(Received 16th October 1969)
|
|
|
- Charlotte Arnold
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EFFECT OF AN ANTI-ANDROGEN ON THE DIFFERENTIATION OF THE INTERNAL GENITAL ORGANS IN DOGS H. STEINBECK, F. NEUMANN and W. ELGER Main Laboratory of Schering AG, Berlin, West Germany (Received 16th October 1969) Summary. From experiments with anti-androgens, it can be concluded which processes in the sex differentiation of dogs are androgen\x=req-\ dependent and which are not. In contrast to rats but as in rabbits, retrogression of the Wolffian ducts can be induced in the treated members of this species compared to their controls, but retrogression of the M\l=u"\llerianducts is uninfluenced in both treated and control animals. From this, it is concluded that the latter process is not androgen-dependent. INTRODUCTION The most potent known anti-androgen was discovered by its ability to feminize male rat foetuses (Hamada, Neumann & Junkmann, 1963). It was found in subsequent experiments that this compound is capable of inhibiting effects of endogenously produced as well as exogenously administered androgens (Junk mann & Neumann, 1964; Neumann, Richter & Günzel, 1965; Neumann, 1966). Cyproterone acetate proved to be a valuable tool for the exploration of the biological rôle of androgens, especially when the surgical approach is diffi cult or even impossible, e.g. in investigations regarding the effects of testosterone within the testis itself (Neumann & von Berswordt-Wallrabe, 1965, 1966) or in foetal sex differentiation processes (Elger & Neumann, 1966; Neumann & Elger, 1966; Neumann, Elger & Kramer, 1966; Neumann & Kramer, 1964). The first species in which the entire genital tract was studied was the rabbit (Elger, 1966). In addition to feminization of the external genital organs, the following results were of special importance in male foetuses : the gonads were differentiated and descended normally; retrogression of the Müllerian ducts could not be prevented; above a critical dose level (5 mg/kg/day i.m.), involu tion of the Wolffian ducts was almost complete. This result was considered to be a proof of Jost's theory postulating that, besides androgens, other factors of the male gonad a play rôle in sex differentia tion (Müllerian duct inhibiting hormone). Initial studies on the rat foetus were confined to the differentiation of the feminization was found external genital organs, where more or less complete (Hamada et al., 1963; Junkmann & Neumann, 1964). In subsequent studies, 223
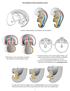
2 224 H. Steinbeck et al. the results obtained in rabbits after relatively low doses of cyproterone acetate could never be achieved in rats, although excessive doses were administered (Jost, 1967; Forsberg, Jacobsohn & Norgren, 1968; Elger, Neumann & von Berswordt-Wallrabe, personal communication). In spite ofmaximal feminization of the external genitalia, retrogressed Wolffian ducts were never found. The reason for these species differences is unknown and an extension of the seemed desirable in order to find out whether one experiments to other species or other reaction is the rule or the exception. MATERIAL AND METHODS Two beagle bitches were used as experimental animals. The bitches were mated once daily on 3 consecutive days, the middle day being regarded as Day 1 of pregnancy, when this condition had subsequently been established. Cyproterone acetate was injected i.m. as an oily solution (benzyl benzoate/ castor oil 1: 10) in a daily dose of 10 mg/kg from the 23rd to the 44th day of pregnancy. The foetuses were removed from the uterus by Caesarean section were embedded in on the 45th day. After fixing in Bouin's solution, they paraffin and serial sections were made at mm intervals, every twentieth section being mounted on microscope slides. Thus, two successive sections a represented distance of 0-1 mm. RESULTS Three male foetuses were examined from each of the two litters. As controls, two male and two female untreated foetuses of the same age were used. The internal genital organs of treated males and untreated controls are shown schematically in Text-fig. 1, after reconstruction from serial sections. Gonads In treated animals as well as in male and female controls, the gonads were still located in the immediate vicinity of the caudal kidney pole. No abnormal gonads were found. Müllerian ducts In all males, whether treated or not, the Müllerian ducts had retrogressed to minute epithelial and mesenchymal traces. These remnants, however, were found almost constantly throughout the whole length of the genital tract (PI. 1, Fig. 1). Only in the close proximity of the urogenital sinus did a caudal remnant (PI. 1, Fig. 2), which ended blindly in the forepart, persist in three treated males (967/1, 967/4, 722/2). Wolffian ducts All treated foetuses had degenerated Wolffian ducts, with the exception of one foetus (967/1) in which the ducts were not affected by the anti-androgen. In the remaining five foetuses, the Wolffian ducts had retrogressed either unilaterally or bilaterally and short sections of discontinuity were also found, particularly in the immediate vicinity of the urogenital sinus (722/4 and 722/7).
