Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis. Barbara LeVarge MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Pulmonary Hypertension Center COPYRIGHT
|
|
|
- Sheila Murphy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis Barbara LeVarge MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Pulmonary Hypertension Center
2 Acute PE and DVT No disclosures.
3 Acute PE and DVT Learning objectives Understand the pathophysiology of clinical symptoms and signs of PE. Review the appropriate evaluation of a patient with suspected PE or DVT, in a variety of clinical circumstances. Discuss treatment recommendations for the clinically stable PE/DVT patient, including new guidelines from 10 th edition ACCP report. Explore management options for massive and high risk submassive PE.
4 Acute PE and DVT Epidemiology and risk factors Pathophysiology and clinical consequences of pulmonary embolism Diagnostic workup Severity assessment Management
5 Epidemiology Annual incidence of VTE around 1 in 1000 US population. Estimates up to 100,000 VTE-related deaths/year in US. Incidence rates consistently underestimated using antemortem data alone Significant morbidity and mortality: Incident or recurrent events Adverse events from anticoagulation/treatments Post-thrombotic syndrome (DVT) Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension cdc.gov; Beckman et al, Am J Prev Med 2010
6 Risk factors Previous VTE event Malignancy Pregnancy OCPs/hormonal therapy Hospitalization or immobilization Surgery or major trauma Inherited thrombophilias (factor V Leiden, prothrombin gene mutation, protein C/S deficiency, antithrombin deficiency Nephrotic syndrome Inflammatory bowel disease
7 Clinical consequences of pulmonary embolism Infarction (pain, hemoptysis, dyspnea) Abnormal gas exchange (dyspnea, hypoxemia) Right ventricular compromise (hypotension, tachycardia, dyspnea, hypoxemia)
8 Clinical consequences of pulmonary embolism Infarction Small distal thrombi à ischemic necrosis Increased perfusion by bronchial arteries à high pressure extravasation/hemorrhage Pleural inflammation à pain
9 Clinical consequences of pulmonary embolism Abnormal gas exchange Obstructed vascular flow à dead space If ventilation fixed à hypercarbia Usually stimulus to increase ventilation à low pco 2
10 Clinical consequences of pulmonary embolism Abnormal gas exchange Overall disruption of V/Q matching à hypoxemia Calkovska et al, Eur J Med Res (2009) 14(Suppl. IV): 38-41
11 Clinical consequences of pulmonary embolism Right ventricular compromise Acute increase in RV afterload Pathologic RV spiral Loss of RV stroke volume à tachycardia If compensatory mechanisms insufficient à hypotension and shock Poor cardiac output à low mixed venous O 2 à arterial hypoxemia
12 Poor et al, Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2012
13 Diagnostic workup Pulmonary embolism, stable patients Pulmonary embolism, pregnant patients Pulmonary embolism, unstable patients Deep vein thrombosis
14 Diagnostic workup: PE, stable patients Wells criteria for pulmonary embolism Clinical signs/symptoms of DVT Other diagnoses less likely than PE Heart rate >100 Immobilization ( 3 days) or surgery (4 weeks) Previous DVT or PE Hemoptysis Malignancy Dichotomized Low likelihood: score 4 points High likelihood: score > 4 points 3 points 3 points 1.5 points 1.5 points 1.5 points 1 point 1 point
15 Diagnostic workup: PE, stable patients Low likelihood: PE unlikely D-dimer testing If <500 ng/ml à PE excluded If 500 ng/ml à perform imaging Age-adjusted D-dimer D-dimer: low specificity (elevated in older patients, pregnancy, acute illness, etc) 28.2% of low probability patients had D-dimer <500 à0.1% VTE risk 11.6% of low probability patients had D-dimer >500 but less than age adjusted à0.3% VTE risk
16 Diagnostic workup: PE, stable patients Low likelihood: PE unlikely D-dimer testing PERC testing (Kline et al, J Thromb Haemost 2004 and 2008) If all 8 fulfilled à PE excluded (~1% VTE incidence) Age <50 HR <100 O2 sat 95% No hemoptysis No estrogen use No prior DVT/PE No unilateral leg swelling No recent surgery or trauma (4 weeks)
17 Diagnostic workup: PE, stable patients High likelihood: PE likely (or unlikely with positive D-dimer) D-dimer testing for high likelihood: no role Most patients à CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA): sensitivity >90% Indeterminate findings à need for more imaging
18 Diagnostic workup: PE, stable patients <500 ng/ml Low likelihood for PE D-dimer 500 ng/ml Wells Score: clinical likelihood for PE High likelihood of PE Negative CT pulmonary angiogram Positive PE excluded PE confirmed
19 Diagnostic workup: PE, stable patients High likelihood: PE likely (or unlikely with positive D-dimer) Ventilation/perfusion (VQ) scan Clinical low probability Clinical high probability VQ normal PE excluded PE excluded VQ low probability PE excluded * VQ intermediate probability * * VQ high probability * PE confirmed
20 Diagnostic workup: PE, pregnant patients Pregnant patients Wells score: utility? D-dimer: can be elevated in normal pregnancy; sensitivity only 73% VQ scan: relatively low prevalence of indeterminate studies Ensure CXR normal CTPA: if CXR abnormal, or VQ indeterminate Consider lower extremity ultrasound (if leg symptoms)
21 Diagnostic workup: PE, unstable patients Evidence based algorithms not applicable Balance of benefits of confirming the diagnosis versus risks of patient traveling from unit PE not the only entity that causes shock/rv mediated shock
22 Diagnostic workup: DVT There is a Wells criteria for deep vein thrombosis to assign low, moderate, high probability of DVT, though use of this tool in practice is variable. Compression ultrasonography has good test performance characteristics, and is low risk and easily available.
