Chapter 34: Digestive Systems and Nutrition
|
|
|
- Pauline Nicholson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 34: Digestive Systems and Nutrition AP Curriculum Alignment In order to maintain homeostasis, each cell of a living organism must have the correct surface area to volume ration to move nutrients into the cell and waste products out of the cell. This concept is explained in Big Idea 2. Chapter 34 discusses how the lining of the intestines has an increased surface area for absorption of nutrients due to enfolding of the intestinal lining to form villi which are then covered with microvilli. These structures are illustrative examples and can provide students with information about maintenance of homeostasis within the limitations of cell size. Any biological system needs to obtain nutrients and Chapter 34 explains how this need is met among very simple animals that are filter feeders through the human digestive system. The complex interactions between the human stomach and intestines are fully explained in Chapter 34. These interactions are illustrative examples in Big Idea 4 of the contribution of organs interactions to the well-being of the organism. The specialization of organs and their associated functions, such as those contained in the digestive system, contributes to the overall well-being of an organism. Big Idea 4 also acknowledges as an illustrative example the contribution that bacteria make to the digestion of food for some animals, such as ruminates. Chapter 34 goes into great detail about the anatomy of ruminates and their interaction with bacteria and other microorganisms in order to obtain nutrients. ALIGNMENT OF CONTENT TO THE CURRICULUM FRAMEWORK Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce, and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. Enduring understanding (EU) 2.A: Growth, reproduction and maintenance of the organization of living systems require free energy and matter. Essential knowledge (EK) 2.A.3: Organisms must exchange matter with the environment to grow, reproduce and maintain organization. b. Surface area-to-volume ratios affect a biological system s ability to obtain necessary resources or eliminate waste products. Evidence of student learning is a demonstrated understanding of each of the following: 1. As cells increase in volume, the relative surface area decreases and demand for material resources increases; more cellular structures are necessary to adequately exchange materials and energy with the environment. These limitations restrict cell size. To foster student understanding of this concept, instructors can choose an illustrative example such as: Root hairs Cells of the alveoli Cells of the villi Microvilli 484
2 Enduring understanding (EU) 2.D: Growth and dynamic homeostasis of a biological system are influenced by changes in the system s environment. Essential knowledge (EK) 2.D.2: Homeostatic mechanisms reflect both common ancestry and divergence due to adaptation in different environments. a. Continuity of homeostatic mechanisms reflects common ancestry, while changes may occur in response to different environmental conditions. b. Organisms have various mechanisms for obtaining nutrients and eliminating wastes. To foster student understanding of this concept, instructors can choose an illustrative example such as: Gas exchange in aquatic and terrestrial plants Digestive mechanisms in animals such as food vacuoles, gastrovascular cavities, one-way digestive systems Respiratory systems of aquatic and terrestrial animals Nitrogenous waste production and elimination in aquatic and terrestrial animals Big Idea 4: Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. Enduring understanding (EU) 4.A: Interactions within biological systems lead to complex properties. Essential knowledge (EK) 4.A.4: Organisms exhibit complex properties due to interactions between their constituent parts. a. Interactions and coordination between organs provide essential biological activities. To foster student understanding of this concept, instructors can choose an illustrative example such as: Stomach and small intestines Kidney and bladder Root, stem and leaf Enduring understanding (EU) 4.B: Competition and cooperation are important aspects of biological systems. Essential knowledge (EK) 4.B.2: Cooperative interactions within organisms promote efficiency in the use of energy and matter. a. Organisms have areas or compartments that perform a subset of functions related to energy and matter, and these parts contribute to the whole. Evidence of student learning is a demonstrated understanding of each of the following: 1. At the cellular level, the plasma membrane, cytoplasm and, for eukaryotes, the organelles contribute to the overall specialization and functioning of the cell. 2. Within multicellular organisms, specialization of organs contributes to the overall functioning of the organism. To foster student understanding of this concept, instructors can choose an illustrative example such as: Exchange of gases 485
