ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT ARTICLE INFO
|
|
|
- Myrtle Cobb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (6): , November - December, 2018 doi: /S IBJU Artificial sphincter BR - SL - AS 904 in the treatment of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: efficacy, practicality and safety in a prospective and multicenter study Salvador Vilar Correia Lima 1, 2, Evandilson Guenes Campos de Barros 1, Fabio de Oliveira Vilar 1, Flavia Cristina Morone Pinto 2, Thomé Décio Pinheiro Barros 1, 2, José Carlos Truzzi 3, Luiz Gustavo M. de Toledo 4, Francisco Kanasiro 5, João Luiz Amaro 6 1 Serviço de Urologia, Hospital das Clínicas, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, UFPE, Recife, PE, Brasil; 2 Departamento de Cirurgia, Centro de Ciências da Saúde, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, UFPE, Recife, PE, Brasil; 3 Departamento de Urologia, Instituto do Câncer Dr. Arnaldo Vieira de Carvalho, São Paulo, SP, Brasil; 4 Santa Casa de Misericórdia de São Paulo, São Paulo, SP, Brasil; 5 Serviço de Urologia, Hospital Santa Marcelina, Porto Velho, RO, Brasil; 6 Disciplina de Urologia, Unesp - Universidade Estadual Paulista, São Paulo, SP, Brasil ABSTRACT Purpose: The objective of the present study is to test the efficiency and practicality of a new artificial sphincter BR - SL - AS in the control of urinary incontinence in post - PR patients and to evaluate their complications. Patients and Methods: Fifteen patients with incontinence after one year of radical prostatectomy were included prospectively. All patients underwent artificial urethral sphincter (AUS) implant BR - SL - AS according to established technique. Independent variables such as free urinary flow, PAD weight test, ICIQ - SF score and urinary symptoms through the IPSS score were compared in different follow-up moments. Results: Patients submitted to AUS implantation did not present trans - operative or post - operative complications related to the surgical act such as: infection, hematoma, erosion or urinary retention. Device was inert to the body during the follow-up, showing an excellent adaptation of the patients, besides the easy handling. The mean age was years 40% of the patients had systemic arterial hypertension, 6.7% diabetes mellitus, 6.7% were hypertensive and diabetic, 13.4% were hypertensive, had diabetes and hypercholesterolemia and 26.7% patients had no comorbidities. It was evidenced that the urinary flow peak during the follow-up remained stable. Decreased averages and median PAD weight test were to and to 23.50, respectively. The IPSS score decreased and the quality of life increased (12.33 to 3.40 and 2.50 to 3.20 respectively). The ICQF - SF questionnaire score also showed a decrease, ranging from 16, 71 to Conclusion: The artificial sphincter implant BR - SL - AS 904 was reproducible, safe and effective in the control of urinary incontinence in post - PR patients. ARTICLE INFO Keywords: Urinary Incontinence; Urinary Sphincter, Artificial; Prostatic Neoplasms Int Braz J Urol. 2018; 44: Submitted for publication: March 06, 2018 Accepted after revision: June 26, 2018 Published as Ahead of Print: September 20,
2 INTRODUCTION Prostate cancer is the most frequently diagnosed non - skin cancer in the United States and the third leading cause of cancer deaths. In 2017, new cancer cases and cancer deaths were projected to occur in the United States (1). Radical prostatectomy (PR) is the currently treatment with satisfactory cancer results in patients with localized or locally advanced prostate neoplasia without major comorbidities. However, the main complication PR - associated is the involuntary loss of urine, ie, urinary incontinence (UI). After one year of persistent UI pos - PR, the artificial sphincter implant is the main treatment option. AMS 800 artificial sphincter is currently considered the gold standard treatment for men with UI. However, this system has high complexity for the implantation of the device. It is necessary to perform a high number of procedures to obtain satisfactory rates of urinary continence associated with acceptable rates of surgical complications (2). In a retrospective study, from January 1972 to September 2015, cases were included from the AMS 800 implants, of which required either revision or explantation (21.1%). Younger age and penoscrotal approach were associated with higher device explantation and revision rates, while use of a tandem cuff was associated with higher explantation rates (3). In addition, another limiting factor for this type of device is that the operating mechanism is static, ie, the pressure exerted on the urethra through the cuff is constant as the patient is at rest, exercising, coughing or performing maneuvers that increase abdominal pressure (personal findings). Finally, those implants have a high economic cost making its accessibility quite limited, especially for those patients assisted in the public health system. The BR - SL - AS 904 sphincter was developed in order to reduce the restrictions of the currently available devices, to improve the postoperative results and to make the implantation of an artificial urinary sphincter feasible and accessible. PATIENTS AND METHODS This was a prospective, multicenter, nonrandomized trial with patients with urinary incon- tinence after radical retropubic prostatectomy and submitted to artificial urethral sphincter implant BR - SL - AS The trial was carried out in accordance to the National Council of Health, the Helsinque Declaration and the Nuremberg Code for human experiment. The study is also listed on and was approved by the National Ethics Committee in Research (CONEP # ). The non - inclusion of a control group was discussed and accepted by the Ethical Committee of the Institution. Patient eligibility criteria Fifteen patients with moderate and severe incontinence after one year of radical prostatectomy were included prospectively. All patients underwent artificial urethral sphincter (UE) implant BR - SL - AS according to established technique. Patients submitted to previous radiotherapy; patients with urethral stenosis or previously submitted to internal urethrotomy due to vesico - urethral anastomosis stenosis were excluded. BR - SL - AS 904 sphincter appearances The proposed device operating mechanism including two parts: constriction - pumping system and activating valve (Figure-1). The resting device maintains urethral compression preserving urinary continence. During pumping, the fluid present in the device is displaced from the urethral cuff to the reservoir located in the peritoneal cavity and through a flow reducing system it slowly returns to the cuff, causing it to remain deflated for about three minutes allowing urination (Figure-2). Surgical technique and device s implant The implant of the device was performed through two incisions: one perineal and one inguinal. In the perineal incision, a five - centimeter incision was made at the bulbar urethra level, allowing the passage of the constrictor balloon. After the cuff is passed, it is locked through the safety catch. After the perineal surgical time, an inguinal incision was made close to the external inguinal ring, dissected by anatomic planes, with communication between the inguinal and perineal incisions, parallel to the inguinal canal, forming a tunnel through which the device is carefully introduced. In the inguinal region, an 1216
3 Figure 1 - Appearance of the disassembled BR-SL-AS 904 sphincter (A), consisting of the following parts: 1; 2; 4; and 5: constriction-pumping system and 3: activating valve. B) sphincter ready to be implanted after air removal by injecting 15ml of saline through the activator valve (B). A B Figure 2 - A) Pressure reducing system and B) Operating system. The resting device maintains urethral compression preserving urinary continence. A B (A). During pumping, the fluid present in the apparatus is displaced from the urethral cuff to the reservoir located in the peritoneal cavity and through a flow reducing system it slowly returns to the cuff, causing it to remain deflated for about three minutes allowing urination (B). incision was made in the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle to gain access to the Retzius space. This space is dissected carefully forming a retropubic virtual cavity, where the reservoir of the urethral sphincter would be placed. After the reservoir was allocated in the Retzius space, a new subcutaneous tunnel was made towards the patient s flank. After passage of the device through the conduit formed we carefully allocate the periurethral cuff around the bulbar urethra and lock the urethral cuff using the safety clips (Figure-3). The wound suture was performed by planes 1217
