The Frenular Delta A New Preputial Structure
|
|
|
- Andrew McDaniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 From: Understanding Circumcision: A Multi-Disciplinary Approach to a Multi-Dimensional Problem Denniston GC, Hodges FM, Milos MF eds. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, Chapter 11 The Frenular Delta A New Preputial Structure Ken McGrath Senior Lecturer in Pathology, Faculty of Health Studies, Auckland University of Technology Abstract: Textbooks and papers referring to penile function state that the source of penile sensation is solely the glans and often justify the existence of the prepuce by stating it protects the 'sensitive' glans. These statements are contrary to the neuro-anatomical and physiological facts accumulated over more than a century. This study reviews the findings of Taylor, et al., that the prepuce is the primary sensory platform of the penis, and describes a new preputial structure. INTRODUCTION Looking back, it is astounding that the complex nature of the prepuce (or the fact that it is not a simple fold of skin) was not described until and that this did not appear in the mainstream medical media until When Dr. John Taylor faced family enquiries, he asked himself: 'What exactly is removed by circumcision?' A total absence of an answer to that question from the medical literature was the motivation for his investigation. The reason why this had never been asked, during a century of extensive study of the male genitalia and increasing application of circumcision, remains a mystery. No special techniques, or dissections, or equipment were initially required just an observant eye and scientific curiosity. 1. REVIEW OF PREPUTIAL ANATOMY When Taylor and his colleagues examined 22 prepuces in males aged 22 to 58 years, 2 they discovered that the classical description, which simply divided the prepuce into outer and inner (or mucosal) areas, 3 was incomplete. The outer area is a continuation of the shaft skin, up to the rim of junction with the mucosa at the opening of the prepuce at rest, with all its characteristics of form and mild sensitivity. On the other hand, the mucosa, that inner preputial skin from the junctional or transitional zone to the sulcus where it continues as the mucosal covering of the glans, he found to be more sophisticated than had been previously described. Just inside the junctional rim of the prepuce at the dorsal aspect is a transverse band of ridges mm wide. Beyond this ridged band, the remainder of the mucosa is smooth (15-30 mm wide dorsally) the smooth zone. The ridged band is continuous with the frenulum, being a radial band over about 60% of the penile diameter the dorsal and lateral aspects then turning distally to form a 'V shape in the ventral aspect whilst smoothly reducing its width to merge with the frenulum. This continuity is the reason why the ridged band is also known as the frenular band. Under microscopic examination, the entire mucosa is invested with Meissner's corpuscles (the nerve endings which mediate low-threshold and fine-touch sensation) which are heavily concentrated in the projections of the dermis that rise into the ridged band and in the frenulum. These corpuscles are innervated by thick myelinated axons of the epicritical sensory system. A recent quantitative study has shown mean axon bundle counts in the prepuce of 17.9 bundles/mm ventrally, 8.6 bundles/mm laterally and 6.2 bundles/mm dorsally.4 As each bundle contains tens of axons, the nerve supply to the prepuce is obviously very substantial.
