1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2) Nutrition in Human Beings. 3) transportation in human being 4) Excretion in human being
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA VSN NAGPUR HOLIDAY HOMEWORK Class X A and X B (SCIENCE) Learn Chapter 1, 6 And 10 Worksheet on Chapter 1 and Chapter 6 Prepare presentation on 1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2) Nutrition in Human Beings 3) transportation in human being 4) Excretion in human being (1) Life Processes 1 Mark Questions 1. After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps in your leg muscles. Why does this happens? 2. What do the following transport? a) Xylem b) Phloem 3. What do the following transport? a) Pulmonary Vein b) Vena Cava 4. Although bile juice has no digestive enzyme it is considered to be very important during digestion of food. Give reason. 5. What do you mean by life processes? 6. What are outside raw materials used for by an organism? IWhat processes would you consider essential for maintaining life? 7. Define autotrophic nutrition. 8. Define heterotrophic nutrition. 9. How does amoeba obtain its food? 10. Name the site where complete digestion of carbohydrate, protein and fats takes place? 11. What is the name of respiratory pigment? 12. What is the role of HCL in stomach? 13. Name any two glands associated with digestion in humans. 14. Write down the complete reaction of photosynthesis. 15. What is the role of mucus produced by stomach? 16. In which form nitrogen is taken? 17. Which is an essential element used in the synthesis of proteins and other compounds? 18. How is food taken inside paramecium? 19. Which type of movement occurs in the food pipe through which food enters into the stomach? 20. What will happens when we eat more spicy food? 21. The exit of food from stomach is regulated by which muscle?
2 2 22. Which is the longest part of alimentary canal? 23. What is the role of bile? 24. What is the role of intestinal juice? 25. The exit of waste materials regulated by which muscles? 26. Why respiration is called as exothermic reaction? 27. How ATP is synthesized? 28. Which is the energy currency of cellular process? 29. What is the role of rings of cartilage in the throat? 30. What is the function of alveoli? 31. What are the end products of aerobic and anaerobic respiration in yeast? 32. What is the fluid medium of blood? 33. What is the role of platelets? 34. What are the different components of blood? 35. Name the instrument used to measure blood pressure? 36. Why WBC is called soldier of the body? 37. What is lymph? 38. Define excretion. 39. What is the role of saliva in digestion of food? 40. What is the role of mucous in stomach? L 1 (3 Mark) 1. How are Arteries different from vein. State any three differences. 2. What do the following transport? i) Xylem Transport water and minerals in plants. ii) Pulmonary artery Transport deoxygenated blood from lungs to heart. iii) Pulmonary Vein Transport oxygenated blood from heart to lungs. iv) Phloem Transport Synthesized food and hormones in plants v) Vena Cava - Deoxygenated blood from the body to the upper chamber of heart (Right atrium). vi) Ureter Urine from kidney to urinary bladder 3. Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Name anyone organism that use anaerobic mode of respiration. 4. What is transpiration? How does transpiration helpful for the plant? 5. Which organ secretes a hormone when blood sugar rises in our body? Name the hormone and any one enzyme released by this organ. L 2 (3 Mark) 6. Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis? 7. How is small intestine designed to absorb the digested food? 8. a) What is the role of mucus in stomach?
