ZOOLOGY TO FIND OUT THE PRESENCE OF STARCH IN THE GIVEN FOOD SAMPLES OF A AND B USING IODINE SOLUTION
|
|
|
- Maximillian Cain
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EX. NO: 1 ZOOLOGY TO FIND OUT THE PRESENCE OF STARCH IN THE GIVEN FOOD SAMPLES OF A AND B USING IODINE SOLUTION To find out the presence of starch in the given food samples of A and B by using Iodine solution. 1. MATERIALS REQUIRED: (1 mark) Food samples, test tube, iodine solution. 2. PROCEDURE: (1 mark) Take 1 ml of food sample A and B in separate test tubes. Add one drop of Iodine solution in both test tubes. Observe the colour change and record. 3. TABLE: (2 mark) S. No. Food Sample Observation Presence/Absence 1 A No characteristic Absence of starch change 2 B Dark blue colour Presence of starch appears 4. RESULT: (1 mark) The food sample B contains starch. of 16.
2 EX. NO: 2 TO FIND OUT THE RATE OF HEART BEAT OF HUMAN BEINGS BY USING STETHOSCOPE UNDER NORMAL PHYSICAL CONDITIONS To find out the rate of heart beat of a person by using stethoscope. 1. MATERIALS REQUIRED: (1 mark) Stethoscope, Stop watch. 2. PROCEDURE: (1 mark) Use the Stethoscope and hear the Lubb and Dubb sound which make up a heart beats. Count the number of heart beats per minute and record. 3. TABLE: (2 mark) S. No. Name of the Person No of heart beats per minute 1 N. AASHIQ 72 2 J. JAISON 72 3 J. WATSON INFERENCE: (1 mark) Average: Under normal conditions the average human heart beat is found to be 72 per minute of 16.
3 EX. NO: 3 TO FIND OUT THE BODY TEMPERATURE BY USING CLINICAL THERMOMETER AND TO COMPARE WITH SURROUNDING TEMPERATURE To find out the Body Temperature of human being using Clinical Thermometer. 1. MATERIALS REQUIRED: (1 mark) Clinical thermometer, Lab thermometer. 2. PROCEDURE: (1 mark) Find out the temperature by using lab thermometer. Keep the mercury bulb of the clinical thermometer at the arm pit for a minute and record the temperature. 3. TABLE: (2 mark) S. No. Test 1 Inside the room Outside the room Body Temperature 0 F 98.4 F 98.4 F Room C=F-32 Temperature 0 C x 5/ C C 4. INFERENCE: (1 mark) Under normal conditions the body temperature of human beings is F, C of 16.
4 EX. NO: 4 TO CALCULATE CULATE THE BODY MASS INDEX OF A PERSON, BY USING THE BMI FORMULA AND COMPARING THE VALUE WITH BMI CHART. To calculate the BMI of any one of your classmates by using the BMI formula. 1. MATERIALS REQUIRED: (1 mark) Weighing machine, Measuring tape. 2. PROCEDURE: (1 mark) Find out the weight of your classmate by using weighing machine. Find out the height of the same person by using measuring tape. BMI = ( ) ( ) Find out the BMI and record. 3. TABLE: (2 mark) S. No. Persons Weight (kg) Height (meter) Height (meter 2 ) BMI 1 LOGESH X /2.25= INFERENCE: (1 mark) The BMI of my classmate Selvan/Selvi J. LOGESH is and so he/she is normal/obese/lean. of 16.
5 EX. NO: 5 BOTANY TO DISSECT AND DISPLAY THEANDROECIUM AND GYNOECIUM OF ANY LOCALLY AVAILABLE FLOWERS To dissect and display the Androecium and Gynoecium of any locally available flowers. 1. IDENTIFICATION: (1 mark) The flower given for dissection is identified as Hibiscus/ Datura metal 2. DISSECT AND DISPLAY OF GIVEN FLOWER: (1 mark) Dissect and display the Androecium and Gynoecium and given flower on white sheet and label the parts Androecium: Gynoecium 1. Anther 1. Ovary 2. Filament 2. Style 3. Stigma 3. PROCEDURE : (1 mark) The given has been identified and the flower dissected and displayed on white sheet. The parts of the given flower is labled. 3. TABLE: (2 mark) S. No. Name of the flower No. of stemen No. of stigma 1 Hibiscus rosasininsis Infinity 5 2 Datura metal of 16.
6 EX. NO: 6 TO CLASSIFY THE FRUITS.SEPARATE SEPARATE THE PERICARPS AND WRITE THE EDIBLE PARTS To classify the fruits.separate the Pericarps and write the Edible parts. 1. IDENTIFICATION : (1 mark) The given fruits name is Tomato (Berry) or lemon (Hesperidium) 2. PROCEDURE: (2 mark) The given fruit is sliced and separate the epicarp, mesocarp and endocarp. TOMATO: It is differentiate into epicarp and mesocarp. The mesocarp and endocarp is fused together. The edible part is mesocarp. 3. TABLE: (2 mark) S. No. Type of Fruit Nature of Pericarp Edible Part 1 Berry:Tomato or Banana Soft Fleshy Mesocarp 2 Hesperidium: Lemon or orange Hard Juicy Hair 3 Drupe: mango Hard Mesocarp 4. INFERENCE: The given fruits has been classified and labeled the edible parts. of 16.