4 Figure 3 - Surgical technique and device implantation steps: 1-2) Perineal and inguinal incision, respectively; 3) Inguinal tunnel construction and device passage; 4) Device in the perineal region; 5-8) Periurethral cuff being activated and locked with vicryl 3-0 and skin with 4-0 mononylon. The surgical stitches were removed on the tenth postoperative day and the device activated on the thirtieth day by infusing 15 ml of distilled water into the system through the activation valve. After activation of the system, the patient was instructed to manually activate the pump located in the scrotal sac to start voiding (Figure-4). independent variables: free urinary flow, PAD weight test, quality of life through ICIQ SF score; urinary symptoms through the IPSS score, all of them in the different moments of the urologist evaluations and lastly possible complications inherent to the implantation of the device such as infections, erosions and device failure. Figure 4 - Aspect of the sphincter BR-SL-AS 904 (Pump), activation valve (B). Surgical stitches were removed on the tenth postoperative day and the device activated on the thirtieth day by infusing 15 ml of distilled water into the system by the activation valve (C). A B C Clinical and urological outcomes As an independent variable, the implantation of the device was evaluated, and as Statistical analyses Data were analyzed descriptively and inferentially. The descriptive analysis was through 1218
5 absolute frequencies in the categorical variables and the statistics: mean and standard deviation. The inferential analysis was performed through the F (ANOVA) tests for repeated measures and Friedman s test for the comparison between the evaluations. In the case of significant difference by the F test (ANOVA), multiple Bonferroni comparisons were obtained. The verification of the normality hypothesis was through the Shapiro - Wilk test. The margin of error used in the statistical test decisions was 5%. The data were tabulated in Excel and analyzed in the SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, IBM statistics, version 23.0). RESULTS Fifteen patients underwent implantation of AUS at the three centers participating in the study. The mean age was 68.2 ± 7.5 years. In comorbidities analysis, it was observed that 40% of the patients had hypertension, 6.7% presented diabetes mellitus, 6.7% were hypertensive and diabetic patients, 6.7% had chronic renal insufficiency, 13.4% were hypertensive, diabetic and had hypercholesterolemia, and 26.7% of the patients had no comorbidities. The mean postoperative follow-up was months. These data are described in Table-1. Analyzing the complaints of the patients studied, it was identified that two thirds of them did not have voiding urgency, this index remained stable until the end of the study. The percentage of patients classified with the light score on the IPSS scale was 40.0% at visit 1, 46.7% after device activation and 80.0% at visit 4. The percentage of those classified as moderate had a variation of 33.3% at visit 1 to 20% at visit 4. The severe classification in the IPSS was 26.7% in the pre - op, and zero at visit 4. In the analysis of the quality of life an improvement was identified in well and happy, as well as a decrease in unhappy and terrible scores during follow-up visits. Data described in Table-2. Table-3 presents the statistics related to the different clinical and urological variables. Patient s weight and BMI remained stable during the course of the study, as well as the number of daily urinary frequency and free peak flow. It was possible to verify a statistically significant difference (p = 0.016) in the IPSS score: highest mean in the preoperative period (12.3) and the lowest in the visit 4 (3.4) (Figure-5). Although there was no statistical relevance for the other variables, it was observed an objective improvement in the scores of involuntary urinary loss and improvement of quality of life with maintenance of urinary flow force without obstructive symptoms. The device was inert to the body throughout Table 1 - Mean age and medical comorbidities. Outcomes Total n 15 Age (years): mean ± SD ± 7.56 Comorbidity Chronic Renal Insufficiency 1 Hypertension 6 Hypertension + Diabetes Mellitus 1 Hypertension + Diabetes Mellitus + 2 Dyslipidemia Diabetes Mellitus 1 None 4 Satisfaction rate Unsatisfied 15 Post-surgery (weeks) ±
6 Table 2 - Urinary urgency, IPSS and quality of life per urologist visit. Urologist visit Pre-op Visit 1 Visit 2 Visit 3 Visit 4 Outcome n n n n n TOTAL Urinary urgency Yes No Not informed IPSS Mild (0-7) Moderate (8-19) Severe (20-35) Quality of life Unhapy Awful Discomfort Generally well Regular Happy Nor informed The Outpatient Follow-up was performed every 30 days (Visit). Table 3 - Statistics related to the different clinical and urological variables. Urologist evaluation Outcome Pre-op Visit 1 Visit 2 Visit 3 Visit 4 P-value Weight ± ± ± ± ± 7.33 p (1) = BMI ± ± ± ± ± 3.38 p (1) = Daily urination 5.47 ± ± ± ± ± 1.27 p (2) = Urinary free flow ± ± ± ± ± p (1) = PAD test ± ± ± ± ± p (2) = IPSS score ± 7.57 (A) 8.73 ± 6.08 (AB) 9.07 ± 7.20 (AB) 7.67 ± 6.62 (B) 3.40 ± 3.92 (C) *p (1) = Quality of life 2.50 ± ± ± ± ± 1.40 p (2) = ICIQ-SF ± ± ± ± ± 7.17 p (1) = (*) Mean P (1) One way ANOVA; (2) Friedman s test. Different letter at the same line means statistically different. 1220
7 the initial follow-up of the study, showing an excellent adaptation of the patients. After clarification at the device activation visit, the patients were able to handle the device without difficulties, thus demonstrating its practicality. At the second follow-up visit, four patients reported a return of urinary loss and difficulty in activating the device, probably due to a mechanical problem. After information and clarification, two patients decided to exchange for a new device, while two other patients chose to remain with it. In the trans - operatory period, it was observed a UI treatment after RP, through the analysis of the learning curve of the device implant, and through the dependent variables such as PAD weight test, ICIQ SF score, IPSS score and main related complications. After more than 25 years of widespread use, the modern version of the AMS800 has proven to be a reliable surgical option for the management of non - neurogenic UI in men (6). However, large amounts of data regarding efficiency, complications, and patient satisfaction have been published after artificial sphincter implantation, but the quality of Figure 5 - IPSS score per medical evaluation. fracture of the T connection hoses in both exchanged devices. Those complications occurred after the fourth month of surgery. There was no complication related to the surgical procedure or the reaction between the device and the organism, due to the mechanical problem (material fatigue). At the moment, these patients are in clinical follow-up according to established protocol. This event was communicated to the ethics committee of the participating center. DISCUSSION Patients undergoing radical prostatectomy (RP) may suffer of urinary incontinence (UI) mainly due to damage sustained to the distal urethral sphincter, essentially producing stress urinary incontinence. In men, the artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) is currently considered the gold standard treatment for UI (4, 5). In our study, we proposed a new device for these reports does not meet current standards of evidence-based medicine (7-9). The AMS800 remains the gold standard but does not have the ability of rearrange the cuff in case of postoperative urethral atrophy (10, 11) and no option to adjust the issued pressure of the device after activation. The artificial sphincter BR - SL - AS 904, unlike the commercially available sphincters, has a pressure transmission system, where a reservoir in the patient s abdominal cavity has a direct connection with the urethral cuff. Therefore, the pressure exerted on the reservoir is transmitted through the hydraulic system to the urethral cuff, maintaining the continence of the patient only during stress. This device had already been described experimentally and the authors suggests that the direct pressure transmission to the cuff is an interesting concept to improve clinical outcomes of hydraulic sphincters (6). All surgeons reported the implantation of BR - SL - AR 908 being strai- 1221
