International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
|
|
|
- Darrell Jacobs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN: Original Research Article Histopathological Study of Lesions of Prostate - A Five Year Study Bhakti D Deshmukh 1*, Nayan A Ramteerthakar 2, Kalpana R Sulhyan 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor and Head of Dept. Department of Pathology, Government Medical College, Miraj, Maharashtra, India. * Correspondence drbhaks2010@gmail.com Received: 08/10//2013 Revised: 06/11/2013 Accepted: 19/11/2013 ABSTRACT Aims and objectives: 1. To study the incidence, age distribution and gross and histopathological features of lesions of prostate. 2. To classify tumours of prostate as per recommendations of WHO and to analyse cases of adenocarcinoma of prostate according to Gleason grading system. Material and methods: This is a retrospective and prospective study of 226 cases of lesions of prostate during the period of August 2004 to July 2009.The gross specimens were in the form of prostatectomies, transurethral resections and tru cut biopsies. The tissue was fixed in 10% formalin. Sections were cut at 3-5 micron thickness and were subsequently stained by haematoxylin and eosin stain. All the cases were analysed according to age, description of gross specimen and microscopic examination. Morphological types of benign prostatic hyperplasia were described. The tumours of prostate were diagnosed and classified as per WHO classification (2002). The cases of adenocarcinoma were analysed according to Gleason grading system. Results and conclusion: The commonest prostatic lesion was benign prostatic hyperplasia, seen most frequently in 7 th decade with fibromyoadenomatous type being the most common morphological pattern. Eighteen cases of adenocarcinoma were observed, out of which one showed mucinous features. Maximum numbers of cases of adenocarcinoma were seen in 8 th decade. The most common Gleason primary pattern was pattern 3 and the most frequent Gleason score was 9. Key words: lesions, prostate, histopathology. INTRODUCTION The immense medical problems caused by prostate gland are increasing at an alarming rate. The number of cases has continuously increased over the past decades, partly due to the higher life expectancy. Prostate gland specimens account for the significant percentage of diagnostically challenging cases in surgical pathology practice. The goal of tissue sampling is to maximise the opportunity to recognize the presence of carcinoma of prostate and to provide information International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 1
2 regarding its histological grade. A confirmed diagnosis with an indication of tumour grade helps in rational management approach. In short, lesions of prostate are an area of constant interest to clinicians as well as to Pathologists. MATERIALS AND METHODS This is a retrospective and prospective study of five years duration consisting of 226 cases of lesions of prostate. The gross specimens received were prostatectomies, transurethral resections of prostate (TURP) and tru cut biopsies. The clinical data was collected from indoor case papers and biopsy requisition forms. The tissue was fixed in 10% formalin. The relevant data inclusive of gross appearance of the specimen and the histopathological findings was recorded. Routine paraffin processing of the tissue and haematoxylin and eosin staining was done. Special stains (20% ZN staining, PAS) were performed wherever required. All the cases were analysed according to age, description of gross specimen and microscopic examination. The various lesions of prostate were listed. Morphological types of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) were described as per classification given by Franks. ( 1) The tumours of prostate were diagnosed and classified as per WHO classification (2002). The cases of adenocarcinomas were analysed according to Gleason grading system. ( 2) RESULTS Two hundred twenty six cases of lesions of prostate were studied from the hospital records of histopathology section of Government medical college and hospital, Miraj, Maharashtra, over a period of five years i.e. from August 2004 to July Out of 226 cases, 214 (94.69%) were prostatectomy specimens. Grossly, the prostatectomy specimens were bosselated or nodular varied from 2-12 cm in size. The consistency varied from soft to firm to hard. The TURP specimens were in the form of multiple pieces, gray tan to gray pink in colour and soft to firm in consistency. The biopsy specimens were in the form of elongated pieces of gray tan tissues ranging from cm in size. The most common lesion was BPH seen in 207 (92.04%) cases with peak incidence in seventh decade. Acinar adenocarcinoma of prostate was seen in 18 (7.96%) cases with peak incidence in eighth decade. One case showed adenocarcinoma with mucinous features. In one (0.44%) case we found high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. (HGPIN) (Table 1 and 2). Table 1: Distribution of cases on histopathological basis and nature of specimen: NATURE OF SPECIMEN BENIGN PROSTATIC ACINAR ADENOCARCINOMA HGPIN Total HYPERPLASIA OF PROSTATE Prostatectomy Biopsy Transurethral resection of prostate Total HGPIN- High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Microscopically, glandular and stromal hyperplasia was seen. The acini were lined by double layered cuboidal to columnar epithelium which at places showed papillary infoldings. Some of the acini contained corpora amylacea. Maximum numbers of cases of BPH [106 (51.21%)] were seen in 7 th decade followed by 72 (34.78%) cases in 8 th decade. (Table 2). International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 2
3 Table 2: Age wise distribution of cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia and acinar adenocarcinoma of prostate: AGE RANGE BENIGN PROSTATIC ACINAR ADENOCARCINOMA HGPIN (YEARS) HYPERPLASIA OF PROSTATE (1.45%) (7.73%) 3 (16.66%) (51.21%) 3 (16.66%) (34.78%) 9 (50%) 1 (%) (4.35%) 3 (16.66%) (0.48%) - - TOTAL 207 (100%) 18 (~100%) 1 (%) Microscopically, the nodular hyperplasia is the result of proliferation of epithelial cells, smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts in variable proportions. On the basis of histological composition five types of nodules are described: Stromal, Fibromuscular, Muscular, Fibroadenomatous and Fibromyoadenomatous. ( 1) In fibromyoadenomatous type, hyperplasia of both glandular and stromal element was seen. The hyperplastic stroma was fibromuscular. In fibroadenomatous hyperplasia, the predominant hyperplasia was of the glandular component. The glands were closely packed together with less stromal component. In fibromuscular hyperplasia, the hyperplastic nodules were predominantly stromal devoid of glandular element. In stromal hyperplasia, the nodules were made up of a loose fibrous tissue with groups of spindle or star-shaped cells