3 PLATE 1 Fig. 1. Mesogenital folds (MGF) of a male dog foetus whose mother had been treated rectum. Both Müllerian and Wolffian ducts have with cyproterone acetate. R retrogressed. The previous position of both ducts is marked by mesenchymal condensa tions. Fig. 2. Genital cord of a feminized male dog foetus in the vicinity of the urogenital sinus. A segment of a Müllerian vagina (MV) can be seen between the neck of the urinary bladder (NUB) and the rectum (R). Wolffian ducts are definitely absent at this level. Fig. 3. Feminized male dog foetus. Partition of the urogenital sinus into a smaller ventral (U, urethra!) and a wider dorsal (V, vaginal) portion. The prostate development is almost completely suppressed. RPB rudimentary prostatic bud. = = (Facing p. 224)
4 An Text-fig. 1. Scale dog foetuses. anti-androgen and the canine reproductive tract drawings of the internal reproductive tract of anti-androgen-treated 225
5 226 H. Steinbeck et al. Urogenital sinus In all treated male foetuses, a separation of the anterior part of the sinus, resulting in the formation of a (sinus-) vagina (PI. 1, Fig. 3), was observed, as in the female controls. The prostatic development was also suppressed to some extent (PI. 1, Figs. 2 and 3). External genital organs The external genital organs had reached a similar stage of development in the treated males as in female foetuses of the same age. Genital cord In the feminized male foetuses, the distance from the fusion of the urogenital folds to the sinus orifice of the genital ducts was relatively long compared with the male controls. The small number of controls, however, does not allow any definite conclusions to be drawn. DISCUSSION Under the influence of cyproterone acetate, the sexual differentiation in dogs is essentially similar to the pattern already seen in rabbits, thus confirming the androgen-dependence of the Wolffian ducts, the prostate and other structures and differentiation processes. Since the high degree of feminization of the male genital tract, including retrogression of the Wolffian ducts, was not accom panied by a substantial influence on the Müllerian ducts, these experiments further support Jost's theory of sexual differentiation. It can be presumed that the suppression of the Müllerian ducts by a specific testicular activity is the rule in mammals, but in our own experiments in rats, no retrogression of the Wolffian ducts was obtained by anti-androgen treatment. There are also in consistent results in vitro with cultures of the genital tract where spontaneous retrogression of the Müllerian ducts in the absence of the foetal gonad was observed (Price, Ortiz & Zaaijer, 1967). In recent experiments, we were able to stabilize the Wolffian ducts in female rat foetuses by methyl testosterone treatment of pregnant rats, an effect which could be completely abolished by concomitant cyproterone acetate treatment (Elger, Steinbeck, Cupceancu & Neumann, 1970). It seems, therefore, that those hormonal factors (androgens?) which physiologically stabilize the Wolffian ducts in rats differ from synthetic androgens with regard to their biological action. At this time, it is not possible to give a sound general interpretation of the hormonal dependence of the Müllerian and Wolffian ducts. It can only be stated that androgens are not involved in Müllerian duct retrogression (Jost, 1967) and that anti-androgens, consequently, do not prevent this process. REFERENCES Elger, W. (1966) Die Rolle der fetalen Androgene in der Sexual-differenzierung des Kaninchens und ihre Abgrenzung gegen andere hormonale und somatische Faktoren durch Anwendung eines starken Antiandrogens. Archs Anat. microse Morph. exp. 55, 657. Elger, W. & Neumann, F. (1966) The role of androgens in the differentiation of the mammary gland in male mouse fetuses. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med. 123, 637.