8 ghtforward, fast, feasible and reproducible, with also a short learning curve to achieve mastery (personal findings). Unlike the facility offered by our device, the gold standard sphincter (AM800) is still provided in several boxes and separated components to assemble during the procedure with a constraining preparation (12). In addition, none of patients submitted to our implant presented trans - operative or postoperative complications related to the surgical procedure, using Clavien - Dindo score (13). Mean age of the population at surgery was 68.2 years (SD 7.5) and did not appear to be related to any complications, however it is unclear why younger age would lead to higher complication rates. One potential explanation is that younger patients in this series had longer documented follow-ups, and consequentially a higher chance for complications and need for revision surgery. There are limited reports that have specifically examined the effect of age on AUS outcomes (14, 15). While one study did demonstrate that octogenarians were more likely to experience erosion or infection compared with younger patients (28), the 5 - year device survival rates were comparable to those reported in younger men (63% to 70%). As such, current evidence remains unclear to recommend making decisions on AUS placement and outcomes solely based on age. We sought to identify risk factors for AUS complications such as prior radiation, or comorbid conditions as diabetes and hypertension. This study could not identify any statistically significant risk factors for AUS complications. To do so, it will be necessary a higher number of patients and studies. However, we could notice in our study that patient comorbidities, in particular diabetes (40%) and hypertension + diabetes (13%), had similar rates of urinary urgency, IPSS and reported quality of life. In particular, pelvic radiation and high blood pressure have been considered potential risk factors for AUS treatment failure and complication but our study did not have any case of it (16, 17). In general, there was an improvement in urinary urgency (5 patients at pre - op and only 1 at fourth visit); better IPSS score (6 patients with mild score at pre - op and more 6 at visit 4) and finally a better quality of life (just one patient reported being unhappy at visit 4). Assessment of urinary continence was based on daily urination, urinary free flow, PAD weight test, IPSS score, quality of life and ICIQ - SF values. Although not statistically significant when the comparative analysis tests were applied over the following-up, an improvement in the scores of involuntary urinary loss and quality of life was observed with preservation of urinary flow force without the occurrence of obstructive symptoms. Previous studies assessed functional and quality of life outcomes by PAD use or no validated questionnaires measuring urinary incontinence, frequency and nocturia but did not address long - term functional outcomes for health related quality of life (18-20). Our results are similar to other series with patients reporting an improvement in urinary incontinence and quality of life. In our study, four different devices (26.7%) had mechanical problem and needed to be removed. However, from 15 cases those four were the only where complication were found. Recently a retrospective study identified cases of which the main complications were: erosion of the cuff (4%); loss of fluid (3.8%); cuff atrophy (2.4%); infections (8%) and herniation of the pump (0.2%) (3). In contrast, there were no cases of infection related to device implantation during the follow-up period of this study. There was also no evidence of urethral erosion or appliance extrusion. The device was inert, without triggering inflammatory reactions or infectious processes. Another study analyzing artificial sphincter implants followed up for 4.2 years, re - operated 125 patients (11.6%) due to malfunction of the device (21). The urethral cuff was the component that failed the most (46.1%), followed by the abdominal reservoir (22.6%) and the pump (9.6%). Rupture of the tubes were not observed. As the rupture of the ducts is an uncommon complication and the number of patients analyzed was low, we believe that after an improvement in the quality of the T - connection, it would be possible to promote satisfactory urinary continence. However, larger cohort studies with longer follow-up are needed to assess the device efficacy and safety. CONCLUSIONS According to the present study, the artificial sphincter implant BR - SL - AS 904 was reproducible, safe and efficient in the control of urinary in- 1222
9 continence in patients after radical prostatectomy. Improvements in both quality and of the implant material and increase the number of patients can make this treatment modality very attractive and widely practiced. CONFLICT OF INTEREST REFERENCES None declared. 1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67: Lai HH, Boone TB. The surgical learning curve of artificial urinary sphincter implantation: implications for prosthetic training and referral. J Urol. 2013;189: Yafi FA, DeLay KJ, Stewart C, Chiang J, Sangkum P, Hellstrom WJ. Device Survival after Primary Implantation of an Artificial Urinary Sphincter for Male Stress Urinary Incontinence. J Urol. 2017;197(3 Pt 1): Saranchuk JW, Kattan MW, Elkin E, Touijer AK, Scardino PT, Eastham JA. Achieving optimal outcomes after radical prostatectomy. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23: Herschorn S, Bruschini H, Comiter C, Grise P, Hanus T, Kirschner-Hermanns R, et al. Surgical treatment of stress incontinence in men. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29: Gallistl H, Hubner W. Abdominal pressure transmission devices for urethral sphincters: In vitro effects and clinical outcomes. J Urol. 2009;181: Van der Aa F, Drake MJ, Kasyan GR, Petrolekas A, Cornu JN; Young Academic Urologists Functional Urology Group. The artificial urinary sphincter after a quarter of a century: a critical systematic review of its use in male non-neurogenic incontinence. Eur Urol. 2013;63: Linder BJ, de Cogain M, Elliott DS. Long-term device outcomes of artificial urinary sphincter reimplantation following prior explantation for erosion or infection. J Urol. 2014;191: Kim SP, Sarmast Z, Daignault S, Faerber GJ, McGuire EJ, Latini JM. Long-term durability and functional outcomes among patients with artificial urinary sphincters: a 10-year retrospective review from the University of Michigan. J Urol. 2008;179: Ostrowski I, Śledź E, Ciechan J, Golabek T, Bukowczan J, Przydacz M, et al. Current interventional management of male stress urinary incontinence following urological procedures. Cent European J Urol. 2015;68: James MH, McCammon KA. Artificial urinary sphincter for postprostatectomy incontinence: a review. Int J Urol. 2014;21: Ostrowski I, Blewniewski M, Neugart F, von Heyden B, Selvaggio O, Iori F, et al. Multicentre experience with ZSI 375 artificial urinary sphincter for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in men. Urologia. 2017;84: a Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240: O Connor RC, Nanigian DK, Patel BN, Guralnick ML, Ellision LM, Stone AR. Artificial urinary sphincter placement in elderly men. Urology. 2007;69: Ziegelmann MJ, Linder BJ, Rivera ME, Viers BR, Rangel LJ, Elliott DS. Outcomes of artificial urinary sphincter placement in octogenarians. Int J Urol. 2016;23: Smith PJ, Hudak SJ, Scott JF, Zhao LC, Morey AF. Transcorporal artificial urinary sphincter cuff placement is associated with a higher risk of postoperative urinary retention. Can J Urol. 2013;20: Brant WO, Erickson BA, Elliott SP, Powell C, Alsikafi N, McClung C, et al. Risk factors for erosion of artificial urinary sphincters: a multicenter prospective study. Urology. 2014;84: Haab F, Zimmern PE, Leach GE. Urinary stress incontinence due to intrinsic sphincteric deficiency: experience with fat and collagen periurethral injections. J Urol. 1997;157: Erratum in: J Urol 1997;158: Gousse AE, Madjar S, Lambert MM, Fishman IJ. Artificial urinary sphincter for post-radical prostatectomy urinary incontinence: long-term subjective results. J Urol. 2001;166: Knight SL, Susser J, Greenwell T, Mundy AR, Craggs MD. A new artificial urinary sphincter with conditional occlusion for stress urinary incontinence: preliminary clinical results. Eur Urol. 2006;50: Linder BJ, Viers BR, Ziegelmann MJ, Rivera ME, Rangel LJ, Elliott DS. Artificial Urinary Sphincter Mechanical Failures-Is it Better to Replace the Entire Device or Just the Malfunctioning Component? J Urol. 2016;195: Correspondence address: Salvador Vilar Correia Lima, M.D, PhD Departamento de Cirurgia Centro de Ciên. da Saúde, Univ. Fed. de Pernambuco, UFPE. Av. Prof. Moraes Rego, nº 1235 Cidade Universitária, Recife, PE, , Brasil Fax: urology@salvador.net 1223
Artificial urinary sphincter revision for urethral atrophy: comparing single cuff downsizing and tandem cuff placement
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 43 (2): 264-270, March - April, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0240 Artificial urinary sphincter revision for urethral atrophy: comparing single cuff downsizing and tandem
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 43 (2): 264-270, March - April, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0240 Artificial urinary sphincter revision for urethral atrophy: comparing single cuff downsizing and tandem
Four-year follow-up on a Zephyr Surgical Implants 375 artificial urinary sphincter for male urinary incontinence from one urological centre in Poland
 320 O R I G I N A L P A P E R FUNCTIONAL UROLOGY Four-year follow-up on a Zephyr Surgical Implants 375 artificial urinary sphincter for male urinary incontinence from one urological centre in Poland Ireneusz
320 O R I G I N A L P A P E R FUNCTIONAL UROLOGY Four-year follow-up on a Zephyr Surgical Implants 375 artificial urinary sphincter for male urinary incontinence from one urological centre in Poland Ireneusz