3 Circulation of fluids Digestion of food Excretion of wastes 3. Interactions among cells of a population of unicellular organisms can be similar to those of multicellular organisms, and these interactions lead to increased efficiency and utilization of energy and matter. To foster student understanding of this concept, instructors can choose an illustrative example such as: Bacterial community in the rumen of animals Bacterial community in and around deep sea vents Concepts covered in Chapter 34 also align to the learning objectives that provide a foundation for the course, an inquiry-based laboratory experience, class activities, and AP exam questions. Each learning objective (LO) merges required content with one or more of the seven science practices (SP), and one activity or lab can encompass several learning objectives. The learning objectives and science practices from the Curriculum Framework that pertain to the digestive system and nutrition are shown in the table below. Note that other learning objectives may apply as well. LO 2.6 The student is able to use calculated surface area-to-volume ratios to predict which cell(s) might eliminate wastes or procure nutrients faster by diffusion. LO 2.7 Students will be able to explain how cell size and shape affect the overall rate of nutrient intake and the rate of waste elimination. LO 2.8 The student is able to justify the selection of data regarding the types of molecules that an animal, plant or bacterium will take up as necessary building blocks and excrete as waste products. LO 2.9 The student is able to represent graphically or model quantitatively the exchange of molecules between an organism and its environment, and the subsequent use of these molecules to build new molecules that facilitate dynamic homeostasis, growth and reproduction. LO 4.18 The student is able to use representations and models to analyze how cooperative interactions within organisms promote efficiency in the use of energy and matter. Key Concepts Summary Digestive system evolution Digestion contributes to homeostasis by provided all the nutrients to sustain life A digestive system includes all of the organs, tissues, and cells involved in ingestion and breaking down food into smaller pieces for adsorption. A digestive system: o Ingests food; o Breaks food down into small molecules that can cross plasma membranes; 486
4 o Absorbs these nutrient molecules; o Eliminates indigestible remains. Sponges have no digestive system and are filter feeders with specialized cells that break down food and make nutrients available to other cells. An incomplete digestive tract has one opening for food to enter and waster to leave. A complete digestive tract contains a mount and an anus and food moves in one direction through the digestive system. Animals may be herbivores (eat only plants), carnivores (eat only other animals), or omnivores (eat plants and animals). Dentition, types and placement of teeth, of animals aids their digestion and may indicate the type of diet pursued by a particular animal. Human digestive system The human digestive tract is a complete digestive system that requires the cooperation of many other systems. The human digestive tract organs are the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. The accessory organs include the salivary glands, liver, gall bladder and pancreas. It has two major stages: mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. o Salivary glands secrete amylase which starts chemical digestion in the mouth where mechanical digestion also starts. o The muscular walls of the stomach contract vigorously and mix food with gastric juices, hydrochloric acid (HCl) and pepsin that are secreted whenever food enters the stomach. The stomach has a ph of around 2 which is low enough to kill most bacteria and microorganisms that enter the system. Marshall and Warren were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 2005 for discovering that stomach ulcers can be caused by an acidresistant bacterium, Helicobacter pylori. o When the sphincter between the stomach and the intestines relaxes, a small amount of partially digested food, chime, moves from the stomach into the intestines. The first part of the small intestines is the duodenum and receives bile from the liver and gall bladder and pancreatic digestive enzymes. Pancreatic juice contains sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), which neutralizes chyme. o Food digestion is completed in the small intestines. The surface area of the small intestines is increased by fingerlike projections called villi, and each villi has thousands of microscopic extensions called microvilli. Sugars and amino acids enter the blood. Starches are broken down into glucose molecules that are actively transported across the microvilli cell membranes into blood vessels. 487