2 Another feature of the inner prepuce not previously described prior to Taylor's reports is the extensive plexus of venules and capillaries that are collected into the large superficial veins of the outer prepuce and penile shaft skin. These superficial veins begin to divide as they approach the prepuce and have frequent anastomoses especially in the outer prepuce and distal shaft skin. The anastomoses in the prepuce have sometimes been termed 'radial veins' because, in some individuals, they are circumferential. From the junctional rim, the many smaller veins divide frequently as they run towards the sulcus to form a dense plexus of venules and capillaries. This vascularity was noted by Taylor as being pronounced in the ridged band and often seen as a bright flush. 2 In most genitally intact males, some core branches of the superficial veins do not divide further on crossing the inner prepuce. These medium- sized veins continue unchanged to run under the corona to form at least part of the drainage of the glans surface. This is contrary to a report by Breza, et al., that describes the superficial veins as draining the shaft skin and prepuce only. 5 This otherwise excellent and extensive paper is flawed by not reporting the state (intact or circumcised) of the cadaver penises examined. It is reasonable to suppose that, in California, all, or the majority, were circumcised and thus could not present the normal anatomy of the superficial veins. Clearly, the volume of blood gathered by these veins, and their consequent prominence, if greater than could be involved solely in drainage of this skin. Furthermore, the superficial veins become more prominent with erection, suggesting that they may be carrying extra blood from the glans portion of the corpus spongiosum. It may be postulated that (1) as circumcision interrupts this venous circuit and (2) as superficial veins are not restored in the great majority of preputial remnants, the change in the color of the glans from a venous purple in genitally intact males to the pink tint of the penile shaft in circumcised males is due to a dramatic change in circumcised males due to a dramatic change in the circulation in the circumcised penis. The other major feature of the prepuce noted by Taylor, which it shares with the shaft skin, is a layer of smooth muscle bundles..2 This peripenic muscle has been known since at least 1907 and is the continuation of the dartos muscle of the scrotal skin. 6 In the shaft skin, these muscle bundles are oriented in mixed direction but they become specifically oriented in the prepuce to add to its complexity. In the outer prepuce, the bundles are aligned longitudinally to mediate the length of that portion of skin. At the tip of the prepuce (i.e., in the junctional zone), the muscle bundles are radially oriented to form a kind of sphincter which tends to close the orifice when the penis is flaccid. 6 Together with abundant elastic fibers, this muscle layer give the prepuce a very snug fit over the glans. In the absence of construction of the preputial orifice (a preputial stenosis or true pathological as opposed to physiological phimosis, which can cause back-flow of the urinary stream), all extraneous matter (including urine, sand, etc.) Is prevented from gaining access to the preputial space. Finally, a comment on what is probably the longest enduring myth in anatomy. To the present day, textbooks still asset the presence of glands in the mucosa of the sulcus, especially on both sides of the frenulum, despite the existence of these so-called Tyson s glands being rejected by many European investigators as far back as The problem has arisen because of the finding of Tyson s paper of 1699 on the orangutan was interpreted as applying to humans, which it does not. 9 No actual description of them in humans exists and a number of modern investigations have failed to find any glands in the inner prepuce or sulcus My colleague, Christopher Cold, and I have also failed to find any glands in ths region. The 1904 comment of Keith and Shillitoe best sums up this myth: It shows the strength of the faith of anatomists that they have for nearly two centuries described glands which have not, and never had, an existence. 8 It remains to observe that smegma is epithelial debris shed from the mucosa suspended in a proteinaceous fluid; 12,14 Taylor and I believe this fluid to be a transudate extracellular fluid that leaks out from betwen cells that have no tight junctions THE FRENULAR DELTA
