MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Felix Michael Stafford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Hello and welcome back to InterpreterPrep.com! We are going to be covering the Male Reproductive System in this presentation. This means we will be talking about the male sexual organs. It will be a most intimate part of our course. MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM is made up by: 1) THE TESTICLES 2) THE DUCTS 3) THE ACCESSORY GLANDS: THE SEMINAL VESICLES PROSTATE COWPERS GLANDS 4) THE PENIS 1) TESTICLES aka TESTES: The testicles are 2 walnut size glands located in a pouch-like structure made of skin and muscle called the SCROTUM. If you follow the scrotum straight up it ends at and is attached to the in between the legs area called the perineum. In the fetus the testicles are located in the abdomen, up near the kidneys. A couple of months before birth the testicles come down through the inguinal canal (which is located in the groin) to occupy the scrotum. Testicles need a lower temperature than the rest of the body to make sperm and that's why that happens, they come down to cool down. The testicles are: The primary organs of the male reproductive system because it is where sperm is made. The testicle is full of tiny tubes all coiled up called SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES where sperm is made and stored. They are also endocrine organs because they secrete the male hormones called ANDROGENS (like for example, TESTOSTERONE) into the bloodstream. Androgens are responsible for the changes that transform boy into man originating the SECONDARY SEXUAL CHARACTERISTICS like: facial, axillary, and pubic hair, a deeper voice, larger muscles and maturation of sperm. 2) DUCTS: the TESTICLE dangles from a cord-like structure which contains the blood vessels and nerves called the SPERMATIC CORD. Now all those tiny tubules we had mentioned before: the seminiferous tubules drain to the EPIDIDYMIS. The epididymis is the place where the sperm mature and it drains into the VAS DEFERENS which rises into the pelvis through the inguinal canal and then hops over the ureter and goes into the prostate, where it changes its name to ejaculatory duct before connecting to the urethra where it ends. In other words, the sperm will travel through this sperm freeway : going through:
2 1) The epididymis 2) The vas deferens 3) The ejaculatory duct- and finally into 4) The urethra-through which they exit the body. 3) ACCESSORY GLANDS: - SEMINAL VESICLES: Located behind the bladder the seminal vesicles empty their secretions into the vas deferens. These secretions make up most of the semen. - PROSTATE GLAND: The prostate surrounds the urethra and has a duct that discharges its milky secretions into the urethra. Its secretions help neutralize the acidity of the vagina and help the sperm move better. The muscular action of the prostate also helps to squeeze out the semen during ejaculation. - COWPERS GLANDS (aka the Bulbourethral glands): provide a lubricating fluid to aid in penetration during intercourse. The sum of the secretions of these 3 glands make up the total volume of semen. A single EJACULATION goes anywhere from 1.5 to 6 cubic centimeters (a teaspoon has 5 cc). 4) PENIS: Is the male organ of COPULATION. It is sausage-shaped and hangs in front of the scrotum. The head of the penis is called the GLANS and is naturally covered by retractable skin known as the FORESKIN unless it has been removed surgically at birth through a procedure known as CIRCUMCISION. The urethra (musculomembranous tube used to urinate) runs throughout the bottom part of the penis and normally opens at the tip of the glans, opening known as: URINARY MEATUS. The body of the penis is made of erectile tissue which means that these tissues fill up with blood in times of sexual excitement, increasing the size and firmness of the penis (ERECTION) making PENETRATION possible. SOME SIGNS OF DISEASE 1) TESTICULAR PAIN 2) ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION aka IMPOTENCE: impossibility to obtain or maintain an erection 3) ITCH 4) ENLARGED TESTICLE 5) PAINFUL URINATION/ BURNING: burning sensation when urinating 6) NOCTURIA: having to get up at night to go to the bathroom frequently 7) DRIBBLING: dripping urine after having stopped urinating 8) WEAK STREAM: means that the urine comes out with less force. 9) FREQUENCY: increase in urinary frequency means the patient goes to bathroom to urinate more often. 10) URGENCY: need to go NOW! Can't wait!