often arranged around well formed blood vessels. Some of the cells resembled fibroblasts; others resembled smooth muscle cells. Fibromyoadenomatous hyperplasia was found in majority of the cases [97 (46.86%)]. Seventy eight (37.69%) cases were of fibroadenomatous hyperplasia, 31 (14.97%) cases were of fibromuscular hyperplasia and 1(0.48%) case was of stromal hyperplasia. (Table 3) Table 3: Morphological types of hyperplasia in cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia. PATTERN OF HYPERPLASIA NUMBER OF CASES PERCENTAGE Fibromyoadenomatous % Fibroadenomatous % Fibromuscular % Muscular - - Stromal % Total % Of these cases of BPH, 105 (50.73%) cases were associated with chronic nonspecific prostatitis, 63 (30.43%) case were associated with acute on chronic nonspecific prostatitis, 8 (3.86%) cases were associated with granulomatous prostatitis, 4 (1.93%) with acute prostatitis, 3 (1.45%) cases with chronic nonspecific prostatitis with infarction and remaining 24 (11.60%) cases were not associated with any inflammatory process. Acinar Adenocarcinoma The microscopic grading system developed by Gleason is currently the preferred grading system. It is based on the degree of glandular differentiation and the growth pattern of the tumour in relation to the stroma as evaluated on low power examination. ( 2) This system described 5 different patterns; recognised as primary pattern (predominant) and the secondary (second most prevalent) architectural patterns and assigned a grade from 1 to 5 with 1 being most differentiated and 5, the International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 3
4 least differentiated. The two grades are added together to obtain the Gleason score. Most frequently observed predominant patterns were pattern 3 and 4 seen in 8 (44.44%) and 7 (38.89%) cases respectively. No cases showed pattern 1 or 2 in present study (Table 4) Gleason score 9 was the commonest score found [6 (33.34%)] followed by 5 (27.77%) cases each with Gleason score 7 and 8. (Table 5) Table 4: Analysis of cases of acinar adenocarcinoma of prostate according to gleason predominant pattern. PREDOMINANT PATTERN NUMBER OF CASES PERCENTAGE % % % TOTAL % Table 5: Analysis of cases of acinar adenocarcinoma of prostate according of gleason score. GLEASON SCORE NUMBER OF CASES PERCENTAGE % % % % % TOTAL % Fig 1: Adenocarcinoma of prostate. Fig 2: A- Granulomatous prostatitis A- Tumour cells arranged in cribriform pattern without B- Prostatic infarct necrosis (Gleason grade 3c). C- Transitional metaplasia B- Tumour cells having clear cytoplasm- Hypernephomatoid D- Squamous metaplasia. pattern (Gleason grade 4b). C- Infiltrative tumour cells arranged in sheets. (Gleaason grade 5b). D- Adenocarcinoma with mucinous features. DISCUSSION BPH and adenocarcinoma are the two pathological processes which frequently affect the prostate gland. In our study, we had more of [214 (94.69%)] prostatectomy specimens. Other studies conducted by Mittal et al ( 3) and Shakya et al ( 4) had higher percentage of TURP specimens. This may be due to the International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 4
5 different protocols used for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with lesions of prostate. In the present study, we had 91.6% cases of BPH, 7.96% cases of acinar adenocarcinoma and 0.44% case of HGPIN. The findings in our study are comparable with those of Mittal et al, ( 3) Sharma et al ( 5) and Mohammed et al. ( 6) BPH is a regional nodular growth of variegated histological composition that is almost ubiquitous development in men if they have testes and live sufficiently long. The clinical incidence is 8% during the 4 th decade but it reaches 75% in the 8 th decade. Before the recognition of the hyperplastic nature of BPH, the prostatic enlargement in elderly men had been variously interpreted to reflect neoplastic process, compensatory hypertrophy, a response to inflammation or arteriosclerosis. ( 7) Pure stromal hyperplasia with nodule formation was first reported by Reischauer in ( 8) Deming et al ( 9) confirmed this observation and further regarded that the glandular element of prostatic nodule as an event to the stromal stimulus to epithelial proliferation within adjacent ducts. With the development of the BPH, the weight of the gland significantly increases and averages 33±16 gm. Grossly, there are well defined soft to firm nodules with variable solid and cystic composition. ( 3) The cut surface is gray to yellow. If there is prominent epithelial hyperplasia the abundant luminal spaces create soft and grossly spongy nodules from which oozes watery fluid. If the BPH is predominantly fibromuscular, there are numerous trabeculations without prominent nodularity. Focal haemorrhage, calcification and macrocystic change may be present. TURP specimens yield multiple boat shaped, greyish pink chips which do not have distinct appearance. ( 8) Microscopically the nodular hyperplasia is the result of proliferation of epithelial cells, smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts in variable proportions. On the basis of histological composition five types of nodules are described: Stromal, Fibromuscular, Muscular, Fibroadenomatous and Fibromyoadenomatous. ( 1) The earliest change is the stromal proliferation which contains more smooth muscle and less elastic tissue than the normal stroma, followed by hyperplasia of the glandular component. The glands are dilated or even cystic and often contain corpora amylacea which is sometimes calcified. The epithelium ranges from flat to columnar. The cytoplasm is pale and nucleoli are inconspicuous. Papillary infoldings are common. A continuous basal cell layer is present. ( 8) Comparing the incidence of BPH with nature of specimen, in the present study, maximum of our cases [198 (95.65%)] were obtained from prostatectomies. Anim et al ( 10) and Shaky et al ( 4) had more number of BPH in TURP specimens whereas Mwakyoma ( 11) had more of BPH in biopsies. This may be due to different protocols used for the diagnosis and treatment of prostatic lesions in different set ups. Maximum cases of BPH were in the 7 th decade which was similar to other studies like that of Sharma et al ( 5) but studies conducted by Kim KB et al ( 12) had more cases in 8 th decade while Matapurkar et al ( 13) found highest incidence in 6 th decade. Very few studies have classified BPH morphologically. We had maximum number of cases [97 (46.86%)] showing fibromyoadenomatous hyperplasia which was comparable with that of Kim KB et al. ( 12) Chronic prostatitis is most commonly observed in nodular hyperplasia. Kohnen et al ( 14) and Anim et al ( 10) found International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 5
