart Valves Work? MAINTAIN ONE-WAY BLOOD FLOW THROUGH YOUR HEART The four heart
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
Murmur diagnosis in cats. Your pet has a murmur! Meg Sleeper VMD, DACVIM (cardiology) Gainesville, FL. Reasons to work up the murmur in a cat
 Murmur diagnosis in cats Your pet has a murmur! Meg Sleeper VMD, DACVIM (cardiology) Gainesville, FL Heart disease diagnosis in cats and kittens in general is challenging because: Approximately ½ of systolic
Murmur diagnosis in cats Your pet has a murmur! Meg Sleeper VMD, DACVIM (cardiology) Gainesville, FL Heart disease diagnosis in cats and kittens in general is challenging because: Approximately ½ of systolic
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
CHAPTER 14 HEART. Tracey A. Littrell, BA, DC, DACBR, DACO, CCSP
 CHAPTER 14 HEART Tracey A. Littrell, BA, DC, DACBR, DACO, CCSP ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Expected Position In mediastinum Left of midline Above diaphragm Between medial/lower borders of lungs Behind sternum
CHAPTER 14 HEART Tracey A. Littrell, BA, DC, DACBR, DACO, CCSP ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Expected Position In mediastinum Left of midline Above diaphragm Between medial/lower borders of lungs Behind sternum
Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds
 Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds Five physiologic properties of cardiac muscle Automaticity: SA node is the primary pacemaker of the heart, but any cells in the conduction system can initiate their
Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds Five physiologic properties of cardiac muscle Automaticity: SA node is the primary pacemaker of the heart, but any cells in the conduction system can initiate their
Hemodynamic Monitoring
 Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Do Now. Get out work from last class to be checked
 Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system
 Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
SMALL GROUP SESSION 18A January 17th or January 19th. Groups 1-12: VS and Chest Exam and Harvey Stethophone Session
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 18A January 17th or January 19th Groups 1-12: VS and Chest Exam and Harvey Stethophone Session Readings: Complete the cardiac examination web module. Mosby s Physical Examination, 4
SMALL GROUP SESSION 18A January 17th or January 19th Groups 1-12: VS and Chest Exam and Harvey Stethophone Session Readings: Complete the cardiac examination web module. Mosby s Physical Examination, 4
Percussion, auscultation. Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 23. Sept. 2013
 Percussion, auscultation Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 23. Sept. 2013 The physical principles of the percussion Percussion sets the body surface (chest wall) and
Percussion, auscultation Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 23. Sept. 2013 The physical principles of the percussion Percussion sets the body surface (chest wall) and
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Heart 2
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
Proceedings of the 13th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 13th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA October 3-5, 2013 Budapest, Hungary Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission of the WEVA Organizers
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 13th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA October 3-5, 2013 Budapest, Hungary Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission of the WEVA Organizers
CARDIAC PREPURCHASE EXAMINATION: YOUR ROLE AND WHAT TO EXPECT FROM A SPECIALIST
 CARDIAC PREPURCHASE EXAMINATION: YOUR ROLE AND WHAT TO EXPECT FROM A SPECIALIST JoAnn Slack DVM, MS, DACVIM Associate Professor Large Animal Cardiology and Ultrasound University of Pennsylvania New Bolton
CARDIAC PREPURCHASE EXAMINATION: YOUR ROLE AND WHAT TO EXPECT FROM A SPECIALIST JoAnn Slack DVM, MS, DACVIM Associate Professor Large Animal Cardiology and Ultrasound University of Pennsylvania New Bolton
DOWNLOAD PDF HURSTS THE HEART, UPDATE I
 Chapter 1 : Hurstâ s the Heart, 14th Edition (PDF) â ebooks Library [PDF]Free Hursts The Heart Update 1 download Book Hursts The Heart Update blog.quintoapp.com FREE DOWNLOAD** HURSTS THE HEART UPDATE
Chapter 1 : Hurstâ s the Heart, 14th Edition (PDF) â ebooks Library [PDF]Free Hursts The Heart Update 1 download Book Hursts The Heart Update blog.quintoapp.com FREE DOWNLOAD** HURSTS THE HEART UPDATE
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Name Class Date. Bell Diaphragm. Chest piece. Stethoscope
 Name Class Date Sensing Circulation Exploring the Effects of Exercise on Heart Rate Investigative Lab 30 8 Questions How do the sounds you hear through a stethoscope relate to the stages of a heartbeat?
Name Class Date Sensing Circulation Exploring the Effects of Exercise on Heart Rate Investigative Lab 30 8 Questions How do the sounds you hear through a stethoscope relate to the stages of a heartbeat?