3 SOME DISEASES 1) BALANITIS: Before we say any more, please remember that the suffix: ITIS = INFLAMMATION. Anything that ends in itis means that it's inflamed. In this case it means that the glans and the skin around it is red and inflamed. 2) CRYPTORCHIDISM: means that one of the testicles didn't make it down to the scrotum. Remember we had said that in the fetus the testicle is located in the abdomen. This condition needs to be corrected surgically because the testicle that is still up inside is at increased risk to develop testicle cancer. 3) PROSTATITIS : inflammation of the prostate caused by bacterial infection or IDIOPATHIC (fancy medical term for we don't know what's causing it!) 4) BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA (BPH) aka PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY: If you can remember HYPER = MORE and PLASIA = GROWTH it is clear that what's happened is that, over time, the PROSTATE ENLARGES. Since the urethra is surrounded by the prostate, it starts to get squeezed! This makes it harder for the bladder to empty its urine into the urethra giving way to symptoms like : STRAINING (increased difficulty to start urinating) A weak stream, dribbling and Frequency, since less urine comes out- leaving more residual urine in the bladderthe bladder fills up again quickly (patient always looking for a bathroom). 5) PROSTATE CANCER: It is the most frequent cancer in men. Second cause of cancer deaths in MEN (#1 is lung cancer). Can give same symptoms as BPH. 6) TESTICULAR CANCER: generally detected as a non-tender (doesn't hurt) lump in a testicle. 7) EPISPADIAS and HYPOSPADIAS: Is a birth defect where instead of the urethra opening at the tip of the penis it opens on the upper side or underside of the penis. 8) EPIDIDYMITIS: Is the inflammation of the epididymis. Generally caused by STDs: like infection by chlamydia for example. It can spread down to the testicle (ORCHITIS). Orchitis is the inflammation of the testicle. Testicle is tender in both conditions. Orchitis can also occur as a complication of Mumps. 9) PHIMOSIS: means that the uncircumcised foreskin is too snug, can't be pulled back. 10) VARICOCELE: means that the veins in the spermatic cord have dilated. Veins may be palpated (scrotum feels like a bag of worms ). May reduce fertility. Men with fertility problems and varicocele may consider surgery. 11) HYDROCELE: means there is liquid in the scrotum. 12) TESTICULAR TORSION: testicle suffers a twist and the blood flow to the testicle is compromised (ischemia). Testicle starts to hurt a lot and swells up. Medical Emergency to save testicle by restoring blood supply to testicle.
4 SOME DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES 1) RECTAL EXAMINATION: doctor introduces his finger into rectum and is able to feel the prostate through the wall of the rectum and can tell if it's enlarged or if there is an area of hardness in the prostate. 2) LABS: PSA LEVEL: is a blood test to detect a substance produced by the prostate called : PROSTATE SPECIFIC ANTIGEN. May signal prostate cancer when elevated. Elevated levels of HCG: HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN : seen in some forms of testicular cancer. 3) RECTAL ULTRASOUND: uses a special TRANSDUCER (part that emits the sound waves) introduced through the rectum to obtain images of the prostate. At the same time a needle biopsy can be done to obtain tissue samples (called an ULTRASOUND-GUIDED BIOPSY)! The needle is guided by ultrasound and passed through the rectum and into the prostate. 4) URINE FLOW STUDIES: patient urinates into a structure that looks like a walker with a toilet bowl attached to it and the speed and strength of the stream of urine can be measured. 5) CYSTOSCOPY: remember when we talked about colonoscopy? Well in this case they use a small scope to go in through the urethra which helps locate obstruction and see the bladder too ( cysto means bladder). 6) BONE SCAN: test done to look for metastasis. 7) SPERMOGRAM: the patient is asked to provide a sample of his semen which is sent for analysis to determine if his sperm has normal form and mobility. Indicated for couples with fertility issues. SOME TREATMENTS: 1) CREAMS: that contain corticosteroids and/or antibiotics (to treat balanitis) 2) ANTI-ANDROGENS: block androgens and shrink prostate ( e.g. FINASTERIDE) 3) ALPHA BLOCKERS: Alpha blockers act by relaxing smooth muscle (loosens up the bladder neck) which reduces the obstruction to the flow of urine. The GENERIC DRUG: TAMSULOSIN sold under the BRAND NAME: Flomax is an example. The major SIDE EFFECT of alpha blockers is ORTHOSTATIC HYPOTENSION (person gets dizzy when getting up). 4) TURP (stands for: TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF PROSTATE): Surgeon operates prostate by using a small endoscope (resectoscope) introduced through the urethra. 5) ANTIBIOTICS: used to treat infections (e.g. epididymitis)