3 3 b) How exit of food from the stomach is regulated? c) Where does food enter from stomach?. 9. What will happen if a) Peristaltic movements do not occur all along the oesophagus? b) There is no platelets in blood? c) Rings of cartilage are not present in the trachea? 10. What are the major events during photosynthesis? L 3 (3 Mark) 11. a) A product is formed in our muscles due to break down of glucose when there is lack of oxygen. Name the product and also mention the effect of build up of this product. b) Where does the breakdown of pyruvate to give CO2, water and energy takes place? 12. Give reasons for: a) Oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is separate in the heart of mammals. b) Ventricles have thick muscular wall. c) Herbivores have longer intestine as compare to carnivores 13. What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products 14. a) What would be the consequences of deficiency of hemoglobin in our body? 15. Name the following with reference to the alimentary canal. a) The largest gland b) The gland that secretes digestive enzymes and hormones. c) The part where digestive food is absorbed. 5- Marks Questions Level-1 1. a) Draw a diagram of human digestive system and label the following parts: i) that secretes Bile juice - liver ii) that secretes Insulin Pancreas iii) the site of complete digestion of food small intestine iv) HCl acid is release here stomach b)what is peristaltic movement? 2 ) a) Name the hormone which is released into the blood when its sugur level rises. Name the organ which produces this hormone and its effect on blood sugur level. Also mention the digestive enzymes secreated by this organ with one function of each.
4 4 b)explain the need of chemical communication in Multicellular organisms. 3) a) Why are valves needed in the heart? b) What is blood pressure? Name the instrument that use to measure blood pressure. c) Leakage of blood from the blood reduces the efficacy of the pumping system. How is this leakage prevented? d) How are oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human being? Level-2 4. a) State the form in which following are stored? (i) Unused carbohydrates in plants (ii) The energy derived from food in humans b) Describe the process of nutrition in Amoeba with the help of diagram. c) How does paramecium obtain its food? 5. a) Draw the human respiratory system and label the following, bronchi and alveolar sac. b)during breathing cycle, what is the advantage of residual volume of air in lungs? 6. a) What is double circulation in human being? Why it is necessary? b) Why are the valves present in the veins? c) How many chambers are present in the heart of (i) Fish (ii) Frog Level-3 7. During respiration of an organism A one molecule of glucose produces two ATP molecules where in respiration of another organism B, one molecule of glucose produces 38 ATP molecules. a) Which organism is undergoing aerobic respiration? b) Which organism is undergoing anaerobic respiration? c) Which type of organisms A or B convert glucose into alcohol? d) Name one organism which behaves like A. e) Name one organism which behaves like B. a) Organism B b) Organism A c) Organism A d) Yeast e) Human being 9. a) Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with vaseline to block the stomata. Will this plant remain healthy for long? State three reasons for your answer. b) (i) In the following diagram of stomatal apparatus, label parts shown by Roman numerals II and III
5 5 ii) What is the function of guard cell? 10. a) Draw a neat diagram of human excretory system and label the following parts: Aorta, vena cava, Ureter and urinary badder. c) Name the structural and functional unit of Kidney? Write its function. DIAGRAMS DRAW a well labelled diagram of 1) Human Digestive system 2) Human respiratory system 3) Human Heart 4) Human Excertory System 5) Nephron (2) CHEMICAL REACTIONS (40 Marks) 1. Oil and Fat containing food items flushed with nitrogen. Why? (1) 2. Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reactions: a) Silver bromide on exposure to sunlight decomposes into silver and bromine. b) Sodium metal reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas (2) 3. What happens when quick lime is added to water? Write the Equation also. (2) 4. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? (2) 5. a) What are redox reactions? b)why the reaction of Zinc oxide and carbon is called a redox reaction? c) Identify the substance oxidized and the substance reduced in the above reaction. 6. What is neutralisation reaction? Give two examples. 7. a) What is decomposition reaction? Give one example. b) What type of reaction occurs when silver Bromide exposed to sunlight? c) Identify the type of reaction when Lead nitrate solution mixed with potassium iodide solution. 8. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light and electricity. 9. Explain the following terms with one example each; a) Corrosion b) Displacement reaction