6 nonspecific prostatitis in 90-98% cases of BPH. The spectrum of chronic prostatitis includes bacterial, abacterial and granulomatous prostatitis. Bacterial prostatitis is caused by strains of Enterococcus fecalis. The etiologic agent of chronic abacterial prostatitis is unknown but chlamydia, ureaplasma and trichomonas infection has been proposed. Grossly a chronically inflamed prostate is firm or hard in consistency. Microscopically, there is interstitial fibrosis and diffuse patchy or very discrete foci of intraglandular or periglandular infiltrate of lymphocytes, plasma cells and histiocytes. In long standing cases the lining epithelium of large ducts may show squamous metaplasia. Granulomatous prostatitis can be clinically confused with prostatic carcinoma. The reported incidence of granulomatous prostatitis is %. ( 15, 16) Epstein et al ( 17) classified it depending on the possible causative agent into idiopathic (nonspecific), infectious, iatrogenic and allergic (eosinophilic) granulomatous prostatitis and malakoplakia. Granulomatous prostatitis is probably caused by blockage of prostatic ducts and the stasis of secretions, regardless of its aetiology. It is thought to represent an immune mediated process accompanied by reaction to the prostatic secretions released from the obstructed ducts. Grossly the gland is firm to stony hard. The cut surface shows obliteration of the architecture with the formation of yellow granular nodules. Microscopy is characterized by large nodular aggregates of pale staining histiocytes, epithelioid cells, lymphocytes and plasma cells. Characteristically these granulomas are centred in the lobules. ( 8) Prostatic infarcts are common in markedly enlarged prostate gland. Circulatory disturbances, in which there is distortion of blood supply or venous drainage resulting from mechanical compression may be the contributing factor. ( 18) Serum Prostate specific antigen and prostatic acid phosphatase levels are elevated. We had 3 (1.45%) cases of BPH with infarction. Milord et al ( 18) and Moore ( 19) reported prostatic infarcts in 0.07% and 25%.cases of BPH respectively. Grossly prostatic infarcts vary in size. They are speckled, greyish yellow. The peripheral margins are usually sharp and haemorrhagic. Microscopy shows discrete foci of coagulative necrosis involving both epithelial and fibromuscular stromal element with haemorrhage. The surrounding noninfarcted prostatic gland may show immature squamous metaplasia. ( 18) WHO classification of adenocarcinoma prostate (2002) is based primarily on the microscopic characteristics of tumours like morphologically identifiable cell types and histological patterns as seen with conventional light microscopy. Prostate cancer is now the 6 th most common cancer in the world (in terms of new cases) and 3 rd important in men. It is predominantly a disease of elderly men. The risk rises steadily with age. Worldwide about three quarters of all cases occur in men aged 65 years or more. Approximately 20% cases are hereditary. Patients with familial prostate cancer tend to present at an earlier age. The risk of prostate carcinoma increases with number of affected first degree relatives. The positive history of prostate carcinoma in one first degree relative increases the risk by approximately two folds. It may exceed five folds if two or more first degree relatives have history of prostate cancer and increases 11 times for those with three affected first degree relatives. Prostate cancer initiation and progression are influenced by androgens. A meta-analysis of previously published studies on hormonal predictors of prostate cancer concluded that men whose International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 6
7 total testosterone level is in highest quartile are 2.34 times more likely to develop prostate cancer. ( 20) A higher incidence has been reported in men working in industries including machine and rubber manufacturers, plumbers and news paper workers. Reduced risk is associated with increased levels and index of beta carotene intake. Beta carotene may influence carcinogenesis by minimizing free radical damage or by enhancing immunologic function ( 21) The search for the precursor of prostatic adenocarcinoma has focussed in recent years on two distinct histopathological findings: Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia (PIN) and Atypical Small Acinar Proliferation (ASAP). Grossly, the gland is hard or firm yellow gray. The size varies ranging from minute focus to massive growths. On cut surface the carcinomatous foci appear as ill defined, greyish white areas merging into surrounding tissue. Microscopically there is only a single cell type without the basal layer. The pathological diagnosis of carcinoma is indicated by ( 2) crowded glands growing in haphazard fashion, large acini without convolutions, fused glands, glands in glands, columns, cords and solid sheets. The glands oriented perpendicular to each other and glands irregularly separated by bundles of smooth muscle are indicative of an infiltrative process. Nuclear enlargement with prominent nucleoli is the frequent finding. Prostatic crystalloids are the dense eosinophilic rectangular, hexagonal, triangular and rod like crystal like structures seen in low grade prostatic carcinoma. Although not diagnostic of carcinoma, crystalloids are seen more frequently in association of malignancy than benign glands. Intraluminal pink acellular dense secretions or blue tinged mucinous secretions are additional findings seen in low grade prostatic carcinoma. In contrast, corpora amylacea is common in benign glands. Malignancy specific features are perineural invasion, mucinous fibroplasias (collagenous micronodules), and glomerulations. Adenocarcinoma accounted for 7.96% cases in our study. The reported incidence is %. ( 22, 23) Maximum numbers of our cases (50%) were in the 8 th decade whereas Sharma et al ( 5) had more cases in 7 th decade while Gilliland et al ( 24) in 7 th & 8 th decade. Matapurkar et al ( 13) found maximum number of cases in the 7 th decade. Adenocarcinomas are classified by taking into account morphological appearance of glandular cells and the glandular pattern. We found maximum number of cases (50%) showing predominant pattern 3 which was comparable with those of Vollmer. ( 25) Maximum number of cases (33.33%) had Gleason score 9. Brawn et al ( 26) had score 6 & 7 whereas Vollmer ( 25) had score 6 most common. This discrepancy may be due to the less number of cases of acinar adenocarcinoma observed in our study or delayed presentation of patients. PIN is characterized by spectrum of atypical cytological features ranging from minimal changes to those that are indistinguishable from carcinoma. A basal layer is consistently present. Antibodies directed against the high molecular weight keratins (34 βe12) have been employed immunohistochemically to selectively label the prostatic basal cell layer. Initially PIN was categorised as PIN 1, PIN 2 and PIN 3 which is now replaced by low grade PIN and high grade PIN which is based mainly on the cytological characteristics of the cells. Currently conventional use of the term PIN without qualification refers to only high grade PIN. The clinical importance of recognising PIN is based on its strong association with prostatic International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 7