23 Management Pulmonary embolism severity assessment Low/average risk PE or DVT Anticoagulation Outpatient management Massive PE High risk submassive PE IVC filters
24 Management: PE severity assessment PESI
25 Management: PE severity assessment Massive PE (SBP <90 mmhg) High risk submassive RV dysfunction (echo, CT scan) Biomarkers (BNP, troponin) Significant hypoxemia Significant tachycardia without hypotension Clot in transit PFO Impressive clot burden on imaging Low/average risk
26 Management: low/average risk PE/DVT Anticoagulation Disposition
27 Management
28 Management: anticoagulation Major change in 10 th edition of ACCP guidelines: for patients without cancer, direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) suggested over warfarin
29 Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 8, 353 (May 2009)
30 Management: anticoagulation Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) Rivaroxaban (approved 11/2012) EINSTEIN-PE 4832 patients acute symptomatic PE Non-inferiority, event driven design; rivaroxaban vs. enoxaparinàwarfarin. Primary endpoint: recurrent VTE Results: recurrent VTE in 2.1% rivaroxaban vs. 1.8% standard therapy (p=0.003 for non-inferiority) Major hemorrhage reduced (HR 0.49, p=0.003)
31 Management: anticoagulation Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) Apixaban (approved 8/2014) AMPLIFY 5395 patients acute VTE (34% PE +/- DVT) Non-inferiority design, apixaban vs. enoxaparinàwarfarin. Primary endpoint: recurrent VTE or VTE-related death Results: 2.3% apixaban vs. 2.7% standard therapy (p<0.001 for non-inferiority) Major hemorrhage reduced (RR 0.31, p<0.001)
32 Management: anticoagulation Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) Dabigatran (approved 4/2014) RE-COVER 2564 patients acute VTE, started on UFH/LMWH Non-inferiority design, dabigatran vs. warfarin. Primary endpoint: recurrent VTE within 6 months Results: 2.4% dabigatran vs. 2.1% warfarin (p<0.001 for noninferiority) Major hemorrhage (RR 0.82, p=ns)
33 Management: anticoagulation Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) Edoxaban (approved 1/2015) Hokusai-VTE 8240 patients with acute VTE (40% with PE), started on LMWH or UFH Non-inferiority, event driven design, edoxaban vs. warfarin. Primary endpoint: recurrent VTE Results: 3.2% edoxaban vs. 3.5% warfarin (p<0.001 for noninferiority) Major hemorrhage reduced (RR 0.81, p=0.004)
34 Management: anticoagulation Direct oral anticoagulants: summary 3 Xa-inhibitors (rivaroxaban, apixaban, edoxaban) and direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran Rivaroxaban/apixaban can be used at diagnosis, edoxaban/dabigatran following UFH/LMWH ( after 5-10 days of parenteral anticoagulation ) All non-inferior to standard therapy; improvements in bleeding outcomes, though concern for irreversibility Massive PE/high risk for bleeding excluded All tested in patients with GFR >30 (or 25)
35 Management: anticoagulation If up front parenteral therapy is planned (DOACs contraindicated or undesirable, or dabigatran or edoxaban being used), guidelines suggest LMWH over UFH UFH may be preferred in: Renal failure, extreme obesity, anasarca High bleeding risk;?fibrinolysis candidates If warfarin used, start early (day 1), continue parenteral 5 days and until INR 2.0 for 24 hours If dabigatran/edoxaban used, recommended after 5-10 days of parenteral therapy
36 Management: anticoagulation Duration of anticoagulation Provoked (surgical or transient nonsurgical risk factors): 3 months Unprovoked, initial event: at least 3 months, with evaluation of risk-benefit thereafter Unprovoked, second event: extended course Malignancy: extended course (LMWH>VKA)
37 Management: anticoagulation Anticoagulation in pregnancy LMWH recommended Warfarin avoidance especially in first trimester and late pregnancy DOACs avoided during pregnancy, lactation Continue anticoagulation at least 6 weeks postpartum and 3 months therapy
38 Management: subsegmental PE Uncertainty regarding clinical implications of isolated subsegmental PE, as well as likelihood of false positives. 10 th edition ACCP guidelines: In patients with subsegmental PE and no proximal DVT in the legs who have a low risk for recurrent VTE, we suggest clinical surveillance over anticoagulation
39 Management: outpatient Simple DVT often managed outpatient 10 th edition ACCP guidelines: In patients with low-risk PE and whose home circumstances are adequate, we suggest treatment at home or early discharge over standard discharge Clinically stable with good cardiopulmonary reserve Not high risk of bleeding (recent bleeding, renal or liver failure, thrombocytopenia) Expected to be compliant with therapy Feels well enough to be treated at home
40 Management: massive PE 2392 PE patients from ICOPER, patients with massive PE (SBP <90 mmhg)
41 Management: massive PE Massive PE with no contraindication à systemic thrombolysis tpa 100 mg If lysis contraindicated or failed Depending on available options VA ECMO/CPB/surgical embolectomy Percutaneous mechanical embolectomy Rheolytic (saline jet), rotational, suction Evidence: case series based
42 Management: high-risk submassive PE High risk submassive: controversial Anticoagulation alone Systemic thrombolysis (tpa 100 or 50 mg over 2 hrs) Catheter-directed, ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis (tpa ~20 mg over ~24 hrs) Percutaneous mechanical embolectomy Highest Risk Lowest Risk
43 Management: high-risk submassive PE PEITHO study 1005 patients, acute PE with RV dysfunction (CT, echo) and positive troponin Weight-based tenecteplase+ufh vs. placebo+ufh Primary endpoint: death or hemodynamic collapse at 7 days
44 Management: high-risk submassive PE PEITHO study
45 Management: high-risk submassive PE MOPETT study Single center, 121 patients, moderate clot burden Anticoagulation (LMWH>UFH) plus tpa 50 mg (over 2 hours) vs. anticoagulation alone Primary outcome: echo evidence of pulmonary hypertension at followup (mean 28 months) Am J Cardiol 2013; 111: 273-7
46 Management: high-risk submassive PE ULTIMA study 59 patients, acute PE with RV/LV ratio >1 UFH plus catheter-directed, ultrasound accelerated thrombolysis ( 20 mg/15 hrs) vs. UFH alone Primary outcome: difference in ratio at 24 hours Catheter-directed lytic group with significantly improved RV/LV ratio at 24 hours, no major bleeding
47 Management: IVC filters Classic teaching: recurrent PE reduced, DVT increased, neutral on total VTE and mortality PRECIP2 (JAMA 2015): no significant improvement in recurrent PE (3.0% filter group, 1.5% in no filter group at 3 months) Recommend against IVC filters for most Place if contraindication to anticoagulation Massive PE (or near-massive) with DVT ( next PE lethal)? à can be controversial
48 Management: overall goals Prevent immediate/in-hospital mortality related to PE Minimize risks and complications of therapy (anticoagulation, fibrinolysis, interventional procedures) Minimize risk of recurrent PE/DVT Reduce morbidity due to chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension and post thrombotic syndrome Individualize therapeutic choices based on risks/benefit profile of each patient New: Multidisciplinary PE response teams
49 Summary: Acute PE and DVT Venous thromboembolic disease is common; pulmonary embolism, in particular, can be very high risk. PE must be part of the differential diagnosis in appropriate patients with dyspnea, chest pain, syncope, or shock. Pathophysiology impacts gas exchange and cardiovascular mechanics, with a great range of severity. Diagnostic algorithms employ multimodality data, with results of Wells score, D-dimer testing, CT pulmonary angiogram, and compression ultrasonography highly relevant in most patients.