Long-term results of the implantation of the AMS 800 artificial sphincter for post-prostatectomy incontinence: a single-center experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (1): 114-120, January - February, 2018 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0165 Long-term results of the implantation of the AMS 800 artificial sphincter for post-prostatectomy incontinence:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (1): 114-120, January - February, 2018 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0165 Long-term results of the implantation of the AMS 800 artificial sphincter for post-prostatectomy incontinence:
Transcorporal artificial urinary sphincter in radiated and non - radiated compromised urethra. Assessment with a minimum 2 year follow-up
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (3): 494-500, May - June, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0329 Transcorporal artificial urinary sphincter in radiated and non - radiated compromised urethra. Assessment
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (3): 494-500, May - June, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0329 Transcorporal artificial urinary sphincter in radiated and non - radiated compromised urethra. Assessment
The impact of androgen deprivation on artificial urinary sphincter outcomes
 Original Article The impact of androgen deprivation on artificial urinary sphincter outcomes George C. Bailey 1, Brian J. Linder 1, Marcelino E. Rivera 1, Matthew J. Ziegelmann 1, Laureano J. Rangel 2,
Original Article The impact of androgen deprivation on artificial urinary sphincter outcomes George C. Bailey 1, Brian J. Linder 1, Marcelino E. Rivera 1, Matthew J. Ziegelmann 1, Laureano J. Rangel 2,
Evaluating the impact of radiation therapy on patient quality of life following primary artificial urinary sphincter placement
 Original Article Evaluating the impact of radiation therapy on patient quality of life following primary artificial urinary sphincter placement Jason P. Joseph, Marcelino E. Rivera, Brian J. Linder, Boyd
Original Article Evaluating the impact of radiation therapy on patient quality of life following primary artificial urinary sphincter placement Jason P. Joseph, Marcelino E. Rivera, Brian J. Linder, Boyd
Since the first published article, in 1974 by Scott et al on
 Perineal Approach for Artificial Urinary Sphincter Implantation Appears to Control Male Stress Incontinence Better Than the Transscrotal Approach Gerard D. Henry,* Stephen M. Graham, Mario A. Cleves, Caroline
Perineal Approach for Artificial Urinary Sphincter Implantation Appears to Control Male Stress Incontinence Better Than the Transscrotal Approach Gerard D. Henry,* Stephen M. Graham, Mario A. Cleves, Caroline
Periurethral constrictor: late results of the treatment of post prostatectomy urinary incontinence
 Clinical Urology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (4): 483-487, July - August, 2011 Periurethral constrictor: late results of the treatment of post prostatectomy urinary incontinence Roberto S. Lima, Evandilson
Clinical Urology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (4): 483-487, July - August, 2011 Periurethral constrictor: late results of the treatment of post prostatectomy urinary incontinence Roberto S. Lima, Evandilson
I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling
 I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling The CL Medical I-STOP TOMS sling for male stress urinary incontinence was developed in France where it is widely used and is the market leader. It is constructed with
I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling The CL Medical I-STOP TOMS sling for male stress urinary incontinence was developed in France where it is widely used and is the market leader. It is constructed with
Artificial urinary sphincter for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a historical cohort from 2004 to 2015
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 43 (1): 150-154, January - February, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0244 Artificial urinary sphincter for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a historical cohort
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 43 (1): 150-154, January - February, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0244 Artificial urinary sphincter for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a historical cohort
Conclusions. Keywords
 Functional Urology Outcomes of single- vs double-cuff artificial urinary sphincter insertion in low- and high-risk profile male patients with severe stress urinary incontinence Sascha A. Ahyai*, Tim A.
Functional Urology Outcomes of single- vs double-cuff artificial urinary sphincter insertion in low- and high-risk profile male patients with severe stress urinary incontinence Sascha A. Ahyai*, Tim A.
The Surgical Learning Curve for Artificial Urinary Sphincter Procedures Compared to Typical Surgeon Experience
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 60 (2011) 1285 1290 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Reconstructive Urology The Surgical Learning Curve for Artificial Urinary Sphincter Procedures
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 60 (2011) 1285 1290 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Reconstructive Urology The Surgical Learning Curve for Artificial Urinary Sphincter Procedures
Jennifer Locke UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Resident Year 3 October 12, Learning Objectives
 Artificial Urinary Sphincter after 40 Years of Use: Indications, Techniques and Outcomes Jennifer Locke UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Resident Year 3 October 12, 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Identify
Artificial Urinary Sphincter after 40 Years of Use: Indications, Techniques and Outcomes Jennifer Locke UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Resident Year 3 October 12, 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Identify
AdVance Male Sling System
 AdVance Male Sling System Clinical study summary This document is a compilation and summary of several AdVance Male Sling System peer-reviewed journal articles. The information presented here is taken
AdVance Male Sling System Clinical study summary This document is a compilation and summary of several AdVance Male Sling System peer-reviewed journal articles. The information presented here is taken
Fan Zhang 1,2 and Limin Liao 1,2*
 Zhang and Liao BMC Urology (018) 18:3 DOI 10.1186/s1894-018-0314-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Artificial urinary sphincter implantation: an important component of complex surgery for urinary tract reconstruction
Zhang and Liao BMC Urology (018) 18:3 DOI 10.1186/s1894-018-0314-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Artificial urinary sphincter implantation: an important component of complex surgery for urinary tract reconstruction
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF POST-PROSTATECTOMY INCONTINENCE
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF POST-PROSTATECTOMY INCONTINENCE Arthi Satyanarayan, Ryan Mooney, *Nirmish Singla Department of Urology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, USA *Correspondence
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF POST-PROSTATECTOMY INCONTINENCE Arthi Satyanarayan, Ryan Mooney, *Nirmish Singla Department of Urology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, USA *Correspondence
Department of Urology, University Hospital Ulm, Prittwitzstrasse 43, D Ulm, Germany
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 304205, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/304205 Clinical Study The Retrourethral Transobturator Sling Suspension in the Treatment of
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 304205, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/304205 Clinical Study The Retrourethral Transobturator Sling Suspension in the Treatment of
A New Artificial Urinary Sphincter with Conditional Occlusion for Stress Urinary Incontinence: Preliminary Clinical Results
 european urology xxx (2006) xxx xxx available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Ageing Male A New Artificial Urinary Sphincter with Conditional Occlusion for Stress Urinary
european urology xxx (2006) xxx xxx available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Ageing Male A New Artificial Urinary Sphincter with Conditional Occlusion for Stress Urinary
Deirdre M. Bochove-Overgaauw* and Bart Ph. Schrier
 An Adjustable Sling for the Treatment of All Degrees of Male Stress Urinary Incontinence: Retrospective Evaluation of Efficacy and Complications After a Minimal Followup of 14 Months Deirdre M. Bochove-Overgaauw*
An Adjustable Sling for the Treatment of All Degrees of Male Stress Urinary Incontinence: Retrospective Evaluation of Efficacy and Complications After a Minimal Followup of 14 Months Deirdre M. Bochove-Overgaauw*
Long-term functional outcomes after artificial urinary sphincter implantation in men with stress urinary. incontinence
 Long-term functional outcomes after artificial urinary sphincter implantation in men with stress urinary incontinence Priscilla Léon, Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler, Morgan Rouprêt, Vanina Ambrogi, Pierre Mozer,