5 Proteins are broken down into amino acids that are actively transported across the villi cell membranes into blood vessels. Fat droplets are broken down into fatty acids that diffuse scross the villi membranes into lymph vessels. o After nutrients are absorbed, they are eventually carried to all the cells of the body by the bloodstream. Undigested material then passes into the large intestines which includes the caecum (with the appendix), colon, rectum, and anus. o Water is reabsorbed in the large intestines. o Up to 400 different species of bacteria live in the large intestines and help prevent pathogenic bacteria from residing there. Key Terms bile bolus chyme complete digestive tract dentition duodenum gallbladder incomplete digestive tract lacteal liver microvilli mucosa pancreas peristalsis radula rumen ruminates salivary amylase salivary glands sphincters villi Teaching Strategies Class time: Two 45-minute class periods Day 1: Lecture on the human digestive system 25 minutes Activity 1 on digestive enzymes 20 minutes Day 2: Activity 2, investigating the effect of ph on amylase 45 minutes 488
6 Suggested Approaches The best approach to teaching the digestive system and nutrients is to focus on the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into molecules that can be utilized by the animal. The mechanical activity increases the surface area for the enzymatic activity to chemically complete the breaks down of food into molecules that can be used by the animal. Interactions between the stomach, which mechanically and chemically digest food, and the intestines which primarily conduct chemical digestion should be an area of focus. Call attention to the evolutionary trends that are present in lower invertebrates such as a two-way digestive tract and trace the development of the one-way digestive tract. Student Misconceptions and Pitfalls Students may not realize that accessory organs, such as salivary gland, the liver, the gallbladder, and the pancreas, are not part of the passage that food takes through the human body. These accessory organs produce the enzymes that are largely responsible for digestion. The actual path that food takes through the body should be a focus point so that students will completely understand the interactions between all of the digestive organs. 489
7 Suggested Activities Activity 1: Digestive Enzymes 1. Have students make draw the digestive pathway through which food passes in the human body. 2. Students should then add the accessory organs to their drawing. 3. All of the digestive enzymes that are produced and their substrates should be added to this drawing. Activity 2: Investigating the effect of ph on amylase activity Amylase solution and iodine solution are low hazard once made up. Wear eye protection when handling iodine solution. In this activity, students will measure how much time it takes for amylase, a digestive enzyme, to completely break down starch. Find complete directions and student worksheet at: 490
8 Student Edition Chapter Review Answers Answers to Assess Questions 1. d; 2. d; 3. a; 4. d; 5. a; 6. b; 7. c; 8. a; 9. a; 10. c; 11. Test tube 1: no digestion (as a control); Test tube 2: some digestion (enzyme but no acid); Test tube 3: no digestion (no enzyme); Test tube 4: digestion (both enzyme and acid are present); 12. d; 13. b; 14. c Answers to Applying the Big Ideas Questions 1. The small intestine mixes chime with digestive enzymes for final breakdown, absorbs nutrient molecules into the body, and secretes digestive hormones into the blood. a) Describe the specialized structures of the villi and microvilli of the intestine. b) Explain how cell size and shape affect the overall rate of nutrient absorption and waste elimination. Essential Knowledge Science Practice Learning Objective 2.A.3: Organisms must exchange matter with the environment to grow, reproduce and maintain organization. 6.2: The student can construct explanations of phenomena based on evidence produced through scientific practices. 2.7: Students will be able to explain how cell size and shape affect the overall rate of nutrient intake and the rate of waste elimination. 3 points maximum. Explanations for how cell size and shape affect the overall function of the intestine may include: Descriptions of villi and Explanation of related function microvilli (1 point each) The wall of the small intestine contains fingerlike projections called villi. The vessels of a villus contain blood capillaries and a lymphatic capillary, called a lacteal. (1 point each) By projecting from the intestinal wall The surface of the small intestine is increased. Essential molecules (e.g. sugars and amino acids) from digested materials enter the capillaries of a villus. Each villus has an outer layer of columnar epithelial cells, and each of these cells has thousands of microscopic extensions called microvilli. Microvilli contain intestinal enzymes. More microvilli means more enzymes that complete the process of food digestion, which means a greater rate of food digestion. 491