50 Summary: Acute PE and DVT Direct oral anticoagulants are now recommended as preferred treatment in non-cancer patients; some DOACs require up front parenteral therapy. Warfarin and LMWH will continue to be the appropriate choice anticoagulant for many Patients presenting with hypotension and/or shock represent a very high mortality subgroup and require aggressive medical/procedural intervention. Optimal treatment of the stable but high-risk submassive PE patient is still unclear and must be individualized.
51 Questions?
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center
 Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Disclosures. DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Questions To Ask. Dr. Susanna Shin - DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) None
 Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Disclosures. Objectives
 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Treatment of Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Staff Physician, Cardiovascular Division
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Treatment of Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Staff Physician, Cardiovascular Division
Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. PE - Clinical
 Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
Understanding Best Practices in Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism. Rajat Deo, MD, MTR
 Understanding Best Practices in Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism Rajat Deo, MD, MTR Director of Translational Research in Cardiac Arrhythmias Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
Understanding Best Practices in Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism Rajat Deo, MD, MTR Director of Translational Research in Cardiac Arrhythmias Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing (2012) NICE guideline CG144
 Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing (2012) NICE guideline CG144 Appendix A: Summary of new evidence from Summary of evidence from previous year Diagnosis Diagnostic
Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing (2012) NICE guideline CG144 Appendix A: Summary of new evidence from Summary of evidence from previous year Diagnosis Diagnostic
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM. Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow
 CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
Pulmonary Thromboembolism
 Pulmonary Thromboembolism James Allen, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year in the United States Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU
Pulmonary Thromboembolism James Allen, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year in the United States Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU
Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting Calgary, Alberta, October 2014 Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update Benjamin Bell, MD FRCPC James Douketis, MD FRCPC On Behalf of Thrombosis Canada
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting Calgary, Alberta, October 2014 Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update Benjamin Bell, MD FRCPC James Douketis, MD FRCPC On Behalf of Thrombosis Canada
Epidemiology. Update on Pulmonary Embolism. Keys to PE Management 5/5/2014. Diagnosis. Risk stratification. Treatment
 Update on Pulmonary Embolism Steven M. Dean, DO, FACP, RPVI Program Director- Vascular Medicine Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Cardiovascular Medicine The Ohio State University Keys
Update on Pulmonary Embolism Steven M. Dean, DO, FACP, RPVI Program Director- Vascular Medicine Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Cardiovascular Medicine The Ohio State University Keys
Updates in venous thromboembolism. Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia
 Updates in venous thromboembolism Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia News for VTE Diagnosis Treatment the acute phase the agents Pulmonary embolism: diagnosis Vein ultrasonography Meta-analysis 15
Updates in venous thromboembolism Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia News for VTE Diagnosis Treatment the acute phase the agents Pulmonary embolism: diagnosis Vein ultrasonography Meta-analysis 15
Pulmonary embolism: Acute management. Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia, Italy
 Pulmonary embolism: Acute management Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia, Italy Acute pulmonary embolism: Acute management Diagnosis Risk stratification Treatment Non-high risk PE: diagnosis 3-mo VTE
Pulmonary embolism: Acute management Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia, Italy Acute pulmonary embolism: Acute management Diagnosis Risk stratification Treatment Non-high risk PE: diagnosis 3-mo VTE
Single Center 4 year series of 114 consecutive patients treated for massive and submassive PE. Mark Goodwin, MD
 Single Center 4 year series of 114 consecutive patients treated for massive and submassive PE Mark Goodwin, MD Disclosure Speaker name:... I have the following potential conflicts of interest to report:
Single Center 4 year series of 114 consecutive patients treated for massive and submassive PE Mark Goodwin, MD Disclosure Speaker name:... I have the following potential conflicts of interest to report:
Risk factors for DVT. Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Anticoagulation (cont d) Diagnosis 1/5/2018. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Judith Hurdman Consultant Respiratory Physician
 Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism Judith Hurdman Consultant Respiratory Physician Judith.hurdman@sth.nhs.uk Overview Risk Stratification Who can be managed as an outpatient? To thrombolyse or not
Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism Judith Hurdman Consultant Respiratory Physician Judith.hurdman@sth.nhs.uk Overview Risk Stratification Who can be managed as an outpatient? To thrombolyse or not
PE and DVT. Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP
 PE and DVT Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call +256777363201 Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP OBJECTIVES DEFINE DVT AND P.E PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DVT CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF DVT/PE INVESTIGATE DVT MANAGEMENT
PE and DVT Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call +256777363201 Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP OBJECTIVES DEFINE DVT AND P.E PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DVT CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF DVT/PE INVESTIGATE DVT MANAGEMENT
Updates in Management of Pulmonary Embolism (PE) David Ming, MD Duke Hospital Medicine July 24, 2017 Hilton Head, SC
 Updates in Management of Pulmonary Embolism (PE) David Ming, MD Duke Hospital Medicine July 24, 2017 Hilton Head, SC Objectives Highlight clinical features and presentation of acute PE Analyze strategies
Updates in Management of Pulmonary Embolism (PE) David Ming, MD Duke Hospital Medicine July 24, 2017 Hilton Head, SC Objectives Highlight clinical features and presentation of acute PE Analyze strategies
Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis?
 Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? December 19, 2017 Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? Indications for Thrombolytic Therapy in Patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism Case Scenario A 28 year old woman
Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? December 19, 2017 Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? Indications for Thrombolytic Therapy in Patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism Case Scenario A 28 year old woman
Risk-Based Evaluation and Management of VTE
 12:50-1:50pm Risk-Based Evaluation and Management of VTE SPEAKER Gregory Piazza, MD, MS BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Risk-Based Evaluation and Management of VTE Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Assistant Professor
12:50-1:50pm Risk-Based Evaluation and Management of VTE SPEAKER Gregory Piazza, MD, MS BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Risk-Based Evaluation and Management of VTE Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Assistant Professor
PULMONARY EMBOLISM AND PERT. Jonathon Kirkland, DO OSU Department Chair, Radiology Head of Interventional Radiology
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM AND PERT Jonathon Kirkland, DO OSU Department Chair, Radiology Head of Interventional Radiology No financial disclosures 1. What are the clinical signs/symptoms of submassive PE? 2.
PULMONARY EMBOLISM AND PERT Jonathon Kirkland, DO OSU Department Chair, Radiology Head of Interventional Radiology No financial disclosures 1. What are the clinical signs/symptoms of submassive PE? 2.
Thrombolysis in PE. Outline. Disclosure. Overview on Pulmonary Embolism. Hot Topics in Emergency Medicine 2012 Midyear Clinical Meeting
 Disclosure Thrombolysis in PE Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP reports no relevant financial relationships. Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP Outline 55 YOF presents to ED with SOB PMH of DVT + noncompliance
Disclosure Thrombolysis in PE Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP reports no relevant financial relationships. Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP Outline 55 YOF presents to ED with SOB PMH of DVT + noncompliance
UC SF. Division of General Internal Medicine UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA SAN FRANCISCO, DIVISION OF HOSPITAL MEDICINE
 Updates in the Management of Venous Thromboembolism Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF Division of Hospital Medicine Medical Director, Anticoagulation Clinic Venous Thromboembolism
Updates in the Management of Venous Thromboembolism Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF Division of Hospital Medicine Medical Director, Anticoagulation Clinic Venous Thromboembolism
Acute and long-term treatment of PE. Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia
 Acute and long-term treatment of PE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia Acute and long-term treatment of VTE What is the optimal acute phase treatment for the patient? Intravenous thrombolysis One
Acute and long-term treatment of PE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia Acute and long-term treatment of VTE What is the optimal acute phase treatment for the patient? Intravenous thrombolysis One
Acute and long-term treatment of VTE. Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia
 Acute and long-term treatment of VTE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia Acute and long-term treatment of VTE The goals The acute PE phase After the acute phase Treatment for VTE Goals of acute treatment
Acute and long-term treatment of VTE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia Acute and long-term treatment of VTE The goals The acute PE phase After the acute phase Treatment for VTE Goals of acute treatment
PULMONARY EMBOLISM/VTE CARE PROCESS MODEL
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM/VTE CARE PROCESS MODEL IMCP FALL CONFERENCE 2017 Scott Stevens, MD Co-Director, Thrombosis Clinic & Thrombosis Research Group Intermountain Medical Center Professor of Clinical Medicine
PULMONARY EMBOLISM/VTE CARE PROCESS MODEL IMCP FALL CONFERENCE 2017 Scott Stevens, MD Co-Director, Thrombosis Clinic & Thrombosis Research Group Intermountain Medical Center Professor of Clinical Medicine
Venous Thrombosis. Magnitude of the Problem. DVT 2 Million PE 600,000. Death 60,000. Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year.
 Venous Thrombosis Magnitude of the Problem DVT 2 Million Postthrombotic Syndrome 800,000 PE 600,000 Death 60,000 Silent PE 1 Million Pulmonary Hypertension 30,000 Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year
Venous Thrombosis Magnitude of the Problem DVT 2 Million Postthrombotic Syndrome 800,000 PE 600,000 Death 60,000 Silent PE 1 Million Pulmonary Hypertension 30,000 Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year
October 2017 Pulmonary Embolism
 October 2017 Pulmonary Embolism Prof. Ahmed BaHammam, FRCP, FCCP Professor of Medicine College of Medicine King Saud University 1 Objectives Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis Massive PE Treatment
October 2017 Pulmonary Embolism Prof. Ahmed BaHammam, FRCP, FCCP Professor of Medicine College of Medicine King Saud University 1 Objectives Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis Massive PE Treatment
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC 1 st workshop: update to VTE guidelines in 2016 2 nd workshop: VTE controversies + new horizons André Roussin MD, FRCP, CSPQ CHUM
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC 1 st workshop: update to VTE guidelines in 2016 2 nd workshop: VTE controversies + new horizons André Roussin MD, FRCP, CSPQ CHUM
With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis
 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital April
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital April
The spectrum of clinical outcome of PE
 Practical treatment approach for patients with PE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia The spectrum of clinical presentation of PE PE-related shock Mild clinical symptoms The spectrum of clinical outcome
Practical treatment approach for patients with PE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia The spectrum of clinical presentation of PE PE-related shock Mild clinical symptoms The spectrum of clinical outcome
IDEAL MANAGEMENT OF PULMONARY EMBOLISM DISCLOSURES
 IDEAL MANAGEMENT OF PULMONARY EMBOLISM Samuel Z. Goldhaber, MD Section Head, Vascular Medicine Director, Thrombosis Research Group Cardiovascular Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine
IDEAL MANAGEMENT OF PULMONARY EMBOLISM Samuel Z. Goldhaber, MD Section Head, Vascular Medicine Director, Thrombosis Research Group Cardiovascular Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine
UPDATE ON TREATMENT OF ACUTE VENOUS THROMBOSIS
 UPDATE ON TREATMENT OF ACUTE VENOUS THROMBOSIS Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS 16 th National Congress of the Italian Society of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Bologna, 2017 Disclosure I have the following
UPDATE ON TREATMENT OF ACUTE VENOUS THROMBOSIS Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS 16 th National Congress of the Italian Society of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Bologna, 2017 Disclosure I have the following
Recent advances in the management of pulmonary embolism. Kodati Rakesh SR Pulmonary medicine
 Recent advances in the management of pulmonary embolism Kodati Rakesh SR Pulmonary medicine Clinical decision rules & D dimer Outpatient anticoagulation Thrombolysis Anticoagulation Catheter directed therapies
Recent advances in the management of pulmonary embolism Kodati Rakesh SR Pulmonary medicine Clinical decision rules & D dimer Outpatient anticoagulation Thrombolysis Anticoagulation Catheter directed therapies