Long-term functional outcomes after artificial urinary sphincter implantation in men with stress urinary incontinence Priscilla Léon, Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler, Morgan Rouprêt, Vanina Ambrogi, Pierre Mozer,
Male urinary incontinence: Artificial sphincter
 GUIDELINES IN FOCUS Truzzi JC et al. Male urinary incontinence: Artificial sphincter Incontinência urinária masculina: Esfíncter artificial Authorship: Brazilian Society of Urology (SBU) Participants:
GUIDELINES IN FOCUS Truzzi JC et al. Male urinary incontinence: Artificial sphincter Incontinência urinária masculina: Esfíncter artificial Authorship: Brazilian Society of Urology (SBU) Participants:
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Presentation, management, and outcomes of complications following prostate cancer therapy
 Original Article Presentation, management, and outcomes of complications following prostate cancer therapy Uwais B. Zaid, Jack W. McAninch, Allison S. Glass, Nadya M. Cinman, Benjamin N. Breyer Department
Original Article Presentation, management, and outcomes of complications following prostate cancer therapy Uwais B. Zaid, Jack W. McAninch, Allison S. Glass, Nadya M. Cinman, Benjamin N. Breyer Department
Jaspreet S. Sandhu,*,, Geoffrey T. Gotto,*, Luis A. Herran, Peter T. Scardino, James A. Eastham and Farhang Rabbani
 Age, Obesity, Medical Comorbidities and Surgical Technique are Predictive of Symptomatic Anastomotic Strictures After Contemporary Radical Prostatectomy Jaspreet S. Sandhu,*,, Geoffrey T. Gotto,*, Luis
Age, Obesity, Medical Comorbidities and Surgical Technique are Predictive of Symptomatic Anastomotic Strictures After Contemporary Radical Prostatectomy Jaspreet S. Sandhu,*,, Geoffrey T. Gotto,*, Luis
European Urology 47 (2005)
 European Urology European Urology 47 (2005) 209 213 The Comparison of Artificial Urinary Sphincter Implantation and Endourethral Macroplastique Injection for thetreatment of Postprostatectomy Incontinence
European Urology European Urology 47 (2005) 209 213 The Comparison of Artificial Urinary Sphincter Implantation and Endourethral Macroplastique Injection for thetreatment of Postprostatectomy Incontinence
Infrequent Reservoir-Related Complications of Urologic Prosthetics: A Case Series and Literature Review
 CASE REPORT Infrequent Reservoir-Related Complications of Urologic Prosthetics: A Case Series and Literature Review Tao Cui, MD, Ryan Terlecki, MD, and Majid Mirzazadeh, MD Urology Department, Wake Forest
CASE REPORT Infrequent Reservoir-Related Complications of Urologic Prosthetics: A Case Series and Literature Review Tao Cui, MD, Ryan Terlecki, MD, and Majid Mirzazadeh, MD Urology Department, Wake Forest
Department of Urology, Cochin hospital Paris Descartes University
 Technical advances in the treatment of localized prostate cancer Pr Michaël Peyromaure Department of Urology, Cochin hospital Paris Descartes University Introduction Curative treatments of localized prostate
Technical advances in the treatment of localized prostate cancer Pr Michaël Peyromaure Department of Urology, Cochin hospital Paris Descartes University Introduction Curative treatments of localized prostate
Short-term evaluation of the adjustable bulbourethral male sling for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence
 Received: 26 September 2017 Revised: 9 March 2018 Accepted: 23 April 2018 DOI: 10.1111/luts.12227 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Short-term evaluation of the adjustable bulbourethral male sling for post-prostatectomy
Received: 26 September 2017 Revised: 9 March 2018 Accepted: 23 April 2018 DOI: 10.1111/luts.12227 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Short-term evaluation of the adjustable bulbourethral male sling for post-prostatectomy
A transobturator adjustable system for male incontinence: 30-month follow-up of a multicenter study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 40 (6): 781-789, November - December, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.06.09 A transobturator adjustable system for male incontinence: 30-month follow-up of a multicenter study
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 40 (6): 781-789, November - December, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.06.09 A transobturator adjustable system for male incontinence: 30-month follow-up of a multicenter study
Management of Post-Prostatectomy Urinary Incontinence and Sexual Dysfunction
 Management of Post-Prostatectomy Urinary Incontinence and Sexual Dysfunction Robert C. Eyre, MD, FACS Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery (Urology) Harvard Medical School Post-prostatectomy Incontinence
Management of Post-Prostatectomy Urinary Incontinence and Sexual Dysfunction Robert C. Eyre, MD, FACS Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery (Urology) Harvard Medical School Post-prostatectomy Incontinence
Medical Policy Title: Periurethral Bulking ARBenefits Approval: <Date>
 Medical Policy Title: Periurethral Bulking ARBenefits Approval: Agents for the Treatment of Incontinence Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0279 Revision Date: Code(s): 51715 Endoscopic injection
Medical Policy Title: Periurethral Bulking ARBenefits Approval: Agents for the Treatment of Incontinence Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0279 Revision Date: Code(s): 51715 Endoscopic injection
Introduction. Keywords Male urinary incontinence Artificial urinary sphincter Compressive adjustable slings
 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2523-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of adjustable male slings and artificial urinary sphincter in the treatment of male urinary incontinence: a retrospective analysis
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2523-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of adjustable male slings and artificial urinary sphincter in the treatment of male urinary incontinence: a retrospective analysis
A.M.I. ATOMS System. Hydraulic system substitutes urinary sphincter function in incontinent males
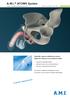 A.M.I. ATOMS System Product Group Urology Issue 11/2016 ATOMS = Adjustable TransObturator Male System Hydraulic system substitutes urinary sphincter function in incontinent males Long-term, adjustable
A.M.I. ATOMS System Product Group Urology Issue 11/2016 ATOMS = Adjustable TransObturator Male System Hydraulic system substitutes urinary sphincter function in incontinent males Long-term, adjustable
Sacral neuromodulation (SNM), using permanent foramen S3 electrode, Early versus late treatment of voiding dysfunction with pelvic neuromodulation
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Early versus late treatment of voiding dysfunction with pelvic neuromodulation Magdy M. Hassouna, MD, PhD; Mohamed S. Elkelini, MD See related article on page 111 Abstract Introduction:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Early versus late treatment of voiding dysfunction with pelvic neuromodulation Magdy M. Hassouna, MD, PhD; Mohamed S. Elkelini, MD See related article on page 111 Abstract Introduction:
Fix your incontinence Find your happiness. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Male stress urinary incontinence
 Fix your incontinence Find your happiness. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Male stress urinary incontinence Understanding your condition What is incontinence? Incontinence is defined as any
Fix your incontinence Find your happiness. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Male stress urinary incontinence Understanding your condition What is incontinence? Incontinence is defined as any
Open RRP versus LRP in Asian Men. International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (2): , March - April, 2009
 Clinical Urology Open RRP versus LRP in Asian Men International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (2): 151-157, March - April, 2009 Perioperative Outcomes of Open Radical Prostatectomy versus Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
Clinical Urology Open RRP versus LRP in Asian Men International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (2): 151-157, March - April, 2009 Perioperative Outcomes of Open Radical Prostatectomy versus Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
Urodynamic study before and after radical porstatectomy 가톨릭의대성바오로병원김현우
 Urodynamic study before and after radical porstatectomy 가톨릭의대성바오로병원김현우 Introduction Radical prostatectomy - treatment of choice for patients with localized prostate cancer. Urinary incontinence and/or
Urodynamic study before and after radical porstatectomy 가톨릭의대성바오로병원김현우 Introduction Radical prostatectomy - treatment of choice for patients with localized prostate cancer. Urinary incontinence and/or
Urodynamic outcome of parasacral transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation for overactive bladder in children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 41 (4): 739-743, July - August, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0303 Urodynamic outcome of parasacral transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation for overactive bladder in