3 Some months ago, whilst rereading the report of Taylor, et al., I realized that their description and illustrations of the inner prepuce and ridged band were confined to the dorsal aspect. 2 The frenular attachment of the ridged band was described, but there was no other mention or an illustration of the ventral aspect. The ridged band is not circumferential over the ventral aspect, since it curves distally to merge with the frenulum, as noted above. This means that the smooth zone is progressively reduced as the median raphe is approached until it disappears at the mid-line. As the smooth zone is reduced, a corresponding zone of the inner prepuce appears proximally between the ridged band and the circumferential junctional rim. Because the length of the inner prepuce actually increases as the median raphe is approached due to the curving of the corona towards the meatus to form the ventral cleft in the glans, the mucosal area of the prepuce is also greater in the ventral aspect. Thus, in the ventral prepuce, there is an undescribed zone that occupied about 20-40% of the mucosa. I propose the name frenular delta for this zone, because of its shape and its association with the frenulum. It may be described as that preputial mucosa of triangular shape proximal to the ridged band in the ventral aspect, having the frenulum at its point, its sides defined by the ridged band and as Figure 1. Ventral and lateral views of the human penis showing the frenular delta (outlined in grey tone) and frenular veins, together with other landmarks. its base the junctional rim (Figure 1). It presents as the greater area of the mucosa ventrally and does not include the ridged band which is a zone in its own right. The median raphe runs longitudinally through its mid-line to become the frenulum and bisects the delta into two equal halves. In males with a short prepuce, the ridged band lies immediately inside the junctional rim at rest and against the glans in a variable position according to the preputial length. The frenular delta in these individuals does not extend beyond the lateral aspects. On the other hand, males with a long prepuce forming an akroposthion (the tubular and tapered part of the prepuce that extends beyond the glans penis) have their ridged band lying over the glans tip at rest. In this situation, the frenular delta base extends beyond the lateral aspects in a ribbon-like band as the extra dorsal strip of mucosa between the junctional rim and the ridged band. The frenular delta is noted by men as the most sensitive area of their penis, especially in the mid-line nearest the frenulum, and the frenulum itself. Two of the medium veins fo passage described above are of relevance here: regardless of the pattern and numbers of superficial veins, two medium-sized branches curve from each side of the outer prepuce to course through the frenular delta ever closer to the median raphe, eventually to lie on either side of the frenulum before disappearing into its depths. In this way, they appear eventually to flank the frenular
4 artery to form a triplet analogous to the two dorsal arteries and deep dorsal vein of the penile shaft. For these two veins, I propose the name frenular veins. After careful observation of a large number of intact penises, I have not found any that lack these veins and would also observe that they are almost never seen in circumcised penises. There is no observable division of these veins into smaller venules before they disappear into the sides of the frenulum, so we may assume that they drain the area of the glans supplied by the frenular artery (i.e., the immediate surroundings of the cleft and meatus). 3. DISCUSSION Our knowledge of penile anatomy is far from complete. Some of the early findings on gross anatomy, such as the peripenic muscle mentioned in the review, are in need of rehabilitation, as they do not appear in modem literature. Another example is the presence of hair on the underside of the penis a source of concern for some men; this is explained by the area scroti of Klatsch, which does not seem to have been reported since This ventral extension of hair-bearing skin from the scrotum (with most of its characteristics) is a triangular region with its base at the penile-scrotal junction, having its point of disappearance at a variable distance up the shaft (but not beyond the beginning of the outer prepuce), and is equally distributed on either side of the median raphe. Even the recent 'detailed anatomy' study of neurovascular structures leaves questions unanswered: 5 the patterns of arterial supply and innervation of the prepuce remain unknown. The nerve supply to the prepuce has been reported as coming from the dorsal nerves (to the dorsal and lateral aspects) and from the perineal nerve (to the ventral aspect and frenulum) with some overlap in the lateral aspect. 16 This recent report explains the frequent failure to provide total skin anesthesia by the dorsal nerve block that is widely recommended for and used in circumcision. 