6 An anti-androgen and the canine reproductive tract 227 Elger, W., Steinbeck, H., Cupceancu, B. & Neumann, F. (1970) Experiments with synthetic andro gens and anti-androgens on Wolffian duct differentiation in rat foetuses. J. Endocr. (In press). Forsberg, J.-G., Jacobsohn, D. & Norgren, A. (1968) Development of the urogenital tract in male offspring of rats injected during pregnancy with a substance with antiandrogenic properties (cyproterone). Z Anat. EntwGesch. 126, 320. Hamada, H., Neumann, F. & Junkmann, K. (1963) Intrauterine antimaskuline Beeinflussung von Rattenfeten durch ein stark gestagen wirksames Steroid. Ada endocr., Copenh. 44, 380. Jost, A. (1967) Steroids and sex differentiation of the mammalian fetus. Proceedings of the Und Int. Congress on Hormonal Steroids, Milan Excerpta med. Int. Congr. Ser. 132, 74. Junkmann, K. & Neumann, F. (1964) Zum Wirkungsmechanismus von an Feten antimaskulin wirk samen Gestagenen. Ada endocr., Copenh. Suppl. 90, 139. Neumann, F. (1966) Methods for evaluating antisexual hormones. In: Proceedings of the Int. Symposium Methods in Drug Evaluation, Milan, 1965, pp North Holland Pubi. Company, Amsterdam. Neumann, F. & von Berswordt-Wallrabe, R. (1965) Effects of a new anti-androgen, l,2a-methylene- 6-chlor-A6-17a-hydroxy-progesterone-17-acetate (SH 714), on the testicular structure of adult testosteronepropionate (TP)-treated hypophysectomized rats. Ada endocr., Copenh. Suppl. 100, 42. Neumann, F. & von Berswordt-Wallrabe, R. (1966) Effects of the androgen antagonist cyproterone acetate on the testicular structure, spermatogenesis and accessory sexual glands of testosteronetreated adult hypophysectomized rats. J. Endocr. 35, 363. Neumann, F. & Elger, W. (1966) The effect of the anti-androgen l,2a-methylene-6-chloro-a4'6 pregnadiene-17o;-ol-3,20-dione-17a-acetate (cyproterone acetate) on the development of the mammary glands of male foetal rats. J. Endocr. 36, 347. Neumann, F., Elger, W. & Kramer, M. (1966) Development of a vagina in male rats by inhibiting androgen receptors with an anti-androgen during the critical phase of organogénesis. Endocrino logy, 78, 628. Neumann, F. & Kramer, M. (1964) Antagonism of androgenic and anti-androgenic agents in their action on the rat fetus. Endocrinology, 75, 428. Neumann, F., Richter, K.-D. & Günzel, P. (1965) Wirkungen von Antiandrogenen. Zenlbl. VetMed., Reihe A, 12, 171. Price, D., Ortiz, E. & Zaaijer, J. P. (1967) Organ culture studies of hormone secretion in endocrine glands of fetal guinea pigs. III. The relation of testicular hormone to sex differentiation of the reproductive ducts. Anat. Ree 157, 27.
EFFECT OF CYPROTERONE ACETATE ON PUBERTY IN RATS. Experimental Research Pharma, Schering AG, period. Certain advantages of antiandrogen
 EFFECT OF CYPROTERONE ACETATE ON PUBERTY IN RATS H. STEINBECK and F. NEUMANN Experimental Research Pharma, Schering AG, Department of Endocrinology, 1 Berlin 651 {Received I5tk August 1970) Summary. Cyproterone
EFFECT OF CYPROTERONE ACETATE ON PUBERTY IN RATS H. STEINBECK and F. NEUMANN Experimental Research Pharma, Schering AG, Department of Endocrinology, 1 Berlin 651 {Received I5tk August 1970) Summary. Cyproterone
androgen on the seminal vesicles it had neither a blocking effect on the penile
 MORPHOLOGICAL AND BEHAVIOURAL EFFECTS OF AN 'ANTIANDROGEN' IN MALE RATS F. A. BEACH and W. H. WESTBROOK Department of Psychology, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720, U.S.A. (Received
MORPHOLOGICAL AND BEHAVIOURAL EFFECTS OF AN 'ANTIANDROGEN' IN MALE RATS F. A. BEACH and W. H. WESTBROOK Department of Psychology, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720, U.S.A. (Received
Developmental Changes of Müllerian and Wolffian Ducts in Domestic Cat Fetuses
 Exp. Anim. 58(1), 41 45, 2009 Note Developmental Changes of Müllerian and Wolffian Ducts in Domestic Cat Fetuses Tomo INOMATA 1), Hiroyoshi NINOMIYA 1), Katsuyasu SAKITA 1), Naomi KASHIWAZAKI 2), Junya
Exp. Anim. 58(1), 41 45, 2009 Note Developmental Changes of Müllerian and Wolffian Ducts in Domestic Cat Fetuses Tomo INOMATA 1), Hiroyoshi NINOMIYA 1), Katsuyasu SAKITA 1), Naomi KASHIWAZAKI 2), Junya
11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION. Germinal cells, gonocytes. Indifferent stage INDIFFERENT STAGE
 11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15 % of the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is formed in the sides of the embryonic tissue, ventral to the mesonephros
11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15 % of the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is formed in the sides of the embryonic tissue, ventral to the mesonephros
Growth pattern of the sex ducts in foetal mouse hermaphrodites
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. 73, 59-68, 1983 59 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Growth pattern of the sex ducts in foetal mouse hermaphrodites By C. YDING ANDERSEN 1, A. G. BYSKOV
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. 73, 59-68, 1983 59 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Growth pattern of the sex ducts in foetal mouse hermaphrodites By C. YDING ANDERSEN 1, A. G. BYSKOV
Sexual differentiation:
 Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs
 Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs Sex determination The SRY + gene is necessary and probably sufficient for testis development The earliest sexual difference appears in the gonad
Sex Determination and Development of Reproductive Organs Sex determination The SRY + gene is necessary and probably sufficient for testis development The earliest sexual difference appears in the gonad
Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract. Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim
 Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim objectives: Revision of embryology. Clinical presentation, investigations and clinical significance of most common developmental
Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim objectives: Revision of embryology. Clinical presentation, investigations and clinical significance of most common developmental
Development of the urogenital system
 Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology"
 Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology" Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development: Part A Development of the Pituitary Gland" Infundibulum" Brain" Rathke s Pouch" Stomodeum" Germ Cell Migration"
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology" Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development: Part A Development of the Pituitary Gland" Infundibulum" Brain" Rathke s Pouch" Stomodeum" Germ Cell Migration"
INTRAUTERINE GONADAL DEVELOPMENT*
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright @ 1976 The American Fertility Society Vol. 27, No.5, May 1976 Printed in U.SA. INTRAUTERINE GONADAL DEVELOPMENT* HANNAH PETERS, M.D. The Finsen Laboratory, The Finsen
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright @ 1976 The American Fertility Society Vol. 27, No.5, May 1976 Printed in U.SA. INTRAUTERINE GONADAL DEVELOPMENT* HANNAH PETERS, M.D. The Finsen Laboratory, The Finsen
DEFINITION: Masculinization of external genitalia in patients with normal 46XX karyotype.