5 6) VASECTOMY: male birth control method. Done by cutting and sealing the vas deferens. Generally not reversible. 7) LUPRON (leuprolide): given in the form of a monthly injection. Reduces production of sexual hormones (androgen and estrogen). Some tumors depend on these sexual hormones to grow so when they don't get them they shrink or slow their growth. Used for prostate cancer. 8) SURGERY AND RADIATION : used for cancer like : RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY: Radical when next to a surgery's name means total removal of. Has drawbacks such as impotence and urinary incontinence (involuntary leakage of urine can occur). Prostate surgery can be: - Laparoscopic or - Open (open = regular incision through the skin) RADIOACTIVE SEEDS: is a form of internal radiation therapy used to treat prostate cancer. It's done by implanting a radioactive substance in the body close to the tumor. All outcomes are better in early stage cancer. The specialist who treats these diseases is called a UROLOGIST. Urologists treat the diseases of the male reproductive system (something like a male gynecologist ) and also the diseases of the urinary system in both men and women. TERMINOLOGY REVIEW. Now it's time for review so let's go over the terminology mentioned in this presentation in English and in the target language. 1) TESTICLES: testículos 2) SCROTUM: escroto 3) SPERM: esperma: semen 4) TESTOSTERONE: testosterona 5) DUCTS: conductos 6) SPERMATIC CORD: cordón espermático 7) EPIDIDYMIS: epidídimo 8) VAS DEFERENS : conducto deferente 9) URETHRA: uretra 10) SEMINAL VESICLES: vesículas seminales 11) SEMEN: semen 12) PROSTATE: próstata 13) LUBRICATION: lubricación 14) EJACULATION: eyaculación 15) PENIS: pene 16) GLANS: glande 17) FORESKIN: prepucio 18) CIRCUMCISION: circuncisión 19) ERECTION: erección 20) PENETRATION: penetración 21) TESTICLE PAIN: dolor de testículo 22) ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION: impotencia 23) ITCH: comezón 24) ENLARGED TESTICLE: testículo agrandado 25) PAINFUL URINATION: dolor al orinar
6 26) BURNING: ardor 27) DRIBBLING: goteo 28) WEAK STREAM: chorro débil 29) FREQUENCY: micción frecuente 30) URGENCY: urgencia urinaria, necesidad imperiosa de orinar 31) BALANITIS: balanitis 32) CRYPTORCHIDISM: criptorquidia 33) PROSTATITIS: prostatitis 34) IDIOPATHIC: idiopático, de causa desconocida 35) BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA (BPH): (HPB) hiperplasia prostática benigna 36) STRAIN: esforzarse 37) EPISPADIAS: epispadias 38) HYPOSPADIAS: hipospadias 39) EPIDIDYMITIS: epididimitis 40) ORCHITIS: orquitis 41) TENDER: sensible 42) PHIMOSIS: fimosis 43) VARICOCELE: varicocele 44) HYDROCELE: hidrocele 45) TESTICULAR TORSION: torsión de testículo 46) RECTAL EXAMINATION: tacto rectal 47) HARDNESS: dureza 48) LABS: análisis 49) PSA (PROSTATE SPECIFIC ANTIGEN): antígeno prostático especifico 50) RECTAL ULTRASOUND: ecografía/ ultrasonido transrectal 51) TRANSDUCER: transductor 52) ULTRASOUND-GUIDED BIOPSY: biopsia guiada por ecografía/ ultrasonido 53) URINE FLOW STUDIES: estudios de urodinamia 54) CYSTOSCOPY: cistoscopía 55) BONE SCAN: centellografía ósea, gammagrafía ósea 56) CREAMS: cremas 57) ANTIANDROGEN: antiandrógeno 58) BRAND NAME: nombre comercial 59) GENERIC DRUG: medicamento genérico 60) SIDE EFFECT: efecto secundario 61) TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF PROSTATE (TURP): prostatectomía transuretral 62) VASECTOMY: vasectomía 63) RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY: prostatectomía radical 64) OPEN PROSTATECTOMY: prostatectomía abierta 65) RADIOACTIVE SEEDS: braquiterapia, implante radioactivo 66) REMISSION: remisión 67) OUTCOME: resultado 68) EARLY STAGE CANCER: cáncer en estadío inicial 69) SPERMOGRAM: espermograma 70) UROLOGIST: urólogo In this presentation we have gone over many terms related to UROLOGY and REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE while we discussed the anatomy of the male reproductive system. Signs and symptoms of
7 sickness, diseases, diagnostic procedures and some treatments were also discussed. At the end of the presentation a list of 70 related terms were provided in English and the target language for you to review. I hope you've enjoyed this lesson and come away with a better understanding of the field of UROLOGY and REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE and the terms related to these fields of medicine. Thank you for choosing InterpreterPrep.com
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Hello and welcome back to InterpreterPrep.com! We are going to be covering the Male Reproductive System in this presentation. This means we will be talking about the male sexual
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Hello and welcome back to InterpreterPrep.com! We are going to be covering the Male Reproductive System in this presentation. This means we will be talking about the male sexual
Male Reproductive System. Anatomy
 Male Reproductive System Medical Terminology Chapter Seven HIT # 141 Anatomy Testis or testicle = main male sex organs, paired, oval shaped, enclosed in a sac called the scrotum. Seminiferous tubules =