Pulmonary Embolectomy:
 Pulmonary Embolectomy: Recommendation for early surgical intervention Tomas A. Salerno, M.D. Professor of Surgery, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and Jackson Memorial Hospital Epidemiology
Pulmonary Embolectomy: Recommendation for early surgical intervention Tomas A. Salerno, M.D. Professor of Surgery, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and Jackson Memorial Hospital Epidemiology
Clinical Guide - Suspected PE (Reviewed 2006)
 Clinical Guide - Suspected (Reviewed 2006) Principal Developer: B. Geerts Secondary Developers: C. Demers, C. Kearon Background Investigation of patients with suspected pulmonary emboli () remains problematic
Clinical Guide - Suspected (Reviewed 2006) Principal Developer: B. Geerts Secondary Developers: C. Demers, C. Kearon Background Investigation of patients with suspected pulmonary emboli () remains problematic
Focus: l embolia polmonare Per quanto la terapia anticoagulante orale? Giulia Magnani 27 Gennaio, 2018
 Focus: l embolia polmonare Per quanto la terapia anticoagulante orale? Giulia Magnani 27 Gennaio, 2018 NO DISCLOSURE Pulmonary Embolism Venous thromboembolism (VT) is the third most common cause of cardiovascular
Focus: l embolia polmonare Per quanto la terapia anticoagulante orale? Giulia Magnani 27 Gennaio, 2018 NO DISCLOSURE Pulmonary Embolism Venous thromboembolism (VT) is the third most common cause of cardiovascular
Heart Health ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism
 Heart Health Open Access Received: Oct 22, 2014 Accepted: Dec 01, 2014 Published: Dec 05, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.14437/hhoa-1-105 Review Jiri Widimsky, Heart Health Open Access 2014, 1:1 2014 ESC Guidelines
Heart Health Open Access Received: Oct 22, 2014 Accepted: Dec 01, 2014 Published: Dec 05, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.14437/hhoa-1-105 Review Jiri Widimsky, Heart Health Open Access 2014, 1:1 2014 ESC Guidelines
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF MASSIVE AND SUBMASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULT PATIENTS.
 RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF MASSIVE AND SUBMASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULT PATIENTS. Target Audience: Physicians managing adult patients with massive and submassive pulmonary emboli in the
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF MASSIVE AND SUBMASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULT PATIENTS. Target Audience: Physicians managing adult patients with massive and submassive pulmonary emboli in the
Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: 2017 Update and Future Directions
 Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: 2017 Update and Future Directions Kush R Desai, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, IL Disclosures
Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: 2017 Update and Future Directions Kush R Desai, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, IL Disclosures
Management of Intermediate-Risk Pulmonary Embolism
 Management of Intermediate-Risk Pulmonary Embolism Stavros V. Konstantinides, MD, PhD, FESC Professor, Clinical Trials in Antithrombotic Therapy Center for Thrombosis und Hemostasis, University of Mainz,
Management of Intermediate-Risk Pulmonary Embolism Stavros V. Konstantinides, MD, PhD, FESC Professor, Clinical Trials in Antithrombotic Therapy Center for Thrombosis und Hemostasis, University of Mainz,
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis. Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS
 Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Catheter-based thrombolysis Local administration of lytic agent Higher local
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Catheter-based thrombolysis Local administration of lytic agent Higher local
RISK STRATIFICATION OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE SYMPTOMATIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM. David Jiménez, MD, PhD, FCCP Ramón y Cajal Hospital, IRYCIS Madrid, Spain
 RISK STRATIFICATION OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE SYMPTOMATIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM David Jiménez, MD, PhD, FCCP Ramón y Cajal Hospital, IRYCIS Madrid, Spain Potential Conflicts of Interest Financial conflicts of
RISK STRATIFICATION OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE SYMPTOMATIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM David Jiménez, MD, PhD, FCCP Ramón y Cajal Hospital, IRYCIS Madrid, Spain Potential Conflicts of Interest Financial conflicts of
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine
 Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Approach to Thrombosis
 Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Changing the Ambulatory Training Paradigm: The Design and Implementation of an Outpatient Pulmonology Fellowship Curriculum
 Online Data Supplement Changing the Ambulatory Training Paradigm: The Design and Implementation of an Outpatient Pulmonology Fellowship Curriculum Stacey M. Kassutto, C. Jessica Dine, Maryl Kreider, Rupal
Online Data Supplement Changing the Ambulatory Training Paradigm: The Design and Implementation of an Outpatient Pulmonology Fellowship Curriculum Stacey M. Kassutto, C. Jessica Dine, Maryl Kreider, Rupal
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism
 Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
Pulmonary Embolism. Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri
 Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
REVIEW ON PULMONARY EMBOLISM
 REVIEW ON PULMONARY EMBOLISM * Shashi Kumar Yadav, Prof. Xiao Wei, Roshan Kumar Yadav, Sanjay Kumar Verma and Deepika Dhakal * Department of Medicine, Clinical College of Yangtze University, The first
REVIEW ON PULMONARY EMBOLISM * Shashi Kumar Yadav, Prof. Xiao Wei, Roshan Kumar Yadav, Sanjay Kumar Verma and Deepika Dhakal * Department of Medicine, Clinical College of Yangtze University, The first
DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO IMPROVING CLINICAL OUTCOMES
 DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO IMPROVING CLINICAL OUTCOMES Jose M. Borromeo M.D. Vascular Surgeon Iowa Heart Center Disclosures: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals Cook CVRx LeMaitre Vascular,
DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO IMPROVING CLINICAL OUTCOMES Jose M. Borromeo M.D. Vascular Surgeon Iowa Heart Center Disclosures: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals Cook CVRx LeMaitre Vascular,
Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs). Dr GM Benson Director NI Haemophilia Comprehensive Care Centre and Thrombosis Unit BHSCT
 Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs). Dr GM Benson Director NI Haemophilia Comprehensive Care Centre and Thrombosis Unit BHSCT OAC WARFARIN Gold standard DABIGATRAN RIVAROXABAN APIXABAN EDOXABAN BETRIXABAN
Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs). Dr GM Benson Director NI Haemophilia Comprehensive Care Centre and Thrombosis Unit BHSCT OAC WARFARIN Gold standard DABIGATRAN RIVAROXABAN APIXABAN EDOXABAN BETRIXABAN
What s New in DVT & PE
 What s New in DVT & PE Mark Buch MD CM CCFP(EM) Attending physician Emergency Department Jewish General Hospital Family Physician and Medical Director GMF Santé Mont-Royal Objectives: Review the diagnostic
What s New in DVT & PE Mark Buch MD CM CCFP(EM) Attending physician Emergency Department Jewish General Hospital Family Physician and Medical Director GMF Santé Mont-Royal Objectives: Review the diagnostic
Epidemiology: Incidence VTE: Mortality Morbidity Risk Factors: Acute Chronic : Genetic
 Submassive PE Pulmonary Embolism Epidemiology: Incidence VTE: 100-200/100,000 = 3rd most frequent cardiovascular disease Symptomatic DVT complicated by PE = 40-50% Sudden fatal PE = 34% Intermediate-risk