8 carcinoma. PIN has a high predictive value as a marker for adenocarcinoma and its identification in biopsy specimens of the prostate warrants for further search for concurrent invasive carcinoma. In the present study, we found 1(0.44%) case of HGPIN in the prostatectomy specimen. We did not observe HGPIN in the biopsy and the TURP specimens. The reported incidence of HGPIN is % in TURP and needle biopsies. ( 27-29) This discrepancy in the observation of HGPIN in present study as compared to other studies is due to the small number of biopsy and TURP specimens received for histopathological examination at our institute. CONCLUSION Histopathological diagnosis and grading plays an important role in the management of prostatic cancer. For satisfactory management of patient, a high degree of the awareness of the advances along with team approach has become imperative. REFERENCES 1. Franks LM. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: A review. Ann R Coll Surg Engl.1954; 14: Epstein JI, Allsbrook WCJr, Amin MB, Egevad LL. The 2005 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 2005; 29(9): Mittal BV, Amin MB, Kinare SG. Spectrum of histological lesions in 185 consecutive prostatic specimens. J Postgrad Med 1989; 35: Shakya G, Malla S, Shakya KN. Salient and comorbid features in benign prostatic hyperplasia: A histopathological study of the Prostate. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2003; 2: Sharma GC, Mathur SC, Sharma ML. Occult carcinoma in benign hypertrophy of prostate (Clinicopathological study of 100 cases). Ind J Surg 1972 April: Mohammed AZ, Alhasn SU, Edino ST, Ochicha O. Histopathological review of prostatic diseases in Kano, Nigeria. Niger Postgrad Med J 2003; 10(1): Mostofi FK, Benign hyperplasia of the prostate gland. In Campbell MF, Harrison JH eds. Urology, 3 rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1970, p Peterson RO, Sesterhenn IA, Davis CJ, editors. Prostate. In: Urologic Pathology. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; p Deming CL, Wolf JS. The anatomical origin of benign prostatic enlargement. J Urol 1939, 42: Anim JT, Ebrahim BH, Sathar A. Benign disorders of prostate: A histopathological study. Ann Saudi Med 1998; 18(1): Mwakyoma HA. The prevalence of high grade intraepithelial neoplasia in prostatic biopsies diagnosed as benign prostatic hyperplasia at Muhimbili National Hospital, Dar es Salaam. Tanzania Med J 2008; 23(1): Kim KB, Kim KS. A Histopathological observation on 48 cases of benign prostatic hypertrophy. Korean J Urol 1982; 23(8): Matapurkar BG, Taneja OP. Incidence of carcinoma prostate. Ind J of Cancer 1969 Sept Kohnen PW, Drach GW. Patterns of inflammation in prostatic hyperplasia: A histologic and bacterial study. J Urol 1979; 12: Oppenheimer JR, Kahane H, Epstein JI. Granulomatous prostatitis on needle biopsy. Arch Path Lab Med 1997; 121(7): International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 8
9 16. Keuhnelian JG. Experiences with granulomatous prostatitis. J Urol 1964; 91: Epstein JI, Hutchins GM. Granulomatous prostatitis: distinction among allergic, nonspecific and post transurethral resection lesions. Hum Pathol 1984; 15: Milord RA, Kahane H, Epstein JI. Infarct of the prostate gland: experience on needle biopsy specimens. Am J Surg Pathol 2000; 24(10): Moore RA. Benign hypertrophy of prostate. J Urol 1943;50: Quoted in Ackermann s Surgical Pathology, 9th ed. vol 1. Mosbey; p Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA. Tumours of prostate. In: World Health Organization classification of tumours: Pathology and genetics of the Urinary system and male genital organs. IARC Press Lyon p Edward Giovannucci: Epidemiologic characteristics of prostate cancer. Cancer [suppl]; 1995: 75(7): Piscator M. Role of cadmium in carcinogenesis with special reference to carcinoma of the prostate. Environ Health Perspect 1998; 40: Karube K. Study of latent carcinoma of the prostate in the Japanese, based on necropsy material. J Urol 1993; 150: Gilliland FD, Key CR. Male genital cancer. Cancer 1995; 75: Vollmer RT. Prostatic cancer and chip specimen: complete versus partial sampling. Hum Pathol 1986; 17: Brawn PN, Ayala AG, voneschenbach AC, Hussey DH, Johnson DE. Histologic grading study of prostate adenocarcinoma: The development of a new system and comparison with other methods- A preliminary study. Cancer 1982; 49: Alsaikafi NF, Brendler CB, Gerber GS, Yang XJ. High grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia with adjacent atypia is associated with a higher incidence of carcinoma on subsequent needle biopsy than high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia alone. Urol 2001; 57: Gaudin PB, Sesterhenn IA, Wonjno KJ, Mostofi FK, Epstein JI. Incidence and clinical significance of high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in TURP specimens. Urol 1997; 49: Pacelli A, Bostwick DG. Clinical significance of high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in TURP specimens. Urol 1997; 50: How to cite this article: Deshmukh BD, Ramteerthakar NA, Sulhyan KR. Histopathological study of lesions of prostate - A five year study. Int J Health Sci Res. 2014;4(1):1-9. ******************* International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 9
5/21/2018. Difficulty in Underdiagnosing Prostate Cancer. Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Evaluation of Prostate Cancer and Atypical on Needle Biopsy
 Evaluation of Prostate Cancer and Atypical on Needle Biopsy Jonathan I. Epstein Difficulty in Underdiagnosing Prostate Cancer Limited tissue on needle biopsy (1 cm. x
Evaluation of Prostate Cancer and Atypical on Needle Biopsy Jonathan I. Epstein Difficulty in Underdiagnosing Prostate Cancer Limited tissue on needle biopsy (1 cm. x
The histomorphological study of prostate lesions
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. VIII (Nov. 2015), PP 85-89 www.iosrjournals.org The histomorphological study of prostate
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. VIII (Nov. 2015), PP 85-89 www.iosrjournals.org The histomorphological study of prostate
Histopathological Study of Prostatic Diseases in Garhwal Region
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/526 Histopathological Study of Prostatic Diseases in Garhwal Region Sachan Bhat 1, Sheela Chaudhri 2, Pawan Bhat 1, Deepa Hatwal 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/526 Histopathological Study of Prostatic Diseases in Garhwal Region Sachan Bhat 1, Sheela Chaudhri 2, Pawan Bhat 1, Deepa Hatwal 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department
ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY. Jonathan I. Epstein.