Male Reproductive System Medical Terminology Chapter Seven HIT # 141 Anatomy Testis or testicle = main male sex organs, paired, oval shaped, enclosed in a sac called the scrotum. Seminiferous tubules =
Chapter 7. Male Reproductive System
 Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System 1 Sexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction two individuals produce offspring that have genetic characteristics from both parents Sexual reproduction introduces new gene
Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System 1 Sexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction two individuals produce offspring that have genetic characteristics from both parents Sexual reproduction introduces new gene
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
What are Varicoceles?
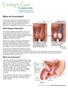 What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
The Reproductive System
 16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 34 Caring for Male Clients with Reproductive System Disorders Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Testosterone
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 34 Caring for Male Clients with Reproductive System Disorders Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Testosterone
Patient Information. Prostate Tissue Ablation. High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for
 High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for Prostate Tissue Ablation Patient Information CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sell by or on the order of a physician CONTENT Introduction... 3 The prostate...
High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for Prostate Tissue Ablation Patient Information CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sell by or on the order of a physician CONTENT Introduction... 3 The prostate...
The prostate can be affected by three conditions that may cause problems for men as they get older.
 The Prostate Gland The Prostate gland specific to males only, located in the pelvis between the bladder and rectum. It is about the shape and size of a walnut or satsuma and gets bigger as you get older.
The Prostate Gland The Prostate gland specific to males only, located in the pelvis between the bladder and rectum. It is about the shape and size of a walnut or satsuma and gets bigger as you get older.
What You Need to Know
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
A USER S GUIDE WHAT EVERY MAN NEEDS TO KNOW
 A USER S GUIDE WHAT EVERY MAN NEEDS TO KNOW 1. Why men need to know more Good health is vital for a happy and full life. But, with work and family responsibilities, men often overlook their own health
A USER S GUIDE WHAT EVERY MAN NEEDS TO KNOW 1. Why men need to know more Good health is vital for a happy and full life. But, with work and family responsibilities, men often overlook their own health
Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
THE UROLOGY GROUP
 THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
Chapter 18: Glossary
 Chapter 18: Glossary Sutter Health Cancer Service Line: Prostate Committee Advanced cancer: When the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (including lymph nodes, bones, or other organs) and is
Chapter 18: Glossary Sutter Health Cancer Service Line: Prostate Committee Advanced cancer: When the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (including lymph nodes, bones, or other organs) and is
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
About the authors Dr S. Larry Goldenberg Dr Tom Pickles Dr Kim N. Chi
 Authors S. Larry Goldenberg, CM, OBC, MD, FRCSC, FCAHS Professor and Head, University of British Columbia Department of Urologic Sciences, Stephen A. Jarislowski Chair in Urologic Sciences at Vancouver
Authors S. Larry Goldenberg, CM, OBC, MD, FRCSC, FCAHS Professor and Head, University of British Columbia Department of Urologic Sciences, Stephen A. Jarislowski Chair in Urologic Sciences at Vancouver
General information about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Appendix D Answers to the KAP Survey
 From Trainer s Resource Book to accompany Management of Men s Reproductive Health Problems 2003 EngenderHealth Appendix D Answers to the KAP Survey In the answer key that follows: The answers appear in
From Trainer s Resource Book to accompany Management of Men s Reproductive Health Problems 2003 EngenderHealth Appendix D Answers to the KAP Survey In the answer key that follows: The answers appear in
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Definition Prostate gland enlargement is a common condition as men get older. Also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate gland enlargement can cause bothersome
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Definition Prostate gland enlargement is a common condition as men get older. Also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate gland enlargement can cause bothersome
