|
|
|
- Alyson Wilkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 R.AMUDAN,M.SC.,M.Phil.,B.Ed., Graduate Teacher in Science Govt.Hr.Sec.School Cholavaram Vellore Dist Cell:
2 NAME OF THE EXPERIMENTS BIO- BOTANY BIO- ZOOLOGY CHEMISTRY PHYSICS Classify the given fruit and give reasons with 1 diagram Dissect and display the floral parts like Calyx, 2 Corolla, Androecium and Gynoecium of any locally available flower. Identify the given slide with help of microscope. 3 (a) T.S. of Anther (b) L.S. of mature ovule 4 Fermentation experiment (Anaerobic Respiration) Identification of given model (a) Human heart 5 (b) Human brain (c) Human kidney Identify the flag labeled endocrine gland and write its location, hormones secreted and any two of its 6 functions. Endocrine glands: (a) Thyroid gland (b) Pancreas Islets of longerhans (c) Adrenal gland 7 Test for Starch (Iodine Test) Identify the given slide, draw neat labeled diagram 8 and write a note on it (a) RBCs (b) WBCs (c) Palsmodium Prepare a solution from the solid sample and 9 identify the type of solution based on filtration To identify the whether the given sample is an acid 10 or a base Find the nature of sample (A & B) as acids / bases / 11 neutral by using ph paper Screw gauge Find out he thickness of the given 12 one rupee coin 13 Ohm's Law verification 14 Mapping of magnetic field Focal length of convex lens (a) distance object 15 method (b) u-v method
3 BIO - BOTONY 01. Classify the given fruit and give reasons with diagram. Aim: To classify the given fruit and give reasons with diagram. Materials required: Fruit, knife Identification: The given fruit / L.S. of fruit was identified as Simple fleshy fruit Berry Tomato. Reasons: (1) Fruit is developed from the single flower, multicarpellary, syncarpous and superior ovary. (2) The succulent pericarp is differentiated into outer epicarp and inner fleshy pulp. (3) The mesocarp and endocarp are fused to form the fleshy pulp where the seeds are embedded. Result: The given fruit / L.S. of fruit was identified as Simple fleshy fruit Berry Tomato. Aim: To classify the given fruit and give reasons with diagram. Materials required: Fruit, knife Identification: The given fruit / L.S. of fruit was identified as aggregate fruit Polyalthia. Reasons: (1) Polyalthia develops from the single the single flower with multicarpellary apocarpous ovary. (2) During fruit formation each free carpel develops into fruitlet. (3) There are many fruitlets seen attached to a common stalk. Result: The given fruit / L.S. of fruit was identified as aggregate fruit Polyalthia. Aim: To classify the given fruit and give reasons with diagram. Materials required: Fruit, knife Identification: The given fruit / L.S. of fruit was identified as Multiple fruit Jack fruit Reasons: (1) The entire female inflorescence develops into a single fruit. (2) The fertilized flowers develop into fleshy fruitlets. (3) The perianth develops into fleshy edible part. Result: The given fruit / L.S. of fruit was identified as Multiple fruit Jack fruit
4 02. Dissect and display the floral parts like Calyx, Corolla, Androecium and Gynoecium of any locally available flower. Aim: To Dissect and display the floral parts like Calyx, Corolla, Androecium and Gynoecium of any locally available flower. Required materials: Hibiscus rosa-sinensis or Datura innoxia, knife Procedure: Separate Androecium and Gynoecium of a given flower and paste in a separate sheet. Calyx, Corolla are accessory organs. Androecium is male part of the flower. Gynoecium is female part of the flower. Figure: Gynoecium Result: The floral parts like Calyx, Corolla,
5 03. Identify the given slide with help of microscope. Aim: To identify the given slide with help of microscope. Required materials: Microscope, Slide Given slide: T.S. of Anther (1) Each anther lobe is covered by 4 layered wall. (2) The inner most layer of the wall is called tapetum. (3) Inner to the anther wall pollen sac (microspore) with pollen mother cell (microspore cell) is present. (4) The pollen mother cell divides meiotically to produce pollen grains. Result: The given slide was identified as T.S. of Anther. Aim: To identify the given slide with help of microscope. Required materials: Microscope, Slide Given slide: L.S. of mature ovule (1) The ovule consists of central nucleus surrounded by two protective coats called Integuments. (2) The integuments leave a small opening at the apex of the ovule called micropyle. (3) The empryosac is found inside the nucleus. (4) Empryosac contains eight nuclei. Result: The given slide was identified as L.S. of mature ovule.
6 04. Fermentation experiment (Anaerobic Respiration) Aim: To prove the anaerobic respiration (Fermentation). Materials required: Sugar solution, baker's yeast, conical flask (250 ml), beaker and lime water Procedure: (1) Sugar solution in a test tube is taken. (2) A little quantity of yeast is added. (3) The mouth of the conical flask closed with one holed rubber cork and a delivery tube was inserted in the cork. (4) The other end of the delivery tube was immersed in a beaker containing lime water (5) The apparatus was kept in sunlight for 2 hours. Inference: Observation Effervescence appeared. The lime water turned milky. Inference Alcohol smell inferred. CO2 released. Result: The alcohol smell indicates that the sugar is converted into alcohol in the fermentation process.