Submassive PE Pulmonary Embolism Epidemiology: Incidence VTE: 100-200/100,000 = 3rd most frequent cardiovascular disease Symptomatic DVT complicated by PE = 40-50% Sudden fatal PE = 34% Intermediate-risk
A Review of the Role of Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants in the Acute and Long-Term Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism
 Cardiol Ther (2018) 7:1 13 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40119-018-0107-0 REVIEW A Review of the Role of Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants in the Acute and Long-Term Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Andrew
Cardiol Ther (2018) 7:1 13 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40119-018-0107-0 REVIEW A Review of the Role of Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants in the Acute and Long-Term Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Andrew
Case. Case. Management of Pulmonary Embolism in the ICU
 Management of Pulmonary Embolism in the ICU Todd M Bull, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Pulmonary Sciences and Critical Care Medicine Pulmonary Hypertension Center University of Colorado
Management of Pulmonary Embolism in the ICU Todd M Bull, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Pulmonary Sciences and Critical Care Medicine Pulmonary Hypertension Center University of Colorado
PE Pathway. The charts are listed as follows:
 PE Pathway This document comprises 6 simple flow charts to assist clinicians in the investigation and treatment of suspected or confirmed Acute Pulmonary Emboli. The pathway has been put together using
PE Pathway This document comprises 6 simple flow charts to assist clinicians in the investigation and treatment of suspected or confirmed Acute Pulmonary Emboli. The pathway has been put together using
Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE
 Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE-SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO Financial Disclosures-NONE
Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE-SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO Financial Disclosures-NONE
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
What is New in Acute Pulmonary Embolism? Interventional Treatment. Prof. Nils Kucher University Hospital Bern Switzerland
 What is New in Acute Pulmonary Embolism? Interventional Treatment Prof. Nils Kucher University Hospital Bern Switzerland nils.kucher@insel.ch Disclosure of Interest Dr. Kucher received research grants
What is New in Acute Pulmonary Embolism? Interventional Treatment Prof. Nils Kucher University Hospital Bern Switzerland nils.kucher@insel.ch Disclosure of Interest Dr. Kucher received research grants
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism: High-Tech versus Low- Tech, which way to go?
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism: High-Tech versus Low- Tech, which way to go? Philip S. Wells MD, FRCPC, MSc Professor Chair and Chief, Department of Medicine, University of Ottawa DISCLOSURE
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism: High-Tech versus Low- Tech, which way to go? Philip S. Wells MD, FRCPC, MSc Professor Chair and Chief, Department of Medicine, University of Ottawa DISCLOSURE
Acute Management of Pulmonary Embolism
 Acute Management of Pulmonary Embolism Dr Alex West Respiratory Consultant Guy s and St Thomas Hospital London Declarations - none Order of Play Up date in Diagnostic Imaging - CTPA and V:Q SPECT Sub-massive
Acute Management of Pulmonary Embolism Dr Alex West Respiratory Consultant Guy s and St Thomas Hospital London Declarations - none Order of Play Up date in Diagnostic Imaging - CTPA and V:Q SPECT Sub-massive
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
PE service. 65 years old lady. What would you do next? Risk stratification. What would you do next? Regional College Lecture PE Management
 PE service Regional College Lecture PE Management Update in medicine (Eastern) Cambridge 29 th June 2017 Dr Rachel M Limbrey DM FRCP University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust Ambulatory acute
PE service Regional College Lecture PE Management Update in medicine (Eastern) Cambridge 29 th June 2017 Dr Rachel M Limbrey DM FRCP University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust Ambulatory acute
Mark H. Meissner, MD Peter Gloviczki Professor of Venous & Lymphatic Disorders University of Washington School of Medicine
 Pulmonary Embolism Response Teams Not So Fast Early Interventions is a House of Cards Mark H. Meissner, MD Peter Gloviczki Professor of Venous & Lymphatic Disorders University of Washington School of Medicine
Pulmonary Embolism Response Teams Not So Fast Early Interventions is a House of Cards Mark H. Meissner, MD Peter Gloviczki Professor of Venous & Lymphatic Disorders University of Washington School of Medicine
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis. Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS
 Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Conflict of Interest BTG Standard PE therapy ANTICOAGULATION (AC) HEPARIN
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Conflict of Interest BTG Standard PE therapy ANTICOAGULATION (AC) HEPARIN
Pulmonary embolism. Paweł Balsam
 Pulmonary embolism Paweł Balsam Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) are two clinical presentations of veonus thromboembolism Pulmonary embolism A pulmonary
Pulmonary embolism Paweł Balsam Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) are two clinical presentations of veonus thromboembolism Pulmonary embolism A pulmonary
4/18/2018. Objectives. Background. 1) Compare and contrast the various validated tools for the identification of patients with pulmonary embolism
 Pulmonary Embolism: Assessment, risk-stratification, and treatment plan for the outpatient management of low-risk patients Presentation by Joshua T. Wood, PharmD/PGY-1 Resident Providence St. Patrick Hospital;
Pulmonary Embolism: Assessment, risk-stratification, and treatment plan for the outpatient management of low-risk patients Presentation by Joshua T. Wood, PharmD/PGY-1 Resident Providence St. Patrick Hospital;
DVT - initial management NSCCG
 Background information Information resources for patients and carers Updates to this care map Synonyms Below knee DVT and bleeding risks Patient with confirmed DVT Scan confirms superficial thrombophlebitis
Background information Information resources for patients and carers Updates to this care map Synonyms Below knee DVT and bleeding risks Patient with confirmed DVT Scan confirms superficial thrombophlebitis
Use of EKOS Catheter in the management of Venous Mr. Manoj Niverthi, Mr. Sarang Pujari, and Ms. Nupur Dandavate, The GTF Group
 Use of EKOS Catheter in the management of Venous Thromboembolism @ Mr. Manoj Niverthi, Mr. Sarang Pujari, and Ms. Nupur Dandavate, The GTF Group Introduction Georgia Thrombosis Forum (GTF, www.gtfonline.net)
Use of EKOS Catheter in the management of Venous Thromboembolism @ Mr. Manoj Niverthi, Mr. Sarang Pujari, and Ms. Nupur Dandavate, The GTF Group Introduction Georgia Thrombosis Forum (GTF, www.gtfonline.net)
Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
 Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Whal Lee, M.D. Seoul National University Hospital Department of Radiology 2 nd EFORT Asia Symposium, 3 rd November 2010, Taipei DVT - Risk Factors Previous
Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Whal Lee, M.D. Seoul National University Hospital Department of Radiology 2 nd EFORT Asia Symposium, 3 rd November 2010, Taipei DVT - Risk Factors Previous
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF MASSIVE AND SUBMASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULT PATIENTS.