 1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Some prostatic diseases
 Some prostatic diseases Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (Nodular Hyperplasia) Extremely common Present in a significant number of men by the age of 40 & its frequency rises progressively with age, reaching
Some prostatic diseases Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (Nodular Hyperplasia) Extremely common Present in a significant number of men by the age of 40 & its frequency rises progressively with age, reaching
3/28/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference. Differential Diagnosis:
 GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1)
 Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1) Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD June 7, 2012 Ten Leading Cancer Types for the Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths By Sex, United States,
Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1) Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD June 7, 2012 Ten Leading Cancer Types for the Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths By Sex, United States,
Internationally indexed journal
 www.ijpbs.net Internationally indexed journal Indexed in Chemical Abstract Services (USA), Index coppernicus, Ulrichs Directory of Periodicals, Google scholar, CABI,DOAJ, PSOAR, EBSCO, Open J gate, Proquest,
www.ijpbs.net Internationally indexed journal Indexed in Chemical Abstract Services (USA), Index coppernicus, Ulrichs Directory of Periodicals, Google scholar, CABI,DOAJ, PSOAR, EBSCO, Open J gate, Proquest,
Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance
 & 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
& 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
Chronic inflammation of long-standing duration has
 Inflammatory Atrophy of the Prostate Prevalence and Significance Athanase Billis, MD; Luis A. Magna, MD Context. Recently, prostatic atrophy associated with chronic inflammation has been linked to carcinoma
Inflammatory Atrophy of the Prostate Prevalence and Significance Athanase Billis, MD; Luis A. Magna, MD Context. Recently, prostatic atrophy associated with chronic inflammation has been linked to carcinoma
PATTERN OF PROSTRATE DISEASES- A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY IN JAMMU
 PATTERN OF PROSTRATE DISEASES- A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY IN JAMMU *Neha Angurana Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana- 141008 Punjab, India *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Benign hypertrophic
PATTERN OF PROSTRATE DISEASES- A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY IN JAMMU *Neha Angurana Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana- 141008 Punjab, India *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Benign hypertrophic
ROLE OF PROSTATIC BASAL CELL MARKER IN DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATIC LESIONS
 Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ROLE OF PROSTATIC BASAL CELL MARKER IN DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATIC LESIONS SUBATHRA K* Department of pathology,
Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ROLE OF PROSTATIC BASAL CELL MARKER IN DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATIC LESIONS SUBATHRA K* Department of pathology,
PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA AND IMPORTANT MIMICKERS PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA
 PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA AND IMPORTANT MIMICKERS PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA 1 A good H & E helps! ADENOCARCINOMA DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA Relatively uniform proliferation
PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA AND IMPORTANT MIMICKERS PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA 1 A good H & E helps! ADENOCARCINOMA DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA Relatively uniform proliferation
Hyperplastic, Premalignant and Malignant Lesions of the Prostate Gland
 Jehoram Tei Anim, md, FRCPath; Sitara Abdul Sathar, MB; Mohammed Ejaz Bhatti, MSc From the Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Kuwait. Address reprint requests and correspondence
Jehoram Tei Anim, md, FRCPath; Sitara Abdul Sathar, MB; Mohammed Ejaz Bhatti, MSc From the Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Kuwait. Address reprint requests and correspondence
ACCME/Disclosures. Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate. Case
 Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate Ming Zhou, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Urology New York University Langone Medical Center New York, NY Ming.Zhou@NYUMC.ORG ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires
Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate Ming Zhou, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Urology New York University Langone Medical Center New York, NY Ming.Zhou@NYUMC.ORG ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires
Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma is a subtype of
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE High-grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasialike Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: A Clinicopathologic Study of 28 Cases Fabio Tavora, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE High-grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasialike Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: A Clinicopathologic Study of 28 Cases Fabio Tavora, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract:
2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
Although current American Cancer Society guidelines
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffuse Adenosis of the Peripheral Zone in Prostate Needle Biopsy and Prostatectomy Specimens Tamara L. Lotan, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract: We have observed a group of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffuse Adenosis of the Peripheral Zone in Prostate Needle Biopsy and Prostatectomy Specimens Tamara L. Lotan, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract: We have observed a group of
STUDY OF PROSTATIC LESION FOR A PERIOD OF FIVE YEARS
 Page222 IJPBS Volume 4 Issue 2 APR-JUN 2014 222-226 Research Article Biological Sciences STUDY OF PROSTATIC LESION FOR A PERIOD OF FIVE YEARS B. Rajashekar Reddy 1, Rameswarapu Suman Babu 1 and Sujatha.P*
Page222 IJPBS Volume 4 Issue 2 APR-JUN 2014 222-226 Research Article Biological Sciences STUDY OF PROSTATIC LESION FOR A PERIOD OF FIVE YEARS B. Rajashekar Reddy 1, Rameswarapu Suman Babu 1 and Sujatha.P*
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017
 Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
PSA. HMCK, p63, Racemase. HMCK, p63, Racemase
 Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE. Jonathan I. Epstein
 INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
Pathology of the Prostate. PathoBasic Tatjana Vlajnic
 Pathology of the Prostate PathoBasic 24.01.17 Tatjana Vlajnic Overview Adenocarcinoma of the prostate Grading Special variants Mimickers of prostate adenocarcinoma Atrophy Inflammatory conditions Granulomatous
Pathology of the Prostate PathoBasic 24.01.17 Tatjana Vlajnic Overview Adenocarcinoma of the prostate Grading Special variants Mimickers of prostate adenocarcinoma Atrophy Inflammatory conditions Granulomatous
They Do Look Alike : Mimics of Prostate Cancer in Biopsy Samples
 They Do Look Alike : in Biopsy Samples Gladell P. Paner, MD Departments of Pathology and Surgery (Urology) University of Chicago, IL USA Gladell.paner@uchospitals.edu Benign in Needle Biopsy 1. Benign
They Do Look Alike : in Biopsy Samples Gladell P. Paner, MD Departments of Pathology and Surgery (Urology) University of Chicago, IL USA Gladell.paner@uchospitals.edu Benign in Needle Biopsy 1. Benign
Study of High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia for a Period of Five Years B. Rajashekar Reddy 1, Rameswarapu Suman Babu 2 and P.