17 How these nerves reach the prepuce from their deeper sites remains unanswered and leaves us with a physiological conundrum: because the whole skin of the penis is uniquely mobile, any direct branches of nerves to the surface would be broken by this extensive longitudinal and radial movement. Nerve bundles must, therefore, enter from either end of the tubular skin, as do the superficial blood vessels. Ironically, circumcision provides an important clue, since nerves running down the skin to the prepuce from the proximal end at the penile base would be severed by that excision of a large circumferential segment of skin, leaving the preputial stump and frenulum denervated. As circumcised men often describe the preputial and frenular remnants as highly sensitive, it seems apparent that innervation of the prepuce must be retrograde, i.e., entering the skin from the distal end and progressing back towards the base. Moreover, nerves regenerating after surgery seldom, if ever, cross the scar, as it is an impenetrable barrier to the delicate growth cones sprouting from the proximal nerve stump which often form neuromata at the scar boundary. Neuromata have been seen recently by Cold in microscope sections of circumcision scars. 18 Given the ventral nerve bundle counts and the universal accounts of its sensitivity, which it shares with the frenulum, the frenular delta must have impressive sensory resources. Tracing of preputial nerve pathways and quantitative studies of nerve endings should provide evidence to confirm these observations. The neurological differences from the female equivalents also need to be more thoroughly investigated. 19 That the so-called 'G-spot' of males could have been ignored by neuro-anatomical studies to the present day is extraordinary. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The author is grateful to Martin Novoa and Christopher Price for helpful discussions and suggestions. REFERENCES
5 1. Taylor J. The prepuce: what, exactly, is removed by circumcision a preliminary report. Second International Symposium on Circumcision. 30 April-3 May 1991, San Francisco, California. 2. Taylor JR, Lockwood AP, Taylor AJ. The prepuce: specialized mucosa of the penis and its loss to circumcision. Br J Urol 1996:77: Williams PL, Warwick R, Dyson M, Bannister L, editors. Gray's Anatomy. 37th edition. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1989; p Moldwin RM, Valderrama E. Immunohistochemical analysis of nerve distribution patterns within preputial tissue. J Urol 1989; 141:499A. 5. Breza J, Aboseif SR, Orvis BR, Lue TF, Tanagho EA. Detailed anatomy of penile neurovascular structures: surgical significance. J Urol 1989;141: Jefferson G. The peripenic muscle; some observations on the anatomy of phimosis. Surg Gynecol Obstet (Chicago) 1916;23: Lakshmanan S, Prakash S. Human prepuce some aspects of structure and function. Indian J Surg 1980:42: Keith A, Shillitoe A. The preputial or odoriferous glands of man. Lancet 1904;1(4194): [16 January 1904]. 9. Tyson E. Orang-Outang, Sive Homo Sylvestris: Or, The Anatomy of a Pygmie Compared with that of a Monkey, an Ape, and a Man. To which is added, A Philological Essay Concerning the Pygmies, the Cynocephali, the Satyrs, and Sphinges of the Ancients. London: s.n; Cited in: Saalfeld E. Uber die Tyson'schen driisen. Arch MikrAnat 1899:53: Dickinson RL. Human Sex Anatomy: A Topographical Hand Atlas. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1949: Hyman AB, Brownstein MH. Tyson's "Glands." Ectopic sebaceous glands and papillomatosis penis. Arch Dermatol 1969:99: Parkash S, Jeyakumar S, Subramanyan K, Chaudhuri S. Human subpreputial collection: its nature and formation. J Urol 1973:110: Barreto J, Caballero C, Cubilla A. Penis. In: Stemberg S, editor. Histology for Pathologists. New York: Raven Press; p Prakash [sic, Parkash] S, Rao R, Venkatesan K, Ramakrishnan S. Sub-preputial wetness: it [sic] nature. Ann Nati Med Sci (India) 1982;18: Taylor JR. Personal communication. 16. Yang CC, Bradley WE. Innervation of the human glans penis. J Urol 1999;161: Van Howe RS. Anaesthesia for circumcision: a review of the literature. In: Denniston GC, Hodges FM, Milos MF, editors. Male and Female Circumcision: Medical, Legal, and Ethical Considerations in Pediatric Practice. New York: Kluwer/Plenum pp Cold CJ. Personal communication. (Confirmed by me during a visit to his laboratory in 1998.) 19. Cold CJ, McGrath KA. Anatomy and histology of the penile and clitoral prepuce in primates: evolutionary perspective of specialised sensory tissue of the external genitalia. In: Denniston GC, Hodges FM, Milos MF, editors. Male and Female Circumcision: Medical, Legal, and Ethical Considerations in Pediatric Practice. New York: Kluwer/Plenum, 1999; pp
NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE PENIS
 NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE PENIS IOANNIS VARKARAKIS ASOSCIATE PROFESSOR OF UROLOGY 2 ND DEPT OF UROLOGY NATIONAL & KAPODISTRIAN UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS PENILE GROSS ANATOMY 3 ERECTILE COLUMNS TWO CORPORA CAVERNOSA
NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE PENIS IOANNIS VARKARAKIS ASOSCIATE PROFESSOR OF UROLOGY 2 ND DEPT OF UROLOGY NATIONAL & KAPODISTRIAN UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS PENILE GROSS ANATOMY 3 ERECTILE COLUMNS TWO CORPORA CAVERNOSA
Male circumcision decreases