7 EX. NO: 7 IDENTIFY THE STRUCTURE OF OVULE The given slide kept for identification is L.S. of ovule. 1. IDENTIFICATION: (1 mark) The given slide consists of the structure of L.S. of ovule. 2. PROCEDURE: (1 mark) The slide is kept in compound microscope and it is viewed and I have seen the structure of L.S. Ovule with components like Nucellus, Egg, Integuments and Funicle. 3. TABLE: (2 mark) S. NO. OBSERVATION (EXPLANATION) 1 The ovule has 2 layers of wall called as Integuments. 2 Inner to the integuments, Nucellus is present. 3 The embryo sac has Egg, Polar nuclei and Antipodal cells. 4 The ovule is small structure present in the ovary. 5 The ovule is converted into seeds. 4. RESULT: (1 mark) The given slide has been identified and explained. of 16.
8 EX. NO: 8 TO PROVE THE ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION (FERMENTATION) To prove the Anaerobic Respiration (Fermentation). 1. MATERIALS REQUIRED: (1 mark) Test Tube, Sugar Solution, Yeast. 2. PROCEDURE: (1 mark) Sugar solution is taken in a test tube. A little quantity of yeast is added. The tube is placed in a warm place. Record the observation and Inference. 3. OBSERVATION AND INFERENCE: (2 mark) Observation Appearance of Effervescence. Inference Smell of alcohol. 4. RESULT: (1 mark) The Alcohol Smell indicates that the sugar is converted into alcohol by fermentation. of 16.
9 EX. NO: 9 CHEMISTRY TO FIND OUT THE P H OF A GIVEN SOLUTION USING P H PAPER To find out the P H of the given solution using P H paper.. 1. PROCEDURE: (1 mark) Take about 10ml of the given samples in different test tubes and label them as A, B, C, D. Dip the P H paper into the test tubes. Compare the colour of P H paper with the colour chart of P H reference. Note the approximate value of P H. 2. TABLE: (2 mark) P H Paper Nature of solution Test Sample Colour tubes Approximate Acidic/Basic/Natural produced P H A Dil. Hcl Red 1 Acidic B Dil. NaOH Violet 13 Basic 3. RESULT: (2 mark) The tube A contains Acid. The tube B contains Basic. of 16.
10 EX. NO: 10 TO IDENTIFY ACIDS AND BASES To identify the presence of an Acid or a Base in a given sample. 1. MATERIALS REQUIRED: (1 mark) Test tubes, Test tube stand, Glass rod, Litmus paper (both red and blue), Acids, Bases, Phenolphthalein, Methyl orange solution. 2. TABLE: (3 mark) S. Experiment No. 1 Take 5ml of the test solution in a test tube, add phenolphthalein in drops to this content. 2 Take 5ml of the test solution in a test tube and add methyl orange in drops. 3 Take 10ml of the test solution in a test tube and dip red or blue litmus paper into the test tube. Observation (Colour change) Pink colour appears No colour appears Yellow colour appears Pink colour appears Red turns into Blue litmus paper Blue turns into Red litmus paper Inference (Acid/Base) Presence of Base Presence of Acid Presence of Base Presence of Acid Presence of Base Presence of Acid 3. RESULT: (1 mark) The given sample contains Acid/ Base. of 16.
11 EX. NO: 11 PREPARATION OF TRUE SOLUTION, COLLOIDAL SOLUTION AND SUSPENSION To prepare true solution, Colloidal solution and Suspension. 1. PROCEDURE: (1 mark) Take 20ml of water in three different beakers and label them as A, B, C. Add common salt in A, starch in B, and chalk power in C. Stir the contents of three different beakers gently. Record your observations. 2. TABLE: (2 mark) Beakers Observation Inference A Particles don t settle down True Solution B C Particles don t settle down but it forms turbid solution Particles settle down to form Sediment Colloidal Solution Suspension 3. RESULT: (2 mark) 1. True solution is in beaker A. 2. Colloidal solution is in beaker B. 3. Suspension is in beaker C. of 16.
12 EX. NO: 12 TO PREDICT WHETHER THE REACTION IS EXOTHERMIC OR ENDOTHERMIC To predict whether a reaction is Exothermic or Endothermic using the given chemicals. 1. MATERIALS REQUIRED: (1 mark) Test tubes, Test tube stand, Water, Glass rod, Sodium hydroxide (pellets), Ammonium chloride etc. 2. TABLE: ( 3 mark) S. No. Experiment 1 2 Take water in a test tube. Add sodium hydroxide pellets one by stirring. Touch the test tube and not the observation. Take water in a test tube. Add ammonium chloride salt and stir well. Touch the test tube and note the observation. Observation (Hot/Cold) Heat is evolved Becomes Hot Inference (Exo./Endo.) Exothermic Heat is absorbed Endothermic 3. RESULT: (1 mark) In Exothermic reaction heat is evolved. In Endothermic reaction heat is absorbed. of 16.
13 EX. NO: 13 SCREW GAUGE MEASURING SMALL DIMENSIONS OF THE OBJECT To find out the Radius of the given wire. 1. APPARATUS REQUIRED: Screw gauge, a uniform thin metal wire. 2. FORMULA: (1 mark) Radius of the wire r = d/2 d Diameter of the wire 3. PROCEDURE: (2 mark) Find the least count, zero error and zero correction of the Screw Gauge. Place the wire between 2 studs and it is held firmly. Take the pitch scale reading (PSR) and head scale coincides (HSC) and tabulate the readings. 4. TABLE: (1 mark) L.C = 0.01 mm Z.E = -3 Z.C = S. No. P.S.R (mm) H.S.C H.S.C X L.C Total reading P.S.R +(H.S.C X L.C)±Z.C (mm) The radius of given wire r = d/2 = 0.80/2 5. RESULT: (1 mark) r=0.40 mm The radius of the given wire= 0.40mm. of 16.