9 2. Organisms exhibit complex properties due to interactions between their constituent parts. Cooperation between the stomach and small intestine ensures an effective digestive process. a) Describe the mechanism by which the food from the stomach enters the small intestine. b) Predict the effect on the digestive process if something were to malfunction in the action of the pyloric sphincter which separates the stomach from the duodenum. Essential Knowledge Science Practice Learning Objective 4.A.4: Organisms exhibit complex properties due to interactions between their constituent parts. 6.4: The student can make claims and predictions about natural phenomena based on scientific theories and models. 4.9: The student is able to predict the effects of a change in a component(s) of a biological system on the functionality of an organism(s). 3 points maximum. Predicted effects of a change in a component of the digestive system may include: Description of mechanism Predicted effects of change (1 point each) (1 point each) The connection between the stomach If the sphincter is unhealthy and not and the duodenum of the small contracting when needed, food may intestine is regulated by the actions reenter the stomach from the intestines of a sphincter (pyloric sphincter can (also known as reflux or regurgitation). be retrieved from the prompt) which If the sphincter is unhealthy and not contracts and relaxes. contracting when needed, food may In the stomach, food mixes with enter the intestines before digestion is gastric juices to become chyme. The fully completed. opening and closing of the sphincter If the sphincter thickens, it can block slows the flow of chyme into the the channel, preventing the passage of small intestine, which allows for more food (chyme) from the stomach to the thorough digestion. In other words, small intestine, blocking the absorption when the sphincter is contracted, it of nutrients into the capillaries of the holds food in the stomach, allowing villi. digestion to continue to process. 492
10 Answers to Applying the Science Practices Questions Think Critically 1. Percent difference = (actual mass - label mass)/actual mass 100 cereal, bran flakes = 28%; cereal, toasted grains = 42%; cookie = 15%; mini danish = 22%; mini donut = 14% 2. All actual masses were greater than the label masses. Cereals have the highest percent difference. 493
11 Additional Questions for AP Practice 1. Describe the interactions between the human stomach and the human intestines. 2. Explain the importance of villi and microvilli to the human digestive system. 494
12 Grid-In Questions 1. The American and Canadian Dietetic Associations recommend that athletes should consume grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. What is the minimum amount of protein a 180 pound athlete should aim to consume during one week? 495
13 Answers to Additional Questions for AP Practice 1. The human stomach provides mechanical breakdown of food. The HCl and pepsin also induce chemical breakdown of the food. A sphincter separates the stomach and the intestines and will open to allow small portions of partially digested food to pass into the duodenum of the intestines for further completion of digestion. The partially digested food has been reduced to small particle that allow the digestive enzymes of the intestine ample surface area to complete the digestive process. 2. The wall of the small intestine has folds that bear fingerlike projections called villi.the surface of each villi is further folded into microvilli. The increased surface area provided by this enfolding allows for quicker digestion of food and absorption of nutrients. The products of digestion are absorbed into the blood capillaries and the lacteals of the villi by microvilli, which project from the villi. Answers to Grid-In Questions ; 180 lll 0.45 kk lll = 81.6 kk 1 g 7 dddd = 567 ggggg/wwww ddd 1 wwww 496
1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals a) Suspension feeders i) (1) Humpback whales b) Substrate feeders i)
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Ch41 Animal Nutrition
 Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body
 Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
10/18/2017 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
38.2 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion. Regents Biology
 38.2 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion Objectives Distinguish intracellular from extracellular digestion Examine how the digestive system evolves across the phyla Identify the components of the human digestive
38.2 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion Objectives Distinguish intracellular from extracellular digestion Examine how the digestive system evolves across the phyla Identify the components of the human digestive
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Harvesting energy from food. Digestion: A Closer Look. Where digestion begins. Salivary Glands 4/17/13. Or how food gets from
 Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Figure Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore
 Figure 41.1 Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore Essential Nutrients: Amino acids Fatty acids Vitamins Minerals Figure 41.2 Complete vs incomplete Omnivore vs herbivore (vegetarian) Table 41.1 Table
Figure 41.1 Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore Essential Nutrients: Amino acids Fatty acids Vitamins Minerals Figure 41.2 Complete vs incomplete Omnivore vs herbivore (vegetarian) Table 41.1 Table
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
SNC4M The Digestive System
 SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Nutrition. Why do humans need food? How do some animals get their food? ROUGHAGE NUTRIENTS. Animals make energy available using:
 Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Digestive System Notes. Biology - Mrs. Kaye
 Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST SUPPLY CHEMICAL ENERGY, ORGANIC MOLECULES, AND ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS
 1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
The Digestive System and Excretory System
 The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
Nutrition and Digestion
 Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Jargon. Chapter. Processing Food and Nutrition. Chapter 21
 One ATP Sandwich With extra phosphate Comin up Chapter Processing Food and Nutrition Chapter 21 Processing Food and Nutrition Objectives: 1. Understand the concepts of 2. Identify the anatomical parts
One ATP Sandwich With extra phosphate Comin up Chapter Processing Food and Nutrition Chapter 21 Processing Food and Nutrition Objectives: 1. Understand the concepts of 2. Identify the anatomical parts
Sphincters heartburn diaphragm The Stomach gastric glands pepsin, chyme The Small Intestine 1-Digestion Is Completed in the Small Intestine duodenum
 Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Monday, October Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page.
 1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
Chapter 3 Reading Guide Be sure to use the many figures and tables provided by the book to help answer these questions.
 Chapter 3 Reading Guide Be sure to use the many figures and tables provided by the book to help answer these questions. 1. What is digestion? What is the difference between mechanical and enzymatic digestion?
Chapter 3 Reading Guide Be sure to use the many figures and tables provided by the book to help answer these questions. 1. What is digestion? What is the difference between mechanical and enzymatic digestion?
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Primary Function. 1. Ingestion: food enters the system
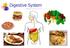 Digestive System Primary Function 1. Ingestion: food enters the system - Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins 2. Digestion: Further breakdown - Chemical/enzymatic 3. Absorption: Nutrients enter circulatory
Digestive System Primary Function 1. Ingestion: food enters the system - Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins 2. Digestion: Further breakdown - Chemical/enzymatic 3. Absorption: Nutrients enter circulatory
Animal Nutrition. Chapter 41. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to:
 Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Mouth. Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion. breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces.
 Digestive System Mouth Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion - Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces. - Chemical digestion
Digestive System Mouth Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion - Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces. - Chemical digestion
POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! )
 POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! ) Life is organized in the following levels: Chemical Level, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ Level, Organ System Level, and finally,
POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! ) Life is organized in the following levels: Chemical Level, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ Level, Organ System Level, and finally,
Digestive System Practice Test
 Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
4/8/16. Digestive System. When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy
 When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy Section 1 Digestive System A group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used
When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy Section 1 Digestive System A group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Different diets; different lives All animals eat other organisms. Mouth
 Digestive and Excretory System TOC #4 Digestive System *3) Digestive System: Mouth, Saliva, Esophagus, Peristalsis, Chyme, Stomach, Small Intestine, Pancreas, Liver, Villi, Large Intestine, Excretory System:
Digestive and Excretory System TOC #4 Digestive System *3) Digestive System: Mouth, Saliva, Esophagus, Peristalsis, Chyme, Stomach, Small Intestine, Pancreas, Liver, Villi, Large Intestine, Excretory System:
(*) (*) Ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination. Uptake of nutrients by body cells (intestine)
 Human Digestive System Food is pushed along the digestive tract by peristalsis the rhythmic waves of contraction of smooth muscles in the wall of the canal Accessory glands. Main stages of food processing
Human Digestive System Food is pushed along the digestive tract by peristalsis the rhythmic waves of contraction of smooth muscles in the wall of the canal Accessory glands. Main stages of food processing
The Small Intestine. The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine.