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Male Reproductive System. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD
 Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP)
 Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Patient Information Author ID: SF Leaflet Number: Urol 010 Version: 6 Name of Leaflet: Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Date Produced: March 2018
Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Patient Information Author ID: SF Leaflet Number: Urol 010 Version: 6 Name of Leaflet: Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Date Produced: March 2018
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Getting Help for Obstructive Azoospermia A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE Getting Help for Obstructive Azoospermia A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE Getting Help for Obstructive Azoospermia A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice
Chapter 7. Male Reproductive System. Copyright 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
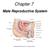 Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System Chapter 7 Objective 1: Pronounce organs and anatomic structures of the male reproductive system. Organs (1 of 2) The organs of the male reproductive system include the
Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System Chapter 7 Objective 1: Pronounce organs and anatomic structures of the male reproductive system. Organs (1 of 2) The organs of the male reproductive system include the
LIVING WITH. Understanding Your Treatment Options 1510
 Get the Support You Need Having prostate cancer can be hard to cope with. But you don t have to keep your feelings to yourself. Talk with family and friends. Try a prostate cancer support group. Sharing
Get the Support You Need Having prostate cancer can be hard to cope with. But you don t have to keep your feelings to yourself. Talk with family and friends. Try a prostate cancer support group. Sharing
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
What is Testicular cancer?
 Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
The Good News. The Comprehensive Approach. Examining the Male Patient: Sexually Transmitted Infections. April 25, 2013 Brittany Grier, M.
 Examining the Male Patient: Sexually Transmitted Infections April 25, 2013 Brittany Grier, M.S, PA-C The Good News Learning how to do a proper male exam can provide high yield information in formulating
Examining the Male Patient: Sexually Transmitted Infections April 25, 2013 Brittany Grier, M.S, PA-C The Good News Learning how to do a proper male exam can provide high yield information in formulating
Male Reproductive System
 21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
Human Reproduction. Male & Female Systems & Menstration
 Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Level I - Lesson 8: Know Your Body
 Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
UNDERSTANDING. Permanent Birth Control for Men
 UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
Saving. Kidneys. Benign Prostate Disease
 Saving Kidneys 9 Benign Prostate Disease This booklet will tell you more about the prostate gland. Its functions and benign hyperplasia have been defined in a simple way. Ways to prevent and treat this
Saving Kidneys 9 Benign Prostate Disease This booklet will tell you more about the prostate gland. Its functions and benign hyperplasia have been defined in a simple way. Ways to prevent and treat this
BLADDER PROSTATE PENIS TESTICLES BE YO ND YO UR CA NC ER
 BLADDER PROSTATE PENIS TESTICLES THE PROSTATE IS A SMALL, WALNUT-SIZED GLAND THAT IS PART OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. IT RESTS BELOW THE BLADDER, IN FRONT OF THE RECTUM AND SURROUNDS PART OF THE URETHRA.
BLADDER PROSTATE PENIS TESTICLES THE PROSTATE IS A SMALL, WALNUT-SIZED GLAND THAT IS PART OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. IT RESTS BELOW THE BLADDER, IN FRONT OF THE RECTUM AND SURROUNDS PART OF THE URETHRA.
Sexual Health Information for Gay & Bisexual Men
 Sexual Health Information for Gay & Bisexual Men When we talk about sexual health, we often focus on HIV and other STIs, but there are a number of other illness and issues that can affect men s sexual
Sexual Health Information for Gay & Bisexual Men When we talk about sexual health, we often focus on HIV and other STIs, but there are a number of other illness and issues that can affect men s sexual
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Prostate Cancer Case Study 1. Medical Student Case-Based Learning
 Prostate Cancer Case Study 1 Medical Student Case-Based Learning The Case of Mr. Powers Prostatic Nodule The effervescent Mr. Powers is found by his primary care provider to have a prostatic nodule. You
Prostate Cancer Case Study 1 Medical Student Case-Based Learning The Case of Mr. Powers Prostatic Nodule The effervescent Mr. Powers is found by his primary care provider to have a prostatic nodule. You
What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen).