 DRAFT-2018 UPDATES RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF MASSIVE AND SUBMASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULT PATIENTS. Target Audience: MultiCare physicians managing adult patients with massive and submassive
DRAFT-2018 UPDATES RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF MASSIVE AND SUBMASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULT PATIENTS. Target Audience: MultiCare physicians managing adult patients with massive and submassive
Duration of Anticoagulation? Peter Verhamme MD, PhD Department of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Leuven Belgium
 Duration of Anticoagulation? Peter Verhamme MD, PhD Department of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Leuven Belgium Disclosures Honoraria and research support: Daiichi-Sankyo, Boehringer Ingelheim,
Duration of Anticoagulation? Peter Verhamme MD, PhD Department of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Leuven Belgium Disclosures Honoraria and research support: Daiichi-Sankyo, Boehringer Ingelheim,
Dr. Riaz JanMohamed Consultant Haematologist The Hillingdon Hospital Foundation Trust
 MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) IN THE COMMUNITY SETTING & ANTICOAGULATION CLINICS THE PAST, PRESENT AND THE FUTURE Dr. Riaz JanMohamed Consultant Haematologist The Hillingdon Hospital
MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) IN THE COMMUNITY SETTING & ANTICOAGULATION CLINICS THE PAST, PRESENT AND THE FUTURE Dr. Riaz JanMohamed Consultant Haematologist The Hillingdon Hospital
The clinical relevance of AMPLIFY programme
 Venice October 16th 2015 The clinical relevance of AMPLIFY programme Francesco Dentali Department of Clinical Medicine Insubria University Varese Disclosures Bayer Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer Boehringer
Venice October 16th 2015 The clinical relevance of AMPLIFY programme Francesco Dentali Department of Clinical Medicine Insubria University Varese Disclosures Bayer Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer Boehringer
Management of Pulmonary Embolism. Michael Hooper, M.D., MSc Associate Professor, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Eastern Virginia Medical School
 Management of Pulmonary Embolism Michael Hooper, M.D., MSc Associate Professor, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Eastern Virginia Medical School I have no conflicts of interest to report. VTE Overview
Management of Pulmonary Embolism Michael Hooper, M.D., MSc Associate Professor, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Eastern Virginia Medical School I have no conflicts of interest to report. VTE Overview
Updates in Medical Management of Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis. By: Justin Youtsey, Elliott Reiff, William Montgomery, Grant Finlan
 Updates in Medical Management of Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis By: Justin Youtsey, Elliott Reiff, William Montgomery, Grant Finlan Objectives Describe the prevalence of PE and DVT as it relates
Updates in Medical Management of Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis By: Justin Youtsey, Elliott Reiff, William Montgomery, Grant Finlan Objectives Describe the prevalence of PE and DVT as it relates
PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT-
 University Goce Delcev, Faculty of Medical sciences, Stip University Clinic of Cardiology, Skopje R. Of Macedonia PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT- Gordana Kamceva MD mr.sci Acknowledgment Marija Vavlukis
University Goce Delcev, Faculty of Medical sciences, Stip University Clinic of Cardiology, Skopje R. Of Macedonia PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT- Gordana Kamceva MD mr.sci Acknowledgment Marija Vavlukis
The latest on the diagnosis and treatment of venous thromboembolism
 The latest on the diagnosis and treatment of venous thromboembolism Vicky Tagalakis MD FRCP Division of General Internal Medicine Jewish General Hospital McGill University Disclosures Advisory board Pfizer
The latest on the diagnosis and treatment of venous thromboembolism Vicky Tagalakis MD FRCP Division of General Internal Medicine Jewish General Hospital McGill University Disclosures Advisory board Pfizer
Developments in the management and treatment of pulmonary embolism
 REVIEW PULMONARY EMBOLISM Developments in the management and treatment of pulmonary embolism Rachel Limbrey 1 and Luke Howard 2 Affiliations: 1 University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, Southampton,
REVIEW PULMONARY EMBOLISM Developments in the management and treatment of pulmonary embolism Rachel Limbrey 1 and Luke Howard 2 Affiliations: 1 University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, Southampton,
Management of sub-massive and massive pulmonary embolism:
 Management of sub-massive and massive pulmonary embolism: Evidence and Controversy Boonsong Patjanasoontorn, MD, FCCP, FCCM Immediate Past President, Thai Society of Critical Care Medicine(TSCCM) Chief,
Management of sub-massive and massive pulmonary embolism: Evidence and Controversy Boonsong Patjanasoontorn, MD, FCCP, FCCM Immediate Past President, Thai Society of Critical Care Medicine(TSCCM) Chief,
Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Hemostasis. PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures
 Hemostasis PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures Disorders of Hemostasis - Hemophilia - von Willebrand Disease HEMOPHILIA A defect in the thrombin propagation phase
Hemostasis PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures Disorders of Hemostasis - Hemophilia - von Willebrand Disease HEMOPHILIA A defect in the thrombin propagation phase
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT?