7 Bio Zoology 5. Identification of given model (a) Human heart (b) Human brain (c) Human kidney Aim: To identify the given model Identification: Given model is identified as L.S. of Human Heart. Diagram: Notes: (1) Heart is a hollow fibro muscular organ, which is conical in shape. (2) Heart is made up of a special type of muscle called cardiac muscle. (3) It has four chambers namely two auricles and two ventricies. (4) Heart is a pumping organ which pumps blood to all parts of the body. Result: Given model is identified as L.S. of Human Heart. Aim: To identify the given model Identification: Given model is identified as L.S. of Human Brain. Diagram: Notes: (1) Human brain is placed inside the cranial cavity.. (2) Human brain is divided into three major parts namely forebrain, mid brain and hind brain. (3) Human brain contains millions of neurons. (4) Brain acts as a command and coordinating system of human body. Result: Given model is identified as L.S. of Human Brain. Aim: To identify the given model Identification: Given model is identified as L.S. of Human Kidney. Diagram: Notes: (1) Kidney is the principle excretory organ of our body. (2) Kidney is bean shaped paired structure and located in the upper abdominal region. (3) The outer portion of the kidney is renal cortex and the inner portion is renal medulla. (4) A kidney has about 1.0 millions of functional units called nephrons. Result: Given model is identified as L.S. of Human Kidney.
8 06. Identify the flag labeled endocrine gland and write its location, hormones secreted and any two of its functions. [No need to draw diagram] Endocrine glands: (a) Thyroid gland (b) Pancreas Islets of longerhans (c) Adrenal gland Aim: To identify the flag labeled endocrine gland in a given model / chart / a neat diagram and write its location, hormones secreted and any two of its functions. Identification: The marked endocrine gland is identified as thyroid gland. Location: Thyroid gland is a bilobed gland located in the neck region on either side of the Trachea. Hormones secreted: Thyroxine Functions of Hormones: (1) Thyroxine is a personality hormone. (2) It increases the basal metabolic rate [BMR]. (3) It increases the body temperature. Result: The marked endocrine gland is identified as thyroid gland. Its location, hormones secreted and its functions were explained. Aim: To identify the flag labeled endocrine gland in a given model / chart / a neat diagram and write its location, hormones secreted and any two of its functions. Identification: The marked endocrine gland is identified as Pancreas Islets of longerhans. Location: Pancreas Islets of longerhans are seen embedded in Pancreas which is located in the abdominal region. Hormones secreted: Functions of Hormones: (1) Alpha cells secret glucagons (2) Bets cells secret Insulin and amylin. (1) Insulin converts glucose into glycogen in liver and muscles. (2) Glucagon converts glycogen into glucose. (3) Decrease in insulin level causes Diabetes mellitus. Result: The marked endocrine gland is identified as Pancreas Islets of longerhans. Its location, hormones secreted and its functions were explained. Aim: To identify the flag labeled endocrine gland in a given model / chart / a neat diagram and write its location, hormones secreted and any two of its functions. Identification: The marked endocrine gland is identified as Adrenal gland. Location: Adrenal glands are located above each kidney in the abdominal region. Hormones secreted: Functions of Hormones: (a) Adrenal cortex Adolsterone and Cortisone (b) Adrenal medulla Adrenaline and nor adrenaline (1) Adolsterone regulates mineral metabolism. (2) Cortisone regulates carbohydrate metabolism. (3) Adrenaline and nor adrenaline are called Emergency hormones and they increase the heart beat rate and respiratory rate. Result: The marked endocrine gland is identified as Adrenal gland. Its location, hormones secreted and its functions were explained.
9 07. Test for Starch (Iodine Test) Aim: To find out the presence of starch in the given food samples A and B by Iodine test. Materials and apparatus required: Food samples A and B, Iodine solution, test tubes, test tube holder, test tube stand Procedure: (1) One ml of food samples A and B were taken in two different test tubes. (2) One drop of Iodine solution was added into each of the test tubes. (3) They were mixed well. (4) The changes occurring in colour were noted and tabulated. Table: Sample Observation Inference A Appearance of dark blue Presence of starch B colour No colour change Absence of starch Result: Appearance of dark blue colour in the sample A indicaes the presence of Starch in it.
10 08. Identify the given slide, draw neat labeled diagram and write a note on it Aim: To identify the given slide, draw neat labeled diagram and write a note on it. Materials required: Microscope, slide Identification: The given slide is identified as Red blood Corpuscles(Erythrocytes) Notes: (1) RBCs are circular, biconcave and disc shaped. (2) The young RBCs have nuclei but. (3) The mature RBCs do not have nuclei. (4) RBCs are red due to the presence of a respiratory pigment called haemoglobin. (5) RBCs are concerned with carriage of oxygen. Result: The given slide was identified and explained. Aim: To identify the given slide, draw neat labeled diagram and write a note on it. Materials required: Microscope, slide Identification: The given slide is identified as White blood Corpuscles (Leauocytes). Notes: (1) WBCa are amoeboid in shape. (2) WBCs have a prominent nuclei. (3) WBCs are concerned with phagocytosis of foreign germs and production of antibodies which provides immunity against infection. (4) There are five different types of WBC. Result: The given slide was identified and explained. Aim: To identify the given slide, draw neat labeled diagram and write a note on it. Materials required: Microscope, slide Identification: The given slide is identified as Palsmodium. Notes: (1) Plasmodium is a protozoan organism. (2) Plasmodium parasite causes Malaria. (3) Plasmodium is transmitted to man through female Anopheles mosquito. (4) Life cycle of Plasmodium requires two hosts namely and female Anopheles mosquito. (5) The infective stage of Plasmodium is Sporozoite. Result: The given slide was identified and explained.