14 10 TH PRACTICALS SCORE SCIENCE EX. NO: 14 RE ESISTANCE OF THE WIRE To determine the Resistance of the given wire. APPARATUS REQUIRE ED: A Battery, Ammeter, Voltmeter, Key, Rheostat, Experimental wire and Connecting wires. 1. FORMULA: (1 mark) Resistance of the wire R = 2. CIRCUIT DIAGRA AM: AM: (1/2 mark) Bt battery, K Key, Rh - rheostat A Ammeter, v voltmeter. 3. PROCEDURE: (1/2 mark) The circuit is connected. The potential difference V is noted for given current I by adjusting the rheostat. The experiment is repeated for different values of the current. Trial No. Ammeter reading I(ampere) V - Potential difference ence e, I Current The average values of gives the resistancee of the wire R. 4. TABULATION: (2 mark) Voltmeter reading V (volt) Mean R = 10 ohm 5. RESULT: (1 mark) Resistance of the given wire R = 10 ohm. 1 2 Resistance R = V/I(ohm) A. JEBASINGH, M.Sc., M.P Phil., B.Ed. A. NAZEER AHAMED M.Sc., M.Phil., B.Ed. Cell: CHENGALPATTU-2. CELL: CHENGALPATTU 2. of 16.
15 EX. NO: 15 MAPPING OF MAGNETIC FIELD QUESTION To map the Magnetic lines of force when the bar magnet is placed with its north pole facing geographic north. 1. APPARATUS REQUIRED: Drawing board, Drawing pins, Bar magnet, Small magnetic compass needle and White sheet. 2. PROCEDURE: (1 mark) A Sheet of paper is fixed on a drawing board. Using a compass needle, the magnetic meridian is drawn it. A bar magnet is placed on the magnetic meridian. The north and south poles of the compass are marked by pencil dots. The process is repeated and the dots are joined as a smooth curve. 3. MAP: (1+2 mark) 4. RESULT: (1 mark) The magnetic meridian and magnetic lines of force are mapped. The mapped sheet is attached. of 16.
16 EX. NO: 16 FOCAL LENGTH OF CONVEX LENS To determine the Focal length of convex lens by distant object method. 1. APPARATUS REQUIRED: The given convex lens, Lens stand, White screen and Meter scale. 2. FORMULA: (1 mark) Focal length f = (f1+f +f2+f +f3)/3 f1,, f2, f, f3 focal f focal length measured by focusing different distant objects. 3. PROCEDURE: (Distance Object Method) (1 mark) The convex lens is mounted on the stand and is kept facing a distant object. The white screen is placed behind the convex lens and its position is adjusted. The distance between the convex lens and the screen is measured. This gives the focal length of the convex lens. 4. TABLE: (2 mark) S. No. Distant object Distance between the convex and screen (cm) 1 Tree f Building f Electric pole f 3 11 Mean f = 11 cm. 5. RESULT: (1 mark) Focal length of the given convex lens f = 11 cm. of 16.
 R.AMUDAN,M.SC.,M.Phil.,B.Ed., Graduate Teacher in Science Govt.Hr.Sec.School Cholavaram Vellore Dist-632 113. Cell:9443006240 NAME OF THE EXPERIMENTS BIO- BOTANY BIO- ZOOLOGY CHEMISTRY PHYSICS Classify
R.AMUDAN,M.SC.,M.Phil.,B.Ed., Graduate Teacher in Science Govt.Hr.Sec.School Cholavaram Vellore Dist-632 113. Cell:9443006240 NAME OF THE EXPERIMENTS BIO- BOTANY BIO- ZOOLOGY CHEMISTRY PHYSICS Classify
SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT. [New Edition ] Prepared by. B. BALAJI.,M.Sc.,M.phil.,B.Ed.
![SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT. [New Edition ] Prepared by. B. BALAJI.,M.Sc.,M.phil.,B.Ed. SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT. [New Edition ] Prepared by. B. BALAJI.,M.Sc.,M.phil.,B.Ed.](/thumbs/75/72411942.jpg) SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT [New Edition - 2016] Prepared by B. BALAJI.,M.Sc.,M.phil.,B.Ed., Graduate Teacher (science) Dr VGN Matric. school Madurantakam, kancheepuram Dist. Ph: 9843359619 Mail:
SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT [New Edition - 2016] Prepared by B. BALAJI.,M.Sc.,M.phil.,B.Ed., Graduate Teacher (science) Dr VGN Matric. school Madurantakam, kancheepuram Dist. Ph: 9843359619 Mail:
(As per New Syllabus Revised)
 (As per New Syllabus Revised) by Lecturer in Physics M.Sc. (Physics), PGDS&TC., B.Ed. ARIGNAR ANNA GOVT. HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL KUNICHAMPET, PUDUCHERRY-605501 Contact Number 9751051581 Email: sridaranesriram@gmail.com
(As per New Syllabus Revised) by Lecturer in Physics M.Sc. (Physics), PGDS&TC., B.Ed. ARIGNAR ANNA GOVT. HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL KUNICHAMPET, PUDUCHERRY-605501 Contact Number 9751051581 Email: sridaranesriram@gmail.com
SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL MANUAL PREPARED BY M.G.RAYMOND, M.Sc., B.Ed., DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY /
 www. S ST.PAUL S MATRICULATION HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL MANUAL 2015-16 PREPARED BY M.G.RAYMOND, M.Sc., B.Ed., DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY 9442980841 / 9629705161
www. S ST.PAUL S MATRICULATION HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL MANUAL 2015-16 PREPARED BY M.G.RAYMOND, M.Sc., B.Ed., DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY 9442980841 / 9629705161
SSLC BIOLOGY PRACTICAL MANUAL
 S ST.PAUL S MATRICULATION HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 SSLC BIOLOGY PRACTICAL MANUAL 2015-16 PREPARED BY M.G.RAYMOND, M.Sc., B.Ed., DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY ST.PAUL S MAT. HR. SEC. SCHOOL,
S ST.PAUL S MATRICULATION HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 SSLC BIOLOGY PRACTICAL MANUAL 2015-16 PREPARED BY M.G.RAYMOND, M.Sc., B.Ed., DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY ST.PAUL S MAT. HR. SEC. SCHOOL,
SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL MANUAL ST.PAUL S MAT. HR. SEC. SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI CUDDALORE Dt.