 INTERSEX DISORDERS DEFINITION: Masculinization of external genitalia in patients with normal 46XX karyotype. - Degree of masculinization variable: - mild clitoromegaly - complete fusion of labia folds
INTERSEX DISORDERS DEFINITION: Masculinization of external genitalia in patients with normal 46XX karyotype. - Degree of masculinization variable: - mild clitoromegaly - complete fusion of labia folds
612.6I7.5:612.6I6.I. different, but most of them appear to be satisfactory from a qualitative
 442 612.6I7.5:612.6I6.I SIZE CHANGES IN THE SEMINAL VESICLES OF THE MOUSE DURING DEVELOPMENT AND AFTER CASTRATION. BY RUTH DEANESLY AND A. S. PARKES'. (From the National Institute for Medical Research,
442 612.6I7.5:612.6I6.I SIZE CHANGES IN THE SEMINAL VESICLES OF THE MOUSE DURING DEVELOPMENT AND AFTER CASTRATION. BY RUTH DEANESLY AND A. S. PARKES'. (From the National Institute for Medical Research,
The role of the Wolffian ducts in the formation of the sinus vagina: an organ culture study
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. 73, 275-295, 1983 275 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists 1982 The role of the Wolffian ducts in the formation of the sinus vagina: an organ culture study By GABRIELE
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. 73, 275-295, 1983 275 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists 1982 The role of the Wolffian ducts in the formation of the sinus vagina: an organ culture study By GABRIELE
under its influence, male development occurs; in its absence, female development is established.
 Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326
 Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Development of the Genital System
 Development of the Genital System Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta The mesonephros develops primitive nephrotomes draining into a mesonephric duct nephrotome mesonephric
Development of the Genital System Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta The mesonephros develops primitive nephrotomes draining into a mesonephric duct nephrotome mesonephric
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 11 Alphabetical alpha-fetoprotein alpha-fetoprotein Alpha-Fetal Protein (AFP) or alpha-1- fetoprotein. During a prenatal sensitive period, estradiol
Bios 90/95. Jennifer Swann, PhD
 Sexual Differentiation Fall 2007 Bios 90/95 Jennifer Swann, PhD Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Why have sexes? What determines sex? Environment Genetics Hormones What causes these differences? The true
Sexual Differentiation Fall 2007 Bios 90/95 Jennifer Swann, PhD Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Why have sexes? What determines sex? Environment Genetics Hormones What causes these differences? The true
EMBRYOLOGIC BASIS OF FEMALE CONGENITAL TRACT MALFORMATIONS
 EMBRYOLOGIC BASIS OF FEMALE CONGENITAL TRACT MALFORMATIONS Prof. Pedro Acién, MD, FRCOG Maribel Acién, MD San Juan University Hospital/ Miguel Hernández University Campus of San Juan. Alicante. Spain Instituto
EMBRYOLOGIC BASIS OF FEMALE CONGENITAL TRACT MALFORMATIONS Prof. Pedro Acién, MD, FRCOG Maribel Acién, MD San Juan University Hospital/ Miguel Hernández University Campus of San Juan. Alicante. Spain Instituto
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
IN SUMMARY HST 071 NORMAL & ABNORMAL SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis and Management of Intersex Abnormalities
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 Title: Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 Title: Fetal Sex Differentiation Postnatal Diagnosis
Urinary System. ectoderm. notochord. mesonephric tubules. Nephrogenic Cord (left)
 Urinary System NOTE: Urine proion requires an increased capillary surface area (glomeruli), epithelial s to collect plasma filtrate and extract desirable constituents, and a system to convey urine away
Urinary System NOTE: Urine proion requires an increased capillary surface area (glomeruli), epithelial s to collect plasma filtrate and extract desirable constituents, and a system to convey urine away
1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase
 Human Sexuality Exam II Review Material Gametogenesis: Oogenesis 1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase 2. Know the relative
Human Sexuality Exam II Review Material Gametogenesis: Oogenesis 1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase 2. Know the relative
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology
 Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology Development of the Pituitary Gland Lec 5: Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development Stomodeum Brain Infundibulum Rathke s Pouch Germ Cell Migration
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology Development of the Pituitary Gland Lec 5: Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development Stomodeum Brain Infundibulum Rathke s Pouch Germ Cell Migration
Development of the Urinary System
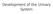 Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Embryology /organogenesis/ Week 4 Development and teratology of reproductive system.