11 CHEMISTRY 09. Prepare a solution from the solid sample and identify the type of solution based on filtration Aim: To prepare a solution from the solid sample and identify the type of solution based on filtration. Materials required: Beaker, water, filter papers, test tube, test tube stand, glass rod, funnel, given sample Theory: True solution Homogeneous and transparent. Solute particles do not remain in the filter paper. Suspension Heterogeneous mixture. Solute particles remain in the filter paper. Procedure: Experiment Observation Inference 50 ml of water was taken in a beaker. The given sample was added to it. It was stirred well with the help of glass rod. By using filter paper the solution was filtered. Solute particles do not remain in the filter paper. True solution Result: the given solid sample forms true solution. Aim: To prepare a solution from the solid sample and identify the type of solution based on filtration. Materials required: Beaker, water, filter papers, test tube, test tube stand, glass rod, funnel, given sample Theory: True solution Homogeneous and transparent. Solute particles do not remain in the filter paper. Suspension Heterogeneous mixture. Solute particles remain in the filter paper. Procedure: Experiment Observation Inference 50 ml of water was taken in a beaker. The given sample was added to it. It was stirred well with the help of glass rod. By using filter paper the solution was filtered. Solute particles remain in the filter paper. Suspension Result: the given solid sample forms suspension.
12 10. To identify the whether the given sample is an acid or a base Aim: To identify the whether the given sample is an acid or a base. Materials required: Test tubes, test tube stand, glass rod, phenolphthalein, methyl orange, sodium carbonate salt, zinc granules, given sample Theory: S. No. Material used Acid Base 1 Phenolphthalein Colourless Turns pink colour 2 Methyl orange Turns pink colour Turns yellow colour 3 Sodium carbonate Brisk effervescence No reaction 4 salt Zinc granules occurs Bubbles (H2) come Bubbles (H2) do not out come out Procedure: 5 ml of the given solution was taken in 4 test tubes. Phenolphthalein, methyl orange, sodium carbonate salt, zinc granules were added to the test tubes. Observations were noted in the table. S. No. Material used Observation Inference 1 Phenolphthalein Colourless Presence of acid 2 Methyl orange Turns pink colour Presence of acid 3 Sodium carbonate Brisk effervescence Presence of acid 4 salt Zinc granules occurs Bubbles (H2) come out Presence of acid Result: The given test solution contains acid. Aim: To identify the whether the given sample is an acid or a base. Materials required: Test tubes, test tube stand, glass rod, phenolphthalein, methyl orange, sodium carbonate salt, zinc granules, given sample Theory: S. No. Material used Acid Base 1 Phenolphthalein Colourless Turns pink colour 2 Methyl orange Turns pink colour Turns yellow colour 3 Sodium carbonate Brisk effervescence No reaction 4 salt Zinc granules occurs Bubbles (H2) come Bubbles (H2) do not Procedure: 5 ml of the given solution was out taken in 4 test tubes. Phenolphthalein, come out methyl orange, sodium carbonate salt, zinc granules were added to the test tubes. Observations were noted in the table. S. No. Material used Observation Inference 1 Phenolphthalein Turns pink colour Presence of base 2 Methyl orange Turns yellow colour Presence of base 3 Sodium carbonate No reaction Presence of base 4 salt Zinc granules Bubbles (H2) do not Presence of base come out Result: The given test solution contains base.
13 11. Find the nature of sample (A & B) as acids / bases / neutral by using ph paper Aim: To identify the nature of the given solution by using ph paper. Materials required: Samples A & B, ph paper, watch glass, glass rod Principle: ph = 7 Neutral, ph < 7 Acidic, ph > 7 Basic Procedure: ph paper was placed on a watch glass. By using glass rod a drop of each sample was dipped on the ph paper. Observations were tabulated. Sample Colour produced Observation Approximate ph Value Inference A Blue 12 Basic B Red 2 Acidic Result: 1. The given sample A is BASIC. 2. The given sample B is ACIDIC
14 PHYSICS 12. Screw gauge Find out he thickness of the given one rupee coin Aim: To find out the thickness of the given one rupee coin. Materials required: Screw gauge, one rupee coin Formula: Least count = Pitch / Number of HSD = 1 mm / 100 = 0.01 m Thickness = PSR + (HSC x LC) ± ZC (mm) Procedure: 1. The least count of the screw gauge [LC = 0.01 m] 2. Zero error of the screw gauge is found. [ZC = 0] 3. The given one rupee coin is placed between two studs 4. The head is rotated until the wire is held firmly. 5. Pitch Scale Reading [PSR] and Head Scale Reading [HSC] are noted. 6. Again they are noted by repeating the experiment. 7. They are tabulated. 8. The experiment was repeated for different positions of the coin. Table: S. No. PSR (mm) HSC HSC x LC Thickness of the coin = PSR + [HSC x LC] ± ZC (mm) Average 1.30 Result: The thickness of the given coin = 1.30 mm
15 13. Ohm's Law verification Aim: To determine resistor's resistance and to verify the Ohm's law. Materials required: Resistor, an ammeter (0-3 A), voltmeter (0-10 V), a battery eliminator, plug keys, connecting wires Formula: Resistance (R) = V / I ohm Potential difference in volt (V), current in ampere (I) Circuit diagram: Procedure: The battery eliminator, ammeter, the given wire, rheostat and key are connected in series. The volt meter is connected in parallel across the given wire.keeping the rate of the eliminator at the minimum (2V) the readings of ammeter and volt meter are tabulated. Increasing the rate of the eliminator (4 V and 6 V) the readings of ammeter and volt meter are tabulated. Table: S. No. "I" is noted from the ammeter. "V" is noted from the voltmeter. Voltage applied in the circuit (Volt) Current through the Register (Ampere) Resistance of resistor R = V / I (Ohm) Graph: 1. Choosing appropriate scale for the values of I and V along the x and y axes respectively on the graph paper. 2. The points were marked on the graph paper. The points were joined. 3. The slope of the straight line was found. 4. The slope is the resistance of the resistor. Result: 1. Resistance of the resistor (Calculations method) = 5 Ohm 2. Resistance of the resistor (Graphical method) = 5 Ohm 3. The graph between V and I is a straight line and passes through the origin. Thus Ohm's law verified.