6 6 10. a) Write the chemical name and formula of Bleaching powder. b) Write chemical equation for the preparation of bleaching powder from slaked lime. c) Write two uses of Bleaching powder. 11. A blue colored salt becomes white on heating. Give reason for the above observations. What happens when we add water to the salt which is obtained after heating? Also write its chemical formula. 12. What happens when silver chloride is exposed to sunlight? Write the chemical equation for this reaction. Also write one use of such reaction. 13. i) Define corrosion. (5) ii) What is corrosion of Iron called? iii) How will you recognize the corrosion of silver? iv) Why corrosion of Iron is a serious problem? v) How can we prevent corrosion of Iron? PBQ 14. On keeping iron nails in blue coloured Copper Sulphate solution, it is observed that the colour of the solution turns light green after sometime. Give reason for this colour change. Name the type of the reaction. (2) 15. You have to perform displacement reaction in the school laboratory to show zinc is more reactive than copper, name the aqueous solution required for this experiment. State the change in colour and give the chemical reaction involved. (2)
CHAPTER6. Multiple Choice Questions NCERT
 CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
 CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
Revision Question Bank
 Revision Question Bank Life Processes 1. Name the passage in sequence through which urine passes from kidney to the outside in human. How is urine prevented from flowing back into the ureter? The passage
Revision Question Bank Life Processes 1. Name the passage in sequence through which urine passes from kidney to the outside in human. How is urine prevented from flowing back into the ureter? The passage
LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER
 MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
o Nutrition in human beings 33
 KEY CONCEPTS & GIST OF THE LESSON Life processes The processes that are necessary for an organism to stay alive. Eg. Nutrition, respiration, etc. Criteria of life- (i) Growth (ii) Movement Nutrition- The
KEY CONCEPTS & GIST OF THE LESSON Life processes The processes that are necessary for an organism to stay alive. Eg. Nutrition, respiration, etc. Criteria of life- (i) Growth (ii) Movement Nutrition- The
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
 CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
Pre- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate assessment for each student
 Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK CLASS X SUBJECT : ENGLISH
 HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK CLASS X SUBJECT : ENGLISH Make a Scrap Book for the ISA Project Voice to Voiceless. The activity will be based on the Study on the following countries - India, Spain, China, Japan and
HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK CLASS X SUBJECT : ENGLISH Make a Scrap Book for the ISA Project Voice to Voiceless. The activity will be based on the Study on the following countries - India, Spain, China, Japan and
Downloaded from
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI-110034 CLASS 10 NOTES TERM 1 Topic: Life processes Q1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI-110034 CLASS 10 NOTES TERM 1 Topic: Life processes Q1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Post- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate prompt for each student
 Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
GURU NANAK INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC SCHOOL (SENIOR SECONDARY)
 GURU NANAK INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC SCHOOL (SENIOR SECONDARY) Hindi CLASS: X-B HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK English 1. Revise the whole syllabus. 2. Do unseen passages (1 to 5) of BBC in book only. 3. Write letter on
GURU NANAK INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC SCHOOL (SENIOR SECONDARY) Hindi CLASS: X-B HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK English 1. Revise the whole syllabus. 2. Do unseen passages (1 to 5) of BBC in book only. 3. Write letter on
The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body
 Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
LIFE PROCESSES
 LIFE PROCESSES Usually we differentiate living organisms from non-living by observing the movements in them. These movements can be: Locomotion movements In animals, e.g. running, chewing cud, etc. Growth
LIFE PROCESSES Usually we differentiate living organisms from non-living by observing the movements in them. These movements can be: Locomotion movements In animals, e.g. running, chewing cud, etc. Growth
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
GURU NANAK INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC SCHOOL (SENIOR SECONDARY)
 GURU NANAK INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC SCHOOL (SENIOR SECONDARY) Hindi CLASS: X-A HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK English 1. Revise the whole syllabus. 2. Do unseen passages (1 to 5) of BBC in book only. 3. Write letter on
GURU NANAK INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC SCHOOL (SENIOR SECONDARY) Hindi CLASS: X-A HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK English 1. Revise the whole syllabus. 2. Do unseen passages (1 to 5) of BBC in book only. 3. Write letter on
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
LIFE PROCESSES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 MARK] 14. Mention two structural features of small intestine which add to the absorptive capacity.