 S SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL MANUAL 2015-16 ST.PAUL S MAT. HR. SEC. SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 CUDDALORE Dt. ST.PAUL S MATRICULATION HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 SSLC BIOLOGY PRACTICAL
S SSLC SCIENCE PRACTICAL MANUAL 2015-16 ST.PAUL S MAT. HR. SEC. SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 CUDDALORE Dt. ST.PAUL S MATRICULATION HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL, BLOCK -4, NEYVELI 607801 SSLC BIOLOGY PRACTICAL
Class 10 Science - Sample Paper Set I
 Time allowed: 3 hours; Maximum marks: 90 General Instructions: a) All Questions are compulsory b) The Question Paper consists of 42 Questions divided in to four sections A, B, C and D c) Section- A comprises
Time allowed: 3 hours; Maximum marks: 90 General Instructions: a) All Questions are compulsory b) The Question Paper consists of 42 Questions divided in to four sections A, B, C and D c) Section- A comprises
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *7531216271* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2012
*7531216271* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2012
SUNSHINE SECONDARY SCHOOL
 Name... Index Number... Student s Signature... 231/3 BIOLOGY PAPER 3 PRACTICAL JUNE, 2017 1 ¾ HOURS SUNSHINE SECONDARY SCHOOL Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY Paper 3 Practical TIME: 1
Name... Index Number... Student s Signature... 231/3 BIOLOGY PAPER 3 PRACTICAL JUNE, 2017 1 ¾ HOURS SUNSHINE SECONDARY SCHOOL Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY Paper 3 Practical TIME: 1
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination
 BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
CARMEL ENGLISH SCHOOL,KALLATA
 CARMEL ENGLISH SCHOOL,KALLATA LABORATORY EQUIPMENTS CHEMISTRY LAB 1 ALUMINIUM SULPHATE 500 gm 2 COPPER SULPHATE 500 gm 3 CALCIUM HYDROXIDE 500 gm 4 IRON SULPHIDE 500 gm 5 SODIUM BIOCARBONATE 500 gm 6 SODIUM
CARMEL ENGLISH SCHOOL,KALLATA LABORATORY EQUIPMENTS CHEMISTRY LAB 1 ALUMINIUM SULPHATE 500 gm 2 COPPER SULPHATE 500 gm 3 CALCIUM HYDROXIDE 500 gm 4 IRON SULPHIDE 500 gm 5 SODIUM BIOCARBONATE 500 gm 6 SODIUM
 Booklet Code C Series HRL/1 This Booklet contains 24 pages PRACTICAL SKILLS IN SCIENCE Time allowed: 1 ½ hours Maximum marks: 20 General Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. There are 30 multiple
Booklet Code C Series HRL/1 This Booklet contains 24 pages PRACTICAL SKILLS IN SCIENCE Time allowed: 1 ½ hours Maximum marks: 20 General Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. There are 30 multiple
"Our Flowering World" PRE-TEST. Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below:
 1 PRE-TEST Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below: 1. fertilization 2. embryo 3. pollen 4. anther 5. pistil 6. stamen 7. ovule 8. nectar 9. ovary 10. style Directions: Use the
1 PRE-TEST Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below: 1. fertilization 2. embryo 3. pollen 4. anther 5. pistil 6. stamen 7. ovule 8. nectar 9. ovary 10. style Directions: Use the
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 1: Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place. Answer :- The male gametophyte or the pollen grain
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 1: Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place. Answer :- The male gametophyte or the pollen grain
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6096073134* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2017 1 hour
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6096073134* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2017 1 hour
Petrolatum. Stage 4, Revision 1. Petrolatum is a purified semi solid mixture of hydrocarbons obtained from petroleum.