 What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen). It is a very common cancer in men; some cancers grow very slowly,
What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen). It is a very common cancer in men; some cancers grow very slowly,
Introduction. Growths in the prostate can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer).
 This information was taken from urologyhealth.org. Feel free to explore their website to learn more. Another trusted website with good information is the national comprehensive cancer network (nccn.org).
This information was taken from urologyhealth.org. Feel free to explore their website to learn more. Another trusted website with good information is the national comprehensive cancer network (nccn.org).
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
What to do about infertility?
 What to do about infertility? Dr. M.A. Fischer Section Head, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton,
What to do about infertility? Dr. M.A. Fischer Section Head, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton,
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM ~::> bladder penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle testicle urethra vas deferens ;:; . l0\ OJ IQ) I"- ...
 MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Growth and Development 6 th Grade
 Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
 What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)? Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is an enlarged prostate. The prostate goes through two main growth periods as a man ages. The first occurs early in puberty,
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)? Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is an enlarged prostate. The prostate goes through two main growth periods as a man ages. The first occurs early in puberty,
THE PATIENT S GUIDE TO VARICOCELE
 The Varicocele Decision Varicoceles are a relatively common problem that can hurt a man's fertility. The good news is that this is a fairly simple problem to fix. Dr. Fisch has treated hundreds of men
The Varicocele Decision Varicoceles are a relatively common problem that can hurt a man's fertility. The good news is that this is a fairly simple problem to fix. Dr. Fisch has treated hundreds of men
Testicular Biopsy and Sperm Extraction for Fertility Preservation
 Testicular Biopsy and Sperm Extraction for Fertility Preservation This fact sheet aims to provide information about why and when a testicular biopsy or aspiration might be offered, what it involves and
Testicular Biopsy and Sperm Extraction for Fertility Preservation This fact sheet aims to provide information about why and when a testicular biopsy or aspiration might be offered, what it involves and
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Transformation Information elearning Kit Combined Program Lesson Plan Page 1. LESSON TITLE: Combined Program
 Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this animated activity, students will go more in depth about changes that happen to both males and females during puberty. The Coach re-introduces Ted Testosterone,
Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this animated activity, students will go more in depth about changes that happen to both males and females during puberty. The Coach re-introduces Ted Testosterone,
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology. Basic Structure of the Human Body. Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology
 Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Treating Prostate Cancer
 Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Prostate surgery. What is the prostate? What is a TURP? Why is a TURP operation necessary? Deciding to have a TURP operation.
 What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT A GUIDE TO URINARY SYMPTOMS IN MEN A BOOKLET IN THE SERIES OF CONSUMER GUIDES ON MALE REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FROM
 PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT A GUIDE TO URINARY SYMPTOMS IN MEN A BOOKLET IN THE SERIES OF CONSUMER GUIDES ON MALE REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FROM AT A GLANCE First published in March 2004 by Andrology Australia 5th
PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT A GUIDE TO URINARY SYMPTOMS IN MEN A BOOKLET IN THE SERIES OF CONSUMER GUIDES ON MALE REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FROM AT A GLANCE First published in March 2004 by Andrology Australia 5th
Reproduced with the kind permission of Health Press Ltd, Oxford
 Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Where is the Prostate Gland? The prostate gland sits below the bladder which lies behind the pubic bone see diagram below. The urethra
Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Where is the Prostate Gland? The prostate gland sits below the bladder which lies behind the pubic bone see diagram below. The urethra
Information for Patients. Male infertility. English
 Information for Patients Male infertility English Table of contents What is male infertility?... 3 Diagnosis... 3 Medical history... 3 Physical examination... 3 Hormone blood tests... 3 Semen analysis...
Information for Patients Male infertility English Table of contents What is male infertility?... 3 Diagnosis... 3 Medical history... 3 Physical examination... 3 Hormone blood tests... 3 Semen analysis...