![LIFE PROCESSES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 MARK] 14. Mention two structural features of small intestine which add to the absorptive capacity. LIFE PROCESSES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 MARK] 14. Mention two structural features of small intestine which add to the absorptive capacity.](/thumbs/76/73956409.jpg) LIFE PROCESSES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 MARK] 1. What will happen to a plant if its xylem is removed? Xylem in plant transports water and dissolved mineral nutrients from the roots to all parts
LIFE PROCESSES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 MARK] 1. What will happen to a plant if its xylem is removed? Xylem in plant transports water and dissolved mineral nutrients from the roots to all parts
UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2
 Science Science UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2 Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Changes in Digestion Engage Eat a Cracker 1. Your teacher will give you two unsalted crackers. 2. Chew
Science Science UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2 Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Changes in Digestion Engage Eat a Cracker 1. Your teacher will give you two unsalted crackers. 2. Chew
Unit 4: Summary. Similarities and Differences Between Living Things
 Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology Duration: 2 Hours Part I Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1. Which of the following does not manufacture
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology Duration: 2 Hours Part I Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1. Which of the following does not manufacture
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
Human Anatomy and Body Systems
 Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems
 Table of Contents Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems Section 1: The Human Organism Section 2: How Your Body Works The Human Organism Organization in the Human Body Although your body is not made of
Table of Contents Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems Section 1: The Human Organism Section 2: How Your Body Works The Human Organism Organization in the Human Body Although your body is not made of
perfect practice makes perfect
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
You downloaded from page [1]
![You downloaded from page [1] You downloaded from page [1]](/thumbs/76/73943662.jpg) 10th Biology: Life LIFE processes PROCESSES solved Questions 1. Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms need more oxygen
10th Biology: Life LIFE processes PROCESSES solved Questions 1. Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms need more oxygen
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1 Food and its use by the body (pp )
 Checkup Chapter 6 1 Food and its use by the body (pp. 160 172) 1. This is what Veronica ate for supper: 1 grilled Atlantic salmon steak 1 baked potato 5 ml of butter (on the potato) 3 boiled broccoli florets
Checkup Chapter 6 1 Food and its use by the body (pp. 160 172) 1. This is what Veronica ate for supper: 1 grilled Atlantic salmon steak 1 baked potato 5 ml of butter (on the potato) 3 boiled broccoli florets
Unit 3 Lesson 5 How Do Our Bodies Digest Food, Remove Wastes, and Send Messages? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Unit 3 Lesson 5 How Do Our Bodies Digest Food, Remove Wastes, and Send Messages? How do our bodies digest food, remove wastes and send messages? Let s think together? Why do we need food? How could food
Unit 3 Lesson 5 How Do Our Bodies Digest Food, Remove Wastes, and Send Messages? How do our bodies digest food, remove wastes and send messages? Let s think together? Why do we need food? How could food
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND VOCATIONAL TRAINING FORM TWO SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION, 2007 INSTRUCTIONS
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA Candidate's No. MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND VOCATIONAL TRAINING FORM TWO SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION, 2007 0033 BIOLOGY TIME: 2½ HOURS INSTRUCTIONS 1. This paper consists
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA Candidate's No. MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND VOCATIONAL TRAINING FORM TWO SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION, 2007 0033 BIOLOGY TIME: 2½ HOURS INSTRUCTIONS 1. This paper consists
Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology
 Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
Standard B-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the flow of energy within and between living systems.
 B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret the chemical equation for the process. Taxonomy Level: 2.4-B and 2.1-B Understand Conceptual
B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret the chemical equation for the process. Taxonomy Level: 2.4-B and 2.1-B Understand Conceptual
Life Processes CHAPTER WHAT ARE LIFE PROCESSES?