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 41 (4): 739-743, July - August, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0303 Urodynamic outcome of parasacral transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation for overactive bladder in
q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE
 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 2 What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Urinary
493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 2 What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Urinary
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI Family Physiotherapy Centre of London
 Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Urinary Incontinence Following Surgery for bph: the Role of Aging on the Incidence of Bladder Dysfunction
 Neurology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (3): 380-387, May - June, 2011 doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382011000300012 Urinary Incontinence Following Surgery for bph: the Role of Aging on the Incidence of Bladder
Neurology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (3): 380-387, May - June, 2011 doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382011000300012 Urinary Incontinence Following Surgery for bph: the Role of Aging on the Incidence of Bladder
A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes
 Neurourology and Urodynamics 19:127 135 (2000) A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes Asnat Groutz, Jerry G. Blaivas,* and Jarrod E. Rosenthal Weill Medical College,
Neurourology and Urodynamics 19:127 135 (2000) A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes Asnat Groutz, Jerry G. Blaivas,* and Jarrod E. Rosenthal Weill Medical College,
Comparison of bone-anchored male sling and collagen implant for the treatment of male incontinence
 Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722006 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd???2006130012071211Original ArticleComparison of male sling and collagen implant
Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722006 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd???2006130012071211Original ArticleComparison of male sling and collagen implant
THE ARTIFICIAL URINARY SPHINCTER:
 THE ARTIFICIAL URINARY SPHINCTER: A TREATMENT FOR POST- PROSTATECTOMY URINARY INCONTINENCE Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Director: Center for Continence Care An
THE ARTIFICIAL URINARY SPHINCTER: A TREATMENT FOR POST- PROSTATECTOMY URINARY INCONTINENCE Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Director: Center for Continence Care An
Understanding your treatment options for male stress urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction
 Understanding your treatment options for male stress urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction Male Stress Urinary Incontinence and Erectile Dysfunction What causes male stress urinary incontinence
Understanding your treatment options for male stress urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction Male Stress Urinary Incontinence and Erectile Dysfunction What causes male stress urinary incontinence
Detrusor underactivity is prevalent after radical prostatectomy: a urodynamic study including risk factors
 original research Detrusor underactivity is prevalent after radical prostatectomy: a urodynamic study including risk factors Doreen E. Chung, MD, FRCSC; * Benjamin Dillon, MD; Jordan Kurta, MD; Alexandra
original research Detrusor underactivity is prevalent after radical prostatectomy: a urodynamic study including risk factors Doreen E. Chung, MD, FRCSC; * Benjamin Dillon, MD; Jordan Kurta, MD; Alexandra
Early-Stage Clinical Experiences of Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP)
 JRural Med 2007 ; 2 : 93 97 Original article Early-Stage Clinical Experiences of Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) Shuzo Hamamoto 1,TakehikoOkamura 1,HideyukiKamisawa 1,KentaroMizuno 1,
JRural Med 2007 ; 2 : 93 97 Original article Early-Stage Clinical Experiences of Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) Shuzo Hamamoto 1,TakehikoOkamura 1,HideyukiKamisawa 1,KentaroMizuno 1,
Laparoscopic Surgery. The Da Vinci Robot. Limits of Laparoscopy. What Robotics Offers. Robotic Urologic Surgery: A New Era in Patient Care
 Laparoscopic Surgery Robotic Urologic Surgery: A New Era in Patient Care Laparoscopic technique was introduced in urologic surgery in the 1990s Benefits: Improved recovery time, decreased morbidity Matthew
Laparoscopic Surgery Robotic Urologic Surgery: A New Era in Patient Care Laparoscopic technique was introduced in urologic surgery in the 1990s Benefits: Improved recovery time, decreased morbidity Matthew
Outcome and complications of adjustable continence therapy (ProACT ) after radical prostatectomy: 10 years experience in 143 patients
 Received: 16 August 2017 Accepted: 13 November 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23463 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Outcome and complications of adjustable continence therapy (ProACT ) after radical prostatectomy: 10
Received: 16 August 2017 Accepted: 13 November 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23463 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Outcome and complications of adjustable continence therapy (ProACT ) after radical prostatectomy: 10
St. Dominic s Annual Cancer Report Outcomes
 St. Dominic s 2017 Annual Cancer Report Outcomes Cancer Program Practice Profile Reports (CP3R) St. Dominic s Cancer Committee monitors and ensures that patients treated at St. Dominic Hospital receive
St. Dominic s 2017 Annual Cancer Report Outcomes Cancer Program Practice Profile Reports (CP3R) St. Dominic s Cancer Committee monitors and ensures that patients treated at St. Dominic Hospital receive
Blue Ridge Urogynecology
 Surgery for Stress Urinary Incontinence Surgery has proved to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence. The best surgical procedures improve or cure the incontinence in 85 to 90 percent of
Surgery for Stress Urinary Incontinence Surgery has proved to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence. The best surgical procedures improve or cure the incontinence in 85 to 90 percent of
Cleveland Clinic Quarterly
 Cleveland Clinic Quarterly Volume 31 JULY 1964 No. 3 A MEDICAL SILASTIC PROSTHESIS FOR THE CONTROL OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN THE MALE A Preliminary Report J A M E S K. W A T K I N S, M. D., * R A L P
Cleveland Clinic Quarterly Volume 31 JULY 1964 No. 3 A MEDICAL SILASTIC PROSTHESIS FOR THE CONTROL OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN THE MALE A Preliminary Report J A M E S K. W A T K I N S, M. D., * R A L P
Introduction/Learning Objectives. Incontinence: Natural History. Course Outline 10/14/2016. Urinary Incontinence: Conservative Measures
 Management of Urinary Complications after Prostatectomy Course Faculty: Introduction/Learning Objectives Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Associate Attending Urologist Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Management of Urinary Complications after Prostatectomy Course Faculty: Introduction/Learning Objectives Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Associate Attending Urologist Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.39 Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
MP 7.01.39 Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
Robotics, Laparoscopy & Endosurgery
 Robotics, Laparoscopy and Endosurgery Robotics, Laparoscopy & Endosurgery How to preserve bladder neck during robotic radical prostatectomy? Abdullah Erdem Canda* Department of Urology, Yildirim Beyazit
Robotics, Laparoscopy and Endosurgery Robotics, Laparoscopy & Endosurgery How to preserve bladder neck during robotic radical prostatectomy? Abdullah Erdem Canda* Department of Urology, Yildirim Beyazit
Suburethral sling at the time of radical prostatectomy in patients at high risk of postoperative incontinence
 Original Article IMMEDIATE SLING DURING RP IN HIGH-RISK PATIENTS WESTNEY et al. Suburethral sling at the time of radical prostatectomy in patients at high risk of postoperative incontinence O. LENAINE
Original Article IMMEDIATE SLING DURING RP IN HIGH-RISK PATIENTS WESTNEY et al. Suburethral sling at the time of radical prostatectomy in patients at high risk of postoperative incontinence O. LENAINE
Product Name or Headline
 Product Name or Headline Subhead goes here Payer policies will vary and should be verified prior to treatment for limitations on diagnosis, coding, or site of service requirements. The coding options listed
Product Name or Headline Subhead goes here Payer policies will vary and should be verified prior to treatment for limitations on diagnosis, coding, or site of service requirements. The coding options listed
MRI evaluation of the Flow-SecureTM artificial urinary sphincter.