 Indian Journal of Mednodent and Allied Sciences Vol. 2, No. 2, June-July, 2014, pp- 149-154 DOI : 10.5958/2347-6206.2014.00004.1 Original Research Study of High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Indian Journal of Mednodent and Allied Sciences Vol. 2, No. 2, June-July, 2014, pp- 149-154 DOI : 10.5958/2347-6206.2014.00004.1 Original Research Study of High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia
!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers.!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1
 !! Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D.!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1!! Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule 1 !!Conventional RCC! Clear
!! Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D.!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1!! Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule 1 !!Conventional RCC! Clear
ISSN: Page 1. SSRG International Journal of Medical Science (SSRG-IJMS) volume 2 Issue 6 June 2015
 Correlation between Prostate Specific Antigen and Acid Phosphatase with Histopathological Findings in Various Prostatic Pathologies Dr Anusha A.M 1, Dr S.Ranjith 2, Dr P.T Annamala 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Correlation between Prostate Specific Antigen and Acid Phosphatase with Histopathological Findings in Various Prostatic Pathologies Dr Anusha A.M 1, Dr S.Ranjith 2, Dr P.T Annamala 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Although partial atrophy is one of the most common
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Partial Atrophy on Prostate Needle Biopsy Cores: A Morphologic and Immunohistochemical Study Wenle Wang, MD, PhD,* Xinlai Sun, MD,w and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*zy Abstract: Partial atrophy
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Partial Atrophy on Prostate Needle Biopsy Cores: A Morphologic and Immunohistochemical Study Wenle Wang, MD, PhD,* Xinlai Sun, MD,w and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*zy Abstract: Partial atrophy
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page December 2016
 JMSCR Vol 4 Issue 12 Page 14471-14478 December 216 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v4i12.29
JMSCR Vol 4 Issue 12 Page 14471-14478 December 216 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v4i12.29
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
ISPUB.COM. Interpretation Of Prostatic Biopsies: A Review. A Chitale, S Khubchandani INTRODUCTION NON-NEOPLASTIC LESIONS GRADING: GLEASON'S SCORE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Urology Volume 3 Number 1 A Chitale, S Khubchandani Citation A Chitale, S Khubchandani.. The Internet Journal of Urology. 2004 Volume 3 Number 1. Abstract The incidence
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Urology Volume 3 Number 1 A Chitale, S Khubchandani Citation A Chitale, S Khubchandani.. The Internet Journal of Urology. 2004 Volume 3 Number 1. Abstract The incidence
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS
 1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
S1.04 Principal clinician. G1.01 Comments. G2.01 *Specimen dimensions (prostate) S2.02 *Seminal vesicles
 Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male
Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male
Epithelial Columnar Breast Lesions: Histopathology and Molecular Markers
 29th Annual International Conference Advances in the Application of Monoclonal Antibodies in Clinical Oncology and Symposium on Cancer Stem Cells 25 th -27t h June, 2012, Mykonos, Greece Epithelial Columnar
29th Annual International Conference Advances in the Application of Monoclonal Antibodies in Clinical Oncology and Symposium on Cancer Stem Cells 25 th -27t h June, 2012, Mykonos, Greece Epithelial Columnar
Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate
 Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate (with emphasis on cancer mimics) Rodolfo Montironi, MD (IT), FRCPath (UK), IFCAP (USA) Polytechnic University of Marche Region (Ancona) School of Medicine,
Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate (with emphasis on cancer mimics) Rodolfo Montironi, MD (IT), FRCPath (UK), IFCAP (USA) Polytechnic University of Marche Region (Ancona) School of Medicine,
PDF of Trial CTRI Website URL -
 Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sun, 25 Nov 2018 12:22:24 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 06/07/2013 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sun, 25 Nov 2018 12:22:24 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 06/07/2013 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Mast Cells in Appendicitis Dr. Jyoti Sharma 1*, Dr. Nitin Chaudhary 2*, Dr. Sunita
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Mast Cells in Appendicitis Dr. Jyoti Sharma 1*, Dr. Nitin Chaudhary 2*, Dr. Sunita
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE. Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT
 2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT 2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE AUTHORS : PROSTATE CHAPTER
2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT 2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE AUTHORS : PROSTATE CHAPTER
RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseud
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole Toole, M.D. RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole Toole, M.D. RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a
Spectrum of Lesions in Cystoscopic Bladder Biopsies -A Histopathological Study
 AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 012 )5 (2 ):1 3 2-1 3 6 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE Spectrum of Lesions in Cystoscopic
AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 012 )5 (2 ):1 3 2-1 3 6 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE Spectrum of Lesions in Cystoscopic
Prostatic stromal hyperplasia with atypia (PSHA) is a
 Prostatic Stromal Hyperplasia With Atypia Follow-up Study of 18 Cases Deloar Hossain, MD, FRCPC; Isabelle Meiers, MD; Junqi Qian, MD; Gregory T. MacLennan, MD; David G. Bostwick, MD, MBA Context. Prostatic
Prostatic Stromal Hyperplasia With Atypia Follow-up Study of 18 Cases Deloar Hossain, MD, FRCPC; Isabelle Meiers, MD; Junqi Qian, MD; Gregory T. MacLennan, MD; David G. Bostwick, MD, MBA Context. Prostatic
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Inverted (hobnail) high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive inverted pattern
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: 2395-2399, 2015 Inverted (hobnail) high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive inverted pattern MELTEM ÖZNUR 1, SEVIM BAYKAL KOCA 2, PELIN YILDIZ 3, BURAK BAHADIR 4
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: 2395-2399, 2015 Inverted (hobnail) high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive inverted pattern MELTEM ÖZNUR 1, SEVIM BAYKAL KOCA 2, PELIN YILDIZ 3, BURAK BAHADIR 4
Normal Morphology. Anatomic Considerations. Normal Urothelial Histology and Cytology
 1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
Muhammad Kashif Baig, Usman Hassan and Samina Mansoor
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of p63 in Differentiating Morphologically Ambiguous Lesions of Prostate Muhammad Kashif Baig, Usman Hassan and Samina Mansoor ABSTRACT Objective: To observe the role of p63 staining
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of p63 in Differentiating Morphologically Ambiguous Lesions of Prostate Muhammad Kashif Baig, Usman Hassan and Samina Mansoor ABSTRACT Objective: To observe the role of p63 staining
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. CYSTIC NEPHROMA
 Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Diagnosis, pathology and prognosis including variant pathology
 PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology and prognosis including variant pathology No Conflict of Interest Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona F.Algaba Section of Pathology PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology
PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology and prognosis including variant pathology No Conflict of Interest Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona F.Algaba Section of Pathology PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
3/23/2017. Significant Changes in Prostate Cancer Classification, Grading, Staging and Reporting. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Staging and Reporting of Prostate Cancer: Major Changes in 8 th Edition AJCC Staging and CAP Cancer Checklists USCAP requires that all planners (Education
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Staging and Reporting of Prostate Cancer: Major Changes in 8 th Edition AJCC Staging and CAP Cancer Checklists USCAP requires that all planners (Education
Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares
 Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares Aatur D. Singhi, MD PhD Assistant Professor University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Department of Pathology singhiad@upmc.edu Objectives Briefly give an overview
Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares Aatur D. Singhi, MD PhD Assistant Professor University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Department of Pathology singhiad@upmc.edu Objectives Briefly give an overview
Grading Prostate Cancer: Recent Changes and Refinements
 USPSTF: 2012 Report on serum PSA Screening Recommendation rating of D Reduced screening, Reduced biopsies, reduced incidence Refinements currently occurring in 2017. WHY? Grading Prostate Cancer: Recent
USPSTF: 2012 Report on serum PSA Screening Recommendation rating of D Reduced screening, Reduced biopsies, reduced incidence Refinements currently occurring in 2017. WHY? Grading Prostate Cancer: Recent
Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia
 Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia A review from Diagnostic Histopathology 19:7 Dr R Hadden ST5 Histopathology Derriford Hospital Plymouth Endometrium Target for sex-steroid hormones Glands Stroma Proliferate
Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia A review from Diagnostic Histopathology 19:7 Dr R Hadden ST5 Histopathology Derriford Hospital Plymouth Endometrium Target for sex-steroid hormones Glands Stroma Proliferate
Columnar Cell Lesions
 Columnar Cell Lesions Laura C. Collins, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Question? Columnar cell lesions are: a) Annoying lesions
Columnar Cell Lesions Laura C. Collins, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Question? Columnar cell lesions are: a) Annoying lesions
Histomorphological spectrum of prostatic lesions: a retrospective analysis of transurethral resection of prostate specimens
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sharma A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Jun;5(6):2373-2378 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20172095
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sharma A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Jun;5(6):2373-2378 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20172095
Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions
 Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Minimal Adenocarcinoma in Prostate Needle Biopsy Tissue
 Anatomic Pathology / MINIMAL PROSTATE CANCER Minimal Adenocarcinoma in Prostate Needle Biopsy Tissue Phataraporn Thorson, MD, and Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Key Words: Prostate; Cancer; Biopsy; Minimal
Anatomic Pathology / MINIMAL PROSTATE CANCER Minimal Adenocarcinoma in Prostate Needle Biopsy Tissue Phataraporn Thorson, MD, and Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Key Words: Prostate; Cancer; Biopsy; Minimal
Disclosures. Parathyroid Pathology. Objectives. The normal parathyroid 11/10/2012
 Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
Histological Spectrum of Prostatic Adenocarcinomas in Correlation with PSA Values
 Original Research Article Histological Spectrum of Prostatic Adenocarcinomas in Correlation with PSA Values Atchyuta. M 1,*, R. Krishna 2, P. Prema Latha 3, I. V. Renuka 4, V. Tejaswini 5, G. Vahini 6
Original Research Article Histological Spectrum of Prostatic Adenocarcinomas in Correlation with PSA Values Atchyuta. M 1,*, R. Krishna 2, P. Prema Latha 3, I. V. Renuka 4, V. Tejaswini 5, G. Vahini 6
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 24/June 16, 2014 Page 6628
 ADENOCARCINOMA OF BLADDER-SIGNET RING CELL MUCINOUS VARIANT S. Senthil Kumar 1, D. Prem Charles 2, B. Krishnaswamy 3, P. Viswanathan 4, S. Sarath Chandran 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: S. Senthil Kumar,
ADENOCARCINOMA OF BLADDER-SIGNET RING CELL MUCINOUS VARIANT S. Senthil Kumar 1, D. Prem Charles 2, B. Krishnaswamy 3, P. Viswanathan 4, S. Sarath Chandran 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: S. Senthil Kumar,
Hypoechoic Rim of Chronically Inflamed Prostate, as Seen at TRUS: Histopathologic Findings
 Hypoechoic Rim of Chronically Inflamed Prostate, as Seen at TRUS: Histopathologic Findings Hak Jong Lee, MD 1 Ghee Young Choe, MD 2 Chang Gyu Seong, MD 3 Seung Hyup Kim, MD 4 Index terms: Prostate Prostate,
Hypoechoic Rim of Chronically Inflamed Prostate, as Seen at TRUS: Histopathologic Findings Hak Jong Lee, MD 1 Ghee Young Choe, MD 2 Chang Gyu Seong, MD 3 Seung Hyup Kim, MD 4 Index terms: Prostate Prostate,
Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys
 Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast. Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London
 Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
B asal cell proliferations in the prostate gland exhibit a
 290 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Basal cell hyperplasia and basal cell carcinoma of the prostate: a comprehensive review and discussion of a case with c-erbb-2 expression R Montironi, R Mazzucchelli, D Stramazzotti,
290 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Basal cell hyperplasia and basal cell carcinoma of the prostate: a comprehensive review and discussion of a case with c-erbb-2 expression R Montironi, R Mazzucchelli, D Stramazzotti,
Crystalloids of Prostatic Adenocarcinoma on Prostatectomy
 福岡大医紀 (Med. Bull. Fukuoka Univ.):42(2),223 227,2015 Crystalloids of Prostatic Adenocarcinoma on Prostatectomy Mikio MIZOGUCHI, Hiroyuki HAYASHI, Kazuki NABESHIMA, Hiroshi IWASAKI, Morishige TAKESHITA Department
福岡大医紀 (Med. Bull. Fukuoka Univ.):42(2),223 227,2015 Crystalloids of Prostatic Adenocarcinoma on Prostatectomy Mikio MIZOGUCHI, Hiroyuki HAYASHI, Kazuki NABESHIMA, Hiroshi IWASAKI, Morishige TAKESHITA Department
Cytology of the prostate
 Cytology of the prostate M. K. MASON1 J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 581 From the Department of Morbid Anatomy, King's College Hospital Medical School. London SYNOPSIS A series of prostates has been studied
Cytology of the prostate M. K. MASON1 J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 581 From the Department of Morbid Anatomy, King's College Hospital Medical School. London SYNOPSIS A series of prostates has been studied
Gleason Scoring System 2017 JASREMAN DHILLON, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY, MOFFITT CANCER CENTER, TAMPA, FLORIDA
 Gleason Scoring System 2017 JASREMAN DHILLON, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY, MOFFITT CANCER CENTER, TAMPA, FLORIDA Learners Objectives u Latest changes per ISUP 2014 that impact
Gleason Scoring System 2017 JASREMAN DHILLON, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY, MOFFITT CANCER CENTER, TAMPA, FLORIDA Learners Objectives u Latest changes per ISUP 2014 that impact
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS
 HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS Kiran H. S, Jayaprakash Shetty, Chandrika Rao Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Yenepoya Medical College, Mangalore. Professor, Department of Pathology,
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS Kiran H. S, Jayaprakash Shetty, Chandrika Rao Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Yenepoya Medical College, Mangalore. Professor, Department of Pathology,
Case Report Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia of the prostate: report of an unprecedented entity in prostate pathology
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(11):5486-5490 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0084960 Case Report Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia of the prostate: report of an unprecedented entity in prostate pathology
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(11):5486-5490 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0084960 Case Report Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia of the prostate: report of an unprecedented entity in prostate pathology
Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary gland A case report of new entity
 Case Report Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary gland A case report of new entity Vaibhav Bhika Bari 1*, Sandhya Unmesh Bholay 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor Rajiv Gandhi Medical
Case Report Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary gland A case report of new entity Vaibhav Bhika Bari 1*, Sandhya Unmesh Bholay 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor Rajiv Gandhi Medical
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF BENIGN EPITHELIAL CHANGES
 Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Uropathology January Jon Oxley
 Uropathology January 2012 Jon Oxley Background to seminar These slides were available to view via the web from scanned slides The junior pathologists answered questions on them via the web The answers
Uropathology January 2012 Jon Oxley Background to seminar These slides were available to view via the web from scanned slides The junior pathologists answered questions on them via the web The answers
5/21/2018. Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma. Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology. Jonathan I.
 Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
A re-audit of Prostate biopsies from January to December 2010 and 2013.
 A re-audit of Prostate biopsies from January to December 2010 and 2013. Dr. M S Siddiqui Consultant Histopathologist University Hospital of North Tees Stockton on Tees. Objectives To assess and compare
A re-audit of Prostate biopsies from January to December 2010 and 2013. Dr. M S Siddiqui Consultant Histopathologist University Hospital of North Tees Stockton on Tees. Objectives To assess and compare
Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma
 Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Mucin-producing urothelial-type adenocarcinoma of prostate: report of two cases of a rare and diagnostically challenging entity
 & 2005 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/05 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Mucin-producing urothelial-type adenocarcinoma of prostate: report of two cases of a rare and diagnostically challenging
& 2005 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/05 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Mucin-producing urothelial-type adenocarcinoma of prostate: report of two cases of a rare and diagnostically challenging
CASE REPORT Malignant transformation of breast ductal adenoma: a diagnostic pitfall
 Malaysian J Pathol 2015; 37(3) : 281 285 CASE REPORT Malignant transformation of breast ductal adenoma: a diagnostic pitfall Hiroko HAYASHI, Hiroshi OHTANI,* Junzo YAMAGUCHI,** and Isao SHIMOKAWA Department
Malaysian J Pathol 2015; 37(3) : 281 285 CASE REPORT Malignant transformation of breast ductal adenoma: a diagnostic pitfall Hiroko HAYASHI, Hiroshi OHTANI,* Junzo YAMAGUCHI,** and Isao SHIMOKAWA Department
Update on 2015 WHO Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma 1/3/ Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. All rights reserved.
 1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
Supplemental Figure 1
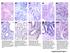 A1 A A5 A7 A9 A A4 A6 A8 A10 A1/A Gleason Score +=6 A/A4 Gleason Score +=6 Small glands with well defined Prominent feature of size variation lumen of various size infiltrating in to and distinct lumina
A1 A A5 A7 A9 A A4 A6 A8 A10 A1/A Gleason Score +=6 A/A4 Gleason Score +=6 Small glands with well defined Prominent feature of size variation lumen of various size infiltrating in to and distinct lumina
encapsulated thyroid nodule with a follicular architecture and some form of atypia. The problem is when to diagnose
 Histological Spectrum of Papillary Carcinoma of Thyroid A Two Years Study Gomathi Srinivasan 1, M. Vennila 2 1 Associate Professor Pathology, Government Medical College, Omandurar Estate, Chennai 600 002
Histological Spectrum of Papillary Carcinoma of Thyroid A Two Years Study Gomathi Srinivasan 1, M. Vennila 2 1 Associate Professor Pathology, Government Medical College, Omandurar Estate, Chennai 600 002
Premalignant Lesions of Prostate and their Association with Nodular Hyperplasia and Carcinoma Prostate
 Original Article Premalignant Lesions of Prostate and their Association with Nodular Hyperplasia and Carcinoma Prostate Rekhi B, Jaswal TS,* Arora B* Institute of Pathology-ICMR, Safdarjung Hospital, New
Original Article Premalignant Lesions of Prostate and their Association with Nodular Hyperplasia and Carcinoma Prostate Rekhi B, Jaswal TS,* Arora B* Institute of Pathology-ICMR, Safdarjung Hospital, New
A Clinicopathological Analysis of 120 Cases of Prostate Biopsies and Their Correlation with Prostate Specific Antigen levels ABSTRACT
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.2237 A Clinicopathological Analysis of 120 Cases of Prostate Biopsies and Their Correlation with Prostate Specific Antigen levels Anu Sumi Issac 1 *, Ashley Ann Varughese
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.2237 A Clinicopathological Analysis of 120 Cases of Prostate Biopsies and Their Correlation with Prostate Specific Antigen levels Anu Sumi Issac 1 *, Ashley Ann Varughese
Original Article Collagenous micronodules in prostate cancer revisited: are they solely associated with Gleason pattern 3 adenocarcinomas?
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(4):3469-3476 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0006673 Original Article Collagenous micronodules in prostate cancer revisited: are they solely associated with Gleason pattern
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(4):3469-3476 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0006673 Original Article Collagenous micronodules in prostate cancer revisited: are they solely associated with Gleason pattern
Ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate: A clinicopathological study
 20 B. SATHESAN, S. A. S. GOONEWARDENA, H. W. D. ANURUDDHIKA AND M. V. C. DE SILVA Sri Lanka Journal of Urology, 2008, 9, 20-24 Original Article Ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate: A clinicopathological
20 B. SATHESAN, S. A. S. GOONEWARDENA, H. W. D. ANURUDDHIKA AND M. V. C. DE SILVA Sri Lanka Journal of Urology, 2008, 9, 20-24 Original Article Ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate: A clinicopathological
Available Online through (or) IJPBS Volume 3 Issue 1 JAN-MAR Review Article Biological Sciences
 Page162 Review Article Biological Sciences CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF BENIGN & MALIGNANT LESIONS OF PROSTATE *1 Chandanwale Shirish, 2 P. S. Jadhav, 3 S. C. Anwekar, 4 H. Kumar, 5 A. C. Buch, 6 U. S.
Page162 Review Article Biological Sciences CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF BENIGN & MALIGNANT LESIONS OF PROSTATE *1 Chandanwale Shirish, 2 P. S. Jadhav, 3 S. C. Anwekar, 4 H. Kumar, 5 A. C. Buch, 6 U. S.
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS
 7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS DR. VIBHUTI H. CHIHLA*, DR. N N. JAGRIT **, DR. JAYASHREE M. SHAH*** *3 rd year Pathology Resident, **Associate Professor,
7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS DR. VIBHUTI H. CHIHLA*, DR. N N. JAGRIT **, DR. JAYASHREE M. SHAH*** *3 rd year Pathology Resident, **Associate Professor,
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Salivary Gland Cytology
 Salivary Gland Cytology Diagnostic challenges and potential pitfalls Tarik M. Elsheikh, MD Professor and Medical Director Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic FNA Salivary Gland Lesions Indications Distinguish
Salivary Gland Cytology Diagnostic challenges and potential pitfalls Tarik M. Elsheikh, MD Professor and Medical Director Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic FNA Salivary Gland Lesions Indications Distinguish