 Male circumcision decreases penile sensitivity Justine Schober MD University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot Hospital, Erie PA Rockefeller University, New York, NY Anatomy is not destiny but a little
Male circumcision decreases penile sensitivity Justine Schober MD University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot Hospital, Erie PA Rockefeller University, New York, NY Anatomy is not destiny but a little
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE INTACT PENIS
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE INTACT PENIS Contains diagrams and photographs of penile anatomy for educational purposes only. THE INTACT PENIS: NOT JUST A FLAP OF SKIN The foreskin is not a flap of skin,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE INTACT PENIS Contains diagrams and photographs of penile anatomy for educational purposes only. THE INTACT PENIS: NOT JUST A FLAP OF SKIN The foreskin is not a flap of skin,
Sexual Anatomy. Monday, 30 March 2009
 Sexual Anatomy 1 2 3 Fallopian Tube Ovary Uterus Bladder Cervix Pubic bone Clitoris Urethra Rectum Vagina Anus G Spot 4 Variety of Vulvae 5 Bladder Corpus Cavernosum Rectum Seminal Vesicle Prostate Glans
Sexual Anatomy 1 2 3 Fallopian Tube Ovary Uterus Bladder Cervix Pubic bone Clitoris Urethra Rectum Vagina Anus G Spot 4 Variety of Vulvae 5 Bladder Corpus Cavernosum Rectum Seminal Vesicle Prostate Glans
Anatomy of the Body for Piercers
 Nipples are devoid of Raised structures on the areolae are Montgomery glands or tubercles, or areolar glands Normal variation Provide lubrication during breastfeeding Best to avoid piercing them Hair follicles
Nipples are devoid of Raised structures on the areolae are Montgomery glands or tubercles, or areolar glands Normal variation Provide lubrication during breastfeeding Best to avoid piercing them Hair follicles
Friday, 11 January 13. Sexual Anatomy
 Friday, 11 January 13 Sexual Anatomy Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Fallopian Tube Ovary Uterus Bladder Cervix Pubic bone Clitoris Urethra Rectum
Friday, 11 January 13 Sexual Anatomy Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Fallopian Tube Ovary Uterus Bladder Cervix Pubic bone Clitoris Urethra Rectum
The Female and Male External Genitalia. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Female and Male External Genitalia Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Anatomy of the female external genitalia This consists of : The vulva which is made up of: o The clitoris o Vestibular apparatus
The Female and Male External Genitalia Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Anatomy of the female external genitalia This consists of : The vulva which is made up of: o The clitoris o Vestibular apparatus
INTRODUCTION. There are three main approaches to studying anatomy: 1. Systemic anatomy 2. Regional anatomy (topographic) 3.
 INTRODUCTION Anatomy is the science of the structure and function of the body. It is the study of internal and external structures, and the physical relationships between the various body parts. INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION Anatomy is the science of the structure and function of the body. It is the study of internal and external structures, and the physical relationships between the various body parts. INTRODUCTION
General Human Histology. The Urinary System
 General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
THE USE OF DEEPITHELIALIZATION
 THE USE OF DEEPITHELIALIZATION IN URETHROPLASTY - Deepithelialization Stratum corneum - Epidermis Papillary dermis Reticular dermis Skin Healing in any reconstructive surgery depends on not only the intact
THE USE OF DEEPITHELIALIZATION IN URETHROPLASTY - Deepithelialization Stratum corneum - Epidermis Papillary dermis Reticular dermis Skin Healing in any reconstructive surgery depends on not only the intact
How to ensure clitoral bud survival in a sexual reassignment surgery for transsexualism
 How We Do It J Cosmet Med 2018;2(1):57-62 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2018.2.1.57 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 How to ensure clitoral bud survival in a sexual reassignment surgery for transsexualism
How We Do It J Cosmet Med 2018;2(1):57-62 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2018.2.1.57 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 How to ensure clitoral bud survival in a sexual reassignment surgery for transsexualism
******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
Repair of Bulbar Urethra Using the Barbagli Technique
 22 Repair of Bulbar Urethra Using the Barbagli Technique G. Barbagli, M. Lazzeri 22.1 Introduction and Historical Background 182 22.2 Anatomical Remarks 182 22.3 Step-by-Step Surgical Details 183 22.3.1
22 Repair of Bulbar Urethra Using the Barbagli Technique G. Barbagli, M. Lazzeri 22.1 Introduction and Historical Background 182 22.2 Anatomical Remarks 182 22.3 Step-by-Step Surgical Details 183 22.3.1
The bell is gently and slowly removed (the foreskin may naturally form an adhesion to