 How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
Pulmonary embolism. Paweł Balsam MD, PhD
 Pulmonary embolism Paweł Balsam MD, PhD Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) are two clinical presentations of veonus thromboembolism Pulmonary embolism A
Pulmonary embolism Paweł Balsam MD, PhD Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) are two clinical presentations of veonus thromboembolism Pulmonary embolism A
DVT and Pulmonary Embolus. Dr Piers Blombery BSc(Biomed), MBBS (Hons), FRACP, FRCPA Consultant Haematologist Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre
 DVT and Pulmonary Embolus Dr Piers Blombery BSc(Biomed), MBBS (Hons), FRACP, FRCPA Consultant Haematologist Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Overview Structure of deep and superficial venous system of upper
DVT and Pulmonary Embolus Dr Piers Blombery BSc(Biomed), MBBS (Hons), FRACP, FRCPA Consultant Haematologist Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Overview Structure of deep and superficial venous system of upper
Disclosures. What is a Specialty Vein Clinic? Prevalence of Venous Disease. Management of Venous Disease: an evidence based approach.
 Management of Venous Disease: an evidence based approach Disclosures Ed Boyle, MD Andrew Jones, MD Dr. Ed Boyle and Dr. Andrew Jones disclose Grants/research support: Medtronic, BTG International, Clearflow,
Management of Venous Disease: an evidence based approach Disclosures Ed Boyle, MD Andrew Jones, MD Dr. Ed Boyle and Dr. Andrew Jones disclose Grants/research support: Medtronic, BTG International, Clearflow,
Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease
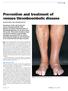 REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
The Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE): Has Warfarin Met Its Match? Michael P. Gulseth, Pharm. D., BCPS, FASHP Program Director for
 The Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE): Has Warfarin Met Its Match? Michael P. Gulseth, Pharm. D., BCPS, FASHP Program Director for Anticoagulation Services Sanford USD Medical Center Sioux Falls,
The Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE): Has Warfarin Met Its Match? Michael P. Gulseth, Pharm. D., BCPS, FASHP Program Director for Anticoagulation Services Sanford USD Medical Center Sioux Falls,
Too much medicine and venous thromboembolism: How can we make things Well again?
 Too much medicine and venous thromboembolism: How can we make things Well again? Emily G McDonald MD MSc; Assistant professor of medicine; McGill University Health Centre Canadian Society of Internal Medicine;
Too much medicine and venous thromboembolism: How can we make things Well again? Emily G McDonald MD MSc; Assistant professor of medicine; McGill University Health Centre Canadian Society of Internal Medicine;
Non commercial use only. The treatment of venous thromboembolism with new oral anticoagulants. Background
 Italian Journal of Medicine 2013; volume 7(s8):29-35 The treatment of venous thromboembolism with new oral anticoagulants Davide Imberti AUSL Piacenza, Italy ABSTRACT Traditional anticoagulants, such as
Italian Journal of Medicine 2013; volume 7(s8):29-35 The treatment of venous thromboembolism with new oral anticoagulants Davide Imberti AUSL Piacenza, Italy ABSTRACT Traditional anticoagulants, such as
Single-Center, Retrospective, Observational Analysis of Patients with Submassive Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Receiving Catheter- Directed Thrombolysis
 Single-Center, Retrospective, Observational Analysis of Patients with Submassive Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Receiving Catheter- Directed Thrombolysis John A. Phillips, M.D. OhioHealth Heart and Vascular Physicians
Single-Center, Retrospective, Observational Analysis of Patients with Submassive Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Receiving Catheter- Directed Thrombolysis John A. Phillips, M.D. OhioHealth Heart and Vascular Physicians
Top 5 (or so) Hematology Consults. Tom DeLoughery, MD FACP FAWM. Oregon Health and Sciences University DISCLOSURE
 Top 5 (or so) Hematology Consults Tom FACP FAWM Oregon Health and Sciences University DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Speaker Bureau - None Consultant/Research none 1 What I am Talking About
Top 5 (or so) Hematology Consults Tom FACP FAWM Oregon Health and Sciences University DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Speaker Bureau - None Consultant/Research none 1 What I am Talking About
SESSION 4 12:45 2:15 PM
 SESSION 4 12:45 2:15 PM Pulmonary Embolism Update SPEAKER Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Gregory Piazza, MD, MS:
SESSION 4 12:45 2:15 PM Pulmonary Embolism Update SPEAKER Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Gregory Piazza, MD, MS:
When and How to Use the Newly Approved Oral Anticoagulants to Treat Acute Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Ian del Conde, MD
 When and How to Use the Newly Approved Oral Anticoagulants to Treat Acute Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Ian del Conde, MD December 12, 2015 Disclosures CONSULTANT Merck; New Haven
When and How to Use the Newly Approved Oral Anticoagulants to Treat Acute Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Ian del Conde, MD December 12, 2015 Disclosures CONSULTANT Merck; New Haven
Thrombophilia. Diagnosis and Management. Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI
 Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
How and Why to Form a PERT, Pulmonary Embolism Response Team
 Disclosures How and Why to Form a PERT, Pulmonary Embolism Response Team Rachel P. Rosovsky, MD, MPH No disclosures Rachel P. Rosovsky, MD, MPH April 21, 2017 AC Forum 2017 2 Agenda Pulmonary Embolism
Disclosures How and Why to Form a PERT, Pulmonary Embolism Response Team Rachel P. Rosovsky, MD, MPH No disclosures Rachel P. Rosovsky, MD, MPH April 21, 2017 AC Forum 2017 2 Agenda Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis & Treatment Guideline
 Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis & Treatment Guideline Background... 2 Evaluation and Diagnosis Adults... 3 Pregnant women... 4 Adults with cancer... 5 Choice of Treatment Setting... 6 Subsegmental PE: Treatment
Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis & Treatment Guideline Background... 2 Evaluation and Diagnosis Adults... 3 Pregnant women... 4 Adults with cancer... 5 Choice of Treatment Setting... 6 Subsegmental PE: Treatment