 CHAPTER 6 Life Processes How do we tell the difference between what is alive and what is not alive? If we see a dog running, or a cow chewing cud, or a man shouting loudly on the street, we know that these
CHAPTER 6 Life Processes How do we tell the difference between what is alive and what is not alive? If we see a dog running, or a cow chewing cud, or a man shouting loudly on the street, we know that these
This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section:
 MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS 5 SYLLABUS CHECKLIST This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 5.1 CELLS, TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS Multicellular organisms have a hierarchical
MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS 5 SYLLABUS CHECKLIST This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 5.1 CELLS, TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS Multicellular organisms have a hierarchical
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
MT - SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY - II (72) - SEMI PRELIM - II : PAPER - 6. Time : 2 Hours Model Answer Paper Max. Marks : 40
 MT 07 00 MT - SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY - II (7) - SEMI PRELIM - II : PAPER - 6 Time : Hours Model Answer Paper Max. Marks : 40 A.. (A) Fill in the blanks: () In some plants, waste is in the form of calcium
MT 07 00 MT - SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY - II (7) - SEMI PRELIM - II : PAPER - 6 Time : Hours Model Answer Paper Max. Marks : 40 A.. (A) Fill in the blanks: () In some plants, waste is in the form of calcium
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Multicellular Organisms Homework
 Multicellular Organisms Homework NAME: CLASS: Reproduction 1. The diagram shows the parts of a flower. 1a. Name part X (1) 1b. Name the sites of production of both male and female gametes in a flowering
Multicellular Organisms Homework NAME: CLASS: Reproduction 1. The diagram shows the parts of a flower. 1a. Name part X (1) 1b. Name the sites of production of both male and female gametes in a flowering
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
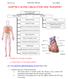 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
Class 10 Science - Sample Paper Set I
 Time allowed: 3 hours; Maximum marks: 90 General Instructions: a) All Questions are compulsory b) The Question Paper consists of 42 Questions divided in to four sections A, B, C and D c) Section- A comprises
Time allowed: 3 hours; Maximum marks: 90 General Instructions: a) All Questions are compulsory b) The Question Paper consists of 42 Questions divided in to four sections A, B, C and D c) Section- A comprises
4.2.1 Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system
 GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p.
 NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p. Food (energy) Delivery System into our Bodies Excretory System digestive breaks down food into molecules that cells can use nutrient molecules pass into the bloodstream
NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p. Food (energy) Delivery System into our Bodies Excretory System digestive breaks down food into molecules that cells can use nutrient molecules pass into the bloodstream
4.2 Organisation Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system.
 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
Life Processes. dronstudy.com
 Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
Book Second Term Test Model Answers. Page 84 to 87
 1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min. Section B
 BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
***Non-living things may show one or more of these Characteristics, but NEVER ALL of them
 -Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
-Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
MAHESH TUTORIALS SECTION - A
 S.S.C. MAHESH TUTORIALS Test - II Batch : SB Marks : 30 Date : SCIENCE Chapter :,, 4, 6, 0, Time : hr. 5 min. SECTION - A Q.I (A) Rewrite the following statements by choosing the correct option : The least
S.S.C. MAHESH TUTORIALS Test - II Batch : SB Marks : 30 Date : SCIENCE Chapter :,, 4, 6, 0, Time : hr. 5 min. SECTION - A Q.I (A) Rewrite the following statements by choosing the correct option : The least
Human Body. The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related.
 Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Unit 2 - Characteristics of Living Things
 Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Intermediate 2. Biology. Learning Outcomes
 Intermediate 2 Biology Learning Outcomes Intermediate 2 Biology Unit 2 Cell structure and function State the similarities and differences between animal, plant and microbial cells. (cheek epithelial cell,
Intermediate 2 Biology Learning Outcomes Intermediate 2 Biology Unit 2 Cell structure and function State the similarities and differences between animal, plant and microbial cells. (cheek epithelial cell,
WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
Chapter 24. Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill.