 Embryology /organogenesis/ Week 4 Development and teratology of reproductive system. Male or female sex is determined by spermatozoon Y in the moment of fertilization SRY gene, on the short arm of the
Embryology /organogenesis/ Week 4 Development and teratology of reproductive system. Male or female sex is determined by spermatozoon Y in the moment of fertilization SRY gene, on the short arm of the
Foetal testes control the prenatal growth and differentiation of the gubernacular cones in rabbits - a tribute to the late Professor Alfred Jost
 Development 118, 1327-1334 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 1327 Foetal testes control the prenatal growth and differentiation of the gubernacular cones in rabbits
Development 118, 1327-1334 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 1327 Foetal testes control the prenatal growth and differentiation of the gubernacular cones in rabbits
Let s Talk About Hormones!
 Let s Talk About Hormones! This lesson was created by Serena Reves and Nichelle Penney, with materials from the BCTF and The Pride Education Network. Hormones are responsible for the regulation of many
Let s Talk About Hormones! This lesson was created by Serena Reves and Nichelle Penney, with materials from the BCTF and The Pride Education Network. Hormones are responsible for the regulation of many
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Animal Reproduction. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. # lectures for cumulative test # 01 book 01
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 05 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 05 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
W.S. O University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
W.S. O University of Hong Kong Development of the Genital System 1. Sexual differentiation 2. Differentiation of the gonads a. Germ cells extragonadal in origin b. Genital ridge intermediate mesoderm consisting
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Sexual Differentiation Fall 2008 Bios 90
 Sexual Differentiation Fall 2008 Bios 90 Jennifer Swann, Professor Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Asexual reproduction Budding : offspring develop as a growth on the body of the parent jellyfishes, echinoderms,
Sexual Differentiation Fall 2008 Bios 90 Jennifer Swann, Professor Dept Biol Sci, Lehigh University Asexual reproduction Budding : offspring develop as a growth on the body of the parent jellyfishes, echinoderms,
PREGNANCY DISTURBANCES IN RATS BY THE ADMINIS- TRATION OF LARGE DOSES OF SEX HORMONES TETSURO ABE AND EIICHI KANEKO
 PREGNANCY DISTURBANCES IN RATS BY THE ADMINIS- TRATION OF LARGE DOSES OF SEX HORMONES TETSURO ABE AND EIICHI KANEKO Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, School of Medicine, Tohoku University, Sendai
PREGNANCY DISTURBANCES IN RATS BY THE ADMINIS- TRATION OF LARGE DOSES OF SEX HORMONES TETSURO ABE AND EIICHI KANEKO Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, School of Medicine, Tohoku University, Sendai
Urinary system development. Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development
 Urinary system development Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development Urogenital system develops from mesodermal uro-genital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) development of male and female genital
Urinary system development Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development Urogenital system develops from mesodermal uro-genital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) development of male and female genital
Male Anatomy. testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics
 Male Anatomy Male Anatomy Primary Organ testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics 1) Secondary Organs internal
Male Anatomy Male Anatomy Primary Organ testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics 1) Secondary Organs internal
A. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis. B. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis.
 USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Identification in rats of a programming window for reproductive tract masculinization, disruption of which leads to hypospadias and cryptorchidism
 Research article Identification in rats of a programming window for reproductive tract masculinization, disruption of which leads to hypospadias and cryptorchidism Michelle Welsh, Philippa T.K. Saunders,
Research article Identification in rats of a programming window for reproductive tract masculinization, disruption of which leads to hypospadias and cryptorchidism Michelle Welsh, Philippa T.K. Saunders,
The Alteration of Aggressive Behavior in Mice Following Parenteral Administration of Sex Steroids and Synthetic Analogues
 Loyola University Chicago Loyola ecommons Dissertations Theses and Dissertations 1969 The Alteration of Aggressive Behavior in Mice Following Parenteral Administration of Sex Steroids and Synthetic Analogues
Loyola University Chicago Loyola ecommons Dissertations Theses and Dissertations 1969 The Alteration of Aggressive Behavior in Mice Following Parenteral Administration of Sex Steroids and Synthetic Analogues
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2
 Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
PERINEAL HYPOSPADIAS IN A CROSS BREED DOG: A CASE REPORT
 Indo-Am. J. Agric. & Vet. Sci., 2014 M Gokulakrishnan ISSN 2321 9602 and L Nagarajan, www.iajavs.com 2014 Vol. 2, No. 3, September 2014 2014 Meghana Publications. All Rights Reserved Case Report PERINEAL
Indo-Am. J. Agric. & Vet. Sci., 2014 M Gokulakrishnan ISSN 2321 9602 and L Nagarajan, www.iajavs.com 2014 Vol. 2, No. 3, September 2014 2014 Meghana Publications. All Rights Reserved Case Report PERINEAL
PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION
 PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Prof. Dr med. Jolanta Słowikowska-Hilczer Department of Andrology and Reproductive Endocrinology Medical University of Łódź, Poland Sexual determination
PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Prof. Dr med. Jolanta Słowikowska-Hilczer Department of Andrology and Reproductive Endocrinology Medical University of Łódź, Poland Sexual determination
Formation of Urine: Formation of Urine
 The Urinary outflow tract: monitors and regulates extra-cellular fluids excretes harmful substances in urine, including nitrogenous wastes (urea) returns useful substances to bloodstream maintain balance
The Urinary outflow tract: monitors and regulates extra-cellular fluids excretes harmful substances in urine, including nitrogenous wastes (urea) returns useful substances to bloodstream maintain balance
Further Observations on the Teratogenic Action of the Thyroid Stimulating Hormone '
 Further Observations on the Teratogenic Action of the Thyroid Stimulating Hormone ' ALLAN R. BEAUDOIN Department of Anatomy, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan ABSTRACT Pregnant Wistar Albino
Further Observations on the Teratogenic Action of the Thyroid Stimulating Hormone ' ALLAN R. BEAUDOIN Department of Anatomy, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan ABSTRACT Pregnant Wistar Albino
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
2. Which male target tissues respond to testosterone, and which require dihydrotestosterone?
 308 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 56 Male Pseudohermaphroditism: Sa-Reductase Deficiency Fourteen years ago, Wally and Wanda Garvey, who live in rural North Carolina, had their first child. The baby
308 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 56 Male Pseudohermaphroditism: Sa-Reductase Deficiency Fourteen years ago, Wally and Wanda Garvey, who live in rural North Carolina, had their first child. The baby
Sensitivity and Specificity of Bioassay of Estrogenicity on Mammary Gland and Uterus of Female Mice
 Physiol. Res. 51: 407-412, 2002 Sensitivity and Specificity of Bioassay of Estrogenicity on Mammary Gland and Uterus of Female Mice J. ŠKARDA Institute of Animal Physiology and Genetics, Academy of Sciences
Physiol. Res. 51: 407-412, 2002 Sensitivity and Specificity of Bioassay of Estrogenicity on Mammary Gland and Uterus of Female Mice J. ŠKARDA Institute of Animal Physiology and Genetics, Academy of Sciences
Chapter 16: Steroid Hormones (Lecture 17)
 Chapter 16: Steroid Hormones (Lecture 17) A) 21 or fewer carbon atoms B) Precursor: 27 carbon cholesterol C) major classes of steroid hormones 1) progestagens a) progesterone- prepares lining of uterus
Chapter 16: Steroid Hormones (Lecture 17) A) 21 or fewer carbon atoms B) Precursor: 27 carbon cholesterol C) major classes of steroid hormones 1) progestagens a) progesterone- prepares lining of uterus
The Reproductive System
 C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
GONADOTROPHIN (LUTEINISING)- RELEASING HORMONE AND ANALOGUES (GnRH OR LHRH)
 GONADOTROPHIN (LUTEINISING)- RELEASING HORMONE AND ANALOGUES (GnRH OR LHRH) Naturally occurring hormone, produced by the hypothalamus and transferred to the anterior pituitary gland in the hypophyseal
GONADOTROPHIN (LUTEINISING)- RELEASING HORMONE AND ANALOGUES (GnRH OR LHRH) Naturally occurring hormone, produced by the hypothalamus and transferred to the anterior pituitary gland in the hypophyseal
Guide to Small Animal Reproductive Imaging using the Vevo 770
 Guide to Small Animal Reproductive Imaging using the Vevo 770 Course Objectives: After completion of this module, the participant will be able to accomplish the following: Recognize reproductive female
Guide to Small Animal Reproductive Imaging using the Vevo 770 Course Objectives: After completion of this module, the participant will be able to accomplish the following: Recognize reproductive female
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Chapter 18 Development. Sexual Differentiation
 Chapter 18 Development Sexual Differentiation There Are Many Levels of Sex Determination Chromosomal Sex Gonadal Sex Internal Sex Organs External Sex Organs Brain Sex Gender Identity Gender Preference
Chapter 18 Development Sexual Differentiation There Are Many Levels of Sex Determination Chromosomal Sex Gonadal Sex Internal Sex Organs External Sex Organs Brain Sex Gender Identity Gender Preference
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
The Reproductive System