16 14. Mapping of magnetic field Aim: To map the magnetic field due to a Bar Magnet placed in a Magnetic Meridian with its Northpole towards North. Apparatus required: Drawing Board, Board pins and cello taps, Compass Needle, Sheets of white paper, Bar Magnet Procedure: A white sheet of paper is fastened to the drawing board using board pins or cello tape. A small plotting compass needle is placed near the edge of the paper. The board is rotated until the edge of the paper is parallel to the Magnetic needle. A bar magnet is placed on the white paper. Outline of magnet is drawn and its poles are noted. The magnetic needle is placed near the north pole of the magnet. Its north pole is marked. The magnetic needle is again placed so that the south-pole touched the dot mark. Its north pole is marked. The procedure is repeated. The dots are joined. This curve is a magnetic line of force. In the same way several magnetic lines are drawn. Result: The magnetic lines of force are mapped when the bar magnet is placed with its north pole facing geographic north. The mapped sheet is attached.
17 15. Focal length of convex lens (a) distance object method (b) u-v method Aim: To determine the focal length of the given convex lens by (a) distance method (b) u-v method. Materials required: Convex lens, lens stand, white screen, meter scale, illuminated wire gauze Formula: Focal length of the convex lens by u-v method, f = uv / u + v Procedure: (a) Distance method: (1) The convex lens is mounted on the stand and is kept facing a distant object. (2) The white screen is placed behind the convex lens and its position is adjusted to get a clear, diminished and inverted image of the object. (3) The distance between the convex lens and the screen is measured. (4) This is an approximate value of the focal length of the convex lens. (b) u-v Method: (1) The convex lens is mounted on the stand.. (2) It was placed in front of the lluminated wire gauze at a certain distance 'u' from the wire gauze. (3) A screen is placed on the other side of lens and its from the lens is adjusted to get a clear image. (4) The distance between the lens and the screen is taken as 'v'. Table: S. No. Nature of image Object distance u ( cm) Image distance v (cm) Focal length f = uv / u + v ( cm) 1 u < 2f Magnified u > 2f Diminished Average 10.1 Result: The focal length of the given convex lens by (a) Distance object method = 10.1 cm (b) u-v method = 10.1 cm
18
SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT. [New Edition ] Prepared by. B. BALAJI.,M.Sc.,M.phil.,B.Ed.
![SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT. [New Edition ] Prepared by. B. BALAJI.,M.Sc.,M.phil.,B.Ed. SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT. [New Edition ] Prepared by. B. BALAJI.,M.Sc.,M.phil.,B.Ed.](/thumbs/75/72411942.jpg) SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT [New Edition - 2016] Prepared by B. BALAJI.,M.Sc.,M.phil.,B.Ed., Graduate Teacher (science) Dr VGN Matric. school Madurantakam, kancheepuram Dist. Ph: 9843359619 Mail:
SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT [New Edition - 2016] Prepared by B. BALAJI.,M.Sc.,M.phil.,B.Ed., Graduate Teacher (science) Dr VGN Matric. school Madurantakam, kancheepuram Dist. Ph: 9843359619 Mail:
(As per New Syllabus Revised)
 (As per New Syllabus Revised) by Lecturer in Physics M.Sc. (Physics), PGDS&TC., B.Ed. ARIGNAR ANNA GOVT. HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL KUNICHAMPET, PUDUCHERRY-605501 Contact Number 9751051581 Email: sridaranesriram@gmail.com
(As per New Syllabus Revised) by Lecturer in Physics M.Sc. (Physics), PGDS&TC., B.Ed. ARIGNAR ANNA GOVT. HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL KUNICHAMPET, PUDUCHERRY-605501 Contact Number 9751051581 Email: sridaranesriram@gmail.com
SSLC BIOLOGY PRACTICAL MANUAL
 S ST.PAUL S MATRICULATION HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 SSLC BIOLOGY PRACTICAL MANUAL 2015-16 PREPARED BY M.G.RAYMOND, M.Sc., B.Ed., DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY ST.PAUL S MAT. HR. SEC. SCHOOL,
S ST.PAUL S MATRICULATION HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 SSLC BIOLOGY PRACTICAL MANUAL 2015-16 PREPARED BY M.G.RAYMOND, M.Sc., B.Ed., DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY ST.PAUL S MAT. HR. SEC. SCHOOL,
ZOOLOGY TO FIND OUT THE PRESENCE OF STARCH IN THE GIVEN FOOD SAMPLES OF A AND B USING IODINE SOLUTION
 EX. NO: 1 ZOOLOGY TO FIND OUT THE PRESENCE OF STARCH IN THE GIVEN FOOD SAMPLES OF A AND B USING IODINE SOLUTION To find out the presence of starch in the given food samples of A and B by using Iodine solution.