 MRI evaluation of the Flow-SecureTM artificial urinary sphincter. Poster No.: C-0793 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Iglesias, A. Urresola Olabarrieta, B. Canteli Padilla, O. Cortazar
MRI evaluation of the Flow-SecureTM artificial urinary sphincter. Poster No.: C-0793 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Iglesias, A. Urresola Olabarrieta, B. Canteli Padilla, O. Cortazar
Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence. Goals of presentation. Preoperative evaluation: Urodynamic Testing? Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D.
 Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence Goals of presentation Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. Director of Urogynecology The Permanente Medical Group Kaiser, San Francisco Review preoperative care & evaluation
Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence Goals of presentation Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. Director of Urogynecology The Permanente Medical Group Kaiser, San Francisco Review preoperative care & evaluation
Policy #: 213 Latest Review Date: September 2012
 Name of Policy: Temporary Prostatic Stent Policy #: 213 Latest Review Date: September 2012 Category: Medicine Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and updates.
Name of Policy: Temporary Prostatic Stent Policy #: 213 Latest Review Date: September 2012 Category: Medicine Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and updates.
Policy #: 370 Latest Review Date: December 2013
 Name of Policy: Nerve Graft in Association with Radical Prostatectomy Policy #: 370 Latest Review Date: December 2013 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits
Name of Policy: Nerve Graft in Association with Radical Prostatectomy Policy #: 370 Latest Review Date: December 2013 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits
Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011
 Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Treatment, Urinary Stress Incontinence, Transurethral Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0359 Revision Date: Code(s): 53860 Transurethral
Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Treatment, Urinary Stress Incontinence, Transurethral Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0359 Revision Date: Code(s): 53860 Transurethral
Combination therapy for male erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence
 sian J ndrol 2008; 10 (1): 149 154 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2008.00364.x www.asiaandro.com. Clinical Experience. Combination therapy for male erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence Helen Zafirakis
sian J ndrol 2008; 10 (1): 149 154 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2008.00364.x www.asiaandro.com. Clinical Experience. Combination therapy for male erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence Helen Zafirakis
This information is intended as an overview only
 This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
Post- prostatectomy Incontinence - PPI
 Post- prostatectomy Incontinence - PPI Dr. Kolombo Ivan, MD, FEBU Assoc.Prof. Popken Gralf MD, PhD, Assoc.Prof. Otčenášek Michal MD, PhD, Dr. Klézl Petr MD, MBA, Dr. Kolombová Jitka MD, MBA, Assoc.Prof.
Post- prostatectomy Incontinence - PPI Dr. Kolombo Ivan, MD, FEBU Assoc.Prof. Popken Gralf MD, PhD, Assoc.Prof. Otčenášek Michal MD, PhD, Dr. Klézl Petr MD, MBA, Dr. Kolombová Jitka MD, MBA, Assoc.Prof.
Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy. Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester
 Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester Themes Can we predict urinary morbidity? Prevention of urinary morbidity
Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester Themes Can we predict urinary morbidity? Prevention of urinary morbidity
LUTS/BPH Medical and Surgical Management. Sung Tae Cho, MD, Ph.D Department of Urology Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital
 LUTS/BPH Medical and Surgical Management Sung Tae Cho, MD, Ph.D Department of Urology Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital AUA Annual Meeting, 2013 Plenary : 8 Poster and Podium : 6 sessions
LUTS/BPH Medical and Surgical Management Sung Tae Cho, MD, Ph.D Department of Urology Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital AUA Annual Meeting, 2013 Plenary : 8 Poster and Podium : 6 sessions
Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence
 Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
RECTAL INJURY IN UROLOGIC SURGERY. Inadvertent rectal injury from a urologic procedure is often subtle but has serious postoperative consequences.