 16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
Reproductive System Purpose General Structures Male Structures Functions Female Anatomy Structures Functions Clinical Applications
 The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
Detection of anti-m\l=u"\llerian activity in boar rete testis fluid
 Detection of anti-m\l=u"\llerian activity in boar rete testis fluid Nathalie Josso, J. Y. Picard, J. L. Dacheux and M. Courot Unité de Recherches de Génétique Médicale (INSERM), Hôpital des Enfants-Malades,
Detection of anti-m\l=u"\llerian activity in boar rete testis fluid Nathalie Josso, J. Y. Picard, J. L. Dacheux and M. Courot Unité de Recherches de Génétique Médicale (INSERM), Hôpital des Enfants-Malades,
17. Sex. Being Male and Female
 17. Sex Being Male and Female Reproduction Asexual: more efficient (Only 1 sex) Low genetic variation Sexual: prevalent (2 sexes, separate or not) High genetic variation Need 2 members of the same species
17. Sex Being Male and Female Reproduction Asexual: more efficient (Only 1 sex) Low genetic variation Sexual: prevalent (2 sexes, separate or not) High genetic variation Need 2 members of the same species
Development of the Urinary System. 3 Distinct Embryonic Kidney Structures
 Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
Chapter 7 DEVELOPMENT AND SEX DETERMINATION
 Chapter 7 DEVELOPMENT AND SEX DETERMINATION Chapter Summary The male and female reproductive systems produce the sperm and eggs, and promote their meeting and fusion, which results in a fertilized egg.
Chapter 7 DEVELOPMENT AND SEX DETERMINATION Chapter Summary The male and female reproductive systems produce the sperm and eggs, and promote their meeting and fusion, which results in a fertilized egg.
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia.
 10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia. Gonads, genital ducts and the external genital organs initially pass through an indifferent period of development, which is
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External genitalia. Gonads, genital ducts and the external genital organs initially pass through an indifferent period of development, which is
Reproductive System:
 Reproductive System: Purpose: The reproductive system combines genetic information from both parents (in most animals) to produce new life forms. This system produces sex cells (gametes), delivers them,
Reproductive System: Purpose: The reproductive system combines genetic information from both parents (in most animals) to produce new life forms. This system produces sex cells (gametes), delivers them,
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY, HPS (B) X CLASS Key:Reproductive system, Endocrine system and Population
 DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY, HPS (B) X CLASS Key:Reproductive system, Endocrine system and Population Question I. Name of the following: 1. The part of the female reproductive system in which fertilization takes
DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY, HPS (B) X CLASS Key:Reproductive system, Endocrine system and Population Question I. Name of the following: 1. The part of the female reproductive system in which fertilization takes
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
7/4/2018. Key Objectives. A and P 2401 Lecture 2 TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS. Negative Feedback Examples. Review of Homeostasis
 Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Experimental contributions to the study of the embryology of the vagina
 Human Reproduction Vol.21, No.6 pp. 1623 1628, 2006 Advance Access publication February 13, 2006. doi:10.1093/humrep/del031 Experimental contributions to the study of the embryology of the vagina M.L.Sánchez-Ferrer
Human Reproduction Vol.21, No.6 pp. 1623 1628, 2006 Advance Access publication February 13, 2006. doi:10.1093/humrep/del031 Experimental contributions to the study of the embryology of the vagina M.L.Sánchez-Ferrer
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS. Hormones
 REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Learning Outcome
 Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Topic from HAPS Guidelines General functions of the endocrine system Chemical classification of hormones & mechanism of hormone actions at receptors. Control of hormone secretion
Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Topic from HAPS Guidelines General functions of the endocrine system Chemical classification of hormones & mechanism of hormone actions at receptors. Control of hormone secretion
HORMONAL SEX REVERSAL IN A FEMALE
 HORMONAL SEX REVERSAL IN A FEMALE BY W. J. MATHESON and E. M. WARD From the Children's Hospital and Pathological Department, Leicester Royal Infirmary (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION SEPTEMBER 15, 1953) The
HORMONAL SEX REVERSAL IN A FEMALE BY W. J. MATHESON and E. M. WARD From the Children's Hospital and Pathological Department, Leicester Royal Infirmary (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION SEPTEMBER 15, 1953) The
different ratios of PMSG and HCG on the occurrence of follicular haemorrhage THE induction of ovulation with PMSG and HCG in the rat has been studied
 Q. Jl exp. Physiol. (1968) 53, 129-135 THE INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN IMMATURE RATS TREATED WITH PREGNANT MARE'S SERUM GONADOTROPHIN AND HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPHIN. By S. F. LUNN and E. T. BELL. From
Q. Jl exp. Physiol. (1968) 53, 129-135 THE INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN IMMATURE RATS TREATED WITH PREGNANT MARE'S SERUM GONADOTROPHIN AND HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPHIN. By S. F. LUNN and E. T. BELL. From
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE
 Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE Prof. Alberto Contri REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE SPERMATOGENESIS AND REPRODUCTIVE BEHAVIOR RELATED TO THE ACTIVITY
Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE Prof. Alberto Contri REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE SPERMATOGENESIS AND REPRODUCTIVE BEHAVIOR RELATED TO THE ACTIVITY
AP Biology Ch ANIMAL REPRODUCTION. Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below.
 AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
LIFE SCIENCES Grade 12 REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014
 REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014 Checklist Make sure you Can describe different reproductive strategies of vertebrates Are able to identify the structure and function of the male and female reproductive organs
REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014 Checklist Make sure you Can describe different reproductive strategies of vertebrates Are able to identify the structure and function of the male and female reproductive organs
Diagram Of A Rabbit Reproductive System
 Diagram Of A Rabbit Free PDF ebook Download: Diagram Of A Rabbit Download or Read Online ebook diagram of a rabbit reproductive system in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Name the accessory
Diagram Of A Rabbit Free PDF ebook Download: Diagram Of A Rabbit Download or Read Online ebook diagram of a rabbit reproductive system in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Name the accessory
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Introduction A. Preparing the Fetal Pig Anterior Posterior Dorsal Ventral length gender mammary papillae
 Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Animal Reproduction Chapter 46. Fission. Budding. Parthenogenesis. Fragmentation 11/27/2017
 Animal Reproduction Chapter 46 Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Sexual reproduction is the creation of an offspring by fusion of a male gamete (sperm) and female gamete
Animal Reproduction Chapter 46 Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Sexual reproduction is the creation of an offspring by fusion of a male gamete (sperm) and female gamete
Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Special Parts: Gender. Why Have Sex?
 Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
hoofdstuk :07 Pagina ix Introduction
 hoofdstuk 00 08-03-2001 15:07 Pagina ix Introduction Incontinence at pediatric age is a problem that can harm the psychological and physical development of children. Starting in 1986 we have searched for
hoofdstuk 00 08-03-2001 15:07 Pagina ix Introduction Incontinence at pediatric age is a problem that can harm the psychological and physical development of children. Starting in 1986 we have searched for
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System
 Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Urogenital System. PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. 钱晓菁 XIAO-JING QIAN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College
 Urogenital System 钱晓菁 XIAO-JING QIAN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College intermediate mesoderm urogenital ridge mesonephric ridge genital ridge I. Urinary System 1. kidney
Urogenital System 钱晓菁 XIAO-JING QIAN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College intermediate mesoderm urogenital ridge mesonephric ridge genital ridge I. Urinary System 1. kidney
Carolina Biological Supply Company. Rats! Inquiry-Based Dissection with Carolina s Perfect Solution Specimens
 Carolina Biological Supply Company Rats! Inquiry-Based Dissection with Carolina s Perfect Solution Specimens Objectives Introduce basic mammalian anatomy using the rat Perform a rat dissection focusing
Carolina Biological Supply Company Rats! Inquiry-Based Dissection with Carolina s Perfect Solution Specimens Objectives Introduce basic mammalian anatomy using the rat Perform a rat dissection focusing
Topic 13 Sex. Being Male and Female
 Topic 13 Sex Being Male and Female Reproduction Asexual (1 individual): more efficient, low genetic variation Sexual: prevalent (2 sexes, separate or not) High genetic variation, need 2 Approaches: External
Topic 13 Sex Being Male and Female Reproduction Asexual (1 individual): more efficient, low genetic variation Sexual: prevalent (2 sexes, separate or not) High genetic variation, need 2 Approaches: External
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
The functional anatomy of the urinary system. Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic
 The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
Sexual Development. 6 Stages of Development
 6 Sexual Development 6 Stages of Development Development passes through distinct stages, the first of which is fertilization, when one sperm enters one ovum. To enter an ovum, a sperm must undergo the
6 Sexual Development 6 Stages of Development Development passes through distinct stages, the first of which is fertilization, when one sperm enters one ovum. To enter an ovum, a sperm must undergo the