 1 001-1208PDG.pdf Petrolatum Stage 4, Revision 1 Definition Petrolatum is a purified semi solid mixture of hydrocarbons obtained from petroleum. It may contain a suitable antioxidant. Description and Solubility
1 001-1208PDG.pdf Petrolatum Stage 4, Revision 1 Definition Petrolatum is a purified semi solid mixture of hydrocarbons obtained from petroleum. It may contain a suitable antioxidant. Description and Solubility
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Four main events must occur in order for sexual reproduction to take place. 1. The organism must be developed and mature sexually. 2. Gametogenesis; production of
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Four main events must occur in order for sexual reproduction to take place. 1. The organism must be developed and mature sexually. 2. Gametogenesis; production of
16B Flower Dissection
 16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *9683650458* BIOLOGY 0610/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour Candidates answer
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *9683650458* BIOLOGY 0610/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour Candidates answer
EXAMINERS REPORTfor2017 PHYSICAL SCIENCE PAPER 4 (ALTERNATIVE TO PRACTICAL)
 EXAMINERS REPORTfor2017 PHYSICAL SCIENCE PAPER 4 (ALTERNATIVE TO PRACTICAL) GENERAL OVERVIEW The Paper was fair since there was a balance between low and high order questions. The level of difficulty of
EXAMINERS REPORTfor2017 PHYSICAL SCIENCE PAPER 4 (ALTERNATIVE TO PRACTICAL) GENERAL OVERVIEW The Paper was fair since there was a balance between low and high order questions. The level of difficulty of
Best IIT coaching in Kote
 Click Here From early adopters of new technology in field of Under class 10th education and 10 to 12th Education. Plutus Academy has helped large number of students during their career. May it be for UPSC
Click Here From early adopters of new technology in field of Under class 10th education and 10 to 12th Education. Plutus Academy has helped large number of students during their career. May it be for UPSC
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *2994000068* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour Candidates
*2994000068* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour Candidates
BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12
 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds
 The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2
 NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Exercise Solutions Exercise : Solutions of Questions on
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Exercise Solutions Exercise : Solutions of Questions on
Original content Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
 TEACHER RESOURCE NOTES Skills Practice Lab Dissecting Flowers Teacher Notes TIME REQUIRED One 45-minute period SKILLS ACQUIRED Collecting data Experimenting Identifying patterns Inferring Interpreting
TEACHER RESOURCE NOTES Skills Practice Lab Dissecting Flowers Teacher Notes TIME REQUIRED One 45-minute period SKILLS ACQUIRED Collecting data Experimenting Identifying patterns Inferring Interpreting
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/06
 www.xtremepapers.com Centre Number Candidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/06 Paper 6 Alternative
www.xtremepapers.com Centre Number Candidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/06 Paper 6 Alternative
(Writing model for laboratory note book)
 Paper: Lab 50 Syllabus *************************************************************************** Experiment: Organic Qualitative analysis 1) Detection of elements (Nitrogen, Sulphur and halogens). 2)
Paper: Lab 50 Syllabus *************************************************************************** Experiment: Organic Qualitative analysis 1) Detection of elements (Nitrogen, Sulphur and halogens). 2)
Lab 6: Cellular Respiration
 Lab 6: Cellular Respiration Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in a living organism. These reactions can be catabolic or anabolic. Anabolic reactions use up energy to actually build complex
Lab 6: Cellular Respiration Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in a living organism. These reactions can be catabolic or anabolic. Anabolic reactions use up energy to actually build complex
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II SCIENCE
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II SCIENCE [Time allowed: 3 hours] [Maximum marks:80] General Instructions: (i) The question paper comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections. (ii) (iii)
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II SCIENCE [Time allowed: 3 hours] [Maximum marks:80] General Instructions: (i) The question paper comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections. (ii) (iii)
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
 Centre Number Candidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/05 Paper 5 Practical Test October/November
Centre Number Candidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/05 Paper 5 Practical Test October/November
Seed Plants Lab. Learning Objectives. Procedure and Questions
 Seed Plants Lab Learning Objectives Define the terms (meanings of the names) angiosperm and gymnosperm State what type of cells create eggs and what type of cells create sperm in gymnosperms and angiosperms
Seed Plants Lab Learning Objectives Define the terms (meanings of the names) angiosperm and gymnosperm State what type of cells create eggs and what type of cells create sperm in gymnosperms and angiosperms
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4373149320* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2012 1 hour
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4373149320* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2012 1 hour
Chapter 40 Flowering Plant Sexual Reproduction
 3.6 Reproduction & Growth 3.6.1 Reproduction of The Flowering Plant Chapter 40 Flowering Plant Sexual Reproduction Learning Objectives 1. Give the structure and function of the floral parts. 2. Outline
3.6 Reproduction & Growth 3.6.1 Reproduction of The Flowering Plant Chapter 40 Flowering Plant Sexual Reproduction Learning Objectives 1. Give the structure and function of the floral parts. 2. Outline
Summative Assessment Science Class IX. Time allowed: 3:00 hours Maximum Marks: 90
 Summative Assessment-1 2014-2015 Science Class IX Time allowed: 3:00 hours Maximum Marks: 90 General Instructions: a) The question paper comprises of two sections A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
Summative Assessment-1 2014-2015 Science Class IX Time allowed: 3:00 hours Maximum Marks: 90 General Instructions: a) The question paper comprises of two sections A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
GCSE (9 1) Biology A (Gateway Science) J247/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) Sample Question Paper SPECIMEN
 GCSE (9 1) Biology A (Gateway Science) J247/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) Sample Question Paper F Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes You may use: a scientific or graphical calculator
GCSE (9 1) Biology A (Gateway Science) J247/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) Sample Question Paper F Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes You may use: a scientific or graphical calculator
SALIVA TEST Introduction
 SALIVA TEST Introduction This is a practical lesson using saliva to learn digestive enzyme activity. We can check the existence of reducing sugars clearly by Benedict s reaction after salivary enzyme decomposes
SALIVA TEST Introduction This is a practical lesson using saliva to learn digestive enzyme activity. We can check the existence of reducing sugars clearly by Benedict s reaction after salivary enzyme decomposes
SCIENCE (REVISED SYLLABUS) HIGHER LEVEL
 J.37 PRE-JUNIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2010 SCIENCE (REVISED SYLLABUS) HIGHER LEVEL TIME : 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name, school name and teacher s name in the boxes provided on this page.
J.37 PRE-JUNIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2010 SCIENCE (REVISED SYLLABUS) HIGHER LEVEL TIME : 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name, school name and teacher s name in the boxes provided on this page.