EX. NO: 1 ZOOLOGY TO FIND OUT THE PRESENCE OF STARCH IN THE GIVEN FOOD SAMPLES OF A AND B USING IODINE SOLUTION To find out the presence of starch in the given food samples of A and B by using Iodine solution.
SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL MANUAL PREPARED BY M.G.RAYMOND, M.Sc., B.Ed., DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY /
 www. S ST.PAUL S MATRICULATION HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL MANUAL 2015-16 PREPARED BY M.G.RAYMOND, M.Sc., B.Ed., DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY 9442980841 / 9629705161
www. S ST.PAUL S MATRICULATION HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL MANUAL 2015-16 PREPARED BY M.G.RAYMOND, M.Sc., B.Ed., DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY 9442980841 / 9629705161
SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL MANUAL ST.PAUL S MAT. HR. SEC. SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI CUDDALORE Dt.
 S SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL MANUAL 2015-16 ST.PAUL S MAT. HR. SEC. SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 CUDDALORE Dt. ST.PAUL S MATRICULATION HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 SSLC BIOLOGY PRACTICAL
S SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL MANUAL 2015-16 ST.PAUL S MAT. HR. SEC. SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 CUDDALORE Dt. ST.PAUL S MATRICULATION HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 SSLC BIOLOGY PRACTICAL
Class 10 Science - Sample Paper Set I
 Time allowed: 3 hours; Maximum marks: 90 General Instructions: a) All Questions are compulsory b) The Question Paper consists of 42 Questions divided in to four sections A, B, C and D c) Section- A comprises
Time allowed: 3 hours; Maximum marks: 90 General Instructions: a) All Questions are compulsory b) The Question Paper consists of 42 Questions divided in to four sections A, B, C and D c) Section- A comprises
Revision Question Bank. MCQs [Practical Based Questions]
![Revision Question Bank. MCQs [Practical Based Questions] Revision Question Bank. MCQs [Practical Based Questions]](/thumbs/90/104148695.jpg) Revision Question Bank 1. What are phytohormones? 2. Name the part of hindbrain which takes part in regulation of respiration. 3. We suddenly pull our hand when a pin pricks. Name the type of response
Revision Question Bank 1. What are phytohormones? 2. Name the part of hindbrain which takes part in regulation of respiration. 3. We suddenly pull our hand when a pin pricks. Name the type of response
Flowering Plant Reproduction
 Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds
 The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity.
 1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity. The correct sequence of processes represented by A, B, and
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity. The correct sequence of processes represented by A, B, and
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *7531216271* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2012
*7531216271* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2012
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 1: Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place. Answer :- The male gametophyte or the pollen grain
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 1: Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place. Answer :- The male gametophyte or the pollen grain
Best IIT coaching in Kote
 Click Here From early adopters of new technology in field of Under class 10th education and 10 to 12th Education. Plutus Academy has helped large number of students during their career. May it be for UPSC
Click Here From early adopters of new technology in field of Under class 10th education and 10 to 12th Education. Plutus Academy has helped large number of students during their career. May it be for UPSC
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2
 NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Exercise Solutions Exercise : Solutions of Questions on
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Exercise Solutions Exercise : Solutions of Questions on
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II SCIENCE
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II SCIENCE [Time allowed: 3 hours] [Maximum marks:80] General Instructions: (i) The question paper comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections. (ii) (iii)
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II SCIENCE [Time allowed: 3 hours] [Maximum marks:80] General Instructions: (i) The question paper comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections. (ii) (iii)
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure
 wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
CARMEL ENGLISH SCHOOL,KALLATA
 CARMEL ENGLISH SCHOOL,KALLATA LABORATORY EQUIPMENTS CHEMISTRY LAB 1 ALUMINIUM SULPHATE 500 gm 2 COPPER SULPHATE 500 gm 3 CALCIUM HYDROXIDE 500 gm 4 IRON SULPHIDE 500 gm 5 SODIUM BIOCARBONATE 500 gm 6 SODIUM
CARMEL ENGLISH SCHOOL,KALLATA LABORATORY EQUIPMENTS CHEMISTRY LAB 1 ALUMINIUM SULPHATE 500 gm 2 COPPER SULPHATE 500 gm 3 CALCIUM HYDROXIDE 500 gm 4 IRON SULPHIDE 500 gm 5 SODIUM BIOCARBONATE 500 gm 6 SODIUM
1 Living organisms: variety and common features
 Living organisms: variety and common features Using and interpreting data a) S = scale linear and uses at least half of the grid L = lines neat, straight and through points A = axes correct way round (Temperature
Living organisms: variety and common features Using and interpreting data a) S = scale linear and uses at least half of the grid L = lines neat, straight and through points A = axes correct way round (Temperature
EXAMINERS REPORTfor2017 PHYSICAL SCIENCE PAPER 4 (ALTERNATIVE TO PRACTICAL)
 EXAMINERS REPORTfor2017 PHYSICAL SCIENCE PAPER 4 (ALTERNATIVE TO PRACTICAL) GENERAL OVERVIEW The Paper was fair since there was a balance between low and high order questions. The level of difficulty of
EXAMINERS REPORTfor2017 PHYSICAL SCIENCE PAPER 4 (ALTERNATIVE TO PRACTICAL) GENERAL OVERVIEW The Paper was fair since there was a balance between low and high order questions. The level of difficulty of
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination
 BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System
 Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
 Booklet Code C Series HRL/1 This Booklet contains 24 pages PRACTICAL SKILLS IN SCIENCE Time allowed: 1 ½ hours Maximum marks: 20 General Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. There are 30 multiple
Booklet Code C Series HRL/1 This Booklet contains 24 pages PRACTICAL SKILLS IN SCIENCE Time allowed: 1 ½ hours Maximum marks: 20 General Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. There are 30 multiple
Chapter 21. Human Endocrine System
 Chapter 21 Human Endocrine System Endocrine System Consist of endocrine glands that secrete hormones which regulate a wide range of activities in humans Hormones- are secreted by glands and diffuse directly
Chapter 21 Human Endocrine System Endocrine System Consist of endocrine glands that secrete hormones which regulate a wide range of activities in humans Hormones- are secreted by glands and diffuse directly
Hearing Balance of the body. (b) Eyes : Photoreceptors Seeing (c) Skin : Thermoreceptors
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Control and coordination are provided by nervous and muscular tissues. Nervous tissue is made up of an organized network of nerve cells or neurons, and is specialized for conducting information
NERVOUS SYSTEM Control and coordination are provided by nervous and muscular tissues. Nervous tissue is made up of an organized network of nerve cells or neurons, and is specialized for conducting information
Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1. Fill in the Blanks.
 Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1 Fill in the Blanks. 1. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands which are poured in to the blood. 2. Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to
Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1 Fill in the Blanks. 1. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands which are poured in to the blood. 2. Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to
GCSE (9 1) Biology A (Gateway Science) J247/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) Sample Question Paper SPECIMEN
 GCSE (9 1) Biology A (Gateway Science) J247/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) Sample Question Paper F Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes You may use: a scientific or graphical calculator
GCSE (9 1) Biology A (Gateway Science) J247/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) Sample Question Paper F Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes You may use: a scientific or graphical calculator
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure. Name
 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
LENTEGEUR SECONDARY GRADE 11 LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 1 NOVEMBER 2016 MARKS: 150 TIME: 2:30
 LENTEGEUR SECONDARY GRADE 11 LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 1 NOVEMBER 2016 MARKS: 150 TIME: 2:30 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. Answer all questions. 2. Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system
LENTEGEUR SECONDARY GRADE 11 LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 1 NOVEMBER 2016 MARKS: 150 TIME: 2:30 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. Answer all questions. 2. Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system
SUNSHINE SECONDARY SCHOOL
 Name... Index Number... Student s Signature... 231/3 BIOLOGY PAPER 3 PRACTICAL JUNE, 2017 1 ¾ HOURS SUNSHINE SECONDARY SCHOOL Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY Paper 3 Practical TIME: 1
Name... Index Number... Student s Signature... 231/3 BIOLOGY PAPER 3 PRACTICAL JUNE, 2017 1 ¾ HOURS SUNSHINE SECONDARY SCHOOL Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY Paper 3 Practical TIME: 1
The Flower - what is it? 1/31/18. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants
 - what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
- what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT. 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys.
 Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Control and Coordination
 CHAPTER 7 Control and Coordination Living organisms respond and react to various stimuli like heat, light, cold, touch, pressure etc. Plants and animals both respond to stimuli but in different manner.
CHAPTER 7 Control and Coordination Living organisms respond and react to various stimuli like heat, light, cold, touch, pressure etc. Plants and animals both respond to stimuli but in different manner.
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants.
 CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *2994000068* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour Candidates
*2994000068* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour Candidates
BIOLOGY PAPER - 1. (THEORY) (Botany and Zoology)
 BIOLOGY PAPER - 1 (THEORY) (Botany and Zoology) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) Answer all questions
BIOLOGY PAPER - 1 (THEORY) (Botany and Zoology) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) Answer all questions
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 5021-1 - Page 1 1) A student measures his pulse rate while he is watching television and records it. Next, he walks to a friend's house nearby and when he arrives, measures and records his pulse
Name: 5021-1 - Page 1 1) A student measures his pulse rate while he is watching television and records it. Next, he walks to a friend's house nearby and when he arrives, measures and records his pulse
plant reproduction chapter 40 Alternation of Generations
 Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS
 BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *9683650458* BIOLOGY 0610/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour Candidates answer
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *9683650458* BIOLOGY 0610/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour Candidates answer
Teaching A2 Biology Practical Skills Appendix 2
 Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *1669880040* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour
*1669880040* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour
Unit 4 Homeostasis. The term homeostasis refers to the body s attempt. Your body systems must to maintain a stable internal environment -
 Unit 4 Homeostasis The term homeostasis refers to the body s attempt Your body systems must to maintain a stable internal environment - The body is trying to maintain, through a series of monitored adjustments.
Unit 4 Homeostasis The term homeostasis refers to the body s attempt Your body systems must to maintain a stable internal environment - The body is trying to maintain, through a series of monitored adjustments.
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL?
 Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Lab 6: Cellular Respiration
 Lab 6: Cellular Respiration Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in a living organism. These reactions can be catabolic or anabolic. Anabolic reactions use up energy to actually build complex
Lab 6: Cellular Respiration Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in a living organism. These reactions can be catabolic or anabolic. Anabolic reactions use up energy to actually build complex
MAHESH TUTORIALS SECTION - A
 S.S.C. MAHESH TUTORIALS Test - II Batch : SB Marks : 30 Date : SCIENCE Chapter :,, 4, 6, 0, Time : hr. 5 min. SECTION - A Q.I (A) Rewrite the following statements by choosing the correct option : The least
S.S.C. MAHESH TUTORIALS Test - II Batch : SB Marks : 30 Date : SCIENCE Chapter :,, 4, 6, 0, Time : hr. 5 min. SECTION - A Q.I (A) Rewrite the following statements by choosing the correct option : The least
Downloaded from
 CHAPTER 7-CONTROL AND COORDINATION Stimulus:-The change in the environment to which an organism respond and react is called stimulus. Control & co-ordination in animals takes place by :-a) Nervous system)
CHAPTER 7-CONTROL AND COORDINATION Stimulus:-The change in the environment to which an organism respond and react is called stimulus. Control & co-ordination in animals takes place by :-a) Nervous system)
1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2) Nutrition in Human Beings. 3) transportation in human being 4) Excretion in human being
 1 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA VSN NAGPUR HOLIDAY HOMEWORK Class X A and X B (SCIENCE) Learn Chapter 1, 6 And 10 Worksheet on Chapter 1 and Chapter 6 Prepare presentation on 1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2)
1 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA VSN NAGPUR HOLIDAY HOMEWORK Class X A and X B (SCIENCE) Learn Chapter 1, 6 And 10 Worksheet on Chapter 1 and Chapter 6 Prepare presentation on 1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2)
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
SCIENCE (REVISED SYLLABUS) HIGHER LEVEL
 J.37 PRE-JUNIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2010 SCIENCE (REVISED SYLLABUS) HIGHER LEVEL TIME : 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name, school name and teacher s name in the boxes provided on this page.
J.37 PRE-JUNIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2010 SCIENCE (REVISED SYLLABUS) HIGHER LEVEL TIME : 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name, school name and teacher s name in the boxes provided on this page.
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 10
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 0 LIFE SCIENCES P3 (PRACTICAL) EXEMPLAR 202 MARKS: 60 TIME: hour This question paper consists of 4 pages. Life Sciences/P3 (Practical) 2 DBE/202 NSC Grade 0 Exemplar QUESTION
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 0 LIFE SCIENCES P3 (PRACTICAL) EXEMPLAR 202 MARKS: 60 TIME: hour This question paper consists of 4 pages. Life Sciences/P3 (Practical) 2 DBE/202 NSC Grade 0 Exemplar QUESTION
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Four main events must occur in order for sexual reproduction to take place. 1. The organism must be developed and mature sexually. 2. Gametogenesis; production of
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Four main events must occur in order for sexual reproduction to take place. 1. The organism must be developed and mature sexually. 2. Gametogenesis; production of
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
Angiosperm Reproduction
 Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems. Chapter 39: Biology II
 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 1
 1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
Control And Coordination 49
 7 All the living organisms respond and react to changes in the environment around them. The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli such as light, heat, cold,
7 All the living organisms respond and react to changes in the environment around them. The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli such as light, heat, cold,
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
Our country, our future 2 HOURS
 Our country, our future NAME:. STREAM SENIOR two Biology Exam 2 2 HOURS INSTRUCTION TO CANDIDATES This paper s consists of three sections; A, B and C. Attempt all questions in both sections A and B, and
Our country, our future NAME:. STREAM SENIOR two Biology Exam 2 2 HOURS INSTRUCTION TO CANDIDATES This paper s consists of three sections; A, B and C. Attempt all questions in both sections A and B, and
Module 2 Endocrine System
 Module 2 Endocrine System Student Name: 1 Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 5 Total Marks Total Possible Marks 10 8 14 21 16 69 Your Mark Teacher Comments: 2 (10 marks) Lesson 1: Structure and
Module 2 Endocrine System Student Name: 1 Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 5 Total Marks Total Possible Marks 10 8 14 21 16 69 Your Mark Teacher Comments: 2 (10 marks) Lesson 1: Structure and
3 Movement in and out of cells
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
Visit For All NCERT Solutions, CSBE Sample papers, Question, papers, Notes For Class 6 to 12
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-I, 2015-16 CLASS- X, SCIENCE gg-ro-104 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90 General Instructions:- 1. This question paper Comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-I, 2015-16 CLASS- X, SCIENCE gg-ro-104 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90 General Instructions:- 1. This question paper Comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt
cellular respiration
 Name: Date: 1. The energy found in ATP molecules synthesized in animal cells comes directly from A. sunlight B. organic molecules C. minerals D. inorganic molecules 2. A green plant is kept in a brightly
Name: Date: 1. The energy found in ATP molecules synthesized in animal cells comes directly from A. sunlight B. organic molecules C. minerals D. inorganic molecules 2. A green plant is kept in a brightly
plant reproduction Alternation of Generations chapter 38
 Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL
 SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL LIFE SCIENCES DEPARTMENT LIFE SCIENCES CONTROL TEST 2-2017 EXAMINER: T. GABRIELS MODERATOR: Z. SHADE GRADE 11 TIME: 1 HOUR MARKS: 60 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION Read the following
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL LIFE SCIENCES DEPARTMENT LIFE SCIENCES CONTROL TEST 2-2017 EXAMINER: T. GABRIELS MODERATOR: Z. SHADE GRADE 11 TIME: 1 HOUR MARKS: 60 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION Read the following
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015
 Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Biology Duration: 3.00 Hours Part 1 Index No:- Choose the correct or most appropriate answer and underline them 1) When
Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Biology Duration: 3.00 Hours Part 1 Index No:- Choose the correct or most appropriate answer and underline them 1) When
MAHESH TUTORIALS SECTION - A
 S.S.C. MAHESH TUTORIALS Test - I Batch : SB Marks : 0 Date : SCIENCE Chapter :,, 4, 6, 0, Time : hr. SECTION - A Q.I (A) Rewrite the following statements by choosing the correct option : (i) The centre
S.S.C. MAHESH TUTORIALS Test - I Batch : SB Marks : 0 Date : SCIENCE Chapter :,, 4, 6, 0, Time : hr. SECTION - A Q.I (A) Rewrite the following statements by choosing the correct option : (i) The centre
CBSE Board Class X Science Term 1 Sample Paper - 2. Time: 3 hrs Total Marks: 90
 CBSE Board Class X Science Term 1 Sample Paper - 2 Time: 3 hrs Total Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. The question paper comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections. 2. There
CBSE Board Class X Science Term 1 Sample Paper - 2 Time: 3 hrs Total Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. The question paper comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections. 2. There
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12
 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
Endocrine system. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
You should wear eye protection throughout this practical. Ammonia is corrosive and dangerous to the environment.