 RECTAL INJURY IN 27 UROLOGIC SURGERY Inadvertent rectal injury from a urologic procedure is often subtle but has serious postoperative consequences. With good mechanical bowel preparation plus antibiotic
RECTAL INJURY IN 27 UROLOGIC SURGERY Inadvertent rectal injury from a urologic procedure is often subtle but has serious postoperative consequences. With good mechanical bowel preparation plus antibiotic
Management of Artificial Urinary Sphincter Dysfunction
 European Urology European Urology 46 (2004) 241 246 Management of Artificial Urinary Sphincter Dysfunction Frédéric Maillet, Jean-Marie Buzelin, Olivier Bouchot, Georges Karam * Clinique Urologique, CHU
European Urology European Urology 46 (2004) 241 246 Management of Artificial Urinary Sphincter Dysfunction Frédéric Maillet, Jean-Marie Buzelin, Olivier Bouchot, Georges Karam * Clinique Urologique, CHU
The role of synthetic slings in male stress incontinence
 Arab Journal of Urology (2011) 9, 129 134 Arab Journal of Urology (Official Journal of the Arab Association of Urology) www.sciencedirect.com URODYNAMICS/FEMALE UROLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE The role of synthetic
Arab Journal of Urology (2011) 9, 129 134 Arab Journal of Urology (Official Journal of the Arab Association of Urology) www.sciencedirect.com URODYNAMICS/FEMALE UROLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE The role of synthetic
Urethral catheter removal 3 days after radical retropubic prostatectomy is feasible and desirable
 Urethral catheter 3 days after radical retropubic prostatectomy is feasible and desirable (2002) 5, 291 295 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1365 7852/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/pcan JM
Urethral catheter 3 days after radical retropubic prostatectomy is feasible and desirable (2002) 5, 291 295 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1365 7852/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/pcan JM
Bladder replacement in men and women: when and when not? Outline. Continent Diversion History
 1 Bladder replacement in men and women: when and when not? Eila C. Skinner, MD Professor of Clinical Urology Keck USC School of Medicine Outline 1) Selection criteria for orthotopic diversion: Tumor-related
1 Bladder replacement in men and women: when and when not? Eila C. Skinner, MD Professor of Clinical Urology Keck USC School of Medicine Outline 1) Selection criteria for orthotopic diversion: Tumor-related
Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence
 Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Effective Date: December 21, 2016 Subject: Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Background: Urinary incontinence (the involuntary
Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Effective Date: December 21, 2016 Subject: Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Background: Urinary incontinence (the involuntary
Life after prostate cancer End your frustration. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Take the next step
 Take the next step Visit EDCure.org to: Take the online ED quiz and get your customized treatment results Find an ED specialist in your area Register for free educational seminars to learn more about treatment
Take the next step Visit EDCure.org to: Take the online ED quiz and get your customized treatment results Find an ED specialist in your area Register for free educational seminars to learn more about treatment
Various Types. Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG
 Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Policy #: 370 Latest Review Date: April 2017
 Name of Policy: Nerve Graft with Radical Prostatectomy Policy #: 370 Latest Review Date: April 2017 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under
Name of Policy: Nerve Graft with Radical Prostatectomy Policy #: 370 Latest Review Date: April 2017 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under
Urodynamic findings in women with insensible incontinence
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
Intussusception of the bladder neck does not promote early restoration to urinary continence after non-nervesparing radical retropubi c prostatectomy
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722004 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty LtdMarch 2004123275279Original ArticleIntussusception of the bladder neck and early continencei
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722004 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty LtdMarch 2004123275279Original ArticleIntussusception of the bladder neck and early continencei
Aus Artificial Uretheral Sphincter Port System
 NORFOLK VET PRODUCTS the AUS for the long-term relief of incontinence in dogs and cats making life easier for pets Speciality Medical Devices For The Veterinary Community the Aus Artificial Uretheral Sphincter
NORFOLK VET PRODUCTS the AUS for the long-term relief of incontinence in dogs and cats making life easier for pets Speciality Medical Devices For The Veterinary Community the Aus Artificial Uretheral Sphincter
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Stress Incontinence. Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS
 Stress Incontinence Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS Definitions Prevalence Assessment Investigation Treatment Surgery Men International Continence Society define as the complaint of any involuntary leakage
Stress Incontinence Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS Definitions Prevalence Assessment Investigation Treatment Surgery Men International Continence Society define as the complaint of any involuntary leakage
PROSTATIC EMBOLIZATION FOR BENIGN HYPERPLASIA
 St. Louis Hospital PROSTATIC EMBOLIZATION FOR BENIGN HYPERPLASIA INITIAL CLINICAL RESULTS Faculty of Medical Sciences New University of Lisbon JOÃO PISCO LUÍS CAMPOS PINHEIRO TIAGO BILHIM HUGO RIO TINTO
St. Louis Hospital PROSTATIC EMBOLIZATION FOR BENIGN HYPERPLASIA INITIAL CLINICAL RESULTS Faculty of Medical Sciences New University of Lisbon JOÃO PISCO LUÍS CAMPOS PINHEIRO TIAGO BILHIM HUGO RIO TINTO
Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion
 Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
MANUALFor Operating Room
 DOCUMENT OPERATING ROOM FOR MANUALFor Operating Room NOTE This document is a complementary checklist to the two training videos, which you can access and download from our website: ZSI 375 Training Video,
DOCUMENT OPERATING ROOM FOR MANUALFor Operating Room NOTE This document is a complementary checklist to the two training videos, which you can access and download from our website: ZSI 375 Training Video,
The importance of maximal restoration of peri-prostatic support
 Providing the best evidence for each surgical option in organ confined prostate cancer The importance of maximal restoration of peri-prostatic support A. Mottrie ORSI-Academy Melle Belgium OLV Hospital
Providing the best evidence for each surgical option in organ confined prostate cancer The importance of maximal restoration of peri-prostatic support A. Mottrie ORSI-Academy Melle Belgium OLV Hospital
Sep \8958 Appell Dmochowski.ppt LMF 1
 Surgical Outcomes (How did we get ourselves into this mess?) Roger R. Dmochowski, MD, FACS Department of Urologic Surgery Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville, Tennessee Considerations Evaluation
Surgical Outcomes (How did we get ourselves into this mess?) Roger R. Dmochowski, MD, FACS Department of Urologic Surgery Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville, Tennessee Considerations Evaluation
Dr. Aso Urinary Symptoms
 Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh Repair: A Prospective Study of 105 Cases
 International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
Primary Realignment of Posterior Urethral Rupture
 Urology Journal UNRC/IUA Vol. 2, No. 4, 211-215 Autumn 2005 Printed in IRAN Mehdi Salehipour, Abdolaziz Khezri, Rashid Askari,* Parham Masoudi Department of Surgery, Division of Urology, Faghihi Hospital,
Urology Journal UNRC/IUA Vol. 2, No. 4, 211-215 Autumn 2005 Printed in IRAN Mehdi Salehipour, Abdolaziz Khezri, Rashid Askari,* Parham Masoudi Department of Surgery, Division of Urology, Faghihi Hospital,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Goals & Objectives by Year in Training: U-1
 Goals & Objectives by Year in Training: U-1 U-1 (PGY-2, 3) Resident Responsibilities, Goals and Objectives In addition to the goals listed for PGY-1, the U-1 resident will add to his/her knowledge base
Goals & Objectives by Year in Training: U-1 U-1 (PGY-2, 3) Resident Responsibilities, Goals and Objectives In addition to the goals listed for PGY-1, the U-1 resident will add to his/her knowledge base
Men s Health Coding & Payment Quick Reference
 Payer policies will vary and should be verified prior to treatment for limitations on diagnosis, coding or site of service requirements. The coding options listed within this guide are commonly used codes
Payer policies will vary and should be verified prior to treatment for limitations on diagnosis, coding or site of service requirements. The coding options listed within this guide are commonly used codes
Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas The artificial genitourinary sphincter
 BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas The artificial genitourinary sphincter John T. Stoffel and David M. Barrett Department of Urology, Lahey Clinic Medical Center, Burlington, USA
BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas The artificial genitourinary sphincter John T. Stoffel and David M. Barrett Department of Urology, Lahey Clinic Medical Center, Burlington, USA
2017 Hospital Coding and Payment Guide
 Reimbursement Men s Health 2017 Hospital Coding and Payment Guide This coding reference guide is intended to illustrate the common coding and payment groups for male prosthetic urology procedures and related
Reimbursement Men s Health 2017 Hospital Coding and Payment Guide This coding reference guide is intended to illustrate the common coding and payment groups for male prosthetic urology procedures and related
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 9 Urinary Tract and Perineum Key Points 2 9.1 Urinary Bladder & Urinary Retention Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 9 Urinary Tract and Perineum Key Points 2 9.1 Urinary Bladder & Urinary Retention Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder
Current Indications for the Use of The Artificial Genitourinary Sphincter and Management of It s Complications
 Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2004) 4 (S1), 114 127 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2004.57 Current Indications for the Use of The Artificial Genitourinary Sphincter and Management of It s Complications
Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2004) 4 (S1), 114 127 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2004.57 Current Indications for the Use of The Artificial Genitourinary Sphincter and Management of It s Complications
LUTS after TURP: How come and how to manage? Matthias Oelke
 LUTS after TURP: How come and how to manage? Matthias Oelke Department of Urology Global Congress on LUTD, Rome, 26 th June 2015 Disclosures Consultant, speaker, trial participant and/or research grants
LUTS after TURP: How come and how to manage? Matthias Oelke Department of Urology Global Congress on LUTD, Rome, 26 th June 2015 Disclosures Consultant, speaker, trial participant and/or research grants