Sexual Anatomy. Monday, 30 March 2009
 Sexual Anatomy 1 2 3 Fallopian Tube Ovary Uterus Bladder Cervix Pubic bone Clitoris Urethra Rectum Vagina Anus G Spot 4 Variety of Vulvae 5 Bladder Corpus Cavernosum Rectum Seminal Vesicle Prostate Glans
Sexual Anatomy 1 2 3 Fallopian Tube Ovary Uterus Bladder Cervix Pubic bone Clitoris Urethra Rectum Vagina Anus G Spot 4 Variety of Vulvae 5 Bladder Corpus Cavernosum Rectum Seminal Vesicle Prostate Glans
Penis Cancer. What is penis cancer? Symptoms. Patient Information. Pagina 1 / 9. Patient Information - Penis Cancer
 Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Lecture Series: Pregnancy
 Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP)
 Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Trans urethral resection of prostate (TURP)
 Trans urethral resection of prostate (TURP) Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST What is the prostate? Only men have a prostate
Trans urethral resection of prostate (TURP) Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST What is the prostate? Only men have a prostate
Prostate Cancer: Low Dose Rate (Seed) Brachytherapy. Information for patients, families and friends
 Prostate Cancer: Low Dose Rate (Seed) Brachytherapy Information for patients, families and friends About this booklet This booklet is designed to give you information about low dose-rate (seed) brachytherapy
Prostate Cancer: Low Dose Rate (Seed) Brachytherapy Information for patients, families and friends About this booklet This booklet is designed to give you information about low dose-rate (seed) brachytherapy
Testicular Cancer: Questions and Answers. Testicular cancer is a disease in which cells become malignant (cancerous) in one or both testicles.
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
(dutasteride/tamsulosin) For the treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
 Combodart (dutasteride/tamsulosin) For the treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) This leaflet is only for use by patients who have been prescribed Combodart. Please see Patient Information Leaflet
Combodart (dutasteride/tamsulosin) For the treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) This leaflet is only for use by patients who have been prescribed Combodart. Please see Patient Information Leaflet
describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it
 You need to be able to: describe spermatogenesis (How is sperm made?) describe the anatomy of a sperm describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it How is sperm made? Spermatogenesis
You need to be able to: describe spermatogenesis (How is sperm made?) describe the anatomy of a sperm describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it How is sperm made? Spermatogenesis
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
The Enlarged Prostate Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 The Enlarged Prostate Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment MAC00031-01 Rev G Financial support for this seminar has been provided by NeoTract, Inc., the manufacturer of the UroLift System. 1 Today s Agenda
The Enlarged Prostate Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment MAC00031-01 Rev G Financial support for this seminar has been provided by NeoTract, Inc., the manufacturer of the UroLift System. 1 Today s Agenda
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE
 TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE A discussion of the operation and the pre and post operative care You and your doctor have considered the possibility that you have a transurethral resection of
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE A discussion of the operation and the pre and post operative care You and your doctor have considered the possibility that you have a transurethral resection of
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
BLADDER HEALTH. Painful Bladder AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
 BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
Penis Cancer. What is penis cancer? Symptoms. Patient Information. Pagina 1 / 9. Patient Information - Penis Cancer
 Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Friday, 11 January 13. Sexual Anatomy
 Friday, 11 January 13 Sexual Anatomy Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Fallopian Tube Ovary Uterus Bladder Cervix Pubic bone Clitoris Urethra Rectum
Friday, 11 January 13 Sexual Anatomy Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Fallopian Tube Ovary Uterus Bladder Cervix Pubic bone Clitoris Urethra Rectum
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP)
 Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Patient Information What What and and where where is the is prostate? the prostate? The prostate is a small gland, about the size of a walnut,
Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Patient Information What What and and where where is the is prostate? the prostate? The prostate is a small gland, about the size of a walnut,
P ROLIEVE. Thermodilatation System. The Prolieve System Patient Information is Directed to You, the Patient. A Transurethral Microwave Therapy Device
 P ROLIEVE Thermodilatation System A Transurethral Microwave Therapy Device The Prolieve System Patient Information is Directed to You, the Patient. Contents Why am I being treated with the Prolieve Thermodilatation
P ROLIEVE Thermodilatation System A Transurethral Microwave Therapy Device The Prolieve System Patient Information is Directed to You, the Patient. Contents Why am I being treated with the Prolieve Thermodilatation
Prostate Gland Disorders
 Prostate Gland Disorders THE PROSTATE GLAND A male s prostate gland is located in the floor of the pelvis surrounding the urethra between the bladder and the penis. The prostate is positioned immediately
Prostate Gland Disorders THE PROSTATE GLAND A male s prostate gland is located in the floor of the pelvis surrounding the urethra between the bladder and the penis. The prostate is positioned immediately
Body Wise. Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only
 Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