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL
 SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL LIFE SCIENCES DEPARTMENT LIFE SCIENCES CONTROL TEST 2-2017 EXAMINER: T. GABRIELS MODERATOR: Z. SHADE GRADE 11 TIME: 1 HOUR MARKS: 60 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION Read the following
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL LIFE SCIENCES DEPARTMENT LIFE SCIENCES CONTROL TEST 2-2017 EXAMINER: T. GABRIELS MODERATOR: Z. SHADE GRADE 11 TIME: 1 HOUR MARKS: 60 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION Read the following
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *1669880040* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour
*1669880040* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure
 wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
Aim: To study the effect of ph on the action of salivary amylase. NCERT
 Exercise 28 Aim: To study the effect of ph on the action of salivary amylase. Principle: Optimal activity for most of the enzymes is generally observed between ph 5.0 and 9.0. However, a few enzymes, e.g.,
Exercise 28 Aim: To study the effect of ph on the action of salivary amylase. Principle: Optimal activity for most of the enzymes is generally observed between ph 5.0 and 9.0. However, a few enzymes, e.g.,
9. Determine the mass of the fat you removed from the milk and record in the table. Calculation:
 Chemistry 100 Instructor s Initials Name: Experiment 14: Biochemistry Analysis of milk for the lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. A. Determining the % Fat in Whole Milk 1. Weigh a clean, dry, empty 50
Chemistry 100 Instructor s Initials Name: Experiment 14: Biochemistry Analysis of milk for the lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. A. Determining the % Fat in Whole Milk 1. Weigh a clean, dry, empty 50
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from
 Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6062662112* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/52 Paper 5 Practical Test October/November 2011 2 hours
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6062662112* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/52 Paper 5 Practical Test October/November 2011 2 hours
I, 2013 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 2013 / SCIENCE. IX / Class IX. Time Allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 90
 EWFGDSK I, 0 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 0 / SCIENCE IX / Class IX 90 Time Allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 90 General Instructions : The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt
EWFGDSK I, 0 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 0 / SCIENCE IX / Class IX 90 Time Allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 90 General Instructions : The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8795360785* BIOLOGY 0610/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2017 1 hour Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8795360785* BIOLOGY 0610/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2017 1 hour Candidates
BIOLOGY PAPER - 1. (THEORY) (Botany and Zoology)
 BIOLOGY PAPER - 1 (THEORY) (Botany and Zoology) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) Answer all questions
BIOLOGY PAPER - 1 (THEORY) (Botany and Zoology) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) Answer all questions
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Organic Compounds in the Foods
 Organic Compounds in the Foods Purpose: This lab activity will help you understand the chemical composition (i.e., carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) of the foods that you eat. Materials we will be using:
Organic Compounds in the Foods Purpose: This lab activity will help you understand the chemical composition (i.e., carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) of the foods that you eat. Materials we will be using:
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
IGCSE BIOLOGY 0610 SCHEME OF WORK 1
 IGCSE BIOLOGY 0610 SCHEME OF WORK 1 UNIT 6: Reproduction in plants Recommended Prior Knowledge: A basic knowledge of cell structure will be helpful, but otherwise the Unit requires very little previous
IGCSE BIOLOGY 0610 SCHEME OF WORK 1 UNIT 6: Reproduction in plants Recommended Prior Knowledge: A basic knowledge of cell structure will be helpful, but otherwise the Unit requires very little previous
MAHESH TUTORIALS SECTION - A
 S.S.C. MAHESH TUTORIALS Test - II Batch : SB Marks : 30 Date : SCIENCE Chapter :,, 4, 6, 0, Time : hr. 5 min. SECTION - A Q.I (A) Rewrite the following statements by choosing the correct option : The least
S.S.C. MAHESH TUTORIALS Test - II Batch : SB Marks : 30 Date : SCIENCE Chapter :,, 4, 6, 0, Time : hr. 5 min. SECTION - A Q.I (A) Rewrite the following statements by choosing the correct option : The least
Topic 9-10: Lab Skills (including 4 NYS required labs)
 1. Base your answer on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Which statement describes two unsafe laboratory practices represented in the diagram? (1) The flame is too high and the test tube
1. Base your answer on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Which statement describes two unsafe laboratory practices represented in the diagram? (1) The flame is too high and the test tube
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT MIDDLE SECTION FINAL EXAMINATION
 Name Roll Number CLSS: VII INDIN SCHOOL MUSCT MIDDLE SECTION FINL EXMINTION 207-8 SCIENCE Code:MYSC04/0 Time llotted: 2 ½ Hrs. 04. 03.208 Max.Marks: 80 General Instructions:. The question paper comprises
Name Roll Number CLSS: VII INDIN SCHOOL MUSCT MIDDLE SECTION FINL EXMINTION 207-8 SCIENCE Code:MYSC04/0 Time llotted: 2 ½ Hrs. 04. 03.208 Max.Marks: 80 General Instructions:. The question paper comprises
You should wear eye protection throughout this practical. Ammonia is corrosive and dangerous to the environment.