 The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Digestive System. What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning?
 Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Digestive System. Digestion Myths
 Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition. Omnivores regularly consume animals as well as plants or algae
 Ch 41 Animal Nutrition Need to Feed Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae
Ch 41 Animal Nutrition Need to Feed Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae
What are you made of????
 What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
Student Exploration: Digestive System
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Digestive System Vocabulary: absorption, amino acid, carbohydrate, chemical digestion, chyme, complex carbohydrate, digestion, digestive system, elimination, enzyme, fat,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Digestive System Vocabulary: absorption, amino acid, carbohydrate, chemical digestion, chyme, complex carbohydrate, digestion, digestive system, elimination, enzyme, fat,
Lesson 1. Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM There are three primary functions for the digestive system 1. Break down food into molecules the body can use 2. The molecules are absorbed into the
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM There are three primary functions for the digestive system 1. Break down food into molecules the body can use 2. The molecules are absorbed into the
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.
 1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
Digestion Review V1 /36
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Digestion Review V1 /36 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the above parts of the digestive system would be
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Digestion Review V1 /36 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the above parts of the digestive system would be
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition
 Metabolic Rate Animals are heterotrophs that require food for: 1) Fuel 2) Carbon Skeletons 3) Essential Nutrients Bioenergetics: Flow of energy through an organism Sets upper / lower limits Metabolic Rate:
Metabolic Rate Animals are heterotrophs that require food for: 1) Fuel 2) Carbon Skeletons 3) Essential Nutrients Bioenergetics: Flow of energy through an organism Sets upper / lower limits Metabolic Rate:
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1. Digestion 101 & H.O.P.E.
 Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System
 The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System The Digestive System The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food. Mechanical
The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System The Digestive System The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food. Mechanical
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics
 Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 2 1 Introduction Some Ecology 3 Mr. Sun 4 2 Nuclear Fusion 5 Light energy from Sun radiates across
Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 2 1 Introduction Some Ecology 3 Mr. Sun 4 2 Nuclear Fusion 5 Light energy from Sun radiates across
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Nutrition, part 2. Because 1 part isn t enough!
 Nutrition, part 2 Because 1 part isn t enough! 4. Calories and Caloric Intake Calories per gram of our Macro and Micro nutrients Macro Carbohydrates: 4 cal/g Fats: 9 cal/g Proteins: 4 cal/g Micro Vitamins:
Nutrition, part 2 Because 1 part isn t enough! 4. Calories and Caloric Intake Calories per gram of our Macro and Micro nutrients Macro Carbohydrates: 4 cal/g Fats: 9 cal/g Proteins: 4 cal/g Micro Vitamins:
Digestion and Excretion
 Digestion and Excretion The Digestive System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Digestion and Excretion The Digestive System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Website: websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition
 Website: websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 2 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 3 Introduction Some Ecology 4 2 Mr. Sun 5 Nuclear Fusion 6 3
Website: websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 2 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 3 Introduction Some Ecology 4 2 Mr. Sun 5 Nuclear Fusion 6 3
The Digestive System: Basics. WedNesday October 24th All organisms need energy to survive. > Use energy to reproduce, grow, and repair
 WedNesday October 24th 2012 QU: What would happen if an organism stopped eating? OBJ: Digestive System Notes All about hydrolysis and surface area Digestive System All organisms need energy to survive
WedNesday October 24th 2012 QU: What would happen if an organism stopped eating? OBJ: Digestive System Notes All about hydrolysis and surface area Digestive System All organisms need energy to survive
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
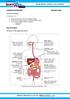 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