 Circumcision Definition: The removal of the foreskin anatomy of the penis; to cut off the clitoris and sometimes the labia of a female. This document only covers male circumcision. Male Anatomy: The foreskin,
Circumcision Definition: The removal of the foreskin anatomy of the penis; to cut off the clitoris and sometimes the labia of a female. This document only covers male circumcision. Male Anatomy: The foreskin,
The fibrous flexor sheaths of the fingers
 J. Anat. (1988), 156, pp. 185-196 185 With 9 figures Printed in Great Britain The fibrous flexor sheaths of the fingers MARILYN M. JONES AND A. A. AMIS* Division of Anatomy, United Medical and Dental Schools,
J. Anat. (1988), 156, pp. 185-196 185 With 9 figures Printed in Great Britain The fibrous flexor sheaths of the fingers MARILYN M. JONES AND A. A. AMIS* Division of Anatomy, United Medical and Dental Schools,
prepuce, hygienic practice, senior school boy, circumcision
 1 2 prepuce, hygienic practice, senior school boy, circumcision 90 3 1 11 30 890 433 (77.8%) (26.9%) (21.8 ) 6 3.41 1.70 7.6 36.1 13.2 56.8 38.3 60.3 (p 0.05) (p 0.05) one-way ANOVA 4 6 ( 2001; 11: 153-63)
1 2 prepuce, hygienic practice, senior school boy, circumcision 90 3 1 11 30 890 433 (77.8%) (26.9%) (21.8 ) 6 3.41 1.70 7.6 36.1 13.2 56.8 38.3 60.3 (p 0.05) (p 0.05) one-way ANOVA 4 6 ( 2001; 11: 153-63)
THE sebaceous glands of the rabbit consist of clusters of about ten cells
 79 On the Relationship between Mammary, Sweat, and Sebaceous Glands By D. B. CARLISLE (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford, and the Plymouth Laboratory of the Marine Biological
79 On the Relationship between Mammary, Sweat, and Sebaceous Glands By D. B. CARLISLE (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford, and the Plymouth Laboratory of the Marine Biological
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system. Lab activity 1: esophagus stomach - small intestines
 Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Urinary system. Urinary system
 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Our Experience in Chordee without Hypospadias: Results
 PEDIATRIC UROLOGY Our Experience in Chordee without Hypospadias: Results of 102 Cases Emre Can Polat, 1 Mehmet Remzi Erdem, 2 Ramazan Topaktas, 3 Cevper Ersoz, 4 Sinasi Yavuz Onol 5 1 Department of Urology,
PEDIATRIC UROLOGY Our Experience in Chordee without Hypospadias: Results of 102 Cases Emre Can Polat, 1 Mehmet Remzi Erdem, 2 Ramazan Topaktas, 3 Cevper Ersoz, 4 Sinasi Yavuz Onol 5 1 Department of Urology,
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE
 ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Perineum It is the diamond-shaped lower end of the trunk
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Perineum It is the diamond-shaped lower end of the trunk
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
A CASE OF DUPLICATION OF PENILE URETHRA. Stoke Mandeville
 A CASE OF DUPLICATION OF PENILE URETHRA By J. P. REIDY, F.R.C.S. Stoke Mandeville THIS congenital deformity is of rare occurrence. Gross and Moore (195o) summarised the findings of eighty-three cases.
A CASE OF DUPLICATION OF PENILE URETHRA By J. P. REIDY, F.R.C.S. Stoke Mandeville THIS congenital deformity is of rare occurrence. Gross and Moore (195o) summarised the findings of eighty-three cases.
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
7/10/18. Introduction. Integumentary System. Physiology. Anatomy. Structure of the Skin. Epidermis
 Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Urinary Anatomy. Lab 40. Kidneys. Nephrons. Renal Corpuscle
 Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Histology of the Eye
 Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Anatomy of the Heart
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
CUT-UP PROTOCOL Foreskin SCC, Glansectomy, and Penectomy BASIC ANATOMY
 BASIC ANATOMY Orientating the specimen is essential. The urethra runs within the corpus spongiosum which expands to form the glans. The frenulum of the foreskin is on the ventral aspect. DORSAL Proximal
BASIC ANATOMY Orientating the specimen is essential. The urethra runs within the corpus spongiosum which expands to form the glans. The frenulum of the foreskin is on the ventral aspect. DORSAL Proximal
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Biomechanics. and Functional Anatomy. of Human Male Genitalia. For designers and creators of biomimetic androids, dolls and robots
 Biomechanics and Functional Anatomy of Human Male Genitalia For designers and creators of biomimetic androids, dolls and robots The Penis The shaft or body of the penis is formed principally by a fused
Biomechanics and Functional Anatomy of Human Male Genitalia For designers and creators of biomimetic androids, dolls and robots The Penis The shaft or body of the penis is formed principally by a fused
Male Reproductive System. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD
 Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta.
 Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
Fundamentals and Principles of Tissue Transfer
 4 Fundamentals and Principles of Tissue Transfer G.H. Jordan, K. Rourke 4.1 Tissue Composition and Physical Characteristics 20 4.1.1 Tissue Composition 20 4.1.2 Vascularity 21 4.1.3 Tissue Characteristics
4 Fundamentals and Principles of Tissue Transfer G.H. Jordan, K. Rourke 4.1 Tissue Composition and Physical Characteristics 20 4.1.1 Tissue Composition 20 4.1.2 Vascularity 21 4.1.3 Tissue Characteristics
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
Clitorolabial Reconstruction in Circumcised Females with Clitoral Inclusion Cyst
 JKAU: Med. Sci., Vol. 16 No. 4, pp: 61-73 (2009 A.D. / 1430 A.H.) DOI: 10.4197/Med. 16-4.5 Clitorolabial Reconstruction in Circumcised Females with Clitoral Inclusion Cyst Yasir S. Jamal, FRCS(I), FICS
JKAU: Med. Sci., Vol. 16 No. 4, pp: 61-73 (2009 A.D. / 1430 A.H.) DOI: 10.4197/Med. 16-4.5 Clitorolabial Reconstruction in Circumcised Females with Clitoral Inclusion Cyst Yasir S. Jamal, FRCS(I), FICS
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49689 1 Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels * Donna Browne Based on Structure and Function of Blood Vessels by OpenStax This work is produced by
OpenStax-CNX module: m49689 1 Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels * Donna Browne Based on Structure and Function of Blood Vessels by OpenStax This work is produced by
A DE-EPITHELIALISED OVERLAP FLAP TECHNIQUE IN THE REPAIR OF HYPOSPADIAS
 British ffournal of Plastie Surgery (I973), 26, :ro6-xi 4 A DE-EPITHELIALISED OVERLAP FLAP TECHNIQUE IN THE REPAIR OF HYPOSPADIAS ]3y DURHAM SMITH, M.D., F.R.A.C.S., F.A.C.S. Royal Ghildren's tlospital,
British ffournal of Plastie Surgery (I973), 26, :ro6-xi 4 A DE-EPITHELIALISED OVERLAP FLAP TECHNIQUE IN THE REPAIR OF HYPOSPADIAS ]3y DURHAM SMITH, M.D., F.R.A.C.S., F.A.C.S. Royal Ghildren's tlospital,
COMPLEX RECONSTRUCTIONS IN HYPOSPADIAS: - - P
 COMPLEX RECONSTRUCTIONS IN HYPOSPADIAS: - Penile straightening - Penile lengthening - Glans and penile skin resurfacing Rados P. Djinovic, Belgrade Growing number of adult patients Majority had multiple
COMPLEX RECONSTRUCTIONS IN HYPOSPADIAS: - Penile straightening - Penile lengthening - Glans and penile skin resurfacing Rados P. Djinovic, Belgrade Growing number of adult patients Majority had multiple
Microneurovascular reimplantation in a case of total penile amputation
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Case Report Microneurovascular reimplantation in a case of total penile amputation Yogesh C. Bhatt, Kinnari A. Vyas, Rajat K. Srivastava, Nikhil S. Panse Department of Plastic
Free full text on www.ijps.org Case Report Microneurovascular reimplantation in a case of total penile amputation Yogesh C. Bhatt, Kinnari A. Vyas, Rajat K. Srivastava, Nikhil S. Panse Department of Plastic
Chapter 5. Integumentary System 5-1
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
A standardized classification of hypospadias
 Journal of Pediatric Urology (2012) 8, 410e414 A standardized classification of hypospadias Marek Orkiszewski* Gizinscy Medical Center, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Bydgoszcz, Poland Received 28 September
Journal of Pediatric Urology (2012) 8, 410e414 A standardized classification of hypospadias Marek Orkiszewski* Gizinscy Medical Center, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Bydgoszcz, Poland Received 28 September
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
20 2 Stomach Fig. 2.1 An illustration showing different patterns of the myenteric plexus peculiar to the regions in the guinea-pig stomach stained wit
 Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Anatomy & Physiology. An Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
cally, a distinct superior crease of the forehead marks this spot. The hairline and
 4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Leo Happel, PhD Professor, Neurology, Neurosurgery, Physiology, and Neuroscience LSU Health Science Center
 Leo Happel, PhD Professor, Neurology, Neurosurgery, Physiology, and Neuroscience LSU Health Science Center Leo Happel disclosed no financial relationships Vascular Lesions of the Spinal Cord The vast majority
Leo Happel, PhD Professor, Neurology, Neurosurgery, Physiology, and Neuroscience LSU Health Science Center Leo Happel disclosed no financial relationships Vascular Lesions of the Spinal Cord The vast majority
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile
 Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile and position sensations (2) Thermoreceptive senses:
Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile and position sensations (2) Thermoreceptive senses:
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
An x-ray microscopic study of the vasa vasorum
 Thorax (1964), 19, 561. An x-ray microscopic study of the vasa vasorum of normal human pulmonary arteries JOHN A. CLARKE From the Department of Anatomy, University of Glasgow The first description of the
Thorax (1964), 19, 561. An x-ray microscopic study of the vasa vasorum of normal human pulmonary arteries JOHN A. CLARKE From the Department of Anatomy, University of Glasgow The first description of the
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION?
 WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION? Jay Smith, M.D. CMO, Sonex Health LLC June 2017 Modern day ultrasound (US) machines provide a powerful combination of submillimeter resolution and dynamic
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION? Jay Smith, M.D. CMO, Sonex Health LLC June 2017 Modern day ultrasound (US) machines provide a powerful combination of submillimeter resolution and dynamic
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
TISSUES TYPES. CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH
 ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
Human Anatomy. Muscle Tissue and Organization. DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1
 Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
Penis Cleanse - I. Structure
 ! Structure Penis Cleanse - I The penis is the male sex organ, reaching its full size during puberty. In addition to its sexual function, the penis acts as a conduit for urine to leave the body. The penis
! Structure Penis Cleanse - I The penis is the male sex organ, reaching its full size during puberty. In addition to its sexual function, the penis acts as a conduit for urine to leave the body. The penis
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
Skin. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
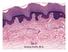 Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
Chapter 6: Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
Nervous tissue. Lab. 7
 Nervous tissue Lab. 7 Nervous tissue :- is responsible for transport nervous impulse (motor and sensory impulse), and it is formed by network more than 100 million nerve cell (neurons), nerve fiber and
Nervous tissue Lab. 7 Nervous tissue :- is responsible for transport nervous impulse (motor and sensory impulse), and it is formed by network more than 100 million nerve cell (neurons), nerve fiber and
Guido Barbagli. Center for Reconstructive ti Urethral lsurgery
 Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive ti Urethral lsurgery Arezzo - Italy E-mail: guido@rdn.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it Portuguese Andrological Association National Meeting June 21-23, 2008 Oporto
Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive ti Urethral lsurgery Arezzo - Italy E-mail: guido@rdn.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it Portuguese Andrological Association National Meeting June 21-23, 2008 Oporto
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY
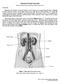 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology
 BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology Roster Business Course Introduction and Syllabus Notecard Name E-mail Why you are taking the course Something interesting you did over break Lecture Tips Use the Study
BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology Roster Business Course Introduction and Syllabus Notecard Name E-mail Why you are taking the course Something interesting you did over break Lecture Tips Use the Study
Combined Use of Mathieu and Incised Plate Technique for Repair of Distal Hypospadias
 Original Article Annals of Pediatric Surgery Vol 5, No 2, April 2009, PP 141-145 Combined Use of Mathieu and Incised Plate Technique for Repair of Distal Hypospadias Hisahm Fayad Aly Pediatric Surgery
Original Article Annals of Pediatric Surgery Vol 5, No 2, April 2009, PP 141-145 Combined Use of Mathieu and Incised Plate Technique for Repair of Distal Hypospadias Hisahm Fayad Aly Pediatric Surgery
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
Lesson Plan: Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
Introduction to Genital Anatomy
 Useful Web Sites The Inter-Circ International Circumcision Forum https://groups.yahoo.com/neo/groups/inter-circ/info The Circumcision Helpdesk Web Sites http://www.circumcisionhelpdesk.org http://www.circinfo.com
Useful Web Sites The Inter-Circ International Circumcision Forum https://groups.yahoo.com/neo/groups/inter-circ/info The Circumcision Helpdesk Web Sites http://www.circumcisionhelpdesk.org http://www.circinfo.com