 Practical 3 - N (d)(m)urine Analysis Evaluating and reporting on observations This practical focuses on Recording data, drawing conclusions and evaluation. You will also be developing other assessed skills
Practical 3 - N (d)(m)urine Analysis Evaluating and reporting on observations This practical focuses on Recording data, drawing conclusions and evaluation. You will also be developing other assessed skills
Carbohydrates Chemical Composition and Identification
 Carbohydrates Chemical Composition and Identification Introduction: Today, scientists use a combination of biology and chemistry for their understanding of life and life processes. Thus, an understanding
Carbohydrates Chemical Composition and Identification Introduction: Today, scientists use a combination of biology and chemistry for their understanding of life and life processes. Thus, an understanding
plant reproduction chapter 40 Alternation of Generations
 Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure. Name
 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
Lab 2. The Chemistry of Life
 Lab 2 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast organic and inorganic molecules Relate hydrogen bonding to macromolecules found in living things Compare and contrast the four major organic macromolecules:
Lab 2 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast organic and inorganic molecules Relate hydrogen bonding to macromolecules found in living things Compare and contrast the four major organic macromolecules:
3/18/2012. Chapter 36. Flower Parts. Flower Parts. Reproduction in Angiosperms
 Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
Flowering Plant Reproduction
 Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
CBSE SAMPLE PAPER 05 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Class-IX (SCIENCE) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 90
 CBSE SAMPLE PAPER 05 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Class-IX (SCIENCE) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 90 General Instructions (i) The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
CBSE SAMPLE PAPER 05 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Class-IX (SCIENCE) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 90 General Instructions (i) The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
Name that Pollinator
 Name that Pollinator Name Date Part A: A short history of pollen The evolutionary success of plants can be easily appreciated by everyone. As autotrophs, plants form the basis of food chains without which
Name that Pollinator Name Date Part A: A short history of pollen The evolutionary success of plants can be easily appreciated by everyone. As autotrophs, plants form the basis of food chains without which
Visit For All NCERT Solutions, CSBE Sample papers, Question, papers, Notes For Class 6 to 12
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-I, 2015-16 CLASS- X, SCIENCE gg-ro-104 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90 General Instructions:- 1. This question paper Comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-I, 2015-16 CLASS- X, SCIENCE gg-ro-104 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90 General Instructions:- 1. This question paper Comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction
 NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
Diffusion and Osmosis
 Diffusion and Osmosis OBJECTIVES: 1. To explore how different molecules move by diffusion and osmosis through semi-permeable membranes. 2. To understand how concentration affects the movement of substances
Diffusion and Osmosis OBJECTIVES: 1. To explore how different molecules move by diffusion and osmosis through semi-permeable membranes. 2. To understand how concentration affects the movement of substances
1.0 Learning Intentions
 Subject: Junior Certificate Science Teacher: Mrs Welby Week: Week 1 Lesson: Living Things, Cell and Microscope and Food 1.0 Learning Intentions At the end of the lesson, tick of each of the learning intentions
Subject: Junior Certificate Science Teacher: Mrs Welby Week: Week 1 Lesson: Living Things, Cell and Microscope and Food 1.0 Learning Intentions At the end of the lesson, tick of each of the learning intentions
(LM pages 91 98) Time Estimate for Entire Lab: 2.5 to 3.0 hours. Special Requirements
 Laboratory 7 Chemical Aspects of Digestion (LM pages 91 98) Time Estimate for Entire Lab: 2.5 to 3.0 hours Special Requirements Incubation. Students should start these sections at the beginning of the
Laboratory 7 Chemical Aspects of Digestion (LM pages 91 98) Time Estimate for Entire Lab: 2.5 to 3.0 hours Special Requirements Incubation. Students should start these sections at the beginning of the
Tests for Carbohydrates
 Goals bserve physical and chemical properties of some common carbohydrates. Use physical and chemical tests to distinguish between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Identify an unknown
Goals bserve physical and chemical properties of some common carbohydrates. Use physical and chemical tests to distinguish between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Identify an unknown
Problem: What would happen to enzyme activity if enzymes are placed outside their normal conditions? Hypothesis:
 Name: Date: Period: Honors Biology: Enzyme Lab Background information What would happen to your cells if they made a poisonous chemical? You might think that they would die. In fact, your cells are always
Name: Date: Period: Honors Biology: Enzyme Lab Background information What would happen to your cells if they made a poisonous chemical? You might think that they would die. In fact, your cells are always
Cell Membranes: Diffusion and Osmosis
 STO-112 Cell Membranes: Diffusion and Osmosis Part 1: Diffusion Diffusion is a process by which molecules move into or out of cells. To diffuse into or out of a cell, molecules must pass through the cell
STO-112 Cell Membranes: Diffusion and Osmosis Part 1: Diffusion Diffusion is a process by which molecules move into or out of cells. To diffuse into or out of a cell, molecules must pass through the cell
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, Class IX
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 0-6 SCIENCE Class IX Time Allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 90 General Instructions :. The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections..
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 0-6 SCIENCE Class IX Time Allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 90 General Instructions :. The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections..
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Modes of Reproduction
 Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
Instruction Manual Updated 8/27/2013 Ver. 1.1
 Water Analysis Kit Part No. 144-95 Instruction Manual Updated 8/27/2013 Ver. 1.1 OFI Testing Equipment, Inc. 11302 Steeplecrest Dr. Houston, Texas 77065 U.S.A. Tele: 832.320.7300 Fax: 713.880.9886 www.ofite.com
Water Analysis Kit Part No. 144-95 Instruction Manual Updated 8/27/2013 Ver. 1.1 OFI Testing Equipment, Inc. 11302 Steeplecrest Dr. Houston, Texas 77065 U.S.A. Tele: 832.320.7300 Fax: 713.880.9886 www.ofite.com
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants.
 CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
Plant Science 1203L Laboratory 5 - Sexual Reproduction (Pollination and Double Fertilization)
 Plant Science 1203L Laboratory 5 - Sexual Reproduction (Pollination and Double Fertilization) Today s lab is about sexual reproduction in plants. As with stem or root structure there are numerous definitions
Plant Science 1203L Laboratory 5 - Sexual Reproduction (Pollination and Double Fertilization) Today s lab is about sexual reproduction in plants. As with stem or root structure there are numerous definitions
the reproductive organs of a flower
 Life Cycles, Reproduction & Heredity flower power the reproductive organs of a flower Frameworks SCIENCE LS 2.6.5 Model and explain the function of plant organs: leaves, roots, stems, flowers. LS 3.7.6
Life Cycles, Reproduction & Heredity flower power the reproductive organs of a flower Frameworks SCIENCE LS 2.6.5 Model and explain the function of plant organs: leaves, roots, stems, flowers. LS 3.7.6
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
SAMPLE PAPER,TERM-I SESSION CLASS VI SCIENCE Time : 3 Hrs. Maximum Marks: 80
 SAMPLE PAPER,TERM-I SESSION 2017-18 CLASS VI SCIENCE Time : 3 Hrs. Maximum Marks: 80 General Instructions: Question paper is divided into two sections A and B. Section - A consists of questions from Physics
SAMPLE PAPER,TERM-I SESSION 2017-18 CLASS VI SCIENCE Time : 3 Hrs. Maximum Marks: 80 General Instructions: Question paper is divided into two sections A and B. Section - A consists of questions from Physics
2018 Version. Introduction to Science Junior Science
 2018 Version Introduction to Science Junior Science 1 What is Science? Science is both a collection of knowledge and the process for building that knowledge. Science asks questions about the natural world
2018 Version Introduction to Science Junior Science 1 What is Science? Science is both a collection of knowledge and the process for building that knowledge. Science asks questions about the natural world
Name... Class... Date...
 Required practical 4: Food tests Aiming for 8 Specification references: Required practical 4: Use qualitative reagents to test for a range of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. To include: Benedict s
Required practical 4: Food tests Aiming for 8 Specification references: Required practical 4: Use qualitative reagents to test for a range of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. To include: Benedict s
Teaching A2 Biology Practical Skills Appendix 2
 Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
YEAR 10 PRACTICE EXAM 1: 2014
 YEAR 10 PRACTICE EXAM 1: 2014 Question One [5 marks] Hazard symbols are used instead of words to warn about the dangers of chemicals. (a) Give one reason why hazard symbols are used instead of words. [1]
YEAR 10 PRACTICE EXAM 1: 2014 Question One [5 marks] Hazard symbols are used instead of words to warn about the dangers of chemicals. (a) Give one reason why hazard symbols are used instead of words. [1]
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *1991539925* BIOLOGY 5090/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2012
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *1991539925* BIOLOGY 5090/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2012
1 st Term Worksheet Subject Science Class V Name : Sec. :
 1 (v) science 1 st Term Worksheet Subject Science Class V Name : Sec. : Chapter 2 [Bones and Muscles] Keywords: [30] Tendons: Ligaments: Exercise: [31-33] [A] Fill in the boxes with the names of the main
1 (v) science 1 st Term Worksheet Subject Science Class V Name : Sec. : Chapter 2 [Bones and Muscles] Keywords: [30] Tendons: Ligaments: Exercise: [31-33] [A] Fill in the boxes with the names of the main
Materials: Activity: Explanation:
 Children will model how fat can be digested by bile. Materials: Whole milk Water Shallow dish or pie pan Food coloring Liquid dish or hand soap Cotton swabs Activity: 1) Pour about ½ inch of milk into
Children will model how fat can be digested by bile. Materials: Whole milk Water Shallow dish or pie pan Food coloring Liquid dish or hand soap Cotton swabs Activity: 1) Pour about ½ inch of milk into
CBSE Board Class X Science Term 1 Sample Paper - 2. Time: 3 hrs Total Marks: 90
 CBSE Board Class X Science Term 1 Sample Paper - 2 Time: 3 hrs Total Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. The question paper comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections. 2. There
CBSE Board Class X Science Term 1 Sample Paper - 2 Time: 3 hrs Total Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. The question paper comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections. 2. There
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet
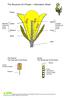 The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants
 Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Welcome back to Science Junior Science. Easy to read Version
 Welcome back to Science Junior Science Easy to read Version 1a What is Science? Science is both a collection of knowledge and the process for building that knowledge. Science asks questions about the natural
Welcome back to Science Junior Science Easy to read Version 1a What is Science? Science is both a collection of knowledge and the process for building that knowledge. Science asks questions about the natural
Class- 1X SCIENCE Paper- 4 Time allowed: 3 hours maximum Marks: 90
 Class- 1X SCIENCE Paper- 4 Time allowed: 3 hours maximum Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. The question paper comprises of two sections, A and B you are to attempt both the sections. 2. All questions
Class- 1X SCIENCE Paper- 4 Time allowed: 3 hours maximum Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. The question paper comprises of two sections, A and B you are to attempt both the sections. 2. All questions
ANGIOSPERM L.S. POLLEN GRAIN
 ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 10
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 0 LIFE SCIENCES P3 (PRACTICAL) EXEMPLAR 202 MARKS: 60 TIME: hour This question paper consists of 4 pages. Life Sciences/P3 (Practical) 2 DBE/202 NSC Grade 0 Exemplar QUESTION
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 0 LIFE SCIENCES P3 (PRACTICAL) EXEMPLAR 202 MARKS: 60 TIME: hour This question paper consists of 4 pages. Life Sciences/P3 (Practical) 2 DBE/202 NSC Grade 0 Exemplar QUESTION
POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S.
 POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC C CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL? EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL CENTRAL
POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC C CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL? EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL CENTRAL