 Practical 3 - N (d)(m)urine Analysis Evaluating and reporting on observations This practical focuses on Recording data, drawing conclusions and evaluation. You will also be developing other assessed skills
Practical 3 - N (d)(m)urine Analysis Evaluating and reporting on observations This practical focuses on Recording data, drawing conclusions and evaluation. You will also be developing other assessed skills
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6096073134* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2017 1 hour
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6096073134* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2017 1 hour
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Cbse-spot.blogspot.com
 13. How would the reading of voltmeter (V) change if it is connected between C and D? Justify your answer. 14. Identify the substance oxidized, substance reduced, oxidizing agent and reducing agent in
13. How would the reading of voltmeter (V) change if it is connected between C and D? Justify your answer. 14. Identify the substance oxidized, substance reduced, oxidizing agent and reducing agent in
Ontwikkeling; bevruchting
 Ontwikkeling; bevruchting http://www.lima.ohiostate.edu/biology/archive/flowers. html Young Lily anther x40. Four pollen sacs and a cross section of the fillament are visible. Diploid (2N chromosomes)
Ontwikkeling; bevruchting http://www.lima.ohiostate.edu/biology/archive/flowers. html Young Lily anther x40. Four pollen sacs and a cross section of the fillament are visible. Diploid (2N chromosomes)
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet
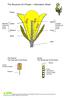 The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY, HPS (B) X CLASS Key:Reproductive system, Endocrine system and Population
 DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY, HPS (B) X CLASS Key:Reproductive system, Endocrine system and Population Question I. Name of the following: 1. The part of the female reproductive system in which fertilization takes
DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY, HPS (B) X CLASS Key:Reproductive system, Endocrine system and Population Question I. Name of the following: 1. The part of the female reproductive system in which fertilization takes
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
Biology Class 12 th NCERT Solutions
 Chapter.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class XII Subject Biology 1. Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place. Answer 1. Pollen grains
Chapter.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class XII Subject Biology 1. Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place. Answer 1. Pollen grains
Control and Coordination. What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus. It does not involve any thinking. For example,
Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus. It does not involve any thinking. For example,
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Respiration Cellular Respiration Understand the relationship between glucose breakdown and ATP when you burn glucose with the help of oxygen, it
 Respiration Cellular Respiration Understand the relationship between glucose breakdown and ATP when you burn glucose with the help of oxygen, it traps chemical energy into ATP Energy found in glucose stores
Respiration Cellular Respiration Understand the relationship between glucose breakdown and ATP when you burn glucose with the help of oxygen, it traps chemical energy into ATP Energy found in glucose stores
Body Systems Notes. Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive
 Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Modes of Reproduction
 Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
16B Flower Dissection
 16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
Topic 9-10: Lab Skills (including 4 NYS required labs)
 1. Base your answer on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Which statement describes two unsafe laboratory practices represented in the diagram? (1) The flame is too high and the test tube
1. Base your answer on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Which statement describes two unsafe laboratory practices represented in the diagram? (1) The flame is too high and the test tube
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction
 Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
10th control and co ordination Solved Board questions By JSUNIL
 10th control and co ordination Solved Board questions By JSUNIL 1. All information for our environment is detected by specialised tips of some nerve cells. Mention the name given to such tips and also
10th control and co ordination Solved Board questions By JSUNIL 1. All information for our environment is detected by specialised tips of some nerve cells. Mention the name given to such tips and also
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium.
 CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Chapter 40 Flowering Plant Sexual Reproduction
 3.6 Reproduction & Growth 3.6.1 Reproduction of The Flowering Plant Chapter 40 Flowering Plant Sexual Reproduction Learning Objectives 1. Give the structure and function of the floral parts. 2. Outline
3.6 Reproduction & Growth 3.6.1 Reproduction of The Flowering Plant Chapter 40 Flowering Plant Sexual Reproduction Learning Objectives 1. Give the structure and function of the floral parts. 2. Outline
Senses and Sense Organs
 Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/06
 www.xtremepapers.com Centre Number Candidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/06 Paper 6 Alternative
www.xtremepapers.com Centre Number Candidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/06 Paper 6 Alternative