 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 24-1 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 24-1 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular
The Circulatory System. Lesson 4. Quick Check. Trace the path of blood after it is pumped from the heart. 22. First
 Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Unit 4: Summary. Similarities and Differences Between Living Things
 Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Life Processes. 3.Why do the walls of trachea do not collapse when there is less air in it?
 Assignment -1: Life Processes 1.The leaves of a plant first prepare Food A by photosynthesis then food A gets converted into Food B What are A and B? 2.What will happen to a plant if its xylem is removed?
Assignment -1: Life Processes 1.The leaves of a plant first prepare Food A by photosynthesis then food A gets converted into Food B What are A and B? 2.What will happen to a plant if its xylem is removed?
THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad , A.P.
 THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad 500 016, A.P. Work Sheet for the Academic Year 2014-15 CLASS VII SECOND TERM SYLLABUS BIOLOGY ===============================================================
THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad 500 016, A.P. Work Sheet for the Academic Year 2014-15 CLASS VII SECOND TERM SYLLABUS BIOLOGY ===============================================================
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium.
 CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose. carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin
 1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
Reporting Category 4: Biological Processes and Systems (11questions)
 Reporting Category 4: Biological Processes and Systems (11questions) Major topics include: 1) Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration (energy and matter) 2) Role of enzymes 3) Animal systems* 4) Plant
Reporting Category 4: Biological Processes and Systems (11questions) Major topics include: 1) Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration (energy and matter) 2) Role of enzymes 3) Animal systems* 4) Plant
INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR Summative Assessment I, 2014 Class: VII SCIENCE M.M: 60 17/09/14 Time: 3 hrs
 INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR Summative Assessment I, 2014 Class: VII SCIENCE M.M: 60 17/09/14 Time: 3 hrs General Instructions: (i) The question paper comprises of three sections A, B and C. (ii) All
INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR Summative Assessment I, 2014 Class: VII SCIENCE M.M: 60 17/09/14 Time: 3 hrs General Instructions: (i) The question paper comprises of three sections A, B and C. (ii) All
Biology I Honors EOC Exam Review: metabolism
 Biology I Honors EOC Exam Review: metabolism 1. One type of anaerobic respiration results in the production of a. water and oxygen c. nitrogen gas and ammonia b. pyruvic acid and glycerol d. alcohol and
Biology I Honors EOC Exam Review: metabolism 1. One type of anaerobic respiration results in the production of a. water and oxygen c. nitrogen gas and ammonia b. pyruvic acid and glycerol d. alcohol and
Biology Test 6 I. NUTRITION
 Biology Test 6 I. NUTRITION A. Process of Nutrition Difference between animal and plant nutrition needs- animals rely on other organisms (Either plants or animals) while plants can produce food/energy
Biology Test 6 I. NUTRITION A. Process of Nutrition Difference between animal and plant nutrition needs- animals rely on other organisms (Either plants or animals) while plants can produce food/energy
Secondary 3 Final Exam Review
 Topics to know: Secondary 3 Final Exam Review - Technological/Material World o Mechanical functions (guiding, linking, sealing, lubricating) o Forces - Matter o Be able to identify chemical and physical
Topics to know: Secondary 3 Final Exam Review - Technological/Material World o Mechanical functions (guiding, linking, sealing, lubricating) o Forces - Matter o Be able to identify chemical and physical
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY
 S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY SCN 3-12a: I have explored the structure and function of organs and organ systems and can relate this to the basic biological processes required to sustain life SCN
S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY SCN 3-12a: I have explored the structure and function of organs and organ systems and can relate this to the basic biological processes required to sustain life SCN
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
The Digestive and Excretory Systems
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 26 The Digestive and Excretory Systems Textbook pages 64 81 Before You Read Section 2.2 Summary Many structures and organs work together to digest food. What parts
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 26 The Digestive and Excretory Systems Textbook pages 64 81 Before You Read Section 2.2 Summary Many structures and organs work together to digest food. What parts
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion
 Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