Proceedings of the 10th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 10th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association Jan. 28 Feb. 1, 2008 - Moscow, Russia Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Conference
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 10th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association Jan. 28 Feb. 1, 2008 - Moscow, Russia Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Conference
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disease
 Chapter 31 Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disease David A. Tate Acquired disease of the right-sided cardiac valves is much less common than disease of the leftsided counterparts, possibly because of the
Chapter 31 Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disease David A. Tate Acquired disease of the right-sided cardiac valves is much less common than disease of the leftsided counterparts, possibly because of the
Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC
 Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC Who am I? Class Outline Gross anatomy of the heart Trip around the heart Micro anatomy: cellular and tissue level Introduction
Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC Who am I? Class Outline Gross anatomy of the heart Trip around the heart Micro anatomy: cellular and tissue level Introduction
Chapter 14. Circulatory System Images. VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II
 Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Skin supplied by T1-4 (medial upper arm and neck) T5-9- epigastrium Visceral afferents from skin and heart are the same dorsal root ganglio
 Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
HEART SOUNDS & BLOOD PRESSURE
 LABORATORY HANDBOOK HEART SOUNDS & BLOOD PRESSURE For the course Systems Biology Karolinska Institutet Department of Physiology and Pharmacology Physiology Education Postal address: 171 77 Stockholm Visiting
LABORATORY HANDBOOK HEART SOUNDS & BLOOD PRESSURE For the course Systems Biology Karolinska Institutet Department of Physiology and Pharmacology Physiology Education Postal address: 171 77 Stockholm Visiting
Proceeding of the LAVC Latin American Veterinary Conference Apr , 2016 Lima, Perú
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceeding of the LAVC Latin American Veterinary Conference Apr. 20-22, 2016 Lima, Perú Next LAVC Conference: Apr. 4-7, 2017 Lima, Perú Reprinted in the
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceeding of the LAVC Latin American Veterinary Conference Apr. 20-22, 2016 Lima, Perú Next LAVC Conference: Apr. 4-7, 2017 Lima, Perú Reprinted in the
The Heart and Cardiovascular System
 The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection
 AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection Project 1 - BLOOD Supply to the Myocardium (Figs. 18.5 &18.10) The myocardium is not nourished by the blood while it is being pumped through the
AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection Project 1 - BLOOD Supply to the Myocardium (Figs. 18.5 &18.10) The myocardium is not nourished by the blood while it is being pumped through the
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13}
 Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
1997, 1999, 2003, 2010, 2016 by Bob Page, M.Ed, NRP, CCP. By the end of this session, participants will be able to:
 An interactive and informative session designed to enhance your knowledge and understanding of the use of your stethoscope, while identifying common and critical lung, heart, and voice sounds in the emergency
An interactive and informative session designed to enhance your knowledge and understanding of the use of your stethoscope, while identifying common and critical lung, heart, and voice sounds in the emergency
Heart Failure with Johnny Crash: LEFT VENTRICULAR EJECTION FRACTION (LVEF) SYMPTOMATOLOGY: Assess VENTRICULAR DYSFUNCTION HEART FAILURE:
 Heart Failure with Johnny Crash: Joan E. King, PhD, ACNP-BC, ANP-BC Melissa Smith, DNP, ANP-BC Vanderbilt University School of Nursing HEART FAILURE: Heart Failure (HF): a complex clinical syndrome resulting
Heart Failure with Johnny Crash: Joan E. King, PhD, ACNP-BC, ANP-BC Melissa Smith, DNP, ANP-BC Vanderbilt University School of Nursing HEART FAILURE: Heart Failure (HF): a complex clinical syndrome resulting
SECTION A. Clinical Entities COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 SECTION A COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 Heart Murmurs and Gallop Heart Sounds Key Points Cardiac murmurs can be present due to primary heart disease (for example, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy with
SECTION A COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 Heart Murmurs and Gallop Heart Sounds Key Points Cardiac murmurs can be present due to primary heart disease (for example, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy with
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
current, and acting like
 Heart 10 IV. HEART PHYSIOLOGY - How the heart beats. How the heart depolarizes the myocardium, which leads to a contraction. A) INTRINSIC CONTROL - Heart controls its own rhythm. HOW? The presence of gap
Heart 10 IV. HEART PHYSIOLOGY - How the heart beats. How the heart depolarizes the myocardium, which leads to a contraction. A) INTRINSIC CONTROL - Heart controls its own rhythm. HOW? The presence of gap
HISTORY. Question: What type of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance.
 HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Cardiac. Deborah Fritz, PhD, APRN, FNP-BC, and Patricia McKenzie, MSN, APRN, ANP-BC
 Deborah Fritz, PhD, APRN, FNP-BC, and Patricia McKenzie, MSN, APRN, ANP-BC Heart disease remains the number one cause of mortality in both men and women in the United States and patients with heart failure
Deborah Fritz, PhD, APRN, FNP-BC, and Patricia McKenzie, MSN, APRN, ANP-BC Heart disease remains the number one cause of mortality in both men and women in the United States and patients with heart failure
SOCM Physical Exam of the Cardiovascular and Peripheral Vascular Systems PFN: SOMPYL0P. Terminal Learning Objective. References. Hours: 1.
 SOCM Physical Exam of the Cardiovascular and Peripheral Vascular Systems PFN: SOMPYL0P Hours: 1.5 Slide 1 Terminal Learning Objective Action: Communicate knowledge of Physical Exam of the Cardiovascular
SOCM Physical Exam of the Cardiovascular and Peripheral Vascular Systems PFN: SOMPYL0P Hours: 1.5 Slide 1 Terminal Learning Objective Action: Communicate knowledge of Physical Exam of the Cardiovascular
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
THE SOUNDS AND MURMURS IN TRANSPOSITION OF THE
 Brit. Heart J., 25, 1963, 748. THE SOUNDS AND MURMURS IN TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT VESSELS BY BERTRAND WELLS From The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London W. C.J Received April 18,
Brit. Heart J., 25, 1963, 748. THE SOUNDS AND MURMURS IN TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT VESSELS BY BERTRAND WELLS From The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London W. C.J Received April 18,
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
